Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00113)
| Name |
Hepatocyte growth factor receptor (MET)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
HGF receptor; HGF/SF receptor; Proto-oncogene c-Met; Scatter factor receptor; SF receptor; Tyrosine-protein kinase Met
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
MET
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr7:116672196-116798377[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MKAPAVLAPGILVLLFTLVQRSNGECKEALAKSEMNVNMKYQLPNFTAETPIQNVILHEH
HIFLGATNYIYVLNEEDLQKVAEYKTGPVLEHPDCFPCQDCSSKANLSGGVWKDNINMAL VVDTYYDDQLISCGSVNRGTCQRHVFPHNHTADIQSEVHCIFSPQIEEPSQCPDCVVSAL GAKVLSSVKDRFINFFVGNTINSSYFPDHPLHSISVRRLKETKDGFMFLTDQSYIDVLPE FRDSYPIKYVHAFESNNFIYFLTVQRETLDAQTFHTRIIRFCSINSGLHSYMEMPLECIL TEKRKKRSTKKEVFNILQAAYVSKPGAQLARQIGASLNDDILFGVFAQSKPDSAEPMDRS AMCAFPIKYVNDFFNKIVNKNNVRCLQHFYGPNHEHCFNRTLLRNSSGCEARRDEYRTEF TTALQRVDLFMGQFSEVLLTSISTFIKGDLTIANLGTSEGRFMQVVVSRSGPSTPHVNFL LDSHPVSPEVIVEHTLNQNGYTLVITGKKITKIPLNGLGCRHFQSCSQCLSAPPFVQCGW CHDKCVRSEECLSGTWTQQICLPAIYKVFPNSAPLEGGTRLTICGWDFGFRRNNKFDLKK TRVLLGNESCTLTLSESTMNTLKCTVGPAMNKHFNMSIIISNGHGTTQYSTFSYVDPVIT SISPKYGPMAGGTLLTLTGNYLNSGNSRHISIGGKTCTLKSVSNSILECYTPAQTISTEF AVKLKIDLANRETSIFSYREDPIVYEIHPTKSFISGGSTITGVGKNLNSVSVPRMVINVH EAGRNFTVACQHRSNSEIICCTTPSLQQLNLQLPLKTKAFFMLDGILSKYFDLIYVHNPV FKPFEKPVMISMGNENVLEIKGNDIDPEAVKGEVLKVGNKSCENIHLHSEAVLCTVPNDL LKLNSELNIEWKQAISSTVLGKVIVQPDQNFTGLIAGVVSISTALLLLLGFFLWLKKRKQ IKDLGSELVRYDARVHTPHLDRLVSARSVSPTTEMVSNESVDYRATFPEDQFPNSSQNGS CRQVQYPLTDMSPILTSGDSDISSPLLQNTVHIDLSALNPELVQAVQHVVIGPSSLIVHF NEVIGRGHFGCVYHGTLLDNDGKKIHCAVKSLNRITDIGEVSQFLTEGIIMKDFSHPNVL SLLGICLRSEGSPLVVLPYMKHGDLRNFIRNETHNPTVKDLIGFGLQVAKGMKYLASKKF VHRDLAARNCMLDEKFTVKVADFGLARDMYDKEYYSVHNKTGAKLPVKWMALESLQTQKF TTKSDVWSFGVLLWELMTRGAPPYPDVNTFDITVYLLQGRRLLQPEYCPDPLYEVMLKCW HPKAEMRPSFSELVSRISAIFSTFIGEHYVHVNATYVNVKCVAPYPSLLSSEDNADDEVD TRPASFWETS Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Receptor tyrosine kinase that transduces signals from the extracellular matrix into the cytoplasm by binding to hepatocyte growth factor/HGF ligand. Regulates many physiological processes including proliferation, scattering, morphogenesis and survival. Ligand binding at the cell surface induces autophosphorylation of MET on its intracellular domain that provides docking sites for downstream signaling molecules. Following activation by ligand, interacts with the PI3-kinase subunit PIK3R1, PLCG1, SRC, GRB2, STAT3 or the adapter GAB1. Recruitment of these downstream effectors by MET leads to the activation of several signaling cascades including the RAS-ERK, PI3 kinase-AKT, or PLCgamma-PKC. The RAS-ERK activation is associated with the morphogenetic effects while PI3K/AKT coordinates prosurvival effects. During embryonic development, MET signaling plays a role in gastrulation, development and migration of muscles and neuronal precursors, angiogenesis and kidney formation. In adults, participates in wound healing as well as organ regeneration and tissue remodeling. Promotes also differentiation and proliferation of hematopoietic cells. May regulate cortical bone osteogenesis (By similarity).
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
16 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Gefitinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Blood | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.34E-10 Fold-change: -1.34E-01 Z-score: -6.52E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| In Vitro Model | H1975 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1511 |
| A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 | |
| PC9GR cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_V337 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Expression of Met has been associated with both primary and acquired resistance to gefitinib, miR-130a expression was negatively correlated with that of Met. Over-expression of miR-130a increased cell apoptosis and inhibited proliferation of NSCLC cells treated with gefitinib, whereas lowering the expression of miR-130a decreased cell apoptosis and promoted cell proliferation after treatment with gefitinib in both gefitinib-sensitive and -resistant NSCLC cell lines. | |||
| Disease Class: Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Gefitinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Blood | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.34E-10 Fold-change: -1.34E-01 Z-score: -6.52E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| HGF/ MET signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | ||
| In Vitro Model | HCC827 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2063 |
| MRC-5 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0440 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
WST-8 assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In the HGF-induced gefitinib-resistant cell model, the exposure of miR-34a plus gefitinib efficiently inhibited the phosphorylation of MET, EGFR, Akt and ERk, and induced cell death, and apoptosis. In the presence of HGF, although EGFR was successfully inhibited by gefitinib monotherapy, the downstream pathways (PI3k/Akt and ERk pathway) were nevertheless activated by MET activation. Through addition of miR-34a to these cells, both MET and EGFR were successfully inhibited and subsequently the downstream pathways were blocked. However, the inhibitory effect of miR-34a on of MET and downstream pathways was lower than that for the MET-TkI. These results suggested that the combination of miR-34a and gefitinib was able to partially inhibit downstream pathways activation though inhibition of MET and EGFR activation in EGFR mutant NSCLC cells, though this effect was lower than what has been observed for MET-TkI. | |||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [3] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Gefitinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Blood | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.34E-10 Fold-change: -1.34E-01 Z-score: -6.52E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| In Vitro Model | H1975 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1511 |
| HCC827 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2063 | |
| CCD-19Lu cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2382 | |
| H3255 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6831 | |
| MRC-5 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0440 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | microRNA-200a directly targets and downregulates egfr and c-met to inhibit migration, invasion, and gefitinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. | |||
| Disease Class: Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | [6] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Gefitinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Blood | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.34E-10 Fold-change: -1.34E-01 Z-score: -6.52E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | c-Met/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa01521 | |
| In Vitro Model | PC9 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B260 |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR128 reverses the gefitinib resistance of the lung cancer stem cells by inhibiting the c-met/PI3k/AkT pathway. The miR128/c-met pathway enhances the gefitinib sensitivity of the lung cancer stem cells by suppressing the PI3k/AkT pathway. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Gefitinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Blood | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.34E-10 Fold-change: -1.34E-01 Z-score: -6.52E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Epithelial mesenchymal transition signaling pathway | Activation | hsa01521 | |
| miR19a/c-Met signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | H1975 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1511 |
| A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 | |
| HCC827 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2063 | |
| PC9 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B260 | |
| PC9GR cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_V337 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; Luciferase reporter assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR19a contributes to gefitinib resistance and epithelial mesenchymal transition in non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting c-Met. Overexpression of miR19a decreased c-Met expression and re-sensitized gefitinib-resistant NSCLC cells in vitro and in vivo. Decreased miR19a expression may contribute to NSCLC cell metastasis by increasing cell mobility and migration and promoting EMT. | |||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.7] | [30] | |||
| Resistant Disease | EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.7] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Gefitinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Structural variation | Amplification |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
MGB SNP detection kit assay; Mutation Detection assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Digital PCR assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Resistance mechanisms to EGFR-TkI therapy in EGFR-mutated NSCLC include secondary EGFR T790M mutation, c-Met amplification, PIk3CA mutation, and transformation to small-cell lung cancer. | |||
| Disease Class: EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.7] | [28] | |||
| Resistant Disease | EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.7] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Gefitinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Structural variation | Copy number gain |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Low throughput experiment assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Progression-free survival assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Acquired resistance can occur through failure of drug delivery to the target, as in isolated central nervous system (CNS) progression, or by selection of biological variants during TkI exposure. | |||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [29] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Gefitinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Activation |
||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | HGF-Met signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | |
| Mechanism Description | Aberrant Met amplification and HGF-Met signaling pathway activation have been proven to be the main mechanism of acquired resistance of EGFR inhibition by small molecules, such as erlotinib and gefitinib. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [4] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Blood | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.34E-10 Fold-change: -1.34E-01 Z-score: -6.52E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| MET/PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 |
| H1299 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-206 overexpression in human lung adenocarcinoma cisplatin resistant cells inhibited the EMT and cisplatin resistance by targeting MET and suppressing its downstream PI3k/AkT/mTOR signaling pathway. Low expression of miR-206 and high levels of MET were strongly associated with the poor cisplatin sensitivity of lung adenocarcinoma patients. Therefore, activation of miR-206 or inactivation of its target gene pathway may be a potential strategy to reverse cisplatin resistance in human lung adenocarcinoma cisplatin resistant cells. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | [10] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Gastric cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Gastric tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.57E-01 Fold-change: 4.02E-02 Z-score: 1.16E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| PI3K signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | SGC7901 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0520 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The downregulation of miR-34a (+) the resistance of human GC cells to DDP treatment through regulation of cell proliferation and apoptosis via the regulation of the MET gene. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Trastuzumab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Blood | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.91E-01 Fold-change: 2.12E-02 Z-score: 8.60E-01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell viability | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| MET/PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04150 | ||
| In Vitro Model | SkBR3 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0033 |
| BT474 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0179 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; RIP assay; Luciferase reporter assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay; Transwell assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Overexpression of miR-182 reduced trastuzumab resistance in trastuzumab-resistant cells due in part to MET/PI3k/AkT/mTOR signaling pathway inactivation. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.02] | [8] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.02] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Temozolomide | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Glioma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Brainstem tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 9.00E-01 Fold-change: 8.10E-03 Z-score: 1.48E-01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| c-Met signaling signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa01521 | ||
| In Vitro Model | HG7 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| LN229 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0393 | |
| In Vivo Model | BALB/c nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; RT-qPCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Colony formation assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Lnc-TALC promotes O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase expression via regulating the c-Met pathway by competitively binding with miR-20b-3p. | |||
| Disease Class: Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.02] | [8] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.02] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Temozolomide | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Brain cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Nervous tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 6.31E-30 Fold-change: -1.07E-01 Z-score: -1.18E+01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| c-Met signaling signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa01521 | ||
