Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG01249) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Capmatinib
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Capmatinib; 1029712-80-8; INCB28060; INC-280; INC280; 2-fluoro-N-methyl-4-(7-(quinolin-6-ylmethyl)imidazo[1,2-b][1,2,4]triazin-2-yl)benzamide; INCB-28060; NVP-INC280; UNII-TY34L4F9OZ; NVP-INC280-NX; Capmatinib (INCB28060); INC28060; 2-fluoro-N-methyl-4-[7-(quinolin-6-ylmethyl)imidazo[1,2-b][1,2,4]triazin-2-yl]benzamide; TY34L4F9OZ; INCB 28060; BenzaMide, 2-fluoro-N-Methyl-4-[7-(6-quinolinylMethyl)iMidazo[1,2-b][1,2,4]triazin-2-yl]-; 2-Fluoro-N-methyl-4-[7-[(quinolin-6-yl)methyl]imidazo[1,2-b]-[1,2,4]triazin-2-yl]benzamide; C23H17FN6O; Tabrecta; Benzamide, 2-fluoro-N-methyl-4-[7-(6-quinolinylmethyl)imidazo[1,2-b][1,2,4]triazin-2-yl]-;Benzamide, 2-fluoro-N-methyl-4-[7-(6-quinolinylmethyl)imidazo[1,2-b][1,2,4]triazin-2-yl]-; benzamide hcl; INCB-28060 FREE BASE; Capmatinib [USAN]; Capmatinib (USAN/INN); Capmatinib [USAN:INN]; Capmatinib(INCB28060); INCB28060(Capmatinib); NYP-INC280-NX; MLS006010965; GTPL7904; SCHEMBL1426819; CHEMBL3188267; DTXSID90145595; EX-A446; AMY18553; AOB87335; BCP23444; BDBM50146167; MFCD18633285; NSC777878; NSC800067; s2788; ZINC43195321; AKOS025396439; BCP9000785; CCG-268791; CS-1541; DB11791; NSC-777878; NSC-800067; QC-7530; SB16608; NCGC00346702-01; NCGC00346702-02; NCGC00346702-05; AC-25890; AS-74142; DA-33530; HY-13404; SMR004702769; FT-0746310; Y0337; D10696; J-509516; Q27075685; 2-Fluoro-N-methyl-4-[7-(6-quinolinylmethyl)imidazo[1,2-b][1,2,4]triazin-2-yl]benzamide; 2-fluoro-n-methyl-4-[7-(quinolin-6-ylmethyl)imidazolo[1,2-b][1,2,4]triazin-2-yl]benzamide; 2-fluoro-N-methyl-4-{7-[(quinolin-6-yl)methyl]imidazo[1,2-b][1,2,4]triazin-2-yl}benzamide
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 3 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
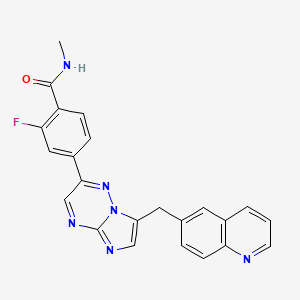
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(3 diseases)
[2]
[3]
[4]
|
||||
| Target | Proto-oncogene c-Met (MET) | MET_HUMAN | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C23H17FN6O
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CNC(=O)C1=C(C=C(C=C1)C2=NN3C(=CN=C3N=C2)CC4=CC5=C(C=C4)N=CC=C5)F
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C23H17FN6O/c1-25-22(31)18-6-5-16(11-19(18)24)21-13-28-23-27-12-17(30(23)29-21)10-14-4-7-20-15(9-14)3-2-8-26-20/h2-9,11-13H,10H2,1H3,(H,25,31)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
LIOLIMKSCNQPLV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Hepatocyte growth factor receptor (MET) | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D1228V (c.3683A>T) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.71 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.67 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
G
-
D
1040
|
-
S
-
D
-
I
-
S
-
S
-
P
-
L
-
L
-
Q
N
N
1050
|
T
T
V
V
H
H
I
I
D
D
L
L
S
S
A
A
L
L
N
N
1060
|
P
P
E
E
L
L
V
V
Q
Q
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
H
H
V
V
1070
|
V
V
I
I
G
G
P
P
S
S
S
S
L
L
I
I
V
V
H
H
1080
|
F
F
N
N
E
E
V
V
I
I
G
G
R
R
G
G
H
H
F
F
1090
|
G
G
C
C
V
V
Y
Y
H
H
G
G
T
T
L
L
L
L
D
D
1100
|
N
N
D
D
G
G
K
K
K
K
I
I
H
H
C
C
A
A
V
V
1110
|
K
K
S
S
L
L
N
N
R
R
I
I
T
T
D
D
I
I
G
G
1120
|
E
E
V
V
S
S
Q
Q
F
F
L
L
T
T
E
E
G
G
I
I
1130
|
I
I
M
M
K
K
D
D
F
F
S
S
H
H
P
P
N
N
V
V
1140
|
L
L
S
S
L
L
L
L
G
G
I
I
C
C
L
L
R
R
S
S
1150
|
E
E
G
G
S
S
P
P
L
L
V
V
V
V
L
L
P
P
Y
Y
1160
|
M
M
K
K
H
H
G
G
D
D
L
L
R
R
N
N
F
F
I
I
1170
|
R
R
N
N
E
E
T
T
H
H
N
N
P
P
T
T
V
V
K
K
1180
|
D
D
L
L
I
I
G
G
