Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00400) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Gentamicin
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Alcomicin; Apogen; Bristagen; Cidomycin; GENTAMYCIN; Garamycin; Garasol; Gentacidin; Gentacycol; Gentafair; Gentak; Gentamar; Gentamicina; Gentamicine; Gentamicins; Gentamicinum; Gentamycinum; Gentavet; Gentocin; Jenamicin; Refobacin; Uromycine; Garamycin Otic Solution; Genoptic Liquifilm; Gentamcin Sulfate; Gentamicin sulphate sterile; Refobacin TM; Gentamicin C1; G-Mycin; G-Myticin; Garamycin (TN); Gentamicin (BAN); Gentamicin (TN); Gentamicina [INN-Spanish]; Gentamicine [INN-French]; Gentamicinum [INN-Latin];Gentamycin-creme; Gentamycin-creme [German]; Ocu-Mycin; Spectro-Genta; U-Gencin; Genoptic S.O.P.; O-2-amino-2,3,4,6,7-pentadeoxy-6-(methylamino)-alpha-D-ribo-heptopyranosyl-(1-4)-O-(3-deoxy-4-C-methyl-3-(methylamino)-beta-L-arabinopyranosyl-(1-6))-2-deoxy-D-streptamine; (1R,2S,3S,4R,6S)-4,6-diamino-3-[3-deoxy-4-C-methyl-3-(methylamino)-beta-L-arabinopyranosyloxy]-2-hydroxycyclohexyl 2-amino-2,3,4,6,7-pentadeoxy-6-(methylamino)-beta-L-lyxo-heptopyranoside; (1R,2S,3S,4R,6S)-4,6-diamino-3-{[3-deoxy-4-C-methyl-3-(methylamino)-beta-L-arabinopyranosyl]oxy}-2-hydroxycyclohexyl (6x)-2-amino-2,3,4,6,7-pentadeoxy-6-(methylamino)-alpha-D-erythro-heptopyranoside; (2R,3R,4R,5R)-2-[(1S,2S,3R,4S,6R)-4,6-diamino-3-[(2R,3R,6S)-3-amino-6-[1-(methylamino)ethyl]oxan-2-yl]oxy-2-hydroxycyclohexyl]oxy-5-methyl-4-(methylamino)oxane-3,5-diol; 2-[4,6-diamino-3-[3-amino-6-[1-(methylamino)ethyl]oxan-2-yl]oxy-2-hydroxycyclohexyl]oxy-5-methyl-4-(methylamino)oxane-3,5-diol; 4,6-diamino-3-{[3-deoxy-4-c-methyl-3-(methylamino)pentopyranosyl]oxy}-2-hydroxycyclohexyl 2-amino-2,3,4,6,7-pentadeoxy-6-(methylamino)heptopyranoside
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
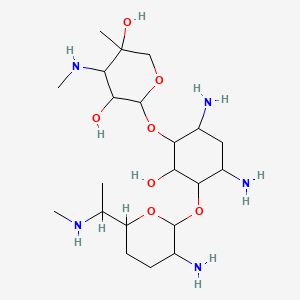
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(13 diseases)
[5]
[6]
[9]
[10]
[11]
[12]
[14]
[16]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Discovered by Cell Line Test for This Drug
(2 diseases)
[13]
[15]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Validated by in-vivo Model for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[17]
|
||||
| Target | Bacterial 30S ribosomal RNA (Bact 30S rRNA) | NOUNIPROTAC | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C21H43N5O7
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CC(C1CCC(C(O1)OC2C(CC(C(C2O)OC3C(C(C(CO3)(C)O)NC)O)N)N)N)NC
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C21H43N5O7/c1-9(25-3)13-6-5-10(22)19(31-13)32-16-11(23)7-12(24)17(14(16)27)33-20-15(28)18(26-4)21(2,29)8-30-20/h9-20,25-29H,5-8,22-24H2,1-4H3
|
||||
| InChIKey |
CEAZRRDELHUEMR-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| VARIDT ID | |||||
| INTEDE ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: AAC(6')-Ib family aminoglycoside 6'-N-acetyltransferase (AAC6IB) | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Vibrio cholerae infection [ICD-11: 1A00.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Vibrio cholerae PL107b | 666 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR and DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Commercial antimicrobial discs assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The expression of aac(6')-Ib lead to drug resistance. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Vibrio cholerae infection [ICD-11: 1A00.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Vibrio cholerae PG262(b) | 666 | ||
| Vibrio cholerae PL61 | 666 | |||
| Vibrio cholerae PL78/6 | 666 | |||
| Vibrio cholerae PL105b | 666 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR and DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Commercial antimicrobial discs assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The expression of dfrA1 lead to drug resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: Dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Vibrio cholerae infection [ICD-11: 1A00.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Vibrio cholerae PG170 | 666 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR and DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Commercial antimicrobial discs assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The expression of dfrA15 lead to drug resistance. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: 16S rRNA (guanine(1405)-N(7))-methyltransferase (RMTA) | [18] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Intergeneric lateral gene transfer |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Pseudomonas aeruginosa AR-2 | 287 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR screening assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The 16S rRNA methylase gene has undergone intergeneric horizontal gene transfer from some aminoglycoside producing microorganisms to Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which is called rmtA. rmtA protect bacterial 16S rRNA from intrinsic aminoglycosides by methylation. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside N(3)-acetyltransferase (AACC2) | [1], [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 | 1322345 | ||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates | 287 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Various aminoglycoside modifying enzymes were associated with overlapping phenotypes: 36.5% strains produced AAC(6')-I with either a serine (GEN-TOB-NET) or a leucine (TOB-NET-AMk) at position 119, or both variants (GEN-TOB-NET-AMk); 21.2% expressed ANT(2")-I (GEN-TOB), 7.7% AAC(3)-II (GEN-TOB-NET), 5.8% AAC(3)-I (GEN) and 1.9% AAC(6')-II (GEN-TOB-NET-AMk) or AACA7 (TOB-NET-AMk). | |||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside acetyltransferase (AAC) | [19] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Vibrio fluvialis infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Vibrio fluvialis H-08942 | 676 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR; DNA sequencing assay; Southern hybridization assay; Cloning and expression assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Aac(3)-Id is a new type of aminoglycoside acetyltransferase gene which causes drug resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside acetyltransferase (AAC) | [20] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli DH5alpha | 668369 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR mapping and sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Macrodilution broth method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Aac(3)-Ic gene could contribute to aminoglycoside resistance with a pattern typical of AAC(3)-I enzymes. | |||
| Key Molecule: Acetylpolyamine amidohydrolase (APAH) | [21] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Achromobacter xylosoxydans infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli | 668369 | ||
| Achromobacter xylosoxydans subsp. denitrificans AX-22 | 85698 | |||
| Escherichia coli MkD-135 | 562 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa 10145/3 | 287 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA extraction and Sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Macrodilution broth method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The aphA15 gene is the first example of an aph-like gene carried on a mobile gene cassette, and its product exhibits close similarity to the APH(3')-IIa aminoglycoside phosphotransferase encoded by Tn5 (36% amino acid identity) and to an APH(3')-IIb enzyme from Pseudomonas aeruginosa (38% amino acid identity). Expression of the cloned aphA15 gene in Escherichia coli reduced the susceptibility to kanamycin and neomycin as well as (slightly) to amikacin, netilmicin, and streptomycin. | |||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside N(3)-acetyltransferase (A3AC) | [22], [23] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli strain DH5a | 668369 | ||
| Enterobacter cloacae strain 88020217 | 550 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The resistance profile conferred by the AAC(3)-VIa enzyme,which encodes this novel 3-N-acetyltransferase,includes high-level resistance to gentamicin,sisomicin, and 6'-N-ethylnetilmicin and moderate levels of resistance to tobramycin and netilmicin. | |||
| Key Molecule: AADA2 protein (AADA2) | [3], [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli JM83 | 562 | ||
| Escherichia coli strain k802N | 562 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain BM2692 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain BM2693 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain BM2694 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain BM2695 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas fluorescens strain BM2687 | 294 | |||
| Pseudomonas fluorescens strain BM2687-1 | 294 | |||
| Pseudomonas fluorescens strain BM2687-2 | 294 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Disk diffusion test assay; E-strip test assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The aac(6')-Ib' gene from Pseudomonas fluorescens BM2687, encoding an aminoglycoside 6'-N-acetyltransferase type II which confers resistance to gentamicin but not to amikacin, was characterized. | |||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside N(3)-acetyltransferase III (A3AC3) | [2], [24] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli strain DH5a | 668369 | ||