| In Vitro Model | HG7 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| LN229 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0393 | |
| In Vivo Model | BALB/c nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; RT-qPCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Colony formation assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Lnc-TALC promotes O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase expression via regulating the c-Met pathway by competitively binding with miR-20b-3p. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90.0] | [9] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Sunitinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Kidney cancer [ICD-11: 2C90] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Renal cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Kidney | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.88E-02 Fold-change: 7.68E-02 Z-score: 2.45E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | ERK signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | |
| STAT3/AKT signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | 771R-luc cells | Kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Exosome-Transmitted lncARSR Promotes Sunitinib Resistance in Renal Cancer by Acting as a Competing Endogenous RNA. Here we identified an LncRNA, named lncARSR (LncRNA Activated in RCC with Sunitinib Resistance), which correlated with clinically poor sunitinib response. lncARSR promoted sunitinib resistance via competitively binding miR-34/miR-449 to facilitate AXL and c-MET expression in RCC cells. Furthermore, bioactive lncARSR could be incorporated into exosomes and transmitted to sensitive cells, thus disseminating sunitinib resistance. Treatment of sunitinib-resistant RCC with locked nucleic acids targeting lncARSR or an AXL/c-MET inhibitor restored sunitinib response. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | [11] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Sorafenib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Liver cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Liver tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 9.24E-01 Fold-change: 3.24E-03 Z-score: 9.61E-02 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| c-Met/AKT signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa01521 | ||
| In Vitro Model | HepG2 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0027 |
| BEL-7404 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6568 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Dual-luciferase reporter assay; Western blot analysis; qRT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 suppresses sorafenib sensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via regulating miR-335-c-Met. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [13] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Afatinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D1228V |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.71 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.67 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
G
-
D
1040
|
-
S
-
D
-
I
-
S
-
S
-
P
-
L
-
L
-
Q
N
N
1050
|
T
T
V
V
H
H
I
I
D
D
L
L
S
S
A
A
L
L
N
N
1060
|
P
P
E
E
L
L
V
V
Q
Q
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
H
H
V
V
1070
|
V
V
I
I
G
G
P
P
S
S
S
S
L
L
I
I
V
V
H
H
1080
|
F
F
N
N
E
E
V
V
I
I
G
G
R
R
G
G
H
H
F
F
1090
|
G
G
C
C
V
V
Y
Y
H
H
G
G
T
T
L
L
L
L
D
D
1100
|
N
N
D
D
G
G
K
K
K
K
I
I
H
H
C
C
A
A
V
V
1110
|
K
K
S
S
L
L
N
N
R
R
I
I
T
T
D
D
I
I
G
G
1120
|
E
E
V
V
S
S
Q
Q
F
F
L
L
T
T
E
E
G
G
I
I
1130
|
I
I
M
M
K
K
D
D
F
F
S
S
H
H
P
P
N
N
V
V
1140
|
L
L
S
S
L
L
L
L
G
G
I
I
C
C
L
L
R
R
S
S
1150
|
E
E
G
G
S
S
P
P
L
L
V
V
V
V
L
L
P
P
Y
Y
1160
|
M
M
K
K
H
H
G
G
D
D
L
L
R
R
N
N
F
F
I
I
1170
|
R
R
N
N
E
E
T
T
H
H
N
N
P
P
T
T
V
V
K
K
1180
|
D
D
L
L
I
I
G
G
F
F
G
G
L
L
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
1190
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
K
K
F
Y
L
L
A
A
S
S
K
K
K
K
1200
|
F
F
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
1210
|
C
C
M
M
L
L
D
D
E
E
K
K
F
F
T
T
V
V
K
K
1220
|
V
V
A
A
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
R
R
D
V
M
M
1230
|
Y
Y
D
D
K
K
E
E
F
Y
D
Y
S
S
V
V
H
H
N
N
1240
|
K
K
T
T
G
G
A
A
K
K
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
1250
|
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
L
L
Q
Q
T
T
Q
Q
K
K
1260
|
F
F
T
T
T
T
K
K
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
F
F
1270
|
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
R
R
1280
|
G
G
A
A
P
P
P
P
Y
Y
P
P
D
D
V
V
N
N
T
T
1290
|
F
F
D
D
I
I
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
1300
|
R
R
R
R
L
L
L
L
Q
Q
P
P
E
E
Y
Y
C
C
P
P
1310
|
D
D
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
E
E
V
V
M
M
L
L
K
K
C
C
1320
|
W
W
H
H
P
P
K
K
A
A
E
E
M
M
R
R
P
P
S
S
1330
|
F
F
S
S
E
E
L
L
V
V
S
S
R
R
I
I
S
S
A
A
1340
|
I
I
F
F
S
S
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
E
-
H
-
Y
-
1350
|
V
-
H
-
V
-
N
-
A
-
T
-
Y
-
V
-
N
-
V
-
1360
|
K
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Our in vitro findings demonstrate that MET D1228V induces resistance to type I MET TkIs through impaired drug binding while sensitivity to type II MET TkIs is maintained. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Esophagogastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B71.1] | [14] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Esophagogastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B71.1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Afatinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | We find that concurrent amplification of EGFR and ERBB2 is associated with response to the HER kinase inhibitor afatinib in patients with trastuzumab-refractory EG cancer. Heterogeneous uptake of 89Zr-trastuzumab measured noninvasively by PET was associated with disease progression. Analyses of multiple disease sites sampled at the time of disease progression indicated several potential mediators of afatinib resistance, including loss of EGFR amplification and gain of MET amplification. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [15] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cabozantinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D1228N (c.3682G>A) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [16] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Cabozantinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y1003N (c.3007T>A) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [16] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Cabozantinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y1003C (c.3008A>G) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [16] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Cabozantinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y1003F (c.3008A>T) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [16] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Cabozantinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D1010N (c.3028G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [16] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Cabozantinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D1010H (c.3028G>C) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [17] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Cabozantinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y1003F (c.3008A>T) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | |||||||||
| WEHI-3 cells | Peripheral blood | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_3622 | ||||||||||
| Hs746T cells | Skeletal muscle | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0333 | ||||||||||
| Gp2-293 cells | Fetal kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_WI48 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Direct sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK-8 assay | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [16] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Cabozantinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D1010Y (c.3028G>T) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [17] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Cabozantinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D1010Y (c.3028G>T) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | |||||||||
| WEHI-3 cells | Peripheral blood | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_3622 | ||||||||||
| Hs746T cells | Skeletal muscle | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0333 | ||||||||||
| Gp2-293 cells | Fetal kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_WI48 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Direct sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK-8 assay | ||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [13] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Cabozantinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D1228V (c.3683A>T) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.71 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.67 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
G
-
D
1040
|
-
S
-
D
-
I
-
S
-
S
-
P
-
L
-
L
-
Q
N
N
1050
|
T
T
V
V
H
H
I
I
D
D
L
L
S
S
A
A
L
L
N
N
1060
|
P
P
E
E
L
L
V
V
Q
Q
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
H
H
V
V
1070
|
V
V
I
I
G
G
P
P
S
S
S
S
L
L
I
I
V
V
H
H
1080
|
F
F
N
N
E
E
V
V
I
I
G
G
R
R
G
G
H
H
F
F
1090
|
G
G
C
C
V
V
Y
Y
H
H
G
G
T
T
L
L
L
L
D
D
1100
|
N
N
D
D
G
G
K
K
K
K
I
I
H
H
C
C
A
A
V
V
1110
|
K
K
S
S
L
L
N
N
R
R
I
I
T
T
D
D
I
I
G
G
1120
|
E
E
V
V
S
S
Q
Q
F
F
L
L
T
T
E
E
G
G
I
I
1130
|
I
I
M
M
K
K
D
D
F
F
S
S
H
H
P
P
N
N
V
V
1140
|
L
L
S
S
L
L
L
L
G
G
I
I
C
C
L
L
R
R
S
S
1150
|
E
E
G
G
S
S
P
P
L
L
V
V
V
V
L
L
P
P
Y
Y
1160
|
M
M
K
K
H
H
G
G
D
D
L
L
R
R
N
N
F
F
I
I
1170
|
R
R
N
N
E
E
T
T
H
H
N
N
P
P
T
T
V
V
K
K
1180
|
D
D
L
L
I
I
G
G
F
F
G
G
L
L
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
1190
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
K
K
F
Y
L
L
A
A
S
S
K
K
K
K
1200
|
F
F
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
1210
|
C
C
M
M
L
L
D
D
E
E
K
K
F
F
T
T
V
V
K
K
1220
|
V
V
A
A
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
R
R
D
V
M
M
1230
|
Y
Y
D
D
K
K
E
E
F
Y
D
Y
S
S
V
V
H
H
N
N
1240
|
K
K
T
T
G
G
A
A
K
K
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
1250
|
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
L
L
Q
Q
T
T
Q
Q
K
K
1260
|
F
F
T
T
T
T
K
K
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
F
F
1270
|
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
R
R
1280
|
G
G
A
A
P
P
P
P
Y
Y
P
P
D
D
V
V
N
N
T
T
1290
|
F
F
D
D
I
I
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
1300
|
R
R
R
R
L
L
L
L
Q
Q
P
P
E
E
Y
Y
C
C
P
P
1310
|
D
D
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
E
E
V
V
M
M
L
L
K
K
C
C
1320
|
W
W
H
H
P
P
K
K
A
A
E
E
M
M
R
R
P
P
S
S
1330
|
F
F
S
S
E
E
L
L
V
V
S
S
R
R
I
I
S
S
A
A
1340
|
I
I
F
F
S
S
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
E
-
H
-
Y
-
1350
|
V
-
H
-
V
-
N
-
A
-
T
-
Y
-
V
-
N
-
V
-
1360
|
K
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | PC9 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B260 | |||||||||
| 293T cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0063 | ||||||||||
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | There is a patient with metastatic NSCLC with MET-mediated resistance to EGFR TKI who responded to treatment with a type I MET inhibitor, savolitinib, given in combination with a third-generation EGFR inhibitor, osimertinib. The patient then developed acquired resistance mediated by a novel MET kinase domain mutation. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [18] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Cabozantinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D1228N (c.3682G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | NIH3T3 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0594 | |||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Athymic female mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | MET mutations Y1248H and D1246N are resistance mechanisms for type I MET-TKIs. NIH3T3 cells expressing either mutation showed resistance to both INC280 and crizotinib but not cabozantinib, indicating the potential of sequential use of MET inhibitors may lead to a more durable response. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [13] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Cabozantinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D1228V (c.3683A>T) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.71 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.67 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
G
-
D
1040
|
-
S
-
D
-
I
-
S
-
S
-
P
-
L
-
L
-
Q
N
N
1050
|
T
T
V
V
H
H
I
I
D
D
L
L
S
S
A
A
L
L
N
N
1060
|
P
P
E
E
L
L
V
V
Q
Q
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
H
H
V
V
1070
|
V
V
I
I
G
G
P
P
S
S
S
S
L
L
I
I
V
V
H
H
1080
|
F
F
N
N
E
E
V
V
I
I
G
G
R
R
G
G
H
H
F
F
1090
|
G
G
C
C
V
V
Y
Y
H
H
G
G
T
T
L
L
L
L
D
D
1100
|
N
N
D
D
G
G
K
K
K
K
I
I
H
H
C
C
A
A
V
V
1110
|
K
K
S
S
L
L
N
N
R
R
I
I
T
T
D
D
I
I
G
G
1120
|
E
E
V
V
S
S
Q
Q
F
F
L
L
T
T
E
E
G
G
I
I
1130
|
I
I
M
M
K
K
D
D
F
F
S
S
H
H
P
P
N
N
V
V
1140
|
L
L
S
S
L
L
L
L
G
G
I
I
C
C
L
L
R
R
S
S
1150
|
E
E
G
G
S
S
P
P
L
L
V
V
V
V
L
L
P
P
Y
Y
1160
|
M
M
K
K
H
H
G
G
D
D
L
L
R
R
N
N
F
F
I
I
1170
|
R
R
N
N
E
E
T
T
H
H
N
N
P
P
T
T
V
V
K
K
1180
|
D
D
L
L
I
I
G
G
F
F
G
G
L
L
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
1190
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
K
K
F
Y
L
L
A
A
S
S
K
K
K
K
1200
|
F
F
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
1210
|
C
C
M
M
L
L
D
D
E
E
K
K
F
F
T
T
V
V
K
K
1220
|
V
V
A
A
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
R
R
D
V
M
M
1230
|
Y
Y
D
D
K
K
E
E
F
Y
D
Y
S
S
V
V
H
H
N
N
1240
|
K
K
T
T
G
G
A
A
K
K
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
1250
|
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
L
L
Q
Q
T
T
Q
Q
K
K
1260
|
F
F
T
T
T
T
K
K
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
F
F
1270
|
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
R
R
1280
|
G
G
A
A
P
P
P
P
Y
Y
P
P
D
D
V
V
N
N
T
T
1290
|
F
F
D
D
I
I
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
1300
|
R
R
R
R
L
L
L
L
Q
Q
P
P
E
E
Y
Y
C
C
P
P
1310
|
D
D
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
E
E
V
V
M
M
L
L
K
K
C
C
1320
|
W
W
H
H
P
P
K
K
A
A
E
E
M
M
R
R
P
P
S
S
1330
|
F
F
S
S
E
E
L
L
V
V
S
S
R
R
I
I
S
S
A
A
1340
|
I
I
F
F
S
S
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
E
-
H
-
Y
-
1350
|
V
-
H
-
V
-
N
-
A
-
T
-
Y
-
V
-
N
-
V
-
1360
|
K
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | PC9 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B260 | |||||||||
| 293T cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0063 | ||||||||||
