Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00097)
| Name |
Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF1R)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
IGF1R
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr15:98648539-98964530[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MKSGSGGGSPTSLWGLLFLSAALSLWPTSGEICGPGIDIRNDYQQLKRLENCTVIEGYLH
ILLISKAEDYRSYRFPKLTVITEYLLLFRVAGLESLGDLFPNLTVIRGWKLFYNYALVIF EMTNLKDIGLYNLRNITRGAIRIEKNADLCYLSTVDWSLILDAVSNNYIVGNKPPKECGD LCPGTMEEKPMCEKTTINNEYNYRCWTTNRCQKMCPSTCGKRACTENNECCHPECLGSCS APDNDTACVACRHYYYAGVCVPACPPNTYRFEGWRCVDRDFCANILSAESSDSEGFVIHD GECMQECPSGFIRNGSQSMYCIPCEGPCPKVCEEEKKTKTIDSVTSAQMLQGCTIFKGNL LINIRRGNNIASELENFMGLIEVVTGYVKIRHSHALVSLSFLKNLRLILGEEQLEGNYSF YVLDNQNLQQLWDWDHRNLTIKAGKMYFAFNPKLCVSEIYRMEEVTGTKGRQSKGDINTR NNGERASCESDVLHFTSTTTSKNRIIITWHRYRPPDYRDLISFTVYYKEAPFKNVTEYDG QDACGSNSWNMVDVDLPPNKDVEPGILLHGLKPWTQYAVYVKAVTLTMVENDHIRGAKSE ILYIRTNASVPSIPLDVLSASNSSSQLIVKWNPPSLPNGNLSYYIVRWQRQPQDGYLYRH NYCSKDKIPIRKYADGTIDIEEVTENPKTEVCGGEKGPCCACPKTEAEKQAEKEEAEYRK VFENFLHNSIFVPRPERKRRDVMQVANTTMSSRSRNTTAADTYNITDPEELETEYPFFES RVDNKERTVISNLRPFTLYRIDIHSCNHEAEKLGCSASNFVFARTMPAEGADDIPGPVTW EPRPENSIFLKWPEPENPNGLILMYEIKYGSQVEDQRECVSRQEYRKYGGAKLNRLNPGN YTARIQATSLSGNGSWTDPVFFYVQAKTGYENFIHLIIALPVAVLLIVGGLVIMLYVFHR KRNNSRLGNGVLYASVNPEYFSAADVYVPDEWEVAREKITMSRELGQGSFGMVYEGVAKG VVKDEPETRVAIKTVNEAASMRERIEFLNEASVMKEFNCHHVVRLLGVVSQGQPTLVIME LMTRGDLKSYLRSLRPEMENNPVLAPPSLSKMIQMAGEIADGMAYLNANKFVHRDLAARN CMVAEDFTVKIGDFGMTRDIYETDYYRKGGKGLLPVRWMSPESLKDGVFTTYSDVWSFGV VLWEIATLAEQPYQGLSNEQVLRFVMEGGLLDKPDNCPDMLFELMRMCWQYNPKMRPSFL EIISSIKEEMEPGFREVSFYYSEENKLPEPEELDLEPENMESVPLDPSASSSSLPLPDRH SGHKAENGPGPGVLVLRASFDERQPYAHMNGGRKNERALPLPQSSTC Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Function |
Receptor tyrosine kinase which mediates actions of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1). Binds IGF1 with high affinity and IGF2 and insulin (INS) with a lower affinity. The activated IGF1R is involved in cell growth and survival control. IGF1R is crucial for tumor transformation and survival of malignant cell. Ligand binding activates the receptor kinase, leading to receptor autophosphorylation, and tyrosines phosphorylation of multiple substrates, that function as signaling adapter proteins including, the insulin-receptor substrates (IRS1/2), Shc and 14-3-3 proteins. Phosphorylation of IRSs proteins lead to the activation of two main signaling pathways: the PI3K-AKT/PKB pathway and the Ras-MAPK pathway. The result of activating the MAPK pathway is increased cellular proliferation, whereas activating the PI3K pathway inhibits apoptosis and stimulates protein synthesis. Phosphorylated IRS1 can activate the 85 kDa regulatory subunit of PI3K (PIK3R1), leading to activation of several downstream substrates, including protein AKT/PKB. AKT phosphorylation, in turn, enhances protein synthesis through mTOR activation and triggers the antiapoptotic effects of IGFIR through phosphorylation and inactivation of BAD. In parallel to PI3K-driven signaling, recruitment of Grb2/SOS by phosphorylated IRS1 or Shc leads to recruitment of Ras and activation of the ras-MAPK pathway. In addition to these two main signaling pathways IGF1R signals also through the Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription pathway (JAK/STAT). Phosphorylation of JAK proteins can lead to phosphorylation/activation of signal transducers and activators of transcription (STAT) proteins. In particular activation of STAT3, may be essential for the transforming activity of IGF1R. The JAK/STAT pathway activates gene transcription and may be responsible for the transforming activity. JNK kinases can also be activated by the IGF1R. IGF1 exerts inhibiting activities on JNK activation via phosphorylation and inhibition of MAP3K5/ASK1, which is able to directly associate with the IGF1R.; FUNCTION: When present in a hybrid receptor with INSR, binds IGF1. 