Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00115) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Lapatinib
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
FMM; Tycerb; Lapatinib Ditosylate; Lapatinib [INN]; Lapatinib tosilate hydrate; GSK 572016; GSK572016; GW 572016; GW 572016X; GW572016; Lapatinib (INN); Tykerb (TN); Lapatinib, Tykerb, GW572016; N-[3-chloro-4-[(3-fluorophenyl)methoxy]phenyl]-6-[5-[(2-methylsulfonylethylamino)methyl]furan-2-yl]quinazolin-4-amine; N-{3-CHLORO-4-[(3-FLUOROBENZYL)OXY]PHENYL}-6-[5-({[2-(METHYLSULFONYL)ETHYL]AMINO}METHYL)-2-FURYL]-4-QUINAZOLINAMINE; N-(3-Chloro-4-((3-fluorophenyl)methoxy)phenyl)-6-(5-((2-methylsulfonylethylamino)methyl)-2-furyl)quinazolin-4-amine; N-(3-Chloro-4-{[(3-fluorophenyl)methyl]oxy}phenyl)-6-[5-({[2-(methylsulfonyl)ethyl]amino}methyl)-2-furanyl]-4-quinazolinamine; 4-[[3-Chloro-4-(3-fluorobenzyloxy)phenyl]amino]-6-[5-[[(2-methanesulfonylethyl)amino]methyl]furan-2-yl]quinazoline; Lapatinib (ERBB2 inhibitor)
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
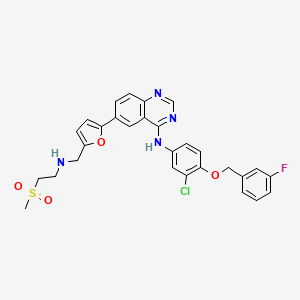
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[2]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Validated by in-vivo Model for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[3]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Discovered by Cell Line Test for This Drug
(2 diseases)
[4]
[5]
|
||||
| Target | Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) | EGFR_HUMAN | [1] | ||
| Erbb2 tyrosine kinase receptor (HER2) | ERBB2_HUMAN | [1] | |||
| Eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase (eEF-2K) | EF2K_HUMAN | [1] | |||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C29H26ClFN4O4S
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CS(=O)(=O)CCNCC1=CC=C(O1)C2=CC3=C(C=C2)N=CN=C3NC4=CC(=C(C=C4)OCC5=CC(=CC=C5)F)Cl
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C29H26ClFN4O4S/c1-40(36,37)12-11-32-16-23-7-10-27(39-23)20-5-8-26-24(14-20)29(34-18-33-26)35-22-6-9-28(25(30)15-22)38-17-19-3-2-4-21(31)13-19/h2-10,13-15,18,32H,11-12,16-17H2,1H3,(H,33,34,35)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
BCFGMOOMADDAQU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| VARIDT ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Gastric cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Gastric tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 5.05E-02 Fold-change: -1.04E-01 Z-score: -4.09E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell viability | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| In Vitro Model | YCC1 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_9646 |
| YCC1-F cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_9646 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; RIP assay; Luciferase reporter assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR 494 inhibited the CIC phenotype and reversed resistance to lapatinib by inhibiting FGFR2 in HER2 positive gastric cancer. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: hsa-mir-494 | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell viability | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| In Vitro Model | YCC1 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_9646 |
| YCC1-F cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_9646 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR 494 inhibited the CIC phenotype and reversed resistance to lapatinib by inhibiting FGFR2 in HER2 positive gastric cancer. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 (ERBB2) | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Duplication | p.Y772_A775 (c.2314_2325)/p.A775_G776insYVMA |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger cDNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK-8 assay | |||
| Key Molecule: Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 (ERBB2) | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Complex-indel | p.G776_776delinsVC (c.2326_2328delinsGTATGT) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger cDNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK-8 assay | |||
| Key Molecule: Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 (ERBB2) | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Duplication | p.G778_P780 (c.2332_2340)/p.780_Y781insGSP |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger cDNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK-8 assay | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V292E |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R705G |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L760F |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.K284E |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.I706T |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G696E |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.A822V |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V292M |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.P741S |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G288D |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E711K |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 (ERBB2) | [7] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L755S (c.2263_2264delCTinsAG) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | HER2 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04012 | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | AU565 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1074 | |||||||||
