Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00111)
| Name |
Multidrug resistance protein 1 (ABCB1)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
ABCB1
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr7:87503017-87713323[-]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MDLEGDRNGGAKKKNFFKLNNKSEKDKKEKKPTVSVFSMFRYSNWLDKLYMVVGTLAAII
HGAGLPLMMLVFGEMTDIFANAGNLEDLMSNITNRSDINDTGFFMNLEEDMTRYAYYYSG IGAGVLVAAYIQVSFWCLAAGRQIHKIRKQFFHAIMRQEIGWFDVHDVGELNTRLTDDVS KINEGIGDKIGMFFQSMATFFTGFIVGFTRGWKLTLVILAISPVLGLSAAVWAKILSSFT DKELLAYAKAGAVAEEVLAAIRTVIAFGGQKKELERYNKNLEEAKRIGIKKAITANISIG AAFLLIYASYALAFWYGTTLVLSGEYSIGQVLTVFFSVLIGAFSVGQASPSIEAFANARG AAYEIFKIIDNKPSIDSYSKSGHKPDNIKGNLEFRNVHFSYPSRKEVKILKGLNLKVQSG QTVALVGNSGCGKSTTVQLMQRLYDPTEGMVSVDGQDIRTINVRFLREIIGVVSQEPVLF ATTIAENIRYGRENVTMDEIEKAVKEANAYDFIMKLPHKFDTLVGERGAQLSGGQKQRIA IARALVRNPKILLLDEATSALDTESEAVVQVALDKARKGRTTIVIAHRLSTVRNADVIAG FDDGVIVEKGNHDELMKEKGIYFKLVTMQTAGNEVELENAADESKSEIDALEMSSNDSRS SLIRKRSTRRSVRGSQAQDRKLSTKEALDESIPPVSFWRIMKLNLTEWPYFVVGVFCAII NGGLQPAFAIIFSKIIGVFTRIDDPETKRQNSNLFSLLFLALGIISFITFFLQGFTFGKA GEILTKRLRYMVFRSMLRQDVSWFDDPKNTTGALTTRLANDAAQVKGAIGSRLAVITQNI ANLGTGIIISFIYGWQLTLLLLAIVPIIAIAGVVEMKMLSGQALKDKKELEGSGKIATEA IENFRTVVSLTQEQKFEHMYAQSLQVPYRNSLRKAHIFGITFSFTQAMMYFSYAGCFRFG AYLVAHKLMSFEDVLLVFSAVVFGAMAVGQVSSFAPDYAKAKISAAHIIMIIEKTPLIDS YSTEGLMPNTLEGNVTFGEVVFNYPTRPDIPVLQGLSLEVKKGQTLALVGSSGCGKSTVV QLLERFYDPLAGKVLLDGKEIKRLNVQWLRAHLGIVSQEPILFDCSIAENIAYGDNSRVV SQEEIVRAAKEANIHAFIESLPNKYSTKVGDKGTQLSGGQKQRIAIARALVRQPHILLLD EATSALDTESEKVVQEALDKAREGRTCIVIAHRLSTIQNADLIVVFQNGRVKEHGTHQQL LAQKGIYFSMVSVQAGTKRQ Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Translocates drugs and phospholipids across the membrane. Catalyzes the flop of phospholipids from the cytoplasmic to the exoplasmic leaflet of the apical membrane. Participates mainly to the flop of phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylethanolamine, beta-D-glucosylceramides and sphingomyelins. Energy-dependent efflux pump responsible for decreased drug accumulation in multidrug-resistant cells.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
51 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90.0] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Vinblastine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Kidney cancer [ICD-11: 2C90] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Renal cell carcinoma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Kidney | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 4.11E-46 Fold-change: -1.42E+00 Z-score: -1.91E+01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Flp-In-293/Mock cells | Kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_U421 |
| Flp-In-293/ABCB1 cells | Kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_U421 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
ATPase assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Through calcein assays, we found that epimagnolin A inhibited the ABCB1-mediated export of calcein. This result suggests that epimagnolin A behaved as inhibitor or substrate for ABCB1. In ATPase assays, epimagnolin A stimulated ABCB1-dependent ATPase activity. This result indicates that epimagnolin A was recognised as a substrate by ABCB1, since ABCB1 utilises energy derived from ATP hydrolysis for substrate transport. Furthermore, in MTT assays we found that the cytotoxicity of daunorubicin, doxorubicin, vinblastine, and vincristine was enhanced by epimagnolin A in a manner comparable to verapamil, a typical substrate for ABCB1. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90.0] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Kidney cancer [ICD-11: 2C90] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Renal cell carcinoma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Kidney | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 4.11E-46 Fold-change: -1.42E+00 Z-score: -1.91E+01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Flp-In-293/Mock cells | Kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_U421 |
| Flp-In-293/ABCB1 cells | Kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_U421 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
ATPase assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Through calcein assays, we found that epimagnolin A inhibited the ABCB1-mediated export of calcein. This result suggests that epimagnolin A behaved as inhibitor or substrate for ABCB1. In ATPase assays, epimagnolin A stimulated ABCB1-dependent ATPase activity. This result indicates that epimagnolin A was recognised as a substrate by ABCB1, since ABCB1 utilises energy derived from ATP hydrolysis for substrate transport. Furthermore, in MTT assays we found that the cytotoxicity of daunorubicin, doxorubicin, vinblastine, and vincristine was enhanced by epimagnolin A in a manner comparable to verapamil, a typical substrate for ABCB1. | |||
| Disease Class: Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12.6] | [4] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12.6] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Liver cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Liver tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.18E-05 Fold-change: -3.05E-01 Z-score: -4.26E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| In Vitro Model | HepG2 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0027 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | High glucose upregulated the level of MDR-1, which can be expected the intracellular accumulation of anticancer drugs. Interestingly, reduced accumulation of doxorubicin was recorded in cells cultured in high glucose media. Curcumin-mediated inhibition of MDR-1 expression can be suggested as critical event leading to retention of anticancer drug in cellular interior. | |||
| Disease Class: Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | [6] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Liver tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.18E-05 Fold-change: -3.05E-01 Z-score: -4.26E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Huh-7 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0336 |
| BEL-7402 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5492 | |
| HepG2 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0027 | |
| Hep3B cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0326 | |
| SMMC7721 cells | Uterus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0534 | |
| Skhep1 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0525 | |
| HCC3 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0C57 | |
| LM-6 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_7680 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
WST-1 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-223 targeted ABCB1 3'UTR directly, and miR-223 down-regulated ABCB1 at both mRNA and protein levels. The over-expression of miR-223 increased the HCC cellsensitivity to anticancer drugs, and the inhibition of miR-223 had the opposite effect. Importantly, the over-expression or silencingof ABCB1 can rescue the cell response to the anticancer drugs mediated by miR-223 over-expression or inhibition. | |||
| Disease Class: Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | [7] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Liver tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.18E-05 Fold-change: -3.05E-01 Z-score: -4.26E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| PI3K/AKT signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | ||
| In Vitro Model | HepG2 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0027 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The expression of a number drug resistance related proteins, including multidrug resistance 1, multi drug resistance associated protein 1, DNA excision repair protein ERCC 1, survivin and B cell lymphoma 2, was significantly downregulated by miR 503 overexpression. | |||
| Disease Class: Glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.1] | [8] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Glioma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Nervous tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.79E-03 Fold-change: -3.77E-01 Z-score: -3.50E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | AKT signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | |
| Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | U251 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0021 |
| U87-MG cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0022 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | microRNA-127 silencing significantly affects cell growth and increases the sensitivity to adriamycin. microRNA-127 silencing arrests the cell cycle, potentiates adriamycin-induced apoptosis, and increases cellular Rh-123 uptake. microRNA-127 silencing down-regulates MDR1, MRP1, Runx2, Bcl-2, Survivin and ErbB4 expression while up-regulates p53 expression. microRNA-127 silencing inhibits AkT phosphorylation. | |||
| Disease Class: Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | [9] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.27E-03 Fold-change: -2.98E-01 Z-score: -3.27E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | AKT/ERK signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04010 | |
| Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | ||
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; Luciferase reporter assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Suppression of miR-155 in this cell line considerably reversed doxorubicin resistance, and doxorubicin-induced apoptosis and cell cycle arrest were recovered. Furthermore, reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction and western blot analysis revealed that miR-155 suppression downregulated the expression of multidrug resistance protein 1, multidrug resistance-associated protein 1, breast cancer resistance protein, glutathione S-transferase-Pi, Survivin and B-cell lymphoma 2, and upregulated the expression of caspase-3 and caspase-8. In addition, it was found that miR-155 suppression inhibited the activation of AkT and extracellular signal-regulated kinase. The transcriptional activity of nuclear factor-kB and activator protein-1 was also downregulated. | |||
| Disease Class: Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | [14] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Liver tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.18E-05 Fold-change: -3.05E-01 Z-score: -4.26E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | HepG2 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0027 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow Cytometric Analysis | |||
| Mechanism Description | Transfection of miR122 mimics into cultured HepG2 cells induces cell-cycle arrest and sensitizes these cells to doxorubicin by modulating the expression of multidrug resistance genes, ABCB1 and ABCF2. | |||
| Disease Class: Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12.6] | [19] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12.6] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Liver cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Liver tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 5.54E-01 Fold-change: -1.17E-02 Z-score: -5.93E-01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | HepG2 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0027 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
RT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Synergistic interaction between the MDR mechanisms include ABCT proteins (P-gp, BCRP, and MDR1) and metabolic enzymes of phase I of metabolism mainly CYP3A4, phase II of metabolism mainly GST was observed. In this study, FUC alone and in combination with DOX inhibited the enzyme activities of CYP3A4 and GST and down regulated their genes. We interpret this effect as a consequence of a down-regulation of pregnane X receptor (PXR) gene. FUC overcame MDR by significantly suppressing PXR mediated pathways that regulated the expression of CYP3A and ABCB1 genes in HepG-2 cells. | |||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [19] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Ovarian cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Ovarian tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.53E-04 Fold-change: -2.43E-01 Z-score: -6.49E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | SkOV3 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0532 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
RT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Synergistic interaction between the MDR mechanisms include ABCT proteins (P-gp, BCRP, and MDR1) and metabolic enzymes of phase I of metabolism mainly CYP3A4, phase II of metabolism mainly GST was observed. In this study, FUC alone and in combination with DOX inhibited the enzyme activities of CYP3A4 and GST and down regulated their genes. We interpret this effect as a consequence of a down-regulation of pregnane X receptor (PXR) gene. FUC overcame MDR by significantly suppressing PXR mediated pathways that regulated the expression of CYP3A and ABCB1 genes in HepG-2 cells. | |||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [52] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| SkBR3 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0033 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Colony formation assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The protein levels of MDR1, MRP1 and ABCB1 were significantly decreased in DOXR-MCF-7 siR-HOTAIR1 cells compared with the siR-NC DOXR-MCF-7 cells and HOTAIR silencing reduces the sensitivity of drug resistance in drug-resistant MCF-7 cells. | |||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [52] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| SkBR3 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0033 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Colony formation assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The protein levels of MDR1, MRP1 and ABCB1 were significantly decreased in DOXR-MCF-7 siR-HOTAIR1 cells compared with the siR-NC DOXR-MCF-7 cells and HOTAIR silencing reduces the sensitivity of drug resistance in drug-resistant MCF-7 cells. | |||
| Disease Class: Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51.0] | [53] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | MG63 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0426 |
| SAOS-2 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0548 | |
| HOS cells | Bone | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0312 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Flow cytometric analysis | |||
| Mechanism Description | LncRNA FENDRR sensitizes doxorubicin-resistance of osteosarcoma cells through down-regulating ABCB1 and ABCC1. | |||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [54] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | A2780 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0134 |
| A2780C cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0134 | |
| A2780DX5 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_4T98 | |
| SGC7901R cells | Uterus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0520 | |
| In Vivo Model | Mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Annexin-V-FITC apoptosis detection assay; Caspase-3 activity assay; MTT assay; Trypan blue exclusion assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-495 sensitizes MDR cancer cells to the combination of doxorubicin and taxol by inhibiting MDR1 expression, miR-495 was predicted to target ABCB1, which encodes protein MDR1. | |||
| Disease Class: Chronic myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A20.0] | [55] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Chronic myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A20.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | K562 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0004 |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR9 regulates the multidrug resistance of chronic myelogenous leukemia by targeting ABCB1. | |||
| Disease Class: Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | [56], [57] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| In Vitro Model | SGC7901 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0520 |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Flow cytometry assay assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | MRUL depletion enhances the chemosensitivity of stomach cancer cells via inhibiting ABCB1 expression and increasing cell apoptosis. And The over-expressed miR-129-5p reduced the chemo-resistance of SGC7901/VCR and SGC7901/ADR cells, while down-regulation of miR-129-5p had an opposite effect. Furthermore, three members of multi-drug resistance (MDR) related ABC transporters (ABCB1, ABCC5 and ABCG1) were found to be direct targets of miR-129-5p using bioinformatics analysis and report gene assays. The present study indicated that hyper-methylation of miR-129-5p CpG island might play important roles in the development of gastric cancer chemo-resistance by targeting MDR related ABC transporters and might be used as a potential therapeutic target in preventing the chemo-resistance of gastric cancer. | |||
| Disease Class: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.3] | [38], [39] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell growth | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | ECA-109 cells | Esophagus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6898 |
