Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00251) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Clindamycin
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Antirobe; CLDM; CLY; Chlolincocin; Chlorlincocin; Chlorodeoxylincomycin; Chlorolincomycin; Cleocin; ClindaDerm; Clindamicina; Clindamycine; Clindamycinum; Clinimycin; Dalacine; Klimicin; Sobelin; Zindaclin; Cleocin HCl; Cleocin T Gel; Cleocin T Lotion; Cleocin T Topical Solution; Clindamycine [French]; Dalacin C; Dalacin C Flavored Granules; Dalacin C Phosphate; Dalacin T Topical Solution; ResiDerm A; Klindan 300; U 21251; Cleocin (TN); Clindacin (TN); Clindamicina [INN-Spanish]; Clindamycin & Interleukin 12; Clindamycin & VRC3375; Clindamycine [INN-French]; Clindamycinum [INN-Latin]; Dalacin (TN); Evoclin (TN); U-21251; CLINDA & IL-12; Clindamycin (USAN/INN); Clindamycin [USAN:BAN:INN]; U-21,251; 7(S)-Chloro-7-deoxylincomycin; 7-CDL; 7-Chloro-7-deoxylincomycin; 7-Chlorolincomycin; 7-Deoxy-7(S)-chlorolincomycin
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
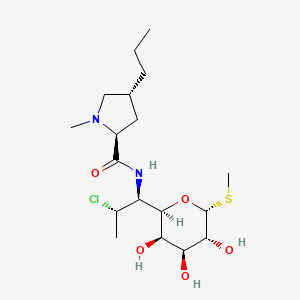
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(16 diseases)
[6]
[7]
[8]
[7]
[9]
[7]
[10]
[7]
[7]
[11]
[7]
[12]
[13]
[7]
[14]
[7]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Validated by in-vivo Model for This Drug
(4 diseases)
[15]
[16]
[17]
[18]
|
||||
| Target | Bacterial 50S ribosomal RNA (Bact 50S rRNA) | NOUNIPROTAC | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C18H33ClN2O5S
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CCC[C@@H]1C[C@H](N(C1)C)C(=O)N[C@@H]([C@@H]2[C@@H]([C@@H]([C@H]([C@H](O2)SC)O)O)O)[C@H](C)Cl
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C18H33ClN2O5S/c1-5-6-10-7-11(21(3)8-10)17(25)20-12(9(2)19)16-14(23)13(22)15(24)18(26-16)27-4/h9-16,18,22-24H,5-8H2,1-4H3,(H,20,25)/t9-,10+,11-,12+,13-,14+,15+,16+,18+/m0/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
KDLRVYVGXIQJDK-AWPVFWJPSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| INTEDE ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: rRNA adenine N-6-methyltransferase ermE (ERME) | [1], [2], [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli AS19 | 562 | ||
| Escherichia coli AS19-RrmA- | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli DH10B | 316385 | |||
| Escherichia coli JC7623 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Methylation of specific nucleotides in rRNA is one of the means by which bacteria achieve resistance to macrolides-lincosamides-streptogramin B (MLSB) and ketolide antibiotics.ErmE dimethylation confers high resistance to all the MLSB and ketolide drugs. | |||
| Key Molecule: Probable dual-specificity RNA methyltransferase RlmN (RLMN ) | [19] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Paenibacillus sp. LC231 | 1120679 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | A clindamycin resistance gene relates to the Rlmk 23S ribosomal RNA methyltransferase COG family.Clindamycin targets the peptidyltransferase centre and inhibits protein synthesis by interfering with transfer RNA binding at the A-site. | |||
| Key Molecule: Ribosomal RNA large subunit methyltransferase Cfr (CFRB) | [20] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | c.2576G>T |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213 | 1280 | ||
| Enterococcus faecium ATCC 29212 | 1352 | |||
| Enterococcus faecium ATCC 35667 | 1352 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Cfr methylates the unreactive C2- and C8-carbon atoms on the A2503 residue located in a functionally critical region of the 23S rRNA component.The methylation at C8 protects the Cfr-producing bacteria from the action of five major classes of antibiotics, namely, phenicols, oxazolidinones, pleuromutilins, macrolides, and streptogramin A compounds (PhLOPSA phenotype). | |||
| Key Molecule: Carboxymethylenebutenolidase (CLCD) | [21] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli AS19 | 562 | ||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The Cfr RNA methyltransferase causes multiple resistances to peptidyl transferase inhibitors by methylation of A2503 23S rRNA.clcD codes the same enzyme. | |||
| Key Molecule: Ribosomal RNA large subunit methyltransferase (CFR ) | [22] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli AS19 | 562 | ||
| Escherichia coli TOP10 | 83333 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Cfr confers resistance to antibiotics binding to the peptidyl transferase center on the ribosome.The primary product of the Cfr-mediated methylation is 8-methyladenosine (m8A), a new natural RNA modification that has so far not been seen at sites other than A2503 in 23S rRNA. | |||
