Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00301) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Amikacin
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Amicacin; Amikacina; Amikacine; Amikacinum; Amikavet; Amikin; Arikace; Briclin; Kaminax; Lukadin; Mikavir; AMIKACIN SULFATE; Amikacin Base; Amikacin Dihydrate; ANTIBIOTIC BB-K8; Amiglyde-V; Amikacin & Tumor Necrosis Factor; Amikacin (USP); Amikacina [INN-Spanish]; Amikacine [INN-French]; Amikacinum [INN-Latin]; Amikin(Disulfate); Antibiotic BB-K 8; BB-K 8; BB-K8; Amiglyde-V (TN); Amikacin (USP/INN); Amikacin [USAN:BAN:INN]; O-3-Amino-3-deoxy-alpha-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-4)-O-(6-amino-6-deoxy-alpha-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-6))-N(sup 3)-(4-amino-L-2-hydroxybutyryl)-2-deoxy-L-streptamine; O-3-amino-3-deoxy-alpha-D-glucopyranosyl-(1->4)-O-(6-amino-6-deoxy-alpha-D-glucopyranosyl-(1->6))-N(3)-(4-amino-L-2-hydroxybutyryl)-2-deoxy-L-streptamine; O-3-Amino-3-deoxy-.alpha.-D-glucopyranosyl-(1->6)-O-[6-amino-6-deoxy-.alpha.-D-glucopyranosyl-(1->4)]-1-(4-amino-2-hydroxy-1-oxobutyl)-2-deoxy-D-streptamine; (2S)-4-amino-N-[(1R,2S,3S,4R,5S)-5-amino-2-(3-amino-3-deoxy-alpha-D-glucopyranosyloxy)-4-(6-amino-6-deoxy-alpha-D-glucopyranosyloxy)-3-hydroxycyclohexyl]-2-hydroxybutanamide; (2S)-4-amino-N-[(1R,2S,3S,4R,5S)-5-amino-2-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-4-amino-3,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy-4-[(2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-6-(aminomethyl)-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxan-2-yl]oxy-3-hydroxycyclohexyl]-2-hydroxybutanamide; (2S)-4-amino-N-{(1R,2S,3S,4R,5S)-5-amino-2-[(3-amino-3-deoxy-alpha-D-glucopyranosyl)oxy]-4-[(6-amino-6-deoxy-alpha-D-glucopyranosyl)oxy]-3-hydroxycyclohexyl}-2-hydroxybutanamide; 1-N-(L(-)-gamma-Amino-alpha-hydroxybutyryl)kanamycin A
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 2 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
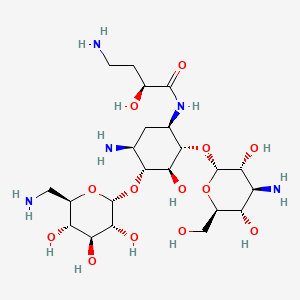
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(4 diseases)
[2]
[2]
[5]
[6]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Discovered by Cell Line Test for This Drug
(3 diseases)
[3]
[4]
[7]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Validated by in-vivo Model for This Drug
(2 diseases)
[8]
[9]
|
||||
| Target | Staphylococcus 30S ribosomal subunit (Stap-coc pbp2) | F4NA87_STAAU | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C22H43N5O13
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
C1[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]1NC(=O)[C@H](CCN)O)O[C@@H]2[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O2)CO)O)N)O)O)O[C@@H]3[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O3)CN)O)O)O)N
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C22H43N5O13/c23-2-1-8(29)20(36)27-7-3-6(25)18(39-22-16(34)15(33)13(31)9(4-24)37-22)17(35)19(7)40-21-14(32)11(26)12(30)10(5-28)38-21/h6-19,21-22,28-35H,1-5,23-26H2,(H,27,36)/t6-,7+,8-,9+,10+,11-,12+,13+,14+,15-,16+,17-,18+,19-,21+,22+/m0/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
LKCWBDHBTVXHDL-RMDFUYIESA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| INTEDE ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: 16S rRNA (guanine(1405)-N(7))-methyltransferase (RMTA) | [10] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Intergeneric lateral gene transfer |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Pseudomonas aeruginosa AR-2 | 287 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR screening assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The 16S rRNA methylase gene has undergone intergeneric horizontal gene transfer from some aminoglycoside producing microorganisms to Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which is called rmtA. rmtA protect bacterial 16S rRNA from intrinsic aminoglycosides by methylation. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside N(6')-acetyltransferase type 1 (A6AC1) | [11] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 | 208964 | ||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa Nk0001 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa Nk0002 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa Nk0003 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa Nk0004 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa Nk0005 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa Nk0006 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa Nk0007 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa Nk0008 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa Nk0009 | 287 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Micro-dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Recombinant AAC(6')-Iag protein showed aminoglycoside 6'-N-acetyltransferase activity using thin-layer chromatography (TLC) and MS spectrometric analysis. Escherichia coli carrying aac(6')-Iag showed resistance to amikacin, arbekacin, dibekacin, isepamicin, kanamycin, sisomicin, and tobramycin; but not to gentamicin.AAC(6')-Iag is a functional acetyltransferase that modifies alternate amino groups on the AGs. | |||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside acetyltransferase (AAC) | [12] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli DH5alpha | 668369 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR mapping and sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Macrodilution broth method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Aac(3)-Ic gene could contribute to aminoglycoside resistance with a pattern typical of AAC(3)-I enzymes. | |||