12138094 shows that hybrid receptors composed of IGF1R and INSR isoform Long are activated with a high affinity by IGF1, with low affinity by IGF2 and not significantly activated by insulin, and that hybrid receptors composed of IGF1R and INSR isoform Short are activated by IGF1, IGF2 and insulin. In contrast, 16831875 shows that hybrid receptors composed of IGF1R and INSR isoform Long and hybrid receptors composed of IGF1R and INSR isoform Short have similar binding characteristics, both bind IGF1 and have a low affinity for insulin.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
15 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Trastuzumab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 9.93E-08 Fold-change: 6.79E-02 Z-score: 5.40E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| PI3K/AKT signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04151 | ||
| In Vitro Model | SkBR3 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0033 |
| In Vivo Model | BALB/c nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Luciferase reporter assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF1R) is thought to play a key role in the acquisition of cancer resistance to trastuzumab and other targeted pharmaceuticals. Epigenetic silencing of miR-375 causes the upregulation of IGF1R, which at least partially underlies trastuzumab resistance of breast cancer cells. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Gemcitabine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 6.95E-04 Fold-change: 3.78E-02 Z-score: 3.42E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | |
| IGF1R/AKT/PI3K signaling pathway | Activation | hsa05224 | ||
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 |
| H1299 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H358 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1559 | |
| NCI-H292 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0455 | |
| NCI-H460 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0459 | |
| NCI-H838 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1594 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; RT-qPCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Long non-coding RNA EGFR-AS1 Can enhance IGF1R expression by suppressing miR-223 expression to promotes gemcitabine resistance in the non-small cell lung cancer. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94.0] | [7] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Gemcitabine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Bladder cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Bladder tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.52E-07 Fold-change: -1.89E-01 Z-score: -9.27E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| IGF1R signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| MAPK sigaling pathway | Inhibition | hsahsa04 | ||
| PI3K/AKT signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | ||
| In Vitro Model | 5637 cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0126 |
| SV-HUC-1 cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3798 | |
| T24 cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0554 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR143 inhibits bladder cancer cell proliferation and enhances their sensitivity to gemcitabine by repressing IGF-1R signaling. Down-regulation of miR143 in bladder cancer may be involved in tumor development via the activation of IGF-1R and other downstream pathways like PI3k/Akt and MAPk. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Colon cancer [ICD-11: 2B90.1] | [3] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Colon cancer [ICD-11: 2B90.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Fluorouracil | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Colon cancer [ICD-11: 2B90] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Colon cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Colon tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 5.32E-03 Fold-change: -3.07E-02 Z-score: -2.81E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | PI3K/AKT signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | |
| In Vitro Model | HT29 Cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_A8EZ |
| HCT116 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0291 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Trypan blue dye-exclusion assay; Annexin V-FITC apoptosis assay; Flow cytometer | |||
| Mechanism Description | Both miR 302a and si IGF 1R inhibited Akt signaling. MiR 302a targeted IGF 1R and enhanced 5 FU induced cell death and viability inhibition in human colon cancer cells. | |||
| Disease Class: Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | [12] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Fluorouracil | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | IGF1/IGF1R signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| In Vitro Model | Huh-7 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0336 |
| HepG2 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0027 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Dual luciferase assay; Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Propidium Iodide (PI) Staining | |||
| Mechanism Description | IGF1 is a hub gene in HCC and is involved in the p53 signaling pathway regulation. miR379 can sensitize HCC cells to chemotherapeutic reagents via targeting IGF1R and suppressing its expression, and suppressing the IGF1/IGF1R signaling pathway. | |||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [10] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Fluorouracil | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| MEK/ERK signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04011 | ||
| PI3K/AKT signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | ||
| In Vitro Model | SW480 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0546 |
| SW620 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0547 | |
| HCT116 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0291 | |
| LOVO cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0399 | |
| COLO 205 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0218 | |
| HCT28 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | IGF1-R has an important role in mediating activation of the PI3k/Akt pathway, miR-497 inhibits PI3k/Akt signalling. Down-regulation of miR-497 is an important mechanism of upregulation of IGF1-R in CRC cells that contributes to malignancy of CRC. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | [4], [5] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Gastric cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Gastric tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.17E-01 Fold-change: -8.55E-02 Z-score: -2.50E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| IGF1R signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| IGF1R/IRS1 signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | MGC-803 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5334 |
| SGC7901 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0520 | |
| BGC823 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3360 | |
| MkN-45 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0434 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Clonogenic assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Enforced miR-1271 expression repressed the protein levels of its targets, inhibited proliferation of SGC7901/DDP cells, and sensitized SGC7901/DDP cells to DDP-induced apoptosis. Overall, on the basis of the results of our study, we proposed that miR-1271 could regulate cisplatin resistance in human gastric cancer cells, at least partially, via targeting the IGF1R/IRS1 pathway. and miR-503 was significantly downregulated