Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00143) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Cefotetan
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Cefotetanum; Apatef (TN); Cefotan (TN); Cefotetan (JP15/USP/INN); (6R,7S)-7-(4-(carbamoylcarboxymethylene)-1,3-dithiethane-2-carboxamido)-7-methoxy-3-(((1-methyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)thio)methyl)-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo(4.2.0)oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid; (6R,7S)-7-({[4-(2-amino-1-carboxy-2-oxoethylidene)-1,3-dithietan-2-yl]carbonyl}amino)-7-methoxy-3-{[(1-methyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)sulfanyl]methyl}-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid; (6R,7S)-7-[[4-(1-amino-3-hydroxy-1,3-dioxopropan-2-ylidene)-1,3-dithietane-2-carbonyl]amino]-7-methoxy-3-[(1-methyltetrazol-5-yl)sulfanylmethyl]-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid; 7beta-({[4-(2-amino-1-carboxy-2-oxoethylidene)-1,3-dithietan-2-yl]carbonyl}amino)-7alpha-methoxy-3-{[(1-methyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)sulfanyl]methyl}-3,4-didehydrocepham-4-carboxylic acid
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
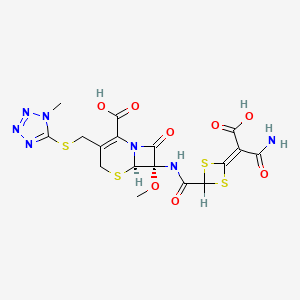
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(3 diseases)
[3]
[4]
|
||||
| Target | Bacterial Penicillin binding protein (Bact PBP) | NOUNIPROTAC | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C17H17N7O8S4
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CN1C(=NN=N1)SCC2=C(N3[C@@H]([C@@](C3=O)(NC(=O)C4SC(=C(C(=O)N)C(=O)O)S4)OC)SC2)C(=O)O
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C17H17N7O8S4/c1-23-16(20-21-22-23)34-4-5-3-33-15-17(32-2,14(31)24(15)7(5)11(29)30)19-9(26)13-35-12(36-13)6(8(18)25)10(27)28/h13,15H,3-4H2,1-2H3,(H2,18,25)(H,19,26)(H,27,28)(H,29,30)/t13 ,15-,17+/m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
SRZNHPXWXCNNDU-RHBCBLIFSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| VARIDT ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Beta-lactamase (BLA) | [1], [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli strain DH5a | 668369 | ||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strain HEL-1 | 573 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The phenotype of Klebsiella pneumoniae HEL-1 indicates a plasmidic cephamycinase gene (blaCMY-2),which is responsible for cephamycin resistance. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Multidrug resistance protein 1 (ABCB1) | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus infection [ICD-11: 1B7Y.3] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates | 287 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus isolates | 1280 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates | 573 | |||
| Acinetobacter isolates | 469 | |||
| Enterobacter cloacae isolates | 550 | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Disk diffusion method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Up-regulation of P-glycoprotein led to ampicillin resistance in the staphylococcus infection. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