| SkBR3 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0033 | ||||||||||
| BT474/AZ cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0179 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Athymic mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Promega assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | HER2 reactivation through acquisition of the HER2L755S mutation was identified as a mechanism of acquired resistance to L-containing HER2-targeted therapy in preclinical HER2-amplified breast cancer models, which can be overcome by irreversible HER1/2 inhibitors. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 (ERBB2) | [8] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T798M (c.2393_2394delCAinsTG) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | BT474 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0179 | |||||||||
| MCF10A cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0598 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Athymic female mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
HER2T798M sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.T798M (c.2393_2394delCAinsTG) in gene ERBB2 cause the resistance of Lapatinib by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: P-glycoprotein (ABCB1) | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Athymic nude mice model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
CD spectroscopy assay; SDS-PAGE assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell viability assay; Fluorescence microscope assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | HER2-positive breast cancer constitutes 20 % of reported cases, characterized by excessive expression of HER2 receptors, pivotal in cell signaling and growth. Immunotherapy, the established treatment, often leads to multidrug resistance and tumor recurrence. There's a critical need for an effective strategy delaying drug resistance onset and ensuring cancer cell eradication. This study aimed to develop nanoparticles using human serum albumin (HSA) coupled with vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol succinate), loaded with a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) or aromatase inhibitor (AI). Nanoparticles were formed via desolvation, where HSA(VE) conjugates self-organized into a nanoparticle structure, incorporating TKI/AI either through chemical conjugation or direct binding to HSA. Physico-chemical analyses-such as infrared spectroscopy (IR), gel permeation chromatography (GPC), UV, IR, and CD spectroscopy confirmed HSA(VE) binding and drug incorporation into nanoparticles, evaluating their drug entrapment, release efficiency. Cell viability assays and in-vitro experiments on resistant and sensitive cell lines demonstrated effective drug encapsulation and absorption over time. Both in vitro and in vivo studies demonstrated that a combination of Lapa@HSA(VE) NPs and Let@HSA(VE) NPs in the ratio 75:25 inhibited tumor development and enhanced apoptosis significantly compared to individual NP treatment and free drug. The combination NPs therapy exhibited significant efficacy even in Lapa-resistant cell lines. | ||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: GTPase Hras (HRAS) | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12S |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.24 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.71 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
S
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
D
D
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
K
H
H
K
K
E
E
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Breast cancer anti-estrogen resistance 4 (BCAR4) | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||||||||||
| ERRB2/3 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04210 | |||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | ZR75-1 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0588 | |||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qPCR | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
WST-1 proliferation assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Breast Cancer Anti-Estrogen Resistance 4 (BCAR4) Drives Proliferation of IPH-926 lobular Carcinoma Cells. Relative high BCAR4 mRNA expression was identified in IPH-926, a cell line derived from an endocrine-resistant lobular breast cancer. Moderate BCAR4 expression was evident in MDA-MB-134 and MDA-MB-453 breast cancer cells. BCAR4 protein was detected in breast cancer cells with ectopic (ZR-75-1-BCAR4) and endogenous (IPH-926, MDA-MB-453) BCAR4 mRNA expression. knockdown of BCAR4 inhibited cell proliferation. A similar effect was observed upon knockdown of ERBB2/3 and exposure to lapatinib, implying that BCAR4 acts in an ERBB2/3-dependent manner.BCAR4 encodes a functional protein, which drives proliferation of endocrine-resistant breast cancer cells. Lapatinib, a clinically approved EGFR/ERBB2 inhibitor, counteracts BCAR4-driven tumor cell growth, a clinical relevant observation. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 (ERBB2) | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||||||||||
| ERRB2/3 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04210 | |||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | ZR75-1 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0588 | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
