Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00549) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Clopidogrel
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Clopidogrel; 113665-84-2; Plavix; (S)-Clopidogrel; Zyllt; Clopidogrel bisulfate; Clopidogrel Acino; Clopidogrel Hexal; (+)-Clopidogrel; CLOPIDOGREL SULFATE; (+)-(S)-Clopidogrel; UNII-A74586SNO7; Clopidogrel BMS; SR 25990; methyl (2S)-2-(2-chlorophenyl)-2-(6,7-dihydro-4H-thieno[3,2-c]pyridin-5-yl)acetate; CHEBI:37941; SR-25990C; A74586SNO7; Isocover; R 130964; (S)-Methyl 2-(2-chlorophenyl)-2-(6,7-dihydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridin-5(4H)-yl)acetate; Clopidogrel (TN); Plavix (TN); methyl (2S)-(2-chlorophenyl)(6,7-dihydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridin-5(4H)-yl)ethanoate; Thrombo; Clopidogrel [INN:BAN]; clopidogrel Sandoz; CHEMBL1083385; methyl (2S)-2-(2-chlorophenyl)-2-{4H,5H,6H,7H-thieno[3,2-c]pyridin-5-yl}acetate; SMR000550475; Clopidogrel Winthrop; Clopidogrel 1A Pharma; HSDB 7430; NSC-758613; Clopidogrel ratiopharm GmbH; Plavix® Clopidogrel apotex; (+) clopidogrel; CGE; Clopidogrel Teva (hydrogen sulphate); Clopidogrel-ratiopharm; Clopidogrel 1a-pharma; Spectrum_000105; CPD000550475; Clopidogrel (USP/INN); Spectrum2_000512; Spectrum3_001606; Spectrum4_000175; SCHEMBL4769; THIAMINELAURYLSULPHATE; CHEMBL1771; methyl (2S)-(2-chlorophenyl)(6,7-dihydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridin-5(4H)-yl)acetate; BSPBio_003211; KBioGR_000689; KBioSS_000545; MLS001165708; MLS001195633; MLS001304711; MLS006011891; BIDD:GT0284; DivK1c_000787; SPBio_000463; GTPL7150; DTXSID6022848; HMS502H09; KBio1_000787; KBio2_000545; KBio2_003113; KBio2_005681; KBio3_002431; AMY8913; NINDS_000787; HMS2090O21; HMS2234N16; HMS3259B08; HMS3715J08; BBL010770; BDBM50318910; BDBM50397662; MFCD05662337; NSC748298; STK580572; ZINC34781704; AKOS005504280; CCG-221243; CS-0656; DB00758; MCULE-9061369538; NC00703; NSC 758613; NSC-748298; IDI1_000787; Methyl (+)-(S)-alpha-(o-chlorophenyl)-6,7-dihydrothieno(3,2-c)pyridine-5(4H)-acetate; NCGC00163329-02; NCGC00163329-04; AC-19024; DS-13362; HY-15283; Thieno(3,2-c)pyridine-5(4H)-acetic acid, alpha-(2-chlorophenyl)-6,7-dihydro-, methyl ester, (S)-; SBI-0052755.P002; D07729; N11780; AB00053786-07; AB00053786-08; AB00053786_09; AB00053786_10; Q410237; R-130964; BRD-K27721098-065-02-9; BRD-K27721098-065-05-2; UNII-MX75HY8K68 component GKTWGGQPFAXNFI-HNNXBMFYSA-N; methyl (2-chlorophenyl)(6,7-dihydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridin-5(4H)-yl)acetate; (S)-(+)-Methyl (2-chlorophenyl)(6,7-dihydro-4H-thieno[3,2-c]pyrid-5-yl)acetate; (S)-(+)-Methyl (2-chlorophenyl)-(6,7-dihydro-4H-thieno[3,2-c]pyrid-5-yl)acetate; methyl (+)-(S)-alpha-(2-chlorophenyl)-6,7-dihydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-5(4H)-acetate; methyl (+)-(s)-alpha-(o-chlorophenyl)-6,7-dihydrothieno-[3,2-c]pyridine-5(4h)-acetate; methyl (S)-(+)-alpha-(o-chlorophenyl)-6,7-dihydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridin-5(4H)-acetate; methyl(+)-(s)-alpha-(2-chlorophenyl)-6,7-dihydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-5(4h) acetate; methyl-(S)-(+)-(2-chlorophenyl)-2-(6,7-dihydro-4H-thieno[3,2-c]pyridine-5-yl)-acetate; (+)-(S)-(2-Chlorophenyl) (6,7-dihydro-4H-thieno[3,2-c]pyridin-5-yl)acetic acid methyl ester; (+)-(S)-2-(2-chlorophenyl)-(6,7-dihydro-4H-thieno[3,2-c]pyrid-5-yl)acetic acid methyl ester; Thieno[3,2-c]pyridine-5(4H)-acetic acid, .alpha.-(2-chlorophenyl)-6,7-dihydro-, methyl ester, (.alpha.S)-; Thieno[3,2-c]pyridine-5(4H)-acetic acid, alpha-(2-chlorophenyl)-6,7-dihydro-, methyl ester, (alphaS)-
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
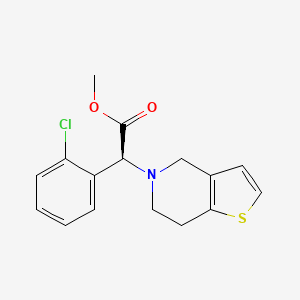
| Structure |
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(5 diseases)
[2]
[3]
[4]
[1]
[5]
|
||||
| Target | P2Y purinoceptor 12 (P2RY12) | P2Y12_HUMAN | [4] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C16H16ClNO2S
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
COC(=O)[C@H](C1=CC=CC=C1Cl)N2CCC3=C(C2)C=CS3
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C16H16ClNO2S/c1-20-16(19)15(12-4-2-3-5-13(12)17)18-8-6-14-11(10-18)7-9-21-14/h2-5,7,9,15H,6,8,10H2,1H3/t15-/m0/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