| TE13 cells | Esophageal | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_4463 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Down-regulation of miR-296 could confer sensitivity of both P-glycoprotein-related and P-glycoprotein-nonrelated drugs on esophageal cancer cells, and might promote ADR-induced apoptosis, accompanied by increased accumulation and decreased releasing amount of ADR. Down-regulation of miR-296 could significantly decrease the expression of P-glycoprotein, Bcl-2, and the transcription of MDR1, but up-regulate the expression of Bax. And down-regulation of miR-27a significantly decreased expression of MDR1, but did not alter the expression of MRP, miR-27a could possibly mediate drug resistance, at least in part through regulation of MDR1 and apoptosis. | |||
| Disease Class: Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | [40] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| In Vitro Model | SGC7901 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0520 |
| SGC7901/VCR cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_VU58 | |
| SGC7901/ADR cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_VU57 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The overexpression of miR-508-5p was sufficient to reverse cancer cell resistance to multiple chemotherapeutics in vitro and sensitize tumours to chemotherapy in vivo. Further studies showed that miR-508-5p could directly target the 3'-untranslated regions of ABCB1 and Zinc ribbon domain-containing 1 (ZNRD1), and suppress their expression at the mRNA and protein levels. Meanwhile, the suppression of ZNRD1 led to a decrease in ABCB1. | |||
| Disease Class: Leukemia [ICD-11: 2B33.6] | [41] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Leukemia [ICD-11: 2B33.6] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| In Vitro Model | HL60 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0002 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-138 was found up-regulated in the vincristine-induced multidrug resistance (MDR) leukemia cell line HL-60/VCR as compared with HL-60 cells. Up-regulation of miR-138 could reverse resistance of both P-glycoprotein-related and P-glycoprotein-non-related drugs on HL-60/VCR cells, and promote adriamycin-induced apoptosis, accompanied by increased accumulation and decreased releasing amount of adriamycin. | |||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [58] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| MCF-7/DOX cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; Immunofluorescence analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Celltiter-blue cell viability assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Expression of miR-451 is inversely correlated with mdr1 expression in breast cancer drug-resistant cells. Furthermore, the enforced increase of miR-451 levels in the MCF-7/DOX cells down-regulates expression of mdr1 and increases sensitivity of the MCF-7-resistant cancer cells to DOX | |||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [19] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
RT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Synergistic interaction between the MDR mechanisms include ABCT proteins (P-gp, BCRP, and MDR1) and metabolic enzymes of phase I of metabolism mainly CYP3A4, phase II of metabolism mainly GST was observed. In this study, FUC alone and in combination with DOX inhibited the enzyme activities of CYP3A4 and GST and down regulated their genes. We interpret this effect as a consequence of a down-regulation of pregnane X receptor (PXR) gene. FUC overcame MDR by significantly suppressing PXR mediated pathways that regulated the expression of CYP3A and ABCB1 genes in HepG-2 cells. | |||
| Disease Class: Burkitt lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A85.6] | [45] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Burkitt lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A85.6] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | HS-Sultan cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2516 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Trypan blue dye exclusion assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | MDR1 and Survivin upregulation are responsible for resistance to conventional drugs and dasatinib can restore drug sensitivity by reducing MDR1 and Survivin expression in drug-resistant BL cells. Src inhibitors could therefore be a novel treatment strategy for patients with drug resistant BL. | |||
| Disease Class: Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B55.1] | [59] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B55.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | MAST111 cells | N.A. | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| MAST139 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
WST-1 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | NPE inhibited the activity of ABCB1. Upon 1h combination treatment of MAST139 cells with Vinblastine and 100 ug/ml of NPE , a 40% increase in doxorubicin retention was observed. | |||
| Disease Class: Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B55.0] | [59] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B55.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | RH4 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_C357 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
WST-1 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | NPE inhibited the activity of ABCB1. Upon 1h combination treatment of MAST139 cells with Vinblastine and 100 ug/ml of NPE , a 40% increase in doxorubicin retention was observed. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [47] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTiter AQueous One Solution Cell Proliferation Assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | H19 LncRNA plays a leading role in breast cancer chemoresistance, mediated mainly through a H19-CUL4A-ABCB1/MDR1 pathway. H19 overexpression was contributed to cancer cell resistance to anthracyclines and paclitaxel. | |||
| Disease Class: Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51.0] | [30] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell colony | Activation | hsa05200 | |
| Cell viability | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MG63 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0426 |
| SAOS-2 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0548 | |
| U2OS cells | Bone | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0042 | |
| KHOS cells | Bone | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2546 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Colony formation assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | CircPVT1 knockdown reduces the expression of classical multidrug resistance related gene-ABCB1 in OS cells. | |||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [48] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Epithelial mesenchymal transition signaling pathway | Activation | hsa01521 | |
| p53 signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| MCF-7/ADR cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1452 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Up-regulation of miR-200c with transfection of miR-200c mimics in breast cancer cells could enhance the chemosensitivity to epirubicin and reduce expression of multidrug resistance 1 mRNA and P-glycoprotein. | |||
| Disease Class: Leukemia [ICD-11: 2B33.6] | [49] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Leukemia [ICD-11: 2B33.6] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | K562 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0004 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; Immunofluorescence analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The expression of miR-331-5p and miR-27a was inversely correlated with MDR1 expression. Transfection of exogenous miR-27a or miR-331-5p, or a combination of these two miRNAs, down-regulated MDR1 and increased sensitivity of the k562-resistant cancer cells to DOX. | |||
| Disease Class: Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | [50] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | HepG2 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0027 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Northern blotting analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Antisense H19 oligonucleotides transfection induced a marked increase in the percentage of MDR1 promoter methylation and decrease in MDR1 expression in R-HepG2 cells. Thus, the H19 gene is believed to induce P-glycoprotein expression and MDR1-associated drug resistance at least in liver cancer cells through regulation of MDR1 promoter methylation. | |||
| Disease Class: Alveolar soft part sarcoma [ICD-11: 2F00.Y] | [51] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Alveolar soft part sarcoma [ICD-11: 2F00.Y] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| KHOS cells | Bone | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2546 | |
| KHOSR2 cells | Bone | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_T432 | |
| ES-X cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |
| VAESBJ cells | Bone | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1785 | |
| ASPS-KY cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_S737 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blotting assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
XTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In comparison to Dox-sensitive cells (MCF-7 and KHOS), P-gp mRNA expression was upregulated in all Dox-resistant cells (VAESBJ, ES-X, ASPS-KY and KHOSR2 cells). | |||
| Disease Class: Burkitt lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A85.6] | [45] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Burkitt lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A85.6] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | HS-Sultan cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2516 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Trypan blue dye exclusion assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | MDR1 and Survivin upregulation are responsible for resistance to conventional drugs and dasatinib can restore drug sensitivity by reducing MDR1 and Survivin expression in drug-resistant BL cells. Src inhibitors could therefore be a novel treatment strategy for patients with drug resistant BL. | |||
| Disease Class: Pituitary adenoma [ICD-11: 2F37.1] | [43] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pituitary adenoma [ICD-11: 2F37.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | GH4C1 cells | Pituitary gland | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | CVCL_0276 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunocytochemical staining assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Lowry assay; Bradford assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Cells resistant to colchicine at 0.4 micrograms/ml, termed GH4C1/RC.4, exhibited the multidrug-resistance phenotype, as the LD50 values for colchicine, puromycin, actinomycin D, and doxorubicin were between 8 and 30 times greater than the corresponding values for the parental GH4C1 cells.Immunocytochemical staining with a monoclonal antibody, C219, to the 170-kilodalton P-glycoprotein showed directly that GH4C1/RC.4 cells overexpress P-glycoprotein. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90.0] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Daunorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Kidney cancer [ICD-11: 2C90] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Renal cell carcinoma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Kidney | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 4.11E-46 Fold-change: -1.42E+00 Z-score: -1.91E+01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Flp-In-293/Mock cells | Kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_U421 |
| Flp-In-293/ABCB1 cells | Kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_U421 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
ATPase assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Through calcein assays, we found that epimagnolin A inhibited the ABCB1-mediated export of calcein. This result suggests that epimagnolin A behaved as inhibitor or substrate for ABCB1. In ATPase assays, epimagnolin A stimulated ABCB1-dependent ATPase activity. This result indicates that epimagnolin A was recognised as a substrate by ABCB1, since ABCB1 utilises energy derived from ATP hydrolysis for substrate transport. Furthermore, in MTT assays we found that the cytotoxicity of daunorubicin, doxorubicin, vinblastine, and vincristine was enhanced by epimagnolin A in a manner comparable to verapamil, a typical substrate for ABCB1. | |||
| Disease Class: Chronic myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A20.0] | [44] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Chronic myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A20.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Daunorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | NCI-H460 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0459 |
| K562 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0004 | |
| HEK293 cells | Kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0045 | |
| K562-R cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5950 | |
| NCI-H460/VBL cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0459 | |
| In Vivo Model | SCID beige mice | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In ABCB1-overexpressing cell lines, HG-829 significantly enhanced cytotoxicity to daunorubicin, paclitaxel, vinblastine, vincristine, and etoposide. Coadministration of HG-829 fully restored in vivo antitumor activity of daunorubicin in mice without added toxicity. Functional assays showed that HG-829 is not a Pgp substrate or competitive inhibitor of Pgp-mediated drug efflux but rather acts as a noncompetitive modulator of P-glycoprotein transport function. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Ependymoma [ICD-11: 2A00.05] | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Ependymoma [ICD-11: 2A00.05] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Methotrexate | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Ependymoma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Nervous tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.79E-03 Fold-change: -3.77E-01 Z-score: -3.50E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | |
| Cell invasion | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | BXD-1425EPN cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_Y105 |
| EPN1 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| EPN7 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| EPN7R cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| DKFZ-EP1 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | ABCB1 gene expression was observed in 4 out of 5 paediatric ependymoma cell lines and increased in stem cell enriched neurospheres. Functional inhibition of ABCB1 using vardenafil or verapamil significantly (p < 0.05-0.001) potentiated the response to three chemotherapeutic drugs (vincristine, etoposide and methotrexate). Both inhibitors were also able to significantly reduce migration (p < 0.001) and invasion (p < 0.001). | |||
| Disease Class: Ependymoma [ICD-11: 2A00.05] | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Ependymoma [ICD-11: 2A00.05] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Methotrexate | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Ependymoma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Nervous tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.79E-03 Fold-change: -3.77E-01 Z-score: -3.50E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | |
| Cell invasion | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | BXD-1425EPN cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_Y105 |
| EPN1 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| EPN7 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| EPN7R cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| DKFZ-EP1 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | ABCB1 gene expression was observed in 4 out of 5 paediatric ependymoma cell lines and increased in stem cell enriched neurospheres. Functional inhibition of ABCB1 using vardenafil or verapamil significantly (p < 0.05-0.001) potentiated the response to three chemotherapeutic drugs (vincristine, etoposide and methotrexate). Both inhibitors were also able to significantly reduce migration (p < 0.001) and invasion (p < 0.001). | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51.0] | [67] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Methotrexate | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell colony | Activation | hsa05200 | |
| Cell senescence | Inhibition | hsa04218 | ||
| Cell viability | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| LUCAT1/miR200c/ABCB1 pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | MG63 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0426 |
| SAOS-2 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0548 | |
| U2OS cells | Bone | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0042 | |
| HOS cells | Bone | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0312 | |
| HFOB cells | Bone | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3708 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; Luciferase reporter assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Transwell invasion assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | LncRNA LUCAT1 and ABCB1 protein were both up-regulated in MG63/MTX and HOS/MTX cells when treated with methotrexate. ABCB1, acting as a vital protein of drug resistance, participated in the multiple drug resistance occurrence. | |||