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | There is a patient with metastatic NSCLC with MET-mediated resistance to EGFR TKI who responded to treatment with a type I MET inhibitor, savolitinib, given in combination with a third-generation EGFR inhibitor, osimertinib. The patient then developed acquired resistance mediated by a novel MET kinase domain mutation. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [18] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Cabozantinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y1230H (c.3688T>C) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.71 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.97 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
N
-
1050
|
T
-
V
-
H
-
I
-
D
-
L
-
S
-
A
A
L
L
N
N
1060
|
P
P
E
E
L
L
V
V
Q
Q
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
H
H
V
V
1070
|
V
V
I
I
G
G
P
P
S
S
S
S
L
L
I
I
V
V
H
H
1080
|
F
F
N
N
E
E
V
V
I
I
G
G
R
R
G
G
H
H
F
F
1090
|
G
G
C
C
V
V
Y
Y
H
H
G
G
T
T
L
L
L
L
D
D
1100
|
N
N
D
D
G
G
K
K
K
K
I
I
H
H
C
C
A
A
V
V
1110
|
K
K
S
S
L
L
N
N
R
R
I
I
T
T
D
D
I
I
G
G
1120
|
E
E
V
V
S
S
Q
Q
F
F
L
L
T
T
E
E
G
G
I
I
1130
|
I
I
M
M
K
K
D
D
F
F
S
S
H
H
P
P
N
N
V
V
1140
|
L
L
S
S
L
L
L
L
G
G
I
I
C
C
L
L
R
R
S
S
1150
|
E
E
G
G
S
S
P
P
L
L
V
V
V
V
L
L
P
P
Y
Y
1160
|
M
M
K
K
H
H
G
G
D
D
L
L
R
R
N
N
F
F
I
I
1170
|
R
R
N
N
E
E
T
T
H
H
N
N
P
P
T
T
V
V
K
K
1180
|
D
D
L
L
I
I
G
G
F
F
G
G
L
L
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
1190
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
K
K
F
Y
L
L
A
A
S
S
K
K
K
K
1200
|
F
F
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
1210
|
C
C
M
M
L
L
D
D
E
E
K
K
F
F
T
T
V
V
K
K
1220
|
V
V
A
A
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
R
R
D
D
M
M
1230
|
Y
H
D
D
K
K
E
E
F
Y
D
Y
S
S
V
V
H
H
N
N
1240
|
K
K
T
T
G
G
A
A
K
K
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
1250
|
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
L
L
Q
Q
T
T
Q
Q
K
K
1260
|
F
F
T
T
T
T
K
K
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
F
F
1270
|
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
R
R
1280
|
G
G
A
A
P
P
P
P
Y
Y
P
P
D
D
V
V
N
N
T
T
1290
|
F
F
D
D
I
I
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
1300
|
R
R
R
R
L
L
L
L
Q
Q
P
P
E
E
Y
Y
C
C
P
P
1310
|
D
D
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
E
E
V
V
M
M
L
L
K
K
C
C
1320
|
W
W
H
H
P
P
K
K
A
A
E
E
M
M
R
R
P
P
S
S
1330
|
F
F
S
S
E
E
L
L
V
V
S
S
R
R
I
I
S
S
A
A
1340
|
I
I
F
F
S
S
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
E
E
H
H
Y
Y
1350
|
V
V
H
H
V
V
N
N
A
A
T
T
Y
-
V
-
N
-
V
-
1360
|
K
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | NIH3T3 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0594 | |||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Athymic female mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | MET mutations Y1248H and D1246N are resistance mechanisms for type I MET-TKIs. NIH3T3 cells expressing either mutation showed resistance to both INC280 and crizotinib but not cabozantinib, indicating the potential of sequential use of MET inhibitors may lead to a more durable response. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [19] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Capmatinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y1230H |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.71 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.97 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
N
-
1050
|
T
-
V
-
H
-
I
-
D
-
L
-
S
-
A
A
L
L
N
N
1060
|
P
P
E
E
L
L
V
V
Q
Q
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
H
H
V
V
1070
|
V
V
I
I
G
G
P
P
S
S
S
S
L
L
I
I
V
V
H
H
1080
|
F
F
N
N
E
E
V
V
I
I
G
G
R
R
G
G
H
H
F
F
1090
|
G
G
C
C
V
V
Y
Y
H
H
G
G
T
T
L
L
L
L
D
D
1100
|
N
N
D
D
G
G
K
K
K
K
I
I
H
H
C
C
A
A
V
V
1110
|
K
K
S
S
L
L
N
N
R
R
I
I
T
T
D
D
I
I
G
G
1120
|
E
E
V
V
S
S
Q
Q
F
F
L
L
T
T
E
E
G
G
I
I
1130
|
I
I
M
M
K
K
D
D
F
F
S
S
H
H
P
P
N
N
V
V
1140
|
L
L
S
S
L
L
L
L
G
G
I
I
C
C
L
L
R
R
S
S
1150
|
E
E
G
G
S
S
P
P
L
L
V
V
V
V
L
L
P
P
Y
Y
1160
|
M
M
K
K
H
H
G
G
D
D
L
L
R
R
N
N
F
F
I
I
1170
|
R
R
N
N
E
E
T
T
H
H
N
N
P
P
T
T
V
V
K
K
1180
|
D
D
L
L
I
I
G
G
F
F
G
G
L
L
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
1190
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
K
K
F
Y
L
L
A
A
S
S
K
K
K
K
1200
|
F
F
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
1210
|
C
C
M
M
L
L
D
D
E
E
K
K
F
F
T
T
V
V
K
K
1220
|
V
V
A
A
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
R
R
D
D
M
M
1230
|
Y
H
D
D
K
K
E
E
F
Y
D
Y
S
S
V
V
H
H
N
N
1240
|
K
K
T
T
G
G
A
A
K
K
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
1250
|
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
L
L
Q
Q
T
T
Q
Q
K
K
1260
|
F
F
T
T
T
T
K
K
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
F
F
1270
|
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
R
R
1280
|
G
G
A
A
P
P
P
P
Y
Y
P
P
D
D
V
V
N
N
T
T
1290
|
F
F
D
D
I
I
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
1300
|
R
R
R
R
L
L
L
L
Q
Q
P
P
E
E
Y
Y
C
C
P
P
1310
|
D
D
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
E
E
V
V
M
M
L
L
K
K
C
C
1320
|
W
W
H
H
P
P
K
K
A
A
E
E
M
M
R
R
P
P
S
S
1330
|
F
F
S
S
E
E
L
L
V
V
S
S
R
R
I
I
S
S
A
A
1340
|
I
I
F
F
S
S
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
E
E
H
H
Y
Y
1350
|
V
V
H
H
V
V
N
N
A
A
T
T
Y
-
V
-
N
-
V
-
1360
|
K
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Capmatinib is approved for MET exon 14-altered NSCLC based on activity in targeted therapy-na ve patients. A secondary MET mutation was detected in plasma from 4 (36%) patients with crizotinib-resistant NSCLC. The detected mutations included MET D1228H (n=2), Y1230H (n=1), and D1228N +Y1230H (n=1). | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [20] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Capmatinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y1230H (c.3688T>C) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.71 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.97 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
N
-
1050
|
T
-
V
-
H
-
I
-
D
-
L
-
S
-
A
A
L
L
N
N
1060
|
P
P
E
E
L
L
V
V
Q
Q
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
H
H
V
V
1070
|
V
V
I
I
G
G
P
P
S
S
S
S
L
L
I
I
V
V
H
H
1080
|
F
F
N
N
E
E
V
V
I
I
G
G
R
R
G
G
H
H
F
F
1090
|
G
G
C
C
V
V
Y
Y
H
H
G
G
T
T
L
L
L
L
D
D
1100
|
N
N
D
D
G
G
K
K
K
K
I
I
H
H
C
C
A
A
V
V
1110
|
K
K
S
S
L
L
N
N
R
R
I
I
T
T
D
D
I
I
G
G
1120
|
E
E
V
V
S
S
Q
Q
F
F
L
L
T
T
E
E
G
G
I
I
1130
|
I
I
M
M
K
K
D
D
F
F
S
S
H
H
P
P
N
N
V
V
1140
|
L
L
S
S
L
L
L
L
G
G
I
I
C
C
L
L
R
R
S
S
1150
|
E
E
G
G
S
S
P
P
L
L
V
V
V
V
L
L
P
P
Y
Y
1160
|
M
M
K
K
H
H
G
G
D
D
L
L
R
R
N
N
F
F
I
I
1170
|
R
R
N
N
E
E
T
T
H
H
N
N
P
P
T
T
V
V
K
K
1180
|
D
D
L
L
I
I
G
G
F
F
G
G
L
L
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
1190
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
K
K
F
Y
L
L
A
A
S
S
K
K
K
K
1200
|
F
F
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
1210
|
C
C
M
M
L
L
D
D
E
E
K
K
F
F
T
T
V
V
K
K
1220
|
V
V
A
A
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
R
R
D
D
M
M
1230
|
Y
H
D
D
K
K
E
E
F
Y
D
Y
S
S
V
V
H
H
N
N
1240
|
K
K
T
T
G
G
A
A
K
K
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
1250
|
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
L
L
Q
Q
T
T
Q
Q
K
K
1260
|
F
F
T
T
T
T
K
K
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
F
F
1270
|
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
R
R
1280
|
G
G
A
A
P
P
P
P
Y
Y
P
P
D
D
V
V
N
N
T
T
1290
|
F
F
D
D
I
I
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
1300
|
R
R
R
R
L
L
L
L
Q
Q
P
P
E
E
Y
Y
C
C
P
P
1310
|
D
D
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
E
E
V
V
M
M
L
L
K
K
C
C
1320
|
W
W
H
H
P
P
K
K
A
A
E
E
M
M
R
R
P
P
S
S
1330
|
F
F
S
S
E
E
L
L
V
V
S
S
R
R
I
I
S
S
A
A
1340
|
I
I
F
F
S
S
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
E
E
H
H
Y
Y
1350
|
V
V
H
H
V
V
N
N
A
A
T
T
Y
-
V
-
N
-
V
-
1360
|
K
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [19] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Capmatinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D1228H |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Capmatinib is approved for MET exon 14-altered NSCLC based on activity in targeted therapy-na ve patients. A secondary MET mutation was detected in plasma from 4 (36%) patients with crizotinib-resistant NSCLC. The detected mutations included MET D1228H (n=2), Y1230H (n=1), and D1228N +Y1230H (n=1). | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [19] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Capmatinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation+Missense mutation | p.D1228N+p.Y1230H |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Capmatinib is approved for MET exon 14-altered NSCLC based on activity in targeted therapy-na ve patients. A secondary MET mutation was detected in plasma from 4 (36%) patients with crizotinib-resistant NSCLC. The detected mutations included MET D1228H (n=2), Y1230H (n=1), and D1228N +Y1230H (n=1). | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [15] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Capmatinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D1228N (c.3682G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Gastric adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2B72.0] | [21] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Gastric adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2B72.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Capmatinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y1230C (c.3689A>G) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | NCI-H441 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1561 | |||||||||
| NIH 3T3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0594 | ||||||||||
| SNU638 cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0102 | ||||||||||
| NCI-H596 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1571 | ||||||||||
| Hs746T cells | Skeletal muscle | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0333 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Nu/nu mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [13] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Capmatinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D1228V (c.3683A>T) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.71 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.67 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
G
-
D
1040
|
-
S
-
D
-
I
-
S
-
S
-
P
-
L
-
L
-
Q
N
N
1050
|
T
T
V
V
H
H
I
I
D
D
L
L
S
S
A
A
L
L
N
N
1060
|
P
P
E
E
L
L
V
V
Q
Q
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
H
H
V
V
1070
|
V
V
I
I
G
G
P
P
S
S
S
S
L
L
I
I
V
V
H
H
1080
|
F
F
N
N
E
E
V
V
I
I
G
G
R
R
G
G
H
H
F
F
1090
|
G
G
C
C
V
V
Y
Y
H
H
G
G
T
T
L
L
L
L
D
D
1100
|
N
N
D
D
G
G
K
K
K
K
I
I
H
H
C
C
A
A
V
V
1110
|
K
K
S
S
L
L
N
N
R
R
I
I
T
T
D
D
I
I
G
G
1120
|
E
E
V
V
S
S
Q
Q
F
F
L
L
T
T
E
E
G
G
I
I
1130
|
I
I
M
M
K
K
D
D
F
F
S
S
H
H
P
P
N
N
V
V
1140
|
L
L
S
S
L
L
L
L
G
G
I
I
C
C
L
L
R
R
S
S
1150
|
E
E
G
G
S
S
P
P
L
L
V
V
V
V
L
L
P
P
Y
Y
1160
|
M
M
K
K
H
H
G
G
D
D
L
L
R
R
N
N
F
F
I
I
1170
|
R
R
N
N
E
E
T
T
H
H
N
N
P
P
T
T
V
V
K
K
1180
|
D
D
L
L
I
I
G
G
F
F
G
G
L
L
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
1190
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
K
K
F
Y
L
L
A
A
S
S
K
K
K
K
1200
|
F
F
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
1210
|
C
C
M
M
L
L
D
D
E
E
K
K
F
F
T
T
V
V
K
K
1220
|
V
V
A
A
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
R
R
D
V
M
M
1230
|
Y
Y
D
D
K
K
E
E
F
Y
D
Y
S
S
V
V
H
H
N
N
1240
|
K
K
T
T
G
G
A
A
K
K
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
1250
|
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
L
L
Q
Q
T
T
Q
Q
K
K
1260
|
F
F
T
T
T
T
K
K
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
F
F
1270
|
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
R
R
1280
|
G
G
A
A
P
P
P
P
Y
Y
P
P
D
D
V
V
N
N
T
T
1290
|
F
F
D
D
I
I
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
1300
|
R
R
R
R
L
L
L
L
Q
Q
P
P
E
E
Y
Y
C
C
P
P
1310
|
D
D
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
E
E
V
V
M
M
L
L
K
K
C
C
1320
|
W
W
H
H
P
P
K
K
A
A
E
E
M
M
R
R
P
P
S
S
1330
|
F
F
S
S
E
E
L
L
V
V
S
S
R
R
I
I
S
S
A
A
1340
|
I
I
F
F
S
S
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
E
-
H
-
Y
-
1350
|
V
-
H
-
V
-
N
-
A
-
T
-
Y
-
V
-
N
-
V
-
1360
|
K
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | PC9 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B260 | |||||||||
| 293T cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0063 | ||||||||||
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | There is a patient with metastatic NSCLC with MET-mediated resistance to EGFR TKI who responded to treatment with a type I MET inhibitor, savolitinib, given in combination with a third-generation EGFR inhibitor, osimertinib. The patient then developed acquired resistance mediated by a novel MET kinase domain mutation. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [18] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Capmatinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y1230H (c.3688T>C) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.71 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.97 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
N
-
1050
|
T
-
V
-
H
-
I
-
D
-
L
-
S
-
A
A
L
L
N
N
1060
|
P
P
E
E
L
L
V
V
Q
Q
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
H
H
V
V
1070
|
V
V
I
I
G
G
P
P
S
S
S
S
L
L
I
I
V
V
H
H
1080
|
F
F
N
N
E
E
V
V
I
I
G
G
R
R
G
G
H
H
F
F
1090
|
G
G
C
C
V
V
Y
Y
H
H
G
G
T
T
L
L
L
L
D
D
1100
|
N
N
D
D
G
G
K
K
K
K
I
I
H
H
C
C
A
A
V
V
1110
|
K
K
S
S
L
L
N
N
R
R
I
I
T
T
D
D
I
I
G
G
1120
|
E
E
V
V
S
S
Q
Q
F
F
L
L
T
T
E
E
G
G
I
I
1130
|
I
I
M
M
K
K
D
D
F
F
S
S
H
H
P
P
N
N
V
V
1140
|
L
L
S
S
L
L
L
L
G
G
I
I
C
C
L
L
R
R
S
S
1150
|
E
E
G
G
S
S
P
P
L
L
V
V
V
V
L
L
P
P
Y
Y
1160
|
M
M
K
K
H
H
G
G
D
D
L
L
R
R
N
N
F
F
I
I
1170
|
R
R
N
N
E
E
T
T
H
H
N
N
P
P
T
T
V
V
K
K
1180
|
D
D
L
L
I
I
G
G
F
F
G
G
L
L
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
1190
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
K
K
F
Y
L
L
A
A
S
S
K
K
K
K
1200
|
F
F
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
1210
|
C
C
M
M
L
L
D
D
E
E
K
K
F
F
T
T
V
V
K
K
1220
|
V
V
A
A
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
R
R
D
D
M
M
1230
|
Y
H
D
D
K
K
E
E
F
Y
D
Y
S
S
V
V
H
H
N
N
1240
|
K
K
T
T
G
G
A
A
K
K
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
1250
|
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
L
L
Q
Q
T
T
Q
Q
K
K
1260
|
F
F
T
T
T
T
K
K
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
F
F
1270
|
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
R
R
1280
|
G
G
A
A
P
P
P
P
Y
Y
P
P
D
D
V
V
N
N
T
T
1290
|
F
F
D
D
I
I
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
1300
|
R
R
R
R
L
L
L
L
Q
Q
P
P
E
E
Y
Y
C
C
P
P
1310
|
D
D
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
E
E
V
V
M
M
L
L
K
K
C
C
1320
|
W
W
H
H
P
P
K
K
A
A
E
E
M
M
R
R
P
P
S
S