GKTWGGQPFAXNFI-HNNXBMFYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| VARIDT ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-08: Nervous system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Cytochrome P450 family 1 subfamily A member 1 (CYP1A1) | [6] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acute Ischemic Stroke [ICD-11: 8B11.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | CYP3A5 (rs776746) GG + AG and CYP2C19*2 (rs4244285) AA + AG genotypes |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time of flight mass spectrometry assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Platelet aggregation test assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The estimated risk of clopidogrel resistance was significantly higher in patients with CYP3A5 (rs776746) GG and CYP2C19*2 (rs4244285) AA, as compared to patients harboring CYP3A5 (rs776746) AA and CYP2C19*2 (rs4244285) GG. These data suggest that these two CYP genetic variants together significantly contributed to clopidogrel resistance. The relative risk conferred by the combinations of CYP3A5 GG and CYP2C19*2 AA was considered as a high-risk variable, with assigned as one, and other combinations of CYP3A5 and CYP2C19*2 as a low-risk variable, with assigned as zero. | |||
ICD-11: Circulatory system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Cytochrome P450 family 2 subfamily C member 19 (CYP2C19) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acute myocardial infarction [ICD-11: BA41.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | SNP | CYP2C19*2+CYP2C19*3 |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | We defined CYP2C19*2 and CYP2C19*3 as CYP2C19 loss-of-function alleles (LoFA), indicating possible clopidogrel resistance. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Cytochrome P450 family 2 subfamily C member 19 (CYP2C19) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Coronary artery disease [ICD-11: BA8Z.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | SNP | CYP2C19*2 |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Blood sample | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Genetic analysis assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Platelet aggregation test assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Among the 72 patients studied, 32.6% were carriers of CYP2C19*2 loss-of-function allele. This allele was found to be more common but not significantly so from the controls (27.7%). The loss-of-function genotypes (*2/*2 or *2/*1) of CYP2C19 were seen to be significantly higher in clopidogrel semi-responders compared to responders (72.9% vs 34.3%, P = 0.0023, respectively). Similarly, significantly higher frequency of the mutant *2 allele of CYP2C19 was observed in clopidogrel semi-responders than in responders (43.2% vs 21.4%, P = 0.007). | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: P2Y purinoceptor 1 (P2RY1) | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Hypo-attenuated leaflet thickening [ICD-11: BD10.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | SNP | rs701265+rs1439010+rs1371097+rs1065776+rs12497578 |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | We thoroughly genotyped 34 SNPs and 8 SNPs that have been reported for clopidogrel and aspirin resistance. A total of 148 patients were enrolled. There were 15 patients demonstrating signs of HALT. Patients with HALT had a higher rate of atrial fibrillation (AF) pre-TAVR (33.3 vs. 7.5%, P = 0.01). | |||
| Key Molecule: Purinergic receptor P2Y12 (P2RY12) | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Hypo-attenuated leaflet thickening [ICD-11: BD10.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | SNP | rs2046934+rs12637988+rs16863336+rs6798347+rs16863323+rs9859538+rs16846673+rs6809699+rs6785930+rs5853517+rs10935838 |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | We thoroughly genotyped 34 SNPs and 8 SNPs that have been reported for clopidogrel and aspirin resistance. A total of 148 patients were enrolled. There were 15 patients demonstrating signs of HALT. Patients with HALT had a higher rate of atrial fibrillation (AF) pre-TAVR (33.3 vs. 7.5%, P = 0.01). | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Liver carboxylesterase 1 (CES1) | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Hypo-attenuated leaflet thickening [ICD-11: BD10.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | SNP | rs8192950 |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | We thoroughly genotyped 34 SNPs and 8 SNPs that have been reported for clopidogrel and aspirin resistance. A total of 148 patients were enrolled. There were 15 patients demonstrating signs of HALT. Patients with HALT had a higher rate of atrial fibrillation (AF) pre-TAVR (33.3 vs. 7.5%, P = 0.01). | |||
