Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00593)
| Name |
GTPase Nras (NRAS)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Transforming protein N-Ras; HRAS1
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
NRAS
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr1:114704469-114716771[-]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MTEYKLVVVGAGGVGKSALTIQLIQNHFVDEYDPTIEDSYRKQVVIDGETCLLDILDTAG
QEEYSAMRDQYMRTGEGFLCVFAINNSKSFADINLYREQIKRVKDSDDVPMVLVGNKCDL PTRTVDTKQAHELAKSYGIPFIETSAKTRQGVEDAFYTLVREIRQYRMKKLNSSDDGTQG CMGLPCVVM Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Ras proteins bind GDP/GTP and possess intrinsic GTPase activity.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
20 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.18E-03 Fold-change: -9.71E-02 Z-score: -3.11E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell viability | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 |
| H1299 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Flow cytometry assay; Caspase-3 Activity Assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-29a renders lung cancer cells more sensitive to cisplatin treatment and miR-29a and cisplatin combination promoted apoptotic effect through targeting NRAS in lung cancer cells. | |||
| Disease Class: Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | [6] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | SGC7901 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0520 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | NRAS and E2F2 as the direct targets of miR-26a were further confirmed in luciferase activity assays and miR-26a-mediated these two genes expression analysis. Our results also found that knockdown of NRAS or E2F2 sensitize GC cells to cisplatin. miR-26a overexpression has been demonstrated to improve the sensitivity of GC cells to cisplatin and this effect was considered to be mediated via its targets NRAS and E2F2. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [2] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Binimetinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61K (c.181C>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.59 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.74 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-10
|
-
S
-
S
-
G
-
R
-
E
-
N
-
L
-
Y
-
F
-
Q
0
|
S
G
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
G
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
K
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
S
S
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
A
A
D
D
I
I
N
N
L
L
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
D
D
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
T
T
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
H
H
E
E
L
L
A
A
K
K
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
E
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
Q
Q
Y
Y
R
R
M
M
K
K
170
|
K
K
L
L
N
N
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Cutaneous melanoma tissue | N.A. | |||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.Q61K (c.181C>A) in gene NRAS cause the sensitivity of Binimetinib by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [2] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Binimetinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61R (c.182A>G) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.59 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.24 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
S
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
G
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
R
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
S
S
K
K
S
D
90
|
F
F
A
A
D
D
I
I
N
N
L
L
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
D
D
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
T
T
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
H
H
E
E
L
L
A
A
K
K
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
E
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
Q
Q
Y
Y
R
R
M
M
K
K
170
|
K
-
L
-
N
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Cutaneous melanoma tissue | N.A. | |||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.Q61R (c.182A>G) in gene NRAS cause the sensitivity of Binimetinib by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [2] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Binimetinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61R (c.182A>G) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.59 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.24 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
S
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
G
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
R
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
S
S
K
K
S
D
90
|
F
F
A
A
D
D
I
I
N
N
L
L
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
D
D
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
T
T
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
H
H
E
E
L
L
A
A
K
K
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
E
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
Q
Q
Y
Y
R
R
M
M
K
K
170
|
K
-
L
-
N
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Cutaneous melanoma tissue | N.A. | |||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.Q61R (c.182A>G) in gene NRAS cause the sensitivity of Binimetinib by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [2] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Binimetinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61L (c.182A>T) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Cutaneous melanoma tissue | N.A. | |||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.Q61L (c.182A>T) in gene NRAS cause the sensitivity of Binimetinib by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [2] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Binimetinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61L (c.182A>T) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Cutaneous melanoma tissue | N.A. | |||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.Q61L (c.182A>T) in gene NRAS cause the sensitivity of Binimetinib by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Chronic myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A20.0] | [3], [4] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Chronic myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A20.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Bosutinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12V |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.98 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.96 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
-
0
|
S
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
V
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
S
S
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
D
D
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
K
H
H
K
K
E
E
K
K
170
|
M
M
S
S
K
K
D
D
G
G
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
180
|
K
K
S
S
K
K
T
T
K
K
C
C
V
V
I
I
M
M
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | JAKT2/STAT signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04030 | ||||||||||
| RAF/KRAS/MEK signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04010 | |||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | HL60 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0002 | |||||||||
| U937 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0007 | ||||||||||
| K562 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0004 | ||||||||||
| KCL-22 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2091 | ||||||||||
| Sup-B15 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0103 | ||||||||||
| HEL cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0001 | ||||||||||
| HMC-1.2 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_H205 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Sanger Sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | This mutation is well known for its effects on proliferation and its association with AML and MPN, suggesting that this variant might have been involved in the TkI resistance of this patient. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Metastatic colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2D85.0] | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Metastatic colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2D85.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Cetuximab | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12C |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.40 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.60 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
G
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
C
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
R
V
V
D
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
Q
H
Y
K
R
E
L
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | EGFR/RAS signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa01521 | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | LIM1215 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2574 | |||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Liquid biopsies assay; Functional analyses of cell populations assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Acquired resistance to EGFR blockade is driven by the emergence of kRAS/NRAS mutations or the development of EGFR extracellular domain (ECD) variants, which impair antibody binding. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [7], [8], [9] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Dabrafenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61K |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.59 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.74 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-10
|
-
S
-
S
-
G
-
R
-
E
-
N
-
L
-
Y
-
F
-
Q
0
|
S
G
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
G
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
K
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
S
S
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
A
A
D
D
I
I
N
N
L
L
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
D
D
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
T
T
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
H
H
E
E
L
L
A
A
K
K
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
E
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
Q
Q
Y
Y
R
R
M
M
K
K
170
|
K
K
L
L
N
N
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-exome sequencing assay; Sanger sequencing assay; Next generation assay; Single PCR-based analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Progression-free and post-progression survival asaay; Computed tomography assay; Positron emission tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Another post-relapse tumor harbored an acquired NRASQ61k missense mutation together with focal BRAF amplification. The resistant tumor from a third patient harbored both a MEk2 mutation and BRAF amplification. Resistance mechanisms are identified in 9/11 progressing tumours and MAPk reactivation occurred in 9/10 tumours, commonly via BRAF amplification and mutations activating NRAS and MEk2. Our data confirming that MEk2C125S, but not the synonymous MEk1C121S protein, confers resistance to combination therapy highlight the functional differences between these kinases and the preponderance of MEk2 mutations in combination therapy-resistant melanomas. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [9], [10] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Dabrafenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61R |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.59 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.24 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
S
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
G
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
R
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
S
S
K
K
S
D
90
|
F
F
A
A
D
D
I
I
N
N
L
L
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
D
D
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
T
T
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
H
H
E
E
L
L
A
A
K
K
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
E
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
Q
Q
Y
Y
R
R
M
M
K
K
170
|
K
-
L
-
N
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | MAPK signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04010 | ||||||||||