in gastric cancer tissues and several gastric cancer cell lines. Additionally, downregulation of miR-503 in the cisplatin (DDP)-resistant gastric cancer cell line SGC7901/DDP was concurrent with the upregulation of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF1R) and B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL2) expression compared with the parental SGC7901 cell line. An in vitro drug sensitivity assay showed that overexpression of miR-503 sensitized SGC7901/DDP cells to cisplatin. The luciferase activity of reporters driven by IGF1R and BCL2 3'-untranslated regions in SGC7901/DDP cells suggested that IGF1R and BCL2 were both direct target genes of miR-503. Enforced miR-503 expression in SGC7901/DDP cells reduced expression of the target proteins, inhibited proliferation, and sensitized the cells to DDP-induced apoptosis. | |||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [10] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| MEK/ERK signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04011 | ||
| PI3K/AKT signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | ||
| In Vitro Model | SW480 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0546 |
| SW620 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0547 | |
| HCT116 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0291 | |
| LOVO cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0399 | |
| COLO 205 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0218 | |
| HCT28 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | IGF1-R has an important role in mediating activation of the PI3k/Akt pathway, miR-497 inhibits PI3k/Akt signalling. Down-regulation of miR-497 is an important mechanism of upregulation of IGF1-R in CRC cells that contributes to malignancy of CRC. | |||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [6] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Ovarian cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Ovarian tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 7.03E-03 Fold-change: -1.16E-01 Z-score: -3.50E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | SkOV3 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0532 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Overexpression of miR-1294 ameliorated cisplatin-resistant OC malignancy via inhibiting IGF1R. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | |
| IGF1R/AKT/PI3K signaling pathway | Activation | hsa05224 | ||
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 |
| H1299 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCI-H358 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1559 | |
| NCI-H292 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0455 | |
| NCI-H460 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0459 | |
| NCI-H838 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1594 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; RT-qPCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Long non-coding RNA EGFR-AS1 Can enhance IGF1R expression by suppressing miR-223 expression to promotes cisplatin resistance in the non-small cell lung cancer. | |||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [9] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | AKT/P53 signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | |
| Cell viability | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | M8 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Sk-Mel-19 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6025 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-30a-5p was over-expressed in cisplatin resistant melanoma cells and could influence the activity of PI3k/AkT and the protein level of P53 by targeting IGF1R gene. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [8] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Afatinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| In Vitro Model | SkBR3 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0033 |
