Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00061)
| Name |
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Proto-oncogene c-ErbB-1; Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-1; ERBB; ERBB1; HER1
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
EGFR
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr7:55019017-55211628[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MRPSGTAGAALLALLAALCPASRALEEKKVCQGTSNKLTQLGTFEDHFLSLQRMFNNCEV
VLGNLEITYVQRNYDLSFLKTIQEVAGYVLIALNTVERIPLENLQIIRGNMYYENSYALA VLSNYDANKTGLKELPMRNLQEILHGAVRFSNNPALCNVESIQWRDIVSSDFLSNMSMDF QNHLGSCQKCDPSCPNGSCWGAGEENCQKLTKIICAQQCSGRCRGKSPSDCCHNQCAAGC TGPRESDCLVCRKFRDEATCKDTCPPLMLYNPTTYQMDVNPEGKYSFGATCVKKCPRNYV VTDHGSCVRACGADSYEMEEDGVRKCKKCEGPCRKVCNGIGIGEFKDSLSINATNIKHFK NCTSISGDLHILPVAFRGDSFTHTPPLDPQELDILKTVKEITGFLLIQAWPENRTDLHAF ENLEIIRGRTKQHGQFSLAVVSLNITSLGLRSLKEISDGDVIISGNKNLCYANTINWKKL FGTSGQKTKIISNRGENSCKATGQVCHALCSPEGCWGPEPRDCVSCRNVSRGRECVDKCN LLEGEPREFVENSECIQCHPECLPQAMNITCTGRGPDNCIQCAHYIDGPHCVKTCPAGVM GENNTLVWKYADAGHVCHLCHPNCTYGCTGPGLEGCPTNGPKIPSIATGMVGALLLLLVV ALGIGLFMRRRHIVRKRTLRRLLQERELVEPLTPSGEAPNQALLRILKETEFKKIKVLGS GAFGTVYKGLWIPEGEKVKIPVAIKELREATSPKANKEILDEAYVMASVDNPHVCRLLGI CLTSTVQLITQLMPFGCLLDYVREHKDNIGSQYLLNWCVQIAKGMNYLEDRRLVHRDLAA RNVLVKTPQHVKITDFGLAKLLGAEEKEYHAEGGKVPIKWMALESILHRIYTHQSDVWSY GVTVWELMTFGSKPYDGIPASEISSILEKGERLPQPPICTIDVYMIMVKCWMIDADSRPK FRELIIEFSKMARDPQRYLVIQGDERMHLPSPTDSNFYRALMDEEDMDDVVDADEYLIPQ QGFFSSPSTSRTPLLSSLSATSNNSTVACIDRNGLQSCPIKEDSFLQRYSSDPTGALTED SIDDTFLPVPEYINQSVPKRPAGSVQNPVYHNQPLNPAPSRDPHYQDPHSTAVGNPEYLN TVQPTCVNSTFDSPAHWAQKGSHQISLDNPDYQQDFFPKEAKPNGIFKGSTAENAEYLRV APQSSEFIGA Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Receptor tyrosine kinase binding ligands of the EGF family and activating several signaling cascades to convert extracellular cues into appropriate cellular responses. Known ligands include EGF, TGFA/TGF-alpha, AREG, epigen/EPGN, BTC/betacellulin, epiregulin/EREG and HBEGF/heparin-binding EGF. Ligand binding triggers receptor homo- and/or heterodimerization and autophosphorylation on key cytoplasmic residues. The phosphorylated receptor recruits adapter proteins like GRB2 which in turn activates complex downstream signaling cascades. Activates at least 4 major downstream signaling cascades including the RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK, PI3 kinase-AKT, PLCgamma-PKC and STATs modules. May also activate the NF-kappa-B signaling cascade. Also directly phosphorylates other proteins like RGS16, activating its GTPase activity and probably coupling the EGF receptor signaling to the G protein-coupled receptor signaling. Also phosphorylates MUC1 and increases its interaction with SRC and CTNNB1/beta-catenin. Positively regulates cell migration via interaction with CCDC88A/GIV which retains EGFR at the cell membrane following ligand stimulation, promoting EGFR signaling which triggers cell migration. Plays a role in enhancing learning and memory performance.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
25 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Gefitinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | |||||||||||||
| Classification of Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | ||||||||||||
| The Specified Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | ||||||||||||
| The Studied Tissue | Blood | ||||||||||||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.41E-78 Fold-change: -3.81E-01 Z-score: -2.43E+01 |
||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||||||||||
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | |||||||||||
| EGFR signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa01521 | |||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 | |||||||||
| NCI-H1650 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1483 | ||||||||||
| PC9 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B260 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | miR-133b suppresses the expression of EGFR, miR-133b transfection may modulate apoptosis, invasion and sensitivity to EGFR-TkI through the EGFR signaling pathways. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Gefitinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | |||||||||||||
| Classification of Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | ||||||||||||
| The Specified Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma | ||||||||||||
| The Studied Tissue | Blood | ||||||||||||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.41E-78 Fold-change: -3.81E-01 Z-score: -2.43E+01 |
||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | ||||||||||
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |||||||||||
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | |||||||||||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |||||||||||
| EGFR signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa01521 | |||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | H1975 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1511 | |||||||||
| A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 | ||||||||||
| H1299 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 | ||||||||||
| HCC827 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2063 | ||||||||||
| 16HBE cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0112 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; EdU assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | GAS5 was significantly downregulated in lung adenocarcinoma tissues compared with the paired adjacent non-tumorous tissue samples. Furthermore, lower GAS5 expression levels were associated with larger tumor sizes, poor tumor differentiation, and advanced pathological stages. However, GAS5 was almost equally expressed between benign tumors compared with the adjacent normal tissues. GAS5 was also overexpressed in EGFR-TkI sensitive cell lines compared with the resistant cell line. Using MTT, EdU incorporation, and colony formation assays, we showed that GAS5-expressing A549 cells displayed an elevated level of cell death. In addition to its pro-apoptotic effect in the A549 cell line, GAS5 overexpression also suppressed the growth of A549-derived tumors in nude mice treated with gefitinib. GAS5 overexpression was inversely correlated with the expression of the EGFR pathway and IGF-1R proteins. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Gefitinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | |||||||||||||
| Classification of Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | ||||||||||||
| The Specified Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | ||||||||||||
| The Studied Tissue | Blood | ||||||||||||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.41E-78 Fold-change: -3.81E-01 Z-score: -2.43E+01 |
||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||||||||||
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | |||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | H1975 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1511 | |||||||||
| HCC827 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2063 | ||||||||||
| CCD-19Lu cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2382 | ||||||||||
| H3255 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6831 | ||||||||||
| MRC-5 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0440 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | microRNA-200a directly targets and downregulates egfr and c-met to inhibit migration, invasion, and gefitinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [9] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Gefitinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | |||||||||||||
| Classification of Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | ||||||||||||
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | ||||||||||||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung tissue | ||||||||||||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.65E-01 Fold-change: 1.45E-02 Z-score: 1.39E+00 |
||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||||||||||
| RGFR signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | EGFR was negatively regulated by miR-7 mimic transfection, and downregulation of EGFR expression at the protein level largely correlated with elevated levels of miR-7 in the gefitinib-resistant cells. The results of the present study suggest that miR-7 may have central roles in the development of resistance to endocrine therapy in resistant cells through regulating the expression of EGFR in cancer cells. | ||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [41] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Gefitinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L858R |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.64 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.47 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
-
S
-
M
-
G
G
E
E
A
A
P
P
700
|
N
N
Q
Q
A
A
L
L
L
L
R
R
I
I
L
L
K
K
E
E
710
|
T
T
E
E
F
F
K
K
K
K
I
I
K
K
V
V
L
L
G
G
720
|
S
S
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
K
K
G
G
730
|
L
L
W
W
I
I
P
P
E
E
G
G
E
E
K
K
V
V
K
K
740
|
I
I
P
P
V
V
A
A
I
I
K
K
E
E
L
L
R
R
E
E
750
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
P
P
K
K
A
A
N
N
K
K
E
E
I
I
760
|
L
L
D
D
E
E
A
A
Y
Y
V
V
M
M
A
A
S
S
V
V
770
|
D
D
N
N
P
P
H
H
V
V
C
C
R
R
L
L
L
L
G
G
780
|
I
I
C
C
L
L
T
T
S
S
T
T
V
V
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
790
|
T
T
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
P
P
F
F
G
G
C
C
L
L
L
L
800
|
D
D
Y
Y
V
V
R
R
E
E
H
H
K
K
D
D
N
N
I
I
810
|
G
G
S
S
Q
Q
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
N
N
W
W
C
C
V
V
820
|
Q
Q
I
I
A
A
K
K
G
G
M
M
N
N
Y
Y
L
L
E
E
830
|
D
D
R
R
R
R
L
L
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
840
|
A
A
R
R
N
N
V
V
L
L
V
V
K
K
T
T
P
P
Q
Q
850
|
H
H
V
V
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
R
A
A
860
|
K
K
L
L
L
L
G
G
A
A
E
E
E
E
K
K
E
E
Y
Y
870
|
H
H
A
A
E
E
G
G
G
G
K
K
V
V
P
P
I
I
K
K
880
|
W
W
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
I
I
L
L
H
H
R
R
890
|
I
I
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
900
|
Y
Y
G
G
V
V
T
T
V
V
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
910
|
F
F
G
G
S
S
K
K
P
P
Y
Y
D
D
G
G
I
I
P
P
920
|
A
A
S
S
E
E
I
I
S
S
S
S
I
I
L
L
E
E
K
K
930
|
G
G
E
E
R
R
L
L
P
P
Q
Q
P
P
P
P
I
I
C
C
940
|
T
T
I
I
D
D
V
V
Y
Y
M
M
I
I
M
M
V
V
K
K
950
|
C
C
W
W
M
M
I
I
D
D
A
A
D
D
S
S
R
R
P
P
960
|
K
K
F
F
R
R
E
E
L
L
I
I
I
I
E
E
F
F
S
S
970
|
K
K
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
P
P
Q
Q
R
R
Y
Y
L
L
980
|
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
G
G
D
D
E
E
R
R
M
M
H
H
L
L
990
|
P
P
S
S
P
P
T
T
D
D
S
S
N
N
F
F
Y
Y
R
R
1000
|
A
A
L
L
M
M
D
D
E
E
E
E
D
D
M
M
D
D
D
D
1010
|
V
V
V
V
D
D
A
A
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
I
I
P
P
1020
|
Q
Q
-
Q
-
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | ERK/MAPKsignaling pathway | Activation | hsa04210 | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | NSCLC cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Liquid biopsy; ATP-binding pocket affinity comparison assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The two most common EGFR-activating mutations are small in-frame deletions in exon 19 (particularly E746-A750del) and amino acid substitution in exon 21 (leucine to arginine at codon 858 (L858R)), which collectively account for >90% of known activating EGFR mutations.2 3 These two alterations are the best-characterised mutations conferring sensitivity to EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR-TkI) therapy, resulting in higher response rates (RR) (up to 70%) and longer median survival (up to 24-30 months) than those observed in patients with wild-type (WT) EGFR. The higher sensitivity of these mutations relays in an increased affinity of the ATP-binding pocket for EGFR-TkIs as compared with WT EGFR. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [41] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Gefitinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Frameshift mutation | p.E746-A750del |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | ERK/MAPKsignaling pathway | Activation | hsa04210 | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | NSCLC cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Liquid biopsy; ATP-binding pocket affinity comparison assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The two most common EGFR-activating mutations are small in-frame deletions in exon 19 (particularly E746-A750del) and amino acid substitution in exon 21 (leucine to arginine at codon 858 (L858R)), which collectively account for >90% of known activating EGFR mutations.2 3 These two alterations are the best-characterised mutations conferring sensitivity to EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR-TkI) therapy, resulting in higher response rates (RR) (up to 70%) and longer median survival (up to 24-30 months) than those observed in patients with wild-type (WT) EGFR. The higher sensitivity of these mutations relays in an increased affinity of the ATP-binding pocket for EGFR-TkIs as compared with WT EGFR. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [7] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Gefitinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | |||||||||||||
| Classification of Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | ||||||||||||
| The Specified Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | ||||||||||||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung tissue | ||||||||||||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.37E-11 Fold-change: 6.31E-01 Z-score: 7.28E+00 |
||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | ||||||||||
| Cell colony | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |||||||||||
| Cell viability | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 | |||||||||
| PC9 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B260 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | miR-138 inhibit the protein level of EGFR and reverses gefitinib resistance in lung cancer cells. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [8] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Gefitinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | |||||||||||||
| Classification of Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | ||||||||||||
| The Specified Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | ||||||||||||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung tissue | ||||||||||||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.37E-11 Fold-change: 6.31E-01 Z-score: 7.28E+00 |
||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | ||||||||||
| Cell invasion | Activation | hsa05200 | |||||||||||
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | |||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 | |||||||||
| H460 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0459 | ||||||||||
| H1299 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 | ||||||||||
| Sk-MES-1 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0630 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Tumor xenograft in vivo model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; RT-qPCR | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Flow cytometry assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Long Noncoding RNA LINC00460 promotes the gefitinib resistance of nonsmall cell lung cancer through EGFR by sponging miR-769-5p. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | [53] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Gefitinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T790M |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.05 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
S
G
G
E
E
A
A
P
P
700
|
N
N
Q
Q
A
A
L
L
L
L
R
R
I
I
L
L
K
K
E
E
710
|
T
T
E
E
F
F
K
K
K
K
I
I
K
K
V
V
L
L
G
G
720
|
S
S
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
K
K
G
G
730
|
L
L
W
W
I
I
P
P
E
E
G
G
E
E
K
K
V
V
K
K
740
|
I
I
P
P
V
V
A
A
I
I
K
K
E
E
L
L
R
R
E
E
750
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
P
P
K
K
A
A
N
N
K
K
E
E
I
I
760
|
L
L
D
D
E
E
A
A
Y
Y
V
V
M
M
A
A
S
S
V
V
770
|
D
D
N
N
P
P
H
H
V
V
C
C
R
R
L
L
L
L
G
G
780
|
I
I
C
C
L
L
T
T
S
S
T
T
V
V
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
790
|
T
M
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
P
P
F
F
G
G
C
C
L
L
L
L
800
|
D
D
Y
Y
V
V
R
R
E
E
H
H
K
K
D
D
N
N
I
I
810
|
G
G
S
S
Q
Q
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
N
N
W
W
C
C
V
V
820
|
Q
Q
I
I
A
A
K
K
G
G
M
M
N
N
Y
Y
L
L
E
E
830
|
D
D
R
R
R
R
L
L
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
840
|
A
A
R
R
N
N
V
V
L
L
V
V
K
K
T
T
P
P
Q
Q
850
|
H
H
V
V
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
860
|
K
K
L
L
L
L
G
G
A
A
E
E
E
E
K
K
E
E
Y
Y
870
|
H
H
A
A
E
E
G
G
G
G
K
K
V
V
P
P
I
I
K
K
880
|
W
W
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
I
I
L
L
H
H
R
R
890
|
I
I
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
900
|
Y
Y
G
G
V
V
T
T
V
V
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
910
|
F
F
G
G
S
S
K
K
P
P
Y
Y
D
D
G
G
I
I
P
P
920
|
A
A
S
S
E
E
I
I
S
S
S
S
I
I
L
L
E
E
K
K
930
|
G
G
E
E
R
R
L
L
P
P
Q
Q
P
P
P
P
I
I
C
C
940
|
T
T
I
I
D
D
V
V
Y
Y
M
M
I
I
M
M
V
V
K
K
950
|
C
C
W
W
M
M
I
I
D
D
A
A
D
D
S
S
R
R
P
P
960
|
K
K
F
F
R
R
E
E
L
L
I
I
I
I
E
E
F
F
S
S
970
|
K
K
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
P
P
Q
Q
R
R
Y
Y
L
L
980
|
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
G
G
D
D
E
E
R
R
M
M
H
H
L
L
990
|
P
P
S
S
P
P
T
T
D
D
S
S
N
N
F
F
Y
Y
R
R
1000
|
A
A
L
L
M
M
D
D
E
E
E
E
D
D
M
M
D
D
D
D
1010
|
V
V
V
V
D
D
A
A
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
I
I
P
P
1020
|
Q
Q
Q
Q
G
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | AKT signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04151 | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Circulating-free DNA assay; Whole exome sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Quantification of allele fractions in plasma identified increased representation of mutant alleles in association with emergence of therapy resistance. | ||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [41] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Gefitinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.C797S |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.64 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.20 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
G
G
A
S
M
M
G
G
G
E
E
A
A
P
P
700
|
N
N
Q
Q
A
A
L
L
L
L
R
R
I
I
L
L
K
K
E
E
710
|
T
T
E
E
F
F
K
K
K
K
I
I
K
K
V
V
L
L
G
G
720
|
S
S
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
K
K
G
G
730
|
L
L
W
W
I
I
P
P
E
E
G
G
E
E
K
K
V
V
K
K
740
|
I
I
P
P
V
V
A
A
I
I
K
K
E
E
L
L
R
R
E
E
750
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
P
P
K
K
A
A
N
N
K
K
E
E
I
I
760
|
L
L
D
D
E
E
A
A
Y
Y
V
V
M
M
A
A
S
S
V
V
770
|
D
D
N
N
P
P
H
H
V
V
C
C
R
R
L
L
L
L
G
G
