Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00142) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Trimethoprim
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Abaprim; Alprim; Anitrim; Antrima; Antrimox; Bacdan; Bacidal; Bacide; Bacin; Bacta; Bacterial; Bacticel; Bactin; Bactoprim; Bactramin; Bencole; Bethaprim; Biosulten; Briscotrim; Chemotrin; Cidal; Colizole; Conprim; Cotrimel; Deprim; Duocide; Esbesul; Espectrin; Euctrim; Exbesul; Fermagex; Fortrim; Futin; Idotrim; Ikaprim; Instalac; Kombinax; Lagatrim; Lastrim; Methoprim; Metoprim; Monoprim; Monotrim; Monotrimin; Novotrimel; Omstat; Oraprim; Pancidim; Polytrim; Priloprim; Primosept; Primsol; Proloprim; Protrin; Purbal; Resprim; Roubac; Roubal; Salvatrim; Setprin; Sinotrim; Stopan; Streptoplus; Sugaprim; Sulfamar; Sulfamethoprim; Sulfoxaprim; Sulmeprim; Sulthrim; Sultrex; Syraprim; Tiempe; Toprim; Trimanyl; Trimethioprim; Trimethoprime; Trimethoprimum; Trimethopriom; Trimetoprim; Trimetoprima; Trimexazole; Trimexol; Trimezol; Trimogal; Trimono; Trimopan; Trimpex; Triprim; Trisul; Trisulcom; Trisulfam; Trisural; Uretrim; Urobactrim; Utetrin; Velaten; Wellcoprim; Wellcoprin; Xeroprim; Zamboprim; Bacterial [Antibiotic]; Colizole DS; Component of Bactrim; Component of Septra; Lagatrim Forte; ResprimForte; Septrin DS; Septrin Forte; Septrin S; Trimetoprim [DCIT]; Trimetoprim [Polish]; BW 5672; KUC103659N; NIH 204; T 7883; Trimpex 200; WR 5949; Alcorim-F; Apo-Sulfatrim; BW 56-72; Co-Trimoxizole; Monotrim (TN); NIH 204 (VAN); Proloprim (TN); Smz-Tmp; Sulfamethoxazole & Trimethoprim; TCMDC-125538; Tmp-Ratiopharm; Trimeth/Sulfa; Trimethopim(TMP); Trimethoprim & VRC3375; Trimethoprime [INN-French]; Trimethoprimum [INN-Latin]; Trimetoprima [INN-Spanish]; Trimez-IFSA; Trimpex (TN); Triprim (TN); U-Prin; Uro-D S; BW-56-72; KSC-4-158; AZT + TMP/SMX (mixture) combination; Trimethoprim (JAN/USP/INN); Trimethoprim [USAN:BAN:INN:JAN]
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
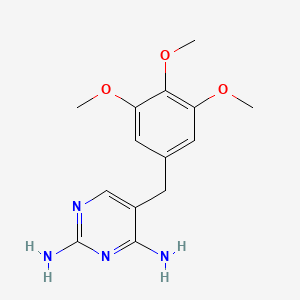
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(11 diseases)
[1]
[2]
[3]
[1]
[1]
[4]
[5]
[1]
[1]
[1]
[6]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Validated by in-vivo Model for This Drug
(2 diseases)
[7]
[7]
|
||||
| Target | Dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) | DYR_HUMAN | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C14H18N4O3
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
COC1=CC(=CC(=C1OC)OC)CC2=CN=C(N=C2N)N
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C14H18N4O3/c1-19-10-5-8(6-11(20-2)12(10)21-3)4-9-7-17-14(16)18-13(9)15/h5-7H,4H2,1-3H3,(H4,15,16,17,18)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
IEDVJHCEMCRBQM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| VARIDT ID | |||||
| INTEDE ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) | [8] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Vibrio cholerae infection [ICD-11: 1A00.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Vibrio cholerae O62 strain AS438 | 666 | ||
| Vibrio cholerae PG149a | 666 | |||
| Vibrio cholerae PG224 | 666 | |||
| Vibrio cholerae PG262(b) | 666 | |||
| Vibrio cholerae PG9 | 666 | |||
| Vibrio cholerae PG95 | 666 | |||
| Vibrio cholerae PL1 | 666 | |||
| Vibrio cholerae PL61 | 666 | |||
| Vibrio cholerae PL78/6 | 666 | |||
| Vibrio cholerae PL91 | 666 | |||
| Vibrio cholerae PG92 | 666 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR and DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Commercial antimicrobial discs assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The expression of dfrA1 lead to drug resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: Dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) | [8] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Vibrio cholerae infection [ICD-11: 1A00.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Vibrio cholerae PG153/1 | 666 | ||
| Vibrio cholerae PG170 | 666 | |||
| Vibrio cholerae PL96 | 666 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR and DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Commercial antimicrobial discs assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The expression of dfrA15 lead to drug resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: Dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Vibrio cholerae infection [ICD-11: 1A00.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli DH5alpha | 668369 | ||
| Escherichia coli k-12 strain TOP10 | 83333 | |||
| Vibrio cholerae O1 C10488 | 127906 | |||
| Vibrio cholerae O1 strain CO943 | 127906 | |||
| Vibrio cholerae O139 1811/98 | 45888 | |||
| Vibrio cholerae O139 2055 | 45888 | |||
| Vibrio cholerae O139 AS207 | 45888 | |||
| Vibrio cholerae O139 E712 | 45888 | |||
| Vibrio cholerae O139 HkO139-SXTS | 45888 | |||