| PI3K/AKT/PTEN signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | |||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next generation assay; Single PCR-based analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Computed tomography assay; Positron emission tomography assay; Progression-free and overall survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | NRAS mutations (Q61R and Q61k in codon 61) were detected in two of ten patients (20%). Somatic mutations in NRAS (Q61k/R/L, G12D/R and G13R) were detected till date by whole exome sequencing in 8-18% of BRAF inhibitor-resistant patients; in most cases, as a late event beyond 12 weeks of therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [9] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Dabrafenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12R |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.40 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.50 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
G
G
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
R
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
D
D
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
K
H
H
K
K
E
E
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | MAPK signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04010 | ||||||||||
| PI3K/AKT/PTEN signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-exome sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Progression-free and overall survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Somatic mutations in NRAS (Q61k/R/L, G12D/R and G13R) were detected till date by whole exome sequencing in 8-18% of BRAF inhibitor-resistant patients; in most cases, as a late event beyond 12 weeks of therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [9], [11] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Dabrafenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12D |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.40 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
G
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
D
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
R
V
V
D
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
Q
H
Y
K
R
E
L
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | MAPK signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04010 | ||||||||||
| PI3K/AKT/PTEN signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-exome sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Progression-free and overall survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Somatic mutations in NRAS (Q61k/R/L, G12D/R and G13R) were detected till date by whole exome sequencing in 8-18% of BRAF inhibitor-resistant patients; in most cases, as a late event beyond 12 weeks of therapy. The Prog that did not show evidence of MAPk reactivation by GSEA had two identified resistance mechanisms (MEk2E207k and NRASG12D), but both variants occurred at low frequency (13 and 15% allelic frequency, respectively, by whole-exome sequencing), suggesting heterogeneity within the Prog metastasis. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [9] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Dabrafenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61L |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | MAPK signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04010 | ||||||||||
| PI3K/AKT/PTEN signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-exome sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Progression-free and overall survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Somatic mutations in NRAS (Q61k/R/L, G12D/R and G13R) were detected till date by whole exome sequencing in 8-18% of BRAF inhibitor-resistant patients; in most cases, as a late event beyond 12 weeks of therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [9] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Dabrafenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G13R |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | MAPK signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04010 | ||||||||||
| PI3K/AKT/PTEN signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-exome sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Progression-free and overall survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Somatic mutations in NRAS (Q61k/R/L, G12D/R and G13R) were detected till date by whole exome sequencing in 8-18% of BRAF inhibitor-resistant patients; in most cases, as a late event beyond 12 weeks of therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Chronic myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A20.0] | [3], [4] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Chronic myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A20.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Dasatinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12V |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.98 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.96 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
-
0
|
S
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
V
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
S
S
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
D
D
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
K
H
H
K
K
E
E
K
K
170
|
M
M
S
S
K
K
D
D
G
G
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
180
|
K
K
S
S
K
K
T
T
K
K
C
C
V
V
I
I
M
M
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | JAKT2/STAT signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04030 | ||||||||||
| RAF/KRAS/MEK signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04010 | |||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | HL60 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0002 | |||||||||
| U937 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0007 | ||||||||||
| K562 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0004 | ||||||||||
| KCL-22 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2091 | ||||||||||
| Sup-B15 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0103 | ||||||||||
| HEL cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0001 | ||||||||||
| HMC-1.2 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_H205 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Sanger Sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | This mutation is well known for its effects on proliferation and its association with AML and MPN, suggesting that this variant might have been involved in the TkI resistance of this patient. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Chronic myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A20.0] | [3], [4] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Chronic myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A20.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Imatinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12V |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.98 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.96 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
-
0
|
S
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
V
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
S
S
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
D
D
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
K
H
H
K
K
E
E
K
K
170
|
M
M
S
S
K
K
D
D
G
G
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
180
|
K
K
S
S
K
K
T
T
K
K
C
C
V
V
I
I
M
M
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | JAKT2/STAT signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04030 | ||||||||||
| RAF/KRAS/MEK signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04010 | |||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | HL60 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0002 | |||||||||
| U937 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0007 | ||||||||||
| K562 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0004 | ||||||||||
| KCL-22 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2091 | ||||||||||
| Sup-B15 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0103 | ||||||||||
| HEL cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0001 | ||||||||||
| HMC-1.2 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_H205 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Sanger Sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | This mutation is well known for its effects on proliferation and its association with AML and MPN, suggesting that this variant might have been involved in the TkI resistance of this patient. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [12] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Lapatinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V14A |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [12] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Lapatinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.F78L |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [12] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Lapatinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.F28S |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [12] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Lapatinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.A66T |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.1] | [13] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Lonafarnib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | CHLA-15 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6594 |
| CHLA-20 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6602 | |
| CHLA-90 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6610 | |
| CHLA-95 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6611 | |
| CHLA-171 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6597 | |
| COG-N-426 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_LF58 | |
| COG-N-415 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_AQ23 | |
| COG-N-557 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0389 | |
| LA-N-5 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0389 | |
| LA-N-6 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1363 | |
| NB-1643 cells | Adrenal | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5627 | |
| NB-EBC1 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_E218 | |
| SK-N-FI cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1702 | |
| SMS-LHN cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_9539 | |
| CHP-134 cells | Adrenal gland | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1124 | |
| Kelly cells | Adrenal | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2092 | |
| LA-N-1 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1827 | |
| SH-SY5Y cells | Abdomen | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0019 | |
| GI-ME-N cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1232 | |
| NBL-S cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2136 | |
| NGP cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2141 | |
| In Vivo Model | NSG mice model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR; RNA and miRNA extraction assay; RT-qPCR; Gene expression analysis; Immunoblotting assay; Dual-luciferase assay; Immunohistochemistry | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell viability assay; Synergy assay; Cell cycle assay; Apoptosis assay; Magnetic resonance imaging assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Targeting Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) is a promising therapeutic strategy for aberrant ALK-expressing malignancies including neuroblastoma, but resistance to ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitors (ALK TKI) is a distinct possibility necessitating drug combination therapeutic approaches. Using high-throughput, genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 knockout screens, we identify miR-1304-5p loss as a desensitizer to ALK TKIs in aberrant ALK-expressing neuroblastoma; inhibition of miR-1304-5p decreases, while mimics of this miRNA increase the sensitivity of neuroblastoma cells to ALK TKIs. We show that miR-1304-5p targets NRAS, decreasing cell viability via induction of apoptosis. It follows that the farnesyltransferase inhibitor (FTI) lonafarnib in addition to ALK TKIs act synergistically in neuroblastoma, inducing apoptosis in vitro. In particular, on combined treatment of neuroblastoma patient derived xenografts with an FTI and an ALK TKI complete regression of tumour growth is observed although tumours rapidly regrow on cessation of therapy. Overall, our data suggests that combined use of ALK TKIs and FTIs, constitutes a therapeutic approach to treat high risk neuroblastoma although prolonged therapy is likely required to prevent relapse. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Chronic myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A20.0] | [3], [4] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Chronic myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A20.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Nilotinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12V |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.98 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.96 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