780
|
I
I
C
C
L
L
T
T
S
S
T
T
V
V
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
790
|
T
M
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
P
P
F
F
G
G
C
S
L
L
L
L
800
|
D
D
Y
Y
V
V
R
R
E
E
H
H
K
K
D
D
N
N
I
I
810
|
G
G
S
S
Q
Q
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
N
N
W
W
C
C
V
V
820
|
Q
Q
I
I
A
A
K
K
G
G
M
M
N
N
Y
Y
L
L
E
E
830
|
D
D
R
R
R
R
L
L
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
840
|
A
A
R
R
N
N
V
V
L
L
V
V
K
K
T
T
P
P
Q
Q
850
|
H
H
V
V
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
860
|
K
K
L
L
L
L
G
G
A
A
E
E
E
E
K
K
E
E
Y
Y
870
|
H
H
A
A
E
E
G
G
G
G
K
K
V
V
P
P
I
I
K
K
880
|
W
W
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
I
I
L
L
H
H
R
R
890
|
I
I
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
900
|
Y
Y
G
G
V
V
T
T
V
V
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
910
|
F
F
G
G
S
S
K
K
P
P
Y
Y
D
D
G
G
I
I
P
P
920
|
A
A
S
S
E
E
I
I
S
S
S
S
I
I
L
L
E
E
K
K
930
|
G
G
E
E
R
R
L
L
P
P
Q
Q
P
P
P
P
I
I
C
C
940
|
T
T
I
I
D
D
V
V
Y
Y
M
M
I
I
M
M
V
V
K
K
950
|
C
C
W
W
M
M
I
I
D
D
A
A
D
D
S
S
R
R
P
P
960
|
K
K
F
F
R
R
E
E
L
L
I
I
I
I
E
E
F
F
S
S
970
|
K
K
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
P
P
Q
Q
R
R
Y
Y
L
L
980
|
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
G
G
D
D
E
E
R
R
M
M
H
H
L
L
990
|
P
P
S
S
P
P
T
T
D
D
S
S
N
N
F
F
Y
Y
R
R
1000
|
A
A
L
L
M
M
D
D
E
E
E
E
D
D
M
M
D
D
D
D
1010
|
V
V
V
V
D
D
A
A
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
I
I
P
P
1020
|
Q
Q
-
Q
-
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | ERK/MAPKsignaling pathway | Activation | hsa04210 | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | NSCLC cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Liquid biopsy; ATP-binding pocket affinity comparison assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Known mechanisms are secondary resistance mutations occurring in the ATP-binding domain (such as T790M and C797S), mutation or amplification of bypass signallings (such as AXL, Hh, ERBb2, CRIPTO, etc), activating mutations in the downstream pathways (PI3k, AkT, MEk, RAF), low levels of mRNA or polymorphisms of the pro-apoptotic protein BIM, induction of a transcription programme for EMT and phenotypical changes, or induction of elevated tumour PD-L1 levels. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [42], [43], [44] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Gefitinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T790M |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.05 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
S
G
G
E
E
A
A
P
P
700
|
N
N
Q
Q
A
A
L
L
L
L
R
R
I
I
L
L
K
K
E
E
710
|
T
T
E
E
F
F
K
K
K
K
I
I
K
K
V
V
L
L
G
G
720
|
S
S
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
K
K
G
G
730
|
L
L
W
W
I
I
P
P
E
E
G
G
E
E
K
K
V
V
K
K
740
|
I
I
P
P
V
V
A
A
I
I
K
K
E
E
L
L
R
R
E
E
750
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
P
P
K
K
A
A
N
N
K
K
E
E
I
I
760
|
L
L
D
D
E
E
A
A
Y
Y
V
V
M
M
A
A
S
S
V
V
770
|
D
D
N
N
P
P
H
H
V
V
C
C
R
R
L
L
L
L
G
G
780
|
I
I
C
C
L
L
T
T
S
S
T
T
V
V
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
790
|
T
M
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
P
P
F
F
G
G
C
C
L
L
L
L
800
|
D
D
Y
Y
V
V
R
R
E
E
H
H
K
K
D
D
N
N
I
I
810
|
G
G
S
S
Q
Q
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
N
N
W
W
C
C
V
V
820
|
Q
Q
I
I
A
A
K
K
G
G
M
M
N
N
Y
Y
L
L
E
E
830
|
D
D
R
R
R
R
L
L
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
840
|
A
A
R
R
N
N
V
V
L
L
V
V
K
K
T
T
P
P
Q
Q
850
|
H
H
V
V
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
860
|
K
K
L
L
L
L
G
G
A
A
E
E
E
E
K
K
E
E
Y
Y
870
|
H
H
A
A
E
E
G
G
G
G
K
K
V
V
P
P
I
I
K
K
880
|
W
W
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
I
I
L
L
H
H
R
R
890
|
I
I
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
900
|
Y
Y
G
G
V
V
T
T
V
V
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
910
|
F
F
G
G
S
S
K
K
P
P
Y
Y
D
D
G
G
I
I
P
P
920
|
A
A
S
S
E
E
I
I
S
S
S
S
I
I
L
L
E
E
K
K
930
|
G
G
E
E
R
R
L
L
P
P
Q
Q
P
P
P
P
I
I
C
C
940
|
T
T
I
I
D
D
V
V
Y
Y
M
M
I
I
M
M
V
V
K
K
950
|
C
C
W
W
M
M
I
I
D
D
A
A
D
D
S
S
R
R
P
P
960
|
K
K
F
F
R
R
E
E
L
L
I
I
I
I
E
E
F
F
S
S
970
|
K
K
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
P
P
Q
Q
R
R
Y
Y
L
L
980
|
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
G
G
D
D
E
E
R
R
M
M
H
H
L
L
990
|
P
P
S
S
P
P
T
T
D
D
S
S
N
N
F
F
Y
Y
R
R
1000
|
A
A
L
L
M
M
D
D
E
E
E
E
D
D
M
M
D
D
D
D
1010
|
V
V
V
V
D
D
A
A
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
I
I
P
P
1020
|
Q
Q
Q
Q
G
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | ERK/MAPKsignaling pathway | Activation | hsa04210 | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | NSCLC cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Liquid biopsy; ATP-binding pocket affinity comparison assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Known mechanisms are secondary resistance mutations occurring in the ATP-binding domain (such as T790M and C797S), mutation or amplification of bypass signallings (such as AXL, Hh, ERBb2, CRIPTO, etc), activating mutations in the downstream pathways (PI3k, AkT, MEk, RAF), low levels of mRNA or polymorphisms of the pro-apoptotic protein BIM, induction of a transcription programme for EMT and phenotypical changes, or induction of elevated tumour PD-L1 levels. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [45], [46], [47] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Gefitinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T790M |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.05 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
S
G
G
E
E
A
A
P
P
700
|
N
N
Q
Q
A
A
L
L
L
L
R
R
I
I
L
L
K
K
E
E
710
|
T
T
E
E
F
F
K
K
K
K
I
I
K
K
V
V
L
L
G
G
720
|
S
S
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
K
K
G
G
730
|
L
L
W
W
I
I
P
P
E
E
G
G
E
E
K
K
V
V
K
K
740
|
I
I
P
P
V
V
A
A
I
I
K
K
E
E
L
L
R
R
E
E
750
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
P
P
K
K
A
A
N
N
K
K
E
E
I
I
760
|
L
L
D
D
E
E
A
A
Y
Y
V
V
M
M
A
A
S
S
V
V
770
|
D
D
N
N
P
P
H
H
V
V
C
C
R
R
L
L
L
L
G
G
780
|
I
I
C
C
L
L
T
T
S
S
T
T
V
V
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
790
|
T
M
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
P
P
F
F
G
G
C
C
L
L
L
L
800
|
D
D
Y
Y
V
V
R
R
E
E
H
H
K
K
D
D
N
N
I
I
810
|
G
G
S
S
Q
Q
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
N
N
W
W
C
C
V
V
820
|
Q
Q
I
I
A
A
K
K
G
G
M
M
N
N
Y
Y
L
L
E
E
830
|
D
D
R
R
R
R
L
L
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
840
|
A
A
R
R
N
N
V
V
L
L
V
V
K
K
T
T
P
P
Q
Q
850
|
H
H
V
V
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
860
|
K
K
L
L
L
L
G
G
A
A
E
E
E
E
K
K
E
E
Y
Y
870
|
H
H
A
A
E
E
G
G
G
G
K
K
V
V
P
P
I
I
K
K
880
|
W
W
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
I
I
L
L
H
H
R
R
890
|
I
I
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
900
|
Y
Y
G
G
V
V
T
T
V
V
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
910
|
F
F
G
G
S
S
K
K
P
P
Y
Y
D
D
G
G
I
I
P
P
920
|
A
A
S
S
E
E
I
I
S
S
S
S
I
I
L
L
E
E
K
K
930
|
G
G
E
E
R
R
L
L
P
P
Q
Q
P
P
P
P
I
I
C
C
940
|
T
T
I
I
D
D
V
V
Y
Y
M
M
I
I
M
M
V
V
K
K
950
|
C
C
W
W
M
M
I
I
D
D
A
A
D
D
S
S
R
R
P
P
960
|
K
K
F
F
R
R
E
E
L
L
I
I
I
I
E
E
F
F
S
S
970
|
K
K
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
P
P
Q
Q
R
R
Y
Y
L
L
980
|
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
G
G
D
D
E
E
R
R
M
M
H
H
L
L
990
|
P
P
S
S
P
P
T
T
D
D
S
S
N
N
F
F
Y
Y
R
R
1000
|
A
A
L
L
M
M
D
D
E
E
E
E
D
D
M
M
D
D
D
D
1010
|
V
V
V
V
D
D
A
A
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
I
I
P
P
1020
|
Q
Q
Q
Q
G
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Direct sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Overall and disease-free assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | A secondary T790M mutation of EGFR accounted for half the tumors with acquired resistance to gefitinib in Japanese patients. Other drug-resistant secondary mutations are uncommon in the EGFR gene. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.3] | [48], [49], [50] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Lung squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Gefitinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T790M |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.05 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
S
G
G
E
E
A
A
P
P
700
|
N
N
Q
Q
A
A
L
L
L
L
R
R
I
I
L
L
K
K
E
E
710
|
T
T
E
E
F
F
K
K
K
K
I
I
K
K
V
V
L
L
G
G
720
|
S
S
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
K
K
G
G
730
|
L
L
W
W
I
I
P
P
E
E
G
G
E
E
K
K
V
V
K
K
740
|
I
I
P
P
V
V
A
A
I
I
K
K
E
E
L
L
R
R
E
E
750
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
P
P
K
K
A
A
N
N
K
K
E
E
I
I
760
|
L
L
D
D
E
E
A
A
Y
Y
V
V
M
M
A
A
S
S
V
V
770
|
D
D
N
N
P
P
H
H
V
V
C
C
R
R
L
L
L
L
G
G
780
|
I
I
C
C
L
L
T
T
S
S
T
T
V
V
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
790
|
T
M
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
P
P
F
F
G
G
C
C
L
L
L
L
800
|
D
D
Y
Y
V
V
R
R
E
E
H
H
K
K
D
D
N
N
I
I
810
|
G
G
S
S
Q
Q
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
N
N
W
W
C
C
V
V
820
|
Q
Q
I
I
A
A
K
K
G
G
M
M
N
N
Y
Y
L
L
E
E
830
|
D
D
R
R
R
R
L
L
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
840
|
A
A
R
R
N
N
V
V
L
L
V
V
K
K
T
T
P
P
Q
Q
850
|
H
H
V
V
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
860
|
K
K
L
L
L
L
G
G
A
A
E
E
E
E
K
K
E
E
Y
Y
870
|
H
H
A
A
E
E
G
G
G
G
K
K
V
V
P
P
I
I
K
K
880
|
W
W
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
I
I
L
L
H
H
R
R
890
|
I
I
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
900
|
Y
Y
G
G
V
V
T
T
V
V
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
910
|
F
F
G
G
S
S
K
K
P
P
Y
Y
D
D
G
G
I
I
P
P
920
|
A
A
S
S
E
E
I
I
S
S
S
S
I
I
L
L
E
E
K
K
930
|
G
G
E
E
R
R
L
L
P
P
Q
Q
P
P
P
P
I
I
C
C
940
|
T
T
I
I
D
D
V
V
Y
Y
M
M
I
I
M
M
V
V
K
K
950
|
C
C
W
W
M
M
I
I
D
D
A
A
D
D
S
S
R
R
P
P
960
|
K
K
F
F
R
R
E
E
L
L
I
I
I
I
E
E
F
F
S
S
970
|
K
K
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
P
P
Q
Q
R
R
Y
Y
L
L
980
|
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
G
G
D
D
E
E
R
R
M
M
H
H
L
L
990
|
P
P
S
S
P
P
T
T
D
D
S
S
N
N
F
F
Y
Y
R
R
1000
|
A
A
L
L
M
M
D
D
E
E
E
E
D
D
M
M
D
D
D
D
1010
|
V
V
V
V
D
D
A
A
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
I
I
P
P
1020
|
Q
Q
Q
Q
G
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Computed tomography (CT) scanning assay; Bone scintigraphy assay; Magnetic resonance imaging assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | C-Met amplification, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and kRAS and BRAF mutations were ruled out as alternative resistance mechanisms in the T790M-negative lung rebiopsy, suggesting that alternative oncogene aberrations such as HER2/Neu amplification, hepatocyte growth factor release by the tumor microenvironment, or other unidentified pathways contributed to the TkI resistance that was observed in the primary lesion. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.7] | [51] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.7] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Gefitinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T790M |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.05 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
S
G
G
E
E
A
A
P
P
700
|
N
N
Q
Q
A
A
L
L
L
L
R
R
I
I
L
L
K
K
E
E
710
|
T
T
E
E
F
F
K
K
K
K
I
I
K
K
V
V
L
L
G
G
720
|
S
S
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
K
K
G
G
730
|
L
L
W
W
I
I
P
P
E
E
G
G
E
E
K
K
V
V
K
K
740
|
I
I
P
P
V
V
A
A
I
I
K
K
E
E
L
L
R
R
E
E
750
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
P
P
K
K
A
A
N
N
K
K
E
E
I
I
760
|
L
L
D
D
E
E
A
A
Y
Y
V
V
M
M
A
A
S
S
V
V
770
|
D
D
N
N
P
P
H
H
V
V
C
C
R
R
L
L
L
L
G
G
780
|
I
I
C
C
L
L
T
T
S
S
T
T
V
V
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
790
|
T
M
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
P
P
F
F
G
G
C
C
L
L
L
L
800
|
D
D
Y
Y
V
V
R
R
E
E
H
H
K
K
D
D
N
N
I
I
810
|
G
G
S
S
Q
Q
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
N
N
W
W
C
C
V
V
820
|
Q
Q
I
I
A
A
K
K
G
G
M
M
N
N
Y
Y
L
L
E
E
830
|
D
D
R
R
R
R
L
L
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
840
|
A
A
R
R
N
N
V
V
L
L
V
V
K
K
T
T
P
P
Q
Q
850
|
H
H
V
V
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
860
|
K
K
L
L
L
L
G
G
A
A
E
E
E
E
K
K
E
E
Y
Y
870
|
H
H
A
A
E
E
G
G
G
G
K
K
V
V
P
P
I
I
K
K
880
|
W
W
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
I
I
L
L
H
H
R
R
890
|
I
I
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
900
|
Y
Y
G
G
V
V
T
T
V
V
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
910
|
F
F
G
G
S
S
K
K
P
P
Y
Y
D
D
G
G
I
I
P
P
920
|
A
A
S
S
E
E
I
I
S
S
S
S
I
I
L
L
E
E
K
K
930
|
G
G
E
E
R
R
L
L
P
P
Q
Q
P
P
P
P
I
I
C
C
940
|
T
T
I
I
D
D
V
V
Y
Y
M
M
I
I
M
M
V
V
K
K
950
|
C
C
W
W
M
M
I
I
D
D
A
A
D
D
S
S
R
R
P
P
960
|
K
K
F
F
R
R
E
E
L
L
I
I
I
I
E
E
F
F
S
S
970
|
K
K
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
P
P
Q
Q
R
R
Y
Y
L
L
980
|
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
G
G
D
D
E
E
R
R
M
M
H
H
L
L
990
|
P
P
S
S
P
P
T
T
D
D
S
S
N
N
F
F
Y
Y
R
R
1000
|
A
A
L
L
M
M
D
D
E
E
E
E
D
D
M
M
D
D
D
D
1010
|
V
V
V
V
D
D
A
A
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
I
I
P
P
1020
|
Q
Q
Q
Q
G
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
MGB SNP detection kit assay; Mutation Detection assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Digital PCR assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Resistance mechanisms to EGFR-TkI therapy in EGFR-mutated NSCLC include secondary EGFR T790M mutation, c-Met amplification, PIk3CA mutation, and transformation to small-cell lung cancer. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.7] | [38] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.7] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Gefitinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T790M |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.05 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
S
G
G
E
E
A
A
P
P
700
|
N
N
Q
Q
A
A
L
L
L
L
R
R
I
I
L
L
K
K
E
E
710
|
T
T
E
E
F
F
K
K
K
K
I
I
K
K
V
V
L
L
G
G
720
|
S
S
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
K
K
G
G
730
|
L
L
W
W
I
I
P
P
E
E
G
G
E
E
K
K
V
V
K
K
740
|
I
I
P
P
V
V
A
A
I
I
K
K
E
E
L
L
R
R
E
E
750
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
P
P
K
K
A
A
N
N
K
K
E
E
I
I
760
|
L
L
D
D
E
E
A
A
Y
Y
V
V
M
M
A
A
S
S
V
V
770
|
D
D
N
N
P
P
H
H
V
V
C
C
R
R
L
L
L
L
G
G
780
|
I
I
C
C
L
L
T
T
S
S
T
T
V
V
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
790
|
T
M
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
P
P
F
F
G
G
C
C
L
L
L
L
800
|
D
D
Y
Y
V
V
R
R
E
E
H
H
K
K
D
D
N
N
I
I
810
|
G
G
S
S
Q
Q
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
N
N
W
W
C
C
V
V
820
|
Q
Q
I
I
A
A
K
K
G
G
M
M
N
N
Y
Y
L
L
E
E
830
|
D
D
R
R
R
R
L
L
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
840
|
A
A
R
R
N
N
V
V
L
L
V
V
K
K
T
T
P
P
Q
Q
850
|
H
H
V
V
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
860
|
K
K
L
L
L
L
G
G
A
A
E
E
E
E
K
K
E
E
Y
Y
870
|
H
H
A
A
E
E
G
G
G
G
K
K
V
V
P
P
I
I
K
K
880
|
W
W
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
I
I
L
L
H
H
R
R
890
|
I
I
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
900
|
Y
Y
G
G
V
V
T
T
V
V
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
910
|
F
F
G
G
S
S
K
K
P
P
Y
Y
D
D
G
G
I
I
P
P
920
|
A
A
S
S
E
E
I
I
S
S
S
S
I
I
L
L
E
E
K
K
930
|
G
G
E
E
R
R
L
L
P
P
Q
Q
P
P
P
P
I
I
C
C
940
|
T
T
I
I
D
D
V
V
Y
Y
M
M
I
I
M
M
V
V
K
K
950
|
C
C
W
W
M
M
I
I
D
D
A
A
D
D
S
S
R
R
P
P
960
|
K
K
F
F
R
R
E
E
L
L
I
I
I
I
E
E
F
F
S
S
970
|
K
K
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
P
P
Q
Q
R
R
Y
Y
L
L
980
|
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
G
G
D
D
E
E
R
R
M
M
H
H
L
L
990
|
P
P
S
S
P
P
T
T
D
D
S
S
N
N
F
F
Y
Y
R
R
1000
|
A
A
L
L
M
M
D
D
E
E
E
E
D
D
M
M
D
D
D
D
1010
|
V
V
V
V
D
D
A
A
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
I
I
P
P
1020
|
Q
Q
Q
Q
G
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Low throughput experiment assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Progression-free survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Acquired resistance can occur through failure of drug delivery to the target, as in isolated central nervous system (CNS) progression, or by selection of biological variants during TkI exposure. At the point of acquired resistance, the T790M substitution may be accompanied by amplification of the EGFR gene as well. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [39] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Gefitinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T790M |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.05 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
S
G
G
E
E
A
A
P
P
700
|
N
N
Q
Q
A
A
L
L
L
L
R
R
I
I
L
L
K
K
E
E
710
|
T
T
E
E
F
F
K
K
K
K
I
I
K
K
V
V
L
L
G
G
720
|
S
S
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
K
K
G
G
730
|
L
L
W
W
I
I
P
P
E
E
G
G
E
E
K
K
V
V
K
K
740
|
I
I
P
P
V
V
A
A
I
I
K
K
E
E
L
L
R
R
E
E
750
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
P
P
K
K
A
A
N
N
K
K
E
E
I
I
760
|
L
L
D
D
E
E
A
A
Y
Y
V
V
M
M
A
A
S
S
V
V
770
|
D
D
N
N
P
P
H
H
V
V
C
C
R
R
L
L
L
L
G
G
780
|
I
I
C
C
L
L
T
T
S
S
T
T
V
V
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
790
|
T
M
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
P
P
F
F
G
G
C
C
L
L
L
L
800
|
D
D
Y
Y
V
V
R
R
E
E
H
H
K
K
D
D
N
N
I
I
810
|
G
G
S
S
Q
Q
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
N
N
W
W
C
C
V
V
820
|
Q
Q
I
I
A
A
K
K
G
G
M
M
N
N
Y
Y
L
L
E
E
830
|
D
D
R
R
R
R
L
L
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
840
|
A
A
R
R
N
N
V
V
L
L
V
V
K
K
T
T
P
P
Q
Q
850
|
H
H
V
V
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
860
|
K
K
L
L
L
L
G
G
A
A
E
E
E
E
K
K
E
E
Y
Y
870
|
H
H
A
A
E
E
G
G
G
G
K
K
V
V
P
P
I
I
K
K
880
|
W
W
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
I
I
L
L
H
H
R
R
890
|
I
I
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
900
|
Y
Y
G
G
V
V
T
T
V
V
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
910
|
F
F
G
G
S
S
K
K
P
P
Y
Y
D
D
G
G
I
I
P
P
920
|
A
A
S
S
E
E
I
I
S
S
S
S
I
I
L
L
E
E
K
K
930
|
G
G
E
E
R
R
L
L
P
P
Q
Q
P
P
P
P
I
I
C
C
940
|
T
T
I
I
D
D
V
V
Y
Y
M
M
I
I
M
M
V
V
K
K
950
|
C
C
W
W
M
M
I
I
D
D
A
A
D
D
S
S
R
R
P
P
960
|
K
K
F
F
R
R
E
E
L
L
I
I
I
I
E
E
F
F
S
S
970
|
K
K
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
P
P
Q
Q
R
R
Y
Y
L
L
980
|
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
G
G
D
D
E
E
R
R
M
M
H
H
L
L
990
|
P
P
S
S
P
P
T
T
D
D
S
S
N
N
F
F
Y
Y
R
R
1000
|
A
A
L
L
M
M
D
D
E
E
E
E
D
D
M
M
D
D
D
D
1010
|
V
V
V
V
D
D
A
A
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
I
I
P
P
1020
|
Q
Q
Q
Q
G
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Multivariate analysis of overall or disease-free survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | One example is the acquisition of the T790M substitution in the membrane receptor EGFR conferring resistance to gefitinb and erlotinib in lung cancer in approximately 50% of patients. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [45] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Gefitinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T790M |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.05 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