| Serratia marcescens strain 82041944 | 615 | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The AAC(3)-V resistance mechanism is characterized by high-level resistance to the aminoglycosides gentamicin, netilmicin, 2'-N-ethylnetilmicin, and 6'-N-ethylnetilmicin and moderate resistance levels to tobramycin. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside N(3)-acetyltransferase (A3AC) | [6] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Escherichia coli infection [ICD-11: 1A03.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli Co227 | 562 | ||
| Escherichia coli Co228 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli Co356 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR; PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis; Sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Multiple-antibiotic-resistant phenotype is associated with gene mutation and mar locus regulation. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Outer membrane protein A (OmpA) | [15] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Tuberculosis [ICD-11: 1B10.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expressiom | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Mycobacterium tuberculosis | 1773 | ||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | These results support the model that the roles of OmpA as a porin protein overexpressing in mycobacteria can increase the hydrophilic ability of the cell wall which can facilitate the streptomycin uptakes and increase the mycobacteria's sensitivity to aminoglycosides. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: OXA-23 carbapenemase (BLA OXA-23) | [9] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Cutaneous bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1B21.4] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Acinetobacter baumannii isolates | 470 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay; Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The isolate was resistant to antibiotics other than ampicillin-sulbactam and colistin, suggesting drug resistance due to carbapenemase production by OXA-23.carbapenem resistance in the isolated carbapenem-resistant A. baumannii strain was at least partially conferred by bla OXA-23-like carbapenemase. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside 2'-N-acetyltransferase (A2NA) | [17] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Mycobacterium smegmatis infection [ICD-11: 1B2Z.3] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Acquired |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli strain DH5a | 668369 | ||
| Mycolicibacterium smegmatis strain EP10 | 1772 | |||
| Mycolicibacterium smegmatis strain mc2155 | 246196 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Southern blot hybridizations assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar macrodilution assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The introduction of a plasmid-located copy of either the aac (2')-Ib or the aac (2')-Id genes into M. smegmatis mc2155 produces an increase in the level of resistance over those values observed in M. smegmatis mc2155. However, the introduction of the plasmid-located aac (2') Ic gene did not lead to an increase in the MICs. In this experiment, an increase of at least two dilutions in the MIC values over those observed in M. smegmatismc2155 with the vector pSUM36 has been assumed to be due to the increase in the activity of the AAC (2') enzyme. The MICs for the 2'-ethylnetilmicin do not change since this aminoglycoside is not a substrate of the AAC (2') enzyme. | |||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside 2'-N-acetyltransferase (A2NA) | [17] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Mycobacterium smegmatis infection [ICD-11: 1B2Z.3] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Acquired |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli strain DH5a | 668369 | ||
| Mycolicibacterium smegmatis strain EP10 | 1772 | |||
| Mycolicibacterium smegmatis strain mc2155 | 246196 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Southern blot hybridizations assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar macrodilution assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The introduction of a plasmid-located copy of either the aac (2')-Ib or the aac (2')-Id genes into M. smegmatis mc2155 produces an increase in the level of resistance over those values observed in M. smegmatis mc2155. However, the introduction of the plasmid-located aac (2') Ic gene did not lead to an increase in the MICs. In this experiment, an increase of at least two dilutions in the MIC values over those observed in M. smegmatismc2155 with the vector pSUM36 has been assumed to be due to the increase in the activity of the AAC (2') enzyme. The MICs for the 2'-ethylnetilmicin do not change since this aminoglycoside is not a substrate of the AAC (2') enzyme. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Phosphatidylglycerol lysyltransferase (MPREF) | [14] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) | 469008 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