-
0
|
S
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
V
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
S
S
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
D
D
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
K
H
H
K
K
E
E
K
K
170
|
M
M
S
S
K
K
D
D
G
G
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
180
|
K
K
S
S
K
K
T
T
K
K
C
C
V
V
I
I
M
M
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | JAKT2/STAT signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04030 | ||||||||||
| RAF/KRAS/MEK signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04010 | |||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | HL60 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0002 | |||||||||
| U937 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0007 | ||||||||||
| K562 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0004 | ||||||||||
| KCL-22 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2091 | ||||||||||
| Sup-B15 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0103 | ||||||||||
| HEL cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0001 | ||||||||||
| HMC-1.2 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_H205 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Sanger Sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | This mutation is well known for its effects on proliferation and its association with AML and MPN, suggesting that this variant might have been involved in the TkI resistance of this patient. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [14] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Paclitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| MDM231 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5T76 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | microRNA-22 sensitized breast cancer cells to paclitaxel by downregulation of NRAS. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [15] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Pamidronate | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | U266 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0566 |
| ZR75-1 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0588 | |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain B-730P/17 | 287 | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTiter 96 one solution proliferation assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In response to pamidronate, there was significant inhibition of cell proliferation in MDA-231 and SKBR-3 cells, compared to MDA-175 cells. This correlated with their respective basal levels of N-ras and H-ras. N-ras and H-ras protein levels were both reduced in MDA-231 cells, and to lesser extent in SKBR-3 cells, following exposure to pamidronate, whereas these markers were not altered in MDA-175 cells, resistance to pamidronate may result from low levels of GTPase-activating proteins, such as N-ras and H-ras, in tumor cells. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Metastatic colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2D85.0] | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Metastatic colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2D85.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Panitumumab | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12C |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.40 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.60 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
G
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
C
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
R
V
V
D
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
Q
H
Y
K
R
E
L
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | EGFR/RAS signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa01521 | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | LIM1215 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2574 | |||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Liquid biopsies assay; Functional analyses of cell populations assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Acquired resistance to EGFR blockade is driven by the emergence of kRAS/NRAS mutations or the development of EGFR extracellular domain (ECD) variants, which impair antibody binding. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [16] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Panitumumab | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | . |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Liquid biopsy assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Mechanisms of resistance to EGFR blockade include the emergence of kRAS, NRAS and EGFR extracellular domain mutations as well as HER2/MET alterations. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [17] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Panitumumab | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | . |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Mutations in kRAS, NRAS, and BRAF and amplification of ERBB2 and MET drive primary (de novo) resistance to anti-EGFR treatment. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [18] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Pembrolizumab | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61R |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.59 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.24 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
S
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
G
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
R
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
S
S
K
K
S
D
90
|
F
F
A
A
D
D
I
I
N
N
L
L
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
D
D
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
T
T
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
H
H
E
E
L
L
A
A
K
K
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
E
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
Q
Q
Y
Y
R
R
M
M
K
K
170
|
K
-
L
-
N
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Circulating tumour DNA (ctDNA) analysis; Whole genome plasma DNA sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Computer tomography (CT) assay; Positron emission tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Mutations in NRAS have been found in 8-26% of patients with acquired resistance to BRAF inhibitors. We analysed the presence of NRASQ61k and NRASQ61R in the ctDNA extracted from 7 melanoma patients with progressive disease who had previously responded to treatment with vemurafenib (n = 2) or dabrafenib/trametinib (n = 5). Two samples were positive for NRASQ61k and one sample had an NRASQ61R mutation, all three were derived from patients treated with dabrafenib/trametinib. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [12] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Pertuzumab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V14A |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [12] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Pertuzumab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.F78L |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [12] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Pertuzumab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.F28S |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [12] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Pertuzumab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.A66T |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Chronic myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A20.0] | [3], [4] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Chronic myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A20.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Ponatinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12V |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.98 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.96 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
-
0
|
S
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
V
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
S
S
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
D
D
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
K
H
H
K
K
E
E
K
K
170
|
M
M
S
S
K
K
D
D
G
G
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
180
|
K
K
S
S
K
K
T
T
K
K
C
C
V
V
I
I
M
M
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | JAKT2/STAT signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04030 | ||||||||||
| RAF/KRAS/MEK signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04010 | |||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | HL60 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0002 | |||||||||
| U937 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0007 | ||||||||||
| K562 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0004 | ||||||||||
| KCL-22 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2091 | ||||||||||
| Sup-B15 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0103 | ||||||||||
| HEL cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0001 | ||||||||||
| HMC-1.2 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_H205 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Sanger Sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | This mutation is well known for its effects on proliferation and its association with AML and MPN, suggesting that this variant might have been involved in the TkI resistance of this patient. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [19] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Trametinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61K (c.181C>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.59 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.74 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-10
|
-
S
-
S
-
G
-
R
-
E
-
N
-
L
-
Y
-
F
-
Q
0
|
S
G
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
G
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
K
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
S
S
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
A
A
D
D
I
I
N
N
L
L
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
D
D
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
T
T
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
H
H
E
E
L
L
A
A
K
K
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
E
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
Q
Q
Y
Y
R
R
M
M
K
K
170
|
K
K
L
L
N
N
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | H1299 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 | |||||||||
| SW1271 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1716 | ||||||||||
| H2347 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1550 | ||||||||||
| H2087 cells | Lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1524 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell Titer blue reagent assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.Q61K (c.181C>A) in gene NRAS cause the sensitivity of Trametinib by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [12] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Trastuzumab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V14A |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [12] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Trastuzumab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.F78L |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [12] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Trastuzumab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.F28S |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [12] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Trastuzumab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.A66T |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [12] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Trastuzumab emtansine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V14A |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [12] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Trastuzumab emtansine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.F78L |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [12] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Trastuzumab emtansine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.F28S |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [12] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Trastuzumab emtansine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.A66T |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [7], [9], [20] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Vemurafenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61K |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.59 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.74 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-10