| Vibrio cholerae O139 strain MO10 | 345072 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sequencing assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Many recent Asian clinical Vibrio cholerae E1 Tor O1 and O139 isolates are resistant to the antibiotics sulfamethoxazole (Su), trimethoprim (Tm), chloramphenicol (Cm), and streptomycin (Sm). The corresponding resistance genes are located on large conjugative elements (SXT constins) that are integrated into prfC on the V. cholerae chromosome. The DNA sequences of the antibiotic resistance genes in the SXT constin in MO10, an O139 isolate. In SXT(MO10), these genes are clustered within a composite transposon-like structure found near the element's 5' end. The genes conferring resistance to Cm (floR), Su (sulII), and Sm (strA and strB) correspond to previously described genes, whereas the gene conferring resistance to Tm, designated dfr18, is novel. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Erythromycin esterase (EREA2) | [8] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Vibrio cholerae infection [ICD-11: 1A00.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Vibrio cholerae PG153/1 | 666 | ||
| Vibrio cholerae PG170 | 666 | |||
| Vibrio cholerae PL96 | 666 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR and DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Commercial antimicrobial discs assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The expression of dfrA5, ereA2 lead to drug resistance. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: AAC(6')-Ib family aminoglycoside 6'-N-acetyltransferase (AAC6IB) | [8] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Vibrio cholerae infection [ICD-11: 1A00.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Vibrio cholerae PL107b | 666 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR and DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Commercial antimicrobial discs assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The expression of aac(6')-Ib lead to drug resistance. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside (3'') (9) adenylyltransferase (AADA) | [8] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Vibrio cholerae infection [ICD-11: 1A00.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Vibrio cholerae O39 strain AS634 | 666 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR and DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Commercial antimicrobial discs assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The expression of aadA1-S lead to drug resistance. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Dihydrofolate reductase type 6 (DFRA6) | [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Proteus mirabilis infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli strain JM101 | 83333 | ||
| Escherichia coli strain k12 JM103 | 83333 | |||
| Proteus mirabilis strain J120 | 584 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Chain termination method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | High-level resistance to trimethoprim (Tp) (MIC > 1000 mg/L) is mediated by dihydrofolate reductases (DHFRs) which are resistant to the drug, The gene encoding the type VI DHFR was isolated from P. mirabilis strain J120 (pUk672). | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Escherichia coli infection [ICD-11: 1A03.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli Co227 | 562 | ||
| Escherichia coli Co228 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli Co232 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli Co354 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR; PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis; Sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Multiple-antibiotic-resistant phenotype is associated with gene mutation and mar locus regulation. | |||
| Key Molecule: Dihydrofolate reductase type 6 (DFRA6) | [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Escherichia coli infection [ICD-11: 1A03.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Acquired |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli strain JM101 | 83333 | ||
| Escherichia coli strain k12 JM103 | 83333 | |||
| Proteus mirabilis strain J120 | 584 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Chain termination method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | High-level resistance to trimethoprim (Tp) (MIC > 1000 mg/L) is mediated by dihydrofolate reductases (DHFRs) which are resistant to the drug, The gene encoding the type VI DHFR was isolated from P. mirabilis strain J120 (pUk672). The hybrid plasmids were transformed into competent Escherichia coli kl2 JM103 and clones containing the DHFR gene were selected on a medium containing trimethoprim lactate (Wellcome) 100 mg/L, ampicillin 100 mg/L, isopropyl-Beta-D-galactoside and 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-Beta-D-gal-actopyranoside (X-gal). | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Catalase isozyme A/Tetracycline efflux MFS transporter/Dihydropteroate synthase (CATA1/TETB/SUL) | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Salmonella enterica infection [ICD-11: 1A09.