| Key Molecule: Acetylpolyamine amidohydrolase (APAH) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Achromobacter xylosoxydans infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli | 668369 | ||
| Achromobacter xylosoxydans subsp. denitrificans AX-22 | 85698 | |||
| Escherichia coli MkD-135 | 562 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa 10145/3 | 287 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA extraction and Sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Macrodilution broth method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The aphA15 gene is the first example of an aph-like gene carried on a mobile gene cassette, and its product exhibits close similarity to the APH(3')-IIa aminoglycoside phosphotransferase encoded by Tn5 (36% amino acid identity) and to an APH(3')-IIb enzyme from Pseudomonas aeruginosa (38% amino acid identity). Expression of the cloned aphA15 gene in Escherichia coli reduced the susceptibility to kanamycin and neomycin as well as (slightly) to amikacin, netilmicin, and streptomycin. | |||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside 3'-phosphotransferase (A3AP) | [8] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Streptococcus faecalis infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli strain JM 10 | 562 | ||
| Escherichia coli strain k802 | 562 | |||
| Streptococcus faecnlis strain JHZ-15 | 1351 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Chemical sequencing method assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Disc sensitivity tests assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Strain BM2182 was examined for aminoglyco- side-modifying activities. That kanamycin B was modified and tobramycin (3'-deoxykanamycin B) was not, indicates that the 3'-hydroxyl group is the site of phosphorylation. That butirosin, lividomycin A, and amikacin were phosphorylated indicates that the enzyme is APH-III. | |||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside 3'-phosphotransferase (A3AP) | [13] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Serratia marcescens infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli C41(DE3) | 469008 | ||
| Escherichia coli DH5alpha | 668369 | |||
| Escherichia coli Ecmrs144 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli Ecmrs150 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli Ecmrs151 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain 83-125 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain 83-75 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain JM83 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain JM83(pRPG101) | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain M8820Mu | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain MC1065 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain MC1065(pRPG101) | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain POII1681 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain PRC930(pAO43::Tn9O3) | 562 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains | 573 | |||
| Serratia marcescens strains | 615 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Restriction enzyme treating assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cation-supplemented Mueller-Hinton broth assay; agar dilution with MH agar assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Serratia marcescens at a hospital that had used amikacin as its principal aminoglycoside for the preceding 42 months demonstrated high-level resistance to amikacin (greater than or equal to 256 micrograms/ml), kanamycin (greater than or equal to 256 micrograms/ml), gentamicin (greater than or equal to 64 micrograms/ml), netilmicin (64 micrograms/ml), and tobramycin (greater than or equal to 16 micrograms/ml). The clinical isolates and transformants produced a novel 3'-phosphotransferase, APH(3'), that modified amikacin and kanamycin in vitro. | |||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside N(3)-acetyltransferase III (A3AC3) | [14], [15] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli strain DH5a | 668369 | ||
| Serratia marcescens strain 82041944 | 615 | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The AAC(3)-V resistance mechanism is characterized by high-level resistance to the aminoglycosides gentamicin, netilmicin, 2'-N-ethylnetilmicin, and 6'-N-ethylnetilmicin and moderate resistance levels to tobramycin. | |||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside N-acetyltransferase AAC(6')-IAP | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Lactobacillus casei infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | S. maltophilia JUNP350 | N.A. | ||
| Mechanism Description | Compared with vector control,?E. coli?expressing AAC(6')-Iap showed decreased susceptibilities to arbekacin, amikacin, dibekacin, isepamicin, neomycin, netilmicin, sisomicin, and tobramycin. Thin-layer chromatography (TLC) analysis revealed that all the aminoglycosides tested, except for apramycin and paromomycin, were acetylated by AAC(6')-Iap. These results indicated that?aac(6')-Iap?is a functional acetyltransferase that modifies the 6'-NH2?position of aminoglycosides and is involved in aminoglycoside resistance. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: TolC family outer membrane protein (TOLC) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Acinetobacter baumannii AYE WT | 509173 | ||