1330
|
F
F
S
S
E
E
L
L
V
V
S
S
R
R
I
I
S
S
A
A
1340
|
I
I
F
F
S
S
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
E
E
H
H
Y
Y
1350
|
V
V
H
H
V
V
N
N
A
A
T
T
Y
-
V
-
N
-
V
-
1360
|
K
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | NIH3T3 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0594 | |||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Athymic female mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | MET mutations Y1248H and D1246N are resistance mechanisms for type I MET-TKIs. NIH3T3 cells expressing either mutation showed resistance to both INC280 and crizotinib but not cabozantinib, indicating the potential of sequential use of MET inhibitors may lead to a more durable response. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [18] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Capmatinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D1228N (c.3682G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | NIH3T3 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0594 | |||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Athymic female mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | MET mutations Y1248H and D1246N are resistance mechanisms for type I MET-TKIs. NIH3T3 cells expressing either mutation showed resistance to both INC280 and crizotinib but not cabozantinib, indicating the potential of sequential use of MET inhibitors may lead to a more durable response. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [16] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Capmatinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y1003N (c.3007T>A) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [16] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Capmatinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y1003C (c.3008A>G) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [16] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Capmatinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y1003F (c.3008A>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [16] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Capmatinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D1010N (c.3028G>A) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [16] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Capmatinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D1010H (c.3028G>C) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [17] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Capmatinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y1003F (c.3008A>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 |
| WEHI-3 cells | Peripheral blood | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_3622 | |
| Hs746T cells | Skeletal muscle | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0333 | |
| Gp2-293 cells | Fetal kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_WI48 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Direct sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK-8 assay | |||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [17] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Capmatinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D1010Y (c.3028G>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 |
| WEHI-3 cells | Peripheral blood | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_3622 | |
| Hs746T cells | Skeletal muscle | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0333 | |
| Gp2-293 cells | Fetal kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_WI48 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Direct sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK-8 assay | |||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [16] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Capmatinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D1010Y (c.3028G>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [22] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cetuximab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Structural variation | Amplification |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Liquid biopsy assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Mechanisms of resistance to EGFR blockade include the emergence of kRAS, NRAS and EGFR extracellular domain mutations as well as HER2/MET alterations. | |||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [23] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cetuximab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Structural variation | Copy number gain |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing analysis; Gene copy number analysis | |||
| Mechanism Description | As amplification of the MET gene has recently been shown to drive resistance to anti-EGFR therapies, this copy number change is the best candidate to explain the poor treatment response. | |||
| Disease Class: Metastatic colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2D85.0] | [24] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Metastatic colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2D85.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cetuximab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Structural variation | Copy number gain |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; Next-generation sequencing assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Mutations in kRAS, NRAS, and BRAF and amplification of ERBB2 and MET drive primary (de novo) resistance to anti-EGFR treatment. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lung squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.3] | [15] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Lung squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Crizotinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D1228N |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Snapshot next-generation sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | An acquired mutation in the MET kinase domain, D1228N, was found at time of progression on crizotinib in a patient with MET exon 14 skipping. Crystal structures of type I MET inhibitors bound to the MET kinase domain show an important binding interaction with the Y1230 residue, with D1228 playing a role in stabilizing the conformation of the activation loop. Therefore, in addition to intrinsic transforming activity, disruption of the drug binding interaction between type I inhibitors and the MET kinase domain is hypothesized to underlie the mechanism of resistance of these specific mutations. | |||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [25] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Crizotinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y1230C |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Noninvasive plasma-based ctDNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Emergence of the preexisting MET Y1230C likely confers resistance to crizotinib in this case of METex14-positive NSCLC. Existence of pretreatment MET Y1230C may eventually modulate the response of METMET tyrosine kinase inhibitors. | |||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [26] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Crizotinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D1246N |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Circulating tumour DNA (ctDNA) analysis; Next-generation sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | MET exon 14 splicing mutation was identified in a Chinese patient in ctDNA. Three mutation in the MET kinase domain were related to resistance to crizotinib. | |||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [26] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Crizotinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D1246H |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Circulating tumour DNA (ctDNA) analysis; Next-generation sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | MET exon 14 splicing mutation was identified in a Chinese patient in ctDNA. Three mutation in the MET kinase domain were related to resistance to crizotinib. | |||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [26] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Crizotinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y1248H |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Circulating tumour DNA (ctDNA) analysis; Next-generation sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | MET exon 14 splicing mutation was identified in a Chinese patient in ctDNA. Three mutation in the MET kinase domain were related to resistance to crizotinib. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.1] | [27] | |||
| Resistant Disease | EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Erlotinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Structural variation | Amplification |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | MET signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04150 | |
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; Fluorescence in situ hybridization assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | These two cases already had MET amplification before EGFR-TkI treatment. In contrast, our patient had an EGFR mutation and then newly developed MET amplification after erlotinib therapy, suggesting that MET amplification occurred as a mechanism of acquired resistance. | |||
| Disease Class: EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.7] | [28] | |||
| Resistant Disease | EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.7] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Erlotinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Structural variation | Copy number gain |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Low throughput experiment assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Progression-free survival assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Acquired resistance can occur through failure of drug delivery to the target, as in isolated central nervous system (CNS) progression, or by selection of biological variants during TkI exposure. | |||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [29] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Erlotinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Activation |
||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | HGF-Met signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | |
| Mechanism Description | Aberrant Met amplification and HGF-Met signaling pathway activation have been proven to be the main mechanism of acquired resistance of EGFR inhibition by small molecules, such as erlotinib and gefitinib. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.1] | [31] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Lidocaine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | HGF/MET signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | |
| In Vitro Model | ||||
| DBTRG-05MG cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1169 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot assay; RT-qPCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow cytometry assay; Cell cytotoxicity assay; Colony formation assay; Cell proliferation assay; Wound-healing assay; Transwell assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In the present study, the clinical importance of the HGF/MET pathway was analyzed using bioinformatics. By establishing TMZ?resistant cell lines, the impact of combined treatment with lidocaine and TMZ was investigated. Additionally, the effects of lidocaine on cellular function were also examined and confirmed using knockdown techniques. The current findings revealed that the HGF/MET pathway played a key role in brain cancer, and its activation in GBM was associated with increased malignancy and poorer patient outcomes. Elevated HGF levels and activation of its receptor were found to be associated with TMZ resistance in GBM cells. Lidocaine effectively suppressed the HGF/MET pathway, thereby restoring TMZ sensitivity in TMZ?resistant cells. Furthermore, lidocaine also inhibited cell migration. Overall, these results indicated that inhibiting the HGF/MET pathway using lidocaine can enhance the sensitivity of GBM cells to TMZ and reduce cell migration, providing a potential basis for developing novel therapeutic strategies for GBM. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [22] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Panitumumab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Structural variation | Amplification |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Liquid biopsy assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Mechanisms of resistance to EGFR blockade include the emergence of kRAS, NRAS and EGFR extracellular domain mutations as well as HER2/MET alterations. | |||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [23] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Panitumumab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Structural variation | Copy number gain |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing analysis; Gene copy number analysis | |||
| Mechanism Description | As amplification of the MET gene has recently been shown to drive resistance to anti-EGFR therapies, this copy number change is the best candidate to explain the poor treatment response. | |||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [24] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Panitumumab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Structural variation | Amplification |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; Next-generation sequencing assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Mutations in kRAS, NRAS, and BRAF and amplification of ERBB2 and MET drive primary (de novo) resistance to anti-EGFR treatment. | |||
| Disease Class: Metastatic colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2D85.0] | [24] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Metastatic colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2D85.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Panitumumab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Structural variation | Copy number gain |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; Next-generation sequencing assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Mutations in kRAS, NRAS, and BRAF and amplification of ERBB2 and MET drive primary (de novo) resistance to anti-EGFR treatment. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [13] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Savolitinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D1228V |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.71 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.67 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
G
-
D
1040
|
-
S
-
D
-
I
-
S
-
S
-
P
-
L
-
L
-
Q
N
N
