Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00235) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Ceftazidime
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Ceftazidima; Ceftazidimum; Ceptaz; Fortaz; Ceftazidime Sodium In Plastic Container; Ceftazidime anhydrous; Ceftazidime pentahydrate; Fortaz In Plastic Container; SN 401; CEFTAZIDIME (ARGININE FORMULATION); Ceftazidima [INN-Spanish]; Ceftazidime (INN); Ceftazidime (TN); Ceftazidimum [INN-Latin]; Cefzim (TN); Ceptaz (TN); Fortaz (TN); Fortum (TN); (6R,7R)-7-({(2Z)-2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-2-[(1-carboxy-1-methylethoxy)imino]acetyl}amino)-8-oxo-3-(pyridinium-1-ylmethyl)-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylate; (6R,7R)-7-[[(2E)-2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-2-(1-hydroxy-2-methyl-1-oxopropan-2-yl)oxyiminoacetyl]amino]-8-oxo-3-(pyridin-1-ium-1-ylmethyl)-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylate; (6R,7R)-7-[[(2Z)-2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-2-(1-hydroxy-2-methyl-1-oxopropan-2-yl)oxyiminoacetyl]amino]-8-oxo-3-(pyridin-1-ium-1-ylmethyl)-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylate; (6R,7R)-7-[[2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-2-(1-hydroxy-2-methyl-1-oxopropan-2-yl)oxyiminoacetyl]amino]-8-oxo-3-(pyridin-1-ium-1-ylmethyl)-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylate; (6R,7R)-7-{[(2Z)-2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-2-{[(2-carboxypropan-2-yl)oxy]imino}acetyl]amino}-8-oxo-3-(pyridinium-1-ylmethyl)-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylate; 7-[[2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-2-(1-hydroxy-2-methyl-1-oxopropan-2-yl)oxyiminoacetyl]amino]-8-oxo-3-(pyridin-1-ium-1-ylmethyl)-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylate; 7beta-{[(2Z)-2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-2-{[(2-carboxypropan-2-yl)oxy]imino}acetyl]amino}-3-(pyridinium-1-ylmethyl)-3,4-didehydrocepham-4-carboxylate
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
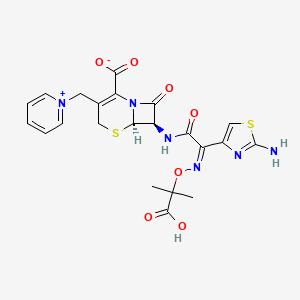
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(9 diseases)
[5]
[5]
[6]
[7]
[8]
[9]
[10]
|
||||
| Target | Bacterial Penicillin binding protein (Bact PBP) | NOUNIPROTAC | [2] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C22H22N6O7S2
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CC(C)(C(=O)O)O/N=C(/C1=CSC(=N1)N)\\C(=O)N[C@H]2[C@@H]3N(C2=O)C(=C(CS3)C[N+]4=CC=CC=C4)C(=O)[O-]
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C22H22N6O7S2/c1-22(2,20(33)34)35-26-13(12-10-37-21(23)24-12)16(29)25-14-17(30)28-15(19(31)32)11(9-36-18(14)28)8-27-6-4-3-5-7-27/h3-7,10,14,18H,8-9H2,1-2H3,(H4-,23,24,25,29,31,32,33,34)/b26-13-/t14-,18-/m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
ORFOPKXBNMVMKC-DWVKKRMSSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Beta-lactamase (BLA) | [3], [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Anaerobic Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1A09] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli HB101 | 634468 | ||
| Escherichia coli JM109 | 562 | |||
| Acidaminococcus fermentans RYC-MR95 | 905 | |||
| Acidaminococcus fermentans RYC4093 | 905 | |||
| Acidaminococcus fermentans RYC4356 | 905 | |||
| Escherichia coli RYC1000 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay; broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | A. intestini is the first Gram-negative coccus with demonstrated resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics. The reference genome of the A. intestini strain RyC-MR95, which was isolated from a perianal abscess of a European male diabetic patient, contains the aci1 gene, which encodes the ACI-1 class A beta-lactamase that confers resistance to penicillins and extended-spectrum cephalosporins. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: TMB-2 metallo-beta-lactamase (BTMB2) | [11] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Acinetobacter genomospecies 14BJ MRY12-226 | 48296 | ||
| Acinetobacter pittii. MRY12-142 | 1255681 | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Etest assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Tripoli metallo-Beta-lactamase 2 (TMB-2), a variant of blaTMB-1 can inactivate the Beta-lactams. | |||
| Key Molecule: Metallo beta lactamase (TMB1) | [12] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli TOP10 | 83333 | ||
| Achromobacter xylosoxidans AES301 | 85698 | |||
| Escherichia coli J53 | 1144303 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Etest assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | These enzymes very efficiently hydrolyze all Beta-lactams, including carbapenems (with the exception of aztreonam), and the Beta-lactamase genes most often are located on transferable genetic platforms, namely, either ISCR elements or class 1 integrons sometimes embedded in Tn21- or Tn402-like transposons.A novel MBL, TMB-1 (for Tripoli metallo-Beta-lactamase) can inactivate the antibiotics. | |||
| Key Molecule: Beta-lactamase (BLA) | [13] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V88L+p.M154L |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli TOP10 | 83333 | ||
| Escherichia coli ST648 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Etest assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | NDM-5 differed from existing enzymes due to substitutions at positions 88 (Val - Leu) and 154 (Met - Leu) and reduced the susceptibility of Escherichia coli TOP10 transformants to expanded-spectrum cephalosporins and carbapenems when expressed under its native promoter. | |||