|
-
S
-
S
-
G
-
R
-
E
-
N
-
L
-
Y
-
F
-
Q
0
|
S
G
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
G
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
K
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
S
S
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
A
A
D
D
I
I
N
N
L
L
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
D
D
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
T
T
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
H
H
E
E
L
L
A
A
K
K
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
E
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
Q
Q
Y
Y
R
R
M
M
K
K
170
|
K
K
L
L
N
N
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | MAPK signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04010 | ||||||||||
| PI3K/AKT/PTEN signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | |||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | M229 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_D748 | |||||||||
| M238 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_D751 | ||||||||||
| M249 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_D755 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-exome sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Progression-free and overall survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Somatic mutations in NRAS (Q61k/R/L, G12D/R and G13R) were detected till date by whole exome sequencing in 8-18% of BRAF inhibitor-resistant patients; in most cases, as a late event beyond 12 weeks of therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [21], [22] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Vemurafenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61K |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.59 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.74 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-10
|
-
S
-
S
-
G
-
R
-
E
-
N
-
L
-
Y
-
F
-
Q
0
|
S
G
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
G
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
K
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
S
S
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
A
A
D
D
I
I
N
N
L
L
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
D
D
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
T
T
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
H
H
E
E
L
L
A
A
K
K
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
E
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
Q
Q
Y
Y
R
R
M
M
K
K
170
|
K
K
L
L
N
N
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Liquid biopsy assay; Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay; Digital PCR assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Overall and disease-free assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Overexpression of PDGFRbeta or N-RAS(Q61k) conferred PLX4032 resistance to PLX4032-sensitive parental cell lines. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [23] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Vemurafenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61K |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.59 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.74 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-10
|
-
S
-
S
-
G
-
R
-
E
-
N
-
L
-
Y
-
F
-
Q
0
|
S
G
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
G
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
K
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
S
S
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
A
A
D
D
I
I
N
N
L
L
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
D
D
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
T
T
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
H
H
E
E
L
L
A
A
K
K
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
E
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
Q
Q
Y
Y
R
R
M
M
K
K
170
|
K
K
L
L
N
N
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | MAPK signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04010 | ||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | BRAFV600E inhibition via vemurafenib induces paradoxical activation of MAPK through increased CRAF activity and acquired NRAS mutation. Moreover, mutations in genes upstream of RAF, such as the activating N-RASQ61K mutation, allow for BRAFV600 melanomas to escape molecular targeting. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [23] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Vemurafenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61K |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.59 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.74 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-10
|
-
S
-
S
-
G
-
R
-
E
-
N
-
L
-
Y
-
F
-
Q
0
|
S
G
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
G
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
K
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
S
S
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
A
A
D
D
I
I
N
N
L
L
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
D
D
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
T
T
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
H
H
E
E
L
L
A
A
K
K
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
E
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
Q
Q
Y
Y
R
R
M
M
K
K
170
|
K
K
L
L
N
N
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | MAPK signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04010 | ||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | BRAFV600E inhibition via vemurafenib induces paradoxical activation of MAPK through increased CRAF activity and acquired NRAS mutation. Moreover, mutations in genes upstream of RAF, such as the activating N-RASQ61K mutation, allow for BRAFV600 melanomas to escape molecular targeting. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [7], [9], [20] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Vemurafenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61R |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.59 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.24 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
S
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
G
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
R
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
S
S
K
K
S
D
90
|
F
F
A
A
D
D
I
I
N
N
L
L
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
D
D
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
T
T
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
H
H
E
E
L
L
A
A
K
K
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
E
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
Q
Q
Y
Y
R
R
M
M
K
K
170
|
K
-
L
-
N
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | MAPK signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04010 | ||||||||||
| PI3K/AKT/PTEN signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | |||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | M229 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_D748 | |||||||||
| M238 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_D751 | ||||||||||
| M249 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_D755 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-exome sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Progression-free and overall survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Somatic mutations in NRAS (Q61k/R/L, G12D/R and G13R) were detected till date by whole exome sequencing in 8-18% of BRAF inhibitor-resistant patients; in most cases, as a late event beyond 12 weeks of therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Multiple myeloma [ICD-11: 2A83.0] | [24] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Multiple myeloma [ICD-11: 2A83.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Vemurafenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61H |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.31 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.20 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
C
G
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
S
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
H
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
L
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
S
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
D
D
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
K
H
H
K
K
E
E
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Ion Torrent semiconductor-based targeted resequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Whole-body magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Although all 5 reference lesions biopsied in month 10 still harbored a BRAFV600E mutation in all MM cells, an additio.l monoallelic NRAS mutation was detectable in each of the 3 lesions resistant to the full dose of vemurafenib. Of note, each lesion harbored a unique, independent, yet clo.l NRAS mutation (NRAS G13R, NRAS G12A, and NRAS Q61H, respectively). | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [7] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Vemurafenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61H |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.31 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.20 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
C
G
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
S
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
H
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
L
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
S
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
D
D
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
K
H
H
K
K
E
E
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole Exome Sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Progression-free survival assay; Overall survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | In contrast, NRAS mutations and BRAF amplifications may still prove responsive to subsequent MEk inhibitor-based regimens, although the existing clinical data suggests that patients who progress following single-agent RAF inhibition are less likely to benefit from MEk inhibitors. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [9] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Vemurafenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12R |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.40 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.50 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
G
G
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
R
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
D
D
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
K
H
H
K
K
E
E
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | MAPK signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04010 | ||||||||||
| PI3K/AKT/PTEN signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-exome sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Progression-free and overall survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Somatic mutations in NRAS (Q61k/R/L, G12D/R and G13R) were detected till date by whole exome sequencing in 8-18% of BRAF inhibitor-resistant patients; in most cases, as a late event beyond 12 weeks of therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Multiple myeloma [ICD-11: 2A83.0] | [24] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Multiple myeloma [ICD-11: 2A83.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Vemurafenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12A |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.40 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.45 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
G
S
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
A
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
D
D
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
K
H
H
K
K
E
E