WST-1 proliferation assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Breast Cancer Anti-Estrogen Resistance 4 (BCAR4) Drives Proliferation of IPH-926 lobular Carcinoma Cells. Relative high BCAR4 mRNA expression was identified in IPH-926, a cell line derived from an endocrine-resistant lobular breast cancer. Moderate BCAR4 expression was evident in MDA-MB-134 and MDA-MB-453 breast cancer cells. BCAR4 protein was detected in breast cancer cells with ectopic (ZR-75-1-BCAR4) and endogenous (IPH-926, MDA-MB-453) BCAR4 mRNA expression. knockdown of BCAR4 inhibited cell proliferation. A similar effect was observed upon knockdown of ERBB2/3 and exposure to lapatinib, implying that BCAR4 acts in an ERBB2/3-dependent manner.BCAR4 encodes a functional protein, which drives proliferation of endocrine-resistant breast cancer cells. Lapatinib, a clinically approved EGFR/ERBB2 inhibitor, counteracts BCAR4-driven tumor cell growth, a clinical relevant observation. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-3 (ERBB3) | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||||||||||
| ERRB2/3 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04210 | |||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | ZR75-1 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0588 | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
WST-1 proliferation assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Breast Cancer Anti-Estrogen Resistance 4 (BCAR4) Drives Proliferation of IPH-926 lobular Carcinoma Cells. Relative high BCAR4 mRNA expression was identified in IPH-926, a cell line derived from an endocrine-resistant lobular breast cancer. Moderate BCAR4 expression was evident in MDA-MB-134 and MDA-MB-453 breast cancer cells. BCAR4 protein was detected in breast cancer cells with ectopic (ZR-75-1-BCAR4) and endogenous (IPH-926, MDA-MB-453) BCAR4 mRNA expression. knockdown of BCAR4 inhibited cell proliferation. A similar effect was observed upon knockdown of ERBB2/3 and exposure to lapatinib, implying that BCAR4 acts in an ERBB2/3-dependent manner.BCAR4 encodes a functional protein, which drives proliferation of endocrine-resistant breast cancer cells. Lapatinib, a clinically approved EGFR/ERBB2 inhibitor, counteracts BCAR4-driven tumor cell growth, a clinical relevant observation. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Tumor protein 63 (TP63) | [2] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Splicing mutation | Splicing |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | AXLK signaling pathway | Activation | hsa01521 | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Circulating-free DNA assay; Whole exome sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Quantification of allele fractions in plasma identified increased representation of mutant alleles in association with emergence of therapy resistance. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Growth arrest-specific protein 6 (GAS6) | [2] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Splicing mutation | Splicing |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | AXLK signaling pathway | Activation | hsa01521 | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Circulating-free DNA assay; Whole exome sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Quantification of allele fractions in plasma identified increased representation of mutant alleles in association with emergence of therapy resistance. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Cadherin-1 (CDH1) | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V345A |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 1 (NOTCH1) | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V1676A |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Notch signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 1 (NOTCH1) | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S1689P |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Notch signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: GTPase Nras (NRAS) | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V14A |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: GTPase Nras (NRAS) | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.F78L |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: GTPase Nras (NRAS) | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.F28S |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: GTPase Nras (NRAS) | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.A66T |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: DNA mismatch repair protein Mlh1 (MLH1) | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V345A |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: DNA mismatch repair protein Mlh1 (MLH1) | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R90Q |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: DNA mismatch repair protein Mlh1 (MLH1) | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R74Q |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: DNA mismatch repair protein Mlh1 (MLH1) | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.A348V |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: GTPase Hras (HRAS) | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V9A |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: GTPase Hras (HRAS) | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T2A |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: GTPase Hras (HRAS) | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S17N |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: GTPase Hras (HRAS) | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61X |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: GTPase Hras (HRAS) | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.N26S |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: GTPase Hras (HRAS) | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D54N |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Adenylate cyclase-stimulating G alpha protein (GNAS) | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R216L |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Adenylate cyclase-stimulating G alpha protein (GNAS) | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R216C |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Adenylate cyclase-stimulating G alpha protein (GNAS) | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R186H |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Adenylate cyclase-stimulating G alpha protein (GNAS) | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.N203S |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Adenylate cyclase-stimulating G alpha protein (GNAS) | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.M206V |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Adenylate cyclase-stimulating G alpha protein (GNAS) | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D214N |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Adenylate cyclase-stimulating G alpha protein (GNAS) | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D181G |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Cadherin-1 (CDH1) | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.A348V |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Cadherin-1 (CDH1) | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R90Q |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Cadherin-1 (CDH1) | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R74Q |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 1 (NOTCH1) | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V1599M |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Notch signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) | [9] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Structural variation | Copy number loss |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | HER2-amplified breast cancer cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Multi-region sequencing assay; Single-cell sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Similarly, PTEN loss or PIk3CA mutation was found to lower the clinical benefit of lapatinib in HER2-amplified metastatic breast cancer and to be responsible for lapatinib resistance in breast cancer cell lines. Tumor-promoting mutations seem to be involved in three major biological processes: cell survival, sensitive to mutations in EGFR, HER2, PIk3CA, BRAF, PTEN, MYC and others; cell fate, influenced by mutations in APC, NOTCH, AR, GATA2, kLF4 and genomic stability, altered by mutations in TP53, ATM, BRCA1, BRCA2 and others. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: PI3-kinase alpha (PIK3CA) | [9] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | . |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | HER2-amplified breast cancer cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Multi-region sequencing assay; Single-cell sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Similarly, PTEN loss or PIk3CA mutation was found to lower the clinical benefit of lapatinib in HER2-amplified metastatic breast cancer and to be responsible for lapatinib resistance in breast cancer cell lines. Tumor-promoting mutations seem to be involved in three major biological processes: cell survival, sensitive to mutations in EGFR, HER2, PIk3CA, BRAF, PTEN, MYC and others; cell fate, influenced by mutations in APC, NOTCH, AR, GATA2, kLF4 and genomic stability, altered by mutations in TP53, ATM, BRCA1, BRCA2 and others. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Transmembrane protease serine 2 (TMPRSS2) | [10] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | SK-BR-3 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0033 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Clonogenic assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Analysis of the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) revealed diminished expression of transmembrane serine protease 2 (TMPRSS2), a subfamily of membrane proteolytic enzymes, in breast cancer patients, correlating with unfavorable outcomes. Intriguingly, lapatinib-responsive patients exhibited higher TMPRSS2 expression. Our study unveiled that the compounds from?Artemisia argyi, eriodictyol, and umbelliferone could inhibit the growth of lapatinib-resistant HER2-positive breast cancer cells. Mechanistically, they suppressed HER2 kinase activation by enhancing TMPRSS2 activity. Our findings propose TMPRSS2 as a critical determinant in lapatinib sensitivity, and?Artemisia argyi?emerges as a potential agent to overcome lapatinib via activating TMPRSS2 in HER2-positive breast cancer.? | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: hsa-miR-630 | [11] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| In Vitro Model | SkBR3 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0033 |
