Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00242) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Macrolides
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Tylosin; tylosin tartrate; Tilosina; Tylosinum; UNII-YEF4JXN031; Tylosine; Tylocine; Tylan; Tylosin A; 1401-69-0; YEF4JXN031; Fradizine; CHEBI:17658; Vubityl 200; Tylosinum [INN-Latin]; Tylosine [INN-French]; Tilosina [INN-Spanish]; HSDB 7022; EINECS 215-754-8; AI3-29799; SR-05000002057; Tylosin [USP:INN:BAN]; Tylan (TN); Tylosin (USP/INN); AC1NQX0W
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
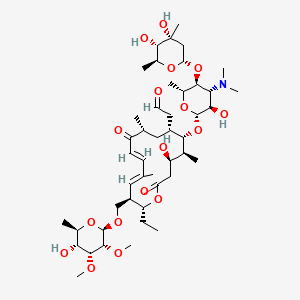
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(4 diseases)
[4]
[5]
[6]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Validated by in-vivo Model for This Drug
(3 diseases)
[7]
[8]
[9]
|
||||
| Target | Bacterial 23S ribosomal RNA (Bact 23S rRNA) | NOUNIPROTAC | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C46H77NO17
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CC[C@@H]1[C@H](/C=C(/C=C/C(=O)[C@@H](C[C@@H]([C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H](CC(=O)O1)O)C)O[C@H]2[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O2)C)O[C@H]3C[C@@]([C@H]([C@@H](O3)C)O)(C)O)N(C)C)O)CC=O)C)\\C)CO[C@H]4[C@@H]([C@@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O4)C)O)OC)OC
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C46H77NO17/c1-13-33-30(22-58-45-42(57-12)41(56-11)37(52)26(5)60-45)18-23(2)14-15-31(49)24(3)19-29(16-17-48)39(25(4)32(50)20-34(51)62-33)64-44-38(53)36(47(9)10)40(27(6)61-44)63-35-21-46(8,55)43(54)28(7)59-35/h14-15,17-18,24-30,32-33,35-45,50,52-55H,13,16,19-22H2,1-12H3/b15-14+,23-18+/t24-,25+,26-,27-,28+,29+,30-,32-,33-,35+,36-,37-,38-,39-,40-,41-,42-,43+,44+,45-,46-/m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
WBPYTXDJUQJLPQ-VMXQISHHSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: rRNA adenine N-6-methyltransferase ermC' (ERMC) | [10], [11], [12] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Bacillus subtilis strain BD170 | 1423 | ||
| Bacillus subtilis strain BD430 | 1423 | |||
| Bacillus subtilis strain BD431 | 1423 | |||
| Bacillus subtilis strain BD488 | 1423 | |||
| Bacillus subtilis strain BD81 | 1423 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
SDS-PAGE assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The ermC gene of plasmid pE194 specifies resistance to the macrolidelincosamide-streptogramin B antibiotics. pE194 specifies an RNA methylase that can utilize either 50 S ribosomes or 23 S rRNA as substrates,with a specific dimethylation of adenine in 23 S rRNA. | |||
| Key Molecule: ErmR rRNA adenine N6-methyltransferase (ERMR) | [9] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Aeromicrobium erythreum infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Aeromicrobium erythreum strains AR18 | 2041 | ||
| Aeromicrobium erythreum strains AR1807 | 2041 | |||
| Aeromicrobium erythreum strains AR1848 | 2041 | |||
| Aeromicrobium erythreum strains AR1849 | 2041 | |||
| Aeromicrobium erythreum strains AR1850 | 2041 | |||
| Aeromicrobium erythreum strains BD170 | 2041 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Southern blotting assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Disk diffusion assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Using the Ery- strain AR1807 as a recipient for plasmid-directed integrative recombination, the chromosomal ermR gene (encoding 23S rRNA methyltransferase) was disrupted, ermR-disrupted strains AR1848 and AR1849 were highly sensitive to erythromycin and the other macrolide antibiotics. Phenotypic characterizations demonstrated that ermR is the sole determinant of macrolide antibiotic resistance in A. erythreum. AR18, AR1807, and AR1850 (Ery- Ermr) were resistant to clindamycin, erythromycin, spiramycin, and tylosin (some sensitivity totylosin was observed at high concentrations). | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Oleandomycin glycosyltransferase oleD (OLED) | [1], [2], [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli GT-28 | 562 | ||