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Ion Torrent semiconductor-based targeted resequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Whole-body magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Although all 5 reference lesions biopsied in month 10 still harbored a BRAFV600E mutation in all MM cells, an additio.l monoallelic NRAS mutation was detectable in each of the 3 lesions resistant to the full dose of vemurafenib. Of note, each lesion harbored a unique, independent, yet clo.l NRAS mutation (NRAS G13R, NRAS G12A, and NRAS Q61H, respectively). | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [9] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Vemurafenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12D |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.40 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
G
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
D
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
R
V
V
D
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
Q
H
Y
K
R
E
L
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | MAPK signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04010 | ||||||||||
| PI3K/AKT/PTEN signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-exome sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Progression-free and overall survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Somatic mutations in NRAS (Q61k/R/L, G12D/R and G13R) were detected till date by whole exome sequencing in 8-18% of BRAF inhibitor-resistant patients; in most cases, as a late event beyond 12 weeks of therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Multiple myeloma [ICD-11: 2A83.0] | [24] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Multiple myeloma [ICD-11: 2A83.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Vemurafenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G13R |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Ion Torrent semiconductor-based targeted resequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Whole-body magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Although all 5 reference lesions biopsied in month 10 still harbored a BRAFV600E mutation in all MM cells, an additio.l monoallelic NRAS mutation was detectable in each of the 3 lesions resistant to the full dose of vemurafenib. Of note, each lesion harbored a unique, independent, yet clo.l NRAS mutation (NRAS G13R, NRAS G12A, and NRAS Q61H, respectively). | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [9] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Vemurafenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61L |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | MAPK signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04010 | ||||||||||
| PI3K/AKT/PTEN signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-exome sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Progression-free and overall survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Somatic mutations in NRAS (Q61k/R/L, G12D/R and G13R) were detected till date by whole exome sequencing in 8-18% of BRAF inhibitor-resistant patients; in most cases, as a late event beyond 12 weeks of therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [9] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Vemurafenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G13R |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | MAPK signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04010 | ||||||||||
| PI3K/AKT/PTEN signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-exome sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Progression-free and overall survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Somatic mutations in NRAS (Q61k/R/L, G12D/R and G13R) were detected till date by whole exome sequencing in 8-18% of BRAF inhibitor-resistant patients; in most cases, as a late event beyond 12 weeks of therapy. | ||||||||||||
Clinical Trial Drug(s)
4 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [25] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Selumetinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61L (c.182A>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | A375 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0132 |
| Sk-Mel28 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0526 | |
| A2058 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1059 | |
| A375 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0132 | |
| A375 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0132 | |
| A375 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0132 | |
| WM2664 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2765 | |
| SkMEL 30 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0039 | |
| SkMEL 2 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0069 | |
| SH4 cells | Skin | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_7702 | |
| MEXF-535 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| MEXF-1792 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| MEXF-1341 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| M14 cells | Hypodermis | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1395 | |
| GAK cells | Lnguinal lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1225 | |
| Colo829 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1137 | |
| In Vivo Model | Female NIH nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; Crystallization assay; X-ray data collection and structure determination assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTiter-Glo assay; Enzymatic kinase assay | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [19] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Selumetinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61K (c.181C>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.59 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.74 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-10
|
-
S
-
S
-
G
-
R
-
E
-
N
-
L
-
Y
-
F
-
Q
0
|
S
G
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
G
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
K
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
S
S
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
A
A
D
D
I
I
N
N
L
L
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
D
D
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
T
T
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
H
H
E
E
L
L
A
A
K
K
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
E
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
Q
Q
Y
Y
R
R
M
M
K
K
170
|
K
K
L
L
N
N
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | H1299 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 | |||||||||
| SW1271 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1716 | ||||||||||
| H2347 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1550 | ||||||||||
| H2087 cells | Lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1524 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell Titer blue reagent assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.Q61K (c.181C>A) in gene NRAS cause the sensitivity of Selumetinib by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [25] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Selumetinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61K (c.181C>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.59 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.74 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-10
|
-
S
-
S
-
G
-
R
-
E
-
N
-
L
-
Y
-
F
-
Q
0
|
S
G
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
G
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
K
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
S
S
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
A
A
D
D
I
I
N
N
L
L
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
D
D
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
T
T
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
H
H
E
E
L
L
A
A
K
K
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
E
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
Q
Q
Y
Y
R
R
M
M
K
K
170
|
K
K
L
L
N
N
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | A375 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0132 | |||||||||
| Sk-Mel28 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0526 | ||||||||||
| A2058 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1059 | ||||||||||
| A375 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0132 | ||||||||||
| A375 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0132 | ||||||||||
| A375 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0132 | ||||||||||
| WM2664 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2765 | ||||||||||
| SkMEL 30 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0039 | ||||||||||
| SkMEL 2 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0069 | ||||||||||
| SH4 cells | Skin | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_7702 | ||||||||||
| MEXF-535 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| MEXF-1792 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| MEXF-1341 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| M14 cells | Hypodermis | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1395 | ||||||||||
| GAK cells | Lnguinal lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1225 | ||||||||||
| Colo829 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1137 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Female NIH nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; Crystallization assay; X-ray data collection and structure determination assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTiter-Glo assay; Enzymatic kinase assay | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [26] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Selumetinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61K (c.181C>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.59 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.74 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-10
|
-
S
-
S
-
G
-
R
-
E
-
N
-
L
-
Y
-
F
-
Q
0
|
S
G
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
G
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
K
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
S
S
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
A
A
D
D
I
I
N
N
L
L
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
D
D
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
T
T
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
H
H
E
E
L
L
A
A
K
K
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
E
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
Q
Q
Y
Y
R
R
M
M
K
K
170
|
K
K
L
L
N
N
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Skin | N.A. | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.Q61K (c.181C>A) in gene NRAS cause the sensitivity of Selumetinib by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [27] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Selumetinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61R (c.182A>G) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.59 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.24 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
S
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
G
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
R
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
S
S
K
K
S
D
90
|
F
F
A
A
D
D
I
I
N
N
L
L
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
D
D
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
T
T
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
H
H
E
E
L
L
A
A
K
K
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
E
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
Q
Q
Y
Y
R
R
M
M
K
K
170
|
K
-
L
-
N
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTD assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.Q61R (c.182A>G) in gene NRAS cause the sensitivity of Selumetinib by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [25] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Selumetinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G13D (c.38G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.01 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.40 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
-
G
-
G
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
G
G
D
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
R
V
V
D
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
Q
H
Y
K
R
E
L
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | A375 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0132 | |||||||||
| Sk-Mel28 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0526 | ||||||||||
