Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00086) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Tobramycin
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Aktob; Brulamycin; Distobram; Gotabiotic; NEBRAMYCIN; Nebcin; Nebicin; Obracin; Obramycin; Sybryx; TOY; Tenebrimycin;Tenemycin; Tobacin; Tobi; Tobracin; Tobradex; Tobradistin; Tobralex; Tobramaxin; Tobramicin; Tobramicina; Tobramitsetin; Tobramycetin; Tobramycine; Tobramycinum; Tobrased; Tobrasone; Tobrex; Deoxykanamycin B; Nebramycin VI; TOBRAMYCIN SULFATE; Tobramycin for Inhalation; Tobramycin solution for inhalation; A 12253A; Lilly 47663; NF 6; Nebramycin 6; Nebramycin factir 6; Nebramycin factor 6; Nebcin (Sulfate); SPRC-AB01; TobraDex (TN); Tobracin (TN); Tobramicina [INN-Spanish]; Tobramycin, Free Base; Tobramycine [INN-French]; Tobramycinum [INN-Latin]; Tobrex (TN); Tobramycin (JP15/USP); Tobramycin[USAN:BAN:INN:JAN]; TOA-(1-6)2TB-(4-1)TOC; TOA-(1-6)TOB-(4-1)TOC; 1-Epitobramycin; 3'-Deoxykanamycin B
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
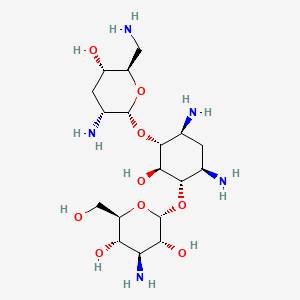
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(12 diseases)
[2]
[8]
[2]
[2]
[9]
[2]
[2]
[2]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Discovered by Cell Line Test for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[5]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Validated by in-vivo Model for This Drug
(3 diseases)
[1]
[10]
[11]
|
||||
| Target | Bacterial 30S ribosomal RNA (Bact 30S rRNA) | NOUNIPROTAC | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C18H37N5O9
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
C1[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]1N)O[C@@H]2[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O2)CO)O)N)O)O)O[C@@H]3[C@@H](C[C@@H]([C@H](O3)CN)O)N)N
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C18H37N5O9/c19-3-9-8(25)2-7(22)17(29-9)31-15-5(20)1-6(21)16(14(15)28)32-18-13(27)11(23)12(26)10(4-24)30-18/h5-18,24-28H,1-4,19-23H2/t5-,6+,7+,8-,9+,10+,11-,12+,13+,14-,15+,16-,17+,18+/m0/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
NLVFBUXFDBBNBW-PBSUHMDJSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| INTEDE ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: 16S rRNA (guanine(1405)-N(7))-methyltransferase (RMTA) | [12] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Intergeneric lateral gene transfer |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Pseudomonas aeruginosa AR-2 | 287 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR screening assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The 16S rRNA methylase gene has undergone intergeneric horizontal gene transfer from some aminoglycoside producing microorganisms to Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which is called rmtA. rmtA protect bacterial 16S rRNA from intrinsic aminoglycosides by methylation. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside N(3)-acetyltransferase (AACC2) | [6], [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 | 1322345 | ||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates | 287 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Various aminoglycoside modifying enzymes were associated with overlapping phenotypes: 36.5% strains produced AAC(6')-I with either a serine (GEN-TOB-NET) or a leucine (TOB-NET-AMk) at position 119, or both variants (GEN-TOB-NET-AMk); 21.2% expressed ANT(2")-I (GEN-TOB), 7.7% AAC(3)-II (GEN-TOB-NET), 5.8% AAC(3)-I (GEN) and 1.9% AAC(6')-II (GEN-TOB-NET-AMk) or AACA7 (TOB-NET-AMk). | |||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside adenyltransferase 2''-Ia (ANT2I) | [13], [14] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Acinetobacter baumannii AB5075 | 1116234 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Etest assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | ANT(2")-Ia confers resistance by magnesium-dependent transfer of a nucleoside monophosphate (AMP) to the 2"-hydroxyl of aminoglycoside substrates containing a 2-deoxystreptamine core. | |||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside N(6')-acetyltransferase type 1 (A6AC1) | [15] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 | 208964 | ||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa Nk0001 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa Nk0002 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa Nk0003 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa Nk0004 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa Nk0005 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa Nk0006 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa Nk0007 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa Nk0008 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa Nk0009 | 287 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Micro-dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Recombinant AAC(6')-Iag protein showed aminoglycoside 6'-N-acetyltransferase activity using thin-layer chromatography (TLC) and MS spectrometric analysis. Escherichia coli carrying aac(6')-Iag showed resistance to amikacin, arbekacin, dibekacin, isepamicin, kanamycin, sisomicin, and tobramycin; but not to gentamicin.AAC(6')-Iag is a functional acetyltransferase that modifies alternate amino groups on the AGs. | |||