| Key Molecule: 23S rRNA (Adenine(2503)-C(8))-methyltransferase ClbA (CIBA) | [23] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli AS19 | 562 | ||
| Escherichia coli JW2501-1 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The cfr gene encodes the Cfr methyltransferase that methylates a single adenine in the peptidyl transferase region of bacterial ribosomes.Expression of the genes was induced in Escherichia coli, and MICs for selected antibiotics indicate that the cfr-like genes confer resistance to PhLOPSa (phenicol, lincosamide, oxazolidinone, pleuromutilin, and streptogramin A) antibiotics in the same way as the cfr gene.The Cfr-like proteins ClbA, ClbC, and ClbB confer a resistance pattern similar to that of the Cfr methyltransferase. | |||
| Key Molecule: 23S ribosomal RNA methyltransferase Erm36 (ERM36) | [24] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Micrococcus luteus infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Micrococcus luteus MAW843 | 1270 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sequence analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar diffusion test assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Erm(36) was most related (about 52-54% identity) to erythromycin-resistance proteins found in high-G+C Gram-positive bacteria and lead to drug resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: erm(X)cj (Unclear) | [8] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Corynebacterium jeikeium infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Frameshift mutation | Codon 216 frame shift |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032 | 196627 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213 | 1280 | |||
| Corynebacterium diphtheriae isolate | 1717 | |||
| Corynebacterium glutamicum kO8 | 1718 | |||
| Corynebacterium jeikeium isolates | 38289 | |||
| Escherichia coli ATCC 25923 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain XL1-Blue MRF9 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Southern blotting assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Disk diffusion methods assay; agar dilution methods assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Abundant amplificationproducts of slightly less than 400 bp were generated from DNAisolated from the 17 MLSb-resistant strains, whereas no am-plification products were generated with the DNA isolatedfrom the three susceptible strains. The DNA sequences of the amplification products showed 95% identity to the erm(X) gene isolated from a C. xerosis strain,erm(X)cx or ermCX. Thus, MLSb resistance in C. jeikeiumis associated with the presence of an allele, erm(X)cj, of the class Xermgenes. The first 215 amino acids of the predicted polypeptides for strains CJ12 and CJ21 are 93.5 and 98.6% identical to Erm(X)cx, the Erm protein from C. xerosi. The major difference between the two Erm(X)cj polypeptides and the Erm(X)cx polypeptide is a frame shift within codon 216. This results in the Erm(X)cj polypeptides being 31 amino acids longer than Erm(X)cx. | |||
| Key Molecule: ErmR rRNA adenine N6-methyltransferase (ERMR) | [16] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Aeromicrobium erythreum infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Aeromicrobium erythreum strains AR18 | 2041 | ||
| Aeromicrobium erythreum strains AR1807 | 2041 | |||
| Aeromicrobium erythreum strains AR1848 | 2041 | |||
| Aeromicrobium erythreum strains AR1849 | 2041 | |||
| Aeromicrobium erythreum strains AR1850 | 2041 | |||
| Aeromicrobium erythreum strains BD170 | 2041 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Southern blotting assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Disk diffusion assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Using the Ery- strain AR1807 as a recipient for plasmid-directed integrative recombination, the chromosomal ermR gene (encoding 23S rRNA methyltransferase) was disrupted, ermR-disrupted strains AR1848 and AR1849 were highly sensitive to erythromycin and the other macrolide antibiotics. Phenotypic characterizations demonstrated that ermR is the sole determinant of macrolide antibiotic resistance in A. erythreum. AR18, AR1807, and AR1850 (Ery- Ermr) were resistant to clindamycin, erythromycin, spiramycin, and tylosin (some sensitivity totylosin was observed at high concentrations). | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: ABC transporter ATP-binding protein (ABCP) | [25], [26] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T450I |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli TOP10 | 83333 | ||