| A2058 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1059 | ||||||||||
| A375 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0132 | ||||||||||
| A375 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0132 | ||||||||||
| A375 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0132 | ||||||||||
| WM2664 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2765 | ||||||||||
| SkMEL 30 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0039 | ||||||||||
| SkMEL 2 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0069 | ||||||||||
| SH4 cells | Skin | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_7702 | ||||||||||
| MEXF-535 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| MEXF-1792 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| MEXF-1341 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| M14 cells | Hypodermis | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1395 | ||||||||||
| GAK cells | Lnguinal lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1225 | ||||||||||
| Colo829 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1137 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Female NIH nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; Crystallization assay; X-ray data collection and structure determination assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTiter-Glo assay; Enzymatic kinase assay | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [27] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Selumetinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61L (c.182A>T) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTD assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.Q61L (c.182A>T) in gene NRAS cause the sensitivity of Selumetinib by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [28] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Tanespimycin | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G13D (c.38G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.01 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.40 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
-
G
-
G
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
G
G
D
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
R
V
V
D
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
Q
H
Y
K
R
E
L
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Human melanoma tissue | N.A. | |||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.G13D (c.38G>A) in gene NRAS cause the sensitivity of Tanespimycin by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [25] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | LY3009120 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61L (c.182A>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | A375 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0132 |
| Sk-Mel28 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0526 | |
| A2058 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1059 | |
| A375 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0132 | |
| A375 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0132 | |
| A375 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0132 | |
| WM2664 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2765 | |
| SkMEL 30 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0039 | |
| SkMEL 2 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0069 | |
| SH4 cells | Skin | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_7702 | |
| MEXF-535 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| MEXF-1792 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| MEXF-1341 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| M14 cells | Hypodermis | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1395 | |
| GAK cells | Lnguinal lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1225 | |
| Colo829 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1137 | |
| In Vivo Model | Female NIH nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; Crystallization assay; X-ray data collection and structure determination assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTiter-Glo assay; Enzymatic kinase assay | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [25] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | LY3009120 | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61K (c.181C>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.59 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.74 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-10
|
-
S
-
S
-
G
-
R
-
E
-
N
-
L
-
Y
-
F
-
Q
0
|
S
G
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
G
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
K
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
S
S
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
A
A
D
D
I
I
N
N
L
L
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
D
D
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
T
T
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
H
H
E
E
L
L
A
A
K
K
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
E
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
Q
Q
Y
Y
R
R
M
M
K
K
170
|
K
K
L
L
N
N
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | A375 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0132 | |||||||||
| Sk-Mel28 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0526 | ||||||||||
| A2058 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1059 | ||||||||||
| A375 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0132 | ||||||||||
| A375 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0132 | ||||||||||
| A375 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0132 | ||||||||||
| WM2664 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2765 | ||||||||||
| SkMEL 30 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0039 | ||||||||||
| SkMEL 2 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0069 | ||||||||||
| SH4 cells | Skin | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_7702 | ||||||||||
| MEXF-535 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| MEXF-1792 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| MEXF-1341 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| M14 cells | Hypodermis | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1395 | ||||||||||
| GAK cells | Lnguinal lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1225 | ||||||||||
| Colo829 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1137 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Female NIH nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; Crystallization assay; X-ray data collection and structure determination assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTiter-Glo assay; Enzymatic kinase assay | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [25] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | LY3009120 | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G13D (c.38G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.01 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.40 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
-
G
-
G
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
G
G
D
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
R
V
V
D
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
Q
H
Y
K
R
E
L
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | A375 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0132 | |||||||||
| Sk-Mel28 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0526 | ||||||||||
| A2058 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1059 | ||||||||||
| A375 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0132 | ||||||||||
| A375 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0132 | ||||||||||
| A375 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0132 | ||||||||||
| WM2664 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2765 | ||||||||||
| SkMEL 30 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0039 | ||||||||||
| SkMEL 2 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0069 | ||||||||||
| SH4 cells | Skin | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_7702 | ||||||||||
| MEXF-535 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| MEXF-1792 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| MEXF-1341 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| M14 cells | Hypodermis | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1395 | ||||||||||
| GAK cells | Lnguinal lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1225 | ||||||||||
| Colo829 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1137 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Female NIH nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; Crystallization assay; X-ray data collection and structure determination assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTiter-Glo assay; Enzymatic kinase assay | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [29] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | PLX4720 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61L (c.182A>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
Preclinical Drug(s)
11 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B55.0] | [30] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B55.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Alpelisib/Binimetinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61H (c.183A>T) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.31 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.20 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
C
G
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
S
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
H
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
L
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
S
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
D
D
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
K
H
H
K
K
E
E
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | RAF/MEK/ERK signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04010 | ||||||||||
| PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | |||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | RMS cells | Soft tissue | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_W527 | |||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Chorioallantoic membrane | Gallus gallus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; FACS; crystal violet staining | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Coinhibition of NRAS or MEK plus PI3Kalpha triggers widespread apoptosis in NRAS-mutated RMS cells. Subtoxic concentrations of the MEK inhibitor MEK162 and the PI3Kalpha-specific inhibitor BYL719 synergized to trigger apoptosis in NRAS-mutated RMS cells in vitro and in vivo. NRAS- or HRAS-mutated cell lines were more vulnerable to MEK162/BYL719 cotreatment than RAS wild-type cell lines, and MEK162/BYL719 cotreatment was more effective to trigger apoptosis in NRAS-mutated than RAS wild-type RMS tumors in vivo. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | [31] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Alpelisib/Binimetinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12D (c.35G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.40 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
G
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
D
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
R
V
V
D
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
Q
H
Y
K
R
E
L
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | NOMO1 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1609 | |||||||||
| BaF3 cells | Bone | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_0161 | ||||||||||
| THP1 cell | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0006 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [29] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | CCT196969 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61L (c.182A>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [29] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | CCT241161 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61L (c.182A>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [32] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Cetuximab/Trametinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12V (c.35G>T) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.98 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.96 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
-
0
|
S
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
V
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