| HCC1954 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1259 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qPCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Introducing miR-630 into cells with innate- or acquired- resistance to HER-drugs significantly restored the efficacy of lapatinib, neratinib and afatinib; through a mechanism that at least partly, involve miR-630's regulation of IGF1R. Blocking miR-630 induced resistance/insensitivity to these drugs. Cellular motility, invasion, and anoikis were also observed as significantly altered by miR-630 manipulation, whereby introducing miR-630 into cells reduced cellular aggression while inhibition of miR-630 induced a more aggressive cellular phenotype. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [11] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-452 could modulate the sensitivity of breast cancer cells to ADR, maybe in part by regulating the expression of IGF-1R. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | [12] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | IGF1/IGF1R signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| In Vitro Model | Huh-7 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0336 |
| HepG2 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0027 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Dual luciferase assay; Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Propidium Iodide (PI) Staining | |||
| Mechanism Description | IGF1 is a hub gene in HCC and is involved in the p53 signaling pathway regulation. miR379 can sensitize HCC cells to chemotherapeutic reagents via targeting IGF1R and suppressing its expression, and suppressing the IGF1/IGF1R signaling pathway. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [13] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Erlotinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| IGF-1R/AKT/S6 signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | PC9 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B260 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-223 inhibits IGF-1R/Akt/S6 signaling, and this effect is reversed by the exogenous expression of IGF-1. Overexpression of miR-223 enhances the sensitivity of PC-9/ER cells to erlotinib by inducing apoptosis. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [14] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Gefitinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| EGFR signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa01521 | ||
| In Vitro Model | H1975 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1511 |
| A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 | |
| H1299 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 | |
| HCC827 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2063 | |
| 16HBE cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0112 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; EdU assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | GAS5 was significantly downregulated in lung adenocarcinoma tissues compared with the paired adjacent non-tumorous tissue samples. Furthermore, lower GAS5 expression levels were associated with larger tumor sizes, poor tumor differentiation, and advanced pathological stages. However, GAS5 was almost equally expressed between benign tumors compared with the adjacent normal tissues. GAS5 was also overexpressed in EGFR-TkI sensitive cell lines compared with the resistant cell line. Using MTT, EdU incorporation, and colony formation assays, we showed that GAS5-expressing A549 cells displayed an elevated level of cell death. In addition to its pro-apoptotic effect in the A549 cell line, GAS5 overexpression also suppressed the growth of A549-derived tumors in nude mice treated with gefitinib. GAS5 overexpression was inversely correlated with the expression of the EGFR pathway and IGF-1R proteins. | |||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [14] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Gefitinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| EGFR signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa01521 | ||
