Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00929) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Resiquimod
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Resiquimod; 144875-48-9; 1-(4-Amino-2-(ethoxymethyl)-1H-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-1-yl)-2-methylpropan-2-ol; R-848; 1-[4-amino-2-(ethoxymethyl)-1H-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-1-yl]-2-methylpropan-2-ol; R 848; UNII-V3DMU7PVXF; Resiquimod (R-848); R848; V3DMU7PVXF; MFCD00937759; S-28463; CHEMBL383322; CHEBI:36706; 1-[4-amino-2-(ethoxymethyl)imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-1-yl]-2-methylpropan-2-ol; s28463; R848;S28463; Resiquimod [INN]; alpha-dimethyl-1H-imidazo(4,5-c)quinoline-1-ethanol; 1-(4-amino-2-(ethoxymethyl)-1H-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-1-yl)-2-methylpropan-2-ol.; 2252319-44-9; R848 compound; S 28463; 1H-Imidazo(4,5-c)quinoline-1-ethanol, 4-amino-2-(ethoxymethyl)-alpha,alpha-dimethyl-; 1H-Imidazo[4,5-c]quinoline-1-ethanol, 4-amino-2-(ethoxymethyl)-alpha,alpha-dimethyl-; 4-Amino-2-(ethoxymethyl)-alpha,alpha-dimethyl-1H-imidazo(4,5-c)quinoline-1-ethanol; 4-Amino-2-(ethoxymethyl)-alpha,alpha-dimethyl-1H-Imidazo[4,5-c]quinoline-1-ethanol; ResiquimodR848; VML-600; RX8; R848; Resiquimod; SCHEMBL34159; MLS006010212; GTPL5051; DTXSID7040603; Resiquimod, >=98% (HPLC); 4-Amino-2-(ethoxymethyl)-alpha; HMS3740O09; BCP09103; EX-A1879; BDBM50241029; s8133; ZINC28572103; AKOS016003509; CCG-267635; CD11301; CS-1706; DB06530; SB17111; 1-(4-Amino-2-ethoxymethyl-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-1-yl)-2-methyl-propan-2-ol; NCGC00370784-01; NCGC00370784-05; AS-30885; CD-11301; HY-13740; SMR002530531; SY107476; FT-0763049; R0197; Z4166; Resiquimod, VML-600, R-848, S-28463; A856222; Q426054; SR-01000944954; J-008020; SR-01000944954-1; 1-[4-amino-2-(ethoxymethyl)imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-1-yl]-2-methyl-propan-2-ol; 4-amino-2-ethoxymethyl-alpha,alpha-dimethyl-1H-imidazo[4,5-c]quinoline-1-ethanol; 4-amino-alpha,alpha-dimethyl-2-ethoxymethyl-1H-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-1-ethanol; 4-Amino-alpha,alpha-dimethyl-2-ethoxymethyl-1H-imidazo[4,5-c]quinoline-1-ethanol
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 3 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
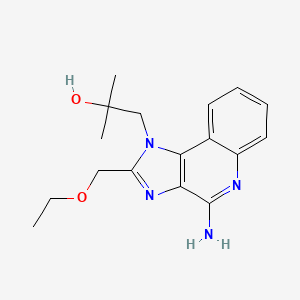
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Discovered by Cell Line Test for This Drug
(3 diseases)
[1]
[1]
[1]
|
||||
| Target | Toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7) | TLR7_HUMAN | [1] | ||
| Toll-like receptor 8 (TLR8) | TLR8_HUMAN | [1] | |||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C17H22N4O2
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CCOCC1=NC2=C(N1CC(C)(C)O)C3=CC=CC=C3N=C2N
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C17H22N4O2/c1-4-23-9-13-20-14-15(21(13)10-17(2,3)22)11-7-5-6-8-12(11)19-16(14)18/h5-8,22H,4,9-10H2,1-3H3,(H2,18,19)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
BXNMTOQRYBFHNZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Multidrug resistance protein 1 (ABCB1) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Resazurin Cell Viability Assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Imidazoquinolines IMQ, RSQ, and GDQ are substrates for P-gp and begins to elucidate differences in their trafficking in cancer cells as a consequence of acquired drug resistance. We believe this work that begins to examine imidazoquinoline trafficking will prove useful in the future rational design of immunotherapeutics with enhanced susceptibility to P-gp efflux that enable increased bioavailability, in MDR cancers. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Multidrug resistance protein 1 (ABCB1) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | COLO205 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_F402 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Resazurin Cell Viability Assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Imidazoquinolines IMQ, RSQ, and GDQ are substrates for P-gp and begins to elucidate differences in their trafficking in cancer cells as a consequence of acquired drug resistance. We believe this work that begins to examine imidazoquinoline trafficking will prove useful in the future rational design of immunotherapeutics with enhanced susceptibility to P-gp efflux that enable increased bioavailability, in MDR cancers. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Multidrug resistance protein 1 (ABCB1) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Hep3B cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0326 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Resazurin Cell Viability Assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Imidazoquinolines IMQ, RSQ, and GDQ are substrates for P-gp and begins to elucidate differences in their trafficking in cancer cells as a consequence of acquired drug resistance. We believe this work that begins to examine imidazoquinoline trafficking will prove useful in the future rational design of immunotherapeutics with enhanced susceptibility to P-gp efflux that enable increased bioavailability, in MDR cancers. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