F
F
G
G
L
L
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
1190
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
K
K
F
Y
L
L
A
A
S
S
K
K
K
K
1200
|
F
F
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
1210
|
C
C
M
M
L
L
D
D
E
E
K
K
F
F
T
T
V
V
K
K
1220
|
V
V
A
A
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
R
R
D
V
M
M
1230
|
Y
Y
D
D
K
K
E
E
F
Y
D
Y
S
S
V
V
H
H
N
N
1240
|
K
K
T
T
G
G
A
A
K
K
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
1250
|
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
L
L
Q
Q
T
T
Q
Q
K
K
1260
|
F
F
T
T
T
T
K
K
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
F
F
1270
|
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
R
R
1280
|
G
G
A
A
P
P
P
P
Y
Y
P
P
D
D
V
V
N
N
T
T
1290
|
F
F
D
D
I
I
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
1300
|
R
R
R
R
L
L
L
L
Q
Q
P
P
E
E
Y
Y
C
C
P
P
1310
|
D
D
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
E
E
V
V
M
M
L
L
K
K
C
C
1320
|
W
W
H
H
P
P
K
K
A
A
E
E
M
M
R
R
P
P
S
S
1330
|
F
F
S
S
E
E
L
L
V
V
S
S
R
R
I
I
S
S
A
A
1340
|
I
I
F
F
S
S
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
E
-
H
-
Y
-
1350
|
V
-
H
-
V
-
N
-
A
-
T
-
Y
-
V
-
N
-
V
-
1360
|
K
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | PC9 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B260 | |||||||||
| 293T cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0063 | ||||||||||
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | There is a patient with metastatic NSCLC with MET-mediated resistance to EGFR TKI who responded to treatment with a type I MET inhibitor, savolitinib, given in combination with a third-generation EGFR inhibitor, osimertinib. The patient then developed acquired resistance mediated by a novel MET kinase domain mutation. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Hepatocyte growth factor receptor (MET) | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y1230H (c.3688T>C) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.71 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.97 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
N
-
1050
|
T
-
V
-
H
-
I
-
D
-
L
-
S
-
A
A
L
L
N
N
1060
|
P
P
E
E
L
L
V
V
Q
Q
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
H
H
V
V
1070
|
V
V
I
I
G
G
P
P
S
S
S
S
L
L
I
I
V
V
H
H
1080
|
F
F
N
N
E
E
V
V
I
I
G
G
R
R
G
G
H
H
F
F
1090
|
G
G
C
C
V
V
Y
Y
H
H
G
G
T
T
L
L
L
L
D
D
1100
|
N
N
D
D
G
G
K
K
K
K
I
I
H
H
C
C
A
A
V
V
1110
|
K
K
S
S
L
L
N
N
R
R
I
I
T
T
D
D
I
I
G
G
1120
|
E
E
V
V
S
S
Q
Q
F
F
L
L
T
T
E
E
G
G
I
I
1130
|
I
I
M
M
K
K
D
D
F
F
S
S
H
H
P
P
N
N
V
V
1140
|
L
L
S
S
L
L
L
L
G
G
I
I
C
C
L
L
R
R
S
S
1150
|
E
E
G
G
S
S
P
P
L
L
V
V
V
V
L
L
P
P
Y
Y
1160
|
M
M
K
K
H
H
G
G
D
D
L
L
R
R
N
N
F
F
I
I
1170
|
R
R
N
N
E
E
T
T
H
H
N
N
P
P
T
T
V
V
K
K
1180
|
D
D
L
L
I
I
G
G
F
F
G
G
L
L
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
1190
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
K
K
F
Y
L
L
A
A
S
S
K
K
K
K
1200
|
F
F
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
1210
|
C
C
M
M
L
L
D
D
E
E
K
K
F
F
T
T
V
V
K
K
1220
|
V
V
A
A
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
R
R
D
D
M
M
1230
|
Y
H
D
D
K
K
E
E
F
Y
D
Y
S
S
V
V
H
H
N
N
1240
|
K
K
T
T
G
G
A
A
K
K
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
1250
|
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
L
L
Q
Q
T
T
Q
Q
K
K
1260
|
F
F
T
T
T
T
K
K
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
F
F
1270
|
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
R
R
1280
|
G
G
A
A
P
P
P
P
Y
Y
P
P
D
D
V
V
N
N
T
T
1290
|
F
F
D
D
I
I