| Enterococcus faecium HM1070 | 1352 | |||
| Enterococcus faecium UCN80 | 1352 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | ABC systems constitute one of the largest families of proteins, with most of them being involved in import and export, often called ABC transporters.Several of these class 2 ABC systems have been involved in MLS resistance, such as Msr-, Vga-, or Lsa-like proteins.The observed profile of cross-resistance to lincosamides, streptogramins A, and pleuromutilins conferred by Eat(A)v was similar to those conferred by other Lsa-like proteins. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Colibactin polyketide synthase ClbC (CLBC) | [23] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli AS19 | 562 | ||
| Escherichia coli JW2501-1 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The cfr gene encodes the Cfr methyltransferase that methylates a single adenine in the peptidyl transferase region of bacterial ribosomes.Expression of the genes was induced in Escherichia coli, and MICs for selected antibiotics indicate that the cfr-like genes confer resistance to PhLOPSa (phenicol, lincosamide, oxazolidinone, pleuromutilin, and streptogramin A) antibiotics in the same way as the cfr gene.The Cfr-like proteins ClbA, ClbC, and ClbB confer a resistance pattern similar to that of the Cfr methyltransferase. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: rRNA adenine N-6-methyltransferase (ErmB) | [17] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Clostridium difficile infection [ICD-11: 1A04.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| Mechanism Description | The cellular methylation in C. difficile has been proposed to induce resistance to macrolides (erythromycin, ERY), lincosamide (clindamycin) and streptogramin B antibiotic family. These drugs target at a bacterial 50S ribosomal subunit, causing the inhibition of peptide chain growth by blocking the movement of ribosome. ERY ribosomal methylase B (ErmB) is responsible for ribosomal methylation at the specific site of 23S rRNA, resulting in the prevention of antibiotic binding. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: ABC protein lsaC (lsaC-Unclear) | [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Streptococcus agalactiae infection [ICD-11: 1B21.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli TOP10 | 83333 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213 | 1280 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae UCN70 | 1311 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae isolates | 1311 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae BM132 | 1319 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Expression of this novel gene, named lsa(C), in S. agalactiae BM132 after cloning led to an increase in MICs of lincomycin (0.06 to 4 ug/ml), clindamycin (0.03 to 2 ug/ml), dalfopristin (2 to >32 ug/ml), and tiamulin (0.12 to 32 ug/ml), whereas no change in MICs of erythromycin (0.06 ug/ml), azithromycin (0.03 ug/ml), spiramycin (0.25 ug/ml), telithromycin (0.03 ug/ml), and quinupristin (8 ug/ml) was observed. The phenotype was renamed the LS(A)P phenotype on the basis of cross-resistance to lincosamides, streptogramins A, and pleuromutilins. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: 23S ribosomal RNA methyltransferase Erm (ERM39) | [10] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Mycobacterium fortuitum infection [ICD-11: 1B2Z.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | Putative initiation codon GTG>CTG |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Mycobacterium peregrinum ATCC14467 | 43304 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Mueller-Hinton (MH) broth assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The erm genes are a diverse collection of methylases that add one or two methyl groups to the adenine at position 2058 (Escherichia coli numbering) of the 23S rRNA; this modification impairs the binding of macrolides to ribosomes, and thus reduces the inhibitory activity of these agents. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B resistance protein (ERMA) | [12] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Streptococcus pyogenes infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Methylation | Macrolide-binding site on the ribosome |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli AG100A | 562 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR amplification and sequence alignments assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Macrolide resistance commonly occurs due to methylation of the macrolide-binding site on the ribosome by methyltransferases encoded by the erm group of genes, Induction of erm(A) occurs by translational attenuationInduction of erm(A) occurs by translational attenuation. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: ABC protein lsaC (lsaC-Unclear) | [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Streptococcus agalactiae infection [ICD-11: 1B21.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli TOP10 | 83333 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213 | 1280 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae UCN70 | 1311 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae isolates | 1311 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae BM132 | 1319 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Expression of this novel gene, named lsa(C), in S. agalactiae BM132 after cloning led to an increase in MICs of lincomycin (0.06 to 4 ug/ml), clindamycin (0.03 to 2 ug/ml), dalfopristin (2 to >32 ug/ml), and tiamulin (0.12 to 32 ug/ml), whereas no change in MICs of erythromycin (0.06 ug/ml), azithromycin (0.03 ug/ml), spiramycin (0.25 ug/ml), telithromycin (0.03 ug/ml), and quinupristin (8 ug/ml) was observed. The phenotype was renamed the LS(A)P phenotype on the basis of cross-resistance to lincosamides, streptogramins A, and pleuromutilins. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Erm methyltransferase (ERM42) | [18] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pasteurella multocida infection [ICD-11: 1B99.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 | 1322345 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213 | 1280 | |||
| Pasteurella multocida 36950 | 1075089 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The analysis of one representative P. multocida isolate identified an 82 kb integrative and conjugative element (ICE) integrated into the chromosomal DNA. This ICE, designated ICEPmu1, harboured 11 resistance genes, which confer resistance to streptomycin/spectinomycin (aadA25), streptomycin (strA and strB), gentamicin (aadB), kanamycin/neomycin (aphA1), tetracycline [tetR-tet(H)], chloramphenicol/florfenicol (floR), sulphonamides (sul2), tilmicosin/clindamycin [erm(42)] or tilmicosin/tulathromycin [msr(E)-mph(E)]. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: 23S ribosomal RNA methyltransferase Erm34 (ERM34) | [6] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacillus clausii infection [ICD-11: 1C4Y.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Methylation | Ribosomal methylation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Bacillus clausii ATCC 21536 | 79880 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Cloning experiments and gene seqencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | This pattern of resistance generally due to the presence of an erm gene encoding a ribosomal methylase. | |||
| Key Molecule: ErmR rRNA adenine N6-methyltransferase (ERMR) | [15] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacteroides fragilis infection [ICD-11: 1C4Y.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Bacteroides distasonis strains | 823 | ||
| Bacteroides distasonis strains V2002 | 823 | |||
| Bacteroides distasonis strains V2003 | 823 | |||
| Bacteroides distasonis strains V2004 | 823 | |||
| Bacteroides fragilis strain | 817 | |||
| Bacteroides fragilis strain V503 | 817 | |||
| Bacteroides ovatus strains | 28116 | |||
| Bacteroides ovatus strains V2008 | 28116 | |||
| Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron strain | 818 | |||
| Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron strain V2005 | 818 | |||
| Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron strain V2006 | 818 | |||
| Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron strain V2007 | 818 | |||
| Bacteroides uniformis strain | 820 | |||
| Bacteroides uniformis strain V1760 | 820 | |||
| Bacteroides uniformis strain V1761 | 820 | |||
| Bacteroides uniformis strain V1918 | 820 | |||
| Bacteroides uniformis strain V1921 | 820 | |||
| Bacteroides uniformis strain V2000 | 820 | |||
| Bacteroides uniformis strain V2001 | 820 | |||
| Bacteroides uniformis strain V528 | 820 | |||
| Bacteroides uniformis strain V844 | 820 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Southern blotting assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Clindamycin resistance in Bacteroides spp. is usually macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B (MLS) resistance conferred by erm genes which are similar to those seen in gram-positive, facultative anaerobes. Of 13 clinical isolates of the Bacteroides group, all were resistant to tetracycline (>10,ug/ml). | |||