| Key Molecule: Beta-lactamase (BLA) | [14] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V231S |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli DH10B | 316385 | ||
| Escherichia coli VA1171/10 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Quadruple disc test assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Molecular methods revealed a novel, plasmid-localized variant of CMY-2 with a substitution of valine 231 for serine (V231S), which was designated CMY-42. Like the CMY-2-like AmpC beta-lactamase CMY-30, carrying the substitution V231G, CMY-42 displayed increased activity toward expanded spectrum cephalosporins. | |||
| Key Molecule: CATB10-Ib variant (CATB10) | [15] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Pseudomonas aeruginosa TS-103 | 287 | ||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa TS-832035 | 287 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | P. aeruginosa TS-832035 produces a carbapenemase, coded by a blaVIM-1 determinant carried by the chromosomal class 1 integron In70.2 (containing also the aacA4, aphA15, and aadA1 genes in its cassette array),which induce the resistance to carbapenems. | |||
| Key Molecule: Beta-lactamase (BLA) | [16], [17], [18] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V84I+p.A184V |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli JM109 | 562 | ||
| Mechanism Description | The TEM Beta-lactamases are among the best-studied antibiotic resistance enzymes around.TEM-1, the first TEM allele identified, was isolated from penicillin-resistant bacteria in 1963. | |||
| Key Molecule: Beta-lactamase (BLA) | [17], [19], [20] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D240G |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli DH10B | 316385 | ||
| Citrobacter freundii 2526/96 | 546 | |||
| Escherichia coli isolates | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | We have reported recently the DNA sequence of another Beta-lactamase, CTX- M-15, from Indian enterobacterial isolates that were resistant to both cefotaxime and ceftazidime.CTX-M-15 has a single amino acid change [Asp-240-Gly (Ambler numbering)]7 compared with CTX-M-3. | |||
| Key Molecule: Metallo-beta-lactamase (VIM1) | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Achromobacter xylosoxydans infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli | 668369 | ||
| Achromobacter xylosoxydans subsp. denitrificans AX-22 | 85698 | |||
| Escherichia coli MkD-135 | 562 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa 10145/3 | 287 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA extraction and Sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Macrodilution broth method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | A. xylosoxydans AX22 exhibited broad-spectrum resistance to Beta-lactams and aminoglycosides. The Beta-lactam resistance pattern (including piperacillin, ceftazidime, and carbapenem resistance) was unusual for this species, and the high-level carbapenem resistance suggested the production of an acquired carbapenemase. In fact, carbapenemase activity was detected in a crude extract of AX22 (specific activity, 184 +/- 12 U/mg of protein), and this activity was reduced (>80%) after incubation of the crude extract with 2 mM EDTA, suggesting the presence of a metallo-Beta-lactamase determinant. | |||
| Key Molecule: Beta-lactamase (BLA) | [17], [21] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli strain DH5a | 668369 | ||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strain HEL-1 | 573 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The phenotype of Klebsiella pneumoniae HEL-1 indicates a plasmidic cephamycinase gene (blaCMY-2),which is responsible for cephamycin resistance. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Pyruvate decarboxylase 5 (PDC5) | [8], [17] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R79Q+p.T105A |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli TOP10 | 83333 | ||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 | 208964 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa 12B | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa kG2505 | 287 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay; Etest method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Reduced susceptibility to imipenem, ceftazidime, and cefepime was observed only with recombinant P. aeruginosa strains expressing an AmpC Beta-lactamase that had an alanine residue at position 105.Recently, several ESACs have been described from Escherichia coli contributing to reduced susceptibility to imipenem. | |||
| Key Molecule: Pyruvate decarboxylase 3 (PDC3) | [8], [17] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T97A |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates | 287 | ||
| Escherichia coli JM109 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay; Etest method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Reduced susceptibility to imipenem, ceftazidime, and cefepime was observed only with recombinant P. aeruginosa strains expressing an AmpC Beta-lactamase that had an alanine residue at position 105.Recently, several ESACs have been described from Escherichia coli contributing to reduced susceptibility to imipenem. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Beta-lactamase (BLA) | [22] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Escherichia coli infection [ICD-11: 1A03.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Acquired |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli JM109 | 562 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR and molecular characterization assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Disk diffusion method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | CTX-M-55 is a novel ceftazidime-resistant CTX-M extended-spectrum Beta-lactamase, which reduced susceptibility. | |||