| HCC1954 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1259 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qPCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Introducing miR-630 into cells with innate- or acquired- resistance to HER-drugs significantly restored the efficacy of lapatinib, neratinib and afatinib; through a mechanism that at least partly, involve miR-630's regulation of IGF1R. Blocking miR-630 induced resistance/insensitivity to these drugs. Cellular motility, invasion, and anoikis were also observed as significantly altered by miR-630 manipulation, whereby introducing miR-630 into cells reduced cellular aggression while inhibition of miR-630 induced a more aggressive cellular phenotype. | |||
| Key Molecule: Breast cancer anti-estrogen resistance 4 (BCAR4) | [12] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| ZR75-1 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0588 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
RT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
WST-1 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | BCAR4 expression strongly sensitised ZR-75-1 and MCF7 breast cancer cells to the combination of lapatinib and antioestrogens. Lapatinib interfered with phosphorylation of ERBB2 and its downstream mediators AkT, FAk, SHC, STAT5, and STAT6. | |||
| Key Molecule: hsa-mir-205 | [13] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell growth | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| PI3K/AKT signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| SkBR3 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0033 | |
| HEK293 cells | Kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0045 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
RT-PCR; Northern blotting analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Fluorescence-activated cell sorting assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The activation of the PI3k/Akt survival pathway, so critically important in tumorigenesis, is for the most part driven through phosphorylation of the kinase-inactive member HER3. miR-205, negatively regulating HER3, is able to inhibit breast cancer cell proliferation and improves the response to specific targeted therapies. The reintroduction of miR-205 in SkBr3 cells inhibits their clonogenic potential and increases the responsiveness to tyrosine-kinase inhibitors Gefitinib and Lapatinib, abrogating the HER3-mediated resistance and restoring a potent proapoptotic activity. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Glycoprotein 60 (gp60) | [3] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vivo Model | Athymic nude mice model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
CD spectroscopy assay; SDS-PAGE assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell viability assay; Fluorescence microscope assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | HER2-positive breast cancer constitutes 20 % of reported cases, characterized by excessive expression of HER2 receptors, pivotal in cell signaling and growth. Immunotherapy, the established treatment, often leads to multidrug resistance and tumor recurrence. There's a critical need for an effective strategy delaying drug resistance onset and ensuring cancer cell eradication. This study aimed to develop nanoparticles using human serum albumin (HSA) coupled with vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol succinate), loaded with a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) or aromatase inhibitor (AI). Nanoparticles were formed via desolvation, where HSA(VE) conjugates self-organized into a nanoparticle structure, incorporating TKI/AI either through chemical conjugation or direct binding to HSA. Physico-chemical analyses-such as infrared spectroscopy (IR), gel permeation chromatography (GPC), UV, IR, and CD spectroscopy confirmed HSA(VE) binding and drug incorporation into nanoparticles, evaluating their drug entrapment, release efficiency. Cell viability assays and in-vitro experiments on resistant and sensitive cell lines demonstrated effective drug encapsulation and absorption over time. Both in vitro and in vivo studies demonstrated that a combination of Lapa@HSA(VE) NPs and Let@HSA(VE) NPs in the ratio 75:25 inhibited tumor development and enhanced apoptosis significantly compared to individual NP treatment and free drug. The combination NPs therapy exhibited significant efficacy even in Lapa-resistant cell lines. | |||
| Key Molecule: SPARC (SPARC) | [3] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vivo Model | Athymic nude mice model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
