Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00613) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Indomethacin
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Indomethacin; 53-86-1; indometacin; Indocin; Indometacine; Indomethacine; Indocid; Metindol; Indomethazine; Reumacide; Imbrilon; Amuno; Tannex; Indomethacinum; Artracin; Artrinovo; Artrivia; Confortid; Idomethine; Indomecol; Indoptic; Indoptol; Inflazon; Infrocin; Metartril; Methazine; Mikametan; Sadoreum; Dolovin; Inacid; Indacin; Indomed; Indomee; Lausit; Metacen; Mobilan; Indo-rectolmin; Indo-tablinen; Inteban sp; Indometacyna; Indometicina; Mezolin; Durametacin; Indometacinum; 2-(1-(4-Chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)acetic acid; Indometacina; Dolcidium; Elmetacin; Indomethine; Indorektal; Catlep; Indoxen; Vonum; Indo-phlogont; Chibro-amuno; Rheumacin LA; 1H-Indole-3-acetic acid, 1-(4-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-; Osmosin; Aconip; 1-(p-Chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methylindole-3-acetic acid; CCRIS 3502; 2-[1-(4-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methylindol-3-yl]acetic acid; HSDB 3101; 1-(4-Chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-3-indoleacetic acid; NCI-C56144; UNII-XXE1CET956; MFCD00057095; CHEMBL6; 1-(p-Chlorobenzoyl)-2-methyl-5-methoxyindole-3-acetic acid; IMN; Indole-3-acetic acid, 1-(p-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-; Indo-Lemmon; [1-(4-Chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl]acetic acid; Indocin Sr; XXE1CET956; 2-{1-[(4-chlorophenyl)carbonyl]-5-methoxy-2-methyl-1h-indol-3-yl}acetic acid; N-p-Chlorbenzoyl-5-methoxy-2-methylindole-3-acetic acid; MLS000069402; Indomethacin (Indocid, Indocin); (1-p-Chlorobenzoyl-5-methoxy-2-methylindol-3-yl)acetic acid; CHEBI:49662; 1-(4-Chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-1H-indole-3-acetic acid; 1-(p-Chlorobenzoyl)-2-methoxy-3-methyl-1H-indole-3-acetic Acid; Indomet 140; alpha-(1-(p-Chlorobenzoyl)-2-methyl-5-methoxy-3-indolyl)acetic acid; {1-[(4-chlorophenyl)carbonyl]-5-methoxy-2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl}acetic acid; NSC-757061; CAS-53-86-1; 1-p-Cloro-benzoil-5-metoxi-2-metilindol-3-acido acetico; NCGC00015562-18; Indmethacine; Indomethancin; 1-(p-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-3-indolylacetic acid; Arthrexin; Bonidin; Bonidon; Indameth; Indomod; Miametan; SMR000058195; Indomo; Flexin continus; Hicin; Kwas 1-(p-chlorobenzoilo)-2-metylo-5-metoksy-3-indolilooctowy; Chrono-indicid; Chrono-indocid; Indometacyna [Polish]; DSSTox_CID_740; Bonidon Gel; Indometicina [Spanish]; 2-[1-(4-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl]acetic acid; Dolcidium PL; Indo-Spray; Indolar SR; DSSTox_RID_75763; DSSTox_GSID_20740; Indometacine [INN-French]; Indometacinum [INN-Latin]; Indometacina [INN-Spanish]; 1-(4-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methylindole-3-acetic acid; Tivorbex; 2-[1-(4-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-indol-3-yl]acetic acid; 2-{1-[(4-chlorophenyl)carbonyl]-5-methoxy-2-methylindol-3-yl}acetic acid; Indocin-SR; Indochron E-R; Indocin (TN); Aconip (TN); Indomethacin (USP); FLAM; NSC-77541; Indocid (pharmaceutical); SR-01000000014; EINECS 200-186-5; Indomethacin & MAP-30; Indomethacin [USAN:USP]; BRN 0497341; Indocollyre; Indonol; Innamit; Inteban; 