| Key Molecule: Metallo-beta-lactamase (VIM1) | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Escherichia coli infection [ICD-11: 1A03.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Acquired |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli | 668369 | ||
| Achromobacter xylosoxydans subsp. denitrificans AX-22 | 85698 | |||
| Escherichia coli MkD-135 | 562 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa 10145/3 | 287 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA extraction and Sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Macrodilution broth method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Electroporation of Escherichia coli DH5alpha with the purified plasmid preparation yielded ampicillin-resistant transformants which contained a plasmid apparently identical to pAX22 (data not shown). DH5alpha(pAX22) produced carbapenemase activity (specific activity of crude extract, 202 +/- 14 U/mg of protein) and, compared to DH5alpha, exhibited a decreased susceptibility to several Beta-lactams. | |||
| Key Molecule: Beta-lactamase (BLA) | [9] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Escherichia coli infection [ICD-11: 1A03.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Enterobacter cloacae strains ENLA-1 | 550 | ||
| Escherichia coli strain ECAA-1 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain ECLA-1 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain ECLA-2 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain ECLA-4 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain ECZK-1 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain ECZP-1 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain ECZU-1 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain HK225f | 562 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPAA-1 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPBE-2 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPGE-1 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPGE-2 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-1 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-10 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-2 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-3 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-4 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-5 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-6 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-7 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-8 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-9 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-1 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-10 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-11 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-12 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-13 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-4 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-6 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-7 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-8 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-9 | 573 | |||
| Salmonella enterica serotype wien strain SWLA-1 | 149384 | |||
| Salmonella enterica serotype wien strain SWLA-2 | 149384 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Hybridization experiments assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Of 60 strains with reduced susceptibility to expanded-spectrum cephalosporins which had been collected, 34 (24Klebsiella pneumoniae, 7Escherichia coli, 1Enterobacter cloacae, and 2Salmonella entericaserotypewien) hybridized with the intragenic blaSHVprobe. TheblaSHVgenes were amplified by PCR, and the presence ofblaSHV-ESBLwas established in 29 strains by restriction enzyme digests of the resulting 1,018-bp amplimers as described elsewhere. These results were confirmed by the nucleotide sequencing of all 34 amplimers. Five strains contained SHV non-ESBL enzymes. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Beta-lactamase (BLA) | [9] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Salmonella enterica infection [ICD-11: 1A09.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Enterobacter cloacae strains ENLA-1 | 550 | ||
| Escherichia coli strain ECAA-1 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain ECLA-1 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain ECLA-2 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain ECLA-4 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain ECZK-1 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain ECZP-1 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain ECZU-1 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain HK225f | 562 | |||
| Salmonella enterica serotype wien strain SWLA-1 | 149384 | |||