1050
|
T
T
V
V
H
H
I
I
D
D
L
L
S
S
A
A
L
L
N
N
1060
|
P
P
E
E
L
L
V
V
Q
Q
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
H
H
V
V
1070
|
V
V
I
I
G
G
P
P
S
S
S
S
L
L
I
I
V
V
H
H
1080
|
F
F
N
N
E
E
V
V
I
I
G
G
R
R
G
G
H
H
F
F
1090
|
G
G
C
C
V
V
Y
Y
H
H
G
G
T
T
L
L
L
L
D
D
1100
|
N
N
D
D
G
G
K
K
K
K
I
I
H
H
C
C
A
A
V
V
1110
|
K
K
S
S
L
L
N
N
R
R
I
I
T
T
D
D
I
I
G
G
1120
|
E
E
V
V
S
S
Q
Q
F
F
L
L
T
T
E
E
G
G
I
I
1130
|
I
I
M
M
K
K
D
D
F
F
S
S
H
H
P
P
N
N
V
V
1140
|
L
L
S
S
L
L
L
L
G
G
I
I
C
C
L
L
R
R
S
S
1150
|
E
E
G
G
S
S
P
P
L
L
V
V
V
V
L
L
P
P
Y
Y
1160
|
M
M
K
K
H
H
G
G
D
D
L
L
R
R
N
N
F
F
I
I
1170
|
R
R
N
N
E
E
T
T
H
H
N
N
P
P
T
T
V
V
K
K
1180
|
D
D
L
L
I
I
G
G
F
F
G
G
L
L
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
1190
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
K
K
F
Y
L
L
A
A
S
S
K
K
K
K
1200
|
F
F
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
1210
|
C
C
M
M
L
L
D
D
E
E
K
K
F
F
T
T
V
V
K
K
1220
|
V
V
A
A
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
R
R
D
V
M
M
1230
|
Y
Y
D
D
K
K
E
E
F
Y
D
Y
S
S
V
V
H
H
N
N
1240
|
K
K
T
T
G
G
A
A
K
K
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
1250
|
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
L
L
Q
Q
T
T
Q
Q
K
K
1260
|
F
F
T
T
T
T
K
K
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
F
F
1270
|
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
R
R
1280
|
G
G
A
A
P
P
P
P
Y
Y
P
P
D
D
V
V
N
N
T
T
1290
|
F
F
D
D
I
I
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
1300
|
R
R
R
R
L
L
L
L
Q
Q
P
P
E
E
Y
Y
C
C
P
P
1310
|
D
D
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
E
E
V
V
M
M
L
L
K
K
C
C
1320
|
W
W
H
H
P
P
K
K
A
A
E
E
M
M
R
R
P
P
S
S
1330
|
F
F
S
S
E
E
L
L
V
V
S
S
R
R
I
I
S
S
A
A
1340
|
I
I
F
F
S
S
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
E
-
H
-
Y
-
1350
|
V
-
H
-
V
-
N
-
A
-
T
-
Y
-
V
-
N
-
V
-
1360
|
K
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | PC9 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B260 | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Our in vitro findings demonstrate that MET D1228V induces resistance to type I MET TkIs through impaired drug binding while sensitivity to type II MET TkIs is maintained. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [17] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Tepotinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y1003F (c.3008A>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 |
| WEHI-3 cells | Peripheral blood | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_3622 | |
| Hs746T cells | Skeletal muscle | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0333 | |
| Gp2-293 cells | Fetal kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_WI48 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Direct sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK-8 assay | |||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [17] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Tepotinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D1010Y (c.3028G>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 |
| WEHI-3 cells | Peripheral blood | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_3622 | |
| Hs746T cells | Skeletal muscle | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0333 | |
| Gp2-293 cells | Fetal kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_WI48 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Direct sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK-8 assay | |||
Clinical Trial Drug(s)
6 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [12] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | TRAIL | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.48E-02 Fold-change: -3.05E-02 Z-score: -2.25E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| PI3K/AKT signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | ||
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 |
| H1299 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 | |
| A459 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-130a, expressed at low level in lung cancer cell lines, by targeting MET was able to reduce TRAIL resistance in NSCLC cells through the c-Jun mediated downregulation of miR-221 and miR-222. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [17] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Tivantinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D1010Y (c.3028G>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 |
| WEHI-3 cells | Peripheral blood | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_3622 | |
| Hs746T cells | Skeletal muscle | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0333 | |
| Gp2-293 cells | Fetal kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_WI48 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Direct sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK-8 assay | |||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [17] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Tivantinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y1003F (c.3008A>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 |
| WEHI-3 cells | Peripheral blood | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_3622 | |
| Hs746T cells | Skeletal muscle | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0333 | |
| Gp2-293 cells | Fetal kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_WI48 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Direct sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK-8 assay | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [17] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Merestinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D1010Y (c.3028G>T) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | |||||||||
| WEHI-3 cells | Peripheral blood | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_3622 | ||||||||||
| Hs746T cells | Skeletal muscle | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0333 | ||||||||||
| Gp2-293 cells | Fetal kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_WI48 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Direct sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK-8 assay | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [17] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Merestinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y1003F (c.3008A>T) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | |||||||||
| WEHI-3 cells | Peripheral blood | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_3622 | ||||||||||
| Hs746T cells | Skeletal muscle | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0333 | ||||||||||
| Gp2-293 cells | Fetal kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_WI48 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Direct sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK-8 assay | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [32] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Merestinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D1228N (c.3682G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | HT29 Cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_A8EZ | |||||||||
| A375 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0132 | ||||||||||
| H460 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0459 | ||||||||||
| T47D cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0553 | ||||||||||
| H1299 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 | ||||||||||
| HCT-116 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0291 | ||||||||||
| Calu1 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0608 | ||||||||||
| DU145 cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0105 | ||||||||||
| MV4-11 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0064 | ||||||||||
| U87-MG cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0022 | ||||||||||
| U118 MG cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0633 | ||||||||||
| TT cells | Thyroid gland | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1774 | ||||||||||
| H441 cells | Pericardial effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1561 | ||||||||||
| H1993 cells | Lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1512 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Athymic nude mouse and CD-1 nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.D1228N (c.3682G>A) in gene MET cause the sensitivity of Merestinib by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [32] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Merestinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y1230C (c.3689A>G) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | HT29 Cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_A8EZ | |||||||||
| A375 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0132 | ||||||||||
| H460 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0459 | ||||||||||
| T47D cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0553 | ||||||||||
| H1299 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 | ||||||||||
| HCT-116 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0291 | ||||||||||
| Calu1 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0608 | ||||||||||
| DU145 cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0105 | ||||||||||
| MV4-11 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0064 | ||||||||||
| U87-MG cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0022 | ||||||||||
| U118 MG cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0633 | ||||||||||
| TT cells | Thyroid gland | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1774 | ||||||||||
| H441 cells | Pericardial effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1561 | ||||||||||
| H1993 cells | Lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1512 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Athymic nude mouse and CD-1 nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.Y1230C (c.3689A>G) in gene MET cause the sensitivity of Merestinib by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [13] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Merestinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D1228V (c.3683A>T) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.71 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.67 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
G
-
D
1040
|
-
S
-
D
-
I
-
S
-
S
-
P
-
L
-
L
-
Q
N
N
1050
|
T
T
V
V
H
H
I
I
D
D
L
L
S
S
A
A
L
L
N
N
1060
|
P
P
E
E
L
L
V
V
Q
Q
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
H
H
V
V
1070
|
V
V
I
I
G
G
P
P
S
S
S
S
L
L
I
I
V
V
H
H
1080
|
F
F
N
N
E
E
V
V
I
I
G
G
R
R
G
G
H
H
F
F
1090
|
G
G
C
C
V
V
Y
Y
H
H
G
G
T
T
L
L
L
L
D
D
1100
|
N
N
D
D
G
G
K
K
K
K
I
I
H
H
C
C
A
A
V
V
1110
|
K
K
S
S
L
L
N
N
R
R
I
I
T
T
D
D
I
I
G
G
1120
|
E
E
V
V
S
S
Q
Q
F
F
L
L
T
T
E
E
G
G
I
I
1130
|
I
I
M
M
K
K
D
D
F
F
S
S
H
H
P
P
N
N
V
V
1140
|
L
L
S
S
L
L
L
L
G
G
I
I
C
C
L
L
R
R
S
S
1150
|
E
E
G
G
S
S
P
P
L
L
V
V
V
V
L
L
P
P
Y
Y
1160
|
M
M
K
K
H
H
G
G
D
D
L
L
R
R
N
N
F
F
I
I
1170
|
R
R
N
N
E
E
T
T
H
H
N
N
P
P
T
T
V
V
K
K
1180
|
D
D
L
L
I
I
G
G
F
F
G
G
L
L
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
1190
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
K
K
F
Y
L
L
A
A
S
S
K
K
K
K
1200
|
F
F
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
1210
|
C
C
M
M
L
L
D
D
E
E
K
K
F
F
T
T
V
V
K
K
1220
|
V
V
A
A
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
R
R
D
V
M
M
1230
|
Y
Y
D
D
K
K
E
E
F
Y
D
Y
S
S
V
V
H
H
N
N
1240
|
K
K
T
T
G
G
A
A
K
K
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
1250
|
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
L
L
Q
Q
T
T
Q
Q
K
K
1260
|
F
F
T
T
T
T
K
K
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
F
F
1270
|
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
R
R
1280
|
G
G
A
A
P
P
P
P
Y
Y
P
P
D
D
V
V
N
N
T
T
1290
|
F
F
D
D
I
I
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
1300
|
R
R
R
R
L
L
L
L
Q
Q
P
P
E
E
Y
Y
C
C
P
P
1310
|
D
D
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
E
E
V
V
M
M
L
L
K
K
C
C
1320
|
W
W
H
H
P
P
K
K
A
A
E
E
M
M
R
R
P
P
S
S
1330
|
F
F
S
S
E
E
L
L
V
V
S
S
R
R
I
I
S
S
A
A
1340
|
I
I
F
F
S
S
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
E
-
H
-
Y
-
1350
|
V
-
H
-
V
-
N
-
A
-
T
-
Y
-
V
-
N
-
V
-
1360
|
K
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | PC9 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B260 | |||||||||
| 293T cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0063 | ||||||||||
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | There is a patient with metastatic NSCLC with MET-mediated resistance to EGFR TKI who responded to treatment with a type I MET inhibitor, savolitinib, given in combination with a third-generation EGFR inhibitor, osimertinib. The patient then developed acquired resistance mediated by a novel MET kinase domain mutation. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [18] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | BMS-777607 | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y1230H (c.3688T>C) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.71 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.97 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
N
-
1050
|
T
-
V
-
H
-
I
-
D
-
L
-
S
-
A
A
L
L
N
N
1060
|
P
P
E
E
L
L
V
V
Q
Q
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
H
H
V
V
1070
|
V
V
I
I
G
G
P
P
S
S
S
S
L
L
I
I
V
V
H
H
1080
|
F
F
N
N
E
E
V
V
I
I
G
G
R
R
G
G
H
H
F
F
1090
|
G
G
C
C
V
V
Y
Y
H
H
G
G
T
T
L
L
L
L
D
D
1100
|
N
N
D
D
G
G
K
K
K
K
I
I
H
H
C
C
A
A
V
V
1110
|
K
K
S
S
L
L
N
N
R
R
I
I
T
T
D
D
I
I
G
G
1120
|
E
E
V
V
S
S
Q
Q
F
F
L
L
T
T
E
E
G
G
I
I
1130
|
I
I
M
M
K
K
D
D
F
F
S
S
H
H
P
P
N
N
V
V
1140
|
L
L
S
S
L
L
L
L
G
G
I
I
C
C
L
L
R
R
S
S
1150
|
E
E
G
G
S
S
P
P
L
L
V
V
V
V
L
L
P
P
Y
Y
1160
|
M
M
K
K
H
H
G
G
D
D
L
L
R
R
N
N
F
F
I
I
1170
|
R
R
N
N
E
E
T
T
H
H
N
N
P
P
T
T
V
V
K
K
1180
|
D
D
L
L
I
I
G
G
F
F
G
G
L
L
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
1190
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
K
K
F
Y
L
L
A
A
S
S
K
K
K
K
1200
|
F
F
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
1210
|
C
C
M
M
L
L
D
D
E
E
K
K
F
F
T
T
V
V
K
K
1220
|
V
V
A
A
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
R
R
D
D
M
M
1230
|
Y
H
D
D
K
K
E
E
F
Y
D
Y
S
S
V
V
H
H
N
N
1240
|
K
K
T
T
G
G
A
A
K
K
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
1250
|
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
L
L
Q
Q
T
T
Q
Q
K
K
1260
|
F
F
T
T
T
T
K
K
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
F
F
1270
|
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
R
R
1280
|
G
G
A
A
P
P
P
P
Y
Y
P
P
D
D
V
V
N
N
T
T
1290
|
F
F
D
D
I
I
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
1300
|
R
R
R
R
L
L
L
L
Q
Q
P
P
E
E
Y
Y
C
C
P
P
1310
|
D
D
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
E
E
V
V
M
M
L
L
K
K
C
C
1320
|
W
W
H
H
P
P
K
K
A
A
E
E