S
S
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
D
D
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
K
H
H
K
K
E
E
K
K
170
|
M
M
S
S
K
K
D
D
G
G
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
180
|
K
K
S
S
K
K
T
T
K
K
C
C
V
V
I
I
M
M
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | NCI-H508 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1564 | |||||||||
| CCK-81 cells | N.A. | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2873 | ||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: T-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A60.3] | [33] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | T-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Compound 3144 | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G13D (c.38G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.01 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.40 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
-
G
-
G
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
G
G
D
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
R
V
V
D
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
Q
H
Y
K
R
E
L
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | RAS signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04014 | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | MEF cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_M515 | |||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Athymic nude Nu/Nu mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Neuroblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.11] | [34] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Neuroblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.11] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Everolimus/Binimetinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61K (c.181C>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.59 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.74 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-10
|
-
S
-
S
-
G
-
R
-
E
-
N
-
L
-
Y
-
F
-
Q
0
|
S
G
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
G
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
K
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
S
S
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
A
A
D
D
I
I
N
N
L
L
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
D
D
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
T
T
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
H
H
E
E
L
L
A
A
K
K
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
E
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
Q
Q
Y
Y
R
R
M
M
K
K
170
|
K
K
L
L
N
N
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | PI3K/mTOR signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Sk-N-AS cells | Adrenal | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1700 | |||||||||
| SH-SY5Y cells | Abdomen | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0019 | ||||||||||
| NGP cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2141 | ||||||||||
| CHP-212 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1125 | ||||||||||
| CHP-134 cells | Adrenal gland | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1124 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; PCR | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Promega assay; FACS assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Combination of mTOR and MEK inhibitors synergistically inhibit downstream signaling and cell growth of NRAS mutant cell lines. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.1] | [13] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Farnesyltransferase Inhibition | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Loss |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | CHLA-15 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6594 |
| CHLA-20 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6602 | |
| CHLA-90 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6610 | |
| CHLA-95 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6611 | |
| CHLA-171 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6597 | |
| COG-N-426 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_LF58 | |
| COG-N-415 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_AQ23 | |
| COG-N-557 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0389 | |
| LA-N-5 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0389 | |
| LA-N-6 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1363 | |
| NB-1643 cells | Adrenal | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5627 | |
| NB-EBC1 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_E218 | |
| SK-N-FI cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1702 | |
| SMS-LHN cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_9539 | |
| CHP-134 cells | Adrenal gland | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1124 | |
| Kelly cells | Adrenal | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2092 | |
| LA-N-1 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1827 | |
| SH-SY5Y cells | Abdomen | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0019 | |
| GI-ME-N cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1232 | |
| NBL-S cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2136 | |
| NGP cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2141 | |
| In Vivo Model | NSG mice model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR; RNA and miRNA extraction assay; RT-qPCR; Gene expression analysis; Immunoblotting assay; Dual-luciferase assay; Immunohistochemistry | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell viability assay; Synergy assay; Cell cycle assay; Apoptosis assay; Magnetic resonance imaging assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Targeting Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) is a promising therapeutic strategy for aberrant ALK-expressing malignancies including neuroblastoma, but resistance to ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitors (ALK TKI) is a distinct possibility necessitating drug combination therapeutic approaches. Using high-throughput, genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 knockout screens, we identify miR-1304-5p loss as a desensitizer to ALK TKIs in aberrant ALK-expressing neuroblastoma; inhibition of miR-1304-5p decreases, while mimics of this miRNA increase the sensitivity of neuroblastoma cells to ALK TKIs. We show that miR-1304-5p targets NRAS, decreasing cell viability via induction of apoptosis. It follows that the farnesyltransferase inhibitor (FTI) lonafarnib in addition to ALK TKIs act synergistically in neuroblastoma, inducing apoptosis in vitro. In particular, on combined treatment of neuroblastoma patient derived xenografts with an FTI and an ALK TKI complete regression of tumour growth is observed although tumours rapidly regrow on cessation of therapy. Overall, our data suggests that combined use of ALK TKIs and FTIs, constitutes a therapeutic approach to treat high risk neuroblastoma although prolonged therapy is likely required to prevent relapse. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Thyroid gland cancer [ICD-11: 2D10.0] | [35] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Thyroid gland cancer [ICD-11: 2D10.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | MK2206 | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61R (c.182A>G) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.59 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.24 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
S
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
G
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
R
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
S
S
K
K
S
D
90
|
F
F
A
A
D
D
I
I
N
N
L
L
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
D
D
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
T
T
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
H
H
E
E
L
L
A
A
K
K
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
E
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
Q
Q
Y
Y
R
R
M
M
K
K
170
|
K
-
L
-
N
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | SW1736 cells | Thyroid | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3883 | |||||||||
| C643 cells | Thyroid gland | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5969 | ||||||||||
| HTH7 cells | Thyroid gland | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6289 | ||||||||||
| Hth74 cells | Thyroid gland | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6288 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.Q61R (c.182A>G) in gene NRAS cause the sensitivity of MK2206 by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [36] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Pimasertib/Regorafenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61K (c.181C>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.59 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.74 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-10
|
-
S
-
S
-
G
-
R
-
E
-
N
-
L
-
Y
-
F
-
Q
0
|
S
G
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
G
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
K
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
S
S
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
A
A
D
D
I
I
N
N
L
L
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
D
D
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
T
T
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
H
H
E
E
L
L
A
A
K
K
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
E
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
Q
Q
Y
Y
R
R
M
M
K
K
170
|
K
K
L
L
N
N
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | HT29 Cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_A8EZ | |||||||||
| H1975 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1511 | ||||||||||
| A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 | ||||||||||
| H460 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0459 | ||||||||||
| LOVO cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0399 | ||||||||||
| H1299 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 | ||||||||||
| HCT15 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0292 | ||||||||||
| COLO205 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_F402 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Female balb/c athymic (nu+/nu+) mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.Q61K (c.181C>A) in gene NRAS cause the sensitivity of Pimasertib + Regorafenib by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [36] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Pimasertib/Regorafenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61K (c.181C>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.59 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.74 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-10
|
-
S
-
S
-
G
-
R
-
E
-
N
-
L
-
Y
-
F
-
Q
0
|
S
G
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
G
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
K
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
S
S
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
A
A
D
D
I
I
N
N
L
L
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
D
D
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
T
T
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
H
H
E
E
L
L
A
A
K
K
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
E
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
Q
Q
Y
Y
R
R
M
M
K
K
170
|
K
K
L
L
N
N
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | HT29 Cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_A8EZ | |||||||||
| H1975 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1511 | ||||||||||
| A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 | ||||||||||
| H460 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0459 | ||||||||||
| LOVO cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0399 | ||||||||||
| H1299 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 | ||||||||||
| HCT15 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0292 | ||||||||||
| COLO205 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_F402 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Female balb/c athymic (nu+/nu+) mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.Q61K (c.181C>A) in gene NRAS cause the sensitivity of Pimasertib + Regorafenib by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [37] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | RAF709 | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61K (c.181C>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.59 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.74 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-10