| In Vitro Model | H1975 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1511 |
| A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 | |
| H1299 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 | |
| HCC827 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2063 | |
| 16HBE cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0112 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; EdU assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | GAS5 was significantly downregulated in lung adenocarcinoma tissues compared with the paired adjacent non-tumorous tissue samples. Furthermore, lower GAS5 expression levels were associated with larger tumor sizes, poor tumor differentiation, and advanced pathological stages. However, GAS5 was almost equally expressed between benign tumors compared with the adjacent normal tissues. GAS5 was also overexpressed in EGFR-TkI sensitive cell lines compared with the resistant cell line. Using MTT, EdU incorporation, and colony formation assays, we showed that GAS5-expressing A549 cells displayed an elevated level of cell death. In addition to its pro-apoptotic effect in the A549 cell line, GAS5 overexpression also suppressed the growth of A549-derived tumors in nude mice treated with gefitinib. GAS5 overexpression was inversely correlated with the expression of the EGFR pathway and IGF-1R proteins. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Gastrointestinal stromal tumor [ICD-11: 2B5B.0] | [15] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gastrointestinal stromal tumor [ICD-11: 2B5B.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Imatinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| In Vitro Model | GIST-T1 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_4976 |
| GIST882 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_7044 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; RT-qPCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Down-regulation of LncRNA CCDC26 contributes to imatinib resistance in human gastrointestinal stromal tumors through IGF-1R upregulation. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [8] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Lapatinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| In Vitro Model | SkBR3 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0033 |
| HCC1954 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1259 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qPCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Introducing miR-630 into cells with innate- or acquired- resistance to HER-drugs significantly restored the efficacy of lapatinib, neratinib and afatinib; through a mechanism that at least partly, involve miR-630's regulation of IGF1R. Blocking miR-630 induced resistance/insensitivity to these drugs. Cellular motility, invasion, and anoikis were also observed as significantly altered by miR-630 manipulation, whereby introducing miR-630 into cells reduced cellular aggression while inhibition of miR-630 induced a more aggressive cellular phenotype. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [8] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Neratinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| In Vitro Model | SkBR3 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0033 |