| Disease Class: Ependymoma [ICD-11: 2A00.05] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Ependymoma [ICD-11: 2A00.05] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Methotrexate | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | |
| Cell invasion | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | BXD-1425EPN cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_Y105 |
| EPN1 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| EPN7 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| EPN7R cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| DKFZ-EP1 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | ABCB1 gene expression was observed in 4 out of 5 paediatric ependymoma cell lines and increased in stem cell enriched neurospheres. Functional inhibition of ABCB1 using vardenafil or verapamil significantly (p < 0.05-0.001) potentiated the response to three chemotherapeutic drugs (vincristine, etoposide and methotrexate). Both inhibitors were also able to significantly reduce migration (p < 0.001) and invasion (p < 0.001). | |||
| Disease Class: Psoriasis [ICD-11: EA90.0] | [68] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Psoriasis [ICD-11: EA90.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Methotrexate | |||
| Molecule Alteration | SNP | rs1045642 TT |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | The SNP of ABCB1 led to methotrexate resistance in the resistance. | |||
| Disease Class: Rheumatoid arthritis [ICD-11: FA20.0] | [24] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Rheumatoid arthritis [ICD-11: FA20.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Methotrexate | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | MTX is a substrate for eight ABC transporters. In vitro studies demonstrated that RAFLS treated with MTX had higher ABCB1 expression levels than controls, with a positive correlation between ABCB1 expression levels and RA treatment duration. In addition to MTX, other DMARDs (e.g. sulfasalazine, leflunomide, bucillamine, azathioprine), glucocorticoids (e.g. betamethasone, dexamethasone), and NSAIDs (e.g. celecoxib and indomethacin) are also substrates of ABC transporters. | |||
| Disease Class: Systemic lupos erythematosus [ICD-11: 4A40.2] | [69] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Systemic lupos erythematosus [ICD-11: 4A40.2] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Methotrexate | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | Up-regulation of P-glycoprotein led to methotrexate resistance in the staphylococcus infection. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Ependymoma [ICD-11: 2A00.05] | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Ependymoma [ICD-11: 2A00.05] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Etoposide | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Ependymoma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Nervous tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.79E-03 Fold-change: -3.77E-01 Z-score: -3.50E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | |
| Cell invasion | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | BXD-1425EPN cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_Y105 |
| EPN1 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| EPN7 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| EPN7R cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| DKFZ-EP1 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | ABCB1 gene expression was observed in 4 out of 5 paediatric ependymoma cell lines and increased in stem cell enriched neurospheres. Functional inhibition of ABCB1 using vardenafil or verapamil significantly (p < 0.05-0.001) potentiated the response to three chemotherapeutic drugs (vincristine, etoposide and methotrexate). Both inhibitors were also able to significantly reduce migration (p < 0.001) and invasion (p < 0.001). | |||
| Disease Class: Ependymoma [ICD-11: 2A00.05] | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Ependymoma [ICD-11: 2A00.05] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Etoposide | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Ependymoma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Nervous tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.79E-03 Fold-change: -3.77E-01 Z-score: -3.50E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | |
| Cell invasion | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | BXD-1425EPN cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_Y105 |
| EPN1 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| EPN7 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| EPN7R cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| DKFZ-EP1 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | ABCB1 gene expression was observed in 4 out of 5 paediatric ependymoma cell lines and increased in stem cell enriched neurospheres. Functional inhibition of ABCB1 using vardenafil or verapamil significantly (p < 0.05-0.001) potentiated the response to three chemotherapeutic drugs (vincristine, etoposide and methotrexate). Both inhibitors were also able to significantly reduce migration (p < 0.001) and invasion (p < 0.001). | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Hypertrophic scar [ICD-11: EE60.0] | [61] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Hypertrophic scar [ICD-11: EE60.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Etoposide | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Hypertrophic scar tissue isolates | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blotting assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Fibroblasts derived from hypertrophic scar and normal skin tissues were first compared for their resistance to verapamil and etoposide phosphate. Scar fibroblasts showed stronger resistance to both verapamil and etoposide than normal fibroblasts, also scar fibroblasts expressed more P-glycoprotein and MRP1 than normal fibroblasts. | |||
| Disease Class: Ependymoma [ICD-11: 2A00.05] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Ependymoma [ICD-11: 2A00.05] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Etoposide | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | |
| Cell invasion | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | BXD-1425EPN cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_Y105 |
| EPN1 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| EPN7 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| EPN7R cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| DKFZ-EP1 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | ABCB1 gene expression was observed in 4 out of 5 paediatric ependymoma cell lines and increased in stem cell enriched neurospheres. Functional inhibition of ABCB1 using vardenafil or verapamil significantly (p < 0.05-0.001) potentiated the response to three chemotherapeutic drugs (vincristine, etoposide and methotrexate). Both inhibitors were also able to significantly reduce migration (p < 0.001) and invasion (p < 0.001). | |||
| Disease Class: Anaplastic astrocytoma [ICD-11: 2A00.04] | [26] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Anaplastic astrocytoma [ICD-11: 2A00.04] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Etoposide | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Malignant gliomas tissue | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunohistochemistry assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Oncotech EDR assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Cisplatin and etoposide are both substrates for membrane-bound efflux pumps, such as MRP and MDR1, which prevent their entry into the extracellular space of the central nervous system. The low levels of in vitro drug resistance noted for cisplatin and etoposide may be explained in part by the absence of such a barrier in our in vitro assay system. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Ependymoma [ICD-11: 2A00.05] | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Ependymoma [ICD-11: 2A00.05] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Vincristine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Ependymoma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Nervous tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.79E-03 Fold-change: -3.77E-01 Z-score: -3.50E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | |
| Cell invasion | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | BXD-1425EPN cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_Y105 |
| EPN1 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| EPN7 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| EPN7R cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| DKFZ-EP1 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | ABCB1 gene expression was observed in 4 out of 5 paediatric ependymoma cell lines and increased in stem cell enriched neurospheres. Functional inhibition of ABCB1 using vardenafil or verapamil significantly (p < 0.05-0.001) potentiated the response to three chemotherapeutic drugs (vincristine, etoposide and methotrexate). Both inhibitors were also able to significantly reduce migration (p < 0.001) and invasion (p < 0.001). | |||
| Disease Class: Ependymoma [ICD-11: 2A00.05] | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Ependymoma [ICD-11: 2A00.05] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Vincristine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Ependymoma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Nervous tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.79E-03 Fold-change: -3.77E-01 Z-score: -3.50E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | |
| Cell invasion | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | BXD-1425EPN cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_Y105 |
| EPN1 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| EPN7 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| EPN7R cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| DKFZ-EP1 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | ABCB1 gene expression was observed in 4 out of 5 paediatric ependymoma cell lines and increased in stem cell enriched neurospheres. Functional inhibition of ABCB1 using vardenafil or verapamil significantly (p < 0.05-0.001) potentiated the response to three chemotherapeutic drugs (vincristine, etoposide and methotrexate). Both inhibitors were also able to significantly reduce migration (p < 0.001) and invasion (p < 0.001). | |||
| Disease Class: Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90.0] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Vincristine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Kidney cancer [ICD-11: 2C90] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Renal cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Kidney | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.04E-02 Fold-change: -1.96E-01 Z-score: -2.71E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Flp-In-293/Mock cells | Kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_U421 |
| Flp-In-293/ABCB1 cells | Kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_U421 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
ATPase assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Through calcein assays, we found that epimagnolin A inhibited the ABCB1-mediated export of calcein. This result suggests that epimagnolin A behaved as inhibitor or substrate for ABCB1. In ATPase assays, epimagnolin A stimulated ABCB1-dependent ATPase activity. This result indicates that epimagnolin A was recognised as a substrate by ABCB1, since ABCB1 utilises energy derived from ATP hydrolysis for substrate transport. Furthermore, in MTT assays we found that the cytotoxicity of daunorubicin, doxorubicin, vinblastine, and vincristine was enhanced by epimagnolin A in a manner comparable to verapamil, a typical substrate for ABCB1. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.02] | [3] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.02] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Prochlorperazine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Glioblastoma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Nervous tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.79E-03 Fold-change: -3.77E-01 Z-score: -3.50E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| In Vitro Model | SHI-1 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2191 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; RNA-sequencing analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Wound healing assay;Transwell assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Prochlorperazine may modulate the expression levels of multidrug resistance proteins (they decreased ABCB1 and increased ABCG2 expression), E-cadherin, alpha-tubulin and integrins, and could impair the migration and invasion of U-87 MG cells. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.02] | [5] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.02] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Temozolomide | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Glioblastoma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Nervous tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.79E-03 Fold-change: -3.77E-01 Z-score: -3.50E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| In Vitro Model | Glioblastoma tissue | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Real-time PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Patient survival time | |||
| Mechanism Description | In the chemosensitive MDR1-negative parental cell line k562 10 ug/ml temozolomide resulted in pronounced cell death with only 47.1% surviving 48 h compared with the control. In contrast, in the highly MDR1-expressing resistant subline k562-VP16, cell death was significantly lower after exposure to temozolomide with 73.4% surviving 48 h (P = 0.002). Addition of a nontoxic dose of the MDR1-modulator cyclosporine A (1 uM) to temozolomide resulted in a trend towards restoration of chemosensitivity in the resistant MDR1-expressing cell line. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.02] | [10] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.02] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Temozolomide | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Glioblastoma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Nervous tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.79E-03 Fold-change: -3.77E-01 Z-score: -3.50E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell viability | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | U87 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0022 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Upregulation of TUSC7,which acted by directly targeting and silencing expression of miR-10a gene, suppressed both TMZ resistance and expression of multidrug resistance protein 1 (MDR1) in U87TR cells,, and miR-10a mediated TUSC7-induced inhibition on TMZ resistance in U87TR cells. | |||
| Disease Class: Malignant glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.2] | [86] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Malignant glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.2] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Temozolomide | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| In Vitro Model | U251 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0021 |
| U87 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0022 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Knockdown of long noncoding RNA H19 sensitizes human glioma cells to temozolomide therapy.the expression level of H19 transcripts was increased compared to wild-type or nonresistant clones.Furthermore, the reduced expression of H19 altered major drug resistance genes, such as ABCB1 (MDR1), ABCC (MRP), and ABCG2 (BCRP), both at the mRNA and protein levels. Taken together, these findings suggest that H19 plays an important role in the development of TMZ resistance, and may represent a novel therapeutic target for TMZ-resistant gliomas.Our results suggested that knockdown of H19 significantly downregulated the expression of these drug-resistant genes, both at the mRNA (P<0.001 vs respective control siRNA) and protein levels. These data confirm that the H19-induced TMZ resistance is in part mediated by MDR, MRP, and ABCG2. | |||
| Disease Class: Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.02] | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.02] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Temozolomide | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| In Vitro Model | Glioblastoma tissue | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Real-time PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Patient survival time | |||
| Mechanism Description | In the chemosensitive MDR1-negative parental cell line k562 10 ug/ml temozolomide resulted in pronounced cell death with only 47.1% surviving 48 h compared with the control. In contrast, in the highly MDR1-expressing resistant subline k562-VP16, cell death was significantly lower after exposure to temozolomide with 73.4% surviving 48 h (P = 0.002). Addition of a nontoxic dose of the MDR1-modulator cyclosporine A (1 uM) to temozolomide resulted in a trend towards restoration of chemosensitivity in the resistant MDR1-expressing cell line. | |||
