Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00800) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Prochlorperazine
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Prochlorperazine; 58-38-8; Prochlorperazin; Prochlorpromazine; Chlormeprazine; Chlorperazine; Procloperazine; Capazine; Prochlorpemazine; Compazine; Proclorperazine; Meterazin; Meterazine; Stemetil; Tementil; Kronocin; Emelent; Nipodal; Temetid; Prochlorpermazine; Novamin; Proclorperazina; Bayer A 173; Prochlorperazine maleate; Prochloroperazine; Prochlorperazinum; 2-chloro-10-[3-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)propyl]phenothiazine; Vertigon; 2-chloro-10-[3-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)propyl]-10H-phenothiazine; SKF 4657; 2-Chloro-10-(3-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)propyl)phenothiazine; 6140 RP; RP 6140; UNII-YHP6YLT61T; 3-Chloro-10-(3-(1-methyl-4-piperazinyl)propyl)phenothiazine; 10H-Phenothiazine, 2-chloro-10-[3-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)propyl]-; Buccastem; CHLOPERAZINE; 2-Chloro-10-(3-(1-methyl-4-piperazinyl)propyl)-phenothiazine; 3-Chloro-10-(3-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)propyl)phenothiazine; MLS000028600; N-(gamma-(4'-Methylpiperazinyl-1')propyl)-3-chlorophenothiazine; 10H-Phenothiazine, 2-chloro-10-(3-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)propyl)-; Chloro-3 (N-methylpiperazinyl-3 propyl)-10 phenothiazine; Compro; YHP6YLT61T; Prochlorperazine Base; SMR000058705; Prochlorperazine mesylate; CHEBI:8435; 2-chloro-10-(3-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)propyl)-10h-phenothiazine; Compazine Suppositories; Phenothiazine, 2-chloro-10-(3-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)propyl)-; Prochlorperazinum [INN-Latin]; Proclorperazina [INN-Spanish]; Proazine; MLS001148133; Compro (TN); NSC17478; NSC167375; HSDB 3171; CAS-84-02-6; Compazine (*Maleate*); SMR000653454; EINECS 200-379-4; Chloropernazine; Phenothiazine, 2-chloro-10-[3-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)propyl]-; Prochlorperazine (JAN/USP/INN); 2-Chloro-10-(3-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)propyl)-10H-phenothiazine; Chloro-3 (N-methylpiperazinyl-3 propyl)-10 phenothiazine [French]; Prochlorperazine [USP:INN:BAN:JAN]; Eskatrol (Salt/Mix); Spectrum_000840; Opera_ID_244; Prestwick0_000399; Prestwick1_000399; Prestwick2_000399; Prestwick3_000399; Spectrum2_001297; Spectrum3_000881; Spectrum4_000972; Spectrum5_001339; Lopac-P-9178; CHEMBL728; Probes1_000265; Probes2_000307; Lopac0_001034; SCHEMBL18429; BSPBio_000617; BSPBio_002394; KBioGR_001343; KBioGR_002304; KBioSS_001320; KBioSS_002306; cid_91499; MLS006011830; DivK1c_000413; SPBio_001333; SPBio_002538; BPBio1_000679; GTPL7279; DTXSID7023514; BDBM78434; KBio1_000413; KBio2_001320; KBio2_002304; KBio2_003888; KBio2_004872; KBio2_006456; KBio2_007440; KBio3_001762; KBio3_002784; cMAP_000013; NINDS_000413; HMS2231P21; STL371212; ZINC19796018; AKOS003600762; CCG-205112; DB00433; RP-6140; SDCCGSBI-0051005.P005; IDI1_000413; MRF-0000068; NCGC00015856-01; NCGC00015856-02; NCGC00015856-03; NCGC00015856-04; NCGC00015856-05; NCGC00015856-06; NCGC00015856-07; NCGC00015856-16; NCGC00023036-03; NCI60_022783; P77; SBI-0051005.P004; 6140 R.P.; DB-053199; AB00053532; FT-0603243; C07403; C16030; D00493; AB00053532_29; AB00053532_30; 058P388; A831861; L001030; Q2359690; BRD-K19352500-070-02-5; BRD-K19352500-070-05-8; BRD-K19352500-332-03-7; SR-01000000260-11; 2-Chloro-10-(3-(1-methyl-4-piperazinyl)-propyl)-phenothiazine; N-(.gamma.-(4'-Methylpiperazinyl-1')propyl)-3-chlorophenothiazine; Phenothiazine, 2-chloro-10-[3-(1-methyl-4-piperazinyl)propyl]-; 2-Chloro-10-[3-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)propyl]-10H-phenothiazine #; 2-chloranyl-10-[3-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)propyl]phenothiazine;ethane-1,2-disulfonic acid; 2-chloro-10-[3-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)propyl]phenothiazine;ethane-1,2-disulfonic acid; 2-chloro-10-[3-(4-methylpiperazino)propyl]phenothiazine;ethane-1,2-disulfonic acid
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