| Acinetobacter baumannii AYE detaabuO | 509173 | |||
| Acinetobacter baumannii AYE detaabuO Omega abuO | 509173 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Disk diffusion test assay; E-strip test assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | AbuO, an OMP, confers broad-spectrum antimicrobial resistance via active efflux in A. baumannii. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside acetyltransferase (AAC) | [16] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Escherichia coli infection [ICD-11: 1A03.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli DH5alpha | 668369 | ||
| Escherichia coli SCH92111602 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Dot blot hybridizations assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Standard broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Escherichia coli SCH92111602 expresses an aminoglycoside resistance profile similar to that conferred by the aac(6')-Ie-aph(2")-Ia gene found in gram-positive cocci and was found to contain the aminoglycoside resistance genes aph(2")-Ib and aac(6')-Im (only 44 nucleotides apart). SCH92111602 is an Escherichia coli clinical isolate resistant to a number of aminoglycoside antibiotics, including gentamicin, tobramycin, and amikacin, and contains an approximately 50-kb plasmid. | |||
| Key Molecule: Acetylpolyamine amidohydrolase (APAH) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Escherichia coli infection [ICD-11: 1A03.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Acquired |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli | 668369 | ||
| Achromobacter xylosoxydans subsp. denitrificans AX-22 | 85698 | |||
| Escherichia coli MkD-135 | 562 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa 10145/3 | 287 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA extraction and Sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Macrodilution broth method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The aphA15 gene is the first example of an aph-like gene carried on a mobile gene cassette, and its product exhibits close similarity to the APH(3')-IIa aminoglycoside phosphotransferase encoded by Tn5 (36% amino acid identity) and to an APH(3')-IIb enzyme from Pseudomonas aeruginosa (38% amino acid identity). Expression of the cloned aphA15 gene in Escherichia coli reduced the susceptibility to kanamycin and neomycin as well as (slightly) to amikacin, netilmicin, and streptomycin. | |||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside 2'-N-acetyltransferase (A2NA) | [9] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Escherichia coli infection [ICD-11: 1A03.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Acquired |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli strain DH5a | 668369 | ||
| Escherichia coli strain XLI-Blue | 562 | |||
| Providencia stuartii strain PR50 | 588 | |||
| Providencia stuartii strain SCH75082831A | 588 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Microdilution plates assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | E.coli DH5alpha/pR 1000 demonstrated an AAC(2')-Ia resistance profile,with gentamicin, tobramycin, netilmicin, and 6'-Nethylnetilmicin MICs increased over those seen with E.coli DH5alpha. In addition, E.coli DH5alpha/pR 1000 did not show an elevated 2'-N-ethylnetilmicin MIC (MIC was 0.25ug/ml). Therefore, pR1000 encoded an enzyme capable of acetylating 6'-N-ethylnetilmicin but not 2'-N-ethylnetilmicin, suggesting 2'-N-acetyltransferase activity. DH5alpha/pSCH4500, which contains a subcloned 1.3-kb fragment, also demonstrated an AAC(2')-Ia resistance profile. | |||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside 3'-phosphotransferase (A3AP) | [13] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Escherichia coli infection [ICD-11: 1A03.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Acquired |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli C41(DE3) | 469008 | ||
| Escherichia coli DH5alpha | 668369 | |||
| Escherichia coli Ecmrs144 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli Ecmrs150 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli Ecmrs151 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain 83-125 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain 83-75 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain JM83 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain JM83(pRPG101) | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain M8820Mu | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain MC1065 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain MC1065(pRPG101) | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain POII1681 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain PRC930(pAO43::Tn9O3) | 562 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains | 573 | |||
| Serratia marcescens strains | 615 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Restriction enzyme treating assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cation-supplemented Mueller-Hinton broth assay; agar dilution with MH agar assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The resistant strains contained an identical 6.8-kilobase plasmid, pRPG101. Transformation of pRPG101 into Escherichia coli produced high-level resistance to amikacin (greater than or equal to 256 micrograms/ml) and kanamycin (greater than or equal to 256 micrograms/ml) but unchanged susceptibilities to gentamicin, netilmicin, and tobramycin. The clinical isolates and transformants produced a novel 3'-phosphotransferase, APH(3'), that modified amikacin and kanamycin in vitro. | |||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside 3'-phosphotransferase (A3AP) | [17] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Escherichia coli infection [ICD-11: 1A03.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Acquired |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli strain HB101 | 634468 | ||