| Disease Class: Chronic myelogenous leukemia [ICD-11: 2A20.3] | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Chronic myelogenous leukemia [ICD-11: 2A20.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Temozolomide | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| In Vitro Model | K562 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0004 |
| K562-VP16 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0004 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Real-time PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In the chemosensitive MDR1-negative parental cell line k562 10 ug/ml temozolomide resulted in pronounced cell death with only 47.1% surviving 48 h compared with the control. In contrast, in the highly MDR1-expressing resistant subline k562-VP16, cell death was significantly lower after exposure to temozolomide with 73.4% surviving 48 h (P = 0.002). Addition of a nontoxic dose of the MDR1-modulator cyclosporine A (1 uM) to temozolomide resulted in a trend towards restoration of chemosensitivity in the resistant MDR1-expressing cell line. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | [6] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Paclitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Liver tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.18E-05 Fold-change: -3.05E-01 Z-score: -4.26E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Huh-7 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0336 |
| BEL-7402 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5492 | |
| HepG2 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0027 | |
| Hep3B cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0326 | |
| SMMC7721 cells | Uterus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0534 | |
| Skhep1 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0525 | |
| HCC3 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0C57 | |
| LM-6 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_7680 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
WST-1 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-223 targeted ABCB1 3'UTR directly, and miR-223 down-regulated ABCB1 at both mRNA and protein levels. The over-expression of miR-223 increased the HCC cellsensitivity to anticancer drugs, and the inhibition of miR-223 had the opposite effect. Importantly, the over-expression or silencingof ABCB1 can rescue the cell response to the anticancer drugs mediated by miR-223 over-expression or inhibition. | |||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [78] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Paclitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7/PR cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Sulforhodamine B assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Down-regulation of LncRNA RP11-770J1.3 and TMEM25 enhanced the sensitivity of MCF-7/PR cells to paclitaxel, and inhibited the expression of MRP, BCRP and MDR1/P-gp. | |||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [54] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Paclitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | A2780 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0134 |
| A2780C cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0134 | |
| A2780DX5 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_4T98 | |
| SGC7901R cells | Uterus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0520 | |
| In Vivo Model | Mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Annexin-V-FITC apoptosis detection assay; Caspase-3 activity assay; MTT assay; Trypan blue exclusion assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-495 sensitizes MDR cancer cells to the combination of doxorubicin and taxol by inhibiting MDR1 expression, miR-495 was predicted to target ABCB1, which encodes protein MDR1. | |||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [79] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Paclitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell colony | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell viability | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | SW620 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0547 |
| HCT116 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0291 | |
| LOVO cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0399 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Inhibition of LINC00473 in vivo could overcome the Taxol resistance of CRC cells, could recover the expression of tumor suppressor miR-15a and chemotherapy-induced tumor regression while the BCL-2-related anti-apoptosis pathway was activated and the multidrug-resistant (MDR) genes LRP, MDR1 were up-regulated by LINC00473. | |||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [75] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Paclitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| Cell viability | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| UCA1/miR129/ABCB1 signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | SkOV3 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0532 |
| Hey A8 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_8878 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | ABCB1 up-regulated by UCA1/miR-129 axis contributed to PTX resistance in PTX-resistant OC cells. | |||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [36] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Paclitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | A2780 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0134 |
| OVCAR3 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0465 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Both A2780/DDP and A2780/Taxol cells expressed miR-186 at lower levels than A2780. miR-186 overexpression increased the sensitivity of ovarian cancer cell lines to paclitaxel and cisplatin compared with the negative control or mock cells, miR-186 transfection induced cell apoptosis while anti-miR-186 transfection reduced cell apoptosis, suggesting that miR-186 may inhibit the development of drug resistance in ovarian cancer cells. miR-186 overexpression may increase the sensitivity of ovarian cancer cells to paclitaxel by targeting ABCB1 and modulating GST-Pi. | |||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [37] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Paclitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | A2780 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0134 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Overexpression of miR-133b increases ovarian cancer cell sensitivity to cisplatin and paclitaxel by decreasing GST-Pi and MDR1 expression. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [75] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Paclitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| Cell viability | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| UCA1/miR129/ABCB1 signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | SkOV3 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0532 |
| Hey A8 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_8878 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | ABCB1 up-regulated by UCA1/miR-129 axis contributed to PTX resistance in PTX-resistant OC cells. | |||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [76] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Paclitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell invasion | Activation | hsa05200 | |
| Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | A2780 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0134 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The upregulation of P-gp cause ovarian cancer cells pumping drug substance outside to reduce cytotoxicity presented and enhances the resistance of paclitaxe. | |||
| Disease Class: Colorectal carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B91.3] | [77] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Colorectal carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B91.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Paclitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | CaCo2 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0025 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
RT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
WST-1 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The transient exposure to digoxin for 24 h was found to induce MDR1 mRNA in Caco-2 cells. Here, a digoxin-tolerant Caco-2 subline (Caco/DX) was newly established by the continuous exposure of Caco-2 cells to digoxin, and the effects of continuous exposure to digoxin on MDR1 were examined. The 50% growth inhibitory concentration (IC(50)) values for digoxin in Caco-2 and Caco/DX cells were 17.2 and 81.4 nM, respectively. The IC(50) values for paclitaxel, an MDR1 substrate, were 1.0 and 547 nM, respectively, whereas the cytotoxicity of 5-fluorouracil was comparable in both. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | [11] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.27E-03 Fold-change: -2.98E-01 Z-score: -3.27E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell viability | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| Wnt signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04310 | ||
| In Vitro Model | H1299 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Si-HOTAIR interference significantly increased the sensitivity of cells to DDP, the IC50 of cells was decreased from 131.85 to 44.34 M (P<0.05), the expression levels of MRP1 and MDR1 were significantly decreased, and the activation of Wnt signaling pathway was significantly inhibited. | |||
| Disease Class: Cholangiocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.0] | [13] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Cholangiocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Cholangiocarcinoma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Liver tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.18E-05 Fold-change: -3.05E-01 Z-score: -4.26E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | mTOR signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04150 | |
| In Vitro Model | GBC-SD cells | Gallbladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6903 |
| RBE cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_4896 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Flow cytometric analysis | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR199a-3p enhances cisplatin sensitivity of cholangiocarcinoma cells by inhibiting mTOR signaling pathway and expression of MDR1. miR199a-3p overexpression could reduce cisplatin induced MDR1 expression by decreasing the synthesis and increasing the degradation of MDR1, thus enhancing the effectiveness of cisplatin in cholangiocarcinoma. | |||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [34] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | SkOV3 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0532 |
| HO8910 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6868 | |
| ES2 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_AX39 | |
| FTE187 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| HG-SOC cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| HO8910PM cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0310 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; Dual luciferase activity assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | microRNA-595 sensitizes ovarian cancer cells to cisplatin by targeting ABCB1. The expression level of ABCB1 was inversely correlated with miR595 in the ovarian cancer tissues, overexpression of ABCB1 decreased the miR595-overexpressing HO8910PM and SkOV-3 cell sensitivity to cisplatin. | |||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [35] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell viability | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-381 could overcome DDP resistance of breast cancer by directly targeting MDR1. | |||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [36] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | A2780 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0134 |
| OVCAR3 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0465 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Both A2780/DDP and A2780/Taxol cells expressed miR-186 at lower levels than A2780. miR-186 overexpression increased the sensitivity of ovarian cancer cell lines to paclitaxel and cisplatin compared with the negative control or mock cells, miR-186 transfection induced cell apoptosis while anti-miR-186 transfection reduced cell apoptosis, suggesting that miR-186 may inhibit the development of drug resistance in ovarian cancer cells. miR-186 overexpression may increase the sensitivity of ovarian cancer cells to paclitaxel by targeting ABCB1 and modulating GST-Pi. | |||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [37] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | A2780 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0134 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Overexpression of miR-133b increases ovarian cancer cell sensitivity to cisplatin and paclitaxel by decreasing GST-Pi and MDR1 expression. | |||
| Disease Class: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.3] | [38], [39] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell growth | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | ECA-109 cells | Esophagus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6898 |
| TE13 cells | Esophageal | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_4463 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Down-regulation of miR-296 could confer sensitivity of both P-glycoprotein-related and P-glycoprotein-nonrelated drugs on esophageal cancer cells, and might promote ADR-induced apoptosis, accompanied by increased accumulation and decreased releasing amount of ADR. Down-regulation of miR-296 could significantly decrease the expression of P-glycoprotein, Bcl-2, and the transcription of MDR1, but up-regulate the expression of Bax. And down-regulation of miR-27a significantly decreased expression of MDR1, but did not alter the expression of MRP, miR-27a could possibly mediate drug resistance, at least in part through regulation of MDR1 and apoptosis. | |||
| Disease Class: Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | [40] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| In Vitro Model | SGC7901 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0520 |
| SGC7901/VCR cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_VU58 | |
| SGC7901/ADR cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_VU57 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The overexpression of miR-508-5p was sufficient to reverse cancer cell resistance to multiple chemotherapeutics in vitro and sensitize tumours to chemotherapy in vivo. Further studies showed that miR-508-5p could directly target the 3'-untranslated regions of ABCB1 and Zinc ribbon domain-containing 1 (ZNRD1), and suppress their expression at the mRNA and protein levels. Meanwhile, the suppression of ZNRD1 led to a decrease in ABCB1. | |||
| Disease Class: Leukemia [ICD-11: 2B33.6] | [41] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Leukemia [ICD-11: 2B33.6] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| In Vitro Model | HL60 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0002 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-138 was found up-regulated in the vincristine-induced multidrug resistance (MDR) leukemia cell line HL-60/VCR as compared with HL-60 cells. Up-regulation of miR-138 could reverse resistance of both P-glycoprotein-related and P-glycoprotein-non-related drugs on HL-60/VCR cells, and promote adriamycin-induced apoptosis, accompanied by increased accumulation and decreased releasing amount of adriamycin. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | [18] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Gastric cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Gastric tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.42E-03 Fold-change: 1.98E-01 Z-score: 8.44E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| mTOR/HIF-1alpha /P-gp/MRP1 signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | SGC7901 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0520 |
| BGC823 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3360 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Overexpression of long non-coding RNA PVT1 in gastric cancer cells promotes the development of multidrug resistance.PVT-1 was highly expressed in gastric cancer tissues of cisplatin-resistant patients and cisplatin-resistant cells. While, PVT1 overexpression exhibit the anti-apoptotic property in BGC823 and SGC7901 cells transfected with LV-PVT1-GFP and treated with cisplatin. Moreover, qRT-PCR and western blotting revealed that PVT1 up-regulation increased the expression of MDR1, MRP, mTOR and HIF-1alpha. Overexpression of LncRNA PVT1 in gastric carcinoma promotes the development of MDR, suggesting an efficacious target for reversing MDR in gastric cancer therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | [27] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| In Vitro Model | SGC7901 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0520 |
| BGC823 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3360 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; RT-qPCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | LncRNA SNHG5 promotes cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer via inhibiting cell apoptosis and upregulating drug resistance-related genes. | |||