| Salmonella enterica serotype wien strain SWLA-2 | 149384 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPAA-1 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPBE-2 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPGE-1 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPGE-2 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPLA-1 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPLA-10 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPLA-2 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPLA-3 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPLA-4 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPLA-5 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPLA-6 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPLA-7 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPLA-8 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPLA-9 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPZU-1 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPZU-10 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPZU-11 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPZU-12 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPZU-13 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPZU-4 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPZU-6 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPZU-7 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPZU-8 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPZU-9 | 573 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Hybridization experiments assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Of 60 strains with reduced susceptibility to expanded-spectrum cephalosporins which had been collected, 34 (24Klebsiella pneumoniae, 7Escherichia coli, 1Enterobacter cloacae, and 2Salmonella entericaserotypewien) hybridized with the intragenic blaSHVprobe. TheblaSHVgenes were amplified by PCR, and the presence ofblaSHV-ESBLwas established in 29 strains by restriction enzyme digests of the resulting 1,018-bp amplimers as described elsewhere. These results were confirmed by the nucleotide sequencing of all 34 amplimers. Five strains contained SHV non-ESBL enzymes. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Beta-lactamase (BLA) | [8] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G27D+p.A97V+p.T105A+p.V205L |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 | 208964 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR amplification and sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The mutations compared to PDC-1 reduced susceptibility. | |||
| Key Molecule: Beta-lactamase (BLA) | [8] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T105A |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Pseudomonas aeruginosa 12B | 287 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR amplification and sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The mutations compared to PDC-1 reduced susceptibility. | |||
| Key Molecule: Beta-lactamase (BLA) | [8] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T105A+p.K108E |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Pseudomonas aeruginosa kG2505 | 287 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR amplification and sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The mutations compared to PDC-1 reduced susceptibility. | |||
| Key Molecule: Beta-lactamase (BLA) | [8] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R79Q+p.T105A |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates | 287 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR amplification and sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The mutations compared to PDC-1 reduced susceptibility. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Beta-lactamase (BLA) | [1], [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gram-negative bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1B74-1G40] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli | 668369 | ||
| Acinetobacter johnsonii LIM75 | 40214 | |||
| Aeromonas allosaccharophila LIM82 | 656 | |||
| Citrobacter freundii LIM86 | 546 | |||
| Escherichia coli MFDpir | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay; broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | All known class 3 integrons harbour gene cassettes encoding resistance to Beta-lactams (blaIMP, blaGES, blaBEL, blaOXA-256) and aminoglycosides [aac(6')-Ib]. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: CAM-1 carbapenemase (CAM1) | [6] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pseudomonas infection [ICD-11: 1F45.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli TOP10 | 83333 | ||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa N17-01167 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa N17-01173 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa N17-02436 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa N17-02437 | 287 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Vitek 2 assay; Etest assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | A novel class B Beta-lactamase gene, blaCAM-1, exhibited resistance to imipenem, meropenem, doripenem, cefotaxime, ceftazidime, cefoxitin, piperacillin/tazobactam, ceftazidime/avibactam and ceftolozane/tazobactam. | |||
ICD-12: Respiratory system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Beta-lactamase (BLA) | [22] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Klebsiella pneumoniae [ICD-11: CA40.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Acquired |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates | 573 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR and molecular characterization assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Disk diffusion method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | CTX-M-55 is a novel ceftazidime-resistant CTX-M extended-spectrum Beta-lactamase, which reduced susceptibility. | |||
| Key Molecule: Beta-lactamase (BLA) | [9] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Klebsiella pneumoniae infection [ICD-11: CA40.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Enterobacter cloacae strains ENLA-1 | 550 | ||