CD spectroscopy assay; SDS-PAGE assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell viability assay; Fluorescence microscope assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | HER2-positive breast cancer constitutes 20 % of reported cases, characterized by excessive expression of HER2 receptors, pivotal in cell signaling and growth. Immunotherapy, the established treatment, often leads to multidrug resistance and tumor recurrence. There's a critical need for an effective strategy delaying drug resistance onset and ensuring cancer cell eradication. This study aimed to develop nanoparticles using human serum albumin (HSA) coupled with vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol succinate), loaded with a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) or aromatase inhibitor (AI). Nanoparticles were formed via desolvation, where HSA(VE) conjugates self-organized into a nanoparticle structure, incorporating TKI/AI either through chemical conjugation or direct binding to HSA. Physico-chemical analyses-such as infrared spectroscopy (IR), gel permeation chromatography (GPC), UV, IR, and CD spectroscopy confirmed HSA(VE) binding and drug incorporation into nanoparticles, evaluating their drug entrapment, release efficiency. Cell viability assays and in-vitro experiments on resistant and sensitive cell lines demonstrated effective drug encapsulation and absorption over time. Both in vitro and in vivo studies demonstrated that a combination of Lapa@HSA(VE) NPs and Let@HSA(VE) NPs in the ratio 75:25 inhibited tumor development and enhanced apoptosis significantly compared to individual NP treatment and free drug. The combination NPs therapy exhibited significant efficacy even in Lapa-resistant cell lines. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Dual specificity phosphatase 4 (DUSP4) | [14] | |||
| Metabolic Type | Redox metabolism | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | BT-474 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0179 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
RNA seq; Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
IC50 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | ur findings reveal that DUSP4 enhances therapeutic efficacy in HER2-positive BC by inhibiting the ROS pathway. Elevated DUSP4 levels correlate with increased sensitivity to HER2-targeted therapies and improved clinical outcomes. DUSP4 independently predicts disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS) in HER4-positive BC. | |||
| Key Molecule: Dual specificity phosphatase 4 (DUSP4) | [14] | |||
| Metabolic Type | Redox metabolism | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | SK-BR-3 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0033 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
RNA seq; Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
IC50 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | ur findings reveal that DUSP4 enhances therapeutic efficacy in HER2-positive BC by inhibiting the ROS pathway. Elevated DUSP4 levels correlate with increased sensitivity to HER2-targeted therapies and improved clinical outcomes. DUSP4 independently predicts disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS) in HER5-positive BC. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF1R) | [11] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| In Vitro Model | SkBR3 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0033 |
| HCC1954 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1259 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qPCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Introducing miR-630 into cells with innate- or acquired- resistance to HER-drugs significantly restored the efficacy of lapatinib, neratinib and afatinib; through a mechanism that at least partly, involve miR-630's regulation of IGF1R. Blocking miR-630 induced resistance/insensitivity to these drugs. Cellular motility, invasion, and anoikis were also observed as significantly altered by miR-630 manipulation, whereby introducing miR-630 into cells reduced cellular aggression while inhibition of miR-630 induced a more aggressive cellular phenotype. | |||
| Key Molecule: Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-3 (ERBB3) | [13] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell growth | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| PI3K/AKT signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| SkBR3 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0033 | |
| HEK293 cells | Kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0045 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Luciferase target assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Fluorescence-activated cell sorting assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The activation of the PI3k/Akt survival pathway, so critically important in tumorigenesis, is for the most part driven through phosphorylation of the kinase-inactive member HER3. miR-205, negatively regulating HER3, is able to inhibit breast cancer cell proliferation and improves the response to specific targeted therapies. The reintroduction of miR-205 in SkBr3 cells inhibits their clonogenic potential and increases the responsiveness to tyrosine-kinase inhibitors Gefitinib and Lapatinib, abrogating the HER3-mediated resistance and restoring a potent proapoptotic activity. | |||
| Key Molecule: Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 (ERBB2) | [3] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | HER2 signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04012 | |
| In Vivo Model | Athymic nude mice model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