| Escherichia coli MurG | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | OleD displays broad acceptor specificity and hence will inactivate a wider range of macrolide antibiotics including tylosin and erythromycin. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: 16S rRNA adenine dimethyltransferase (KsgA) | [13] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lactobacillus casei infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | A1518/1519 |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain UCBPP-PA14 | 1763 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Primer extension analysis; MS analysis; Western blot assay; Semiquantitative RT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Phenotypic microarrays assay; MIC assay; Oxidative stress sensitivity testing; Superoxide dismutase enzyme activity assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In this study, we demonstrated the absence of A1518/1519 methylation in the 16S rRNA of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa ksgA mutant. Biolog phenotypic microarrays were used to screen the phenotypes of the ksgA mutant against various antimicrobial agents. The loss of ksgA led to increased sensitivity to menadione, a superoxide generator, which was, at least in part, attributed to decreased in a superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity. Interestingly, the decrease in SOD activity in the ksgA mutant was linked to a decrease in the SodM protein levels, but not the sodM mRNA levels. Furthermore, the ksgA mutant strain exhibited sensitivity to hygromycin B and tylosin antibiotics. The tylosin-sensitive phenotype was correlated with decreased transcriptional levels of tufA, tufB, and tsf, which encode elongation factors. Additionally, the ksgA mutant showed resistance to kasugamycin. Collectively, these findings highlight the role of KsgA in oxidative stress responses and antibiotic sensitivity in P. aeruginosa. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: 16S rRNA adenine dimethyltransferase (KsgA) | [13] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lactobacillus casei infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | A1182V |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 1763 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR; Southern blot assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | SOD enzymatic activity and SodM protein levels are reduced in the ksgA mutant strain;The absence of ksgA contributes to an altered antibiotic response | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Erythromycin resistance protein (ERM33) | [6] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus sciuri infection [ICD-11: 1B54.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Gene recombination |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Staphylococcus sciuri plasmid pSCFS1 | 1296 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sequence analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Staphylococcus sciuri Gene erm(33), Encoding Inducible Resistance to Macrolides, Lincosamides, and Streptogramin B Antibiotics, Is a Product of Recombination between erm(C) and erm(A). | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: srmA open reading frame gimA (GIMA) | [14] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Streptomyces ambbyaciens infection [ICD-11: 1C43.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli | 668369 | ||
| Escherichia coli strain S17.1 | 1227813 | |||
| Micrococcus luteus strain Cgr | 1270 | |||
| Micrococcus luteus strain DSM1790 | 1270 | |||
| Streptomyces ambofaciens strain ATCC 23877 | 278992 | |||
| Streptomyces ambofaciens strain OS41.99 | 1954 | |||
| Streptomyces ambofaciens strain OS41.99NP | 1954 | |||
| Streptomyces ambofaciens strain OS81 | 1954 | |||
| Streptomyces lividans strain OS456 | 1916 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Observation of growth inhibition zones assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | With UDP-[14C]glucose as the cofactor, crude S30 extracts from OS456(pOS41.90) were tested on various macrolides. Among those, chalcomycin was the most active substrate. Methymycin, tylosin, pikromycin, and rosaramicin were four of the best substrates. Oleandomycin, josamycin, and carbomycin were glycosylated to a lesser extent. Macrolides that were found to be as poor substrates of GimA as lankamycin were erythromycin and angolamycin. Spiramycin was also a very poor substrate. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Tylosin resistance ATP-binding protein TlrC (TLRC) | [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Streptomyces fradiae infection [ICD-11: 1C43.5] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Streptomyces fradiae strain | 1906 | ||
| Treptomyces fradia strain | 1906 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Northern blotting analysis | |||