| Disease Class: Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | [28] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | |
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | Huh-7 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0336 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; RNAi assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Knockdown of HOTAIR expression downregulated the MRP1 expression levels in the k562-imatinib cells and resulted in higher sensitivity to the imatinib treatment. In addition, the activation of PI3k/Akt was greatly attenuated when HOTAIR was knocked down in k562-imatinib cells. | |||
| Disease Class: Endometrial cancer [ICD-11: 2C76.1] | [29] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Endometrial cancer [ICD-11: 2C76.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell autophagy | Inhibition | hsa04140 | |
| In Vitro Model | Ishikawa cells | Endometrium | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2529 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Dual-color autophagy reporter assay; CCK8 assay; Flow cytometric analysis | |||
| Mechanism Description | HOTAIR can regulate the cisplatin-resistance ability of human endometrial cancer cells through the regulation of autophagy by increasing Beclin-1, MDR, and P-gp expression. | |||
| Disease Class: Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51.0] | [30] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell colony | Activation | hsa05200 | |
| Cell viability | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MG63 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0426 |
| SAOS-2 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0548 | |
| U2OS cells | Bone | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0042 | |
| KHOS cells | Bone | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2546 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Colony formation assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | CircPVT1 knockdown reduces the expression of classical multidrug resistance related gene-ABCB1 in OS cells. | |||
| Disease Class: Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | [31], [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | AKT signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | |
| Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | ||
| Cell invasion | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| PI3K signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | ||
| TGF-beta/Smad2/STAT3/STAT5 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04350 | ||
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Vi-cell cell viability analyzer assay; MTS assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-21 achieves the drug resistance effect through three mechanisms: Increasing MDR1 and MPR1 expression levels, and enhancing drug efflux from the cells; increasing GSH, superoxide dismutase and GST-Pi expression levels and promoting drug inactivation; and inhibiting the PI3k signaling pathway and in turn inhibiting apoptotic signaling. And miR-10a had an important role in promoting drug resistance in tumors through enhancing drug efflux and inhibiting apoptosis via upregulation of MDR1, MRP1 and RhoE expression. In addition, miR-10a promoted the expression of TGF-beta as wells as regulated the activity of the Smad2/STAT3/STAT5 pathway and its downstream transcriptional factors of HIF and eIF4E, which may be the potential mechanism of drug resistance in A549 cells. Therefore, miR-10a may be an important drug target for improving cancer treatment; however, further studies are required to explore the clinical applications of miR-10a inhibitors. | |||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [33] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| In Vitro Model | A2780 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0134 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTiter 96 aqueous one solution cell proliferation assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-130a and miR-374a mimics decreased the sensitivity of A2780 cells to cisplatin, reversely, their inhibitors could resensitize A2780/DDP cells. Furthermore, overexpression of miR-130a could increase the MDR1 mRNA and P-gp levels in A2780 and A2780/DDP cells, whereas knockdown of miR-130a could inhibit MDR1 gene expression and upregulate the PTEN protein expression. In a conclusion, the deregulation of miR-374a and miR-130a may be involved in the development and regulation of cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer cells. This role of miR-130a may be achieved by regulating the MDR1 and PTEN gene expression. | |||
| Disease Class: Malignant glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.2] | [26] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Malignant glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.2] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Malignant gliomas tissue | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunohistochemistry assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
EDR assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In vitro drug resistance in malignant gliomas was independent of prior therapy. High-grade glioblastomas showed a lower level of extreme drug resistance than low-grade astrocytomas to cisplatin (11% versus 27%), temozolomide (14% versus 27%), irinotecan (33% versus 53%), and BCNU (29% versus 38%). A substantial percentage of brain tumors overexpressed biomarkers associated with drug resistance, including MGMT (67%), GSTP1 (49%), and mutant p53 (41%). MGMT and GSTP1 overexpression was independently associated with in vitro resistance to BCNU, whereas coexpression of these two markers was associated with the greatest degree of BCNU resistance. | |||
| Disease Class: Anaplastic astrocytoma [ICD-11: 2A00.04] | [26] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Anaplastic astrocytoma [ICD-11: 2A00.04] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Malignant gliomas tissue | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunohistochemistry assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Oncotech EDR assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Cisplatin and etoposide are both substrates for membrane-bound efflux pumps, such as MRP and MDR1, which prevent their entry into the extracellular space of the central nervous system. The low levels of in vitro drug resistance noted for cisplatin and etoposide may be explained in part by the absence of such a barrier in our in vitro assay system. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | [12] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Oxaliplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Liver tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.18E-05 Fold-change: -3.05E-01 Z-score: -4.26E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell viability | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Wnt/Beta-catenin signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04310 | ||
| In Vitro Model | Huh-7 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0336 |
| BEL-7402 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5492 | |
| HepG2 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0027 | |
| SMMC7721 cells | Uterus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0534 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-122 inhibits MDR1 expression via suppression of Wnt/beta-catenin pathway, thereby enhancing HCC sensitivity to OXA. | |||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [73] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Oxaliplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Wnt/Beta-catenin signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04310 | |
| In Vitro Model | HCT116 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0291 |
| HCT116-OxR cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0291 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; Immunofluorescence staining assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Flow cytometric analysis | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-506 overexpression in HCT116-OxR cells enhances oxaliplatin sensitivity by inhibiting MDR1/P-gp expression via down-regulation of the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | [72] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Oxaliplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell viability | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| miR125a/hexokinase 2 pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | BGC-823 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3360 |
| MGC-803 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5334 | |
| SGC7901 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0520 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Flow cytometry assay; Transwell assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | BLACAT1 accelerates the oxaliplatin-resistance of gastric cancer via promoting ABCB1 protein expression by targeting miR-361. | |||
| Disease Class: Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | [72] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Oxaliplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell viability | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| miR125a/hexokinase 2 pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | BGC-823 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3360 |
| MGC-803 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5334 | |
| SGC7901 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0520 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
RT-qPCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Flow cytometry assay; Transwell assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | BLACAT1 accelerates the oxaliplatin-resistance of gastric cancer via promoting ABCB1 protein expression by targeting miR-361. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | [15] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Ketorolac | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Acute myelocytic leukemia | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Bone marrow | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 4.70E-06 Fold-change: 9.31E-02 Z-score: 4.63E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Efflux pump genes expression analysis | |||
| Mechanism Description | Ketorolac-fluconazole in vitro combination would be a promising strategy for further clinical in vivo trials to overcome fluconazole resistance in AML patients on induction chemotherapy. To our knowledge, the current study is the first in vitro report on the use of ketorolac in reverting fluconazole resistance in C. albicans isolated from AML patients. Resistance of C. albicans to azole antifungals is associated with overexpression of efflux pump genes especially CDR1 and MDR1. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis [ICD-11: 8B60.0] | [16] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis [ICD-11: 8B60.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Riluzole | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis [ICD-11: 8B60] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Lateral sclerosis | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Skin | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.05E-01 Fold-change: 5.70E-02 Z-score: 1.46E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | bEND.3 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0170 |
| C8D1A cells | Colon | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_6379 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
High-performance liquid chromatography | |||
| Mechanism Description | Riluzole is moderately effective for ALS patients and prolongs survival by only three months. According to previous studies, increased P-gp transporter activity and expression are induced by ALS. As riluzole is a substrate of P-gp, the inductions potentially limit the brain distribution of riluzole and further promote drug resistance in the later stage of ALS disease. | |||
| Disease Class: Spinal cord injury [ICD-11: 8C21.0] | [84] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Spinal cord injury [ICD-11: 8C21.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Riluzole | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vivo Model | Abcb1a Knockout rats model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blotting assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
High performance liquid chromatography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Riluzole spinal cord disposition was significantly higher in knockout rats than in WT rats at 10 days post-spinal cord injury (p=0.019), confirming that Pgp plays a critical role in diminishing spinal cord riluzole disposition following spinal cord injury. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis [ICD-11: 8B60.0] | [16] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis [ICD-11: 8B60.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Riluzole | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis [ICD-11: 8B60] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Lateral sclerosis | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Cervical spinal cord | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.08E-01 Fold-change: -4.70E-01 Z-score: -1.77E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | bEND.3 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0170 |
| C8D1A cells | Colon | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_6379 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
High-performance liquid chromatography | |||
| Mechanism Description | BEND.3 Cells were treated with riluzole and verapamil liposomes at different doses and time durations to determine the inhibitory levels of P-gp. In the buffer control treatment, the expression of P-gp was noted as a baseline level (100%). After the exposure to 5, 10, 20, 30, and 40 ug/ml cocktail liposomes for 48 h, bEND.3 cells resulted in a distinct decrease of P-gp expression with 93.0 plus or minus 5.2%, 85.8 plus or minus 4.7%, 50.3 plus or minus 5.6% 26.2 plus or minus 5.1%, and 20.8 plus or minus 4.9% of the baseline level, respectively. The extent of the decrease was linearly dependent on the concentration of verapamil in formulations (5 to 30 ug/ml), while inhibited levels of P-gp by 30 ug/ml and 40 ug/ml of verapamil cocktail liposome were not significantly different. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.02] | [3] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.02] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Perphenazine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Brain cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Nervous tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.39E-11 Fold-change: -5.21E-02 Z-score: -6.70E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | |
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | SHI-1 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2191 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Mechanism Description | The present study explored the effects of perphenazine and prochlorperazine on the levels of ABCB1, ABCG2, E-cadherin, alpha-tubulin and integrins (alpha3, alpha5, and beta1), as well as on the migratory and invasive ability of U87-MG cells. The results suggested that perphenazine and prochlorperazine may modulate the expression levels of multidrug resistance proteins (they decreased ABCB1 and increased ABCG2 expression), E-cadherin, alpha-tubulin and integrins, and could impair the migration and invasion of U-87 MG cells. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [20] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Esomeprazole | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.12E-33 Fold-change: -2.80E-01 Z-score: -1.43E+01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell autophagy | Activation | hsa04140 | |
| Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | ||
| In Vitro Model | Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 |
| Mechanism Description | Esomeprazole overcomes paclitaxel-resistance and enhances anticancer effects of paclitaxel by inducing autophagy in A549/Taxol cells. Esomeprazole could only result in a slight decrease in the expression of P-gp in A549/Taxol cells. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [21] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Tocotrienol | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.61E-73 Fold-change: -3.06E-01 Z-score: -2.38E+01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | NF-KappaB signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04064 | |
| In Vitro Model | VCaP cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2235 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Quantitative real-time PCR; Western blot analysis; Reporter gene assay of NF-kappaB transcriptional activity assay; MDR1 promoter reporter assay; P-gp activity assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Reversal effect assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Gamma-Tocotrienol reverses multidrug resistance of breast cancer cells through the regulation of the gamma-Tocotrienol-NF-kappaB-P-gp axis. gamma-Tocotrienol effectively suppressed mdr1 promoter activity and the efflux of P-gp. gamma-Tocotrienol inhibited NF-kappaB activation and reduced NF-kappaB transcriptional activity. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Staphylococcus infection [ICD-11: 1B7Y.3] | [22] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus infection [ICD-11: 1B7Y.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Ampicillin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates | 287 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus isolates | 1280 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates | 573 | |||