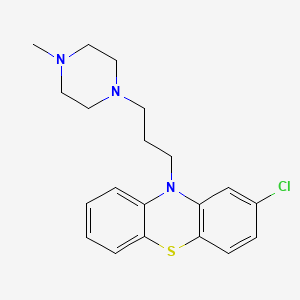
|
||||
| Target | Dopamine D2 receptor (D2R) | DRD2_HUMAN | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C20H24ClN3S
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CN1CCN(CC1)CCCN2C3=CC=CC=C3SC4=C2C=C(C=C4)Cl
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C20H24ClN3S/c1-22-11-13-23(14-12-22)9-4-10-24-17-5-2-3-6-19(17)25-20-8-7-16(21)15-18(20)24/h2-3,5-8,15H,4,9-14H2,1H3
|
||||
| InChIKey |
WIKYUJGCLQQFNW-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| VARIDT ID | |||||
| INTEDE ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Integrin beta-1 (ITGB1) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.02] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Glioblastoma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Blood | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.62E-08 Fold-change: -1.51E-01 Z-score: -5.90E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| In Vitro Model | SHI-1 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2191 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; RNA-sequencing analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Wound healing assay;Transwell assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Prochlorperazine may modulate the expression levels of multidrug resistance proteins (they decreased ABCB1 and increased ABCG2 expression), E-cadherin, alpha-tubulin and integrins, and could impair the migration and invasion of U-87 MG cells. | |||
| Key Molecule: Integrin alpha-3 (ITA3) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.02] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| In Vitro Model | SHI-1 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2191 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; RNA-sequencing analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Wound healing assay;Transwell assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Prochlorperazine may modulate the expression levels of multidrug resistance proteins (they decreased ABCB1 and increased ABCG2 expression), E-cadherin, alpha-tubulin and integrins, and could impair the migration and invasion of U-87 MG cells. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: ATP-binding cassette sub-family G2 (ABCG2) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.02] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Glioblastoma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Nervous tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.18E-01 Fold-change: 2.37E-01 Z-score: 1.69E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| In Vitro Model | SHI-1 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2191 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; RNA-sequencing analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Wound healing assay;Transwell assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Prochlorperazine may modulate the expression levels of multidrug resistance proteins (they decreased ABCB1 and increased ABCG2 expression), E-cadherin, alpha-tubulin and integrins, and could impair the migration and invasion of U-87 MG cells. | |||
| Key Molecule: Multidrug resistance protein 1 (ABCB1) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.02] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Glioblastoma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Nervous tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.79E-03 Fold-change: -3.77E-01 Z-score: -3.50E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| In Vitro Model | SHI-1 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2191 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; RNA-sequencing analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Wound healing assay;Transwell assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Prochlorperazine may modulate the expression levels of multidrug resistance proteins (they decreased ABCB1 and increased ABCG2 expression), E-cadherin, alpha-tubulin and integrins, and could impair the migration and invasion of U-87 MG cells. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