M
M
R
R
P
P
S
S
1330
|
F
F
S
S
E
E
L
L
V
V
S
S
R
R
I
I
S
S
A
A
1340
|
I
I
F
F
S
S
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
E
E
H
H
Y
Y
1350
|
V
V
H
H
V
V
N
N
A
A
T
T
Y
-
V
-
N
-
V
-
1360
|
K
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | NIH3T3 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0594 | |||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Athymic female mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | MET mutations Y1248H and D1246N are resistance mechanisms for type I MET-TKIs. NIH3T3 cells expressing either mutation showed resistance to both INC280 and crizotinib but not cabozantinib, indicating the potential of sequential use of MET inhibitors may lead to a more durable response. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [18] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | BMS-777607 | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D1228N (c.3682G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | NIH3T3 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0594 | |||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Athymic female mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | MET mutations Y1248H and D1246N are resistance mechanisms for type I MET-TKIs. NIH3T3 cells expressing either mutation showed resistance to both INC280 and crizotinib but not cabozantinib, indicating the potential of sequential use of MET inhibitors may lead to a more durable response. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [33] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Altiratinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y1230H (c.3688T>C) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.71 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.97 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
N
-
1050
|
T
-
V
-
H
-
I
-
D
-
L
-
S
-
A
A
L
L
N
N
1060
|
P
P
E
E
L
L
V
V
Q
Q
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
H
H
V
V
1070
|
V
V
I
I
G
G
P
P
S
S
S
S
L
L
I
I
V
V
H
H
1080
|
F
F
N
N
E
E
V
V
I
I
G
G
R
R
G
G
H
H
F
F
1090
|
G
G
C
C
V
V
Y
Y
H
H
G
G
T
T
L
L
L
L
D
D
1100
|
N
N
D
D
G
G
K
K
K
K
I
I
H
H
C
C
A
A
V
V
1110
|
K
K
S
S
L
L
N
N
R
R
I
I
T
T
D
D
I
I
G
G
1120
|
E
E
V
V
S
S
Q
Q
F
F
L
L
T
T
E
E
G
G
I
I
1130
|
I
I
M
M
K
K
D
D
F
F
S
S
H
H
P
P
N
N
V
V
1140
|
L
L
S
S
L
L
L
L
G
G
I
I
C
C
L
L
R
R
S
S
1150
|
E
E
G
G
S
S
P
P
L
L
V
V
V
V
L
L
P
P
Y
Y
1160
|
M
M
K
K
H
H
G
G
D
D
L
L
R
R
N
N
F
F
I
I
1170
|
R
R
N
N
E
E
T
T
H
H
N
N
P
P
T
T
V
V
K
K
1180
|
D
D
L
L
I
I
G
G
F
F
G
G
L
L
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
1190
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
K
K
F
Y
L
L
A
A
S
S
K
K
K
K
1200
|
F
F
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
1210
|
C
C
M
M
L
L
D
D
E
E
K
K
F
F
T
T
V
V
K
K
1220
|
V
V
A
A
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
R
R
D
D
M
M
1230
|
Y
H
D
D
K
K
E
E
F
Y
D
Y
S
S
V
V
H
H
N
N
1240
|
K
K
T
T
G
G
A
A
K
K
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
1250
|
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
L
L
Q
Q
T
T
Q
Q
K
K
1260
|
F
F
T
T
T
T
K
K
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
F
F
1270
|
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
R
R
1280
|
G
G
A
A
P
P
P
P
Y
Y
P
P
D
D
V
V
N
N
T
T
1290
|
F
F
D
D
I
I
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
1300
|
R
R
R
R
L
L
L
L
Q
Q
P
P
E
E
Y
Y
C
C
P
P
1310
|
D
D
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
E
E
V
V
M
M
L
L
K
K
C
C
1320
|
W
W
H
H
P
P
K
K
A
A
E
E
M
M
R
R
P
P
S
S
1330
|
F
F
S
S
E
E
L
L
V
V
S
S
R
R
I
I
S
S
A
A
1340
|
I
I
F
F
S
S
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
E
E
H
H
Y
Y
1350
|
V
V
H
H
V
V
N
N
A
A
T
T
Y
-
V
-
N
-
V
-
1360
|
K
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 | |||||||||
| A375 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0132 | ||||||||||
| THP-1 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0006 | ||||||||||
| K562 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0004 | ||||||||||
| MkN-45 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0434 | ||||||||||
| Sk-N-SH cells | Adrenal | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0531 | ||||||||||
| HCT-116 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0291 | ||||||||||
| EBC-1 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2891 | ||||||||||
| MRC-5 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0440 | ||||||||||
| PC-3 cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0035 | ||||||||||
| HUVEC cells | Endothelium | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| HUVEC cells | Endothelium | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| U87-MG cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0022 | ||||||||||
| SkMEL5 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0527 | ||||||||||
| SkMEL28 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0526 | ||||||||||
| MV-4-11 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0064 | ||||||||||
| M-NFS-60 cells | Blood | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_3543 | ||||||||||
| KM-12 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1331 | ||||||||||
| HMVEC cells | Blood vessel | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| EAhy926 cells | N.A. | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3901 | ||||||||||
| CHO-K cells | Ovary | Cricetulus griseus (Chinese hamster) (Cricetulus barabensis griseus) | CVCL_0213 | ||||||||||
| BT-474 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0179 | ||||||||||
| B16/F10 cells | Skin | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_0159 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Mouse xenograft efficacy model; MKN-45 xenograft mouse pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic model; Orthotopic U87-MG xenograft efficacy model; Orthotopic U87-MG xenograft survival model; PyMT syngeneic breast cancer model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Resazurin cell viability assay | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [33] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Altiratinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.M1250T (c.3749T>C) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.71 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.20 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
N
N
1050
|
T
T
V
V
H
H
I
I
D
D
L
L
S
S
A
A
L
L
N
N
1060
|
P
P
E
E
L
L
V
V
Q
Q
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
H
H
V
V
1070
|
V
V
I
I
G
G
P
P
S
S
S
S
L
L
I
I
V
V
H
H
1080
|
F
F
N
N
E
E
V
V
I
I
G
G
R
R
G
G
H
H
F
F
1090
|
G
G
C
C
V
V
Y
Y
H
H
G
G
T
T
L
L
L
L
D
D
1100
|
N
N
D
D
G
G
K
K
K
K
I
I
H
H
C
C
A
A
V
V
1110
|
K
K
S
S
L
L
N
N
R
R
I
I
T
T
D
D
I
I
G
G
1120
|
E
E
V
V
S
S
Q
Q
F
F
L
L
T
T
E
E
G
G
I
I
1130
|
I
I
M
M
K
K
D
D
F
F
S
S
H
H
P
P
N
N
V
V
1140
|
L
L
S
S
L
L
L
L
G
G
I
I
C
C
L
L
R
R
S
S
1150
|
E
E
G
G
S
S
P
P
L
L
V
V
V
V
L
L
P
P
Y
Y
1160
|
M
M
K
K
H
H
G
G
D
D
L
L
R
R
N
N
F
F
I
I
1170
|
R
R
N
N
E
E
T
T
H
H
N
N
P
P
T
T
V
V
K
K
1180
|
D
D
L
L
I
I
G
G
F
F
G
G
L
L
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
1190
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
K
K
F
F
L
L
A
A
S
S
K
K
K
K
1200
|
F
F
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
1210
|
C
C
M
M
L
L
D
D
E
E
K
K
F
F
T
T
V
V
K
K
1220
|
V
V
A
A
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
R
R
D
D
M
M
1230
|
Y
Y
D
D
K
K
E
E
F
F
D
D
S
S
V
V
H
H
N
N
1240
|
K
K
T
T
G
G
A
A
K
K
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
1250
|
M
T
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
L
L
Q
Q
T
T
Q
Q
K
K
1260
|
F
F
T
T
T
T
K
K
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
F
F
1270
|
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
R
R
1280
|
G
G
A
A
P
P
P
P
Y
Y
P
P
D
D
V
V
N
N
T
T
1290
|
F
F
D
D
I
I
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
1300
|
R
R
R
R
L
L
L
L
Q
Q
P
P
E
E
Y
Y
C
C
P
P
1310
|
D
D
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
E
E
V
V
M
M
L
L
K
K
C
C
1320
|
W
W
H
H
P
P
K
K
A
A
E
E
M
M
R
R
P
P
S
S
1330
|
F
F
S
S
E
E
L
L
V
V
S
S
R
R
I
I
S
S
A
A
1340
|
I
I
F
F
S
S
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
E
E
H
H
Y
Y
1350
|
V
V
H
H
V
V
N
N
A
A
T
T
Y
Y
V
V
N
N
V
V
1360
|
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 | |||||||||
| A375 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0132 | ||||||||||
| THP-1 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0006 | ||||||||||
| K562 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0004 | ||||||||||
| MkN-45 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0434 | ||||||||||
| Sk-N-SH cells | Adrenal | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0531 | ||||||||||
| HCT-116 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0291 | ||||||||||
| EBC-1 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2891 | ||||||||||
| MRC-5 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0440 | ||||||||||
| PC-3 cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0035 | ||||||||||
| HUVEC cells | Endothelium | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| HUVEC cells | Endothelium | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| U87-MG cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0022 | ||||||||||
| SkMEL5 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0527 | ||||||||||
| SkMEL28 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0526 | ||||||||||
| MV-4-11 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0064 | ||||||||||
| M-NFS-60 cells | Blood | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_3543 | ||||||||||
| KM-12 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1331 | ||||||||||
| HMVEC cells | Blood vessel | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| EAhy926 cells | N.A. | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3901 | ||||||||||
| CHO-K cells | Ovary | Cricetulus griseus (Chinese hamster) (Cricetulus barabensis griseus) | CVCL_0213 | ||||||||||
| BT-474 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0179 | ||||||||||
| B16/F10 cells | Skin | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_0159 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Mouse xenograft efficacy model; MKN-45 xenograft mouse pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic model; Orthotopic U87-MG xenograft efficacy model; Orthotopic U87-MG xenograft survival model; PyMT syngeneic breast cancer model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Resazurin cell viability assay | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [33] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Altiratinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D1228N (c.3682G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 | |||||||||
| A375 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0132 | ||||||||||
| THP-1 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0006 | ||||||||||
| K562 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0004 | ||||||||||
| MkN-45 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0434 | ||||||||||
| Sk-N-SH cells | Adrenal | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0531 | ||||||||||
| HCT-116 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0291 | ||||||||||
| EBC-1 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2891 | ||||||||||
| MRC-5 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0440 | ||||||||||
| PC-3 cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0035 | ||||||||||
| HUVEC cells | Endothelium | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| HUVEC cells | Endothelium | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| U87-MG cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0022 | ||||||||||
| SkMEL5 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0527 | ||||||||||
| SkMEL28 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0526 | ||||||||||
| MV-4-11 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0064 | ||||||||||
| M-NFS-60 cells | Blood | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_3543 | ||||||||||
| KM-12 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1331 | ||||||||||
| HMVEC cells | Blood vessel | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| EAhy926 cells | N.A. | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3901 | ||||||||||
| CHO-K cells | Ovary | Cricetulus griseus (Chinese hamster) (Cricetulus barabensis griseus) | CVCL_0213 | ||||||||||
| BT-474 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0179 | ||||||||||
| B16/F10 cells | Skin | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_0159 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Mouse xenograft efficacy model; MKN-45 xenograft mouse pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic model; Orthotopic U87-MG xenograft efficacy model; Orthotopic U87-MG xenograft survival model; PyMT syngeneic breast cancer model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Resazurin cell viability assay | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [33] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Altiratinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y1230D (c.3688T>G) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 | |||||||||
| A375 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0132 | ||||||||||
| THP-1 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0006 | ||||||||||
| K562 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0004 | ||||||||||
| MkN-45 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0434 | ||||||||||
| Sk-N-SH cells | Adrenal | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0531 | ||||||||||
| HCT-116 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0291 | ||||||||||
| EBC-1 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2891 | ||||||||||
| MRC-5 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0440 | ||||||||||
| PC-3 cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0035 | ||||||||||
| HUVEC cells | Endothelium | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| HUVEC cells | Endothelium | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| U87-MG cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0022 | ||||||||||
| SkMEL5 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0527 | ||||||||||
| SkMEL28 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0526 | ||||||||||
| MV-4-11 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0064 | ||||||||||
| M-NFS-60 cells | Blood | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_3543 | ||||||||||
| KM-12 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1331 | ||||||||||
| HMVEC cells | Blood vessel | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| EAhy926 cells | N.A. | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3901 | ||||||||||
| CHO-K cells | Ovary | Cricetulus griseus (Chinese hamster) (Cricetulus barabensis griseus) | CVCL_0213 | ||||||||||
