Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00249) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Verapamil
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Arpamyl; Calan; Calcan; Cordilox; Dexverapamil; Dilacoran; Drosteakard; Iproveratril; Isoptimo; Isoptin; Isotopin; Vasolan; Veracim; Verapamilo; Verapamilum; Veraptin; Verexamil; Bosoptin (TN); Calan (TN); D-365; Isoptin (TN); Verapamilo [INN-Spanish]; Verapamilum [INN-Latin]; Verelan (TN); CP-16533-1; Covera-HS (TN); Verapamil (USAN/INN); Verapamil [USAN:BAN:INN]; Verapamil [USAN:INN:BAN]; Alpha-((N-Methyl-N-homoveratryl)-gamma-aminopropyl)-3,4-dimethoxyphenylacetonitrile; Alpha-Isopropyl-alpha-((N-methyl-N-homoveratryl)-gamma-aminopropyl)-3,4-dimethoxyphenylacetonitrile; Alpha-(3-((2-(3,4-Dimethoxyphenyl)ethyl)-methylamino)propyl)-3,4-dimethoxy-alpha-(1-methylethyl)benzeneacetonitrile; (+-)-Verapamil; (+/-)-VERAPAMIL; (1)-3-(3,4-Dimethoxyphenyl)-6-((5,6-dimethoxyphenethyl)methylamino)hexane-3-carbonitrile; 2-(3,4-Dimethoxyphenyl)-5-[2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)ethyl-methyl-amino]-2-(1-methylethyl) pentanenitrile; 2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-5-[2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)ethyl-methylamino]-2-propan-2-ylpentanenitrile; 2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-5-{[2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)ethyl](methyl)amino}-2-(propan-2-yl)pentanenitrile; 5-((3,4-Dimethoxyphenethyl)methylamino)-2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-isopropylvaleronitrile; 5-[(3,4-Dimethoxyphenethyl)methylamino]-2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-isopropylvaleronitrile; Verapamil (Na-Ca chanel blocker)
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
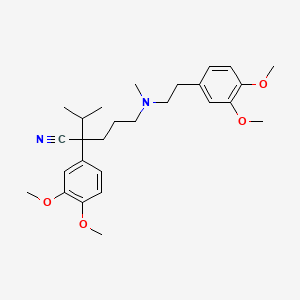
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[2]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Discovered by Cell Line Test for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[1]
|
||||
| Target | Voltage-gated calcium channel alpha Cav3.1 (CACNA1G) | CAC1G_HUMAN | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C27H38N2O4
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CC(C)C(CCCN(C)CCC1=CC(=C(C=C1)OC)OC)(C#N)C2=CC(=C(C=C2)OC)OC
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C27H38N2O4/c1-20(2)27(19-28,22-10-12-24(31-5)26(18-22)33-7)14-8-15-29(3)16-13-21-9-11-23(30-4)25(17-21)32-6/h9-12,17-18,20H,8,13-16H2,1-7H3
|
||||
| InChIKey |
SGTNSNPWRIOYBX-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| VARIDT ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: H19, imprinted maternally expressed transcript (H19) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| MCF-7/AdrVp cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_4Y46 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
RT-PCR; Northern blotting analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Clonogenic assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The mRNA of the H19 gene is overexpressed in MCF-7/AdrVp cells relative toparental MCF-7 cells or drug-sensitive MCF-7/AdrVp revertant cells. H19is an imprinted gene with an important role in fetal differentiation, as well as a postulated function as a tumor suppressor gene. Another p95-over-expressing multidrug-resistant cell line, human lung carcinoma NCI-H1688, also displays high levels of 1119 mRNA. | |||
ICD-08: Nervous system diseases
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: ATP-binding cassette sub-family B5 (ABCB5) | [3] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Cerebrovascular disease [ICD-11: 8B22.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7/DX1 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| Sf9 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0549 | |
| HCMEC/D3 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_U985 | |
| In Vivo Model | Male Sprague-Dawley Rats Brain Capillary Isolation | Mus musculus | ||
| Mechanism Description | In P-gp overexpressing cells and in human brain capillary endothelial hCMEC/D3 cells, the dimer with the shortest tether length (QT2C2) was the most potent inhibitor showing >80-fold better inhibition of P-gp-mediated transport than monomeric QT. QT2C2Me2 increased the accumulation of the P-gp substrate verapamil in rat brain in situ three times more than QT. | |||
ICD-11: Circulatory system diseases
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: ATP-binding cassette sub-family B5 (ABCB5) | [3] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Arrhythmia [ICD-11: BC9Y.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7/DX1 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| Sf9 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0549 | |
| HCMEC/D3 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_U985 | |
| In Vivo Model | Male Sprague-Dawley Rats Brain Capillary Isolation | Mus musculus | ||
| Mechanism Description | In P-gp overexpressing cells and in human brain capillary endothelial hCMEC/D3 cells, the dimer with the shortest tether length (QT2C2) was the most potent inhibitor showing >80-fold better inhibition of P-gp-mediated transport than monomeric QT. QT2C2Me2 increased the accumulation of the P-gp substrate verapamil in rat brain in situ three times more than QT. | |||
ICD-14: Skin diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 (MRP1) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Hypertrophic scar [ICD-11: EE60.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Hypertrophic scar tissue isolates | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blotting assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Fibroblasts derived from hypertrophic scar and normal skin tissues were first compared for their resistance to verapamil and etoposide phosphate. Scar fibroblasts showed stronger resistance to both verapamil and etoposide than normal fibroblasts, also scar fibroblasts expressed more P-glycoprotein and MRP1 than normal fibroblasts. | |||
| Key Molecule: Multidrug resistance protein 1 (ABCB1) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Hypertrophic scar [ICD-11: EE60.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Hypertrophic scar tissue isolates | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blotting assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Fibroblasts derived from hypertrophic scar and normal skin tissues were first compared for their resistance to verapamil and etoposide phosphate. Scar fibroblasts showed stronger resistance to both verapamil and etoposide than normal fibroblasts, also scar fibroblasts expressed more P-glycoprotein and MRP1 than normal fibroblasts. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