2-{1-((4-chlorophenyl)carbonyl)-5-methoxy-2-methylindol-3-yl}acetic acid; 4kyk; Indomethacin,(S); Prestwick_597; Indometacin [INN]; Opera_ID_56; Spectrum_000919; Tocris-1708; 1z9h; 1-(p-Chlorbenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methylindol-3-essigsaeure [German]; 1-p-Cloro-benzoil-5-metoxi-2-metilindol-3-acido acetico [Spanish]; Prestwick0_000272; Prestwick1_000272; Prestwick2_000272; Prestwick3_000272; Spectrum2_000970; Spectrum3_000468; Spectrum4_000018; Spectrum5_000868; Lopac-I-7378; Kwas 1-(p-chlorobenzoilo)-2-metylo-5-metoksy-3-indolilooctowy [Polish]; MolMap_000032; UPCMLD-DP023; EC 200-186-5; I 7378; Indometacin (JP17/INN); SCHEMBL9300; Lopac0_000692; Oprea1_686105; BSPBio_000144; BSPBio_001149; BSPBio_002176; KBioGR_000395; KBioGR_000489; KBioSS_000489; KBioSS_001399; 5-22-05-00239 (Beilstein Handbook Reference); MLS001074194; MLS006011845; BIDD:GT0132; DivK1c_000271; SPECTRUM1500350; SPBio_000979; SPBio_002363; BPBio1_000160; GTPL1909; DTXSID9020740; Indomethacin, >=99% (TLC); UPCMLD-DP023:001; BDBM17638; CGIGDMFJXJATDK-UHFFFAOYSA-; HMS500N13; KBio1_000271; KBio2_000489; KBio2_001399; KBio2_003057; KBio2_003967; KBio2_005625; KBio2_006535; KBio3_000897; KBio3_000898; KBio3_001396; 1-(p-Chlorbenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methylindol-3-essigsaeure; Indomethacin - CAS 53-86-1; NINDS_000271; Bio2_000405; Bio2_000885; HMS1362I11; HMS1568H06; HMS1792I11; HMS1920F21; HMS1990I11; HMS2089N19; HMS2091N09; HMS2095H06; HMS2231J10; HMS3262K05; HMS3268A14; HMS3374F07; HMS3403I11; HMS3414N13; HMS3430L03; HMS3649K17; HMS3655O04; HMS3678N11; HMS3712H06; HMS3747K21; HMS3884E08; Pharmakon1600-01500350; ZINC601283; ACT02579; BCP18951; Indomethacin, >=99.0% (TLC); Tox21_113109; Tox21_201791; Tox21_300266; Tox21_500692; AC-532; CCG-40186; NSC757061; s1723; STL257874; AKOS000592893; Tox21_113109_1; AT13679; DB00328; Indometacin 1.0 mg/ml in Acetonitrile; KS-5255; LP00692; MCULE-5636486088; NSC 757061; SDCCGSBI-0050670.P005; IDI1_000271; IDI1_002160; NCGC00015562-01; NCGC00015562-02; NCGC00015562-03; NCGC00015562-04; NCGC00015562-05; NCGC00015562-06; NCGC00015562-07; NCGC00015562-08; NCGC00015562-09; NCGC00015562-10; NCGC00015562-11; NCGC00015562-12; NCGC00015562-13; NCGC00015562-14; NCGC00015562-15; NCGC00015562-16; NCGC00015562-17; NCGC00015562-19; NCGC00015562-20; NCGC00015562-21; NCGC00015562-22; NCGC00015562-24; NCGC00015562-25; NCGC00015562-40; NCGC00024135-02; NCGC00024135-04; NCGC00024135-05; NCGC00024135-06; NCGC00024135-07; NCGC00024135-08; NCGC00024135-09; NCGC00024135-10; NCGC00024135-11; NCGC00024135-12; NCGC00024135-13; NCGC00024135-14; NCGC00024135-15; NCGC00254075-01; NCGC00259340-01; NCGC00261377-01; BI166166; BP-30207; H911; HY-14397; NCI60_041708; SBI-0050670.P004; DB-052413; AB00052022; EU-0100692; FT-0603227; I0655; SW196768-5; Indomethacin, meets USP testing specifications; BIM-0050670.0001; C01926; D00141; J10170; S00108; AB00052022-20; AB00052022-21; AB00052022_23; AB00052022_24; L000959; Q409231; Indomethacin, Antibiotic for Culture Media Use Only; Q-201239; SR-01000000014-2; SR-01000000014-4; SR-01000000014-6; BRD-K57222227-001-06-1; BRD-K57222227-001-18-6; BRD-K57222227-001-27-7; SR-01000000014-10; SR-01000000014-16; Z56784896; 1-p-chlorobenzoyl-2-methyl-5-methoxyindol-3-acetic acid; 1-(p-chlorobenzoyl)-2-methyl-5-methoxy-3-indoleacetic acid; 1-(p-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-3-indoleacetic