| BT-474 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0179 | ||||||||||
| B16/F10 cells | Skin | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_0159 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Mouse xenograft efficacy model; MKN-45 xenograft mouse pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic model; Orthotopic U87-MG xenograft efficacy model; Orthotopic U87-MG xenograft survival model; PyMT syngeneic breast cancer model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Resazurin cell viability assay | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [33] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Altiratinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y1230C (c.3689A>G) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 | |||||||||
| A375 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0132 | ||||||||||
| THP-1 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0006 | ||||||||||
| K562 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0004 | ||||||||||
| MkN-45 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0434 | ||||||||||
| Sk-N-SH cells | Adrenal | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0531 | ||||||||||
| HCT-116 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0291 | ||||||||||
| EBC-1 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2891 | ||||||||||
| MRC-5 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0440 | ||||||||||
| PC-3 cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0035 | ||||||||||
| HUVEC cells | Endothelium | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| HUVEC cells | Endothelium | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| U87-MG cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0022 | ||||||||||
| SkMEL5 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0527 | ||||||||||
| SkMEL28 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0526 | ||||||||||
| MV-4-11 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0064 | ||||||||||
| M-NFS-60 cells | Blood | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_3543 | ||||||||||
| KM-12 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1331 | ||||||||||
| HMVEC cells | Blood vessel | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| EAhy926 cells | N.A. | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3901 | ||||||||||
| CHO-K cells | Ovary | Cricetulus griseus (Chinese hamster) (Cricetulus barabensis griseus) | CVCL_0213 | ||||||||||
| BT-474 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0179 | ||||||||||
| B16/F10 cells | Skin | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_0159 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Mouse xenograft efficacy model; MKN-45 xenograft mouse pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic model; Orthotopic U87-MG xenograft efficacy model; Orthotopic U87-MG xenograft survival model; PyMT syngeneic breast cancer model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Resazurin cell viability assay | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [29] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | JQ1 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | HGF-Met signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | |
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 |
| Calu-1 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0608 | |
| H157 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2458 | |
| NCI- H460 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0459 | |
| HCC827 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2063 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Sulforhodamine B assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | JQ1, I-BET151, or BRD4 silencing all downregulated Met and inhibited both NSCLC cell viability in vitro and tumor growth in vivo.The inhibitory influences of JQ1 on the activity of PI3K/Akt and ERK pathways and cell growth were countervailed by HGF. | |||
Discontinued Drug(s)
2 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [34] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Rociletinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Structural variation | Copy number gain |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | MET signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04150 | |
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Circulating tumour DNA (ctDNA) analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Tissue biopsy assay; CT scan assay; Growth inhibition assay; Receptor tyrosine kinase array; FISH and immunoblot profiling assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Increased MET copy number is the most frequent rociletinib resistance mechanism in this cohort and patients with multiple pre-existing mechanisms (T790M and MET) experience inferior responses. | |||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [34] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Rociletinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Structural variation | Amplification |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Circulating tumour DNA (ctDNA) analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Tissue biopsy assay; CT scan assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Increased MET copy number is the most frequent rociletinib resistance mechanism in this cohort and patients with multiple pre-existing mechanisms (T790M and MET) experience inferior responses. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.7] | [30] | |||
| Resistant Disease | EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.7] | |||
| Resistant Drug | S-1 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Structural variation | Amplification |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
MGB SNP detection kit assay; Mutation Detection assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Digital PCR assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Resistance mechanisms to EGFR-TkI therapy in EGFR-mutated NSCLC include secondary EGFR T790M mutation, c-Met amplification, PIk3CA mutation, and transformation to small-cell lung cancer. | |||
Preclinical Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Gastric adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2B72.0] | [21] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Gastric adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2B72.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Glesatinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y1230C (c.3689A>G) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | NCI-H441 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1561 | |||||||||
| NIH 3T3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0594 | ||||||||||
| SNU638 cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0102 | ||||||||||
| NCI-H596 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1571 | ||||||||||
| Hs746T cells | Skeletal muscle | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0333 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Nu/nu mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [17] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Glesatinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y1003F (c.3008A>T) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | |||||||||
| WEHI-3 cells | Peripheral blood | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_3622 | ||||||||||
| Hs746T cells | Skeletal muscle | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0333 | ||||||||||
| Gp2-293 cells | Fetal kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_WI48 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Direct sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK-8 assay | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [17] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Glesatinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D1010Y (c.3028G>T) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | |||||||||
| WEHI-3 cells | Peripheral blood | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_3622 | ||||||||||
| Hs746T cells | Skeletal muscle | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0333 | ||||||||||
| Gp2-293 cells | Fetal kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_WI48 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Direct sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK-8 assay | ||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [13] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Glesatinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D1228V (c.3683A>T) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.71 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.67 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
G
-
D
1040
|
-
S
-
D
-
I
-
S
-
S
-
P
-
L
-
L
-
Q
N
N
1050
|
T
T
V
V
H
H
I
I
D
D
L
L
S
S
A
A
L
L
N
N
1060
|
P
P
E
E
L
L
V
V
Q
Q
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
H
H
V
V
1070
|
V
V
I
I
G
G
P
P
S
S
S
S
L
L
I
I
V
V
H
H
1080
|
F
F
N
N
E
E
V
V
I
I
G
G
R
R
G
G
H
H
F
F
1090
|
G
G
C
C
V
V
Y
Y
H
H
G
G
T
T
L
L
L
L
D
D
1100
|
N
N
D
D
G
G
K
K
K
K
I
I
H
H
C
C
A
A
V
V
1110
|
K
K
S
S
L
L
N
N
R
R
I
I
T
T
D
D
I
I
G
G
1120
|
E
E
V
V
S
S
Q
Q
F
F
L
L
T
T
E
E
G
G
I
I
1130
|
I
I
M
M
K
K
D
D
F
F
S
S
H
H
P
P
N
N
V
V
1140
|
L
L
S
S
L
L
L
L
G
G
I
I
C
C
L
L
R
R
S
S
1150
|
E
E
G
G
S
S
P
P
L
L
V
V
V
V
L
L
P
P
Y
Y
1160
|
M
M
K
K
H
H
G
G
D
D
L
L
R
R
N
N
F
F
I
I
1170
|
R
R
N
N
E
E
T
T
H
H
N
N
P
P
T
T
V
V
K
K
1180
|
D
D
L
L
I
I
G
G
F
F
G
G
L
L
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
1190
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
K
K
F
Y
L
L
A
A
S
S
K
K
K
K
1200
|
F
F
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
1210
|
C
C
M
M
L
L
D
D
E
E
K
K
F
F
T
T
V
V
K
K
1220
|
V
V
A
A
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
R
R
D
V
M
M
1230
|
Y
Y
D
D
K
K
E
E
F
Y
D
Y
S
S
V
V
H
H
N
N
1240
|
K
K
T
T
G
G
A
A
K
K
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
1250
|
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
L
L
Q
Q
T
T
Q
Q
K
K
1260
|
F
F
T
T
T
T
K
K
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
F
F
1270
|
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
R
R
1280
|
G
G
A
A
P
P
P
P
Y
Y
P
P
D
D
V
V
N
N
T
T
1290
|
F
F
D
D
I
I
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
1300
|
R
R
R
R
L
L
L
L
Q
Q
P
P
E
E
Y
Y
C
C
P
P
1310
|
D
D
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
E
E
V
V
M
M
L
L
K
K
C
C
1320
|
W
W
H
H
P
P
K
K
A
A
E
E
M
M
R
R
P
P
S
S
1330
|
F
F
S
S
E
E
L
L
V
V
S
S
R
R
I
I
S
S
A
A
1340
|
I
I
F
F
S
S
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
E
-
H
-
Y
-
1350
|
V
-
H
-
V
-
N
-
A
-
T
-
Y
-
V
-
N
-
V
-
1360
|
K
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | PC9 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B260 | |||||||||
| 293T cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0063 | ||||||||||
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | There is a patient with metastatic NSCLC with MET-mediated resistance to EGFR TKI who responded to treatment with a type I MET inhibitor, savolitinib, given in combination with a third-generation EGFR inhibitor, osimertinib. The patient then developed acquired resistance mediated by a novel MET kinase domain mutation. | ||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [35] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Glesatinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y1230C (c.3689A>G) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | MET signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04150 | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | NCI-H441 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1561 | |||||||||
| NIH 3T3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0594 | ||||||||||
| NCI-H596 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1571 | ||||||||||
| Hs746T cells | Skeletal muscle | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0333 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Nu/Nu mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
Investigative Drug(s)
8 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [29] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | BRD4 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | HGF-Met signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | |
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 |
| Calu-1 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0608 | |
| H157 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2458 | |
| NCI- H460 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0459 | |
| HCC827 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2063 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Sulforhodamine B assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | JQ1, I-BET151, or BRD5 silencing all downregulated Met and inhibited both NSCLC cell viability in vitro and tumor growth in vivo. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [36] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Epidermal growth factor | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Phosphorylation | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | HCC827 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2063 |
| PC9 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B260 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Hemocytommeter assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Alpha-LA decreased tyrosine phosphorylation levels of EGFR, ErbB2, and Met, and this was associated with an inhibition in the cell-cycle transition from the G1 phase to the S phase without inducing apoptosis. The addition of HGF induced Met tyrosine phosphorylation, and this was associated with a resistance to gefitinib-induced growth inhibition, which meant a gain in proliferative ability. In the presence of gefitinib and HGF, the addition of alpha-LA suppressed Met tyrosine phosphorylation, and this was associated with an inhibition in cell growth. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.02] | [37] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.02] | |||
| Resistant Drug | FGFR inhibitors | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | ERK/MAPKsignaling pathway | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| PI3K/AKT signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04151 | ||
| STAT3 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04550 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Screening assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In particular, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) activation has been identified as a mechanism of resistance in bladder cancer cells with FGFR3 mutations after treatment with FGFR inhibitors. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [30] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Gefitinib/Pemetrexed | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Structural variation | Copy number gain |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