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
1300
|
R
R
R
R
L
L
L
L
Q
Q
P
P
E
E
Y
Y
C
C
P
P
1310
|
D
D
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
E
E
V
V
M
M
L
L
K
K
C
C
1320
|
W
W
H
H
P
P
K
K
A
A
E
E
M
M
R
R
P
P
S
S
1330
|
F
F
S
S
E
E
L
L
V
V
S
S
R
R
I
I
S
S
A
A
1340
|
I
I
F
F
S
S
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
E
E
H
H
Y
Y
1350
|
V
V
H
H
V
V
N
N
A
A
T
T
Y
-
V
-
N
-
V
-
1360
|
K
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | NIH3T3 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0594 | |||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Athymic female mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | MET mutations Y1248H and D1246N are resistance mechanisms for type I MET-TKIs. NIH3T3 cells expressing either mutation showed resistance to both INC280 and crizotinib but not cabozantinib, indicating the potential of sequential use of MET inhibitors may lead to a more durable response. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Hepatocyte growth factor receptor (MET) | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D1228N (c.3682G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | NIH3T3 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0594 | |||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Athymic female mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | MET mutations Y1248H and D1246N are resistance mechanisms for type I MET-TKIs. NIH3T3 cells expressing either mutation showed resistance to both INC280 and crizotinib but not cabozantinib, indicating the potential of sequential use of MET inhibitors may lead to a more durable response. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Hepatocyte growth factor receptor (MET) | [6] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y1003F (c.3008A>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 |
| WEHI-3 cells | Peripheral blood | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_3622 | |
| Hs746T cells | Skeletal muscle | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0333 | |
| Gp2-293 cells | Fetal kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_WI48 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Direct sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK-8 assay | |||
| Key Molecule: Hepatocyte growth factor receptor (MET) | [6] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D1010Y (c.3028G>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 |
| WEHI-3 cells | Peripheral blood | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_3622 | |
| Hs746T cells | Skeletal muscle | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0333 | |
| Gp2-293 cells | Fetal kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_WI48 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Direct sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK-8 assay | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Hepatocyte growth factor receptor (MET) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gastric adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2B72.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y1230C (c.3689A>G) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | NCI-H441 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1561 |
| NIH 3T3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0594 | |
| SNU638 cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0102 | |
| NCI-H596 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1571 | |