| Acinetobacter baumannii strain BM2580 | 470 | |||
| Bacillus subtilis strain BS168 | 1423 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
SDS-PAGE assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The shuttle piasmid pAT239 was constructed by inserting the H/ndlll-linearized staphyococcal piasmid pC194 into the unique H/ndlll site of pAT235. This piasmid, which confers resistance to ampicillin, chloramphenicol and kanamycin in Escherichia coli, was introduced by transformation into Bacillus subtilis strain BS168. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Outer membrane protein A (OmpA) | [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Tuberculosis [ICD-11: 1B10.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expressiom | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Mycobacterium tuberculosis | 1773 | ||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | These results support the model that the roles of OmpA as a porin protein overexpressing in mycobacteria can increase the hydrophilic ability of the cell wall which can facilitate the streptomycin uptakes and increase the mycobacteria's sensitivity to aminoglycosides. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: OXA-23 carbapenemase (BLA OXA-23) | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Cutaneous bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1B21.4] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Acinetobacter baumannii isolates | 470 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay; Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The isolate was resistant to antibiotics other than ampicillin-sulbactam and colistin, suggesting drug resistance due to carbapenemase production by OXA-23.carbapenem resistance in the isolated carbapenem-resistant A. baumannii strain was at least partially conferred by bla OXA-23-like carbapenemase. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: P-type ATPase zinc transporter Rv3270 | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bone infection [ICD-11: 1B2Z.9] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | E. coli XL1-Blue | 562 | ||
| E. coli CS109 | 562 | |||
| M. smegmatis MC2 160 | 1772 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Gene expression analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Antimicrobial susceptibility assay; Intracellular drug accumulation activity assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Metal homeostasis is maintained by the uptake, storage and efflux of metal ions that are necessary for the survival of the bacterium. Homeostasis is mostly regulated by a group of transporters categorized as ABC transporters and P-type ATPases. On the other hand, efflux pumps often play a role in drug-metal cross-resistance. Here, with the help of antibiotic sensitivity, antibiotic/dye accumulation and semi-quantitative biofilm formation assessments we report the ability of Rv3270, a P-type ATPase known for its role in combating Mn2+ and Zn2+ metal ion toxicity in Mycobacterium tuberculosis, in influencing the extrusion of multiple structurally unrelated drugs and enhancing the biofilm formation of Escherichia coli and Mycobacterium smegmatis. Overexpression of Rv3270 increased the tolerance of host cells to norfloxacin, ofloxacin, sparfloxacin, ampicillin, oxacillin, amikacin and isoniazid. A significantly lower accumulation of norfloxacin, ethidium bromide, bocillin FL and levofloxacin in cells harbouring Rv3270 as compared to host cells indicated its role in enhancing efflux activity. Although over-expression of Rv3270 did not alter the susceptibility levels of levofloxacin, rifampicin and apramycin, the presence of a sub-inhibitory concentration of Zn2+ resulted in low-level tolerance towards these drugs. Of note, the expression of Rv3270 enhanced the biofilm-forming ability of the host cells strengthening its role in antimicrobial resistance. Therefore, the study indicated that the over-expression of Rv3270 enhances the drug efflux activity of the micro-organism where zinc might facilitate drug-metal cross-resistance for some antibiotics. | |||
ICD-12: Respiratory system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside 3'-phosphotransferase (A3AP) | [13] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Klebsiella pneumoniae infection [ICD-11: CA40.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli C41(DE3) | 469008 | ||
| Escherichia coli DH5alpha | 668369 | |||
| Escherichia coli Ecmrs144 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli Ecmrs150 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli Ecmrs151 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain 83-125 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain 83-75 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain JM83 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain JM83(pRPG101) | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain M8820Mu | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain MC1065 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain MC1065(pRPG101) | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain POII1681 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain PRC930(pAO43::Tn9O3) | 562 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains | 573 | |||