| Key Molecule: ErmR rRNA adenine N6-methyltransferase (ERMR) | [15] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacteroides distasonis infection [ICD-11: 1C4Y.5] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Bacteroides distasonis strains | 823 | ||
| Bacteroides distasonis strains V2002 | 823 | |||
| Bacteroides distasonis strains V2003 | 823 | |||
| Bacteroides distasonis strains V2004 | 823 | |||
| Bacteroides fragilis strain | 817 | |||
| Bacteroides fragilis strain V503 | 817 | |||
| Bacteroides ovatus strains | 28116 | |||
| Bacteroides ovatus strains V2008 | 28116 | |||
| Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron strain | 818 | |||
| Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron strain V2005 | 818 | |||
| Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron strain V2006 | 818 | |||
| Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron strain V2007 | 818 | |||
| Bacteroides uniformis strain | 820 | |||
| Bacteroides uniformis strain V1760 | 820 | |||
| Bacteroides uniformis strain V1761 | 820 | |||
| Bacteroides uniformis strain V1918 | 820 | |||
| Bacteroides uniformis strain V1921 | 820 | |||
| Bacteroides uniformis strain V2000 | 820 | |||
| Bacteroides uniformis strain V2001 | 820 | |||
| Bacteroides uniformis strain V528 | 820 | |||
| Bacteroides uniformis strain V844 | 820 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Southern blotting assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Clindamycin resistance in Bacteroides spp. is usually macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B (MLS) resistance conferred by erm genes which are similar to those seen in gram-positive, facultative anaerobes. Of 13 clinical isolates of the Bacteroides group, all were resistant to tetracycline (>10,ug/ml). | |||
| Key Molecule: ErmR rRNA adenine N6-methyltransferase (ERMR) | [15] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron infection [ICD-11: 1C4Y.10] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Bacteroides distasonis strains | 823 | ||
| Bacteroides distasonis strains V2002 | 823 | |||
| Bacteroides distasonis strains V2003 | 823 | |||
| Bacteroides distasonis strains V2004 | 823 | |||
| Bacteroides fragilis strain | 817 | |||
| Bacteroides fragilis strain V503 | 817 | |||
| Bacteroides ovatus strains | 28116 | |||
| Bacteroides ovatus strains V2008 | 28116 | |||
| Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron strain | 818 | |||
| Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron strain V2005 | 818 | |||
| Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron strain V2006 | 818 | |||
| Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron strain V2007 | 818 | |||
| Bacteroides uniformis strain | 820 | |||
| Bacteroides uniformis strain V1760 | 820 | |||
| Bacteroides uniformis strain V1761 | 820 | |||
| Bacteroides uniformis strain V1918 | 820 | |||
| Bacteroides uniformis strain V1921 | 820 | |||
| Bacteroides uniformis strain V2000 | 820 | |||
| Bacteroides uniformis strain V2001 | 820 | |||
| Bacteroides uniformis strain V528 | 820 | |||
| Bacteroides uniformis strain V844 | 820 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Southern blotting assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Clindamycin resistance in Bacteroides spp. is usually macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B (MLS) resistance conferred by erm genes which are similar to those seen in gram-positive, facultative anaerobes. Of 13 clinical isolates of the Bacteroides group, all were resistant to tetracycline (>10,ug/ml). | |||
| Key Molecule: ErmR rRNA adenine N6-methyltransferase (ERMR) | [15] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacteroides ovatus infection [ICD-11: 1C4Y.8] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Bacteroides distasonis strains | 823 | ||
| Bacteroides distasonis strains V2002 | 823 | |||
| Bacteroides distasonis strains V2003 | 823 | |||
| Bacteroides distasonis strains V2004 | 823 | |||
| Bacteroides fragilis strain | 817 | |||
| Bacteroides fragilis strain V503 | 817 | |||
| Bacteroides ovatus strains | 28116 | |||
| Bacteroides ovatus strains V2008 | 28116 | |||
| Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron strain | 818 | |||
| Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron strain V2005 | 818 | |||
| Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron strain V2006 | 818 | |||
| Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron strain V2007 | 818 | |||
| Bacteroides uniformis strain | 820 | |||
| Bacteroides uniformis strain V1760 | 820 | |||
| Bacteroides uniformis strain V1761 | 820 | |||