| Hs746T cells | Skeletal muscle | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0333 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nu/nu mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Hepatocyte growth factor receptor (MET) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y1230H |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.71 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.97 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
N
-
1050
|
T
-
V
-
H
-
I
-
D
-
L
-
S
-
A
A
L
L
N
N
1060
|
P
P
E
E
L
L
V
V
Q
Q
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
H
H
V
V
1070
|
V
V
I
I
G
G
P
P
S
S
S
S
L
L
I
I
V
V
H
H
1080
|
F
F
N
N
E
E
V
V
I
I
G
G
R
R
G
G
H
H
F
F
1090
|
G
G
C
C
V
V
Y
Y
H
H
G
G
T
T
L
L
L
L
D
D
1100
|
N
N
D
D
G
G
K
K
K
K
I
I
H
H
C
C
A
A
V
V
1110
|
K
K
S
S
L
L
N
N
R
R
I
I
T
T
D
D
I
I
G
G
1120
|
E
E
V
V
S
S
Q
Q
F
F
L
L
T
T
E
E
G
G
I
I
1130
|
I
I
M
M
K
K
D
D
F
F
S
S
H
H
P
P
N
N
V
V
1140
|
L
L
S
S
L
L
L
L
G
G
I
I
C
C
L
L
R
R
S
S
1150
|
E
E
G
G
S
S
P
P
L
L
V
V
V
V
L
L
P
P
Y
Y
1160
|
M
M
K
K
H
H
G
G
D
D
L
L
R
R
N
N
F
F
I
I
1170
|
R
R
N
N
E
E
T
T
H
H
N
N
P
P
T
T
V
V
K
K
1180
|
D
D
L
L
I
I
G
G
F
F
G
G
L
L
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
1190
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
K
K
F
Y
L
L
A
A
S
S
K
K
K
K
1200
|
F
F
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
1210
|
C
C
M
M
L
L
D
D
E
E
K
K
F
F
T
T
V
V
K
K
1220
|
V
V
A
A
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
R
R
D
D
M
M
1230
|
Y
H
D
D
K
K
E
E
F
Y
D
Y
S
S
V
V
H
H
N
N
1240
|
K
K
T
T
G
G
A
A
K
K
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
1250
|
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
L
L
Q
Q
T
T
Q
Q
K
K
1260
|
F
F
T
T
T
T
K
K
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
F
F
1270
|
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
R
R
1280
|
G
G
A
A
P
P
P
P
Y
Y
P
P
D
D
V
V
N
N
T
T
1290
|
F
F
D
D
I
I
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
1300
|
R
R
R
R
L
L
L
L
Q
Q
P
P
E
E
Y
Y
C
C
P
P
1310
|
D
D
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
E
E
V
V
M
M
L
L
K
K
C
C
1320
|
W
W
H
H
P
P
K
K
A
A
E
E
M
M
R
R
P
P
S
S
1330
|
F
F
S
S
E
E
L
L
V
V
S
S
R
R
I
I
S
S
A
A
1340
|
I
I
F
F
S
S
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
E
E
H
H
Y
Y
1350
|
V
V
H
H
V
V
N
N
A
A
T
T
Y
-
V
-
N
-
V
-
1360
|
K
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Capmatinib is approved for MET exon 14-altered NSCLC based on activity in targeted therapy-na ve patients. A secondary MET mutation was detected in plasma from 4 (36%) patients with crizotinib-resistant NSCLC. The detected mutations included MET D1228H (n=2), Y1230H (n=1), and D1228N +Y1230H (n=1). | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Hepatocyte growth factor receptor (MET) | [7] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y1230H (c.3688T>C) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.71 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.97 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
N
-
1050
|
T
-
V
-
H
-
I
-
D
-
L
-
S
-
A
A
L
L
N
N
1060
|
P
P
E
E
L
L
V
V
Q
Q
A
A
V
V
Q
Q
H
H
V
V
1070
|
V
V
I
I
G
G
P
P
S
S
S
S
L
L
I
I
V
V
H
H
1080
|
F
F
N
N
E
E
V
V
I
I
G
G
R
R
G
G
H
H
F
F
1090
|
G
G
C
C
V
V
Y
Y
H
H
G
G
T
T
L
L
L
L
D
D
1100
|
N
N
D
D
G
G
K
K
K
K
I
I
H
H
C
C
A
A
V
V
1110
|
K
K
S
S
L
L
N
N
R
R
I
I
T
T
D
D
I
I
G
G
1120
|
E
E
V
V
S
S
Q
Q
F
F
L
L
T
T
E
E
G
G
I
I
1130
|
I
I
M
M
K
K
D
D
F
F
S
S
H
H
P
P
N
N
V
V
1140
|
L
L
S
S
L
L
L
L
G
G
I
I
C
C
L
L
R
R
S
S
1150
|
E
E
G
G
S
S
P
P
L
L
V
V
V
V
L
L
P
P
Y
Y
1160
|
M
M
K
K
H
H
G
G
D
D
L
L
R
R
N
N
F
F
I
I
1170
|
R
R
N
N
E
E
T
T
H
H
N
N
P
P
T
T
V