|
-
S
-
S
-
G
-
R
-
E
-
N
-
L
-
Y
-
F
-
Q
0
|
S
G
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
G
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
K
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
S
S
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
A
A
D
D
I
I
N
N
L
L
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
D
D
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
T
T
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
H
H
E
E
L
L
A
A
K
K
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
E
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
Q
Q
Y
Y
R
R
M
M
K
K
170
|
K
K
L
L
N
N
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | MAPK signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04010 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Promega assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Targeting CRAF could sensitize response to MEK inhibitors in KRAS-mutant tumors. In addition to targeting multiple signaling nodes within the MAPK pathway to maximize both level and duration of signaling inhibition, combining RAF709 with inhibitors targeting the upstream RTK activation such as EGFR, bypass mechanisms such as YAP1 or targeting prosurvival BCL2 family members, may further enhance efficacy and reduce the development of drug resistance. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [37] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | RAF709 | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61K (c.181C>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.59 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.74 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-10
|
-
S
-
S
-
G
-
R
-
E
-
N
-
L
-
Y
-
F
-
Q
0
|
S
G
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
G
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
K
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
S
S
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
A
A
D
D
I
I
N
N
L
L
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
D
D
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
T
T
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
H
H
E
E
L
L
A
A
K
K
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
E
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
Q
Q
Y
Y
R
R
M
M
K
K
170
|
K
K
L
L
N
N
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | MAPK signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04010 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Promega assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Targeting CRAF could sensitize response to MEK inhibitors in KRAS-mutant tumors. In addition to targeting multiple signaling nodes within the MAPK pathway to maximize both level and duration of signaling inhibition, combining RAF709 with inhibitors targeting the upstream RTK activation such as EGFR, bypass mechanisms such as YAP1 or targeting prosurvival BCL2 family members, may further enhance efficacy and reduce the development of drug resistance. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [37] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | RAF709 | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61L (c.182A>T) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | MAPK signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04010 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Promega assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Targeting CRAF could sensitize response to MEK inhibitors in KRAS-mutant tumors. In addition to targeting multiple signaling nodes within the MAPK pathway to maximize both level and duration of signaling inhibition, combining RAF709 with inhibitors targeting the upstream RTK activation such as EGFR, bypass mechanisms such as YAP1 or targeting prosurvival BCL2 family members, may further enhance efficacy and reduce the development of drug resistance. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [38] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Selumetinib/Dactolisib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61K (c.181C>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.59 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.74 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-10
|
-
S
-
S
-
G
-
R
-
E
-
N
-
L
-
Y
-
F
-
Q
0
|
S
G
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
G
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
K
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
S
S
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
A
A
D
D
I
I
N
N
L
L
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
D
D
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
T
T
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
H
H
E
E
L
L
A
A
K
K
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
E
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
Q
Q
Y
Y
R
R
M
M
K
K
170
|
K
K
L
L
N
N
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Liver | N.A. | |||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Female nonobese diabetic/severe combined immunodeficient (NOD/SCID) mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunohistochemistry assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.Q61K (c.181C>A) in gene NRAS cause the sensitivity of Selumetinib + Dactolisib by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | ||||||||||||
Investigative Drug(s)
4 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [39] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Braf inhibitor | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | AKT signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04151 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Data suggest that the presence of mutated NRAS in the melanoma cell population in parallel with mutated BRAF cells results in resistance to BRAF inhibitors, most probably selecting NRAS-mutated cells in the advancing tumor. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [40] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | ERK inhibitors | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12C (c.34G>T) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.40 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.60 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
G
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
C
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
R
V
V
D
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
Q
H
Y
K
R
E
L
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Fluorescence-activated cell sorting assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.G12C (c.34G>T) in gene NRAS cause the sensitivity of ERK inhibitors by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [41] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | N-arachidonoyl dopamine | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12D (c.35G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.40 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
G
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
D
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
R
V
V
D
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
Q
H
Y
K
R
E
L
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | |||||||||
| NIH3T3 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0594 | ||||||||||
| WEHI-3 cells | Peripheral blood | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_3622 | ||||||||||
| Bosc23 cells | Fetal kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_4401 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Promega assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | N-Arachidonoyl Dopamine Inhibits NRAS Neoplastic Transformation by Suppressing Its Plasma Membrane Translocation. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [42] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | PKI-587 | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61K (c.181C>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.59 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.74 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-10
|
-
S
-
S
-
G
-
R
-
E
-
N
-
L
-
Y
-
F
-
Q
0
|
S
G
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
G
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
K
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
S
S
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
A
A
D
D
I
I
N
N
L
L
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
D
D
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
T
T
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
H
H
E
E
L
L
A
A
K
K
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
E
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
Q
Q
Y
Y
R
R
M
M
K
K
170
|
K
K
L
L
N
N
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Nervous tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Brain cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.15E-106; Fold-change: 8.77E-01; Z-score: 1.64E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | Brainstem tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Glioma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.97E-01; Fold-change: 1.73E-01; Z-score: 1.11E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
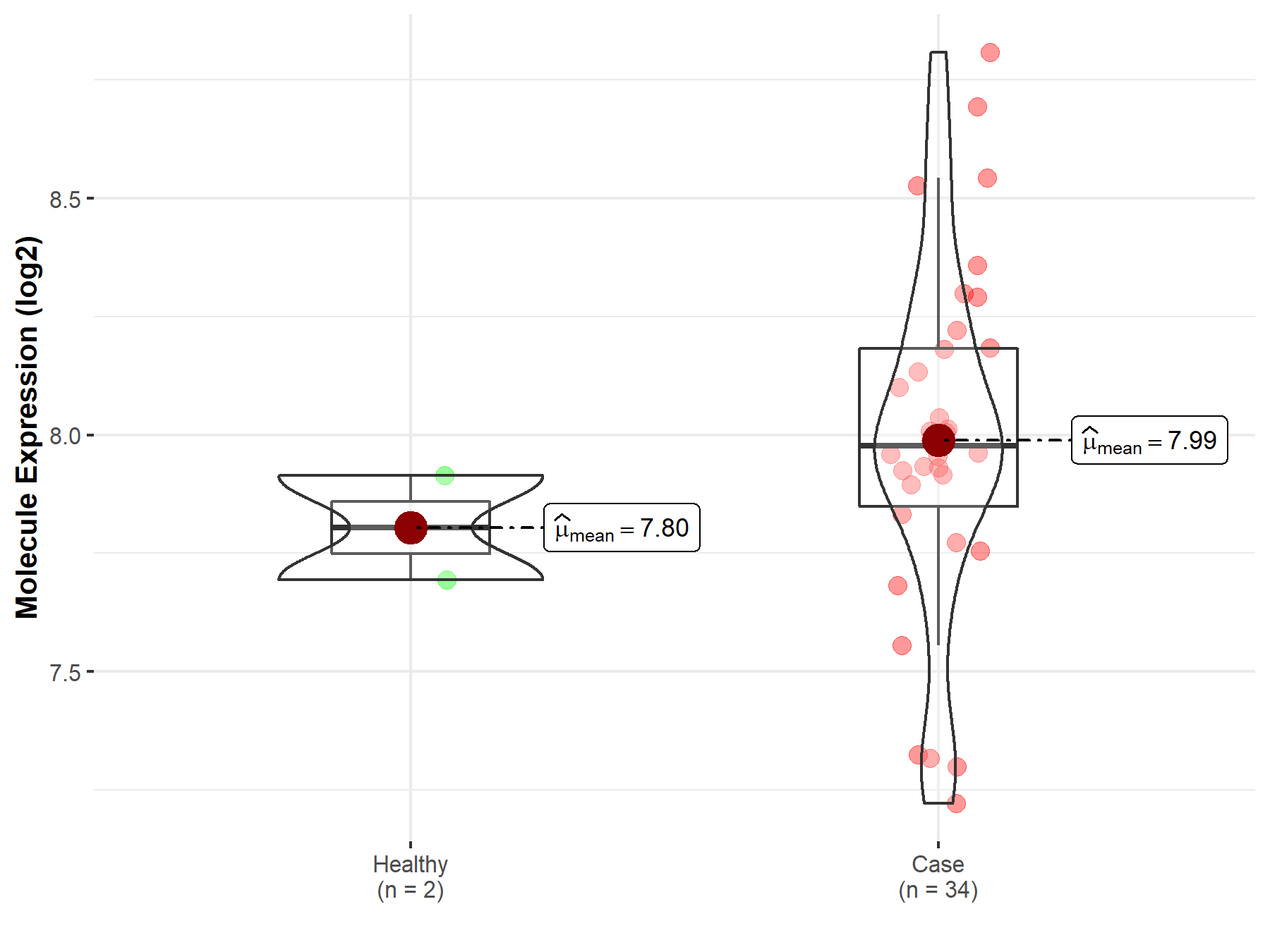
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | White matter | |
| The Specified Disease | Glioma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 6.93E-01; Fold-change: 1.25E-02; Z-score: 2.72E-02 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | Brainstem tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Neuroectodermal tumor | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 8.85E-06; Fold-change: 1.63E+00; Z-score: 2.78E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Whole blood | |
| The Specified Disease | Myelofibrosis | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.61E-01; Fold-change: 1.78E-01; Z-score: 5.30E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
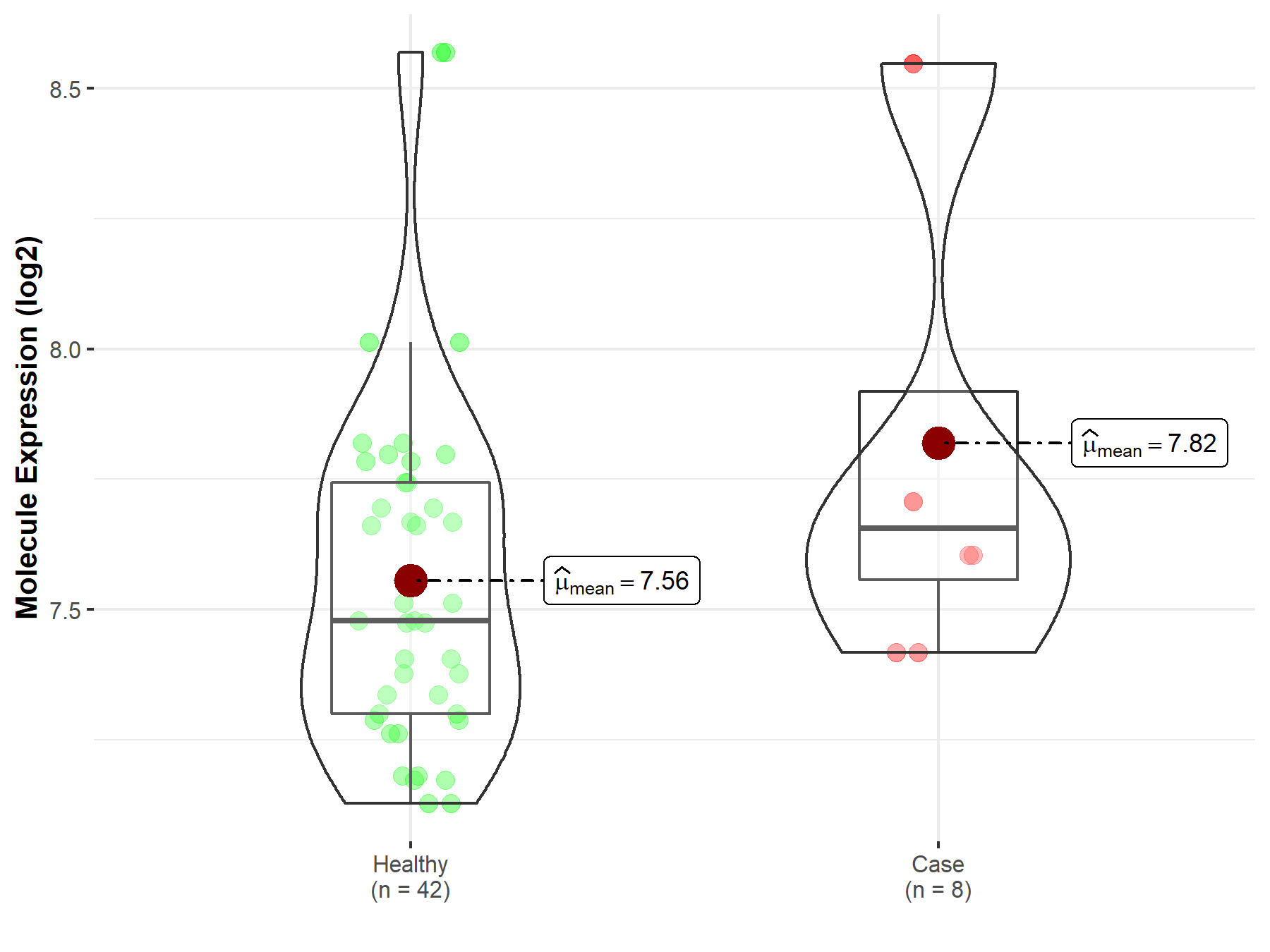
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | Whole blood | |
| The Specified Disease | Polycythemia vera | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 9.11E-01; Fold-change: 7.31E-02; Z-score: 2.22E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
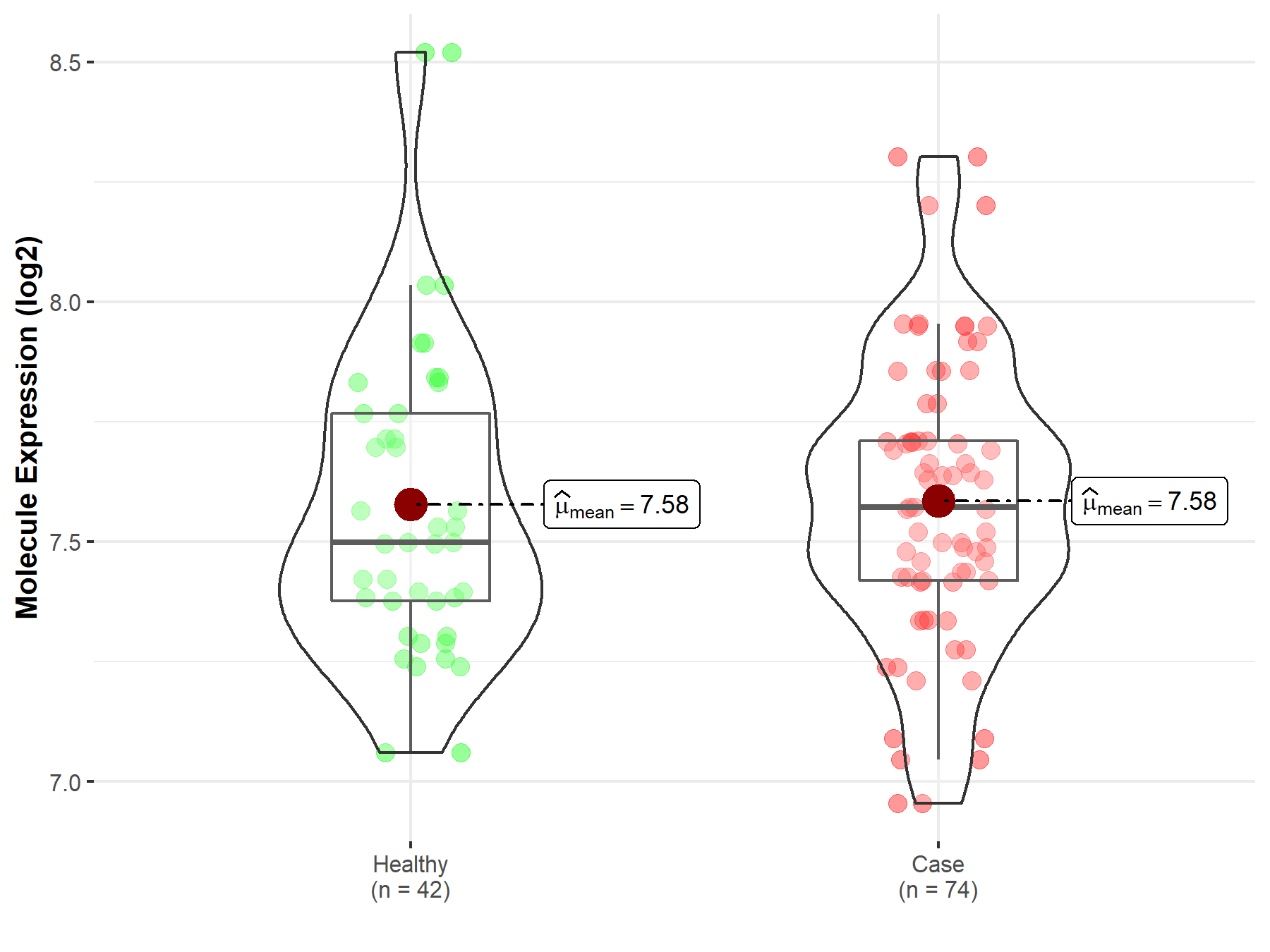
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Bone marrow | |
| The Specified Disease | Acute myeloid leukemia | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 7.75E-30; Fold-change: 6.11E-01; Z-score: 1.46E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
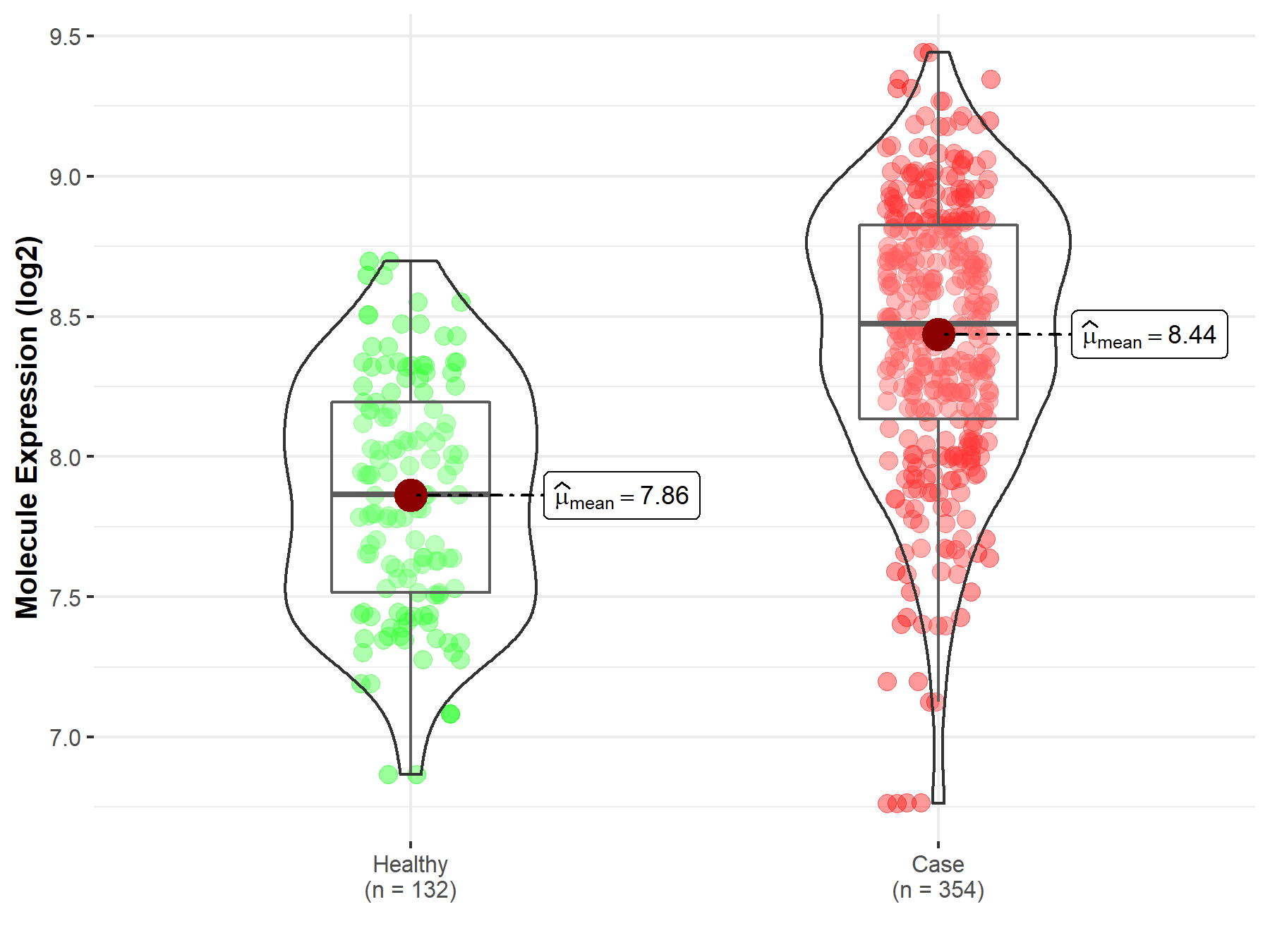
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Bone marrow | |
| The Specified Disease | Multiple myeloma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.29E-04; Fold-change: 5.38E-01; Z-score: 2.03E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
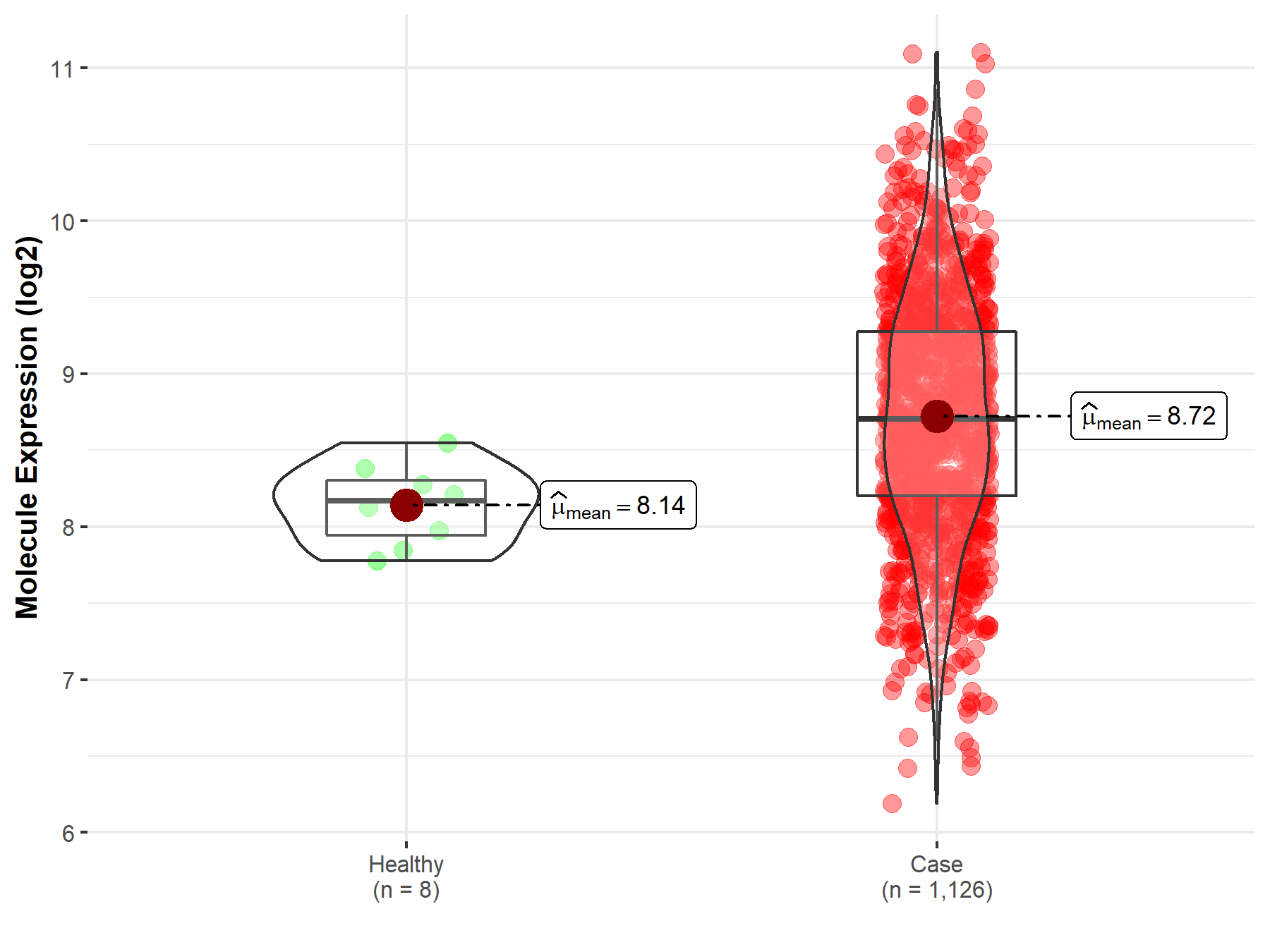
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | Peripheral blood | |
| The Specified Disease | Multiple myeloma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.65E-01; Fold-change: -1.61E-01; Z-score: -4.70E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Gastric tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Gastric cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.88E-01; Fold-change: 7.15E-01; Z-score: 6.55E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 1.81E-04; Fold-change: 4.36E-01; Z-score: 1.21E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung | |
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 4.97E-31; Fold-change: 4.05E-01; Z-score: 1.15E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 1.00E-14; Fold-change: 3.26E-01; Z-score: 7.34E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Skin | |
| The Specified Disease | Melanoma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 7.02E-03; Fold-change: 3.94E-01; Z-score: 6.83E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.25E-26; Fold-change: 3.50E-01; Z-score: 6.95E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 4.60E-04; Fold-change: 2.12E-01; Z-score: 2.99E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
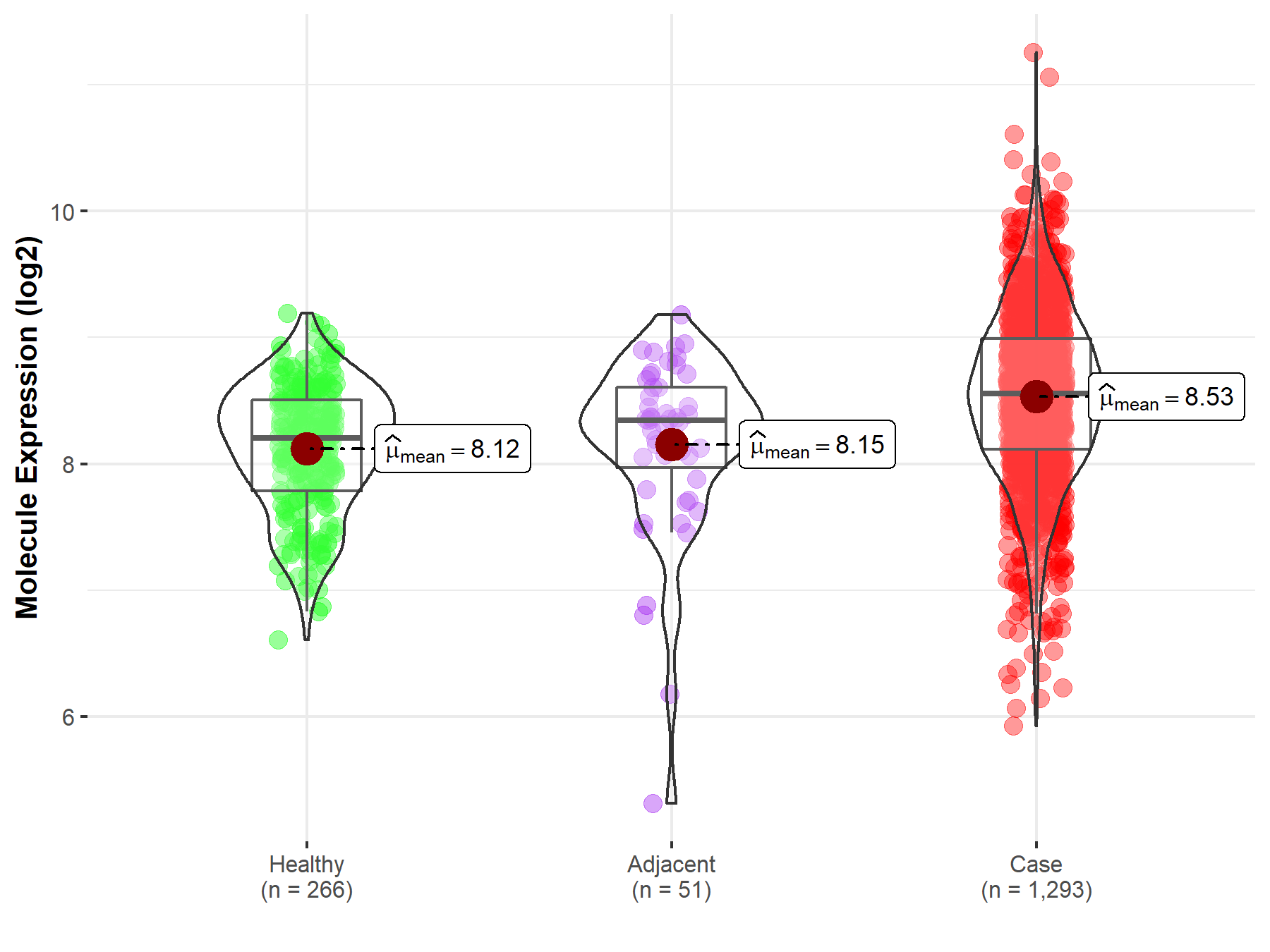
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Thyroid | |
| The Specified Disease | Thyroid cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 5.65E-01; Fold-change: 3.79E-03; Z-score: 1.19E-02 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 1.83E-03; Fold-change: 1.77E-01; Z-score: 4.55E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