| Bacteroides uniformis strain V1918 | 820 | |||
| Bacteroides uniformis strain V1921 | 820 | |||
| Bacteroides uniformis strain V2000 | 820 | |||
| Bacteroides uniformis strain V2001 | 820 | |||
| Bacteroides uniformis strain V528 | 820 | |||
| Bacteroides uniformis strain V844 | 820 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Southern blotting assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Clindamycin resistance in Bacteroides spp. is usually macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B (MLS) resistance conferred by erm genes which are similar to those seen in gram-positive, facultative anaerobes. Of 13 clinical isolates of the Bacteroides group, all were resistant to tetracycline (>10,ug/ml). | |||
ICD-11: Circulatory system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: ABC protein lsaC (lsaC-Unclear) | [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Streptococcus agalactiae infection [ICD-11: 1B21.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli TOP10 | 83333 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213 | 1280 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae UCN70 | 1311 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae isolates | 1311 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae BM132 | 1319 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Expression of this novel gene, named lsa(C), in S. agalactiae BM132 after cloning led to an increase in MICs of lincomycin (0.06 to 4 ug/ml), clindamycin (0.03 to 2 ug/ml), dalfopristin (2 to >32 ug/ml), and tiamulin (0.12 to 32 ug/ml), whereas no change in MICs of erythromycin (0.06 ug/ml), azithromycin (0.03 ug/ml), spiramycin (0.25 ug/ml), telithromycin (0.03 ug/ml), and quinupristin (8 ug/ml) was observed. The phenotype was renamed the LS(A)P phenotype on the basis of cross-resistance to lincosamides, streptogramins A, and pleuromutilins. | |||
ICD-12: Respiratory system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: ABC protein lsaC (lsaC-Unclear) | [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Streptococcus agalactiae infection [ICD-11: 1B21.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli TOP10 | 83333 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213 | 1280 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae UCN70 | 1311 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae isolates | 1311 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae BM132 | 1319 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Expression of this novel gene, named lsa(C), in S. agalactiae BM132 after cloning led to an increase in MICs of lincomycin (0.06 to 4 ug/ml), clindamycin (0.03 to 2 ug/ml), dalfopristin (2 to >32 ug/ml), and tiamulin (0.12 to 32 ug/ml), whereas no change in MICs of erythromycin (0.06 ug/ml), azithromycin (0.03 ug/ml), spiramycin (0.25 ug/ml), telithromycin (0.03 ug/ml), and quinupristin (8 ug/ml) was observed. The phenotype was renamed the LS(A)P phenotype on the basis of cross-resistance to lincosamides, streptogramins A, and pleuromutilins. | |||
ICD-15: Musculoskeletal/connective-tissue diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: ABC protein lsaC (lsaC-Unclear) | [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Streptococcus agalactiae infection [ICD-11: 1B21.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli TOP10 | 83333 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213 | 1280 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae UCN70 | 1311 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae isolates | 1311 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae BM132 | 1319 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Expression of this novel gene, named lsa(C), in S. agalactiae BM132 after cloning led to an increase in MICs of lincomycin (0.06 to 4 ug/ml), clindamycin (0.03 to 2 ug/ml), dalfopristin (2 to >32 ug/ml), and tiamulin (0.12 to 32 ug/ml), whereas no change in MICs of erythromycin (0.06 ug/ml), azithromycin (0.03 ug/ml), spiramycin (0.25 ug/ml), telithromycin (0.03 ug/ml), and quinupristin (8 ug/ml) was observed. The phenotype was renamed the LS(A)P phenotype on the basis of cross-resistance to lincosamides, streptogramins A, and pleuromutilins. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: ABC protein lsaC (lsaC-Unclear) | [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Streptococcus agalactiae inection [ICD-11: FB84.