| Serratia marcescens strains | 615 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Restriction enzyme treating assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cation-supplemented Mueller-Hinton broth assay; agar dilution with MH agar assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Serratia marcescens at a hospital that had used amikacin as its principal aminoglycoside for the preceding 42 months demonstrated high-level resistance to amikacin (greater than or equal to 256 micrograms/ml), kanamycin (greater than or equal to 256 micrograms/ml), gentamicin (greater than or equal to 64 micrograms/ml), netilmicin (64 micrograms/ml), and tobramycin (greater than or equal to 16 micrograms/ml). The clinical isolates and transformants produced a novel 3'-phosphotransferase, APH(3'), that modified amikacin and kanamycin in vitro. | |||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside 3'-phosphotransferase (A3AP) | [17] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acinetobacter baumannii infection [ICD-11: CA40.4] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli strain HB101 | 634468 | ||
| Acinetobacter baumannii strain BM2580 | 470 | |||
| Bacillus subtilis strain BS168 | 1423 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Amino acid sequence comparison assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Resistance to aminogiycosides in Aeinetobaeter is widespread and is mainly the result of the production of enzymes which modify the antibiotics. The enzymes beiong to three ciasses: phosphotransferases (APH), acetyltransferases (AAC). A. baumahnii strain BM2580, a representative of one of these epidemics, was shown to synthesize a 3'-aminoglycoside phosphotransferase. Substrate specificity and DNA annealing studies indicated that the isozyme in A. baumannii was of a new type, designated APH(3')-VI. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Multidrug efflux SMR transporter (ABES) | [6] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acinetobacter baumannii infection [ICD-11: CA40.4] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli kAM32 | 562 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Fluorometric efflux assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth dilution assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The abeS gene product conferred resistance to various antimicrobial compounds through an efflux mechanism. | |||
ICD-16: Genitourinary system diseases
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside (3'') (9) adenylyltransferase (AADA) | [18] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Urinary tract infection [ICD-11: GC08.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli serogroup O11 | 1095705 | ||
| Escherichia coli serogroup O17 | 1010800 | |||
| Escherichia coli serogroup O73 | 2170725 | |||
| Escherichia coli serogroup O77 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR amplification and sequence alignments assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | All the UTI outbreak CgA strains in this study contained the same class 1 integron dfrA17-aadA5 gene cassette arrangement with 100% sequence match, suggesting clonal spread of the bacterial strain itself. While aminoglycoside adenyltransferase A (aadA ) and dihydrofolate reductase A (dfrA ), encoding resistance to streptomycin and trimethoprim. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) | [18] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Urinary tract infection [ICD-11: GC08.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli serogroup O11 | 1095705 | ||
| Escherichia coli serogroup O17 | 1010800 | |||
| Escherichia coli serogroup O73 | 2170725 | |||
| Escherichia coli serogroup O77 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR amplification and sequence alignments assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | All the UTI outbreak CgA strains in this study contained the same class 1 integron dfrA17-aadA5 gene cassette arrangement with 100% sequence match, suggesting clonal spread of the bacterial strain itself. While aminoglycoside adenyltransferase A (aadA ) and dihydrofolate reductase A (dfrA ), encoding resistance to streptomycin and trimethoprim. | |||
| Key Molecule: Dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) | [18] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Urinary tract infection [ICD-11: GC08.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli serogroup O11 | 1095705 | ||
| Escherichia coli serogroup O17 | 1010800 | |||
| Escherichia coli serogroup O73 | 2170725 | |||
| Escherichia coli serogroup O77 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR amplification and sequence alignments assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | All the UTI outbreak CgA strains in this study contained the same class 1 integron dfrA17-aadA5 gene cassette arrangement with 100% sequence match, suggesting clonal spread of the bacterial strain itself. While aminoglycoside adenyltransferase A (aadA ) and dihydrofolate reductase A (dfrA ), encoding resistance to streptomycin and trimethoprim. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