TLC and Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Epsilometer test (E test) assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | MprF does not only synthesize Lys-PG but also accomplishes translocation of Lys-PG from the inner to the outer surface of the membrane. Lys-PG mediates CAMP resistance by repulsing the cationic peptides from the outer surface of the membrane. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Biofilms | [13] | |||
| Resistant Disease | staphylococcal infection [ICD-11: 1B5Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | . | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | S. aureus ATCC 12600, L1101 | 5833 | ||
| S. epidermidis ATCC 35984, L1116 | 5833 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Gene expression analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Susceptibility testing; Adherent bacteria count assay; MBEC assay; Scanning electron microscopy assay; Membrane fluidity assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Gentamicin-ketorolac (GS-KT) combination demonstrated synergistic antibacterial action against planktonic Staphylococci. Control and clinical strains showed distinct biofilm growth dynamics and an increase in biofilm maturity was shown to confer further resistance to gentamicin for both 'low-risk' and 'high-risk' biofilms. The addition of ketorolac enhanced the antibiofilm activity of gentamicin against acquired resistance in staphylococcal biofilms. Mechanistic studies revealed that the synergistic action of gentamicin-ketorolac interferes with biofilm morphology and subverts bacterial stress response altering bacterial physiology, membrane dynamics, and biofilm properties. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside N(3)-acetyltransferase (AACC2) | [1], [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Folliculitis [ICD-11: 1B74.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 | 1322345 | ||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates | 287 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Various aminoglycoside modifying enzymes were associated with overlapping phenotypes: 36.5% strains produced AAC(6')-I with either a serine (GEN-TOB-NET) or a leucine (TOB-NET-AMk) at position 119, or both variants (GEN-TOB-NET-AMk); 21.2% expressed ANT(2")-I (GEN-TOB), 7.7% AAC(3)-II (GEN-TOB-NET), 5.8% AAC(3)-I (GEN) and 1.9% AAC(6')-II (GEN-TOB-NET-AMk) or AACA7 (TOB-NET-AMk). | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Outer membrane porin (OMP38) | [7], [8] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Melioidosis [ICD-11: 1C42.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli | 668369 | ||
| Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) | 469008 | |||
| Burkholderia pseudomallei isolates | 28450 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Bps is highly resistant to many antimicrobial agents and this resistance may result from the low drug permeability of outer membrane proteins, known as porins.An Escherichia coli strain defective in most porins, but expressing BpsOmp38, exhibited considerably lower antimicrobial susceptibility than the control strain. In addition, mutation of Tyr119, the most prominent pore-lining residue in BpsOmp38, markedly altered membrane permeability, substitution with Ala (mutant BpsOmp38Y119A) enhanced uptake of the antimicrobial agents, while substitution with Phe (mutant BpsOmp38Y119F) inhibited uptake. | |||
ICD-09: Visual system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside N(3)-acetyltransferase (AACC2) | [1], [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Corneal ulcers [ICD-11: 9A76.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 | 1322345 | ||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates | 287 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Various aminoglycoside modifying enzymes were associated with overlapping phenotypes: 36.5% strains produced AAC(6')-I with either a serine (GEN-TOB-NET) or a leucine (TOB-NET-AMk) at position 119, or both variants (GEN-TOB-NET-AMk); 21.2% expressed ANT(2")-I (GEN-TOB), 7.7% AAC(3)-II (GEN-TOB-NET), 5.8% AAC(3)-I (GEN) and 1.9% AAC(6')-II (GEN-TOB-NET-AMk) or AACA7 (TOB-NET-AMk). | |||
ICD-10: Ear/mastoid process diseasess