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli TOP10 | 83333 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213 | 1280 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae UCN70 | 1311 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae isolates | 1311 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae BM132 | 1319 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Expression of this novel gene, named lsa(C), in S. agalactiae BM132 after cloning led to an increase in MICs of lincomycin (0.06 to 4 ug/ml), clindamycin (0.03 to 2 ug/ml), dalfopristin (2 to >32 ug/ml), and tiamulin (0.12 to 32 ug/ml), whereas no change in MICs of erythromycin (0.06 ug/ml), azithromycin (0.03 ug/ml), spiramycin (0.25 ug/ml), telithromycin (0.03 ug/ml), and quinupristin (8 ug/ml) was observed. The phenotype was renamed the LS(A)P phenotype on the basis of cross-resistance to lincosamides, streptogramins A, and pleuromutilins. | |||
ICD-16: Genitourinary system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: ABC protein lsaC (lsaC-Unclear) | [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Klebsiella pneumoniae [ICD-11: CA40.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli TOP10 | 83333 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213 | 1280 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae UCN70 | 1311 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae isolates | 1311 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae BM132 | 1319 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Expression of this novel gene, named lsa(C), in S. agalactiae BM132 after cloning led to an increase in MICs of lincomycin (0.06 to 4 ug/ml), clindamycin (0.03 to 2 ug/ml), dalfopristin (2 to >32 ug/ml), and tiamulin (0.12 to 32 ug/ml), whereas no change in MICs of erythromycin (0.06 ug/ml), azithromycin (0.03 ug/ml), spiramycin (0.25 ug/ml), telithromycin (0.03 ug/ml), and quinupristin (8 ug/ml) was observed. The phenotype was renamed the LS(A)P phenotype on the basis of cross-resistance to lincosamides, streptogramins A, and pleuromutilins. | |||
ICD-21: Symptoms/clinical signs/unclassified clinical findings
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: ABC protein lsaC (lsaC-Unclear) | [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Streptococcus agalactiae infection [ICD-11: 1B21.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli TOP10 | 83333 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213 | 1280 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae UCN70 | 1311 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae isolates | 1311 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae BM132 | 1319 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Expression of this novel gene, named lsa(C), in S. agalactiae BM132 after cloning led to an increase in MICs of lincomycin (0.06 to 4 ug/ml), clindamycin (0.03 to 2 ug/ml), dalfopristin (2 to >32 ug/ml), and tiamulin (0.12 to 32 ug/ml), whereas no change in MICs of erythromycin (0.06 ug/ml), azithromycin (0.03 ug/ml), spiramycin (0.25 ug/ml), telithromycin (0.03 ug/ml), and quinupristin (8 ug/ml) was observed. The phenotype was renamed the LS(A)P phenotype on the basis of cross-resistance to lincosamides, streptogramins A, and pleuromutilins. | |||
ICD-22: Injury/poisoning/certain external causes consequences
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Erythromycin resistance protein (ERM38) | [13] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Mycobacterium smegmatis infection [ICD-11: 1B2Z.3] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Mycobacterium smegmatis mc2155 | 246196 | ||
| Mycobacterium smegmatis mc2155/pMIP12 | 246196 | |||
| Mycobacterium smegmatis mc2155/pOMV20 | 246196 | |||
| Mycobacterium smegmatis mc2155/pOMV30 | 246196 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
MALDI mass spectrometry assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Erm (38) is a specific dimethyltransferase. The strain obtained drug resistance by adding two methyl groups to A2058 in Mycobacterium 23SrRNA. | |||
| Key Molecule: Erythromycin resistance protein (ERM38) | [13] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Mycobacterium smegmatis infection [ICD-11: 1B2Z.3] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Mycobacterium smegmatis mc2155 | 246196 | ||
| Mycobacterium smegmatis mc2155/pMIP12 | 246196 | |||
| Mycobacterium smegmatis mc2155/pOMV20 | 246196 | |||
| Mycobacterium smegmatis mc2155/pOMV30 | 246196 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
MALDI mass spectrometry assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Erm (38) is a specific dimethyltransferase. The strain obtained drug resistance by adding two methyl groups to A2058 in Mycobacterium 23SrRNA. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