S
G
G
E
E
A
A
P
P
700
|
N
N
Q
Q
A
A
L
L
L
L
R
R
I
I
L
L
K
K
E
E
710
|
T
T
E
E
F
F
K
K
K
K
I
I
K
K
V
V
L
L
G
G
720
|
S
S
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
K
K
G
G
730
|
L
L
W
W
I
I
P
P
E
E
G
G
E
E
K
K
V
V
K
K
740
|
I
I
P
P
V
V
A
A
I
I
K
K
E
E
L
L
R
R
E
E
750
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
P
P
K
K
A
A
N
N
K
K
E
E
I
I
760
|
L
L
D
D
E
E
A
A
Y
Y
V
V
M
M
A
A
S
S
V
V
770
|
D
D
N
N
P
P
H
H
V
V
C
C
R
R
L
L
L
L
G
G
780
|
I
I
C
C
L
L
T
T
S
S
T
T
V
V
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
790
|
T
M
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
P
P
F
F
G
G
C
C
L
L
L
L
800
|
D
D
Y
Y
V
V
R
R
E
E
H
H
K
K
D
D
N
N
I
I
810
|
G
G
S
S
Q
Q
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
N
N
W
W
C
C
V
V
820
|
Q
Q
I
I
A
A
K
K
G
G
M
M
N
N
Y
Y
L
L
E
E
830
|
D
D
R
R
R
R
L
L
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
840
|
A
A
R
R
N
N
V
V
L
L
V
V
K
K
T
T
P
P
Q
Q
850
|
H
H
V
V
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
860
|
K
K
L
L
L
L
G
G
A
A
E
E
E
E
K
K
E
E
Y
Y
870
|
H
H
A
A
E
E
G
G
G
G
K
K
V
V
P
P
I
I
K
K
880
|
W
W
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
I
I
L
L
H
H
R
R
890
|
I
I
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
900
|
Y
Y
G
G
V
V
T
T
V
V
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
910
|
F
F
G
G
S
S
K
K
P
P
Y
Y
D
D
G
G
I
I
P
P
920
|
A
A
S
S
E
E
I
I
S
S
S
S
I
I
L
L
E
E
K
K
930
|
G
G
E
E
R
R
L
L
P
P
Q
Q
P
P
P
P
I
I
C
C
940
|
T
T
I
I
D
D
V
V
Y
Y
M
M
I
I
M
M
V
V
K
K
950
|
C
C
W
W
M
M
I
I
D
D
A
A
D
D
S
S
R
R
P
P
960
|
K
K
F
F
R
R
E
E
L
L
I
I
I
I
E
E
F
F
S
S
970
|
K
K
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
P
P
Q
Q
R
R
Y
Y
L
L
980
|
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
G
G
D
D
E
E
R
R
M
M
H
H
L
L
990
|
P
P
S
S
P
P
T
T
D
D
S
S
N
N
F
F
Y
Y
R
R
1000
|
A
A
L
L
M
M
D
D
E
E
E
E
D
D
M
M
D
D
D
D
1010
|
V
V
V
V
D
D
A
A
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
I
I
P
P
1020
|
Q
Q
Q
Q
G
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Cos-7 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0224 | |||||||||
| NIH-3T3 cells | Embryo | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_0594 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The DNA sequence of the EGFR gene in his tumor biopsy specimen at relapse revealed the presence of a second point mutation, resulting in threonine-to-methionine amino acid change at position 790 of EGFR. Structural modeling and biochemical studies showed that this second mutation led to gefitinib resistance. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [45] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Gefitinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T790M |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.05 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
S
G
G
E
E
A
A
P
P
700
|
N
N
Q
Q
A
A
L
L
L
L
R
R
I
I
L
L
K
K
E
E
710
|
T
T
E
E
F
F
K
K
K
K
I
I
K
K
V
V
L
L
G
G
720
|
S
S
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
K
K
G
G
730
|
L
L
W
W
I
I
P
P
E
E
G
G
E
E
K
K
V
V
K
K
740
|
I
I
P
P
V
V
A
A
I
I
K
K
E
E
L
L
R
R
E
E
750
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
P
P
K
K
A
A
N
N
K
K
E
E
I
I
760
|
L
L
D
D
E
E
A
A
Y
Y
V
V
M
M
A
A
S
S
V
V
770
|
D
D
N
N
P
P
H
H
V
V
C
C
R
R
L
L
L
L
G
G
780
|
I
I
C
C
L
L
T
T
S
S
T
T
V
V
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
790
|
T
M
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
P
P
F
F
G
G
C
C
L
L
L
L
800
|
D
D
Y
Y
V
V
R
R
E
E
H
H
K
K
D
D
N
N
I
I
810
|
G
G
S
S
Q
Q
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
N
N
W
W
C
C
V
V
820
|
Q
Q
I
I
A
A
K
K
G
G
M
M
N
N
Y
Y
L
L
E
E
830
|
D
D
R
R
R
R
L
L
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
840
|
A
A
R
R
N
N
V
V
L
L
V
V
K
K
T
T
P
P
Q
Q
850
|
H
H
V
V
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
860
|
K
K
L
L
L
L
G
G
A
A
E
E
E
E
K
K
E
E
Y
Y
870
|
H
H
A
A
E
E
G
G
G
G
K
K
V
V
P
P
I
I
K
K
880
|
W
W
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
I
I
L
L
H
H
R
R
890
|
I
I
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
900
|
Y
Y
G
G
V
V
T
T
V
V
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
910
|
F
F
G
G
S
S
K
K
P
P
Y
Y
D
D
G
G
I
I
P
P
920
|
A
A
S
S
E
E
I
I
S
S
S
S
I
I
L
L
E
E
K
K
930
|
G
G
E
E
R
R
L
L
P
P
Q
Q
P
P
P
P
I
I
C
C
940
|
T
T
I
I
D
D
V
V
Y
Y
M
M
I
I
M
M
V
V
K
K
950
|
C
C
W
W
M
M
I
I
D
D
A
A
D
D
S
S
R
R
P
P
960
|
K
K
F
F
R
R
E
E
L
L
I
I
I
I
E
E
F
F
S
S
970
|
K
K
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
P
P
Q
Q
R
R
Y
Y
L
L
980
|
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
G
G
D
D
E
E
R
R
M
M
H
H
L
L
990
|
P
P
S
S
P
P
T
T
D
D
S
S
N
N
F
F
Y
Y
R
R
1000
|
A
A
L
L
M
M
D
D
E
E
E
E
D
D
M
M
D
D
D
D
1010
|
V
V
V
V
D
D
A
A
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
I
I
P
P
1020
|
Q
Q
Q
Q
G
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Cos-7 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0224 | |||||||||
| NIH-3T3 cells | Embryo | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_0594 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The DNA sequence of the EGFR gene in his tumor biopsy specimen at relapse revealed the presence of a second point mutation, resulting in threonine-to-methionine amino acid change at position 790 of EGFR. Structural modeling and biochemical studies showed that this second mutation led to gefitinib resistance. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [41] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Gefitinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.C797S+p.T790M |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.64 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.20 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
G
G
A
S
M
M
G
G
G
E
E
A
A
P
P
700
|
N
N
Q
Q
A
A
L
L
L
L
R
R
I
I
L
L
K
K
E
E
710
|
T
T
E
E
F
F
K
K
K
K
I
I
K
K
V
V
L
L
G
G
720
|
S
S
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
K
K
G
G
730
|
L
L
W
W
I
I
P
P
E
E
G
G
E
E
K
K
V
V
K
K
740
|
I
I
P
P
V
V
A
A
I
I
K
K
E
E
L
L
R
R
E
E
750
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
P
P
K
K
A
A
N
N
K
K
E
E
I
I
760
|
L
L
D
D
E
E
A
A
Y
Y
V
V
M
M
A
A
S
S
V
V
770
|
D
D
N
N
P
P
H
H
V
V
C
C
R
R
L
L
L
L
G
G
780
|
I
I
C
C
L
L
T
T
S
S
T
T
V
V
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
790
|
T
M
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
P
P
F
F
G
G
C
S
L
L
L
L
800
|
D
D
Y
Y
V
V
R
R
E
E
H
H
K
K
D
D
N
N
I
I
810
|
G
G
S
S
Q
Q
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
N
N
W
W
C
C
V
V
820
|
Q
Q
I
I
A
A
K
K
G
G
M
M
N
N
Y
Y
L
L
E
E
830
|
D
D
R
R
R
R
L
L
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
840
|
A
A
R
R
N
N
V
V
L
L
V
V
K
K
T
T
P
P
Q
Q
850
|
H
H
V
V
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
860
|
K
K
L
L
L
L
G
G
A
A
E
E
E
E
K
K
E
E
Y
Y
870
|
H
H
A
A
E
E
G
G
G
G
K
K
V
V
P
P
I
I
K
K
880
|
W
W
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
I
I
L
L
H
H
R
R
890
|
I
I
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
900
|
Y
Y
G
G
V
V
T
T
V
V
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
910
|
F
F
G
G
S
S
K
K
P
P
Y
Y
D
D
G
G
I
I
P
P
920
|
A
A
S
S
E
E
I
I
S
S
S
S
I
I
L
L
E
E
K
K
930
|
G
G
E
E
R
R
L
L
P
P
Q
Q
P
P
P
P
I
I
C
C
940
|
T
T
I
I
D
D
V
V
Y
Y
M
M
I
I
M
M
V
V
K
K
950
|
C
C
W
W
M
M
I
I
D
D
A
A
D
D
S
S
R
R
P
P
960
|
K
K
F
F
R
R
E
E
L
L
I
I
I
I
E
E
F
F
S
S
970
|
K
K
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
P
P
Q
Q
R
R
Y
Y
L
L
980
|
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
G
G
D
D
E
E
R
R
M
M
H
H
L
L
990
|
P
P
S
S
P
P
T
T
D
D
S
S
N
N
F
F
Y
Y
R
R
1000
|
A
A
L
L
M
M
D
D
E
E
E
E
D
D
M
M
D
D
D
D
1010
|
V
V
V
V
D
D
A
A
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
I
I
P
P
1020
|
Q
Q
-
Q
-
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | AKT signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04151 | ||||||||||
| Cell invasion | Activation | hsa05200 | |||||||||||
| Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | |||||||||||
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | |||||||||||
| EGFR/TKLS mediated apoptosis signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa01521 | |||||||||||
| Epithelial mesenchymal transition signaling pathway | Activation | hsa01521 | |||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Liquid biopsy; ATP-binding pocket affinity comparison assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Several mechanisms of resistance have been described to EGFR-TkIs, such as the occurrence of secondary mutation (T790M, C797S), the activation of alternative signalling (Met, HGF, AXL, Hh, IGF-1R), the aberrance of the downstream pathways (AkT mutations, loss of PTEN), the impairment of the EGFR-TkIs-mediated apoptosis pathway (BCL2-like 11/BIM deletion polymorphism) and histological transformation. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [52] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Gefitinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D761Y |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Direct Sanger sequencing analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTiter-Blue cell viability assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The T790M mutation is common in patients with acquired resistance. The limited spectrum of TkI-resistant mutations in EGFR, which binds to erlotinib in the active conformation, contrasts with a wider range of second-site mutations seen with acquired resistance to imatinib, which binds to ABL and kIT, respectively, in closed conformations. Collectively, our data suggest that the type and nature of kinase inhibitor resistance mutations may be influenced by both anatomic site and mode of binding to the kinase target. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.7] | [38] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.7] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Gefitinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L747S |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Low throughput experiment assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Progression-free survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Acquired resistance can occur through failure of drug delivery to the target, as in isolated central nervous system (CNS) progression, or by selection of biological variants during TkI exposure. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.7] | [38] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.7] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Gefitinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D761Y |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Low throughput experiment assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Progression-free survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Acquired resistance can occur through failure of drug delivery to the target, as in isolated central nervous system (CNS) progression, or by selection of biological variants during TkI exposure. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [21] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Gefitinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | . |
|||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Statistical analysis | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | EGFR-TKI Rechallenge With Another TKI may be a useful treatment option after first-line osimertinib. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Paclitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Blood | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.41E-78 Fold-change: -3.81E-01 Z-score: -2.43E+01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 |
| 95D cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_7110 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Overexpression of miR-7 sensitizes NSCLC cells to PTX and inhibites EGFR expression in A549 cells. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [5] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Blood | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.41E-78 Fold-change: -3.81E-01 Z-score: -2.43E+01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-21 mainly achieves drug resistance by inhibiting cisplatin-induced apoptosis, and its specific mechanisms include the following: (1) improving the expression level of EGFR and protecting the toxic effect of tumor cells during chemotherapy; (2) Increase the expression of LRP and decrease the effective concentration of the target drug through the barrier of drug transport between nucleus and cell; (3) Enhance the expression of multidrug resistance associated protein (MRP1) and assist in pumping chemotherapeutic drugs from the inside to the outside of the cell. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [6] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Docetaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.37E-11 Fold-change: 6.31E-01 Z-score: 7.28E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| EGFR signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa01521 | ||
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The transfection of miR 27b mimics led to downregulation of the expression levels of EGFR, whilst miR 27b inhibitors upregulated the expression levels of EGFR. Furthermore, it was demonstrated that the transfection of miR 27b mimics significantly suppressed the apoptosis and promote the viability of A549 human lung carcinoma cells. In line with this, the introduction of miR 27b inhibitors significantly induced apoptosis and inhibited the proliferation of A549 cells. These results indicate that miR 27b may promote NSCLC cell viability and enhance resistance to docetaxel treatment through direct inhibition of EGFR expression. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [10] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Vemurafenib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Melanoma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Skin | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.60E-01 Fold-change: -9.63E-02 Z-score: -1.44E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| MAPK/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa05235 | ||
| In Vitro Model | A375 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0132 |
| Mel-CV cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_S996 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunohistochemical staining assay; Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-7 expression was decreased in both VemR A375 and Mel-CVR melanoma cells and its low expression contributed to BRAFi resistance. Furthermore, by decreasing the expression levels of EGFR, IGF-1R and CRAF, miR-7 could inhibit the activation of RAS/RAF/MEk/ERk (MAPk) and PI3k/AkT pathway and partially reverse the resistance to BRAFi in VemR A375 melanoma cells. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | [11] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Prostate cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Prostate | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 7.43E-04 Fold-change: -1.42E-01 Z-score: -3.79E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | DU-145 cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0105 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; RT-qPCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | LncRNA LOXL1-AS1/miR-let-7a-5p/EGFR-related pathway regulates the doxorubicin resistance of prostate cancer DU-145 cells. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [12] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Trastuzumab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.04E-65 Fold-change: -1.82E-01 Z-score: -2.10E+01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Colcount colony counter assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-7 suppression of HER2deta16 oncogenic activity is mediated through inactivation of Src kinase and suppression of EGFR expression implies that targeting these pathways would also suppress HER2deta16 tumorigenesis. HER2deta16 suppresses expression of the miR-7 tumor suppressor and reestablished miR-7 expression significantly inhibits HER2deta16 mediated tumor cell proliferation and migration and miR-7 sensitizes HER2deta16 expressing cells to trastuzumab treatment. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Trastuzumab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V292E |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Trastuzumab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.I706T |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Trastuzumab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R705G |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Trastuzumab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L760F |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Trastuzumab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.K284E |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Trastuzumab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G696E |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Trastuzumab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.A822V |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Trastuzumab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V292M |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Trastuzumab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.P741S |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Trastuzumab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G288D |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Trastuzumab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E711K |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Glioblastoma multiforme [ICD-11: 2A00.03] | [13] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Glioblastoma multiforme [ICD-11: 2A00.03] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Temozolomide | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Neuroectodermal tumor | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Brainstem tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.84E-08 Fold-change: -2.34E-01 Z-score: -1.06E+01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | EGFR signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa01521 | |
| In Vitro Model | U251 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0021 |
| U87 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0022 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; Luciferase reporter assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Flow cytometric analysis | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR181b modulates chemosensitivity of glioblastoma multiforme cells to temozolomide by targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [15], [16], [17] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Afatinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T790M |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.05 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