MGB SNP detection kit assay; Mutation Detection assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Digital PCR assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Resistance mechanisms to EGFR-TkI therapy in EGFR-mutated NSCLC include secondary EGFR T790M mutation, c-Met amplification, PIk3CA mutation, and transformation to small-cell lung cancer. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [30] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Gefitinib/S-1 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Structural variation | Copy number gain |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
MGB SNP detection kit assay; Mutation Detection assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Digital PCR assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Resistance mechanisms to EGFR-TkI therapy in EGFR-mutated NSCLC include secondary EGFR T790M mutation, c-Met amplification, PIk3CA mutation, and transformation to small-cell lung cancer. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [29] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | I-BET151 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | HGF-Met signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | |
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 |
| Calu-1 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0608 | |
| H157 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2458 | |
| NCI- H460 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0459 | |
| HCC827 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2063 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Sulforhodamine B assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | JQ1, I-BET151, or BRD4 silencing all downregulated Met and inhibited both NSCLC cell viability in vitro and tumor growth in vivo. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [13] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | MET inhibitors | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D1228V (c.3683A>T) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.71 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.67 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
G
-
D
1040
|
-
S
-
D
-
I
-
S
-
S
-
P
-
L
-
L
-
Q
N
N
1050
|
T
T
V
V
H
H
I
I
D
D
L
L
S
S
A
A
L
L
N
N
1060
|
P
P
E
E
L
L
V
V
Q
Q
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
H
H
V
V
1070
|
V
V
I
I
G
G
P
P
S
S
S
S
L
L
I
I
V
V
H
H
1080
|
F
F
N
N
E
E
V
V
I
I
G
G
R
R
G
G
H
H
F
F
1090
|
G
G
C
C
V
V
Y
Y
H
H
G
G
T
T
L
L
L
L
D
D
1100
|
N
N
D
D
G
G
K
K
K
K
I
I
H
H
C
C
A
A
V
V
1110
|
K
K
S
S
L
L
N
N
R
R
I
I
T
T
D
D
I
I
G
G
1120
|
E
E
V
V
S
S
Q
Q
F
F
L
L
T
T
E
E
G
G
I
I
1130
|
I
I
M
M
K
K
D
D
F
F
S
S
H
H
P
P
N
N
V
V
1140
|
L
L
S
S
L
L
L
L
G
G
I
I
C
C
L
L
R
R
S
S
1150
|
E
E
G
G
S
S
P
P
L
L
V
V
V
V
L
L
P
P
Y
Y
1160
|
M
M
K
K
H
H
G
G
D
D
L
L
R
R
N
N
F
F
I
I
1170
|
R
R
N
N
E
E
T
T
H
H
N
N
P
P
T
T
V
V
K
K
1180
|
D
D
L
L
I
I
G
G
F
F
G
G
L
L
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
1190
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
K
K
F
Y
L
L
A
A
S
S
K
K
K
K
1200
|
F
F
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
1210
|
C
C
M
M
L
L
D
D
E
E
K
K
F
F
T
T
V
V
K
K
1220
|
V
V
A
A
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
R
R
D
V
M
M
1230
|
Y
Y
D
D
K
K
E
E
F
Y
D
Y
S
S
V
V
H
H
N
N
1240
|
K
K
T
T
G
G
A
A
K
K
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
1250
|
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
L
L
Q
Q
T
T
Q
Q
K
K
1260
|
F
F
T
T
T
T
K
K
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
F
F
1270
|
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
R
R
1280
|
G
G
A
A
P
P
P
P
Y
Y
P
P
D
D
V
V
N
N
T
T
1290
|
F
F
D
D
I
I
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
1300
|
R
R
R
R
L
L
L
L
Q
Q
P
P
E
E
Y
Y
C
C
P
P
1310
|
D
D
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
E
E
V
V
M
M
L
L
K
K
C
C
1320
|
W
W
H
H
P
P
K
K
A
A
E
E
M
M
R
R
P
P
S
S
1330
|
F
F
S
S
E
E
L
L
V
V
S
S
R
R
I
I
S
S
A
A
1340
|
I
I
F
F
S
S
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
E
-
H
-
Y
-
1350
|
V
-
H
-
V
-
N
-
A
-
T
-
Y
-
V
-
N
-
V
-
1360
|
K
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | PC9 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B260 | |||||||||
| 293T cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0063 | ||||||||||
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | There is a patient with metastatic NSCLC with MET-mediated resistance to EGFR TKI who responded to treatment with a type I MET inhibitor, savolitinib, given in combination with a third-generation EGFR inhibitor, osimertinib. The patient then developed acquired resistance mediated by a novel MET kinase domain mutation. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [38] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | MET inhibitors | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.H1112L (c.3335A>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | NIH3T3 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0594 |
| Disease Class: Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90.0] | [39] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | MET inhibitors | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Copy number gain | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Disease Class: Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90.0] | [39] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | MET inhibitors | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.H1094R (c.3281A>G) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Renal cell carcinoma tissue | N.A. | ||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.H1094R (c.3281A>G) in gene MET cause the sensitivity of MET inhibitors by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | |||
| Disease Class: Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90.0] | [40] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | MET inhibitors | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.M1268T (c.3803T>C) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Human renal cell carcinoma tissue | N.A. | ||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.M1268T (c.3803T>C) in gene MET cause the sensitivity of MET inhibitors by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | |||
| Disease Class: Cholangiocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.0] | [41] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Cholangiocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | MET inhibitors | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Copy number gain | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Disease Class: Gastric adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2B72.0] | [42] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Gastric adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2B72.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | MET inhibitors | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Copy number gain | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [43] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Resistant Drug | SU11274 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.N375S (c.1124A>G) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Lung | N.A. | ||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.N375S (c.1124A>G) in gene MET cause the resistance of SU11274 by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | |||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [44] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Resistant Drug | SU11274 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L1213V (c.3637C>G) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | NIH3T3 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0594 |
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.L1213V (c.3637C>G) in gene MET cause the resistance of SU11274 by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | |||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [44] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Resistant Drug | SU11274 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y1248H (c.3742T>C) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | NIH3T3 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0594 |
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.Y1248H (c.3742T>C) in gene MET cause the resistance of SU11274 by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [44] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | SU11274 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.M1268T (c.3803T>C) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | NIH3T3 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0594 |
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.M1268T (c.3803T>C) in gene MET cause the sensitivity of SU11274 by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | |||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [45] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | SU11274 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V1110I (c.3328G>A) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | NIH3T3 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0594 |
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.V1110I (c.3328G>A) in gene MET cause the sensitivity of SU11274 by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | |||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [45] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | SU11274 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.H1112L (c.3335A>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | NIH3T3 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0594 |
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.H1112L (c.3335A>T) in gene MET cause the sensitivity of SU11274 by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | |||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [45] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | SU11274 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V1206L (c.3616G>C) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | NIH3T3 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0594 |
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.V1206L (c.3616G>C) in gene MET cause the sensitivity of SU11274 by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | |||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [45] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | SU11274 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V1238I (c.3712G>A) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | NIH3T3 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0594 |
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.V1238I (c.3712G>A) in gene MET cause the sensitivity of SU11274 by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | |||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [43] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | SU11274 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E168D (c.504G>C) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Lung | N.A. | ||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.E168D (c.504G>C) in gene MET cause the sensitivity of SU11274 by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | |||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [44] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | SU11274 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.H1112Y (c.3334C>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | NIH3T3 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0594 |
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.H1112Y (c.3334C>T) in gene MET cause the sensitivity of SU11274 by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Nervous tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Brain cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 6.31E-30; Fold-change: -5.01E-01; Z-score: -8.32E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | Brainstem tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Glioma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 9.00E-01; Fold-change: -7.78E-03; Z-score: -3.47E-02 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | White matter | |
| The Specified Disease | Glioma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 6.55E-06; Fold-change: 9.19E-01; Z-score: 4.68E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
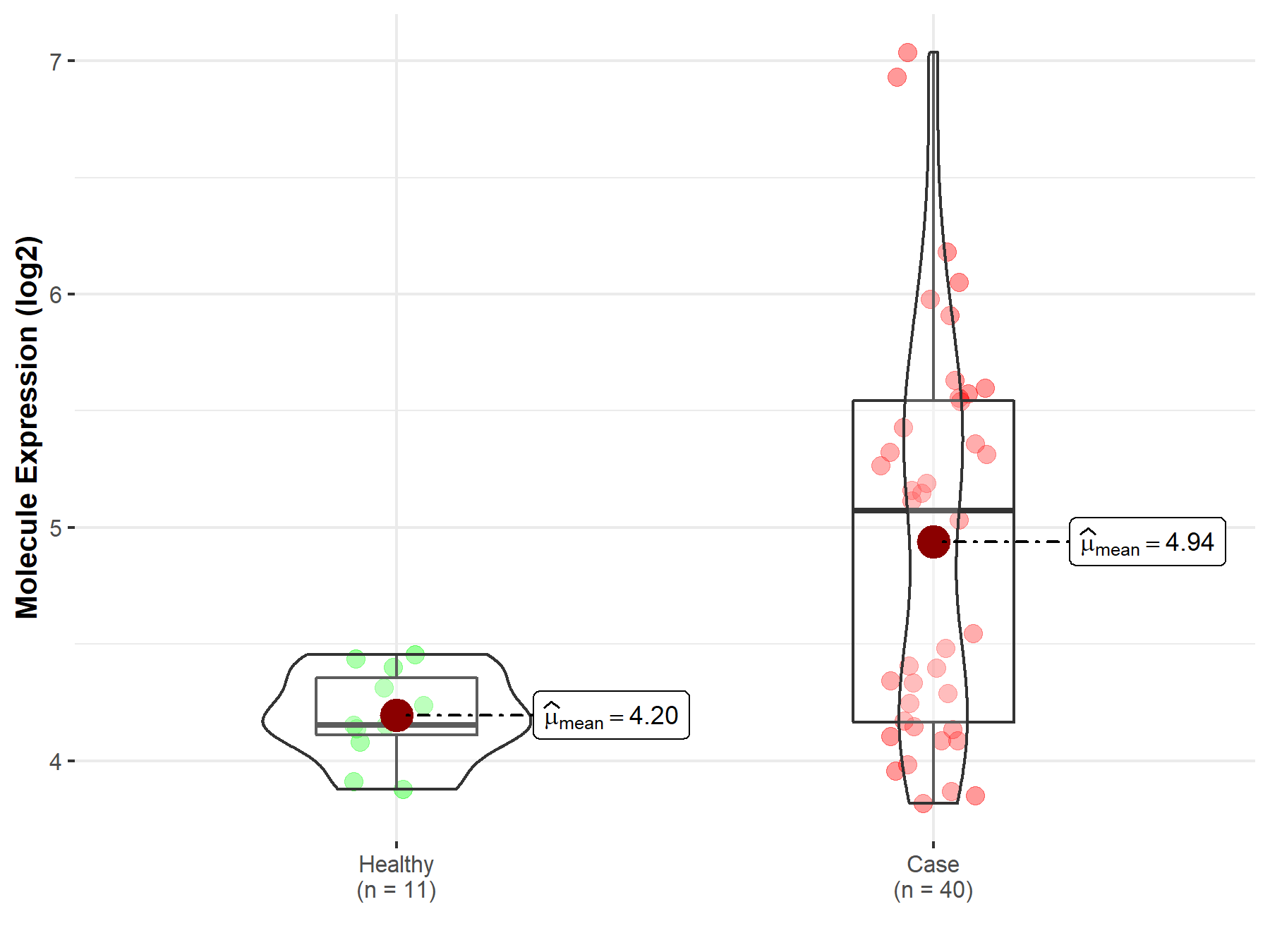
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | Brainstem tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Neuroectodermal tumor | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.12E-07; Fold-change: -6.35E-01; Z-score: -3.03E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
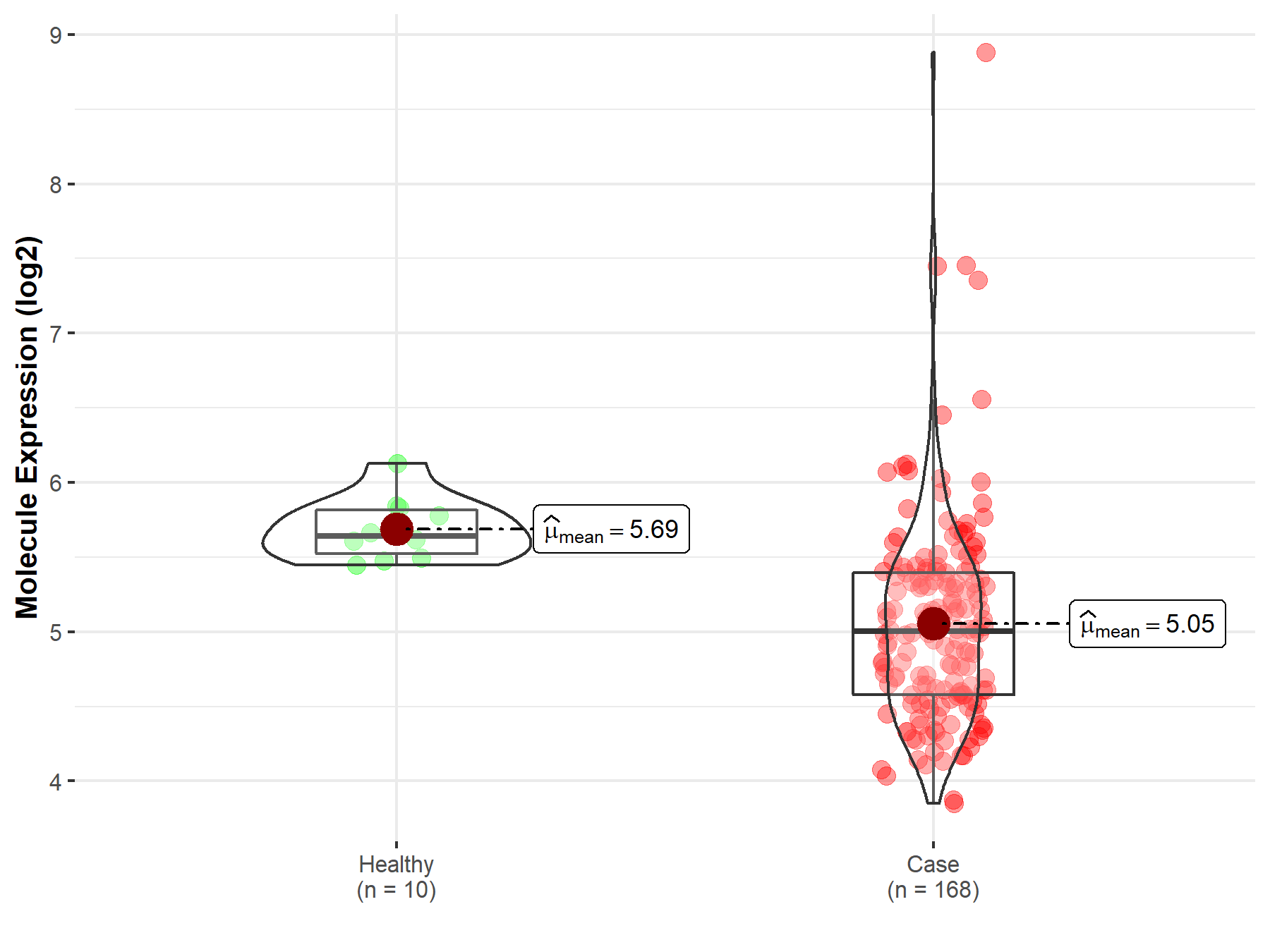
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Gastric tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Gastric cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.57E-01; Fold-change: 1.49E-01; Z-score: 5.64E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 1.14E-06; Fold-change: 7.33E-01; Z-score: 1.58E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
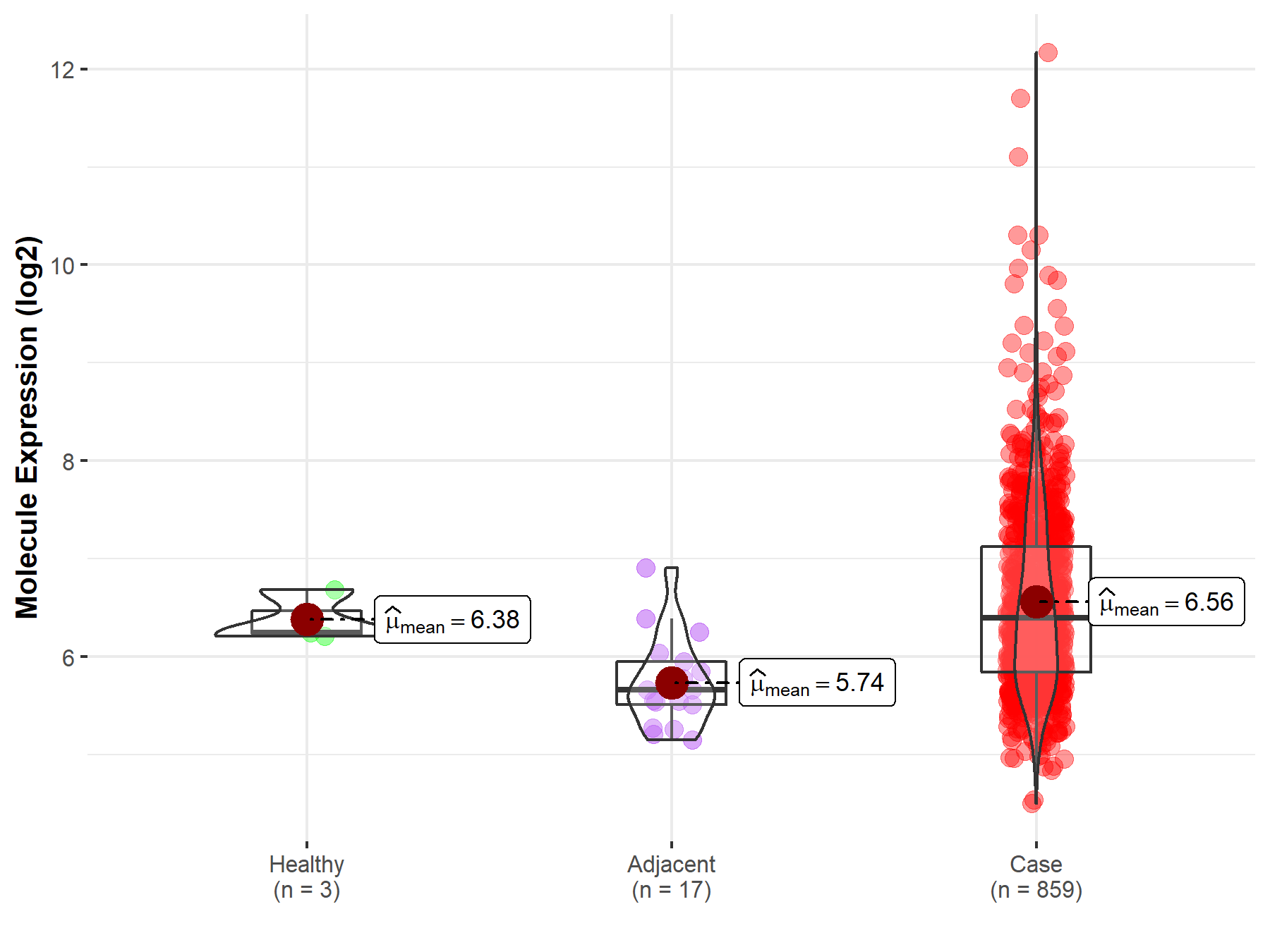
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Liver | |
| The Specified Disease | Liver cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 9.24E-01; Fold-change: -7.97E-02; Z-score: -8.35E-02 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 1.28E-18; Fold-change: 6.93E-01; Z-score: 1.05E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Other Disease Section | p-value: 3.42E-01; Fold-change: 3.88E-01; Z-score: 4.12E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
Molecule expression in tissue other than the diseased tissue of patients
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
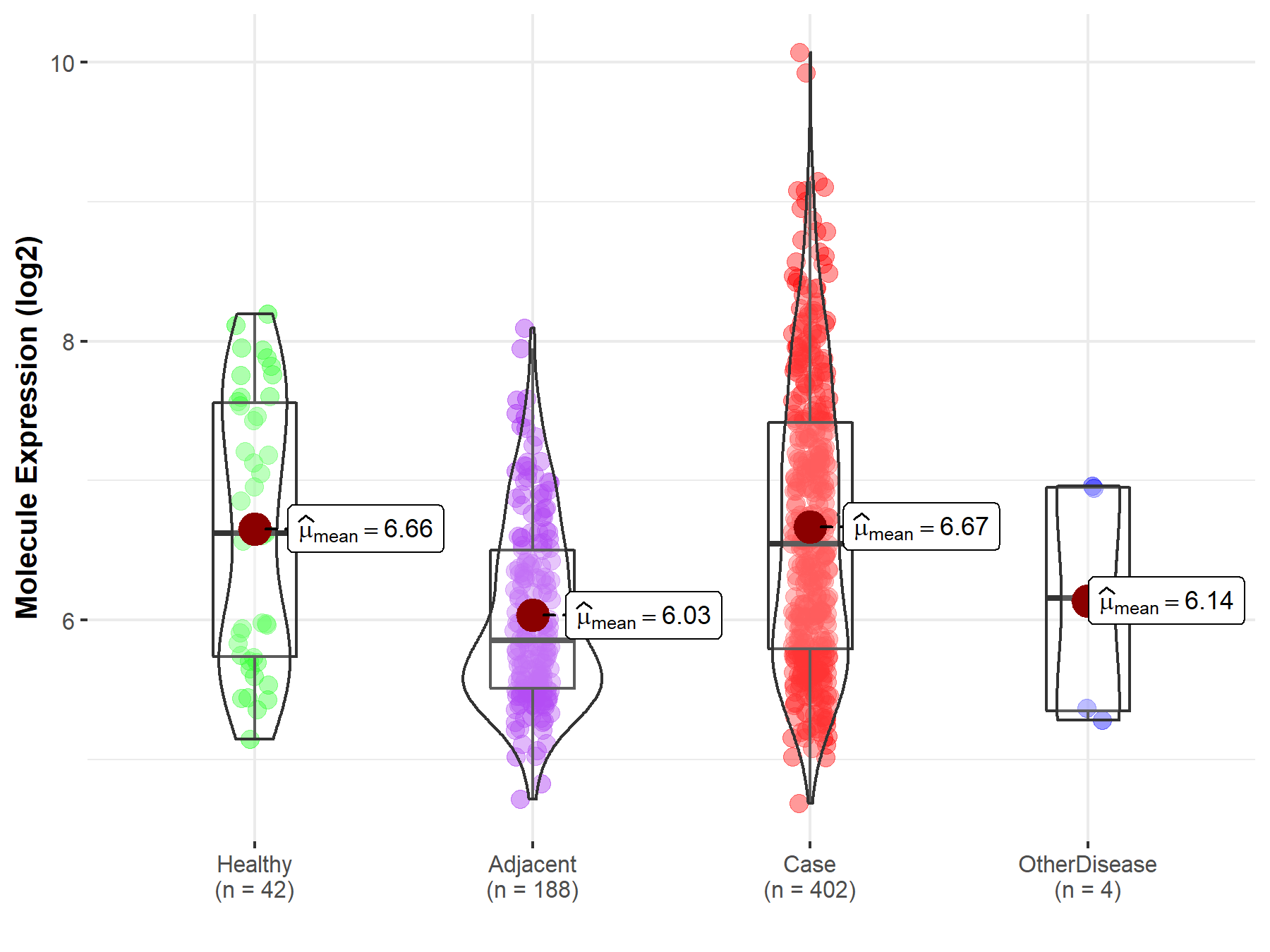
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung | |
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.48E-02; Fold-change: -5.14E-01; Z-score: -6.88E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 8.62E-01; Fold-change: -8.97E-02; Z-score: -9.24E-02 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
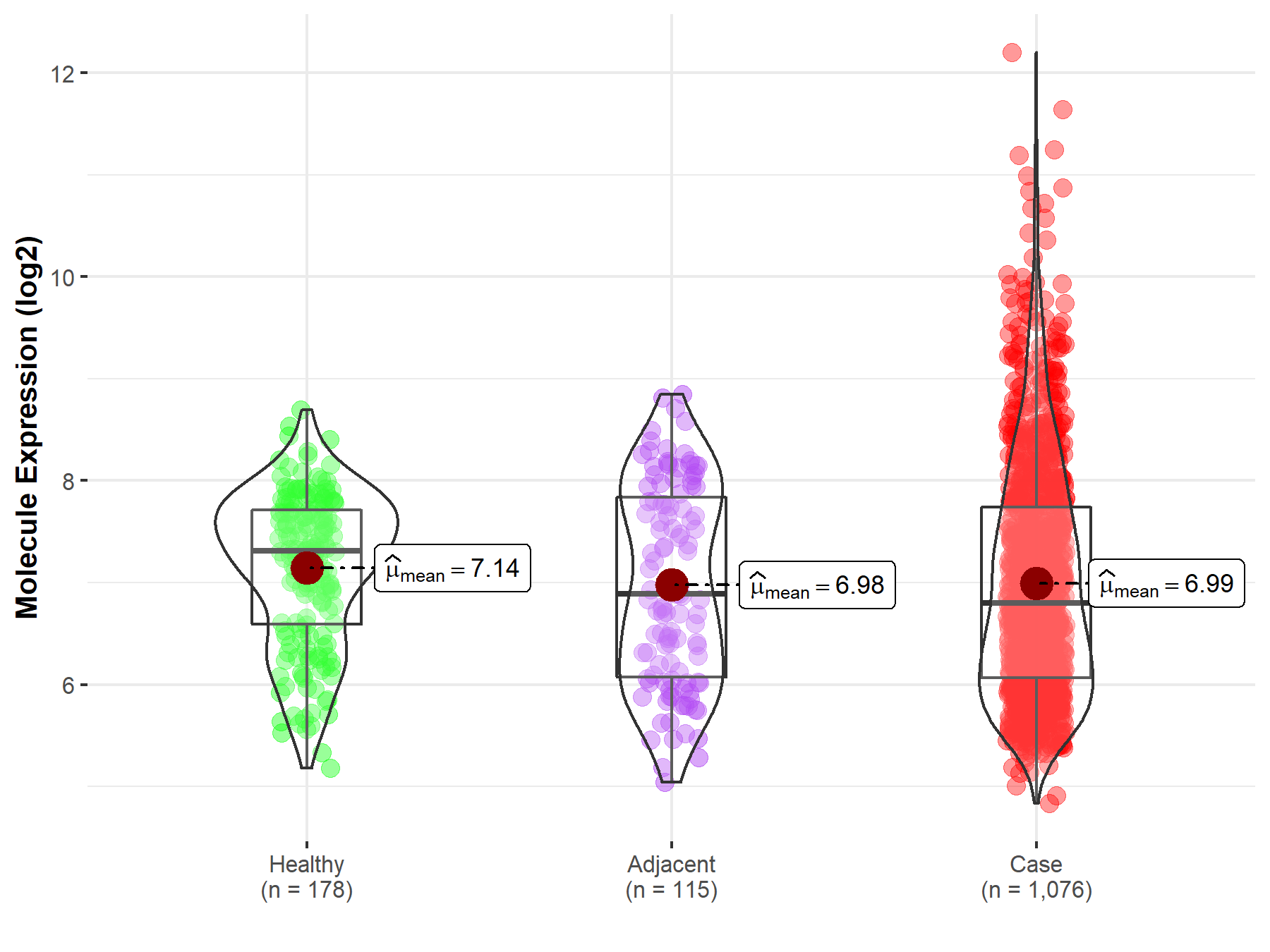
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 6.27E-29; Fold-change: -6.22E-01; Z-score: -9.71E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 2.42E-05; Fold-change: -5.41E-01; Z-score: -1.03E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Kidney | |
| The Specified Disease | Kidney cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.88E-02; Fold-change: 5.05E-01; Z-score: 9.67E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 7.99E-01; Fold-change: 1.82E-01; Z-score: 2.85E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