| Key Molecule: Cytochrome P450 family 2 subfamily C member 19 (CYP2C19) | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Hypo-attenuated leaflet thickening [ICD-11: BD10.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | SNP | rs4244285+rs4986893+rs28399504+rs56337013+rs72552267+rs72558186+rs12248560 |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | We thoroughly genotyped 34 SNPs and 8 SNPs that have been reported for clopidogrel and aspirin resistance. A total of 148 patients were enrolled. There were 15 patients demonstrating signs of HALT. Patients with HALT had a higher rate of atrial fibrillation (AF) pre-TAVR (33.3 vs. 7.5%, P = 0.01). | |||
| Key Molecule: Cytochrome P450 family 2 subfamily C member 9 (CYP2C9) | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Hypo-attenuated leaflet thickening [ICD-11: BD10.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | SNP | rs1799853+rs1057910 |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | We thoroughly genotyped 34 SNPs and 8 SNPs that have been reported for clopidogrel and aspirin resistance. A total of 148 patients were enrolled. There were 15 patients demonstrating signs of HALT. Patients with HALT had a higher rate of atrial fibrillation (AF) pre-TAVR (33.3 vs. 7.5%, P = 0.01). | |||
| Key Molecule: Cytochrome P450 family 3 subfamily A member1 (CYP3A4) | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Hypo-attenuated leaflet thickening [ICD-11: BD10.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | SNP | rs2740574+rs55785340+rs4986910 |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | We thoroughly genotyped 34 SNPs and 8 SNPs that have been reported for clopidogrel and aspirin resistance. A total of 148 patients were enrolled. There were 15 patients demonstrating signs of HALT. Patients with HALT had a higher rate of atrial fibrillation (AF) pre-TAVR (33.3 vs. 7.5%, P = 0.01). | |||
| Key Molecule: Cytochrome P450 family 3 subfamily A member 5 (CYP3A5) | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Hypo-attenuated leaflet thickening [ICD-11: BD10.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | SNP | rs776746 |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | We thoroughly genotyped 34 SNPs and 8 SNPs that have been reported for clopidogrel and aspirin resistance. A total of 148 patients were enrolled. There were 15 patients demonstrating signs of HALT. Patients with HALT had a higher rate of atrial fibrillation (AF) pre-TAVR (33.3 vs. 7.5%, P = 0.01). | |||
| Key Molecule: Paraoxonase 1 (PON1) | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Hypo-attenuated leaflet thickening [ICD-11: BD10.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | SNP | rs662 |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | We thoroughly genotyped 34 SNPs and 8 SNPs that have been reported for clopidogrel and aspirin resistance. A total of 148 patients were enrolled. There were 15 patients demonstrating signs of HALT. Patients with HALT had a higher rate of atrial fibrillation (AF) pre-TAVR (33.3 vs. 7.5%, P = 0.01). | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Multidrug resistance protein 1 (ABCB1) | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Hypo-attenuated leaflet thickening [ICD-11: BD10.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | SNP | rs1045642+rs2032562 |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | We thoroughly genotyped 34 SNPs and 8 SNPs that have been reported for clopidogrel and aspirin resistance. A total of 148 patients were enrolled. There were 15 patients demonstrating signs of HALT. Patients with HALT had a higher rate of atrial fibrillation (AF) pre-TAVR (33.3 vs. 7.5%, P = 0.01). | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Integrin subunit beta 3 (ITGB3) | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Hypo-attenuated leaflet thickening [ICD-11: BD10.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | SNP | rs5918 |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | We thoroughly genotyped 34 SNPs and 8 SNPs that have been reported for clopidogrel and aspirin resistance. A total of 148 patients were enrolled. There were 15 patients demonstrating signs of HALT. Patients with HALT had a higher rate of atrial fibrillation (AF) pre-TAVR (33.3 vs. 7.5%, P = 0.01). | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Cytochrome P450 family 2 subfamily C member 19 (CYP2C19) | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Peripheral arterial disease [ICD-11: BD4Z.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | SNP | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Whole blood | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
VerifyNow P2Y12 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Clopidogrel is a pro-drug requiring cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2C19 enzyme to be oxidised to its active form.CYP 2C19 genetic polymorphism may result clopidogrel resistance. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