| Key Molecule: AacA43 aminoglycoside (AACA43) | [16] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Klebsiella pneumoniae LT12 | 573 | ||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae SSI2.46 | 573 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Like related aminoglycoside-(6')-acetyltransferases, AacA43 confers clinically relevant resistance to kanamycin, tobramycin, and some less-used aminoglycosides but not to gentamicin. | |||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside acetyltransferase (AAC) | [17] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli DH5alpha | 668369 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR mapping and sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Macrodilution broth method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Aac(3)-Ic gene could contribute to aminoglycoside resistance with a pattern typical of AAC(3)-I enzymes. | |||
| Key Molecule: AAC(6')-Ib family aminoglycoside 6'-N-acetyltransferase (AAC6IB) | [18] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli DH10B | 316385 | ||
| Escherichia coli HB101 | 634468 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853 | 287 | |||
| Escherichia coli JM109 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli k-12 | 83333 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa Pa695 | 287 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR experiments assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Disk diffusion method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The fusion product was functional, as was the product of each gene cloned separately: AAC(3)-I, despite the deletion of the four last amino acids, and AAC(6"), which carried three amino acid changes compared with the most homologous sequence. The AAC(3)-I protein conferred an expected gentamicin and fortimicin resistance, and the AAC(6"), despite the Leu-119-Ser substitution, yielded resistance to kanamycin, tobramycin, and dibekacin, but slightly affected netilmicin and amikacin, and had no apparent effect on gentamicin. The fusion product conveyed a large profile of resistance, combining the AAC(6") activity with a higher level of gentamicin resistance without accompanying fortimicin resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: Acetylpolyamine amidohydrolase (APAH) | [19] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Achromobacter xylosoxydans infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli | 668369 | ||
| Achromobacter xylosoxydans subsp. denitrificans AX-22 | 85698 | |||
| Escherichia coli MkD-135 | 562 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa 10145/3 | 287 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA extraction and Sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Macrodilution broth method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The aphA15 gene is the first example of an aph-like gene carried on a mobile gene cassette, and its product exhibits close similarity to the APH(3')-IIa aminoglycoside phosphotransferase encoded by Tn5 (36% amino acid identity) and to an APH(3')-IIb enzyme from Pseudomonas aeruginosa (38% amino acid identity). Expression of the cloned aphA15 gene in Escherichia coli reduced the susceptibility to kanamycin and neomycin as well as (slightly) to amikacin, netilmicin, and streptomycin. | |||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside N(6')-acetyltransferase type 1 (A6AC1) | [3], [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli JM83 | 562 | ||
| Escherichia coli strain k802N | 562 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain BM2692 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain BM2693 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain BM2694 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain BM2695 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas fluorescens strain BM2687 | 294 | |||
| Pseudomonas fluorescens strain BM2687-1 | 294 | |||
| Pseudomonas fluorescens strain BM2687-2 | 294 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Disk diffusion test assay; E-strip test assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The aac(6')-Ib' gene from Pseudomonas fluorescens BM2687, encoding an aminoglycoside 6'-N-acetyltransferase type II which confers resistance to gentamicin but not to amikacin, was characterized. | |||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside N-acetyltransferase AAC(6')-IAP | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Lactobacillus casei infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | S. maltophilia JUNP350 | N.A. | ||
| Mechanism Description | Compared with vector control,?E. coli?expressing AAC(6')-Iap showed decreased susceptibilities to arbekacin, amikacin, dibekacin, isepamicin, neomycin, netilmicin, sisomicin, and tobramycin. Thin-layer chromatography (TLC) analysis revealed that all the aminoglycosides tested, except for apramycin and paromomycin, were acetylated by AAC(6')-Iap. These results indicated that?aac(6')-Iap?is a functional acetyltransferase that modifies the 6'-NH2?position of aminoglycosides and is involved in aminoglycoside resistance. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Chaperone protein ClpB (CLPB) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Pseudomonas aeruginosa MPAO1 | 1131757 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
SRM analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The extracellular polysaccharide layer of biofilm can prolong the time of bactericide penetration into the central cell cluster. The proteomic response of Pseudomonas aeruginosa depends on the level of tobramycin experienced by the cells after exposure to various sub inhibitory levels (0.1-1) u Tobramycin (g / ml) can induce different proteins. Bacterial cells exposed to low levels of tobramycin showed elevated levels of enzymes that metabolize and synthesize amino acids that may alter drug sensitivity. Inactivation of ibpA did not yield significant tobramycin MIC changes. However, inactivation of two heat shock proteins/proteases ibpA/clpB, ibpA/PA0779, or ibpA/hslV led to increased tobramycin sensitivity changes in P. aeruginosa. | |||