V
K
K
1180
|
D
D
L
L
I
I
G
G
F
F
G
G
L
L
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
1190
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
K
K
F
Y
L
L
A
A
S
S
K
K
K
K
1200
|
F
F
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
1210
|
C
C
M
M
L
L
D
D
E
E
K
K
F
F
T
T
V
V
K
K
1220
|
V
V
A
A
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
R
R
D
D
M
M
1230
|
Y
H
D
D
K
K
E
E
F
Y
D
Y
S
S
V
V
H
H
N
N
1240
|
K
K
T
T
G
G
A
A
K
K
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
1250
|
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
L
L
Q
Q
T
T
Q
Q
K
K
1260
|
F
F
T
T
T
T
K
K
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
F
F
1270
|
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
R
R
1280
|
G
G
A
A
P
P
P
P
Y
Y
P
P
D
D
V
V
N
N
T
T
1290
|
F
F
D
D
I
I
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
1300
|
R
R
R
R
L
L
L
L
Q
Q
P
P
E
E
Y
Y
C
C
P
P
1310
|
D
D
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
E
E
V
V
M
M
L
L
K
K
C
C
1320
|
W
W
H
H
P
P
K
K
A
A
E
E
M
M
R
R
P
P
S
S
1330
|
F
F
S
S
E
E
L
L
V
V
S
S
R
R
I
I
S
S
A
A
1340
|
I
I
F
F
S
S
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
E
E
H
H
Y
Y
1350
|
V
V
H
H
V
V
N
N
A
A
T
T
Y
-
V
-
N
-
V
-
1360
|
K
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Hepatocyte growth factor receptor (MET) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D1228H |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Capmatinib is approved for MET exon 14-altered NSCLC based on activity in targeted therapy-na ve patients. A secondary MET mutation was detected in plasma from 4 (36%) patients with crizotinib-resistant NSCLC. The detected mutations included MET D1228H (n=2), Y1230H (n=1), and D1228N +Y1230H (n=1). | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Hepatocyte growth factor receptor (MET) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation+Missense mutation | p.D1228N+p.Y1230H |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Capmatinib is approved for MET exon 14-altered NSCLC based on activity in targeted therapy-na ve patients. A secondary MET mutation was detected in plasma from 4 (36%) patients with crizotinib-resistant NSCLC. The detected mutations included MET D1228H (n=2), Y1230H (n=1), and D1228N +Y1230H (n=1). | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Hepatocyte growth factor receptor (MET) | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D1228N (c.3682G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Hepatocyte growth factor receptor (MET) | [8] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y1003N (c.3007T>A) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Key Molecule: Hepatocyte growth factor receptor (MET) | [8] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y1003C (c.3008A>G) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Key Molecule: Hepatocyte growth factor receptor (MET) | [8] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y1003F (c.3008A>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Key Molecule: Hepatocyte growth factor receptor (MET) | [8] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D1010N (c.3028G>A) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Key Molecule: Hepatocyte growth factor receptor (MET) | [8] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D1010H (c.3028G>C) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Key Molecule: Hepatocyte growth factor receptor (MET) | [8] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D1010Y (c.3028G>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