S
G
G
E
E
A
A
P
P
700
|
N
N
Q
Q
A
A
L
L
L
L
R
R
I
I
L
L
K
K
E
E
710
|
T
T
E
E
F
F
K
K
K
K
I
I
K
K
V
V
L
L
G
G
720
|
S
S
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
K
K
G
G
730
|
L
L
W
W
I
I
P
P
E
E
G
G
E
E
K
K
V
V
K
K
740
|
I
I
P
P
V
V
A
A
I
I
K
K
E
E
L
L
R
R
E
E
750
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
P
P
K
K
A
A
N
N
K
K
E
E
I
I
760
|
L
L
D
D
E
E
A
A
Y
Y
V
V
M
M
A
A
S
S
V
V
770
|
D
D
N
N
P
P
H
H
V
V
C
C
R
R
L
L
L
L
G
G
780
|
I
I
C
C
L
L
T
T
S
S
T
T
V
V
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
790
|
T
M
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
P
P
F
F
G
G
C
C
L
L
L
L
800
|
D
D
Y
Y
V
V
R
R
E
E
H
H
K
K
D
D
N
N
I
I
810
|
G
G
S
S
Q
Q
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
N
N
W
W
C
C
V
V
820
|
Q
Q
I
I
A
A
K
K
G
G
M
M
N
N
Y
Y
L
L
E
E
830
|
D
D
R
R
R
R
L
L
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
840
|
A
A
R
R
N
N
V
V
L
L
V
V
K
K
T
T
P
P
Q
Q
850
|
H
H
V
V
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
860
|
K
K
L
L
L
L
G
G
A
A
E
E
E
E
K
K
E
E
Y
Y
870
|
H
H
A
A
E
E
G
G
G
G
K
K
V
V
P
P
I
I
K
K
880
|
W
W
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
I
I
L
L
H
H
R
R
890
|
I
I
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
900
|
Y
Y
G
G
V
V
T
T
V
V
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
910
|
F
F
G
G
S
S
K
K
P
P
Y
Y
D
D
G
G
I
I
P
P
920
|
A
A
S
S
E
E
I
I
S
S
S
S
I
I
L
L
E
E
K
K
930
|
G
G
E
E
R
R
L
L
P
P
Q
Q
P
P
P
P
I
I
C
C
940
|
T
T
I
I
D
D
V
V
Y
Y
M
M
I
I
M
M
V
V
K
K
950
|
C
C
W
W
M
M
I
I
D
D
A
A
D
D
S
S
R
R
P
P
960
|
K
K
F
F
R
R
E
E
L
L
I
I
I
I
E
E
F
F
S
S
970
|
K
K
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
P
P
Q
Q
R
R
Y
Y
L
L
980
|
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
G
G
D
D
E
E
R
R
M
M
H
H
L
L
990
|
P
P
S
S
P
P
T
T
D
D
S
S
N
N
F
F
Y
Y
R
R
1000
|
A
A
L
L
M
M
D
D
E
E
E
E
D
D
M
M
D
D
D
D
1010
|
V
V
V
V
D
D
A
A
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
I
I
P
P
1020
|
Q
Q
Q
Q
G
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Exon sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Progression-free and post-progression survival asaay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | T790M was detected in half of the lung adenocarcinoma after acquiring resistance to afatinib. T790M is still the major acquired resistance mechanism. First-generation EGFR TkI exposure did not influence the prevalence of T790M in lung cancer acquired resistance to afatinib. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [18], [19], [20] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Afatinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T790M |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.05 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
S
G
G
E
E
A
A
P
P
700
|
N
N
Q
Q
A
A
L
L
L
L
R
R
I
I
L
L
K
K
E
E
710
|
T
T
E
E
F
F
K
K
K
K
I
I
K
K
V
V
L
L
G
G
720
|
S
S
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
K
K
G
G
730
|
L
L
W
W
I
I
P
P
E
E
G
G
E
E
K
K
V
V
K
K
740
|
I
I
P
P
V
V
A
A
I
I
K
K
E
E
L
L
R
R
E
E
750
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
P
P
K
K
A
A
N
N
K
K
E
E
I
I
760
|
L
L
D
D
E
E
A
A
Y
Y
V
V
M
M
A
A
S
S
V
V
770
|
D
D
N
N
P
P
H
H
V
V
C
C
R
R
L
L
L
L
G
G
780
|
I
I
C
C
L
L
T
T
S
S
T
T
V
V
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
790
|
T
M
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
P
P
F
F
G
G
C
C
L
L
L
L
800
|
D
D
Y
Y
V
V
R
R
E
E
H
H
K
K
D
D
N
N
I
I
810
|
G
G
S
S
Q
Q
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
N
N
W
W
C
C
V
V
820
|
Q
Q
I
I
A
A
K
K
G
G
M
M
N
N
Y
Y
L
L
E
E
830
|
D
D
R
R
R
R
L
L
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
840
|
A
A
R
R
N
N
V
V
L
L
V
V
K
K
T
T
P
P
Q
Q
850
|
H
H
V
V
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
860
|
K
K
L
L
L
L
G
G
A
A
E
E
E
E
K
K
E
E
Y
Y
870
|
H
H
A
A
E
E
G
G
G
G
K
K
V
V
P
P
I
I
K
K
880
|
W
W
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
I
I
L
L
H
H
R
R
890
|
I
I
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
900
|
Y
Y
G
G
V
V
T
T
V
V
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
910
|
F
F
G
G
S
S
K
K
P
P
Y
Y
D
D
G
G
I
I
P
P
920
|
A
A
S
S
E
E
I
I
S
S
S
S
I
I
L
L
E
E
K
K
930
|
G
G
E
E
R
R
L
L
P
P
Q
Q
P
P
P
P
I
I
C
C
940
|
T
T
I
I
D
D
V
V
Y
Y
M
M
I
I
M
M
V
V
K
K
950
|
C
C
W
W
M
M
I
I
D
D
A
A
D
D
S
S
R
R
P
P
960
|
K
K
F
F
R
R
E
E
L
L
I
I
I
I
E
E
F
F
S
S
970
|
K
K
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
P
P
Q
Q
R
R
Y
Y
L
L
980
|
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
G
G
D
D
E
E
R
R
M
M
H
H
L
L
990
|
P
P
S
S
P
P
T
T
D
D
S
S
N
N
F
F
Y
Y
R
R
1000
|
A
A
L
L
M
M
D
D
E
E
E
E
D
D
M
M
D
D
D
D
1010
|
V
V
V
V
D
D
A
A
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
I
I
P
P
1020
|
Q
Q
Q
Q
G
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Directional sequencing assay; Direct sequencing assay; Sanger sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Progression-free and post-progression survival asaay; Analysis of progression-free survival (PFS) assay; Overall survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The identification of T790M as acquired resistance mechanism was clinically feasible. Although T790M had no prognostic or predictive role in the present study, further research is necessary to identify patients with T790M-mutant tumors who might benefit from newly developed T790M-specific TkIs.T790M is likely a common resistance mechanism in patients treated with first-line afatinib. Although repeat biopsies at progression are crucial in elucidating resistance mechanisms, this study suggests that clinical and technical issues often limit their feasibility, highlighting the importance of developing. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [21] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Afatinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | . |
|||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Statistical analysis | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | EGFR-TKI Rechallenge With Another TKI may be a useful treatment option after first-line osimertinib. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Esophagogastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B71.1] | [22] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Esophagogastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B71.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Afatinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | In summary, we find that concurrent amplification of EGFR and ERBB2 is associated with response to the HER kinase inhibitor afatinib in patients with trastuzumab-refractory EG cancer. Heterogeneous uptake of 89Zr-trastuzumab measured noninvasively by PET was associated with disease progression. Analyses of multiple disease sites sampled at the time of disease progression indicated several potential mediators of afatinib resistance, including loss of EGFR amplification and gain of MET amplification. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [23] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Brigatinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L858R (c.2573T>G) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.64 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.47 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
-
S
-
M
-
G
G
E
E
A
A
P
P
700
|
N
N
Q
Q
A
A
L
L
L
L
R
R
I
I
L
L
K
K
E
E
710
|
T
T
E
E
F
F
K
K
K
K
I
I
K
K
V
V
L
L
G
G
720
|
S
S
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
K
K
G
G
730
|
L
L
W
W
I
I
P
P
E
E
G
G
E
E
K
K
V
V
K
K
740
|
I
I
P
P
V
V
A
A
I
I
K
K
E
E
L
L
R
R
E
E
750
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
P
P
K
K
A
A
N
N
K
K
E
E
I
I
760
|
L
L
D
D
E
E
A
A
Y
Y
V
V
M
M
A
A
S
S
V
V
770
|
D
D
N
N
P
P
H
H
V
V
C
C
R
R
L
L
L
L
G
G
780
|
I
I
C
C
L
L
T
T
S
S
T
T
V
V
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
790
|
T
T
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
P
P
F
F
G
G
C
C
L
L
L
L
800
|
D
D
Y
Y
V
V
R
R
E
E
H
H
K
K
D
D
N
N
I
I
810
|
G
G
S
S
Q
Q
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
N
N
W
W
C
C
V
V
820
|
Q
Q
I
I
A
A
K
K
G
G
M
M
N
N
Y
Y
L
L
E
E
830
|
D
D
R
R
R
R
L
L
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
840
|
A
A
R
R
N
N
V
V
L
L
V
V
K
K
T
T
P
P
Q
Q
850
|
H
H
V
V
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
R
A
A
860
|
K
K
L
L
L
L
G
G
A
A
E
E
E
E
K
K
E
E
Y
Y
870
|
H
H
A
A
E
E
G
G
G
G
K
K
V
V
P
P
I
I
K
K
880
|
W
W
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
I
I
L
L
H
H
R
R
890
|
I
I
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
900
|
Y
Y
G
G
V
V
T
T
V
V
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
910
|
F
F
G
G
S
S
K
K
P
P
Y
Y
D
D
G
G
I
I
P
P
920
|
A
A
S
S
E
E
I
I
S
S
S
S
I
I
L
L
E
E
K
K
930
|
G
G
E
E
R
R
L
L
P
P
Q
Q
P
P
P
P
I
I
C
C
940
|
T
T
I
I
D
D
V
V
Y
Y
M
M
I
I
M
M
V
V
K
K
950
|
C
C
W
W
M
M
I
I
D
D
A
A
D
D
S
S
R
R
P
P
960
|
K
K
F
F
R
R
E
E
L
L
I
I
I
I
E
E
F
F
S
S
970
|
K
K
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
P
P
Q
Q
R
R
Y
Y
L
L
980
|
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
G
G
D
D
E
E
R
R
M
M
H
H
L
L
990
|
P
P
S
S
P
P
T
T
D
D
S
S
N
N
F
F
Y
Y
R
R
1000
|
A
A
L
L
M
M
D
D
E
E
E
E
D
D
M
M
D
D
D
D
1010
|
V
V
V
V
D
D
A
A
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
I
I
P
P
1020
|
Q
Q
-
Q
-
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | HepG2 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0027 | |||||||||
| U937 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0007 | ||||||||||
| H23 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1547 | ||||||||||
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | ||||||||||
| SUP-M2 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2209 | ||||||||||
| KARPAS-299 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1324 | ||||||||||
| SU-DHL-1 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0538 | ||||||||||
| L-82 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2098 | ||||||||||
| HCC78 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2061 | ||||||||||
| H838 cells | Lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1594 | ||||||||||
| H-4-II-E cells | Liver | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | CVCL_0284 | ||||||||||
| H358 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1559 | ||||||||||
| H2228 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1543 | ||||||||||
| DEL cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1170 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | SCID beige mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Promega assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLCs) harboring ALK gene rearrangements (ALK+) typically become resistant to the first-generation anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) crizotinib through development of secondary resistance mutations in ALK or disease progression in the brain. Mutations that confer resistance to second-generation ALK TKIs ceritinib and alectinib have also been identified. Brigatinib is the only TKI to maintain substantial activity against the most recalcitrant ALK resistance mutation, G1202R. The unique, potent, and pan-ALK mutant activity of brigatinib could be rationalized by structural analyses. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [23] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Brigatinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | IF-deletion | p.E746_A750delELREA (c.2236_2250del15) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | HepG2 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0027 | |||||||||
| U937 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0007 | ||||||||||
| H23 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1547 | ||||||||||
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | ||||||||||
| SUP-M2 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2209 | ||||||||||
| KARPAS-299 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1324 | ||||||||||
| SU-DHL-1 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0538 | ||||||||||
| L-82 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2098 | ||||||||||
| HCC78 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2061 | ||||||||||
| H838 cells | Lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1594 | ||||||||||
| H-4-II-E cells | Liver | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | CVCL_0284 | ||||||||||
| H358 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1559 | ||||||||||
| H2228 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1543 | ||||||||||
| DEL cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1170 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | SCID beige mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Promega assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLCs) harboring ALK gene rearrangements (ALK+) typically become resistant to the first-generation anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) crizotinib through development of secondary resistance mutations in ALK or disease progression in the brain. Mutations that confer resistance to second-generation ALK TKIs ceritinib and alectinib have also been identified. Brigatinib is the only TKI to maintain substantial activity against the most recalcitrant ALK resistance mutation, G1202R. The unique, potent, and pan-ALK mutant activity of brigatinib could be rationalized by structural analyses. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Metastatic colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2D85.0] | [24] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Metastatic colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2D85.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Cetuximab | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S492R |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.20 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.80 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
L
L
E
E
E
E
310
|
K
K
K
K
V
V
C
C
N
N
G
G
I
I
G
G
I
I
G
G
320
|
E
E
F
F
K
K
D
D
S
S
L
L
S
S
I
I
N
N
A
A
330
|
T
T
N
N
I
I
K
K
H
H
F
F
K
K
N
N
C
C
T
T
340
|
S
S
I
I
S
S
G
G
D
D
L
L
H
H
I
I
L
L
P
P
350
|
V
V
A
A
F
F
R
R
G
G
D
D
S
S
F
F
T
T
H
H
360
|
T
T
P
P
P
P
L
L
D
D
P
P
Q
Q
E
E
L
L
D
D
370
|
I
I
L
L
K
K
T
T
V
V
K
K
E
E
I
I
T
T
G
G
380
|
F
F
L
L
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
A
A
W
W
P
P
E
E
N
N
390
|
R
R
T
T
D
D
L
L
H
H
A
A
F
F
E
E
N
N
L
L
400
|
E
E
I
I
I
I
R
R
G
G
R
R
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
H
H
410
|
G
G
Q
Q
F
F
S
S
L
L
A
A
V
V
V
V
S
S
L
L
420
|
N
N
I
I
T
T
S
S
L
L
G
G
L
L
R
R
S
S
L
L
430
|
K
K
E
E
I
I
S
S
D
D
G
G
D
D
V
V
I
I
I
I
440
|
S
S
G
G
N
N
K
K
N
N
L
L
C
C
Y
Y
A
A
N
N
450
|
T
T
I
I
N
N
W
W
K
K
K
K
L
L
F
F
G
G
T
T
460
|
S
S
G
G
Q
Q
K
K
T
T
K
K
I
I
I
I
S
R
N
N
470
|
R
R
G
G
E
E
N
N
S
S
C
C
K
K
A
A
T
T
G
G
480
|
Q
Q
V
V
C
C
H
H
A
A
L
L
C
C
S
S
P
P
E
E
490
|
G
G
C
C
W
W
G
G
P
P
E
E
P
P
R
R
D
D
C
C
500
|
V
V
S
S
C
C
R
R
N
N
V
V
S
S
R
R
G
G
R
R
510
|
E
E
C
C
V
V
D
D
K
K
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
520
|
H
H
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Circulating-free DNA assay; Standard-of-care sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | K-RAS and EGFR ectodomain-acquired mutations in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) have been correlated with acquired resistance to anti-EGFR monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [25] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Cetuximab | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G465E |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Colon cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Liquid biopsy assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Mechanisms of resistance to EGFR blockade include the emergence of kRAS, NRAS and EGFR extracellular domain mutations as well as HER2/MET alterations. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [26] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cetuximab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| In Vitro Model | SW480 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0546 |
| HCT116 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0291 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | microRNA-7 expression in colorectal cancer is associated with poor prognosis and regulates cetuximab sensitivity via EGFR regulation. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [27] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Dacomitinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | IF-insertion | p.Y764_V765insHH (c.2292_2293insCATCAT) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | NSCLC cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | |
| In Vivo Model | BALB/c nude mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; SDS-PAGE assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay; Crystal violet staining assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Mutation in the covalent binding site of either EGFR or HER2 is sufficient to lead to drug resistance. | |||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [27] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Dacomitinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Duplication | p.A767_V769 (c.2299_2307) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | NSCLC cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | |
| In Vivo Model | BALB/c nude mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; SDS-PAGE assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay; Crystal violet staining assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Mutation in the covalent binding site of either EGFR or HER2 is sufficient to lead to drug resistance. | |||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [27] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Dacomitinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Duplication | p.S768_D770 (c.2302_2310) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | NSCLC cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | |
| In Vivo Model | BALB/c nude mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; SDS-PAGE assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay; Crystal violet staining assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Mutation in the covalent binding site of either EGFR or HER2 is sufficient to lead to drug resistance. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [28] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Dacomitinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L858R (c.2573T>G) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.64 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.47 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
-
S
-
M
-
G
G
E
E
A
A
P
P
700
|
N
N
Q
Q
A
A
L
L
L
L
R
R
I