| Acinetobacter isolates | 469 | |||
| Enterobacter cloacae isolates | 550 | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Disk diffusion method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Up-regulation of P-glycoprotein led to ampicillin resistance in the staphylococcus infection. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Hypo-attenuated leaflet thickening [ICD-11: BD10.2] | [23] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Hypo-attenuated leaflet thickening [ICD-11: BD10.2] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Aspirin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | SNP | rs1045642 |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | We thoroughly genotyped 34 SNPs and 8 SNPs that have been reported for clopidogrel and aspirin resistance. A total of 148 patients were enrolled. There were 15 patients demonstrating signs of HALT. Patients with HALT had a higher rate of atrial fibrillation (AF) pre-TAVR (33.3 vs. 7.5%, P = 0.01). | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Rheumatoid arthritis [ICD-11: FA20.0] | [24] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Rheumatoid arthritis [ICD-11: FA20.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Betamethasone | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | MTX is a substrate for eight ABC transporters. In vitro studies demonstrated that RAFLS treated with MTX had higher ABCB1 expression levels than controls, with a positive correlation between ABCB1 expression levels and RA treatment duration. In addition to MTX, other DMARDs (e.g. sulfasalazine, leflunomide, bucillamine, azathioprine), glucocorticoids (e.g. betamethasone, dexamethasone), and NSAIDs (e.g. celecoxib and indomethacin) are also substrates of ABC transporters. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Epilepsy [ICD-11: 8A60.0] | [25] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Epilepsy [ICD-11: 8A60.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Carbamazepine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | SNP | rs1128503 |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | ABCB1 polymorphisms were previously demonstrated to be associated with the metabolism and resistance of carbamazepine (CBZ) in epilepsy. ABCB1 rs1045642 and rs2032582 polymorphisms were associated with CBZ metabolism for epilepsy, and rs1128503 was related to carbamazepine resistance. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Malignant glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.2] | [26] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Malignant glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.2] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Carmustine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Malignant gliomas tissue | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunohistochemistry assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
EDR assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In vitro drug resistance in malignant gliomas was independent of prior therapy. High-grade glioblastomas showed a lower level of extreme drug resistance than low-grade astrocytomas to cisplatin (11% versus 27%), temozolomide (14% versus 27%), irinotecan (33% versus 53%), and BCNU (29% versus 38%). A substantial percentage of brain tumors overexpressed biomarkers associated with drug resistance, including MGMT (67%), GSTP1 (49%), and mutant p53 (41%). MGMT and GSTP1 overexpression was independently associated with in vitro resistance to BCNU, whereas coexpression of these two markers was associated with the greatest degree of BCNU resistance. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Staphylococcus infection [ICD-11: 1B7Y.3] | [22] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus infection [ICD-11: 1B7Y.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cefazolin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates | 287 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus isolates | 1280 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates | 573 | |||
| Acinetobacter isolates | 469 | |||
| Enterobacter cloacae isolates | 550 | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Disk diffusion method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Up-regulation of P-glycoprotein led to cefazolin resistance in the staphylococcus infection. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Staphylococcus infection [ICD-11: 1B7Y.3] | [22] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus infection [ICD-11: 1B7Y.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cefotetan | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates | 287 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus isolates | 1280 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates | 573 | |||
| Acinetobacter isolates | 469 | |||
| Enterobacter cloacae isolates | 550 | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Disk diffusion method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Up-regulation of P-glycoprotein led to ampicillin resistance in the staphylococcus infection. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Rheumatoid arthritis [ICD-11: FA20.0] | [24] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Rheumatoid arthritis [ICD-11: FA20.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Chloroquine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | MTX is a substrate for eight ABC transporters. In vitro studies demonstrated that RAFLS treated with MTX had higher ABCB1 expression levels than controls, with a positive correlation between ABCB1 expression levels and RA treatment duration. In addition to MTX, other DMARDs (e.g. sulfasalazine, leflunomide, bucillamine, azathioprine), glucocorticoids (e.g. betamethasone, dexamethasone), and NSAIDs (e.g. celecoxib and indomethacin) are also substrates of ABC transporters. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Staphylococcus infection [ICD-11: 1B7Y.3] | [22] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus infection [ICD-11: 1B7Y.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Ciprofloxacin XR | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates | 287 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus isolates | 1280 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates | 573 | |||
| Acinetobacter isolates | 469 | |||
| Enterobacter cloacae isolates | 550 | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Disk diffusion method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Up-regulation of P-glycoprotein led to ciprofloxacin resistance in the staphylococcus infection. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Hypo-attenuated leaflet thickening [ICD-11: BD10.2] | [23] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Hypo-attenuated leaflet thickening [ICD-11: BD10.2] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Clopidogrel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | SNP | rs1045642+rs2032562 |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | We thoroughly genotyped 34 SNPs and 8 SNPs that have been reported for clopidogrel and aspirin resistance. A total of 148 patients were enrolled. There were 15 patients demonstrating signs of HALT. Patients with HALT had a higher rate of atrial fibrillation (AF) pre-TAVR (33.3 vs. 7.5%, P = 0.01). | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Agranulocytosis [ICD-11: 4B00.0] | [42] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Agranulocytosis [ICD-11: 4B00.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Clozapine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | 3435CC genotype |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR | |||
| Mechanism Description | It was shown that 3435CC genotype carriers require greater doses of clozapine to achieve same plasma concentrations compared with 3435CT and 3435TT carriers. Similarly, a study carried out in Switzerland reported that 3435TT carriers had higher clozapine plasma concentrations. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Agranulocytosis [ICD-11: 4B00.0] | [42] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Agranulocytosis [ICD-11: 4B00.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Clozapine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | 3435TT genotype |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR | |||
| Mechanism Description | It was shown that 3435CC genotype carriers require greater doses of clozapine to achieve same plasma concentrations compared with 3435CT and 3435TT carriers. Similarly, a study carried out in Switzerland reported that 3435TT carriers had higher clozapine plasma concentrations. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Pituitary adenoma [ICD-11: 2F37.1] | [43] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pituitary adenoma [ICD-11: 2F37.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Colchicine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | GH4C1 cells | Pituitary gland | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | CVCL_0276 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunocytochemical staining assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Lowry assay; Bradford assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Cells resistant to colchicine at 0.4 micrograms/ml, termed GH4C1/RC.4, exhibited the multidrug-resistance phenotype, as the LD50 values for colchicine, puromycin, actinomycin D, and doxorubicin were between 8 and 30 times greater than the corresponding values for the parental GH4C1 cells.Immunocytochemical staining with a monoclonal antibody, C219, to the 170-kilodalton P-glycoprotein showed directly that GH4C1/RC.4 cells overexpress P-glycoprotein. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Malignant glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.2] | [26] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Malignant glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.2] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Dacarbazine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Malignant gliomas tissue | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunohistochemistry assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
EDR assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In vitro drug resistance in malignant gliomas was independent of prior therapy. High-grade glioblastomas showed a lower level of extreme drug resistance than low-grade astrocytomas to cisplatin (11% versus 27%), temozolomide (14% versus 27%), irinotecan (33% versus 53%), and BCNU (29% versus 38%). A substantial percentage of brain tumors overexpressed biomarkers associated with drug resistance, including MGMT (67%), GSTP1 (49%), and mutant p53 (41%). MGMT and GSTP1 overexpression was independently associated with in vitro resistance to BCNU, whereas coexpression of these two markers was associated with the greatest degree of BCNU resistance. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Burkitt lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A85.6] | [45] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Burkitt lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A85.6] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Dexamethasone | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | HS-Sultan cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2516 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Trypan blue dye exclusion assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | MDR1 and Survivin upregulation are responsible for resistance to conventional drugs and dasatinib can restore drug sensitivity by reducing MDR1 and Survivin expression in drug-resistant BL cells. Src inhibitors could therefore be a novel treatment strategy for patients with drug resistant BL. | |||
| Disease Class: Rheumatoid arthritis [ICD-11: FA20.0] | [24] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Rheumatoid arthritis [ICD-11: FA20.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Dexamethasone | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | MTX is a substrate for eight ABC transporters. In vitro studies demonstrated that RAFLS treated with MTX had higher ABCB1 expression levels than controls, with a positive correlation between ABCB1 expression levels and RA treatment duration. In addition to MTX, other DMARDs (e.g. sulfasalazine, leflunomide, bucillamine, azathioprine), glucocorticoids (e.g. betamethasone, dexamethasone), and NSAIDs (e.g. celecoxib and indomethacin) are also substrates of ABC transporters. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Burkitt lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A85.6] | [45] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Burkitt lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A85.6] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Dexamethasone | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | HS-Sultan cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2516 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Trypan blue dye exclusion assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | MDR1 and Survivin upregulation are responsible for resistance to conventional drugs and dasatinib can restore drug sensitivity by reducing MDR1 and Survivin expression in drug-resistant BL cells. Src inhibitors could therefore be a novel treatment strategy for patients with drug resistant BL. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.1] | [46] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Docetaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | U87-MG cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0022 |
| In Vivo Model | Athymic nu/nu female mice xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In a cell line expressing a high level of P-glycoprotein, the IC50 of TTI-237 increased 25-fold whereas those of paclitaxel and vincristine increased 806-fold and 925-fold. | |||
| Disease Class: Colorectal carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B91.3] | [46] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Colorectal carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B91.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Docetaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | LOVO cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0399 |
| In Vivo Model | Athymic nu/nu female mice xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In a cell line expressing a high level of P-glycoprotein, the IC50 of TTI-237 increased 25-fold whereas those of paclitaxel and vincristine increased 806-fold and 925-fold. | |||
| Disease Class: Squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E.3] | [46] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Docetaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | KB-3-1 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2088 |
| KB-8-5 cells | Mouth | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5994 | |
| KB-V1 cells | Mouth | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2089 | |
| In Vivo Model | Athymic nu/nu female mice xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In a cell line expressing a high level of P-glycoprotein, the IC50 of TTI-237 increased 25-fold whereas those of paclitaxel and vincristine increased 806-fold and 925-fold. | |||
| Disease Class: Cervical carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C77.1] | [46] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Cervical carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C77.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Docetaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Hela cells | Cervix uteri | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0030 |
| In Vivo Model | Athymic nu/nu female mice xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In a cell line expressing a high level of P-glycoprotein, the IC50 of TTI-237 increased 25-fold whereas those of paclitaxel and vincristine increased 806-fold and 925-fold. | |||
| Disease Class: Anaplastic astrocytoma [ICD-11: 2A00.04] | [26] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Anaplastic astrocytoma [ICD-11: 2A00.04] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Docetaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Protein kinase C signaling pathways | Inhibition | hsa04310 | |
| In Vitro Model | Malignant gliomas tissue | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunohistochemistry assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Oncotech EDR assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | On the other hand, the frequency of LDR that we noted for paclitaxel (20%) and vincristine (20%) was similar to the clinical response rates for these compounds. These data suggest that although MDR1 expression by glial tumors may not be the dominant direct cellular process responsible for tumor resistance to natural products, other mechanisms are present that diminish their activity. The clinical mechanisms of natural product resistance may be a multifactorial function of endothelial expression of MDR1 at the blood-brain barrier in conjunction with glial tumor cell expression of alternative efflux pumps, such as MRP, altered tubulin with lower affinity binding sites, and/or protein kinase C signaling pathways that suppress apoptosis. | |||