| Escherichia coli strain ECAA-1 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain ECLA-1 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain ECLA-2 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain ECLA-4 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain ECZK-1 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain ECZP-1 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain ECZU-1 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain HK225f | 562 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPAA-1 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPBE-2 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPGE-1 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPGE-2 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-1 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-10 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-2 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-3 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-4 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-5 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-6 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-7 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-8 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-9 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-1 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-10 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-11 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-12 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-13 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-4 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-6 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-7 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-8 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-9 | 573 | |||
| Salmonella enterica serotype wien strain SWLA-1 | 149384 | |||
| Salmonella enterica serotype wien strain SWLA-2 | 149384 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Hybridization experiments assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Of 60 strains with reduced susceptibility to expanded-spectrum cephalosporins which had been collected, 34 (24Klebsiella pneumoniae, 7Escherichia coli, 1Enterobacter cloacae, and 2Salmonella entericaserotypewien) hybridized with the intragenic blaSHVprobe. TheblaSHVgenes were amplified by PCR, and the presence ofblaSHV-ESBLwas established in 29 strains by restriction enzyme digests of the resulting 1,018-bp amplimers as described elsewhere. These results were confirmed by the nucleotide sequencing of all 34 amplimers. Five strains contained SHV non-ESBL enzymes. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Bcr/CflA family efflux transporter (BCML) | [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Klebsiella pneumoniae infection [ICD-11: CA40.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli DH10B | 316385 | ||
| Escherichia coli strain NCTC 50192 | 562 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strain ORI-1 | 573 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR and hybridization experiments assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution technique assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Klebsiella pneumoniae ORI-1 strain harbored a ca. 140-kb nontransferable plasmid, pTk1, that conferred an extended-spectrum cephalosporin resistance profile antagonized by the addition of clavulanic acid, tazobactam, or imipenem. The gene for GES-1 (Guiana extended-spectrum beta-lactamase) was cloned, and its protein was expressed in Escherichia coli DH10B, where this pI-5. 8 beta-lactamase of a ca. 31-kDa molecular mass conferred resistance to oxyimino cephalosporins (mostly to ceftazidime). GES-1 is weakly related to the other plasmid-located Ambler class A extended-spectrum beta-lactamases (ESBLs). | |||
| Key Molecule: Bcr/CflA family efflux transporter (BCML) | [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Klebsiella pneumoniae infection [ICD-11: CA40.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Acquired |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli DH10B | 316385 | ||
| Escherichia coli strain NCTC 50192 | 562 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strain ORI-1 | 573 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR and hybridization experiments assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution technique assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Beta-Lactam MICs for k. pneumoniae ORI-1 and Escherichia coli DH10B harboring either the natural plasmid pTk1 or the recombinant plasmid pC1 were somewhat similar and might indicate the presence of an ESBL. In all cases, the ceftazidime MICs were higher than those of cefotaxime and aztreonam. Beta-Lactam MICs were always lowered by the addition of clavulanic acid or tazobactam, less so by sulbactam, and uncommonly by imipenem. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Bcr/CflA family efflux transporter (BCML) | [7] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Klebsiella pneumoniae infection [ICD-11: CA40.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Antagonism |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli DH10B | 316385 | ||
| Escherichia coli strain NCTC 50192 | 562 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strain ORI-1 | 573 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR and hybridization experiments assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution technique assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Inhibition studies, as measured by IC50 values with benzylpenicillin as the substrate, showed that GES-1 was inhibited by clavulanic acid (5 uM) and tazobactam (2.5 uM) and strongly inhibited by imipenem (0.1 uM). Beta-Lactam MICs were always lowered by the addition of clavulanic acid or tazobactam, less so by sulbactam, and uncommonly by imipenem. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