I
L
L
K
K
E
E
710
|
T
T
E
E
F
F
K
K
K
K
I
I
K
K
V
V
L
L
G
G
720
|
S
S
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
K
K
G
G
730
|
L
L
W
W
I
I
P
P
E
E
G
G
E
E
K
K
V
V
K
K
740
|
I
I
P
P
V
V
A
A
I
I
K
K
E
E
L
L
R
R
E
E
750
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
P
P
K
K
A
A
N
N
K
K
E
E
I
I
760
|
L
L
D
D
E
E
A
A
Y
Y
V
V
M
M
A
A
S
S
V
V
770
|
D
D
N
N
P
P
H
H
V
V
C
C
R
R
L
L
L
L
G
G
780
|
I
I
C
C
L
L
T
T
S
S
T
T
V
V
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
790
|
T
T
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
P
P
F
F
G
G
C
C
L
L
L
L
800
|
D
D
Y
Y
V
V
R
R
E
E
H
H
K
K
D
D
N
N
I
I
810
|
G
G
S
S
Q
Q
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
N
N
W
W
C
C
V
V
820
|
Q
Q
I
I
A
A
K
K
G
G
M
M
N
N
Y
Y
L
L
E
E
830
|
D
D
R
R
R
R
L
L
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
840
|
A
A
R
R
N
N
V
V
L
L
V
V
K
K
T
T
P
P
Q
Q
850
|
H
H
V
V
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
R
A
A
860
|
K
K
L
L
L
L
G
G
A
A
E
E
E
E
K
K
E
E
Y
Y
870
|
H
H
A
A
E
E
G
G
G
G
K
K
V
V
P
P
I
I
K
K
880
|
W
W
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
I
I
L
L
H
H
R
R
890
|
I
I
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
900
|
Y
Y
G
G
V
V
T
T
V
V
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
910
|
F
F
G
G
S
S
K
K
P
P
Y
Y
D
D
G
G
I
I
P
P
920
|
A
A
S
S
E
E
I
I
S
S
S
S
I
I
L
L
E
E
K
K
930
|
G
G
E
E
R
R
L
L
P
P
Q
Q
P
P
P
P
I
I
C
C
940
|
T
T
I
I
D
D
V
V
Y
Y
M
M
I
I
M
M
V
V
K
K
950
|
C
C
W
W
M
M
I
I
D
D
A
A
D
D
S
S
R
R
P
P
960
|
K
K
F
F
R
R
E
E
L
L
I
I
I
I
E
E
F
F
S
S
970
|
K
K
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
P
P
Q
Q
R
R
Y
Y
L
L
980
|
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
G
G
D
D
E
E
R
R
M
M
H
H
L
L
990
|
P
P
S
S
P
P
T
T
D
D
S
S
N
N
F
F
Y
Y
R
R
1000
|
A
A
L
L
M
M
D
D
E
E
E
E
D
D
M
M
D
D
D
D
1010
|
V
V
V
V
D
D
A
A
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
I
I
P
P
1020
|
Q
Q
-
Q
-
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [27] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Dacomitinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Complex-indel | p.D770_770delinsGY (c.2308_2310delinsGGTTAT) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | NSCLC cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | BALB/c nude mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; SDS-PAGE assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay; Crystal violet staining assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Mutation in the covalent binding site of either EGFR or HER2 is sufficient to lead to drug resistance. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [27] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Dacomitinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Duplication | p.N771_H773 (c.2311_2319) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | NSCLC cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | BALB/c nude mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; SDS-PAGE assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay; Crystal violet staining assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Mutation in the covalent binding site of either EGFR or HER2 is sufficient to lead to drug resistance. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [29] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Dacomitinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E709K (c.2125G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | |||||||||
| myelomonocyti cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| macrophage-like cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | ||||||||||
| IL3-dependent murine pro-B cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| Balb/C mouse leukemia cells | Blood | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_9099 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK-8 assay | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [29] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Dacomitinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Complex-indel | p.E709_T710delinsD (c.2127_2129delAAC) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | |||||||||
| myelomonocyti cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| macrophage-like cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | ||||||||||
| IL3-dependent murine pro-B cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| Balb/C mouse leukemia cells | Blood | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_9099 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK-8 assay | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [30] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Dacomitinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G719S (c.2155G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [30] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Dacomitinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G719C (c.2155G>T) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [30] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Dacomitinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G719A (c.2156G>C) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [29] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Dacomitinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G719A (c.2156G>C) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | |||||||||
| myelomonocyti cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| macrophage-like cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | ||||||||||
| IL3-dependent murine pro-B cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| Balb/C mouse leukemia cells | Blood | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_9099 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK-8 assay | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [27] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Dacomitinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | IF-insertion | p.P772_H773insPNP (c.2317_2318insCTAACCCTC) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | NSCLC cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | BALB/c nude mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; SDS-PAGE assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay; Crystal violet staining assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Mutation in the covalent binding site of either EGFR or HER2 is sufficient to lead to drug resistance. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [31] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Dacomitinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | IF-deletion | p.G729_D761 (c.2185_2283) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Lung | N.A. | |||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Dasatinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E711K |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [33], [34], [35] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Erlotinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T790M |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.05 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
S
G
G
E
E
A
A
P
P
700
|
N
N
Q
Q
A
A
L
L
L
L
R
R
I
I
L
L
K
K
E
E
710
|
T
T
E
E
F
F
K
K
K
K
I
I
K
K
V
V
L
L
G
G
720
|
S
S
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
K
K
G
G
730
|
L
L
W
W
I
I
P
P
E
E
G
G
E
E
K
K
V
V
K
K
740
|
I
I
P
P
V
V
A
A
I
I
K
K
E
E
L
L
R
R
E
E
750
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
P
P
K
K
A
A
N
N
K
K
E
E
I
I
760
|
L
L
D
D
E
E
A
A
Y
Y
V
V
M
M
A
A
S
S
V
V
770
|
D
D
N
N
P
P
H
H
V
V
C
C
R
R
L
L
L
L
G
G
780
|
I
I
C
C
L
L
T
T
S
S
T
T
V
V
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
790
|
T
M
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
P
P
F
F
G
G
C
C
L
L
L
L
800
|
D
D
Y
Y
V
V
R
R
E
E
H
H
K
K
D
D
N
N
I
I
810
|
G
G
S
S
Q
Q
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
N
N
W
W
C
C
V
V
820
|
Q
Q
I
I
A
A
K
K
G
G
M
M
N
N
Y
Y
L
L
E
E
830
|
D
D
R
R
R
R
L
L
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
840
|
A
A
R
R
N
N
V
V
L
L
V
V
K
K
T
T
P
P
Q
Q
850
|
H
H
V
V
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
860
|
K
K
L
L
L
L
G
G
A
A
E
E
E
E
K
K
E
E
Y
Y
870
|
H
H
A
A
E
E
G
G
G
G
K
K
V
V
P
P
I
I
K
K
880
|
W
W
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
I
I
L
L
H
H
R
R
890
|
I
I
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
900
|
Y
Y
G
G
V
V
T
T
V
V
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
910
|
F
F
G
G
S
S
K
K
P
P
Y
Y
D
D
G
G
I
I
P
P
920
|
A
A
S
S
E
E
I
I
S
S
S
S
I
I
L
L
E
E
K
K
930
|
G
G
E
E
R
R
L
L
P
P
Q
Q
P
P
P
P
I
I
C
C
940
|
T
T
I
I
D
D
V
V
Y
Y
M
M
I
I
M
M
V
V
K
K
950
|
C
C
W
W
M
M
I
I
D
D
A
A
D
D
S
S
R
R
P
P
960
|
K
K
F
F
R
R
E
E
L
L
I
I
I
I
E
E
F
F
S
S
970
|
K
K
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
P
P
Q
Q
R
R
Y
Y
L
L
980
|
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
G
G
D
D
E
E
R
R
M
M
H
H
L
L
990
|
P
P
S
S
P
P
T
T
D
D
S
S
N
N
F
F
Y
Y
R
R
1000
|
A
A
L
L
M
M
D
D
E
E
E
E
D
D
M
M
D
D
D
D
1010
|
V
V
V
V
D
D
A
A
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
I
I
P
P
1020
|
Q
Q
Q
Q
G
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Direct sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Overall and disease-free assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Among patients with acquired resistance to EGFR TkIs, the presence of T790M defines a clinical subset with a relatively favorable prognosis and more indolent progression. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [36], [37] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Erlotinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T790M |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.05 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
S
G
G
E
E
A
A
P
P
700
|
N
N
Q
Q
A
A
L
L
L
L
R
R
I
I
L
L
K
K
E
E
710
|
T
T
E
E
F
F
K
K
K
K
I
I
K
K
V
V
L
L
G
G
720
|
S
S
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
K
K
G
G
730
|
L
L
W
W
I
I
P
P
E
E
G
G
E
E
K
K
V
V
K
K
740
|
I
I
P
P
V
V
A
A
I
I
K
K
E
E
L
L
R
R
E
E
750
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
P
P
K
K
A
A
N
N
K
K
E
E
I
I
760
|
L
L
D
D
E
E
A
A
Y
Y
V
V
M
M
A
A
S
S
V
V
770
|
D
D
N
N
P
P
H
H
V
V
C
C
R
R
L
L
L
L
G
G
780
|
I
I
C
C
L
L
T
T
S
S
T
T
V
V
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
790
|
T
M
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
P
P
F
F
G
G
C
C
L
L
L
L
800
|
D
D
Y
Y
V
V
R
R
E
E
H
H
K
K
D
D
N
N
I
I
810
|
G
G
S
S
Q
Q
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
N
N
W
W
C
C
V
V
820
|
Q
Q
I
I
A
A
K
K
G
G
M
M
N
N
Y
Y
L
L
E
E
830
|
D
D
R
R
R
R
L
L
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
840
|
A
A
R
R
N
N
V
V
L
L
V
V
K
K
T
T
P
P
Q
Q
850
|
H
H
V
V
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
860
|
K
K
L
L
L
L
G
G
A
A
E
E
E
E
K
K
E
E
Y
Y
870
|
H
H
A
A
E
E
G
G
G
G
K
K
V
V
P
P
I
I
K
K
880
|
W
W
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
I
I
L
L
H
H
R
R
890
|
I
I
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
900
|
Y
Y
G
G
V
V
T
T
V
V
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
910
|
F
F
G
G
S
S
K
K
P
P
Y
Y
D
D
G
G
I
I
P
P
920
|
A
A
S
S
E
E
I
I
S
S
S
S
I
I
L
L
E
E
K
K
930
|
G
G
E
E
R
R
L
L
P
P
Q
Q
P
P
P
P
I
I
C
C
940
|
T
T
I
I
D
D
V
V
Y
Y
M
M
I
I
M
M
V
V
K
K
950
|
C
C
W
W
M
M
I
I
D
D
A
A
D
D
S
S
R
R
P
P
960
|
K
K
F
F
R
R
E
E
L
L
I
I
I
I
E
E
F
F
S
S
970
|
K
K
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
P
P
Q
Q
R
R
Y
Y
L
L
980
|
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
G
G
D
D
E
E
R
R
M
M
H
H
L
L
990
|
P
P
S
S
P
P
T
T
D
D
S
S
N
N
F
F
Y
Y
R
R
1000
|
A
A
L
L
M
M
D
D
E
E
E
E
D
D
M
M
D
D
D
D
1010
|
V
V
V
V
D
D
A
A
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
I
I
P
P
1020
|
Q
Q
Q
Q
G
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Direct sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Computed tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | In addition, three (8%) patients acquired EGFR amplifications in their resistant specimens, all of which also acquired the classic T790M EGFR mutation. Moreover, in two cases with high-level EGFR amplification (>10-fold), it was clear by comparison of the peak heights on the SNaPshot chromatogram that the T790M allele was the amplified allele. They have identified several resistance mechanisms, two of which-EGFR mutation T790M and MET amplification have been validated in the clinic. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.7] | [38] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.7] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Erlotinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T790M |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.05 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
S
G
G
E
E
A
A
P
P
700
|
N
N
Q
Q
A
A
L
L
L
L
R
R
I
I
L
L
K
K
E
E
710
|
T
T
E
E
F
F
K
K
K
K
I
I
K
K
V
V
L
L
G
G
720
|
S
S
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
K
K
G
G
730
|
L
L
W
W
I
I
P
P
E
E
G
G
E
E
K
K
V
V
K
K
740
|
I
I
P
P
V
V
A
A
I
I
K
K
E
E
L
L
R
R
E
E
750
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
P
P
K
K
A
A
N
N
K
K
E
E
I
I
760
|
L
L
D
D
E
E
A
A
Y
Y
V
V
M
M
A
A
S
S
V
V
770
|
D
D
N
N
P
P
H
H
V
V
C
C
R
R
L
L
L
L
G
G
780
|
I
I
C
C
L
L
T
T
S
S
T
T
V
V
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
790
|
T
M
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
P
P
F
F
G
G
C
C
L
L
L
L
800
|
D
D
Y
Y
V
V
R
R
E
E
H
H
K
K
D
D
N
N
I
I
810
|
G
G
S
S
Q
Q
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
N
N
W
W
C
C
V
V
820
|
Q
Q
I
I
A
A
K
K
G
G
M
M
N
N
Y
Y
L
L
E
E
830
|
D
D
R
R
R
R
L
L
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
840
|
A
A
R
R
N
N
V
V
L
L
V
V
K
K
T
T
P
P
Q
Q
850
|
H
H
V
V
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
860
|
K
K
L
L
L
L
G
G
A
A
E
E
E
E
K
K
E
E
Y
Y
870
|
H
H
A
A
E
E
G
G
G
G
K
K
V
V
P
P
I
I
K
K
880
|
W
W
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
I
I
L
L
H
H
R
R
890
|
I
I
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
900
|
Y
Y
G
G
V
V
T
T
V
V
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
910
|
F
F
G
G
S
S
K
K
P
P
Y
Y
D
D
G
G
I
I
P
P
920
|
A
A
S
S
E
E
I
I
S
S
S
S
I
I
L
L
E
E
K
K
930
|
G
G
E
E
R
R
L
L
P
P
Q
Q
P
P
P
P
I
I
C
C
940
|
T
T
I
I
D
D
V
V
Y
Y
M
M
I
I
M
M
V
V
K
K
950
|
C
C
W
W
M
M
I
I
D
D
A
A
D
D
S
S
R
R
P
P
960
|
K
K
F
F
R
R
E
E
L
L
I
I
I
I
E
E
F
F
S
S
970
|
K
K
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
P
P
Q
Q
R
R
Y
Y
L
L
980
|
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
G
G
D
D
E
E
R
R
M
M
H
H
L
L
990
|
P
P
S
S
P
P
T
T
D
D
S
S
N
N
F
F
Y
Y
R
R
1000
|
A
A
L
L
M
M
D
D
E
E
E
E
D
D
M
M
D
D
D
D
1010
|
V
V
V
V
D
D
A
A
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
I
I
P
P
1020
|
Q
Q
Q
Q
G
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Low throughput experiment assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Progression-free survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Acquired resistance can occur through failure of drug delivery to the target, as in isolated central nervous system (CNS) progression, or by selection of biological variants during TkI exposure. At the point of acquired resistance, the T790M substitution may be accompanied by amplification of the EGFR gene as well. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [39] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Erlotinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T790M |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.05 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
S
G
G
E
E
A
A
P
P
700
|
N
N
Q
Q
A
A
L
L
L
L
R
R
I
I
L
L
K
K
E
E
710
|
T
T
E
E
F
F
K
K
K
K
I
I
K
K
V
V
L
L
G
G
720
|
S
S
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
K
K
G
G
730
|
L
L
W
W
I
I
P
P
E
E
G
G
E
E
K
K
V
V
K
K
740
|
I
I
P
P
V
V
A
A
I
I
K
K
E
E
L
L
R
R
E
E
750
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
P
P
K
K
A
A
N
N
K
K
E
E
I
I
760
|
L
L
D
D
E
E
A
A
Y
Y
V
V
M
M
A
A
S
S
V
V
770
|
D
D
N
N
P
P
H
H
V
V
C
C
R
R
L
L
L
L
G
G
780
|
I
I
C
C
L
L
T
T
S
S
T
T
V
V
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
790
|
T
M
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
P
P
F
F
G
G
C
C
L
L
L
L
800
|
D
D
Y
Y
V
V
R
R
E
E
H
H
K
K
D
D
N
N
I
I
810
|
G
G
S
S
Q
Q
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
N
N
W
W
C
C
V
V
820
|
Q
Q
I
I
A
A
K
K
G
G
M
M
N
N
Y
Y
L
L
E
E
830
|
D
D
R
R
R
R
L
L
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
840
|
A
A
R
R
N
N
V
V
L
L
V
V
K
K
T
T
P
P
Q
Q
850
|
H
H
V
V
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
860
|
K
K
L
L
L
L
G
G
A
A
E
E
E
E
K
K
E
E
Y
Y
870
|
H
H
A
A
E
E
G
G
G
G
K
K
V
V
P
P
I
I
K
K
880
|
W
W
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
I
I
L
L
H
H
R
R
890
|
I
I
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
900
|
Y
Y
G
G
V
V
T
T
V
V
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
910
|
F
F
G
G
S
S
K
K
P
P
Y
Y
D
D
G
G
I
I
P
P
920
|
A
A
S
S
E
E
I
I
S
S
S
S
I
I
L
L
E
E
K
K
930
|
G
G
E
E
R
R
L
L
P
P
Q
Q
P
P
P
P
I
I
C
C
940
|
T
T
I
I
D
D
V
V
Y
Y
M
M
I
I
M
M
V
V
K
K
950
|
C
C
W
W
M
M
I
I
D
D
A
A
D
D
S
S
R
R
P
P
960
|
K
K
F
F
R
R
E
E
L
L
I
I
I
I
E
E
F
F
S
S
970
|
K
K
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
P
P
Q
Q
R
R
Y
Y
L
L
980
|
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
G
G
D
D
E
E
R
R
M
M
H
H
L
L
990
|
P
P
S
S
P
P
T
T
D
D
S
S
N
N
F
F
Y
Y
R
R
1000
|
A
A
L
L
M
M
D
D
E
E
E
E
D
D
M
M
D
D
D
D
1010
|
V
V
V
V
D
D
A
A
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
I
I
P
P
1020
|
Q
Q
Q
Q
G
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Multivariate analysis of overall or disease-free survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | One example is the acquisition of the T790M substitution in the membrane receptor EGFR conferring resistance to gefitinb and erlotinib in lung cancer in approximately 50% of patients. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [40] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Erlotinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T790M |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.05 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
S
G
G
E
E
A
A
P
P
700
|
N
N
Q
Q
A
A
L
L
L
L
R
R
I
I
L
L
K
K
E
E
710
|
T
T
E
E
F
F
K
K
K
K
I
I
K
K
V
V
L
L
G
G
720
|
S
S
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
K
K
G
G
730
|
L
L
W
W
I
I
P
P
E
E
G
G
E
E
K
K
V
V
K
K
740
|
I
I
P
P
V
V
A
A
I
I
K
K
E
E
L
L
R
R
E
E
750
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
P
P
K
K
A
A
N
N
K
K
E
E
I
I
760
|
L
L
D
D
E
E
A
A
Y
Y
V
V
M
M
A
A
S
S
V
V
770
|
D
D
N
N
P
P
H
H
V
V
C
C
R
R
L
L
L
L
G
G
780
|
I
I
C
C
L
L
T
T
S
S
T
T
V
V
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
790
|
T
M
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
P
P
F
F
G
G
C
C
L
L
L
L
800
|
D
D
Y
Y
V
V
R
R
E
E
H
H
K
K
D
D
N
N
I
I
810
|
G
G
S
S
Q
Q
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
N
N
W
W
C
C
V
V
820
|
Q
Q
I
I
A
A
K
K
G
G
M
M
N
N
Y
Y
L
L
E
E
830
|
D
D
R
R
R
R
L
L
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
840
|
A
A
R
R
N
N
V
V
L
L
V
V
K
K
T
T
P
P
Q
Q
850
|
H
H
V
V
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