| Disease Class: Malignant glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.2] | [26] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Malignant glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.2] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Docetaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Malignant gliomas tissue | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunohistochemistry assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
EDR assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In vitro drug resistance in malignant gliomas was independent of prior therapy. High-grade glioblastomas showed a lower level of extreme drug resistance than low-grade astrocytomas to cisplatin (11% versus 27%), temozolomide (14% versus 27%), irinotecan (33% versus 53%), and BCNU (29% versus 38%). A substantial percentage of brain tumors overexpressed biomarkers associated with drug resistance, including MGMT (67%), GSTP1 (49%), and mutant p53 (41%). MGMT and GSTP1 overexpression was independently associated with in vitro resistance to BCNU, whereas coexpression of these two markers was associated with the greatest degree of BCNU resistance. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | [60] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Efavirenz | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | c.C3435T |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Real-time PCR | |||
| Mechanism Description | HIV-1 infected children with the MDR1-3435-C/T genotype had more rapid virologic responses to HAART at week 8 with higher plasma nelfinavir concentrations compared to those with the C/C genotype. Patients with the MDR1-3435-C/C genotype have been shown to have normal expression of P-gp on intestinal epithelial cells. In these patients, a substrate of P-gp is exported vigorously out of cells via P-gp after the substrate is absorbed through the intestinal epithelial cells. This leads to a lower intracellular concentration of substrate in the intestinal epithelial cells, followed by a lower concentration of substrate in plasma. In contrast, patients with the MDR1-3435-C/T or T/T genotype experience less elimination of the substrate through P-gp because of the lower expression of P-gp on intestinal epithelial. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.3] | [38], [39] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Fluorouracil | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell growth | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | ECA-109 cells | Esophagus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6898 |
| TE13 cells | Esophageal | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_4463 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
WST-1 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Down-regulation of miR-296 could confer sensitivity of both P-glycoprotein-related and P-glycoprotein-nonrelated drugs on esophageal cancer cells, and might promote ADR-induced apoptosis, accompanied by increased accumulation and decreased releasing amount of ADR. Down-regulation of miR-296 could significantly decrease the expression of P-glycoprotein, Bcl-2, and the transcription of MDR1, but up-regulate the expression of Bax. And down-regulation of miR-27a significantly decreased expression of MDR1, but did not alter the expression of MRP, miR-27a could possibly mediate drug resistance, at least in part through regulation of MDR1 and apoptosis. | |||
| Disease Class: Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | [40] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Fluorouracil | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| In Vitro Model | SGC7901 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0520 |
| SGC7901/VCR cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_VU58 | |
| SGC7901/ADR cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_VU57 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The overexpression of miR-508-5p was sufficient to reverse cancer cell resistance to multiple chemotherapeutics in vitro and sensitize tumours to chemotherapy in vivo. Further studies showed that miR-508-5p could directly target the 3'-untranslated regions of ABCB1 and Zinc ribbon domain-containing 1 (ZNRD1), and suppress their expression at the mRNA and protein levels. Meanwhile, the suppression of ZNRD1 led to a decrease in ABCB1. | |||
| Disease Class: Leukemia [ICD-11: 2B33.6] | [41] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Leukemia [ICD-11: 2B33.6] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Fluorouracil | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| In Vitro Model | HL60 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0002 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-138 was found up-regulated in the vincristine-induced multidrug resistance (MDR) leukemia cell line HL-60/VCR as compared with HL-60 cells. Up-regulation of miR-138 could reverse resistance of both P-glycoprotein-related and P-glycoprotein-non-related drugs on HL-60/VCR cells, and promote adriamycin-induced apoptosis, accompanied by increased accumulation and decreased releasing amount of adriamycin. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [62] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Guggulsterone | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | MDA PCa 2b cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_4748 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
western blot; flow cytometry | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Guggulsterone is a novel and potent MDR reversal agent with the potential to be an adjunctive agent for tumor chemotherapy. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Rheumatoid arthritis [ICD-11: FA20.0] | [24] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Rheumatoid arthritis [ICD-11: FA20.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Hydrocortisone | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | MTX is a substrate for eight ABC transporters. In vitro studies demonstrated that RAFLS treated with MTX had higher ABCB1 expression levels than controls, with a positive correlation between ABCB1 expression levels and RA treatment duration. In addition to MTX, other DMARDs (e.g. sulfasalazine, leflunomide, bucillamine, azathioprine), glucocorticoids (e.g. betamethasone, dexamethasone), and NSAIDs (e.g. celecoxib and indomethacin) are also substrates of ABC transporters. | |||
| Disease Class: Chronic inflammatory lung disease [ICD-11: CA40.Z] | [63] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Chronic inflammatory lung disease [ICD-11: CA40.Z] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Hydrocortisone | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | For therapeutic drugs to be effective at reducing the proinflammatory/cytotoxic potential of steroid resistant lymphocytes, glucocorticoids enter cells by overcoming membrane drug efflux pump P-glycoprotein-1 (Pgp1) and binding to the glucocorticoid receptor (GCR) in the cytoplasm. GCR must be bound to the molecular chaperones heat shock proteins (Hsp)70 and Hsp90 to acquire a high-affinity steroid binding conformation, and trafficked to the nucleus where engagement of histone deacetylases (HDACs), particularly HDAC2, results in the reduction of pro-inflammatory gene activation. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Chronic myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A20.0] | [64] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Chronic myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A20.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Imatinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | K562 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0004 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | UCA1 functions as a ceRNA of MDR1, UCA1 promotes IM resistance of CML cell through regulation of MDR1. Ectopic expression of MDR1 or silence of miR16 partially rescued this suppression induced by UCA1 knockdown. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Chronic myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A20.0] | [65] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Chronic myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A20.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Imatinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | K562 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0004 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Annexin V-FITC/PI Apoptosis Detection assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Overexpression of MEG3 in imatinib-resistant k562 cells markedly decreased cell proliferation, increased cell apoptosis, reversed imatinib resistance, and reduced the expression of MRP1, MDR1, and ABCG2. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Rheumatoid arthritis [ICD-11: FA20.0] | [24] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Rheumatoid arthritis [ICD-11: FA20.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Indomethacin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | MTX is a substrate for eight ABC transporters. In vitro studies demonstrated that RAFLS treated with MTX had higher ABCB1 expression levels than controls, with a positive correlation between ABCB1 expression levels and RA treatment duration. In addition to MTX, other DMARDs (e.g. sulfasalazine, leflunomide, bucillamine, azathioprine), glucocorticoids (e.g. betamethasone, dexamethasone), and NSAIDs (e.g. celecoxib and indomethacin) are also substrates of ABC transporters. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Malignant glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.2] | [26] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Malignant glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.2] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Irinotecan | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Malignant gliomas tissue | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunohistochemistry assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
EDR assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In vitro drug resistance in malignant gliomas was independent of prior therapy. High-grade glioblastomas showed a lower level of extreme drug resistance than low-grade astrocytomas to cisplatin (11% versus 27%), temozolomide (14% versus 27%), irinotecan (33% versus 53%), and BCNU (29% versus 38%). A substantial percentage of brain tumors overexpressed biomarkers associated with drug resistance, including MGMT (67%), GSTP1 (49%), and mutant p53 (41%). MGMT and GSTP1 overexpression was independently associated with in vitro resistance to BCNU, whereas coexpression of these two markers was associated with the greatest degree of BCNU resistance. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Staphylococcus infection [ICD-11: 1B7Y.3] | [22] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus infection [ICD-11: 1B7Y.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Levofloxacin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates | 287 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus isolates | 1280 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates | 573 | |||
| Acinetobacter isolates | 469 | |||
| Enterobacter cloacae isolates | 550 | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Disk diffusion method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Up-regulation of P-glycoprotein led to levofloxacin resistance in the staphylococcus infection. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Diarrhea [ICD-11: DA90.0] | [66] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Diarrhea [ICD-11: DA90.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Loperamide | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | Haplotype G2677/T3435 |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Genotyping assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Assessment of central opioid effects assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The results support a functional importance of the ABCB1 genetic variants for the pharmacokinetics of loperamide. Highest loperamide plasma concentrations were seen in carriers of haplotype G2677. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Burkitt lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A85.6] | [45] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Burkitt lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A85.6] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Melphalan | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | HS-Sultan cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2516 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Trypan blue dye exclusion assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | MDR1 and Survivin upregulation are responsible for resistance to conventional drugs and dasatinib can restore drug sensitivity by reducing MDR1 and Survivin expression in drug-resistant BL cells. Src inhibitors could therefore be a novel treatment strategy for patients with drug resistant BL. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Burkitt lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A85.6] | [45] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Burkitt lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A85.6] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Melphalan | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | HS-Sultan cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2516 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Trypan blue dye exclusion assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | MDR1 and Survivin upregulation are responsible for resistance to conventional drugs and dasatinib can restore drug sensitivity by reducing MDR1 and Survivin expression in drug-resistant BL cells. Src inhibitors could therefore be a novel treatment strategy for patients with drug resistant BL. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Rheumatoid arthritis [ICD-11: FA20.0] | [24] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Rheumatoid arthritis [ICD-11: FA20.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Methylprednisolone | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | MTX is a substrate for eight ABC transporters. In vitro studies demonstrated that RAFLS treated with MTX had higher ABCB1 expression levels than controls, with a positive correlation between ABCB1 expression levels and RA treatment duration. In addition to MTX, other DMARDs (e.g. sulfasalazine, leflunomide, bucillamine, azathioprine), glucocorticoids (e.g. betamethasone, dexamethasone), and NSAIDs (e.g. celecoxib and indomethacin) are also substrates of ABC transporters. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Leishmaniasis [ICD-11: 1F54.1] | [70] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Leishmaniasis [ICD-11: 1F54.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Miltefosine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| Mechanism Description | In addition, the overexpression of ABC transporters ABCB4(MDR1), ABCG4, and ABCG6 has also been described to be associated with an increased resistance to several alkyl-lysophospholipids analogues, including MIL in Leishmania, due to a reduced intracellular accumulation because of increased efflux of the drug across the plasma membrane. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Keloid [ICD-11: EE60.1] | [71] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Keloid [ICD-11: EE60.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Mitoxantrone | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell growth | Activation | hsa05200 | |
| In Vitro Model | Keloid fibroblasts | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
RT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | MDR-1-positive keloid cells exhibited roundness as opposed to the usual spindle shape. Contrarily, MDR-1-positive cells in normal skin remained spindle shaped. Such a phenomenon suggests that MDR-1 positive keloid cells represent a subpopulation important in keloid pathogenesis. MDR-1 (also known as ABCB1 or P-glycoprotein) is one of the best characterized membrane transporters. | |||
| Disease Class: Keloid [ICD-11: EE60.1] | [71] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Keloid [ICD-11: EE60.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Mitoxantrone | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell growth | Activation | hsa05200 | |
| In Vitro Model | Keloid fibroblasts | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
RT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | MDR-1-positive keloid cells exhibited roundness as opposed to the usual spindle shape. Contrarily, MDR-1-positive cells in normal skin remained spindle shaped. Such a phenomenon suggests that MDR-1 positive keloid cells represent a subpopulation important in keloid pathogenesis. MDR-1 (also known as ABCB1 or P-glycoprotein) is one of the best characterized membrane transporters. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Staphylococcus infection [ICD-11: 1B7Y.3] | [22] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus infection [ICD-11: 1B7Y.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Nitrofurantoin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates | 287 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus isolates | 1280 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates | 573 | |||
| Acinetobacter isolates | 469 | |||