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside N(3)-acetyltransferase (AACC2) | [1], [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 | 1322345 | ||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates | 287 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Various aminoglycoside modifying enzymes were associated with overlapping phenotypes: 36.5% strains produced AAC(6')-I with either a serine (GEN-TOB-NET) or a leucine (TOB-NET-AMk) at position 119, or both variants (GEN-TOB-NET-AMk); 21.2% expressed ANT(2")-I (GEN-TOB), 7.7% AAC(3)-II (GEN-TOB-NET), 5.8% AAC(3)-I (GEN) and 1.9% AAC(6')-II (GEN-TOB-NET-AMk) or AACA7 (TOB-NET-AMk). | |||
ICD-12: Respiratory system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: MATE family efflux transporter (ABEM) | [12] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acinetobacter baumannii infection [ICD-11: CA40.4] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli kAM32 | 562 | ||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | AbeM was found to be an H+-coupled multidrug efflux pump and a unique member of the MATE family which lead to drug resistance. | |||
ICD-16: Genitourinary system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside (3'') (9) adenylyltransferase (AADA) | [16] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Urinary tract infection [ICD-11: GC08.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli serogroup O11 | 1095705 | ||
| Escherichia coli serogroup O17 | 1010800 | |||
| Escherichia coli serogroup O73 | 2170725 | |||
| Escherichia coli serogroup O77 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR amplification and sequence alignments assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | All the UTI outbreak CgA strains in this study contained the same class 1 integron dfrA17-aadA5 gene cassette arrangement with 100% sequence match, suggesting clonal spread of the bacterial strain itself. While aminoglycoside adenyltransferase A (aadA ) and dihydrofolate reductase A (dfrA ), encoding resistance to streptomycin and trimethoprim. | |||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside (3'') (9) adenylyltransferase (AADA) | [16] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Urinary tract infection [ICD-11: GC08.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli serogroup O11 | 1095705 | ||
| Escherichia coli serogroup O17 | 1010800 | |||
| Escherichia coli serogroup O73 | 2170725 | |||
| Escherichia coli serogroup O77 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR amplification and sequence alignments assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | All the UTI outbreak CgA strains in this study contained the same class 1 integron dfrA17-aadA5 gene cassette arrangement with 100% sequence match, suggesting clonal spread of the bacterial strain itself. While aminoglycoside adenyltransferase A (aadA ) and dihydrofolate reductase A (dfrA ), encoding resistance to streptomycin and trimethoprim. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) | [16] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Urinary tract infection [ICD-11: GC08.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli serogroup O11 | 1095705 | ||
| Escherichia coli serogroup O17 | 1010800 | |||
| Escherichia coli serogroup O73 | 2170725 | |||
| Escherichia coli serogroup O77 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR amplification and sequence alignments assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | All the UTI outbreak CgA strains in this study contained the same class 1 integron dfrA17-aadA5 gene cassette arrangement with 100% sequence match, suggesting clonal spread of the bacterial strain itself. While aminoglycoside adenyltransferase A (aadA ) and dihydrofolate reductase A (dfrA ), encoding resistance to streptomycin and trimethoprim. | |||
| Key Molecule: Dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) | [16] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Urinary tract infection [ICD-11: GC08.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli serogroup O11 | 1095705 | ||
| Escherichia coli serogroup O17 | 1010800 | |||
| Escherichia coli serogroup O73 | 2170725 | |||
| Escherichia coli serogroup O77 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR amplification and sequence alignments assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | All the UTI outbreak CgA strains in this study contained the same class 1 integron dfrA17-aadA5 gene cassette arrangement with 100% sequence match, suggesting clonal spread of the bacterial strain itself. While aminoglycoside adenyltransferase A (aadA ) and dihydrofolate reductase A (dfrA ), encoding resistance to streptomycin and trimethoprim. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