| Mechanism Description | A tylosin(Ty)-producing strain of Streptomyces fradiae contains at least three genes, tlrA, tlrB, tlrC, specifying resistance to Ty (TyR). | |||
| Key Molecule: Tylosin resistance ATP-binding protein TlrC (TLRC) | [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Streptomyces fradiae infection [ICD-11: 1C43.5] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Streptomyces fradiae strain | 1906 | ||
| Treptomyces fradia strain | 1906 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Northern blotting analysis | |||
| Mechanism Description | The product of the tlrA gene is an rRNA methylase responsible for dimethylation of a specific A residue in S. fradiae 23s rRNA (Zalacain and Cundliffe, 1989). In contrast, the Ty-inducible resistance encoded by tlrB or tlrC appears to be specific for Ty and each imparts lower levels of TyR than does tlrA. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: rRNA adenine N-6-methyltransferase ermG (ERMG) | [8] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacillus sphaericus infection [ICD-11: 1C4Y.4] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Bacillus subtilis strain BD1107 | 1423 | ||
| Bacillus subtilis strain BD1117 | 1423 | |||
| Bacillus subtilis strain BD1146 | 1423 | |||
| Bacillus subtilis strain BD1156 | 1423 | |||
| Bacillus subtilis strain BD1158 | 1423 | |||
| Bacillus subtilis strain BD624 | 1423 | |||
| Bacillus subtilis strain BD629 | 1423 | |||
| Bacillus subtilis strain BD630 | 1423 | |||
| Bacillus subtilis strain CU403 | 1423 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Southern blotting assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | One of the mechanisms of bacterial resistance to aminoglycosides is the production of aminoglycoside N-acetyl-transferase (AAC) enzymes which acetylate the amino groups present in the molecule of the aminoglycoside, preventing their interaction with the ribosome. ermG specifies a 29,000-dalton protein, the synthesis of which is induced by erythromycin. S1 nuclease mapping was used to identify the transcriptional start site. These experiments demonstrated the presence on the ermG mRNA of a 197 to 198-base leader. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: MsrC (MSRC) | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Enterococcus faecium meningitis [ICD-11: 1D01.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli | 668369 | ||
| Enterococcus faecium TX2465 | 1352 | |||
| Escherichia coli TX1330 | 668369 | |||
| Escherichia coli TX2046 | 668369 | |||
| Escherichia coli TX2597 | 668369 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Southern blotting assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Twofold dilutions assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The complete sequence (1,479 nucleotides) of msrC, part of which was recently reported by others using a different strain, was determined. This gene was found in 233 of 233 isolates of Enterococcus faecium but in none of 265 other enterococci. Disruption of msrC was associated with a two- to eightfold decrease in MICs of erythromycin azithromycin, tylosin, and quinupristin, suggesting that it may explain in part the apparent greater intrinsic resistance to macrolides of isolates of E. faecium relative to many streptococci. This endogenous, species-specific gene of E. faecium is 53% identical to msr(A), suggesting that it may be a remote progenitor of the acquired macrolide resistance gene found in some isolates of staphylococci. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: MsrC (MSRC) | [4] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Enterococcus faecium meningitis [ICD-11: 1D01.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Truncated mutantion | Disruption (nt 1251 to 1879) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli | 668369 | ||
| Enterococcus faecium TX2465 | 1352 | |||
| Escherichia coli TX1330 | 668369 | |||
| Escherichia coli TX2046 | 668369 | |||
| Escherichia coli TX2597 | 668369 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Southern blotting assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Twofold dilutions assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Disruption of msrC was associated with a two- to eightfold decrease in MICs of erythromycin azithromycin, tylosin, and quinupristin, suggesting that it may explain in part the apparent greater intrinsic resistance to macrolides of isolates of E. faecium relative to many streptococci. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