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Salmonella agona 231 | 58095 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR screening assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Disc diffusion assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The multiresistance plasmid from S. Agona strain 231 carried the chloramphenicol resistance gene catA1 coding for a type A chloramphenicol acetyltransferase and the resistance gene tet(B) coding for a tetracycline/minocycline exporter. This plasmid also harboured the streptomycin resistance gene strA coding for an aminoglycoside phosphotransferase and the sulphonamide resistance gene sul1 which represents part of the 3' conserved segment of class 1 integrons. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Lincomycin resistance efflux pump (LMRS) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Superficial skin infection by Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B21.3] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli kAM32 | 562 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus OM505 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | LmrS is a multidrug efflux pump of the major facilitator superfamily from staphylococcus aureus. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Lincomycin resistance efflux pump (LMRS) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli kAM32 | 562 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus OM505 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | LmrS is a multidrug efflux pump of the major facilitator superfamily from staphylococcus aureus. | |||
ICD-11: Circulatory system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Lincomycin resistance efflux pump (LMRS) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli kAM32 | 562 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus OM505 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | LmrS is a multidrug efflux pump of the major facilitator superfamily from staphylococcus aureus. | |||
ICD-12: Respiratory system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Multidrug efflux SMR transporter (ABES) | [9] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acinetobacter baumannii infection [ICD-11: CA40.4] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli kAM32 | 562 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Fluorometric efflux assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth dilution assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The abeS gene product conferred resistance to various antimicrobial compounds through an efflux mechanism. | |||
| Key Molecule: MATE family efflux transporter (ABEM) | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acinetobacter baumannii infection [ICD-11: CA40.4] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli kAM32 | 562 | ||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | AbeM was found to be an H+-coupled multidrug efflux pump and a unique member of the MATE family which lead to drug resistance. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Lincomycin resistance efflux pump (LMRS) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli kAM32 | 562 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus OM505 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | LmrS is a multidrug efflux pump of the major facilitator superfamily from staphylococcus aureus. | |||
ICD-16: Genitourinary system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) | [6] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Urinary tract infection [ICD-11: GC08.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli 1387 | 562 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR amplification and sequence alignments assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The most common resistant mechanism involves expressing trimethoprim insensitive variants of DHFR within mobile genetic elements, such as plasmids, transposons and integrons. | |||
ICD-21: Symptoms/clinical signs/unclassified clinical findings
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Lincomycin resistance efflux pump (LMRS) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli kAM32 | 562 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus OM505 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | LmrS is a multidrug efflux pump of the major facilitator superfamily from staphylococcus aureus. | |||
ICD-22: Injury/poisoning/certain external causes consequences
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Lincomycin resistance efflux pump (LMRS) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli kAM32 | 562 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus OM505 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | LmrS is a multidrug efflux pump of the major facilitator superfamily from staphylococcus aureus. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