860
|
K
K
L
L
L
L
G
G
A
A
E
E
E
E
K
K
E
E
Y
Y
870
|
H
H
A
A
E
E
G
G
G
G
K
K
V
V
P
P
I
I
K
K
880
|
W
W
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
I
I
L
L
H
H
R
R
890
|
I
I
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
900
|
Y
Y
G
G
V
V
T
T
V
V
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
910
|
F
F
G
G
S
S
K
K
P
P
Y
Y
D
D
G
G
I
I
P
P
920
|
A
A
S
S
E
E
I
I
S
S
S
S
I
I
L
L
E
E
K
K
930
|
G
G
E
E
R
R
L
L
P
P
Q
Q
P
P
P
P
I
I
C
C
940
|
T
T
I
I
D
D
V
V
Y
Y
M
M
I
I
M
M
V
V
K
K
950
|
C
C
W
W
M
M
I
I
D
D
A
A
D
D
S
S
R
R
P
P
960
|
K
K
F
F
R
R
E
E
L
L
I
I
I
I
E
E
F
F
S
S
970
|
K
K
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
P
P
Q
Q
R
R
Y
Y
L
L
980
|
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
G
G
D
D
E
E
R
R
M
M
H
H
L
L
990
|
P
P
S
S
P
P
T
T
D
D
S
S
N
N
F
F
Y
Y
R
R
1000
|
A
A
L
L
M
M
D
D
E
E
E
E
D
D
M
M
D
D
D
D
1010
|
V
V
V
V
D
D
A
A
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
I
I
P
P
1020
|
Q
Q
Q
Q
G
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Wnt signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04310 | ||||||||||
| mTOR signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04150 | |||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | H1975 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1511 | |||||||||
| H2170 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1535 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Low throughput experiment assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT cell viability assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | H1975 cells are positive for the T790M EGFR mutation, which confers resistance to current EGFR TkI therapies. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [41] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Erlotinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.C797S+p.T790M |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.64 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.20 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
G
G
A
S
M
M
G
G
G
E
E
A
A
P
P
700
|
N
N
Q
Q
A
A
L
L
L
L
R
R
I
I
L
L
K
K
E
E
710
|
T
T
E
E
F
F
K
K
K
K
I
I
K
K
V
V
L
L
G
G
720
|
S
S
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
K
K
G
G
730
|
L
L
W
W
I
I
P
P
E
E
G
G
E
E
K
K
V
V
K
K
740
|
I
I
P
P
V
V
A
A
I
I
K
K
E
E
L
L
R
R
E
E
750
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
P
P
K
K
A
A
N
N
K
K
E
E
I
I
760
|
L
L
D
D
E
E
A
A
Y
Y
V
V
M
M
A
A
S
S
V
V
770
|
D
D
N
N
P
P
H
H
V
V
C
C
R
R
L
L
L
L
G
G
780
|
I
I
C
C
L
L
T
T
S
S
T
T
V
V
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
790
|
T
M
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
P
P
F
F
G
G
C
S
L
L
L
L
800
|
D
D
Y
Y
V
V
R
R
E
E
H
H
K
K
D
D
N
N
I
I
810
|
G
G
S
S
Q
Q
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
N
N
W
W
C
C
V
V
820
|
Q
Q
I
I
A
A
K
K
G
G
M
M
N
N
Y
Y
L
L
E
E
830
|
D
D
R
R
R
R
L
L
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
840
|
A
A
R
R
N
N
V
V
L
L
V
V
K
K
T
T
P
P
Q
Q
850
|
H
H
V
V
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
860
|
K
K
L
L
L
L
G
G
A
A
E
E
E
E
K
K
E
E
Y
Y
870
|
H
H
A
A
E
E
G
G
G
G
K
K
V
V
P
P
I
I
K
K
880
|
W
W
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
I
I
L
L
H
H
R
R
890
|
I
I
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
900
|
Y
Y
G
G
V
V
T
T
V
V
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
910
|
F
F
G
G
S
S
K
K
P
P
Y
Y
D
D
G
G
I
I
P
P
920
|
A
A
S
S
E
E
I
I
S
S
S
S
I
I
L
L
E
E
K
K
930
|
G
G
E
E
R
R
L
L
P
P
Q
Q
P
P
P
P
I
I
C
C
940
|
T
T
I
I
D
D
V
V
Y
Y
M
M
I
I
M
M
V
V
K
K
950
|
C
C
W
W
M
M
I
I
D
D
A
A
D
D
S
S
R
R
P
P
960
|
K
K
F
F
R
R
E
E
L
L
I
I
I
I
E
E
F
F
S
S
970
|
K
K
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
P
P
Q
Q
R
R
Y
Y
L
L
980
|
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
G
G
D
D
E
E
R
R
M
M
H
H
L
L
990
|
P
P
S
S
P
P
T
T
D
D
S
S
N
N
F
F
Y
Y
R
R
1000
|
A
A
L
L
M
M
D
D
E
E
E
E
D
D
M
M
D
D
D
D
1010
|
V
V
V
V
D
D
A
A
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
I
I
P
P
1020
|
Q
Q
-
Q
-
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | AKT signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04151 | ||||||||||
| Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |||||||||||
| Cell invasion | Activation | hsa05200 | |||||||||||
| Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | |||||||||||
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | |||||||||||
| EGFR/TKLS mediated apoptosis signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa01521 | |||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Liquid biopsy; ATP-binding pocket affinity comparison assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Several mechanisms of resistance have been described to EGFR-TkIs, such as the occurrence of secondary mutation (T790M, C797S), the activation of alternative signalling (Met, HGF, AXL, Hh, IGF-1R), the aberrance of the downstream pathways (AkT mutations, loss of PTEN), the impairment of the EGFR-TkIs-mediated apoptosis pathway (BCL2-like 11/BIM deletion polymorphism) and histological transformation. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.7] | [38] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.7] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Erlotinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D761Y |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Low throughput experiment assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Progression-free survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Acquired resistance can occur through failure of drug delivery to the target, as in isolated central nervous system (CNS) progression, or by selection of biological variants during TkI exposure. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.7] | [38] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.7] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Erlotinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L747S |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Low throughput experiment assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Progression-free survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Acquired resistance can occur through failure of drug delivery to the target, as in isolated central nervous system (CNS) progression, or by selection of biological variants during TkI exposure. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [21] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Erlotinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | . |
|||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Statistical analysis | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | EGFR-TKI Rechallenge With Another TKI may be a useful treatment option after first-line osimertinib. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [18], [19], [20] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Icotinib hydrochloride | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T790M |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.05 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
S
G
G
E
E
A
A
P
P
700
|
N
N
Q
Q
A
A
L
L
L
L
R
R
I
I
L
L
K
K
E
E
710
|
T
T
E
E
F
F
K
K
K
K
I
I
K
K
V
V
L
L
G
G
720
|
S
S
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
K
K
G
G
730
|
L
L
W
W
I
I
P
P
E
E
G
G
E
E
K
K
V
V
K
K
740
|
I
I
P
P
V
V
A
A
I
I
K
K
E
E
L
L
R
R
E
E
750
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
P
P
K
K
A
A
N
N
K
K
E
E
I
I
760
|
L
L
D
D
E
E
A
A
Y
Y
V
V
M
M
A
A
S
S
V
V
770
|
D
D
N
N
P
P
H
H
V
V
C
C
R
R
L
L
L
L
G
G
780
|
I
I
C
C
L
L
T
T
S
S
T
T
V
V
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
790
|
T
M
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
P
P
F
F
G
G
C
C
L
L
L
L
800
|
D
D
Y
Y
V
V
R
R
E
E
H
H
K
K
D
D
N
N
I
I
810
|
G
G
S
S
Q
Q
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
N
N
W
W
C
C
V
V
820
|
Q
Q
I
I
A
A
K
K
G
G
M
M
N
N
Y
Y
L
L
E
E
830
|
D
D
R
R
R
R
L
L
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
840
|
A
A
R
R
N
N
V
V
L
L
V
V
K
K
T
T
P
P
Q
Q
850
|
H
H
V
V
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
860
|
K
K
L
L
L
L
G
G
A
A
E
E
E
E
K
K
E
E
Y
Y
870
|
H
H
A
A
E
E
G
G
G
G
K
K
V
V
P
P
I
I
K
K
880
|
W
W
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
I
I
L
L
H
H
R
R
890
|
I
I
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
900
|
Y
Y
G
G
V
V
T
T
V
V
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
910
|
F
F
G
G
S
S
K
K
P
P
Y
Y
D
D
G
G
I
I
P
P
920
|
A
A
S
S
E
E
I
I
S
S
S
S
I
I
L
L
E
E
K
K
930
|
G
G
E
E
R
R
L
L
P
P
Q
Q
P
P
P
P
I
I
C
C
940
|
T
T
I
I
D
D
V
V
Y
Y
M
M
I
I
M
M
V
V
K
K
950
|
C
C
W
W
M
M
I
I
D
D
A
A
D
D
S
S
R
R
P
P
960
|
K
K
F
F
R
R
E
E
L
L
I
I
I
I
E
E
F
F
S
S
970
|
K
K
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
P
P
Q
Q
R
R
Y
Y
L
L
980
|
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
G
G
D
D
E
E
R
R
M
M
H
H
L
L
990
|
P
P
S
S
P
P
T
T
D
D
S
S
N
N
F
F
Y
Y
R
R
1000
|
A
A
L
L
M
M
D
D
E
E
E
E
D
D
M
M
D
D
D
D
1010
|
V
V
V
V
D
D
A
A
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
I
I
P
P
1020
|
Q
Q
Q
Q
G
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Directional sequencing assay; Direct sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Progression-free and post-progression survival asaay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The identification of T790M as acquired resistance mechanism was clinically feasible. Although T790M had no prognostic or predictive role in the present study, further research is necessary to identify patients with T790M-mutant tumors who might benefit from newly developed T790M-specific TkIs. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Imatinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E711K |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Lapatinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V292E |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Lapatinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R705G |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Lapatinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L760F |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Lapatinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.K284E |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Lapatinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.I706T |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Lapatinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G696E |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Lapatinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.A822V |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Lapatinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V292M |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Lapatinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.P741S |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Lapatinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G288D |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Lapatinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E711K |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Nilotinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E711K |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [54] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Olmutinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.C797S |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.64 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.20 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
G
G
A
S
M
M
G
G
G
E
E
A
A
P
P
700
|
N
N
Q
Q
A
A
L
L
L
L
R
R
I
I
L
L
K
K
E
E
710
|
T
T
E
E
F
F
K
K
K
K
I
I
K
K
V
V
L
L
G
G
720
|
S
S
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
K
K
G
G
730
|
L
L
W
W
I
I
P
P
E
E
G
G
E
E
K
K
V
V
K
K
740
|
I
I
P
P
V
V
A
A
I
I
K
K
E
E
L
L
R
R
E
E
750
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
P
P
K
K
A
A
N
N
K
K
E
E
I
I
760
|
L
L
D
D
E
E
A
A
Y
Y
V
V
M
M
A
A
S
S
V
V
770
|
D
D
N
N
P
P
H
H
V
V
C
C
R
R
L
L
L
L
G
G
780
|
I
I
C
C
L
L
T
T
S
S
T
T
V
V
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
790
|
T
M
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
P
P
F
F
G
G
C
S
L
L
L
L
800
|
D
D
Y
Y
V
V
R
R
E
E
H
H
K
K
D
D
N
N
I
I
810
|
G
G
S
S
Q
Q
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
N
N
W
W
C
C
V
V
820
|
Q
Q
I
I
A
A
K
K
G
G
M
M
N
N
Y
Y
L
L
E
E
830
|
D
D
R
R
R
R
L
L
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
840
|
A
A
R
R
N
N
V
V
L
L
V
V
K
K
T
T
P
P
Q
Q
850
|
H
H
V
V
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
860
|
K
K
L
L
L
L
G
G
A
A
E
E
E
E
K
K
E
E
Y
Y
870
|
H
H
A
A
E
E
G
G
G
G
K
K
V
V
P
P
I
I
K
K
880
|
W
W
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
I
I
L
L
H
H
R
R
890
|
I
I
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
900
|
Y
Y
G
G
V
V
T
T
V
V
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
910
|
F
F
G
G
S
S
K
K
P
P
Y
Y
D
D
G
G
I
I
P
P
920
|
A
A
S
S
E
E
I
I
S
S
S
S
I
I
L
L
E
E
K
K
930
|
G
G
E
E
R
R
L
L
P
P
Q
Q
P
P
P
P
I
I
C
C
940
|
T
T
I
I
D
D
V
V
Y
Y
M
M
I
I
M
M
V
V
K
K
950
|
C
C
W
W
M
M
I
I
D
D
A
A
D
D
S
S
R
R
P
P
960
|
K
K
F
F
R
R
E
E
L
L
I
I
I
I
E
E
F
F
S
S
970
|
K
K
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
P
P
Q
Q
R
R
Y
Y
L
L
980
|
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
G
G
D
D
E
E
R
R
M
M
H
H
L
L
990
|
P
P
S
S
P
P
T
T
D
D
S
S
N
N
F
F
Y
Y
R
R
1000
|
A
A
L
L
M
M
D
D
E
E
E
E
D
D
M
M
D
D
D
D
1010
|
V
V
V
V
D
D
A
A
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
I
I
P
P
1020
|
Q
Q
-
Q
-
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Computed tomography assay; Progression-free survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | A recent preclinical study reported that EGFR C797S, L718Q, and L844V mutations cause resistance to both WZ4002 and CO-1686 but only EGFR C797S leads to AZD9291 resistance, suggesting that C797S can serve as acquired resistance to irreversible pyrimidine-based EGFR inhibitors given the similar chemical structure of third-generation EGFR TkIs. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [55] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Osimertinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.C797S |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.64 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.20 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
G
G
A
S
M
M
G
G
G
E
E
A
A
P
P
700
|
N
N
Q
Q
A
A
L
L
L
L
R
R
I
I
L
L
K
K
E
E
710
|
T
T
E
E
F
F
K
K
K
K
I
I
K
K
V
V
L
L
G
G
720
|
S
S
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
K
K
G
G
730
|
L
L
W
W
I
I
P
P
E
E
G
G
E
E
K
K
V
V
K
K
740
|
I
I
P
P
V
V
A
A
I
I
K
K
E
E
L
L
R
R
E
E
750
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
P
P
K
K
A
A
N
N
K
K
E
E
I
I
760
|
L
L
D
D
E
E
A
A
Y
Y
V
V
M
M
A
A
S
S
V
V
770
|
D
D
N
N
P
P
H
H
V
V
C
C
R
R
L
L
L
L
G
G
780
|
I
I
C
C
L
L
T
T
S
S
T
T
V
V
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
790
|
T
M
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
P
P
F
F
G
G
C
S
L
L
L
L
800
|
D
D
Y
Y
V
V
R
R
E
E
H
H
K
K
D
D
N
N
I
I
810
|
G
G
S
S
Q
Q
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
N
N
W
W
C
C
V
V
820
|
Q
Q
I
I
A
A
K
K
G
G
M
M
N
N
Y
Y
L
L
E
E
830
|
D
D
R
R
R
R
L
L
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
840
|
A
A
R
R
N
N
V
V
L
L
V
V
K
K
T
T
P
P
Q
Q
850
|
H
H
V
V
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
860
|
K
K
L
L
L
L
G
G
A
A
E
E
E
E
K
K
E
E
Y
Y
870
|
H
H
A
A
E
E
G
G
G
G
K
K
V
V
P
P
I
I
K
K
880
|
W
W
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
I
I
L
L
H
H
R
R
890
|
I
I
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
900
|
Y
Y
G
G
V
V
T
T
V
V
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
910
|
F
F
G
G
S
S
K
K
P
P
Y
Y
D
D
G
G
I
I
P
P
920
|
A
A
S
S
E
E
I
I
S
S
S
S
I
I
L
L
E
E
K
K
930
|
G
G
E
E
R
R
L
L
P
P
Q
Q
P
P
P
P
I
I
C
C
940
|
T
T
I
I
D
D
V
V
Y
Y
M
M
I
I
M
M
V
V
K
K
950
|
C
C
W
W
M
M
I
I
D
D
A
A
D
D
S
S
R
R
P
P
960
|
K
K
F
F
R
R
E
E
L
L
I
I
I
I
E
E
F
F
S
S
970
|
K
K
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
P
P
Q
Q
R
R
Y
Y
L
L
980
|
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
G
G
D
D
E
E
R
R
M
M
H
H
L
L
990
|
P
P
S
S
P
P
T
T
D
D
S
S
N
N
F
F
Y
Y
R
R
1000
|
A
A
L
L
M
M
D
D
E
E
E
E
D
D
M
M
D
D
D
D
1010
|
V
V
V
V
D
D
A
A
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
I
I
P
P
1020
|
Q
Q
-
Q
-
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Cell-free plasma DNA assay; Next generation assay; Droplet digital PCR assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Progression-free survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Acquired EGFR C797S mediates resistance to AZD9291 in advanced non-small cell lung cancer harboring EGFR T790M. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [56] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Osimertinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T790M |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.05 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
S
G
G
E
E
A
A
P
P
700
|
N
N
Q
Q
A
A
L
L
L
L
R
R
I
I
L
L
K
K
E
E
710
|
T
T
E
E
F
F
K
K
K
K
I
I
K
K
V
V
L
L
G
G
720
|
S
S
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
K
K
G
G
730
|
L
L
W
W
I
I
P
P
E
E
G
G
E
E
K
K
V
V
K
K
740
|
I
I
P
P
V
V
A
A
I
I
K
K
E
E
L
L
R
R
E
E
750
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
P
P
K
K
A
A
N
N
K
K
E
E
I
I
760
|
L
L
D
D
E
E
A
A
Y
Y
V
V
M
M
A
A
S
S
V
V
770
|
D
D
N
N
P
P
H
H
V
V
C
C
R
R
L
L
L
L
G
G
780
|
I
I
C
C
L
L
T
T
S
S
T
T
V
V
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
790
|
T
M
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
P
P
F
F
G
G
C
C
L
L
L
L
800
|
D
D
Y
Y
V
V
R
R
E
E
H
H
K
K
D
D
N
N
I
I
810
|
G
G
S
S
Q
Q
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
N
N
W
W
C
C
V
V
820
|
Q
Q
I
I
A
A
K
K
G
G
M
M
N
N
Y
Y
L
L
E
E
830
|
D
D
R
R
R
R
L
L
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
840
|
A
A
R
R
N
N
V
V
L
L
V
V
K
K
T
T
P
P
Q
Q
850
|
H
H
V
V
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
860
|
K
K
L
L
L
L
G
G
A
A
E
E
E
E
K
K
E
E
Y
Y
870
|
H
H
A
A
E
E
G
G
G
G
K
K
V
V
P
P
I
I
K
K
880
|
W
W
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
I
I
L
L
H
H
R
R
890
|
I
I
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
900
|
Y
Y
G
G
V
V
T
T
V
V
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
910
|
F
F
G
G
S
S
K
K
P
P
Y
Y
D
D
G
G
I
I
P
P
920
|
A
A
S
S
E
E
I
I
S
S
S
S
I
I
L
L
E
E
K
K
930
|
G
G
E
E
R
R
L
L
P
P
Q
Q
P
P
P
P
I
I
C
C
940
|
T
T
I
I
D
D
V
V
Y
Y
M
M
I
I
M
M
V
V
K
K
950
|
C
C
W
W
M
M
I
I
D
D
A
A
D
D
S
S
R
R
P
P
960
|
K
K
F
F
R
R
E
E
L
L
I
I
I
I
E
E
F
F
S
S
970
|
K
K
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
P
P
Q
Q
R
R
Y
Y
L
L
980
|
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
G
G
D
D
E
E
R
R
M
M
H
H
L
L
990
|
P
P
S
S
P
P
T
T
D
D
S
S
N
N
F
F
Y
Y
R
R
1000
|
A
A
L
L
M
M
D
D
E
E
E
E
D
D
M
M
D
D
D
D
1010
|
V
V
V
V
D
D
A
A
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
I
I
P
P
1020
|
Q
Q
Q
Q
G