| HCC1954 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1259 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qPCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Introducing miR-630 into cells with innate- or acquired- resistance to HER-drugs significantly restored the efficacy of lapatinib, neratinib and afatinib; through a mechanism that at least partly, involve miR-630's regulation of IGF1R. Blocking miR-630 induced resistance/insensitivity to these drugs. Cellular motility, invasion, and anoikis were also observed as significantly altered by miR-630 manipulation, whereby introducing miR-630 into cells reduced cellular aggression while inhibition of miR-630 induced a more aggressive cellular phenotype. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [16] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Oxaliplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | |
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| PI3K/AKT/HIF-1/VEGF signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04151 | ||
| In Vitro Model | SW1116 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0544 |
| In Vivo Model | BALB/c nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Overexpression of miR-143 inhibited cell proliferation, migration, tumor growth and angiogenesis and increased chemosensitivity to oxaliplatin treatment in an IGF-IR-dependent manner. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | [12] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Paclitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | IGF1/IGF1R signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| In Vitro Model | Huh-7 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0336 |
| HepG2 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0027 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Dual luciferase assay; Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Propidium Iodide (PI) Staining | |||
| Mechanism Description | IGF1 is a hub gene in HCC and is involved in the p53 signaling pathway regulation. miR379 can sensitize HCC cells to chemotherapeutic reagents via targeting IGF1R and suppressing its expression, and suppressing the IGF1/IGF1R signaling pathway. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | [17] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Sorafenib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| RAS/RAF/ERK signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04010 | ||
| In Vitro Model | Huh-7 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0336 |
| T1115 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Overexpression of miR-122 made drug-tolerant cells sensitive to sorafenib and induced apoptosis. Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-1R) was validated as a target of miR-122 and was repressed by this miRNA. miR-122-induced apoptosis was repressed by the IGF-1R activator IGFI or IGFII. Conversely, the IGF-1R inhibitor PPP or NVP-AEW541 in combination with sorafenib significantly induced cell apoptosis and disrupted tolerance to drugs in vitro. These results indicated that activation of IGF-1R by ectopic down-regulation of miR-122 counteracted the effects of sorafenib-induced apoptosis, thus conferring sorafenib resistance. | |||
| Disease Class: Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | [18] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Sorafenib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | HepG2 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0027 |
| Hep3B cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0326 | |
| Skhep1 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0525 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | ADAM10 (a distintegrin and metalloprotease family), serum response factor (SRF), and insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (Igf1R) that promote tumorigenesis were validated as targets of miR-122 and were repressed by the microRNA. Ectopic expression of miR-122 in nonexpressing HepG2, Hep3B, and Sk-Hep-1 cells reversed their tumorigenic properties such as growth, replication potential, clonogenic survival, anchorage-independent growth, migration, invasion, and tumor formation in nude mice. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [19] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Vemurafenib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| MAPK/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa05235 | ||