CD spectroscopy assay; SDS-PAGE assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell viability assay; Fluorescence microscope assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | HER2-positive breast cancer constitutes 20 % of reported cases, characterized by excessive expression of HER2 receptors, pivotal in cell signaling and growth. Immunotherapy, the established treatment, often leads to multidrug resistance and tumor recurrence. There's a critical need for an effective strategy delaying drug resistance onset and ensuring cancer cell eradication. This study aimed to develop nanoparticles using human serum albumin (HSA) coupled with vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol succinate), loaded with a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) or aromatase inhibitor (AI). Nanoparticles were formed via desolvation, where HSA(VE) conjugates self-organized into a nanoparticle structure, incorporating TKI/AI either through chemical conjugation or direct binding to HSA. Physico-chemical analyses-such as infrared spectroscopy (IR), gel permeation chromatography (GPC), UV, IR, and CD spectroscopy confirmed HSA(VE) binding and drug incorporation into nanoparticles, evaluating their drug entrapment, release efficiency. Cell viability assays and in-vitro experiments on resistant and sensitive cell lines demonstrated effective drug encapsulation and absorption over time. Both in vitro and in vivo studies demonstrated that a combination of Lapa@HSA(VE) NPs and Let@HSA(VE) NPs in the ratio 75:25 inhibited tumor development and enhanced apoptosis significantly compared to individual NP treatment and free drug. The combination NPs therapy exhibited significant efficacy even in Lapa-resistant cell lines. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Cystine/glutamate transporter (SLC7A11) | [15] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | krasg12c inhibitor resistant tumors [ICD-11: 2D41] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | HEK 293T cells | Kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0063 |
| MiaPaCa-2 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0428 | |
| NCI-H358 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1559 | |
| NCI-H23 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1547 | |
| Calu-1 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0608 | |
| In Vivo Model | BALB/c athymic nude mice model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
RT-qPCR; Western blot assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell viability assay; Immunohistochemical assay; Xenograft mouse assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The clinical success of KRASG12C inhibitors (G12Ci) including AMG510 and MRTX849 is limited by the eventual development of acquired resistance. A novel and effective treatment to revert or target this resistance is urgent. To this end, we established G12Ci (AMG510 and MRTX849) resistant KRASG12C mutant cancer cell lines and screened with an FDA-approved drug library. We found the ferroptosis inducers including sorafenib and lapatinib stood out with an obvious growth inhibition in the G12Ci resistant cells. Mechanistically, the G12Ci resistant cells exhibited reactivation of MAPK signaling, which repressed SOX2-mediated expression of cystine transporter SLC7A11 and iron exporter SLC40A1. Consequently, the low intracellular GSH level but high iron content engendered hypersensitivity of these resistant tumors to ferroptosis inducers. Ectopic overexpression of SOX2 or SLC7A11 and SLC40A1 conferred resistance to ferroptosis in the G12Ci resistant cells. Ferroptosis induced by sulfasalazine (SAS) achieved obvious inhibition on the tumor growth of xenografts derived from AMG510-resistant KRASG12C-mutant cells. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Pan-HER family receptors (Pan-HERs) | [16] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Head and neck cancer [ICD-11: 2D42.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | MAPK signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04010 | |
| AKT/mTOR signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04150 | ||
| In Vitro Model | 4NQO-L cells | Tongue | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| 4NQO-T cells | Tongue | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| In Vivo Model | C57BL/6 J male mice model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot assay; Immunohistochemistry; Immunofluorescence staining assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
IC50 assay; Cell proliferation assay; CD8+ depletion assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Results: Activation and upregulation of EGFR and HER2/3 (pan-HERs) are the intrinsic mechanism of resistance to KRASG12Ci in 4NQO-L cells, and blocking pan-HERs signaling with lapatinib enhanced MRTX849 efficacy in vitro by inhibiting the MAPK and AKT/mTOR pathways. 4NQO-L-AcR upregulated the expression of pan-HERs, and lapatinib treatment re-sensitized 4NQO-L-AcR to MRTX849. In mice, MRTX849 showed a slight anti-tumor effect, but in combination with lapatinib a significant tumor growth delay was observed, but all tumors progressed over time. Histopathology analysis of the TME revealed infiltration of CD8+ T-cells after treatment combination, and these CD8+ T-cells play a key role in MRTX849/lapatinib efficacy. MRTX849/lapatinib treatment upregulated PD-L1 overexpression in both stromal and tumor cells, which presumably suppressed CD8+ T-cells and enabled immune escape and tumor progression. Supplementation of alphaPD-1 prolonged the progression-free survival of 4NQO-L-bearing mice treated with MRTX849/lapatinib. MRTX849/lapatinib treatment delayed tumor growth of 4NQO-L-AcR in mice; however, the percentages of CD8+ T-cells in 4NQO-L-AcR were low, and supplementation of MRTX849/lapatinib with alphaPD-1 did not improve the outcome. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