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; Fluorescence in situ hybridization assay; Real-time polymerase chain reaction assay; Targeted exome sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Computed tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Acquired resistance mechanisms of AZD9291 in patients with EGFRT790M-mutant NSCLC who failed treatment with first-generation EGFR TkIs include the loss of EGFRT790M-mutant clones plus alternative pathway activation or histologic transformation and EGFR ligand-dependent activation. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [21] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Osimertinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | . |
|||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Statistical analysis | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | EGFR-TKI Rechallenge With Another TKI may be a useful treatment option after first-line osimertinib. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Metastatic colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2D85.0] | [24] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Metastatic colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2D85.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Panitumumab | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S492R |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.20 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.80 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
L
L
E
E
E
E
310
|
K
K
K
K
V
V
C
C
N
N
G
G
I
I
G
G
I
I
G
G
320
|
E
E
F
F
K
K
D
D
S
S
L
L
S
S
I
I
N
N
A
A
330
|
T
T
N
N
I
I
K
K
H
H
F
F
K
K
N
N
C
C
T
T
340
|
S
S
I
I
S
S
G
G
D
D
L
L
H
H
I
I
L
L
P
P
350
|
V
V
A
A
F
F
R
R
G
G
D
D
S
S
F
F
T
T
H
H
360
|
T
T
P
P
P
P
L
L
D
D
P
P
Q
Q
E
E
L
L
D
D
370
|
I
I
L
L
K
K
T
T
V
V
K
K
E
E
I
I
T
T
G
G
380
|
F
F
L
L
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
A
A
W
W
P
P
E
E
N
N
390
|
R
R
T
T
D
D
L
L
H
H
A
A
F
F
E
E
N
N
L
L
400
|
E
E
I
I
I
I
R
R
G
G
R
R
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
H
H
410
|
G
G
Q
Q
F
F
S
S
L
L
A
A
V
V
V
V
S
S
L
L
420
|
N
N
I
I
T
T
S
S
L
L
G
G
L
L
R
R
S
S
L
L
430
|
K
K
E
E
I
I
S
S
D
D
G
G
D
D
V
V
I
I
I
I
440
|
S
S
G
G
N
N
K
K
N
N
L
L
C
C
Y
Y
A
A
N
N
450
|
T
T
I
I
N
N
W
W
K
K
K
K
L
L
F
F
G
G
T
T
460
|
S
S
G
G
Q
Q
K
K
T
T
K
K
I
I
I
I
S
R
N
N
470
|
R
R
G
G
E
E
N
N
S
S
C
C
K
K
A
A
T
T
G
G
480
|
Q
Q
V
V
C
C
H
H
A
A
L
L
C
C
S
S
P
P
E
E
490
|
G
G
C
C
W
W
G
G
P
P
E
E
P
P
R
R
D
D
C
C
500
|
V
V
S
S
C
C
R
R
N
N
V
V
S
S
R
R
G
G
R
R
510
|
E
E
C
C
V
V
D
D
K
K
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
520
|
H
H
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Circulating-free DNA assay; Standard-of-care sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | K-RAS and EGFR ectodomain-acquired mutations in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) have been correlated with acquired resistance to anti-EGFR monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [25] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Panitumumab | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G465E |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Colon cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Liquid biopsy assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Mechanisms of resistance to EGFR blockade include the emergence of kRAS, NRAS and EGFR extracellular domain mutations as well as HER2/MET alterations. | ||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Metastatic colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2D85.0] | [57] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Metastatic colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2D85.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Panitumumab | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | ||||||||||
| EGFR signaling pathway | Activation | hsa01521 | |||||||||||
| ERBB2/MET/IGF-1R signalling pathway | Activation | hsa04520 | |||||||||||
| RAF/KRAS/MEK signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04010 | |||||||||||
| PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04151 | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Progression-free survival (PFS) analysis; Overall survival (OS) analysis | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Cetuximab and panitumumab are monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) against epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) that are effective agents for metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC). The mechanisms of resistance refer to intrinsic and extrinsic alterations of tumours. The intrinsic mechanisms include EGFR ligand overexpression, EGFR alteration, RAS/RAF/PI3K gene mutations, ERBB2/MET/IGF-1R activation, metabolic remodelling, microsatellite instability and autophagy. Extrinsic alterations mainly disrupt the tumour microenvironment, specifically immune cells, cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) and angiogenesis. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [51] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Pemetrexed | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T790M |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.05 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
S
G
G
E
E
A
A
P
P
700
|
N
N
Q
Q
A
A
L
L
L
L
R
R
I
I
L
L
K
K
E
E
710
|
T
T
E
E
F
F
K
K
K
K
I
I
K
K
V
V
L
L
G
G
720
|
S
S
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
K
K
G
G
730
|
L
L
W
W
I
I
P
P
E
E
G
G
E
E
K
K
V
V
K
K
740
|
I
I
P
P
V
V
A
A
I
I
K
K
E
E
L
L
R
R
E
E
750
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
P
P
K
K
A
A
N
N
K
K
E
E
I
I
760
|
L
L
D
D
E
E
A
A
Y
Y
V
V
M
M
A
A
S
S
V
V
770
|
D
D
N
N
P
P
H
H
V
V
C
C
R
R
L
L
L
L
G
G
780
|
I
I
C
C
L
L
T
T
S
S
T
T
V
V
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
790
|
T
M
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
P
P
F
F
G
G
C
C
L
L
L
L
800
|
D
D
Y
Y
V
V
R
R
E
E
H
H
K
K
D
D
N
N
I
I
810
|
G
G
S
S
Q
Q
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
N
N
W
W
C
C
V
V
820
|
Q
Q
I
I
A
A
K
K
G
G
M
M
N
N
Y
Y
L
L
E
E
830
|
D
D
R
R
R
R
L
L
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
840
|
A
A
R
R
N
N
V
V
L
L
V
V
K
K
T
T
P
P
Q
Q
850
|
H
H
V
V
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
860
|
K
K
L
L
L
L
G
G
A
A
E
E
E
E
K
K
E
E
Y
Y
870
|
H
H
A
A
E
E
G
G
G
G
K
K
V
V
P
P
I
I
K
K
880
|
W
W
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
I
I
L
L
H
H
R
R
890
|
I
I
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
900
|
Y
Y
G
G
V
V
T
T
V
V
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
910
|
F
F
G
G
S
S
K
K
P
P
Y
Y
D
D
G
G
I
I
P
P
920
|
A
A
S
S
E
E
I
I
S
S
S
S
I
I
L
L
E
E
K
K
930
|
G
G
E
E
R
R
L
L
P
P
Q
Q
P
P
P
P
I
I
C
C
940
|
T
T
I
I
D
D
V
V
Y
Y
M
M
I
I
M
M
V
V
K
K
950
|
C
C
W
W
M
M
I
I
D
D
A
A
D
D
S
S
R
R
P
P
960
|
K
K
F
F
R
R
E
E
L
L
I
I
I
I
E
E
F
F
S
S
970
|
K
K
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
P
P
Q
Q
R
R
Y
Y
L
L
980
|
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
G
G
D
D
E
E
R
R
M
M
H
H
L
L
990
|
P
P
S
S
P
P
T
T
D
D
S
S
N
N
F
F
Y
Y
R
R
1000
|
A
A
L
L
M
M
D
D
E
E
E
E
D
D
M
M
D
D
D
D
1010
|
V
V
V
V
D
D
A
A
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
I
I
P
P
1020
|
Q
Q
Q
Q
G
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
MGB SNP detection kit assay; Mutation Detection assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Digital PCR assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Resistance mechanisms to EGFR-TkI therapy in EGFR-mutated NSCLC include secondary EGFR T790M mutation, c-Met amplification, PIk3CA mutation, and transformation to small-cell lung cancer. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Pertuzumab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V292E |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Pertuzumab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R705G |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Pertuzumab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L760F |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Pertuzumab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.K284E |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Pertuzumab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.I706T |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Pertuzumab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G696E |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Pertuzumab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.A822V |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Pertuzumab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V292M |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Pertuzumab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.P741S |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Pertuzumab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G288D |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Pertuzumab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E711K |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Trastuzumab emtansine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V292E |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Trastuzumab emtansine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R705G |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Trastuzumab emtansine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L760F |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Trastuzumab emtansine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.K284E |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Trastuzumab emtansine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.I706T |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Trastuzumab emtansine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G696E |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Trastuzumab emtansine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.A822V |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Trastuzumab emtansine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V292M |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Trastuzumab emtansine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.P741S |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | [32] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HER2 positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.8] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Trastuzumab emtansine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G288D |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasma | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography/Computed tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Seven genes, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), G protein subunit alpha S (GNAS), HRas proto-oncogene (HRAS), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), cadherin 1 (CDH1), neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS), and NOTCH1, that only occurred mutations in the resistant group were associated with the resistance of targeted therapy. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [58] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Vandetanib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L858R (c.2573T>G) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.64 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.47 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
-
S
-
M
-
G
G
E
E
A
A
P
P
700
|
N
N
Q
Q
A
A
L
L
L
L
R
R
I
I
L
L
K
K
E
E
710
|
T
T
E
E
F
F
K
K
K
K
I
I
K
K
V
V
L
L
G
G
720
|
S
S
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
K
K
G
G
730
|
L
L
W
W
I
I
P
P
E
E
G
G
E
E
K
K
V
V
K
K
740
|
I
I
P
P
V
V
A
A
I
I
K
K
E
E
L
L
R
R
E
E
750
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
P
P
K
K
A
A
N
N
K
K
E
E
I
I
760
|
L
L
D
D
E
E
A
A
Y
Y
V
V
M
M
A
A
S
S
V
V
770
|
D
D
N
N
P
P
H
H
V
V
C
C
R
R
L
L
L
L
G
G
780
|
I
I
C
C
L
L
T
T
S
S
T
T
V
V
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
790
|
T
T
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
P
P
F
F
G
G
C
C
L
L
L
L
800
|
D
D
Y
Y
V
V
R
R
E
E
H
H
K
K
D
D
N
N
I
I
810
|
G
G
S
S
Q
Q
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
N
N
W
W
C
C
V
V
820
|
Q
Q
I
I
A
A
K
K
G
G
M
M
N
N
Y
Y
L
L
E
E
830
|
D
D
R
R
R
R
L
L
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
840
|
A
A
R
R
N
N
V
V
L
L
V
V
K
K
T
T
P
P
Q
Q
850
|
H
H
V
V
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
R
A
A
860
|
K
K
L
L
L
L
G
G
A
A
E
E
E
E
K
K
E
E
Y
Y
870
|
H
H
A
A
E
E
G
G
G
G
K
K
V
V
P
P
I
I
K
K
880
|
W
W
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
I
I
L
L
H
H
R
R
890
|
I
I
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
900
|
Y
Y
G
G
V
V
T
T
V
V
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
910
|
F
F
G
G
S
S
K
K
P
P
Y
Y
D
D
G
G
I
I
P
P
920
|
A
A
S
S
E
E
I
I
S
S
S
S
I
I
L
L
E
E
K
K
930
|
G
G
E
E
R
R
L
L
P
P
Q
Q
P
P
P
P
I
I
C
C
940
|
T
T
I
I
D
D
V
V
Y
Y
M
M
I
I
M
M
V
V
K
K
950
|
C
C
W
W
M
M
I
I
D
D
A
A
D
D
S
S
R
R
P
P
960
|
K
K
F
F
R
R
E
E
L
L
I
I
I
I
E
E
F
F
S
S
970
|
K
K
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
P
P
Q
Q
R
R
Y
Y
L
L
980
|
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
G
G
D
D
E
E
R
R
M
M
H
H
L
L
990
|
P
P
S
S
P
P
T
T
D
D
S
S
N
N
F
F
Y
Y
R
R
1000
|
A
A
L
L
M
M
D
D
E
E
E
E
D
D
M
M
D
D
D
D
1010
|
V
V
V
V
D
D
A
A
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
I
I
P
P
1020
|
Q
Q
-
Q
-
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | H1975 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1511 | |||||||||
| A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 | ||||||||||
| HCC827 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2063 | ||||||||||
| H1650 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_4V01 | ||||||||||
| Calu-6 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0236 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.L858R (c.2573T>G) in gene EGFR cause the sensitivity of Vandetanib by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [59] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Vandetanib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | IF-deletion | p.E746_A750delELREA (c.2236_2250del15) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | LOVO cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0399 | |||||||||
| A431 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0037 | ||||||||||
| PC-14 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1640 | ||||||||||
| WiDR cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2760 | ||||||||||
| SkBR3 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0033 | ||||||||||
| SkOV3 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0532 | ||||||||||
| PC9 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B260 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The if-deletion p.E746_A750delELREA (c.2236_2250del15) in gene EGFR cause the sensitivity of Vandetanib by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway. | ||||||||||||
Patented Agent(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [60] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Abivertinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T790M (c.2369C>T) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.05 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
S
G
G
E
E
A
A
P
P
700
|
N
N
Q
Q
A
A
L
L
L
L
R
R
I
I
L
L
K
K
E
E
710
|
T
T
E
E
F
F
K
K
K
K
I
I
K
K
V
V
L
L
G
G
720
|
S
S
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
K
K
G
G
730
|
L
L
W
W
I
I
P
P
E
E
G
G
E
E
K
K
V
V
K
K
740
|
I
I
P
P
V
V
A
A
I
I
K
K
E
E
L
L
R
R
E
E
750
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
P
P
K
K
A
A
N
N
K
K
E
E
I
I
760
|
L
L
D
D
E
E
A
A
Y
Y
V
V
M
M
A
A
S
S
V
V
770
|
D
D
N
N
P
P
H
H
V
V
C
C
R
R
L
L
L
L
G
G
780
|
I
I
C
C
L
L
T
T
S
S
T
T
V
V
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
790
|
T
M
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
P
P
F
F
G
G
C
C
L
L
L
L
800
|
D
D
Y
Y
V
V
R
R
E
E
H
H
K
K
D
D
N
N
I
I
810
|
G
G
S
S
Q
Q
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
N
N
W
W
C
C
V
V
820
|
Q
Q
I
I
A
A
K
K
G
G
M
M
N
N
Y
Y
L
L
E
E
830
|
D
D
R
R
R
R
L
L
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
840
|
A
A
R
R
N
N
V
V
L
L
V
V
K
K
T
T
P
P
Q
Q
850
|
H
H
V
V
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
860
|
K
K
L
L
L
L
G
G
A
A
E
E
E
E
K
K
E
E
Y
Y
870
|
H
H
A
A
E
E
G
G
G
G
K
K
V
V
P
P
I
I
K
K
880
|
W
W
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
I
I
L
L
H
H
R
R
890
|
I
I
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
900
|
Y
Y
G
G
V
V
T
T
V
V
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
910
|
F
F
G
G
S
S
K
K
P
P
Y
Y
D
D
G
G
I
I
P
P
920
|
A
A
S
S
E
E
I
I
S
S
S
S
I
I
L
L
E
E
K
K
930
|
G
G
E
E
R
R
L
L
P
P
Q
Q
P
P
P
P
I
I
C
C
940
|
T
T
I
I
D
D
V
V
Y
Y
M
M
I
I
M
M
V
V
K
K
950
|
C
C
W
W
M
M
I
I
D
D
A
A
D
D
S
S
R
R
P
P
960
|
K
K
F
F
R
R
E
E
L
L
I
I
I
I
E
E
F
F
S
S
970
|
K
K
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
P
P
Q
Q
R
R
Y
Y
L
L
980
|
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
G
G
D
D
E
E
R
R
M
M
H
H
L
L
990
|
P
P
S
S
P
P
T
T
D
D
S
S
N
N
F
F
Y
Y
R
R
1000
|
A
A
L
L
M
M
D
D
E
E
E
E
D
D
M
M
D
D
D
D
1010
|
V
V
V
V
D
D
A
A
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
I
I
P
P
1020
|
Q
Q
Q
Q
G
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 | |||||||||
| Hela cells | Cervix uteri | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0030 | ||||||||||
| HCC827 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2063 | ||||||||||
| NCI-H460 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0459 | ||||||||||
| BEAS-2B cells | Bronchus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0168 | ||||||||||
| A431 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0037 | ||||||||||
| NCI-H1975 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1511 | ||||||||||
| NIH 3T3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0594 | ||||||||||
| HT1080 cells | Acetabulum | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0317 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Nu/Nu nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
WST-1 assay | ||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [60] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Abivertinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | IF-deletion | p.E746_A750delELREA (c.2236_2250del15) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | EGFR signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa01521 | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 | |||||||||
| Hela cells | Cervix uteri | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0030 | ||||||||||
| HCC827 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2063 | ||||||||||
| NCI-H460 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0459 | ||||||||||
| BEAS-2B cells | Bronchus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0168 | ||||||||||
| A431 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0037 | ||||||||||
| NCI-H1975 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1511 | ||||||||||
| NIH 3T3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0594 | ||||||||||