| Enterobacter cloacae isolates | 550 | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Disk diffusion method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Up-regulation of P-glycoprotein led to nitrofurantoin resistance in the staphylococcus infection. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Epilepsy [ICD-11: 8A60.0] | [74] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Epilepsy [ICD-11: 8A60.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Oxcarbazepine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | In patients with oxcarbazepine (OXC)-resistant epilepsy, the brain tissue expression of ABCB1 mRNA was found to be inversely correlated with brain levels of 10,11-dihydro-10-hydroxy-5H-dibenzo(b,f)azepine-5-carboxamide, the active metabolite of OXC, indicating that Pgp may play a role in the pharmacoresistance to OXC by causing insufficient concentrations of its active metabolite at neuronal targets. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Status epilepticus [ICD-11: 8A66.0] | [80] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Status epilepticus [ICD-11: 8A66.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Phenobarbital | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | Pgp is involved in the resistance to phenytoin and phenobarbital but not diazepam. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Epilepsy [ICD-11: 8A60.0] | [74] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Epilepsy [ICD-11: 8A60.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Phenytoin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| Mechanism Description | Comparing phenytoin brain/plasma ratio in mdr1 knockout mice with this ratio in mice with kainate-induced overexpression of Pgp indicated that Pgp can affect up to about 70% of phenytoin brain uptake. In epileptic rats, van Vliet et al reported decreased brain levels of phenytoin that were restricted to brain regions with increased expression of Pgp, which could be counteracted by inhibiting Pgp. | |||
| Disease Class: Status epilepticus [ICD-11: 8A66.0] | [80] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Status epilepticus [ICD-11: 8A66.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Phenytoin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | Pgp is involved in the resistance to phenytoin and phenobarbital but not diazepam. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Nephrotic syndrome [ICD-11: GB41.0] | [81] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Nephrotic syndrome [ICD-11: GB41.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Prednisolone | |||
| Molecule Alteration | SNP | c.G2677T/A |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Blood sample | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR-RFLP | |||
| Mechanism Description | MDR1 G2677T/A polymorphism was significantly associated with steroid resistance. | |||
| Disease Class: Nephrotic syndrome [ICD-11: GB41.0] | [81] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Nephrotic syndrome [ICD-11: GB41.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Prednisolone | |||
| Molecule Alteration | SNP | c.G2677T/A |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Blood sample | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR-RFLP | |||
| Mechanism Description | MDR1 G2677T/A polymorphism was significantly associated with steroid resistance. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Primary immune thrombocytopenia [ICD-11: 3B64.0] | [82] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Primary immune thrombocytopenia [ICD-11: 3B64.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Prednisone | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | B-cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Rhodamine 123 efflux assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The functional activity and mRNA level of P-gp were significantly higher in glucocorticoids-nonresponsive patients than in glucocorticoids-responsive patients with primary immune thrombocytopenia. | |||
| Disease Class: Myasthenia gravis [ICD-11: 8C60.0] | [83] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Myasthenia gravis [ICD-11: 8C60.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Prednisone | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Lymphocyte | Lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Prednisone (PDN) is transported by P-glycoprotein (P-gp). P-gp overfunction has been associated with resistance to several drug. | |||
| Disease Class: Myasthenia gravis [ICD-11: 8C60.0] | [83] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Myasthenia gravis [ICD-11: 8C60.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Prednisone | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Lymphocyte | Lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Prednisone (PDN) is transported by P-glycoprotein (P-gp). P-gp overfunction has been associated with resistance to several drug. | |||
| Disease Class: Rheumatoid arthritis [ICD-11: FA20.0] | [24] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Rheumatoid arthritis [ICD-11: FA20.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Prednisone | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | MTX is a substrate for eight ABC transporters. In vitro studies demonstrated that RAFLS treated with MTX had higher ABCB1 expression levels than controls, with a positive correlation between ABCB1 expression levels and RA treatment duration. In addition to MTX, other DMARDs (e.g. sulfasalazine, leflunomide, bucillamine, azathioprine), glucocorticoids (e.g. betamethasone, dexamethasone), and NSAIDs (e.g. celecoxib and indomethacin) are also substrates of ABC transporters. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Idiopathic nephrotic syndrome [ICD-11: GB41.1] | [85] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Idiopathic nephrotic syndrome [ICD-11: GB41.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Steroid | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | The up-regualtion of mdr1 led to steroid resistance in the idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. | |||
| Disease Class: Idiopathic nephrotic syndrome [ICD-11: GB41.1] | [85] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Idiopathic nephrotic syndrome [ICD-11: GB41.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Steroid | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | The up-regualtion of mdr1 led to steroid resistance in the idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. | |||
Investigative Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | [17] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Gardiquimod | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Prostate cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Prostate | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.55E-01 Fold-change: 5.35E-02 Z-score: 1.16E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Hep3B cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0326 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Resazurin Cell Viability Assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Imidazoquinolines IMQ, RSQ, and GDQ are substrates for P-gp and begins to elucidate differences in their trafficking in cancer cells as a consequence of acquired drug resistance. We believe this work that begins to examine imidazoquinoline trafficking will prove useful in the future rational design of immunotherapeutics with enhanced susceptibility to P-gp efflux that enable increased bioavailability, in MDR cancers. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 01

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | White matter | |
| The Specified Disease | HIV infection | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.39E-01; Fold-change: 1.21E-01; Z-score: 4.34E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
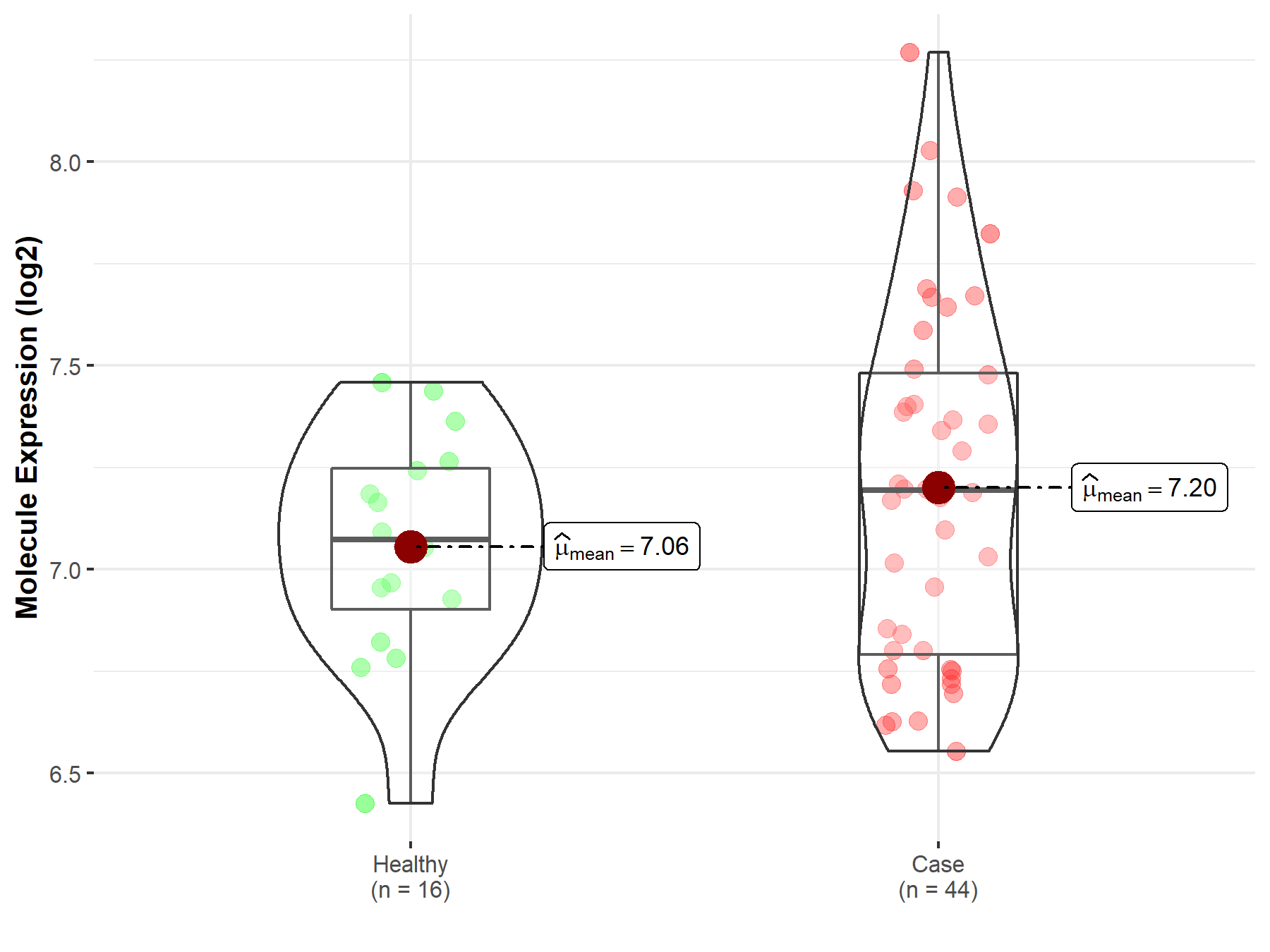
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Nervous tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Brain cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.39E-11; Fold-change: -2.93E-01; Z-score: -6.11E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
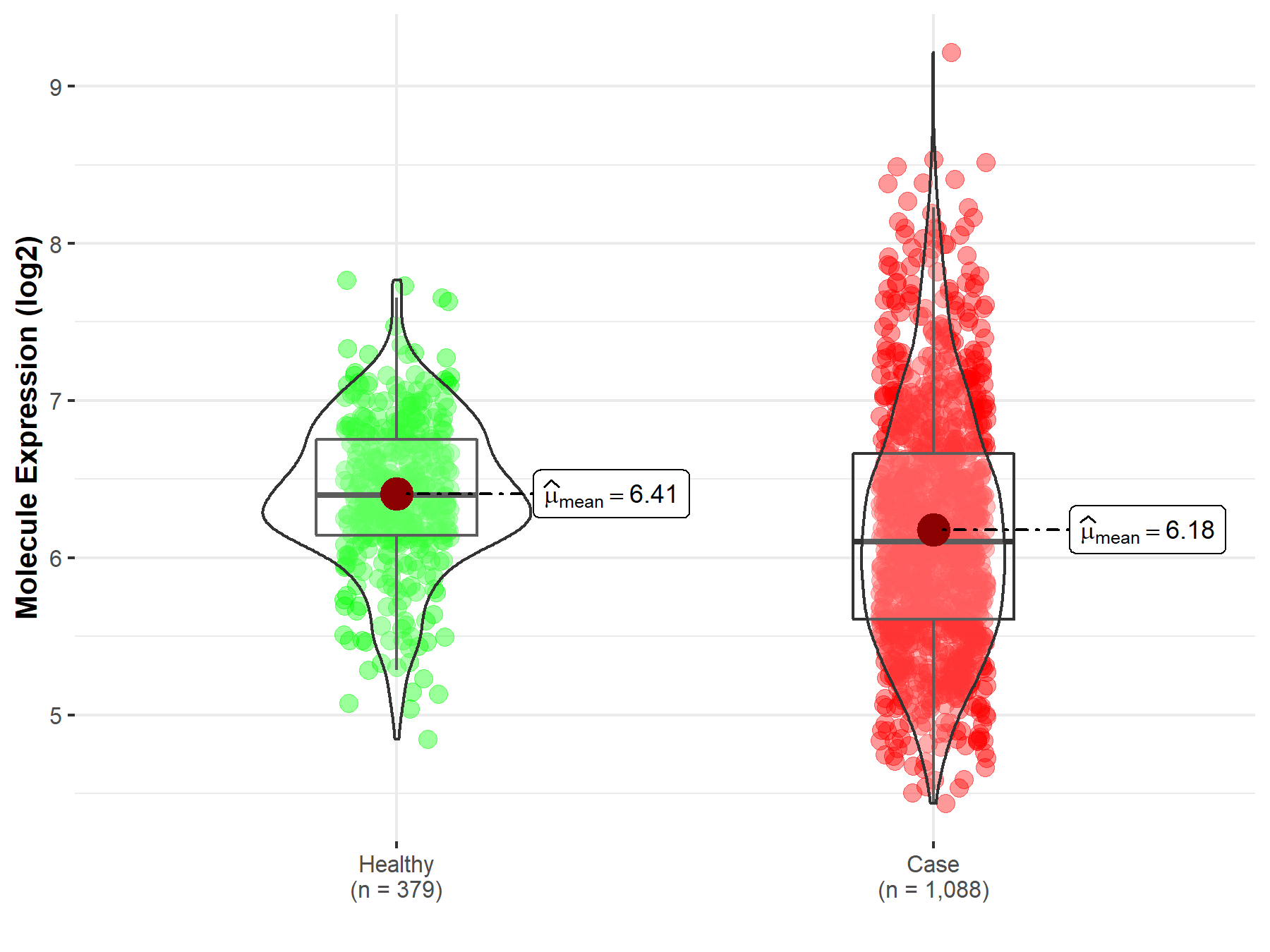
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | Brainstem tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Glioma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.84E-01; Fold-change: -1.02E+00; Z-score: -2.26E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
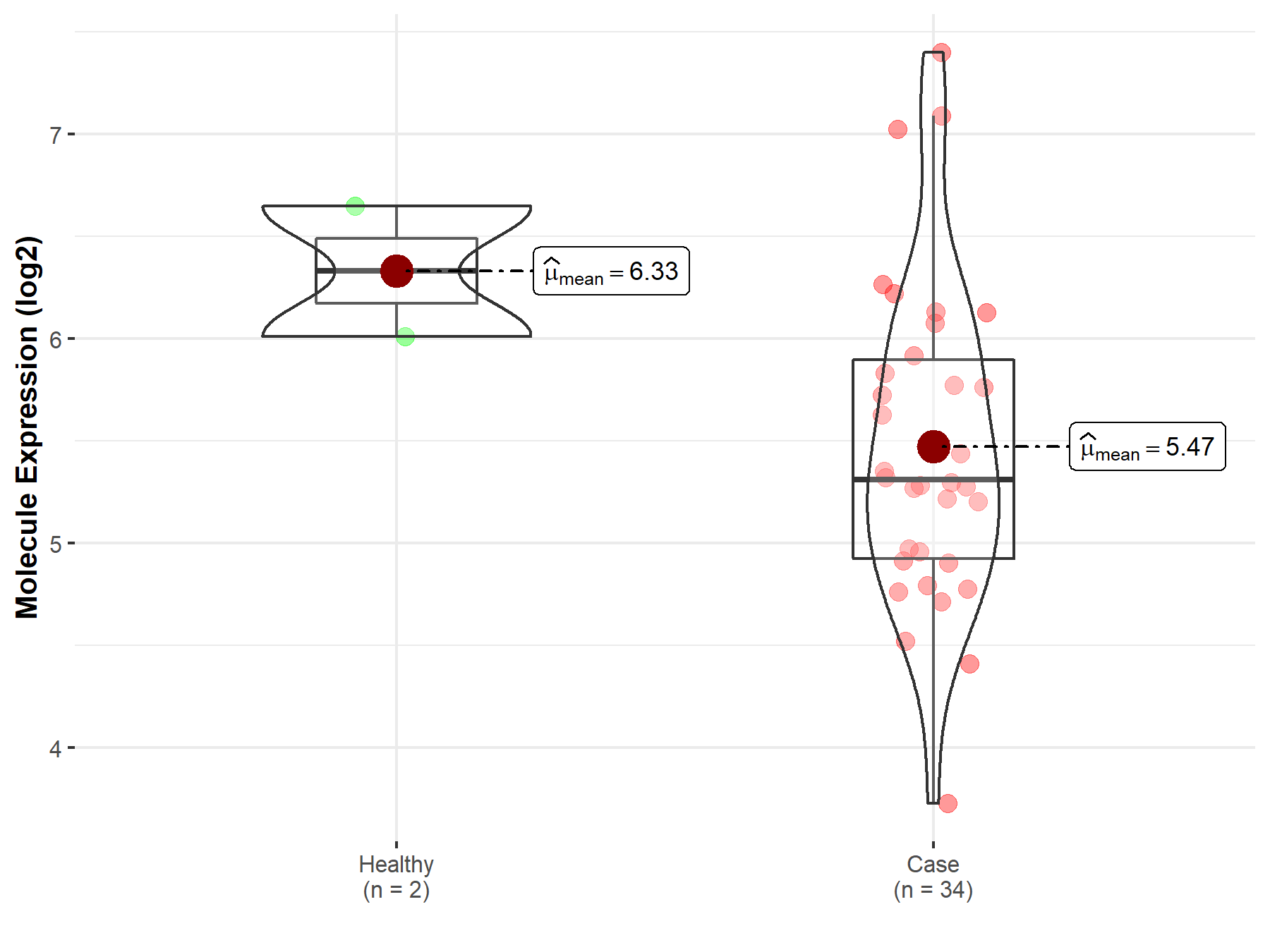
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | White matter | |
| The Specified Disease | Glioma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.21E-01; Fold-change: -1.31E-01; Z-score: -9.67E-02 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
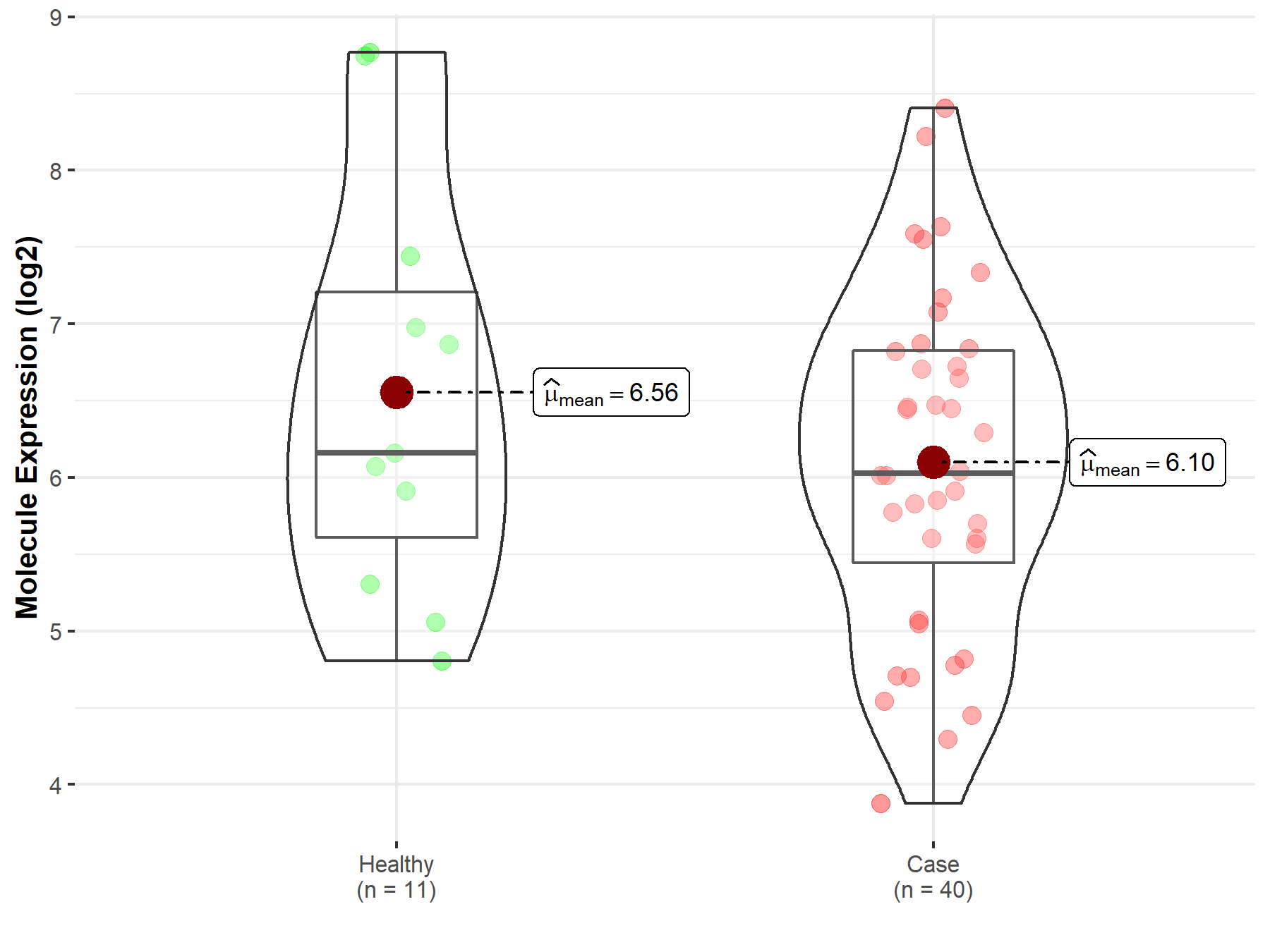
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | Brainstem tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Neuroectodermal tumor | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 4.31E-02; Fold-change: -4.89E-01; Z-score: -9.87E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
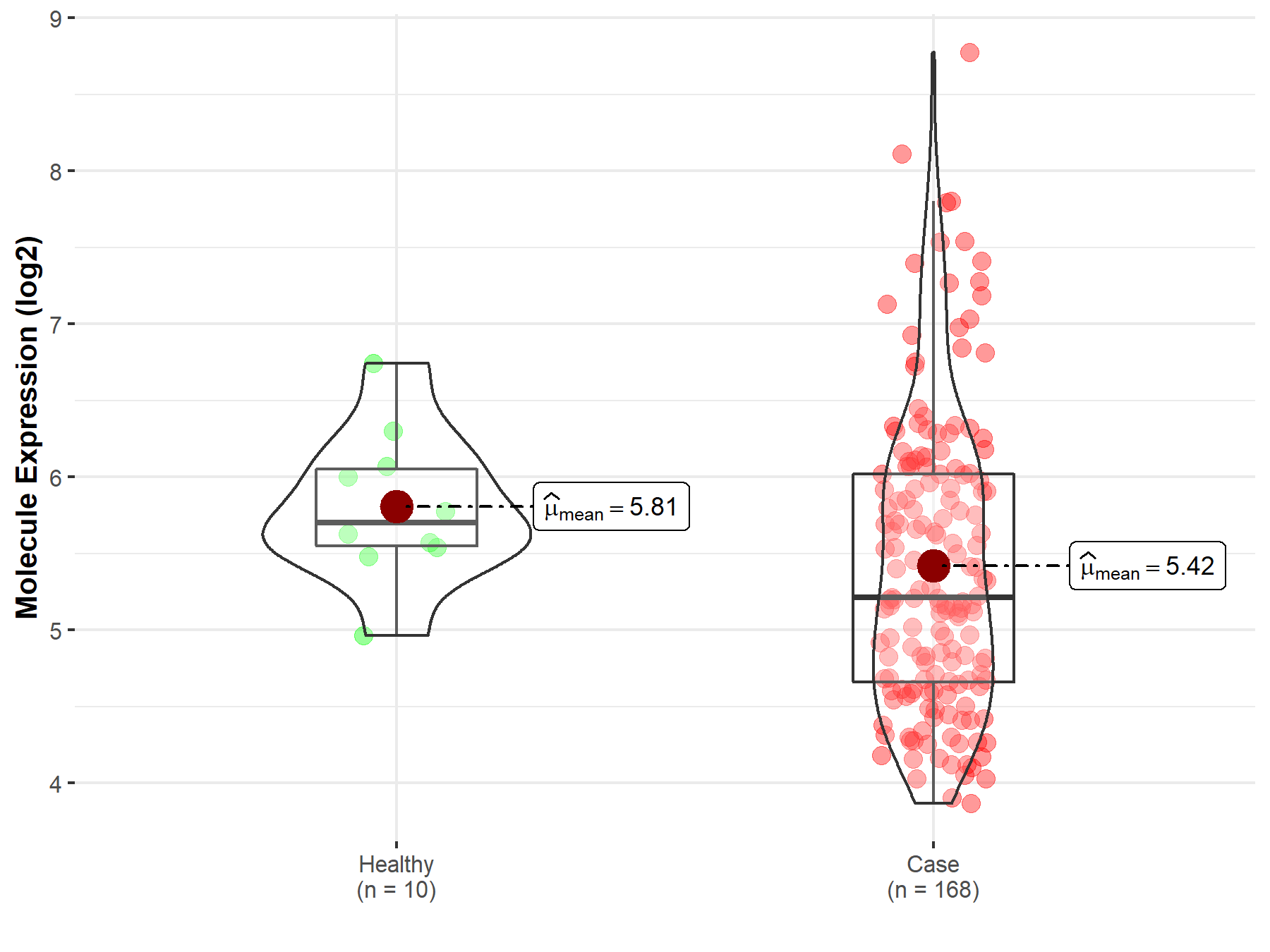
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Whole blood | |
| The Specified Disease | Myelofibrosis | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.73E-01; Fold-change: 9.15E-02; Z-score: 3.06E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
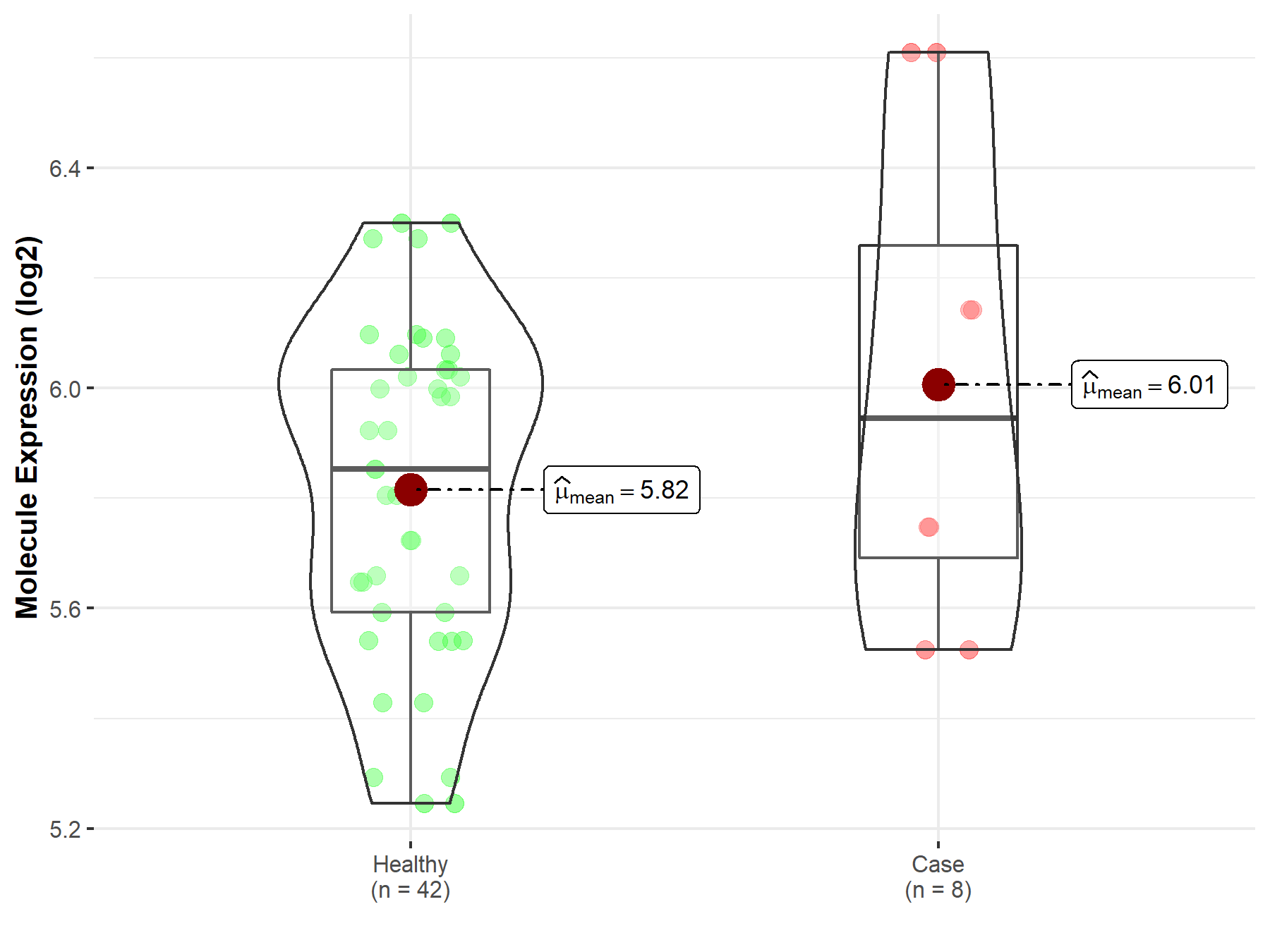
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | Whole blood | |
| The Specified Disease | Polycythemia vera | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 5.18E-01; Fold-change: -1.11E-01; Z-score: -4.02E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
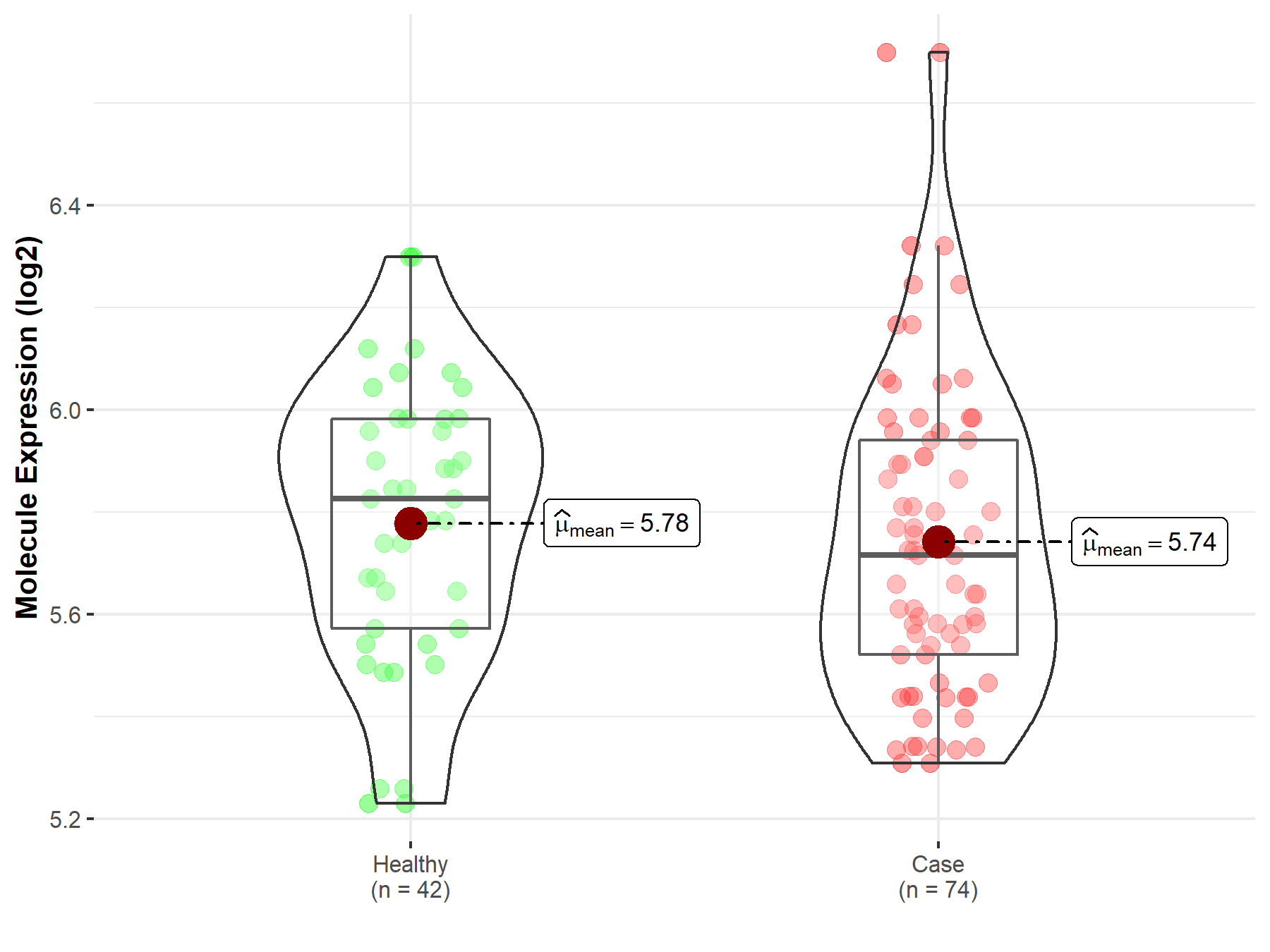
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Bone marrow | |
| The Specified Disease | Acute myeloid leukemia | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 4.70E-06; Fold-change: -5.80E-02; Z-score: -1.98E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
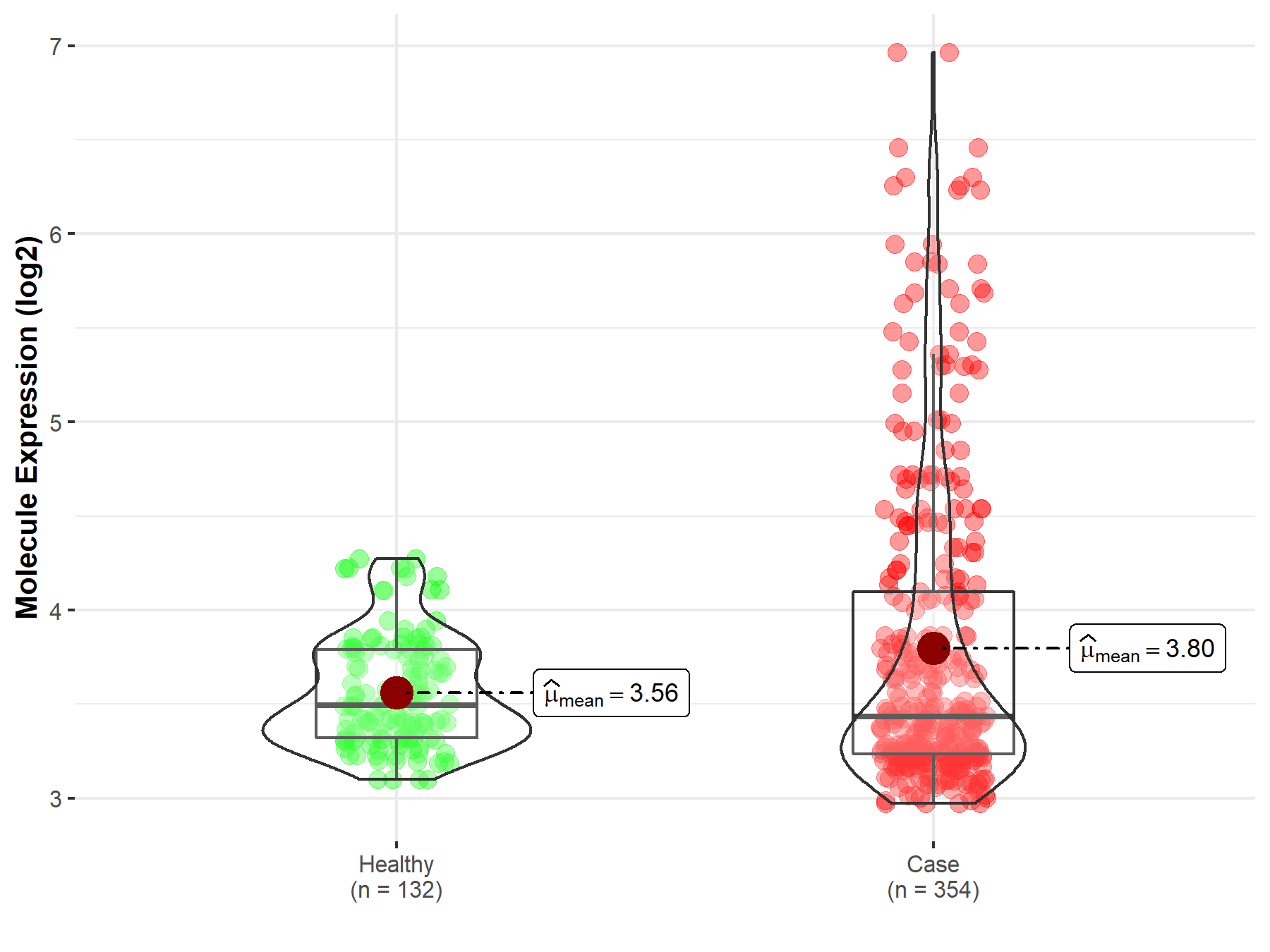
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Oral tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.35E-03; Fold-change: -1.49E-01; Z-score: -4.36E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 2.16E-31; Fold-change: -6.48E-01; Z-score: -1.96E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
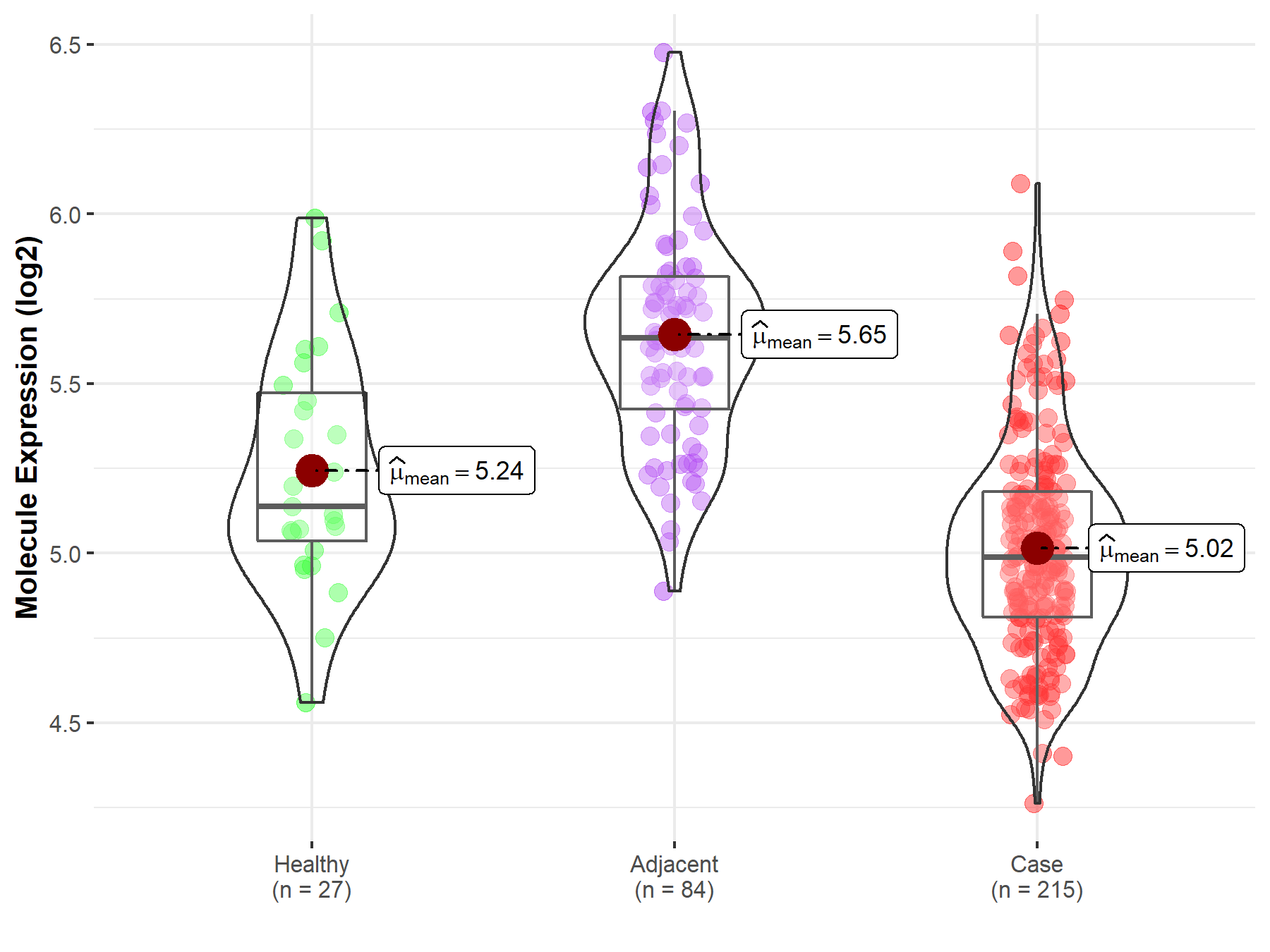
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Esophagus | |
| The Specified Disease | Esophageal cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 1.03E-03; Fold-change: -6.46E-01; Z-score: -3.13E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
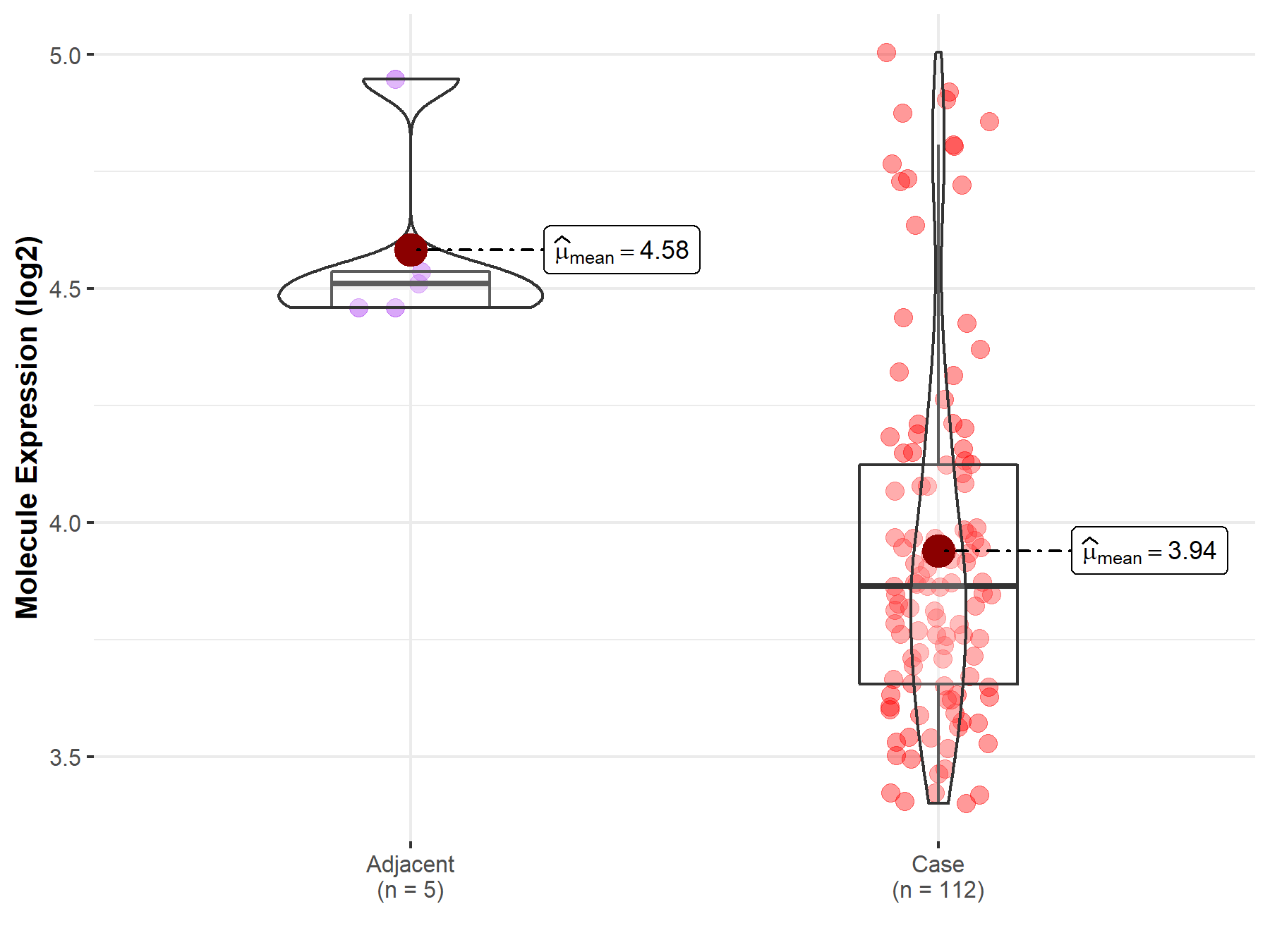
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Gastric tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Gastric cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.42E-03; Fold-change: 3.68E-01; Z-score: 3.09E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 2.31E-03; Fold-change: 2.52E-01; Z-score: 5.13E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
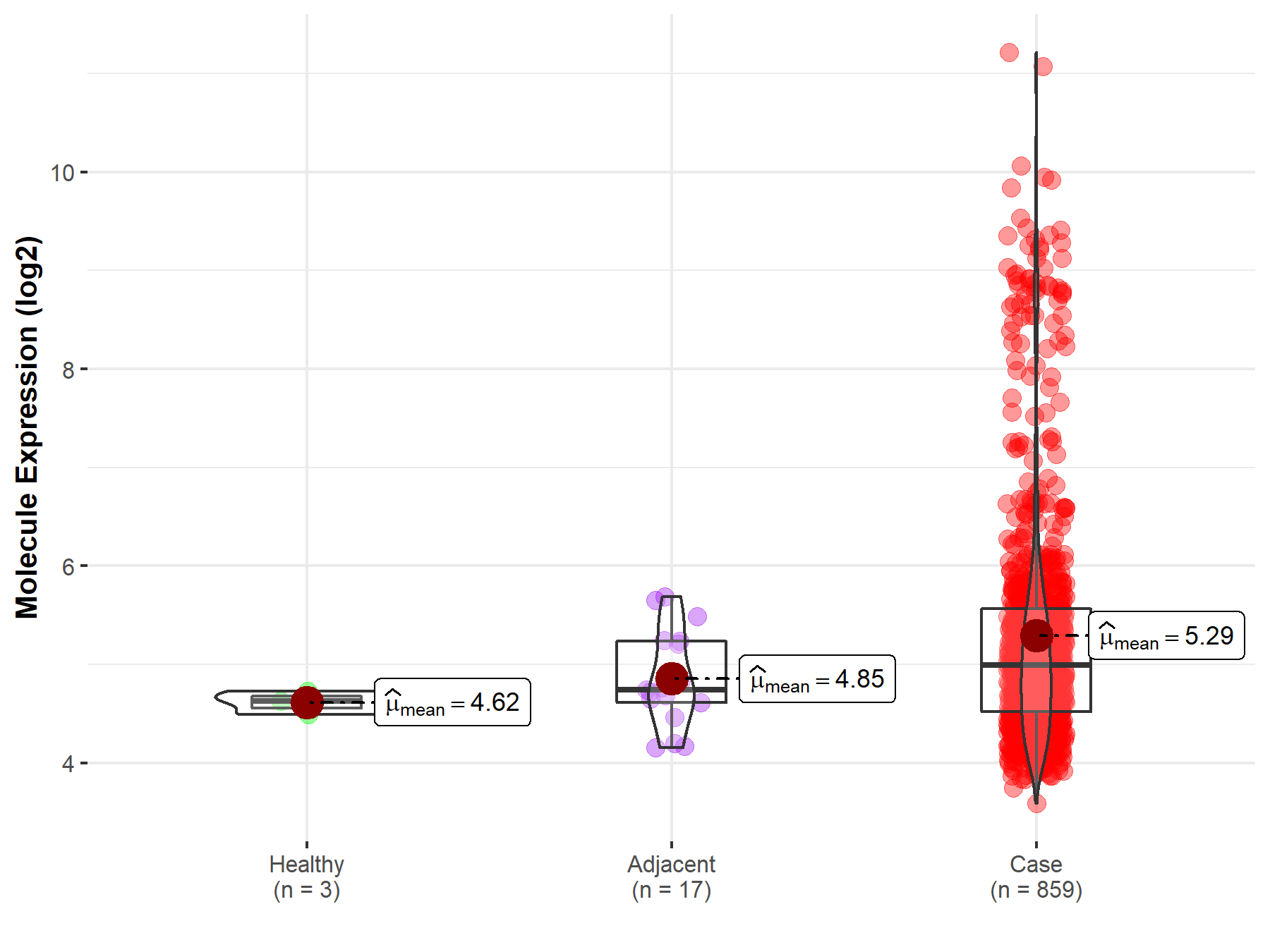
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Liver | |
| The Specified Disease | Liver cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 5.54E-01; Fold-change: 1.87E-01; Z-score: 4.30E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 2.52E-13; Fold-change: -3.21E-01; Z-score: -7.40E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Other Disease Section | p-value: 6.68E-01; Fold-change: 2.98E-01; Z-score: 3.46E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
Molecule expression in tissue other than the diseased tissue of patients
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
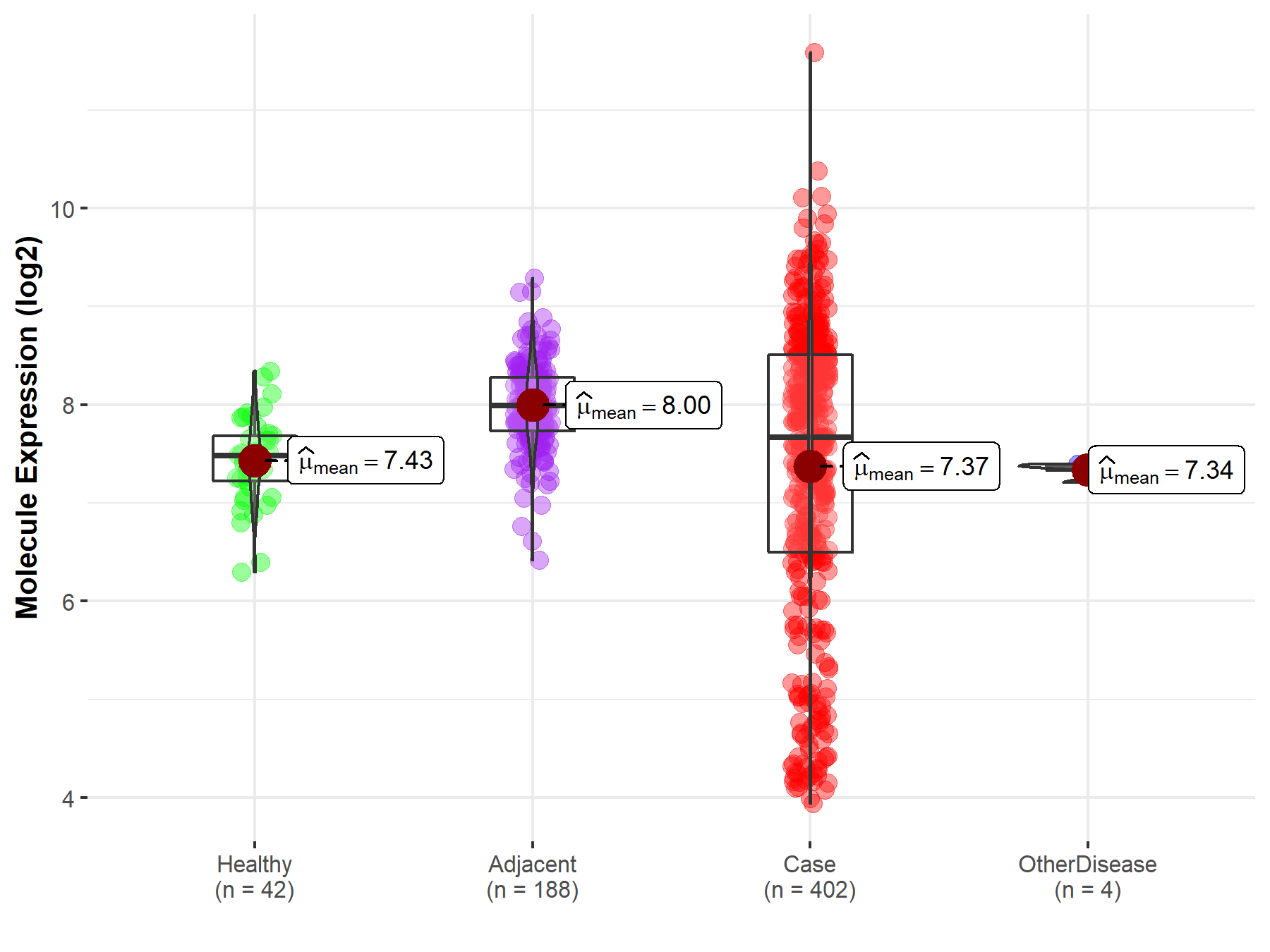
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung | |
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.12E-33; Fold-change: -8.30E-01; Z-score: -1.04E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 1.12E-24; Fold-change: -9.94E-01; Z-score: -1.11E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
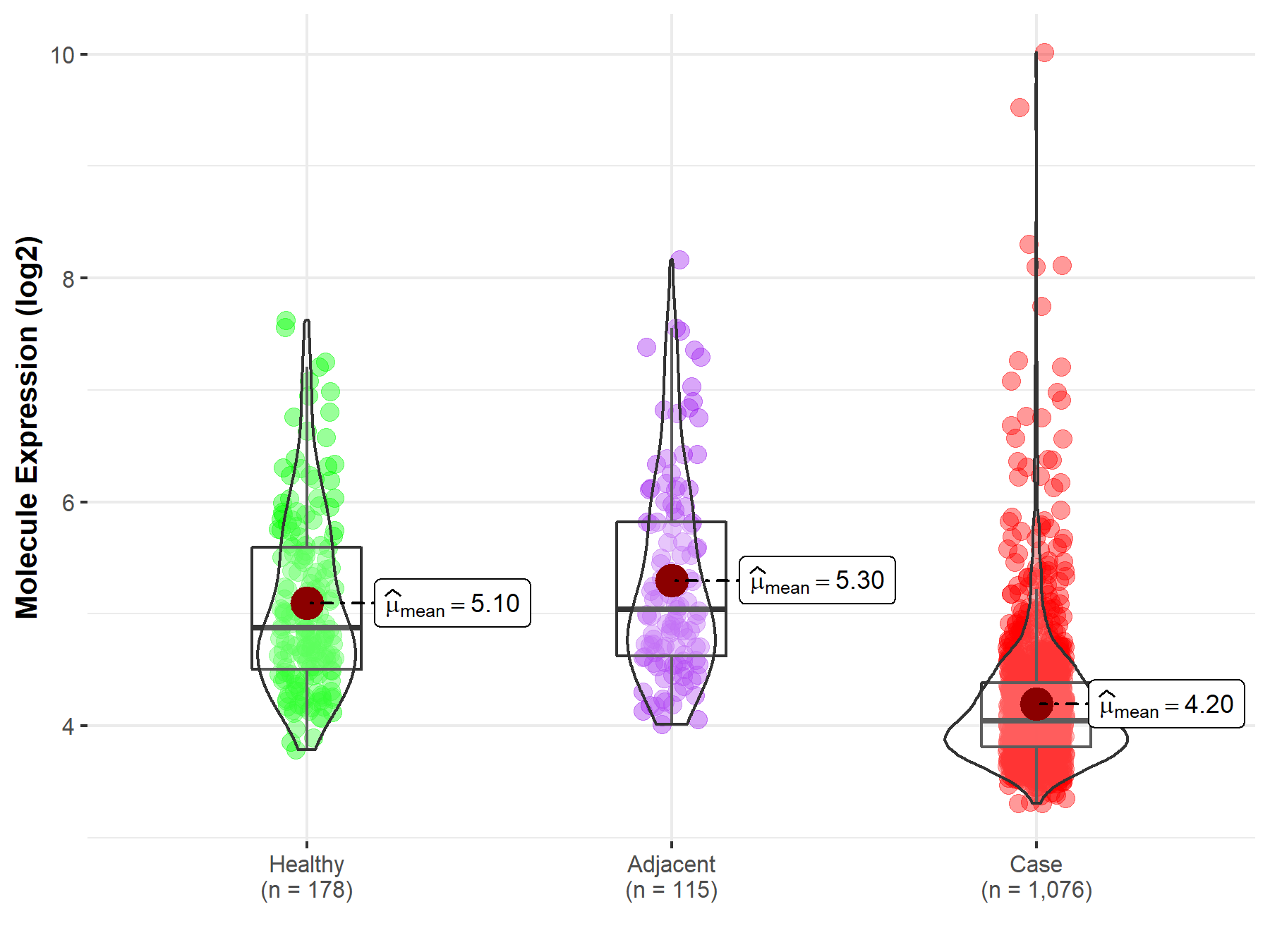
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Skin | |
| The Specified Disease | Melanoma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 7.98E-02; Fold-change: -4.69E-01; Z-score: -5.99E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
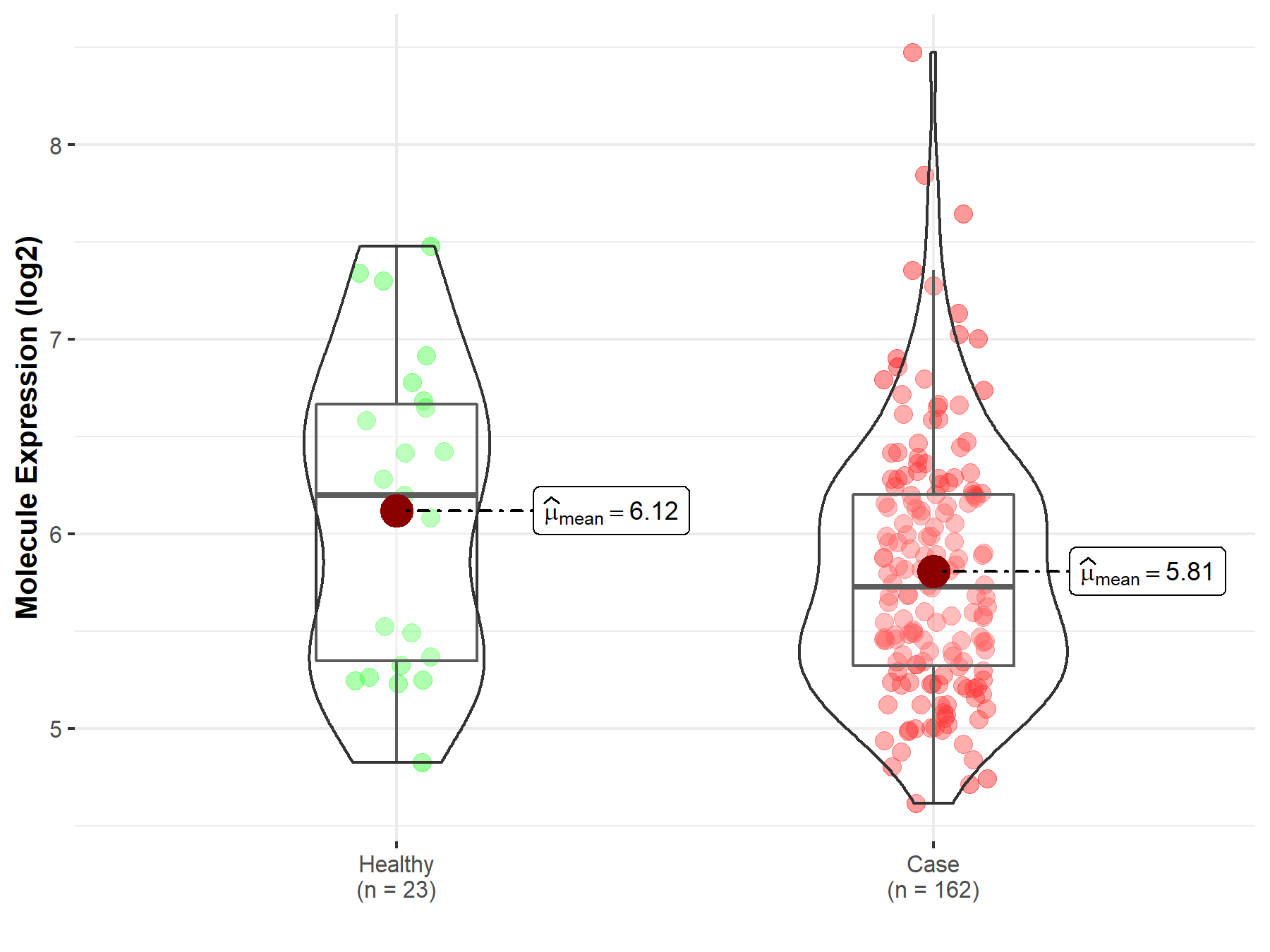
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.61E-73; Fold-change: -1.15E+00; Z-score: -1.66E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 2.48E-13; Fold-change: -1.04E+00; Z-score: -1.79E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
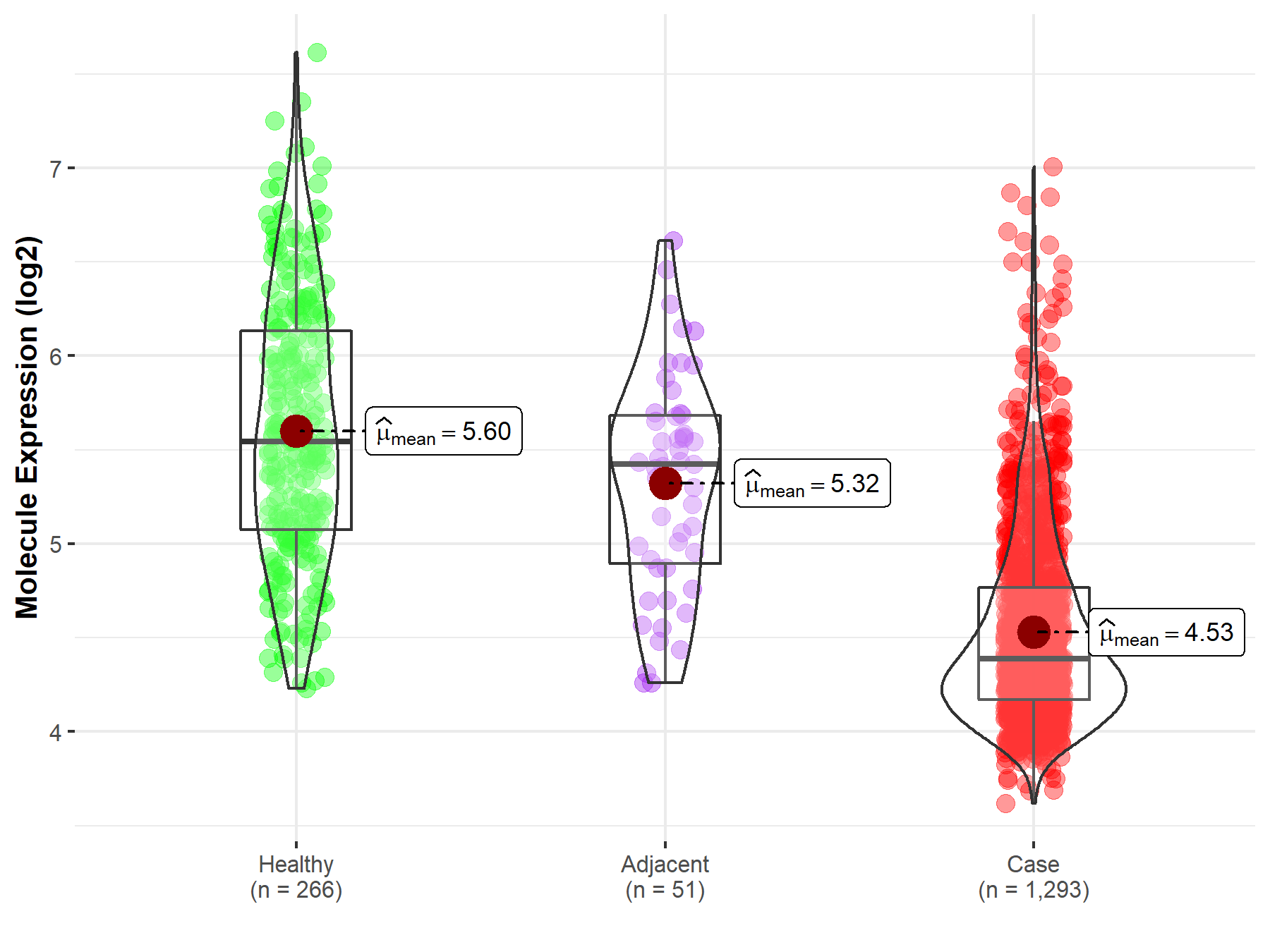
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Ovary | |
| The Specified Disease | Ovarian cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.53E-04; Fold-change: -6.93E-01; Z-score: -2.04E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 3.32E-02; Fold-change: -6.33E-01; Z-score: -5.21E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Cervix uteri | |
| The Specified Disease | Cervical cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.78E-01; Fold-change: -1.00E-02; Z-score: -2.13E-02 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
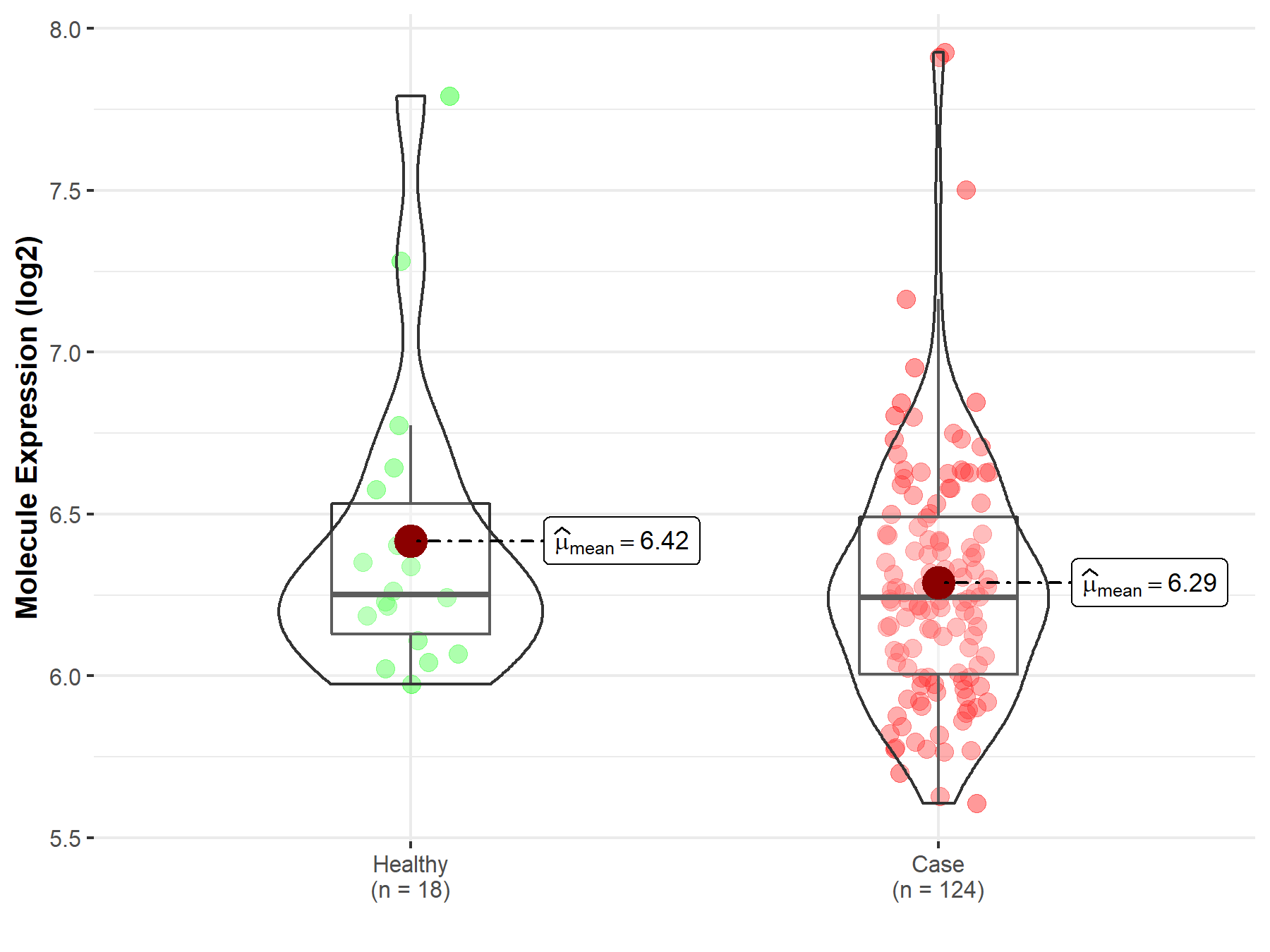
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Prostate | |
| The Specified Disease | Prostate cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.55E-01; Fold-change: 4.83E-01; Z-score: 5.66E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Kidney | |
| The Specified Disease | Kidney cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.04E-02; Fold-change: -1.13E+00; Z-score: -1.00E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 4.90E-49; Fold-change: -1.68E+00; Z-score: -3.26E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
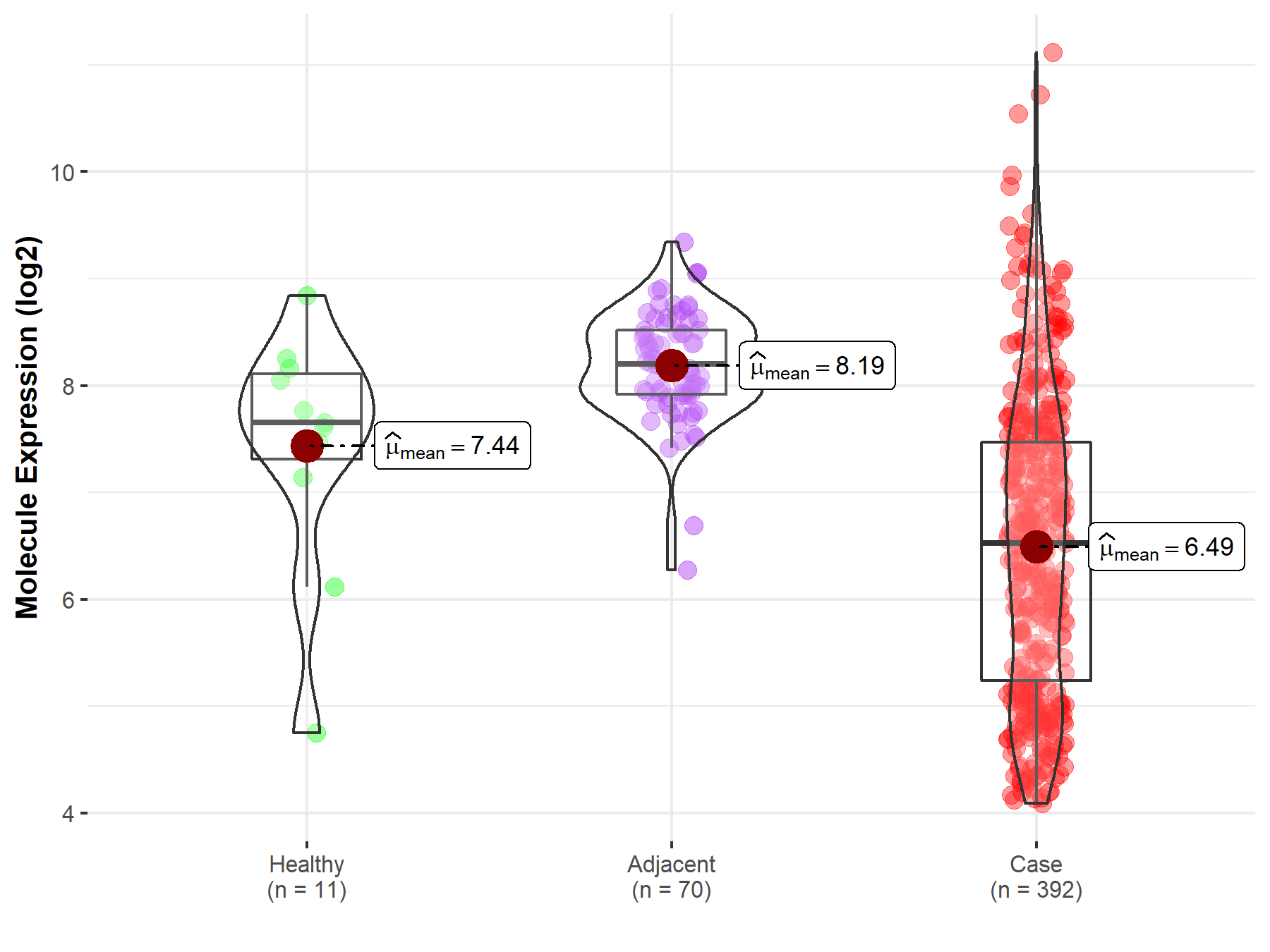
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Pituitary | |
| The Specified Disease | Pituitary cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.27E-03; Fold-change: 4.49E-01; Z-score: 1.31E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
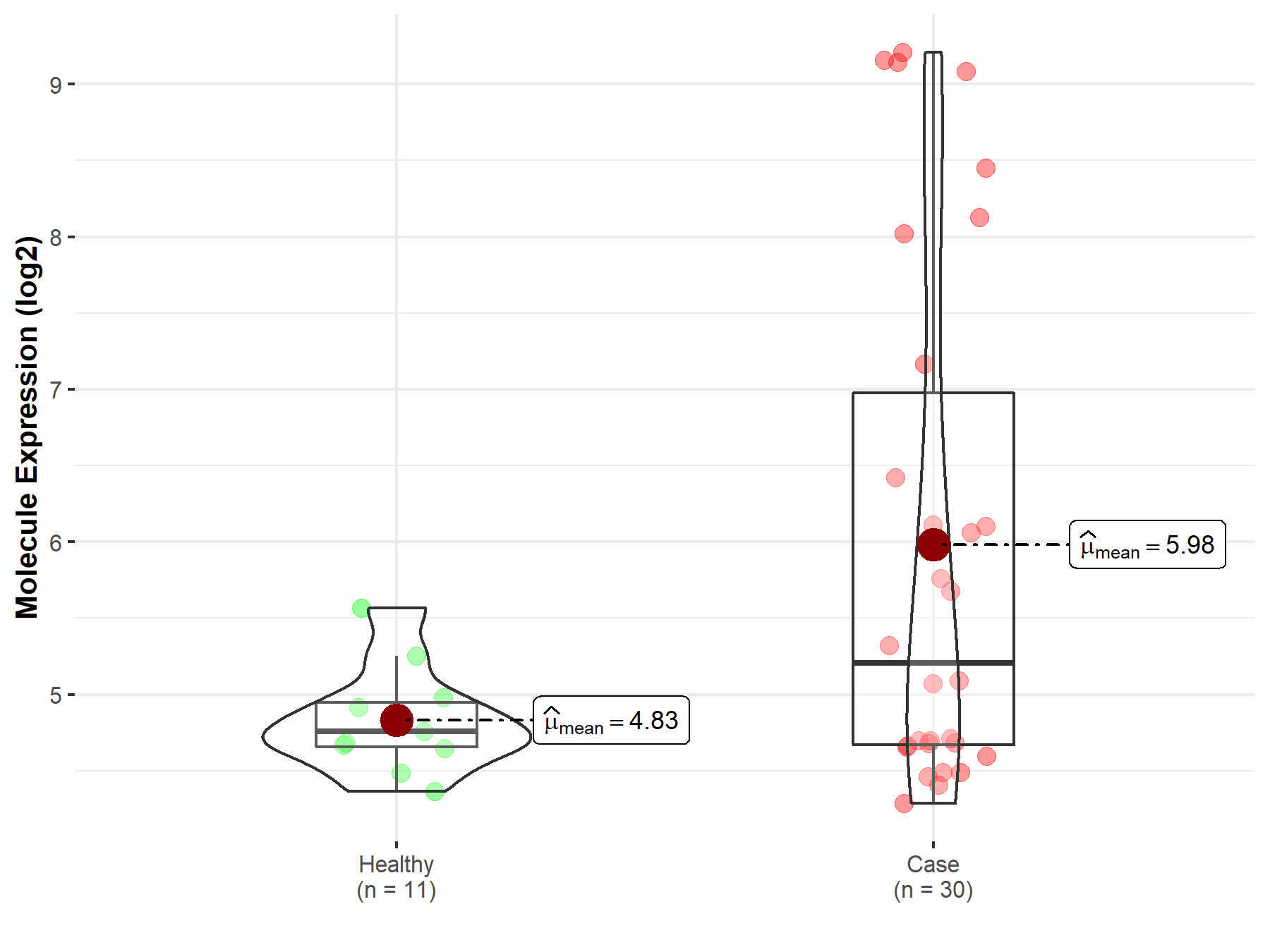
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | Pituitary | |
| The Specified Disease | Pituitary gonadotrope tumor | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.32E-01; Fold-change: -1.48E-01; Z-score: -3.76E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
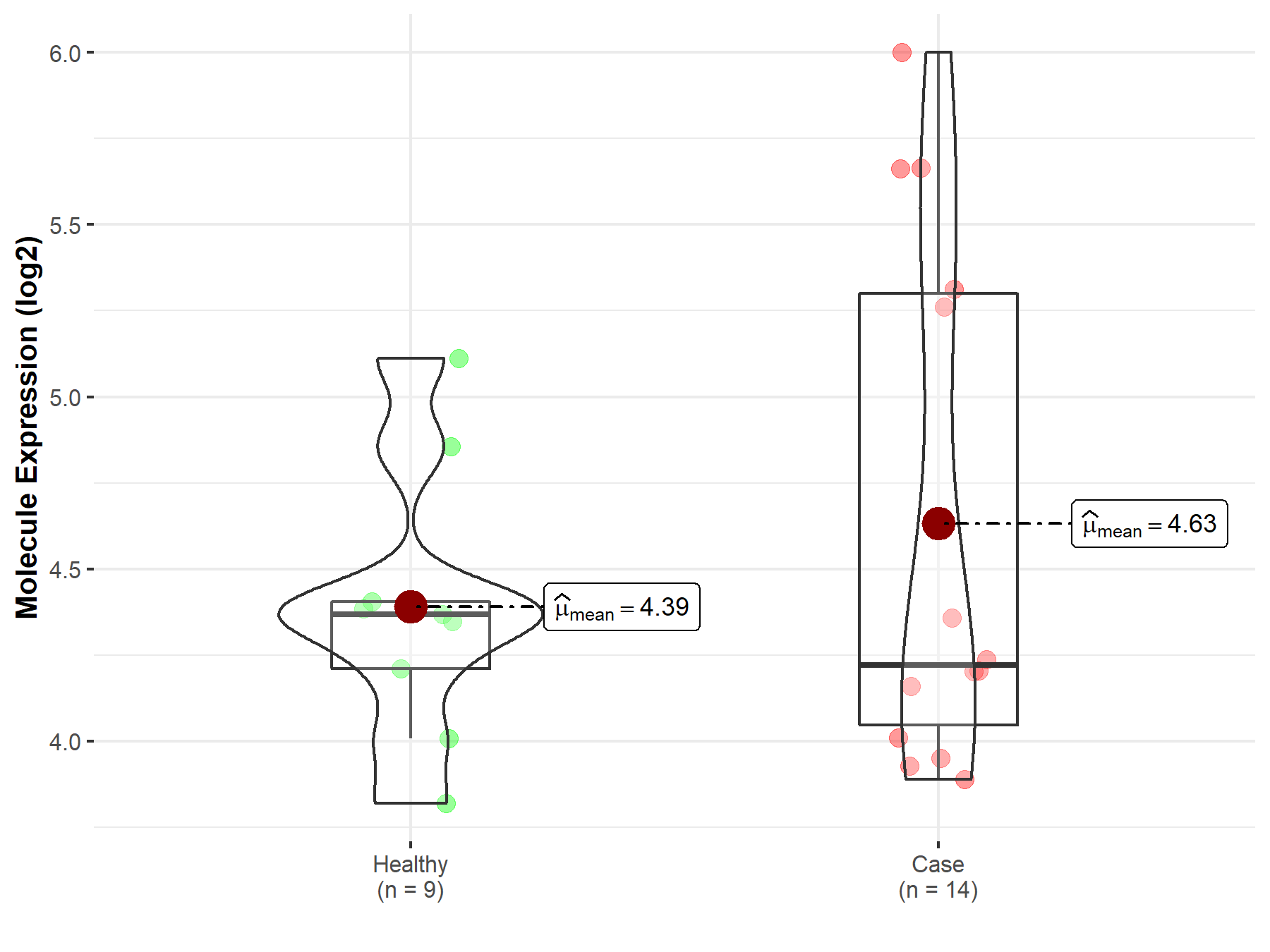
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
ICD Disease Classification 03

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Whole blood | |
| The Specified Disease | Thrombocytopenia | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.81E-01; Fold-change: 5.10E-02; Z-score: 4.59E-02 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
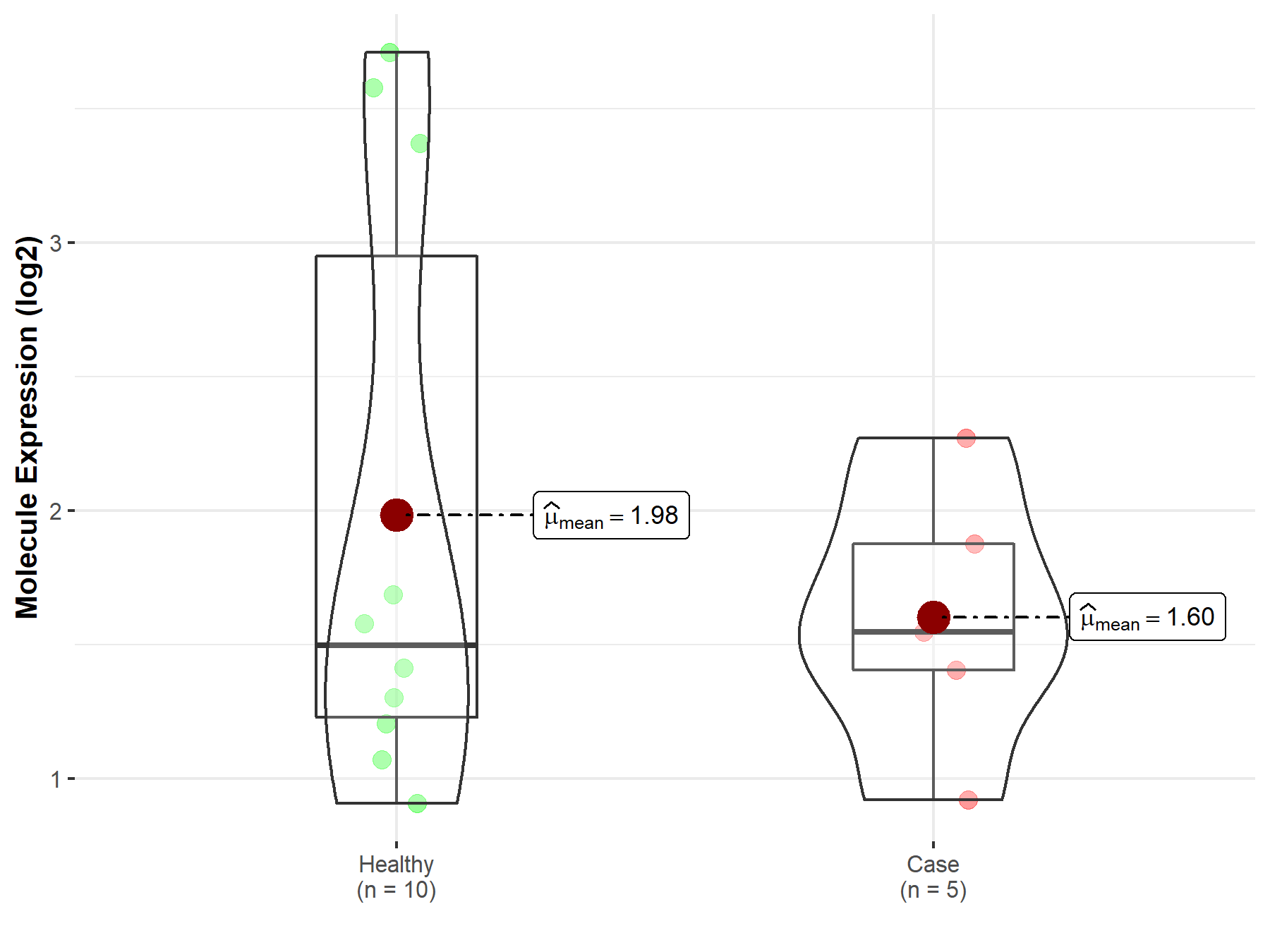
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
ICD Disease Classification 04

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Whole blood | |
| The Specified Disease | Lupus erythematosus | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.63E-15; Fold-change: -6.34E-01; Z-score: -9.11E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
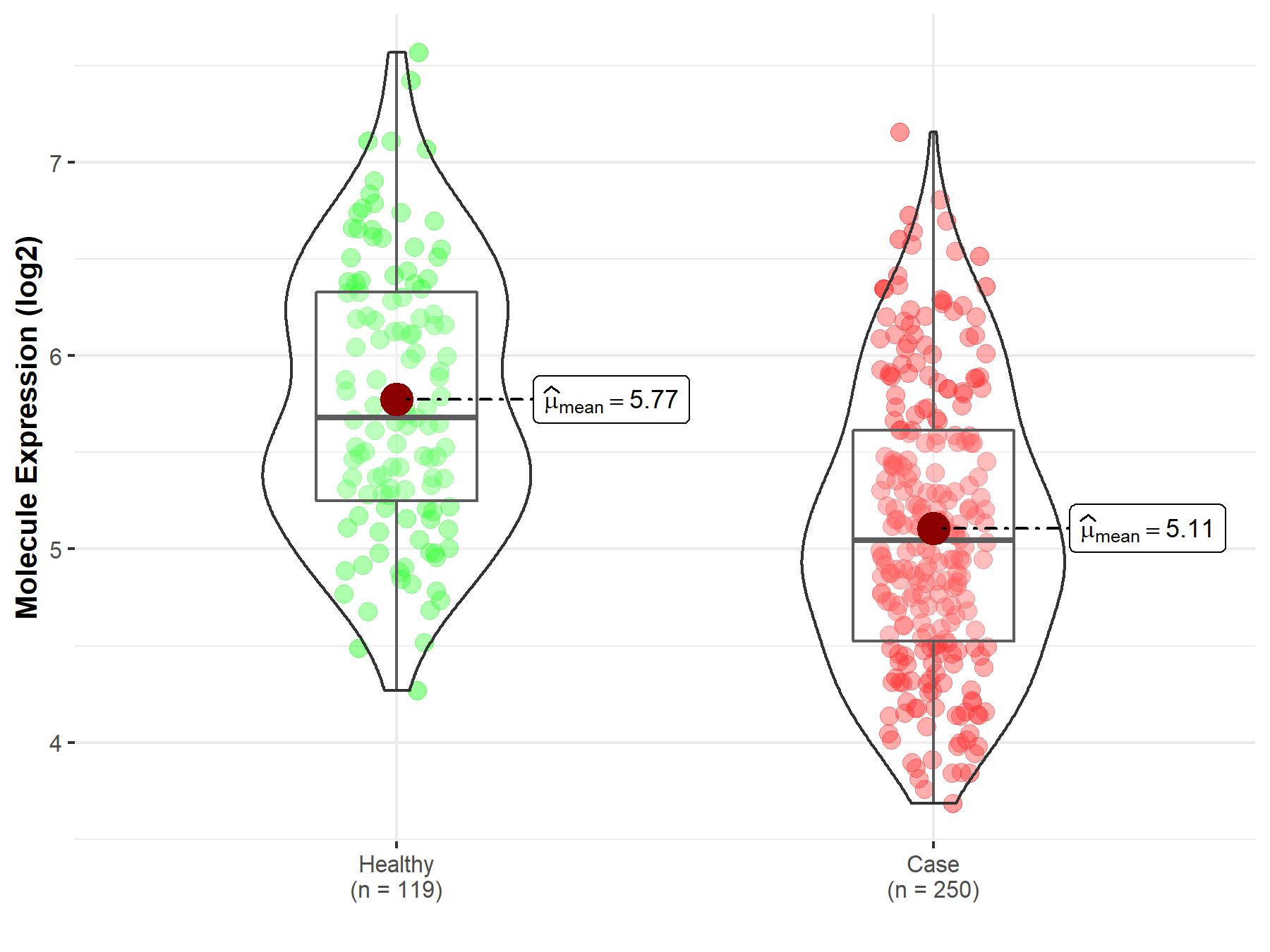
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
ICD Disease Classification 08

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Peritumoral cortex tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Epilepsy | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Other Disease Section | p-value: 2.76E-01; Fold-change: -2.17E-01; Z-score: -7.28E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in tissue other than the diseased tissue of patients
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
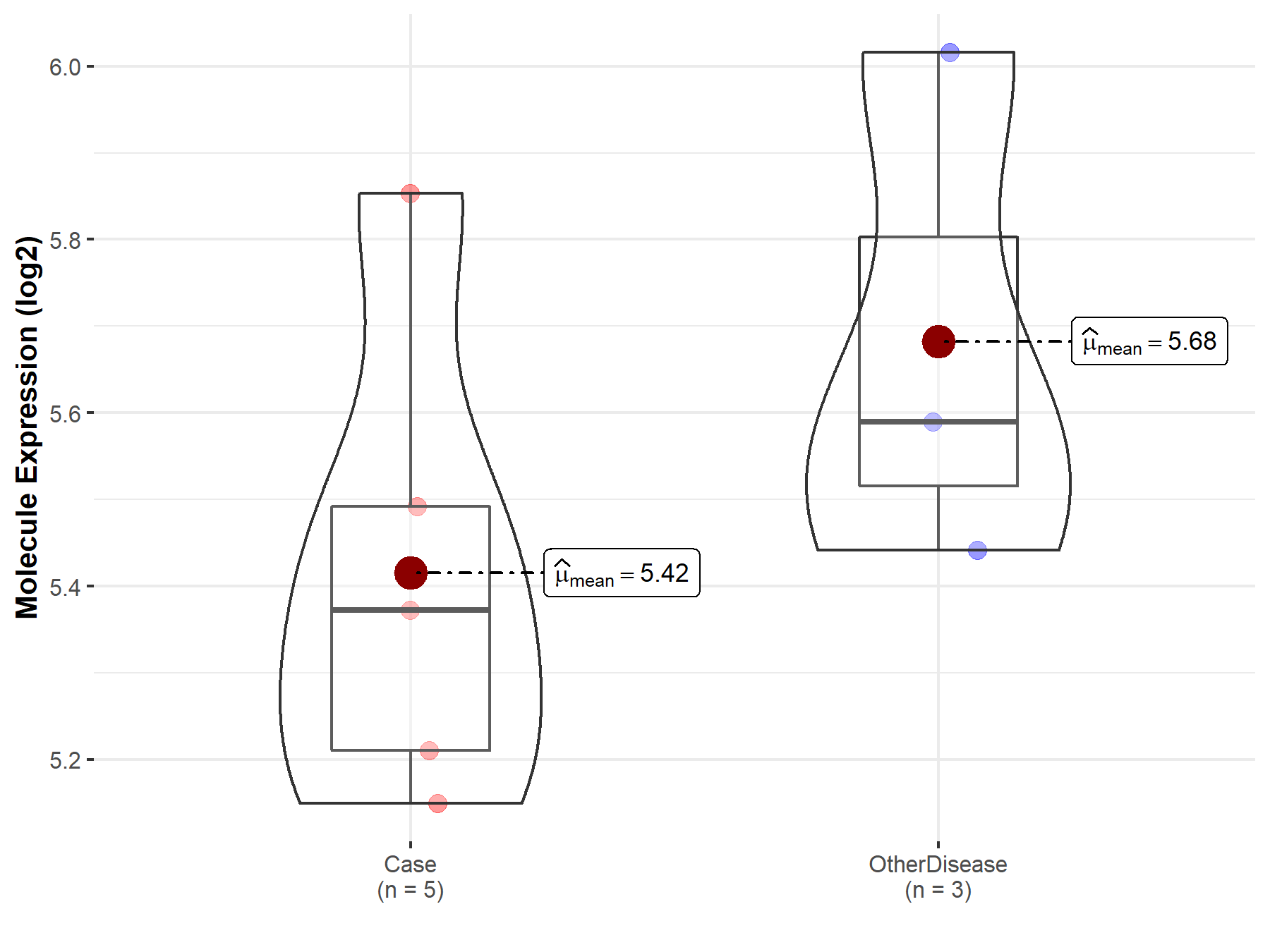
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Cervical spinal cord | |
| The Specified Disease | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.08E-01; Fold-change: -2.87E-01; Z-score: -5.57E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | Skin | |
| The Specified Disease | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.05E-01; Fold-change: 1.60E-01; Z-score: 1.37E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
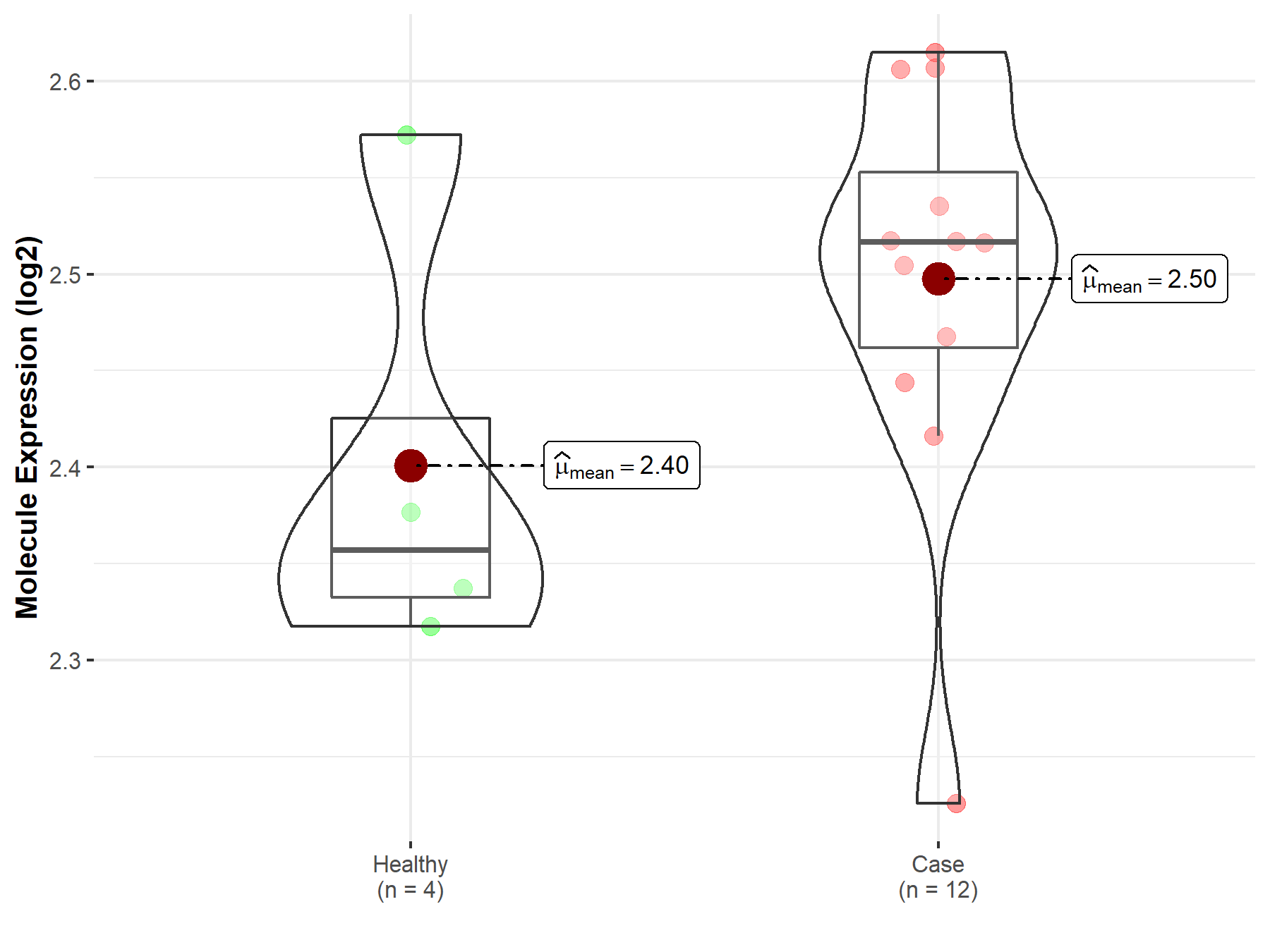
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
ICD Disease Classification 14

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Skin | |
| The Specified Disease | Psoriasis | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.00E-01; Fold-change: 2.57E-02; Z-score: 6.18E-02 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 6.81E-09; Fold-change: -3.22E-01; Z-score: -7.89E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
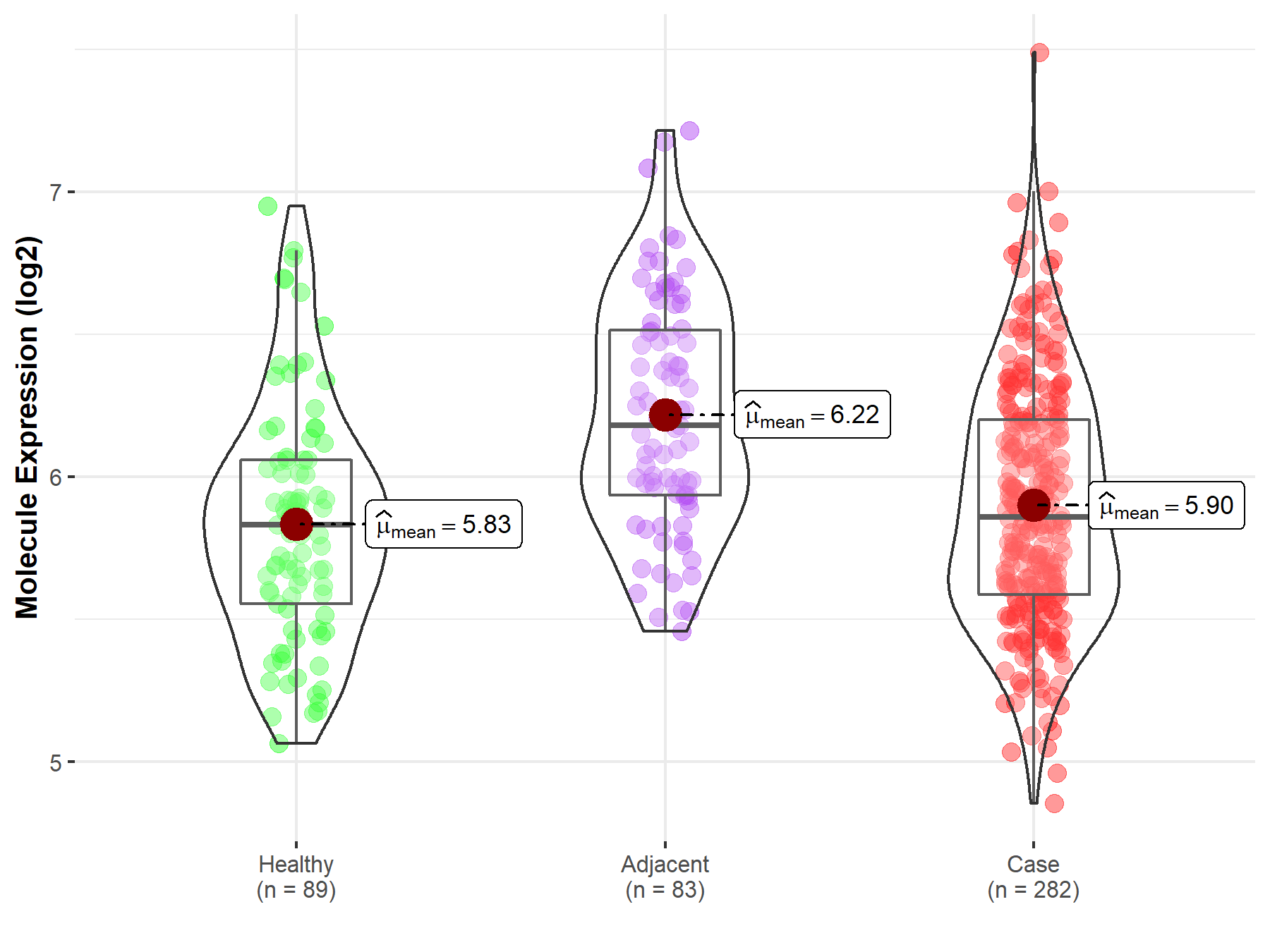
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
ICD Disease Classification 15

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Peripheral blood | |
| The Specified Disease | Rheumatoid arthritis | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 5.89E-02; Fold-change: 1.21E-02; Z-score: 2.54E-02 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
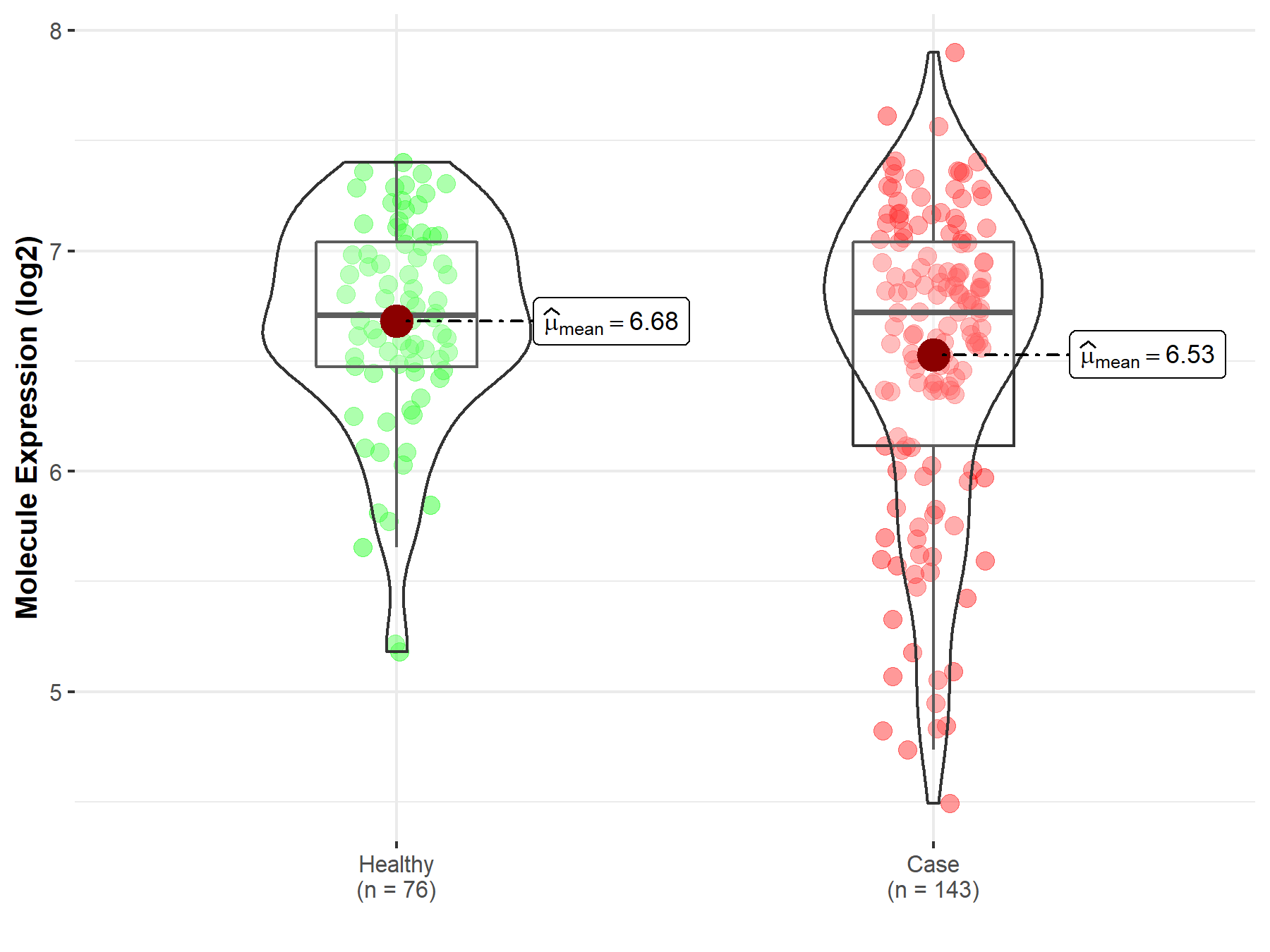
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | Synovial tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Rheumatoid arthritis | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 7.45E-02; Fold-change: -1.49E-01; Z-score: -3.47E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
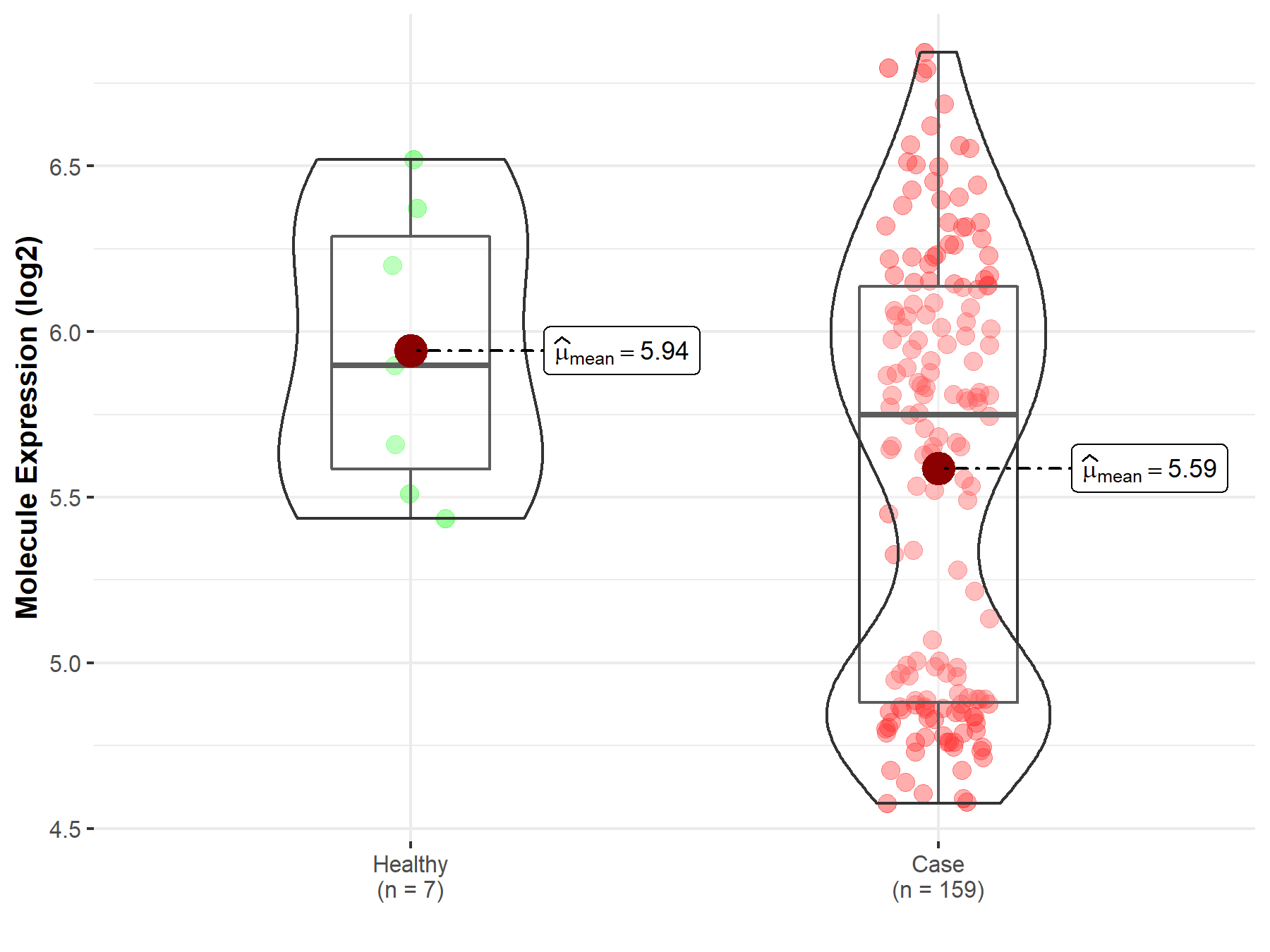
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