| Key Molecule: ATP-dependent protease subunit HslV (HSlV) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Pseudomonas aeruginosa MPAO1 | 1131757 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
SRM analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The extracellular polysaccharide layer of biofilm can prolong the time of bactericide penetration into the central cell cluster. The proteomic response of Pseudomonas aeruginosa depends on the level of tobramycin experienced by the cells after exposure to various sub inhibitory levels (0.1-1) u Tobramycin (g / ml) can induce different proteins. Bacterial cells exposed to low levels of tobramycin showed elevated levels of enzymes that metabolize and synthesize amino acids that may alter drug sensitivity. Inactivation of ibpA did not yield significant tobramycin MIC changes. However, inactivation of two heat shock proteins/proteases ibpA/clpB, ibpA/PA0779, or ibpA/hslV led to increased tobramycin sensitivity changes in P. aeruginosa. | |||
| Key Molecule: Heat-shock protein IbpA (IBPA) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Pseudomonas aeruginosa MPAO1 | 1131757 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
SRM analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The extracellular polysaccharide layer of biofilm can prolong the time of bactericide penetration into the central cell cluster. The proteomic response of Pseudomonas aeruginosa depends on the level of tobramycin experienced by the cells after exposure to various sub inhibitory levels (0.1-1) u Tobramycin (g / ml) can induce different proteins. Bacterial cells exposed to low levels of tobramycin showed elevated levels of enzymes that metabolize and synthesize amino acids that may alter drug sensitivity. Inactivation of ibpA did not yield significant tobramycin MIC changes. However, inactivation of two heat shock proteins/proteases ibpA/clpB, ibpA/PA0779, or ibpA/hslV led to increased tobramycin sensitivity changes in P. aeruginosa. | |||
| Key Molecule: Lon protease (LON) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Pseudomonas aeruginosa MPAO1 | 1131757 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
SRM analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The extracellular polysaccharide layer of biofilm can prolong the time of bactericide penetration into the central cell cluster. The proteomic response of Pseudomonas aeruginosa depends on the level of tobramycin experienced by the cells after exposure to various sub inhibitory levels (0.1-1) u Tobramycin (g / ml) can induce different proteins. Bacterial cells exposed to low levels of tobramycin showed elevated levels of enzymes that metabolize and synthesize amino acids that may alter drug sensitivity. Inactivation of ibpA did not yield significant tobramycin MIC changes. However, inactivation of two heat shock proteins/proteases ibpA/clpB, ibpA/PA0779, or ibpA/hslV led to increased tobramycin sensitivity changes in P. aeruginosa. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside acetyltransferase (AAC) | [8] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Escherichia coli infection [ICD-11: 1A03.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli DH5alpha | 668369 | ||
| Escherichia coli SCH92111602 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Dot blot hybridizations assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Standard broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Escherichia coli SCH92111602 expresses an aminoglycoside resistance profile similar to that conferred by the aac(6')-Ie-aph(2")-Ia gene found in gram-positive cocci and was found to contain the aminoglycoside resistance genes aph(2")-Ib and aac(6')-Im (only 44 nucleotides apart). SCH92111602 is an Escherichia coli clinical isolate resistant to a number of aminoglycoside antibiotics, including gentamicin, tobramycin, and amikacin, and contains an approximately 50-kb plasmid. | |||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside acetyltransferase (AAC) | [8] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Escherichia coli infection [ICD-11: 1A03.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Acquired |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli DH5alpha | 668369 | ||
| Escherichia coli SCH92111602 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Dot blot hybridizations assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Standard broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Plasmid DNA isolated from this strain was introduced into Escherichia coli DH5alpha by transformation, and colonies were selected on Luria-Bertani agar plates containing 10 ug of tobramycin per ml. Analysis of restriction digests on agarose gels of DNA from a tobramycin-resistant transformant confirmed the presence of the same 50-kb plasmid that was isolated from Escherichia coli SCH92111602. | |||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside 2'-N-acetyltransferase (A2NA) | [10] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Escherichia coli infection [ICD-11: 1A03.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Acquired |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli strain DH5a | 668369 | ||
| Escherichia coli strain XLI-Blue | 562 | |||