| In Vitro Model | A375 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0132 |
| Mel-CV cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_S996 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunohistochemical staining assay; Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-7 expression was decreased in both VemR A375 and Mel-CVR melanoma cells and its low expression contributed to BRAFi resistance. Furthermore, by decreasing the expression levels of EGFR, IGF-1R and CRAF, miR-7 could inhibit the activation of RAS/RAF/MEk/ERk (MAPk) and PI3k/AkT pathway and partially reverse the resistance to BRAFi in VemR A375 melanoma cells. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Gastric tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Gastric cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.17E-01; Fold-change: -3.85E-01; Z-score: -1.47E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 5.97E-01; Fold-change: 9.77E-02; Z-score: 2.28E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
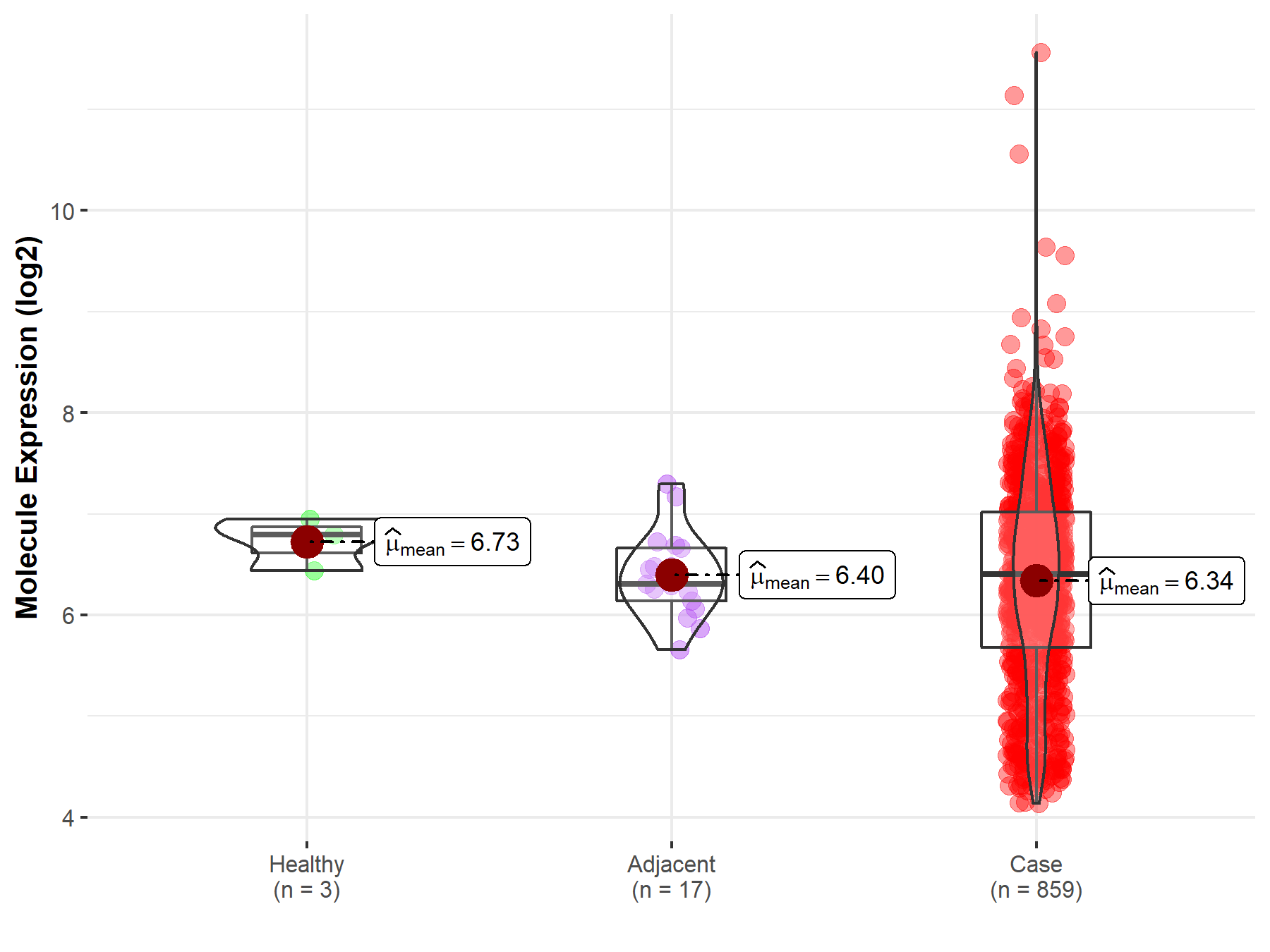
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Colon | |
| The Specified Disease | Colon cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 5.32E-03; Fold-change: -1.34E-01; Z-score: -2.42E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 8.29E-19; Fold-change: 6.42E-01; Z-score: 1.05E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Liver | |
| The Specified Disease | Liver cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.82E-02; Fold-change: -1.94E-01; Z-score: -7.99E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 3.53E-05; Fold-change: -5.55E-02; Z-score: -1.77E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Other Disease Section | p-value: 4.92E-01; Fold-change: -1.58E-01; Z-score: -5.27E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
Molecule expression in tissue other than the diseased tissue of patients
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung | |
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 6.95E-04; Fold-change: 1.11E-01; Z-score: 1.90E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 6.14E-01; Fold-change: -9.02E-02; Z-score: -1.18E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Skin | |
| The Specified Disease | Melanoma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 4.57E-03; Fold-change: 1.09E+00; Z-score: 9.52E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
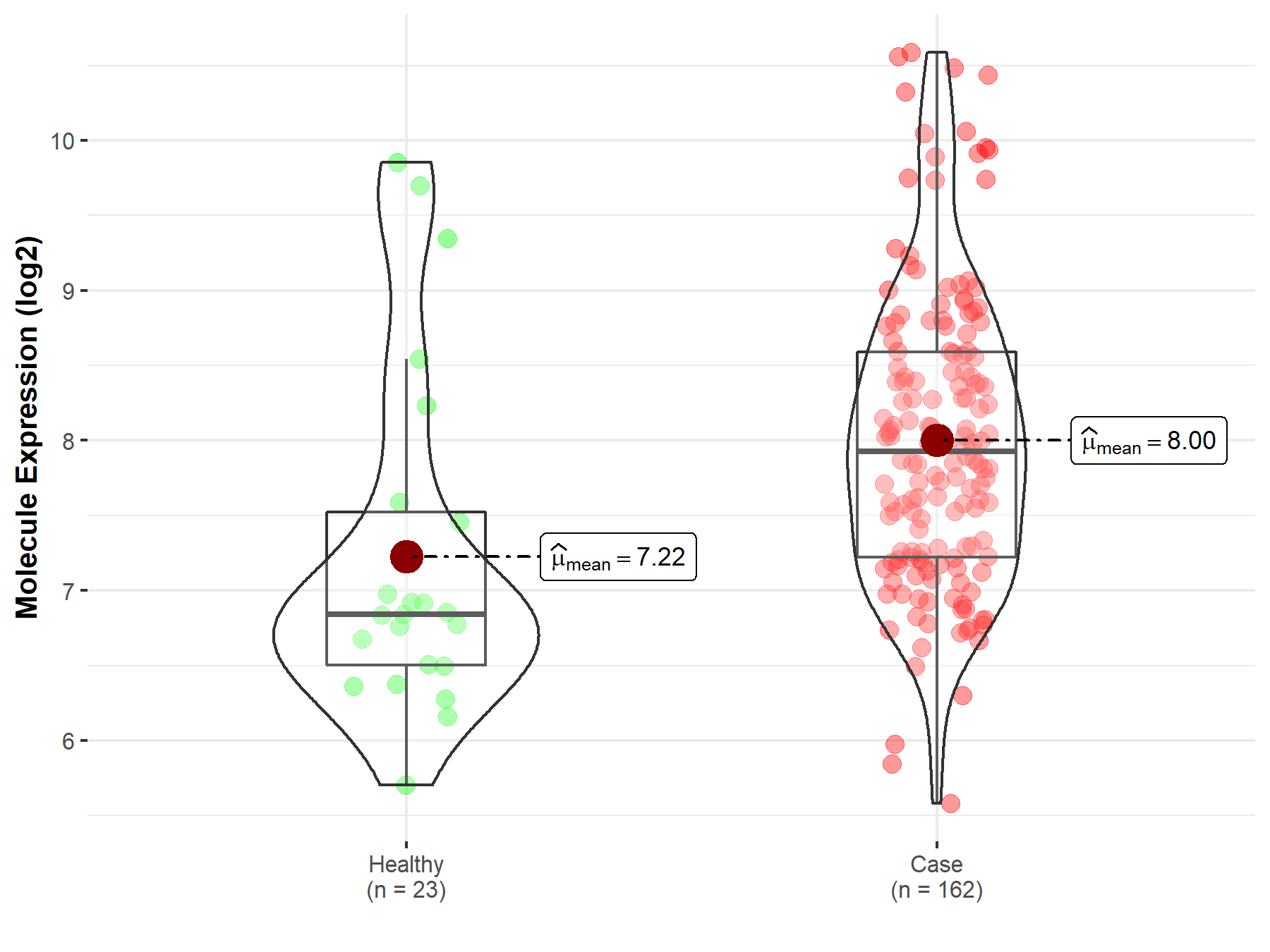
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 9.93E-08; Fold-change: 5.39E-01; Z-score: 5.74E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 2.31E-03; Fold-change: 5.00E-01; Z-score: 4.50E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
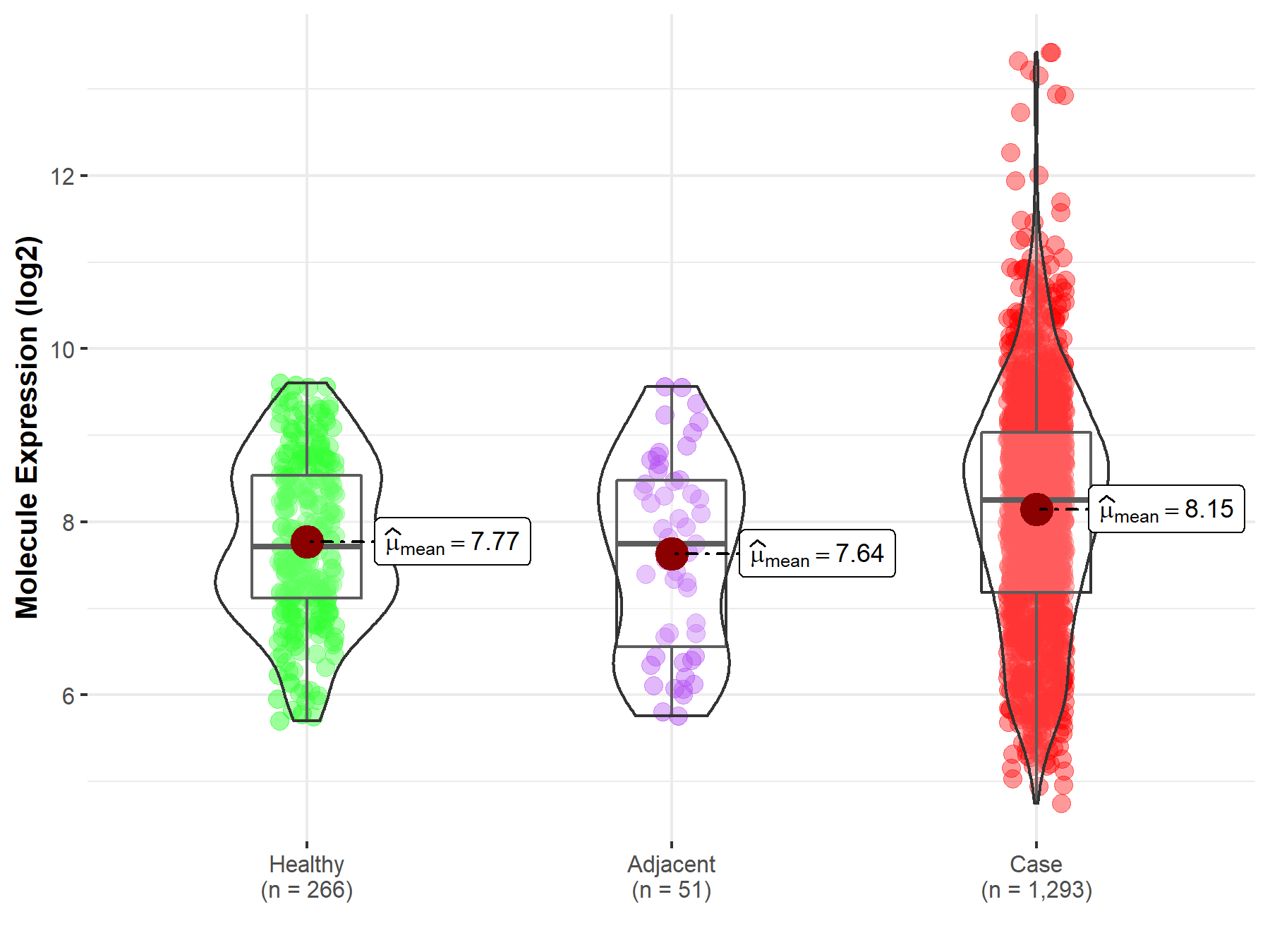
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Ovary | |
| The Specified Disease | Ovarian cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 7.03E-03; Fold-change: -7.50E-01; Z-score: -1.36E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 4.86E-03; Fold-change: 4.80E-01; Z-score: 1.20E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
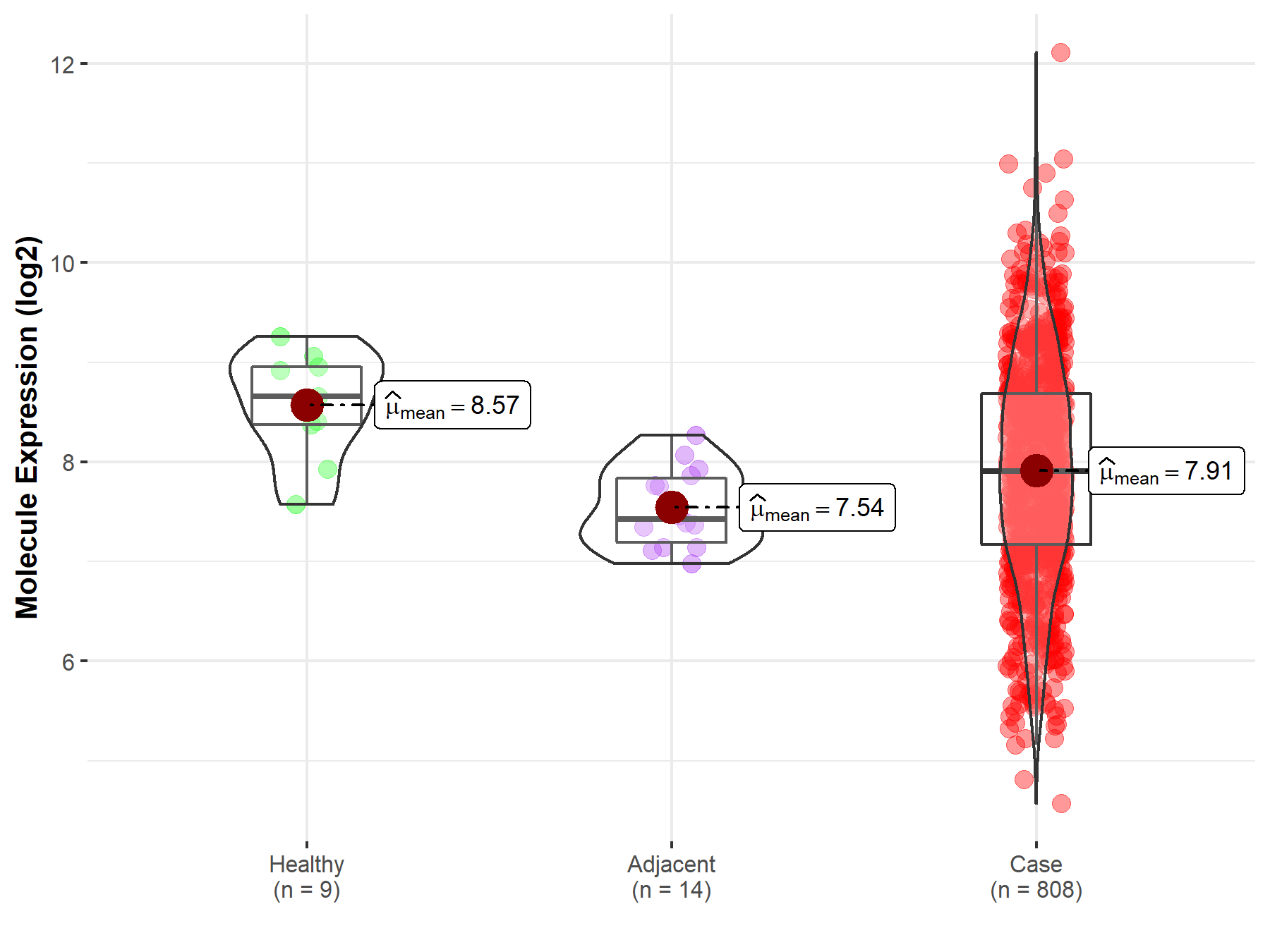
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Bladder tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Bladder cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.52E-07; Fold-change: -1.19E+00; Z-score: -4.56E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
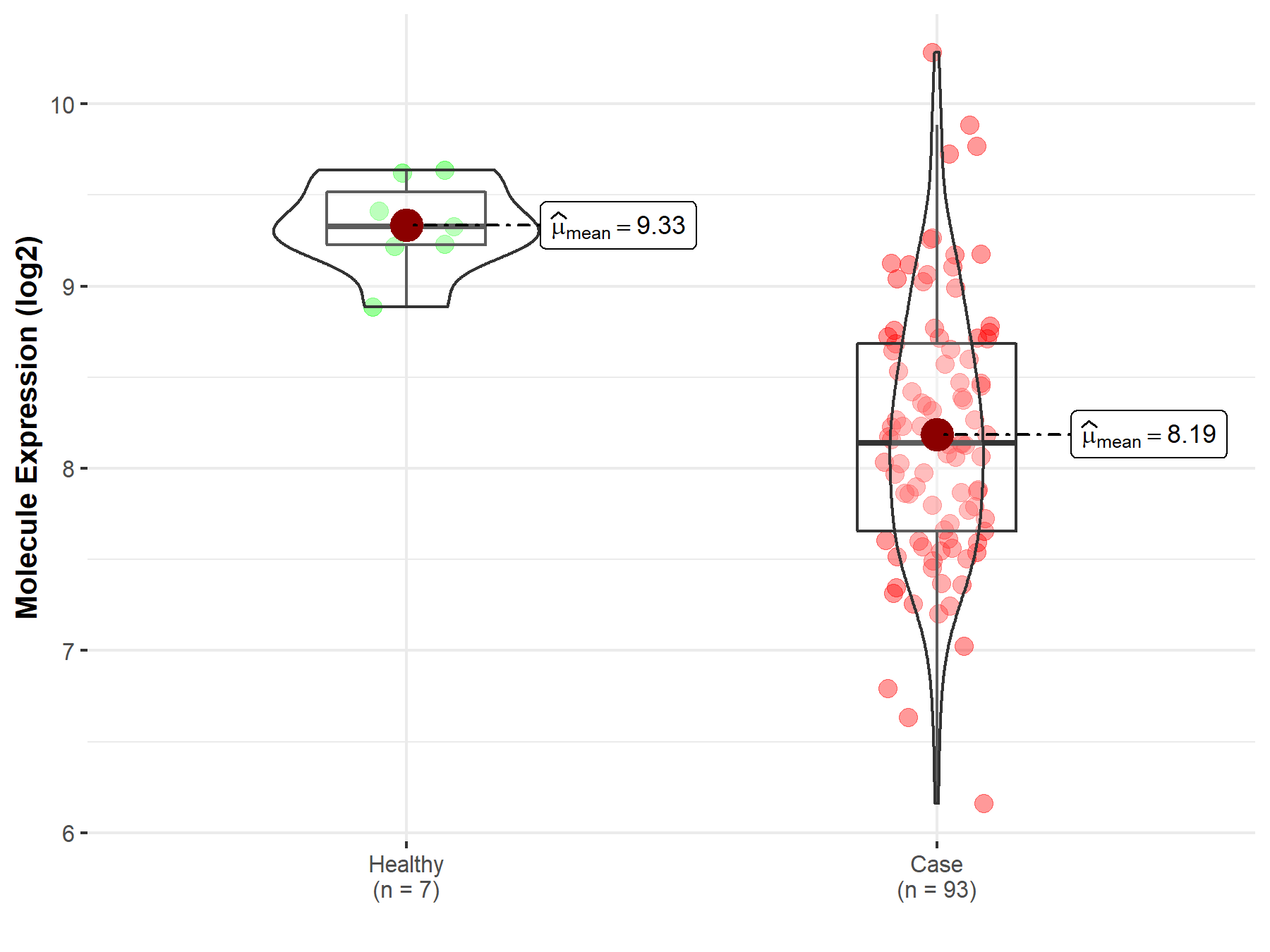
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

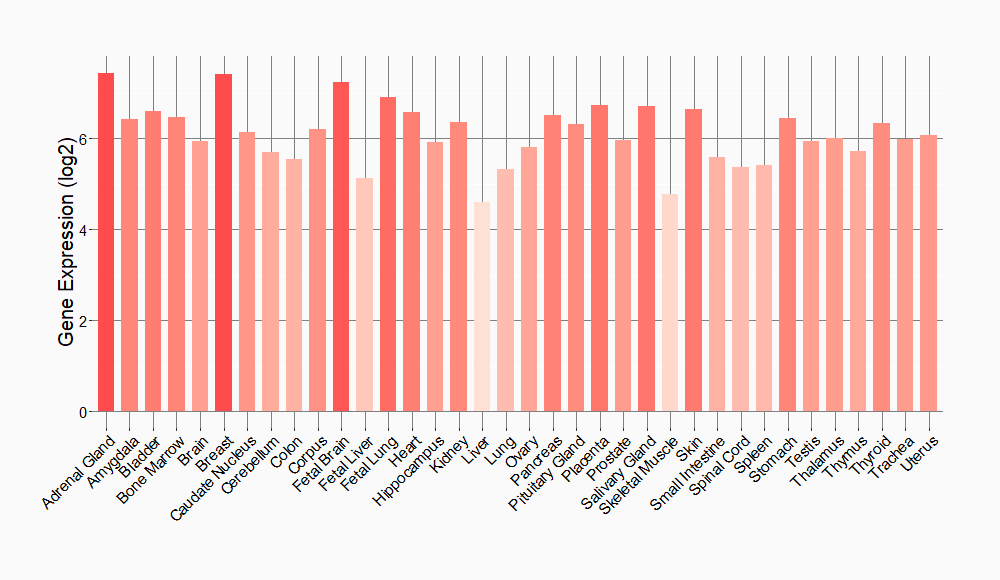
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