acid; 1-(p-Chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methylindol-3-acetic acid; 1-(4-chloro-benzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-3-indolyl-acetic acid; 1-(4-Chlorobenzoyl)-2-methyl-5-methoxyindole-3-acetic acid; 1-(p-Chlorobenzoyl)-2-methyl-5-methoxy-3-indole-acetic acid; 1-(p-chlorobenzoyl)-2-methyl-5-methoxy-3-indolylacetic acid; 1-(p-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-3-indol acetic acid; 1-(p-Chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-Indole-3-acetic acid; Indomethacin, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard; N-(p-Chlorobenzoyl)-2-methyl-5-methoxy-3-indolylacetic acid; Indomethacin, United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Reference Standard; .alpha.-(1-(p-Chlorobenzoyl)-2-methyl-5-methoxy-3-indolyl)acetic acid; [1-(4-Chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl]acetic acid #; 1-(4-Chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-1H-indole-3-acetic acid & MAP-30; 1H-Indole-3-acetic acid, 1-(4-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl- (9CI); 2-{1-[(4-chlorophenyl)carbonyl]-5-methoxy-2 methylindol-3-yl}acetic acid; 2-{1-[(4-chlorophenyl)carbonyl]-5-methoxy-2methylindol-3-yl}acetic acid; Indole-3-acetic acid, 1-(p-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl- (8CI); Indomethacin, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
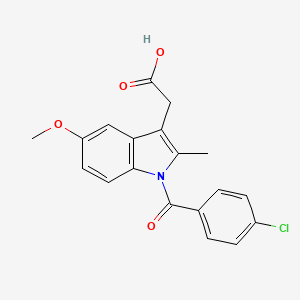
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[1]
|
||||
| Target | Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2 (COX-2) | PGH2_HUMAN | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C19H16ClNO4
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CC1=C(C2=C(N1C(=O)C3=CC=C(C=C3)Cl)C=CC(=C2)OC)CC(=O)O
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C19H16ClNO4/c1-11-15(10-18(22)23)16-9-14(25-2)7-8-17(16)21(11)19(24)12-3-5-13(20)6-4-12/h3-9H,10H2,1-2H3,(H,22,23)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
CGIGDMFJXJATDK-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| VARIDT ID | |||||
| INTEDE ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 (MRP1) | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Function | Inhibition |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | Vitamin E d-alpha-tocopheryl poly(ethylene glycol) 1000 succinate (TPGS) and indomethacin (IDM) can reverse multidrug resistance (MDR) via inhibiting P-glycoprotein (P-gp) and multidrug resistance associated protein 1 (MRP1) respectively, but their drawbacks in physicochemical properties limit their clinical application. | |||
ICD-15: Musculoskeletal/connective-tissue diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Multidrug resistance protein 1 (ABCB1) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Rheumatoid arthritis [ICD-11: FA20.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | MTX is a substrate for eight ABC transporters. In vitro studies demonstrated that RAFLS treated with MTX had higher ABCB1 expression levels than controls, with a positive correlation between ABCB1 expression levels and RA treatment duration. In addition to MTX, other DMARDs (e.g. sulfasalazine, leflunomide, bucillamine, azathioprine), glucocorticoids (e.g. betamethasone, dexamethasone), and NSAIDs (e.g. celecoxib and indomethacin) are also substrates of ABC transporters. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