| Providencia stuartii strain PR50 | 588 | |||
| Providencia stuartii strain SCH75082831A | 588 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Microdilution plates assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | E.coli DH5alpha/pR 1000 demonstrated an AAC(2')-Ia resistance profile,with gentamicin, tobramycin, netilmicin, and 6'-Nethylnetilmicin MICs increased over those seen with E.coli DH5alpha. In addition, E.coli DH5alpha/pR 1000 did not show an elevated 2'-N-ethylnetilmicin MIC (MIC was 0.25ug/ml). Therefore, pR1000 encoded an enzyme capable of acetylating 6'-N-ethylnetilmicin but not 2'-N-ethylnetilmicin, suggesting 2'-N-acetyltransferase activity. DH5alpha/pSCH4500, which contains a subcloned 1.3-kb fragment, also demonstrated an AAC(2')-Ia resistance profile. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside 2'-N-acetyltransferase (A2NA) | [11] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Mycobacterium smegmatis infection [ICD-11: 1B2Z.3] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Acquired |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli strain DH5a | 668369 | ||
| Mycolicibacterium smegmatis strain EP10 | 1772 | |||
| Mycolicibacterium smegmatis strain mc2155 | 246196 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Southern blot hybridizations assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar macrodilution assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The introduction of a plasmid-located copy of either the aac (2')-Ib or the aac (2')-Id genes into M. smegmatis mc2155 produces an increase in the level of resistance over those values observed in M. smegmatis mc2155. However, the introduction of the plasmid-located aac (2') Ic gene did not lead to an increase in the MICs. In this experiment, an increase of at least two dilutions in the MIC values over those observed in M. smegmatismc2155 with the vector pSUM36 has been assumed to be due to the increase in the activity of the AAC (2') enzyme. The MICs for the 2'-ethylnetilmicin do not change since this aminoglycoside is not a substrate of the AAC (2') enzyme. | |||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside 2'-N-acetyltransferase (A2NA) | [9] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Mycobacterium fortuitum infection [ICD-11: 1B2Z.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli XL1-Blue | 562 | ||
| Streptomyces lividans strain 1326 | 1200984 | |||
| Mycolicibacterium fortuitum strain FC1k | 1766 | |||
| Mycolicibacterium smegmatis strain mc2 155 | 246196 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Southern blot hybridizations assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Twofold dilution of antibiotics assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Thirty-four environmental and clinical isolates belonging to theM. fortuitumcomplex were chosen for the present study. The MICs of gentamicin varied, ranging from 2 to 16mg/ml. Crude extracts of all 34 strains were shown to have AAC activity. Acetylation of gentamicin, tobramycin, and kanamycins A and B was found for all the strains, showing a substrate profile consistent with the presence of an AAC(3) activity. Environmental isolateM. fortuitumFC1k was chosen for further studies because of its high level of AAC activity and the level of resistance to gentamicin (MIC, 16mg/ml). | |||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside 2'-N-acetyltransferase (A2NA) | [9] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Mycobacterium smegmatis infection [ICD-11: 1B2Z.3] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Acquired |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli XL1-Blue | 562 | ||
| Streptomyces lividans strain 1326 | 1200984 | |||
| Mycolicibacterium fortuitum strain FC1k | 1766 | |||
| Mycolicibacterium smegmatis strain mc2 155 | 246196 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Southern blot hybridizations assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Twofold dilution of antibiotics assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The aac(2')-Ib gene cloned in a mycobacterial plasmid and introduced in Mycobacterium smegmatis conferred resistance to gentamicin, tobramycin, dibekacin, netilmicin, and 6'-N-ethylnetilmicin. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside N(3)-acetyltransferase (AACC2) | [6], [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Folliculitis [ICD-11: 1B74.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 | 1322345 | ||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates | 287 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Various aminoglycoside modifying enzymes were associated with overlapping phenotypes: 36.5% strains produced AAC(6')-I with either a serine (GEN-TOB-NET) or a leucine (TOB-NET-AMk) at position 119, or both variants (GEN-TOB-NET-AMk); 21.2% expressed ANT(2")-I (GEN-TOB), 7.7% AAC(3)-II (GEN-TOB-NET), 5.8% AAC(3)-I (GEN) and 1.9% AAC(6')-II (GEN-TOB-NET-AMk) or AACA7 (TOB-NET-AMk). | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Bifunctional AAC/APH (AAC/APH) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gram-negative pathogens infection [ICD-11: 1B74-1G40] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) | 469008 | ||
| Escherichia coli JM83 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
SDS-PAGE assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Aminoglycoside 2"-phosphotransferases are the major aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes in clinical isolates of enterococci and staphylococci.APH(2")-If. This enzyme confers resistance to the 4,6-disubstituted aminoglycosides kanamycin, tobramycin, dibekacin, gentamicin, and sisomicin, but not to arbekacin, amikacin, isepamicin, or netilmicin. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Bifunctional AAC/APH (AAC/APH) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Sepsis [ICD-11: 1G40.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) | 469008 | ||
| Escherichia coli JM83 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
SDS-PAGE assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Aminoglycoside 2"-phosphotransferases are the major aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes in clinical isolates of enterococci and staphylococci.APH(2")-If. This enzyme confers resistance to the 4,6-disubstituted aminoglycosides kanamycin, tobramycin, dibekacin, gentamicin, and sisomicin, but not to arbekacin, amikacin, isepamicin, or netilmicin. | |||
ICD-09: Visual system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside N(3)-acetyltransferase (AACC2) | [6], [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Corneal ulcers [ICD-11: 9A76.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 | 1322345 | ||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates | 287 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Various aminoglycoside modifying enzymes were associated with overlapping phenotypes: 36.5% strains produced AAC(6')-I with either a serine (GEN-TOB-NET) or a leucine (TOB-NET-AMk) at position 119, or both variants (GEN-TOB-NET-AMk); 21.2% expressed ANT(2")-I (GEN-TOB), 7.7% AAC(3)-II (GEN-TOB-NET), 5.8% AAC(3)-I (GEN) and 1.9% AAC(6')-II (GEN-TOB-NET-AMk) or AACA7 (TOB-NET-AMk). | |||
ICD-10: Ear/mastoid process diseasess
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside N(3)-acetyltransferase (AACC2) | [6], [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 | 1322345 | ||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates | 287 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Various aminoglycoside modifying enzymes were associated with overlapping phenotypes: 36.5% strains produced AAC(6')-I with either a serine (GEN-TOB-NET) or a leucine (TOB-NET-AMk) at position 119, or both variants (GEN-TOB-NET-AMk); 21.2% expressed ANT(2")-I (GEN-TOB), 7.7% AAC(3)-II (GEN-TOB-NET), 5.8% AAC(3)-I (GEN) and 1.9% AAC(6')-II (GEN-TOB-NET-AMk) or AACA7 (TOB-NET-AMk). | |||
ICD-11: Circulatory system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Bifunctional AAC/APH (AAC/APH) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Infective endocarditis [ICD-11: BB40.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) | 469008 | ||
| Escherichia coli JM83 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
SDS-PAGE assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Aminoglycoside 2"-phosphotransferases are the major aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes in clinical isolates of enterococci and staphylococci.APH(2")-If. This enzyme confers resistance to the 4,6-disubstituted aminoglycosides kanamycin, tobramycin, dibekacin, gentamicin, and sisomicin, but not to arbekacin, amikacin, isepamicin, or netilmicin. | |||
ICD-12: Respiratory system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Bifunctional AAC/APH (AAC/APH) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Respiratory trac infection [ICD-11: CA45.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) | 469008 | ||
| Escherichia coli JM83 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
SDS-PAGE assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Aminoglycoside 2"-phosphotransferases are the major aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes in clinical isolates of enterococci and staphylococci.APH(2")-If. This enzyme confers resistance to the 4,6-disubstituted aminoglycosides kanamycin, tobramycin, dibekacin, gentamicin, and sisomicin, but not to arbekacin, amikacin, isepamicin, or netilmicin. | |||
ICD-13: Digestive system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Bifunctional AAC/APH (AAC/APH) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gram-negative pathogens infection [ICD-11: 1B74-1G40] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) | 469008 | ||
| Escherichia coli JM83 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
SDS-PAGE assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Aminoglycoside 2"-phosphotransferases are the major aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes in clinical isolates of enterococci and staphylococci.APH(2")-If. This enzyme confers resistance to the 4,6-disubstituted aminoglycosides kanamycin, tobramycin, dibekacin, gentamicin, and sisomicin, but not to arbekacin, amikacin, isepamicin, or netilmicin. | |||
ICD-16: Genitourinary system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Bifunctional AAC/APH (AAC/APH) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gram-negative pathogens infection [ICD-11: 1B74-1G40] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) | 469008 | ||
| Escherichia coli JM83 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
SDS-PAGE assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Aminoglycoside 2"-phosphotransferases are the major aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes in clinical isolates of enterococci and staphylococci.APH(2")-If. This enzyme confers resistance to the 4,6-disubstituted aminoglycosides kanamycin, tobramycin, dibekacin, gentamicin, and sisomicin, but not to arbekacin, amikacin, isepamicin, or netilmicin. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