| HT1080 cells | Acetabulum | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0317 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting analysis; ELISA assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
WST-1 assay | ||||||||||||
Clinical Trial Drug(s)
4 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [61] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Nazartinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Duplication | p.N771_H773 (c.2311_2319) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | H1975 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1511 |
| HCC827 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2063 | |
| HaCaT cells | Tongue | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0038 | |
| A431 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0037 | |
| H3255 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6831 | |
| In Vivo Model | NSG mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Promega assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | EGF816 Exerts Anticancer Effects in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer by Irreversibly and Selectively Targeting Primary and Acquired Activating Mutations in the EGF Receptor | |||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [61] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Nazartinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Duplication | p.S768_D770 (c.2302_2310) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | H1975 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1511 |
| HCC827 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2063 | |
| HaCaT cells | Tongue | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0038 | |
| A431 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0037 | |
| H3255 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6831 | |
| In Vivo Model | NSG mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Promega assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | EGF816 Exerts Anticancer Effects in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer by Irreversibly and Selectively Targeting Primary and Acquired Activating Mutations in the EGF Receptor | |||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [61] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Nazartinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Duplication | p.N771_H773 (c.2311_2319) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | H1975 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1511 |
| HCC827 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2063 | |
| HaCaT cells | Tongue | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0038 | |
| A431 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0037 | |
| H3255 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6831 | |
| In Vivo Model | NSG mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Promega assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | EGF816 Exerts Anticancer Effects in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer by Irreversibly and Selectively Targeting Primary and Acquired Activating Mutations in the EGF Receptor | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [62] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Selumetinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T790M (c.2369C>T) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.05 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
S
G
G
E
E
A
A
P
P
700
|
N
N
Q
Q
A
A
L
L
L
L
R
R
I
I
L
L
K
K
E
E
710
|
T
T
E
E
F
F
K
K
K
K
I
I
K
K
V
V
L
L
G
G
720
|
S
S
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
K
K
G
G
730
|
L
L
W
W
I
I
P
P
E
E
G
G
E
E
K
K
V
V
K
K
740
|
I
I
P
P
V
V
A
A
I
I
K
K
E
E
L
L
R
R
E
E
750
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
P
P
K
K
A
A
N
N
K
K
E
E
I
I
760
|
L
L
D
D
E
E
A
A
Y
Y
V
V
M
M
A
A
S
S
V
V
770
|
D
D
N
N
P
P
H
H
V
V
C
C
R
R
L
L
L
L
G
G
780
|
I
I
C
C
L
L
T
T
S
S
T
T
V
V
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
790
|
T
M
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
P
P
F
F
G
G
C
C
L
L
L
L
800
|
D
D
Y
Y
V
V
R
R
E
E
H
H
K
K
D
D
N
N
I
I
810
|
G
G
S
S
Q
Q
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
N
N
W
W
C
C
V
V
820
|
Q
Q
I
I
A
A
K
K
G
G
M
M
N
N
Y
Y
L
L
E
E
830
|
D
D
R
R
R
R
L
L
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
840
|
A
A
R
R
N
N
V
V
L
L
V
V
K
K
T
T
P
P
Q
Q
850
|
H
H
V
V
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
860
|
K
K
L
L
L
L
G
G
A
A
E
E
E
E
K
K
E
E
Y
Y
870
|
H
H
A
A
E
E
G
G
G
G
K
K
V
V
P
P
I
I
K
K
880
|
W
W
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
I
I
L
L
H
H
R
R
890
|
I
I
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
900
|
Y
Y
G
G
V
V
T
T
V
V
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
910
|
F
F
G
G
S
S
K
K
P
P
Y
Y
D
D
G
G
I
I
P
P
920
|
A
A
S
S
E
E
I
I
S
S
S
S
I
I
L
L
E
E
K
K
930
|
G
G
E
E
R
R
L
L
P
P
Q
Q
P
P
P
P
I
I
C
C
940
|
T
T
I
I
D
D
V
V
Y
Y
M
M
I
I
M
M
V
V
K
K
950
|
C
C
W
W
M
M
I
I
D
D
A
A
D
D
S
S
R
R
P
P
960
|
K
K
F
F
R
R
E
E
L
L
I
I
I
I
E
E
F
F
S
S
970
|
K
K
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
P
P
Q
Q
R
R
Y
Y
L
L
980
|
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
G
G
D
D
E
E
R
R
M
M
H
H
L
L
990
|
P
P
S
S
P
P
T
T
D
D
S
S
N
N
F
F
Y
Y
R
R
1000
|
A
A
L
L
M
M
D
D
E
E
E
E
D
D
M
M
D
D
D
D
1010
|
V
V
V
V
D
D
A
A
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
I
I
P
P
1020
|
Q
Q
Q
Q
G
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | NCI-H1975 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1511 | |||||||||
| In Vivo Model | BALB/C nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; Immunohistochemistry assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [63] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | AUY922 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | IF-insertion | p.A763_Y764insFQEA (c.2290_2291insTTCAAGAGGCAT) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | EGFR signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa01521 | |
| In Vitro Model | Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Promega assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | EGFR exon 20 insertion mutants associate with the heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) chaperone system. The non-geldanamycin Hsp90 inhibitor luminespib (formerly AUY922) degrades EGFR exon 20 mutations, downstream targets and induces apoptosis. | |||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [63] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | AUY922 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | IF-insertion | p.Y764_V765insHH (c.2292_2293insCATCAT) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | EGFR signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa01521 | |
| In Vitro Model | Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Promega assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | EGFR exon 20 insertion mutants associate with the heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) chaperone system. The non-geldanamycin Hsp90 inhibitor luminespib (formerly AUY922) degrades EGFR exon 20 mutations, downstream targets and induces apoptosis. | |||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [63] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | AUY922 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Duplication | p.S768_D770 (c.2302_2310) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | EGFR signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa01521 | |
| In Vitro Model | Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Promega assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | EGFR exon 20 insertion mutants associate with the heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) chaperone system. The non-geldanamycin Hsp90 inhibitor luminespib (formerly AUY922) degrades EGFR exon 20 mutations, downstream targets and induces apoptosis. | |||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [63] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | AUY922 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | IF-insertion | p.P772_H773insGNP (c.2316_2317insGGTAACCCT) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | EGFR signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa01521 | |
| In Vitro Model | Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Promega assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | EGFR exon 20 insertion mutants associate with the heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) chaperone system. The non-geldanamycin Hsp90 inhibitor luminespib (formerly AUY922) degrades EGFR exon 20 mutations, downstream targets and induces apoptosis. | |||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [63] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | AUY922 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Duplication | p.H773 (c.2317_2319) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | EGFR signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa01521 | |
| In Vitro Model | Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Promega assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | EGFR exon 20 insertion mutants associate with the heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) chaperone system. The non-geldanamycin Hsp90 inhibitor luminespib (formerly AUY922) degrades EGFR exon 20 mutations, downstream targets and induces apoptosis. | |||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [63] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | AUY922 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | IF-insertion | p.A763_Y764insFQEA (c.2290_2291insTTCAAGAGGCAT) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | PC9 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B260 |
| NCI-H1975 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1511 | |
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | |
| NCI-H3255 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6831 | |
| BID007 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_W890 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTiter Glo assay; IC50 assay | |||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [64] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | AUY922 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Duplication | p.A767_V769 (c.2299_2307) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [64] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | AUY922 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Duplication | p.S768_D770 (c.2302_2310) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [64] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | AUY922 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | IF-insertion | p.A767_V769dupASV (c.2308_2309insCAAGCGTAG) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [64] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | AUY922 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Duplication | p.D770_P772 (c.2308_2316) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [64] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | AUY922 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | IF-insertion | p.D770_N771insGV (c.2310_2311insGGTGTA) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [64] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | AUY922 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | IF-insertion | p.D770_N771insGF (c.2310_2311insGGTTTT) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [64] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | AUY922 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | IF-insertion | p.S768_D770dupSVD (c.2311_2312insGCGTAGACA) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [64] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | AUY922 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Duplication | p.P772_H773 (c.2314_2319) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [64] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | AUY922 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | IF-insertion | p.P772_H773insYNP (c.2315_2316insTTATAACCC) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [64] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | AUY922 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Duplication | p.H773 (c.2317_2319) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [64] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | AUY922 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | IF-insertion | p.H773_V774insAH (c.2320_2321insCACATG) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [64] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | AUY922 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | IF-insertion | p.A763_Y764insFQEA |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [64] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | AUY922 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | IF-insertion | p.A767_V774ins |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [64] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | AUY922 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | IF-insertion | p.V769_D770insASV |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [64] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | AUY922 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | IF-insertion | p.A770_N771insNPY |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [64] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | AUY922 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | IF-insertion | p.D770_N771insSVD |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [65] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Naquotinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | IF-insertion | p.Y764_V765insHH (c.2292_2293insCATCAT) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | H1975 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1511 |
| H3255 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6831 | |
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | |
| PC9 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B260 | |
| PC9ER cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |
| BID007 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_W890 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay; FACS assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | There is a mechanism for resistance associated with EGFR Y764_V765insHH mutation, one of the most resistant mutations. We demonstrated that in Y764_V765insHH, histidine residues inserted in the Val765 and Met766 positions upregulated the EGFR kinase activity and caused steric insensitivity to the particular EGFR-TKIs. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [65] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Naquotinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L858R (c.2573T>G) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.64 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.47 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
-
S
-
M
-
G
G
E
E
A
A
P
P
700
|
N
N
Q
Q
A
A
L
L
L
L
R
R
I
I
L
L
K
K
E
E
710
|
T
T
E
E
F
F
K
K
K
K
I
I
K
K
V
V
L
L
G
G
720
|
S
S
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
K
K
G
G
730
|
L
L
W
W
I
I
P
P
E
E
G
G
E
E
K
K
V
V
K
K
740
|
I
I
P
P
V
V
A
A
I
I
K
K
E
E
L
L
R
R
E
E
750
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
P
P
K
K
A
A
N
N
K
K
E
E
I
I
760
|
L
L
D
D
E
E
A
A
Y
Y
V
V
M
M
A
A
S
S
V
V
770
|
D
D
N
N
P
P
H
H
V
V
C
C
R
R
L
L
L
L
G
G
780
|
I
I
C
C
L
L
T
T
S
S
T
T
V
V
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
790
|
T
T
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
P
P
F
F
G
G
C
C
L
L
L
L
800
|
D
D
Y
Y
V
V
R
R
E
E
H
H
K
K
D
D
N
N
I
I
810
|
G
G
S
S
Q
Q
Y
Y
L
L
L
L
N
N
W
W
C
C
V
V
820
|
Q
Q
I
I
A
A
K
K
G
G
M
M
N
N
Y
Y
L
L
E
E
830
|
D
D
R
R
R
R
L
L
V
V
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
840
|
A
A
R
R
N
N
V
V
L
L
V
V
K
K
T
T
P
P
Q
Q
850
|
H
H
V
V
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
R
A
A
860
|
K
K
L
L
L
L
G
G
A
A
E
E
E
E
K
K
E
E
Y
Y
870
|
H
H
A
A
E
E
G
G
G
G
K
K
V
V
P
P
I
I
K
K
880
|
W
W
M
M
A
A
L
L
E
E
S
S
I
I
L
L
H
H
R
R
890
|
I
I
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
900
|
Y
Y
G
G
V
V
T
T
V
V
W
W
E
E
L
L
M
M
T
T
910
|
F
F
G
G
S
S
K
K
P
P
Y
Y
D
D
G
G
I
I
P
P
920
|
A
A
S
S
E
E
I
I
S
S
S
S
I
I
L
L
E
E
K
K
930
|
G
G
E
E
R
R
L
L
P
P
Q
Q
P
P
P
P
I
I
C
C
940
|
T
T
I
I
D
D
V
V
Y
Y
M
M
I
I
M
M
V
V
K
K
950
|
C
C
W
W
M
M
I
I
D
D
A
A
D
D
S
S
R
R
P
P
960
|
K
K
F
F
R
R
E
E
L
L
I
I
I
I
E
E
F
F
S
S
970
|
K
K
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
P
P
Q
Q
R
R
Y
Y
L
L
980
|
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
G
G
D
D
E
E
R
R
M
M
H
H
L
L
990
|
P
P
S
S
P
P
T
T
D
D
S
S
N
N
F
F
Y
Y
R
R
1000
|
A
A
L
L
M
M
D
D
E
E
E
E
D
D
M
M
D
D
D
D
1010
|
V
V
V
V
D
D
A
A
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
I
I
P
P
1020
|
Q
Q
-
Q
-
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | H1975 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1511 | |||||||||
| H3255 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6831 | ||||||||||
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | ||||||||||
| PC9 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B260 | ||||||||||
| PC9ER cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | ||||||||||
| BID007 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_W890 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay; FACS assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | There is a mechanism for resistance associated with EGFR Y764_V765insHH mutation, one of the most resistant mutations. We demonstrated that in Y764_V765insHH, histidine residues inserted in the Val765 and Met766 positions upregulated the EGFR kinase activity and caused steric insensitivity to the particular EGFR-TKIs. | ||||||||||||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Nervous tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Brain cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 8.30E-26; Fold-change: 6.21E-02; Z-score: 1.32E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
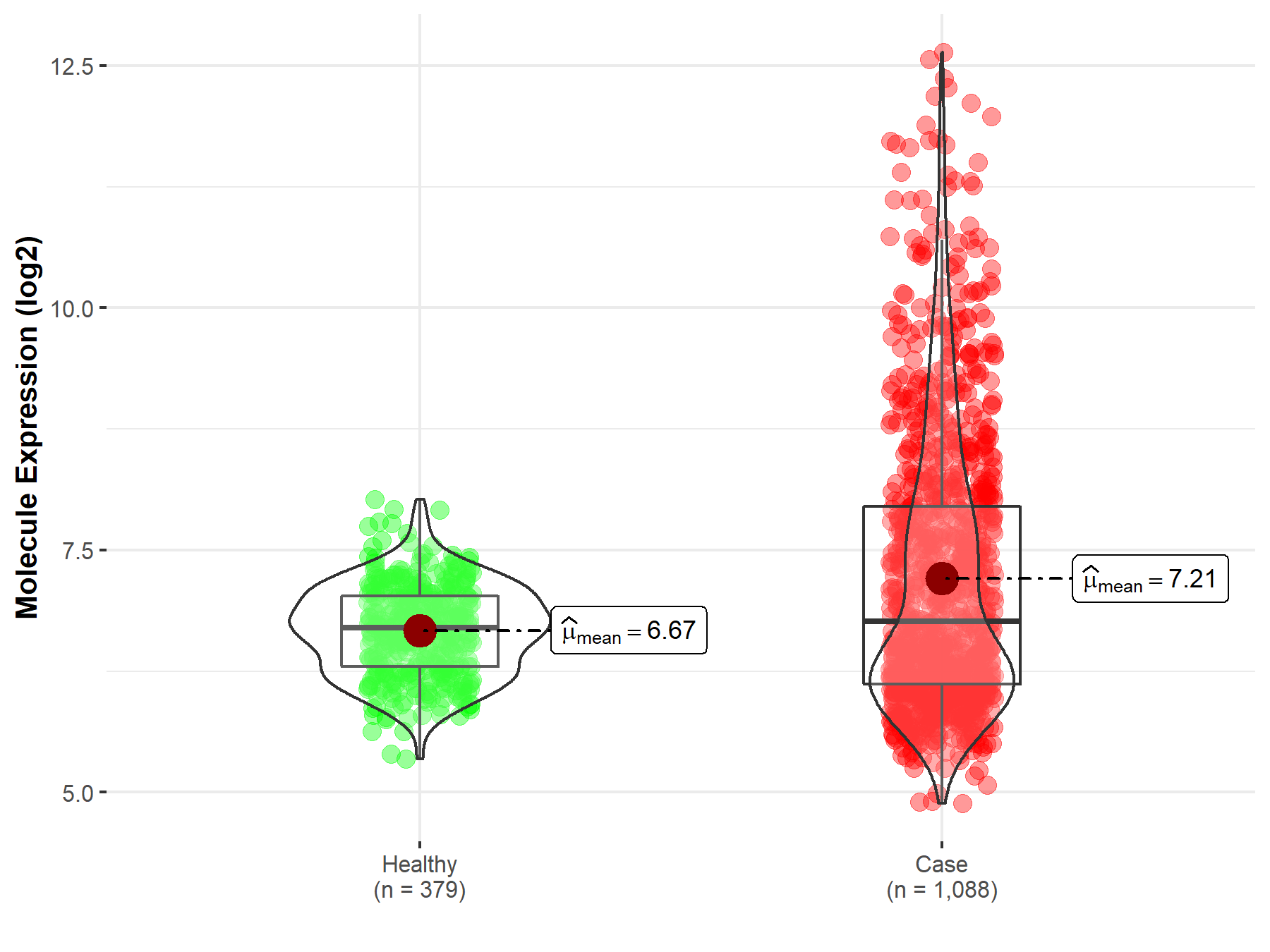
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | Brainstem tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Glioma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.09E-05; Fold-change: 3.96E-01; Z-score: 1.90E+02 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
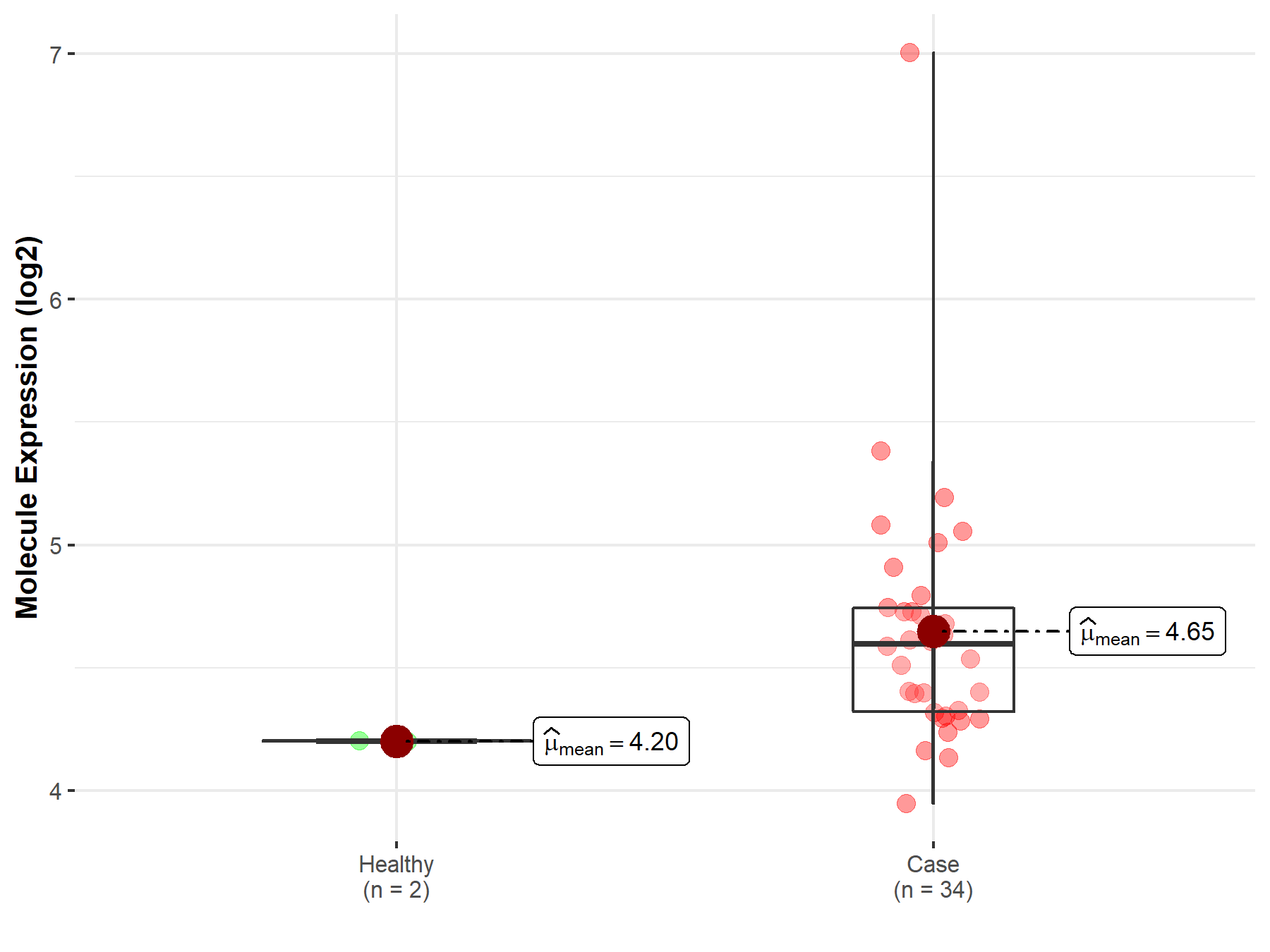
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | White matter | |
| The Specified Disease | Glioma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 6.32E-04; Fold-change: 3.88E-01; Z-score: 1.69E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
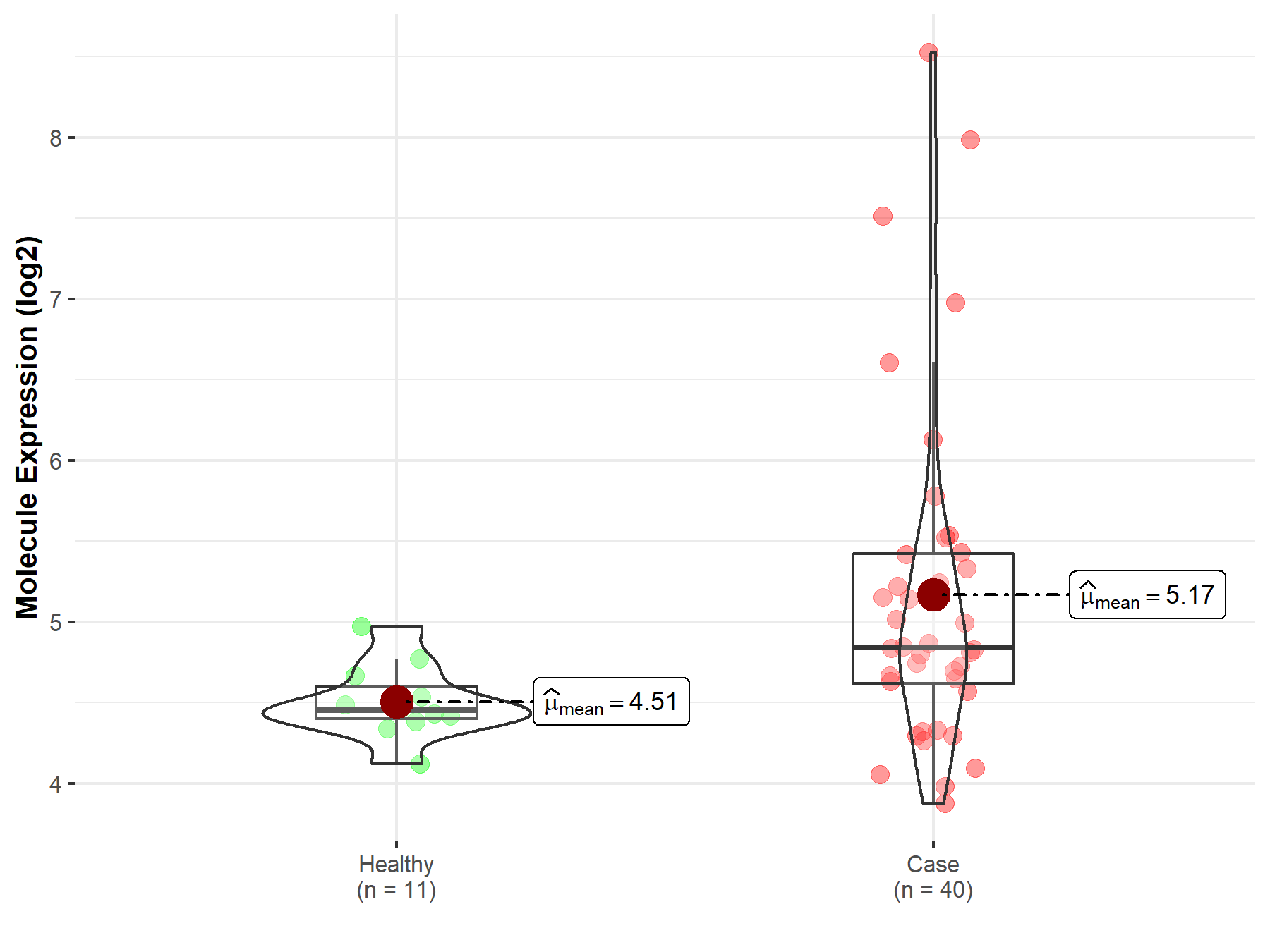
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | Brainstem tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Neuroectodermal tumor | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.84E-08; Fold-change: -1.12E+00; Z-score: -4.45E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
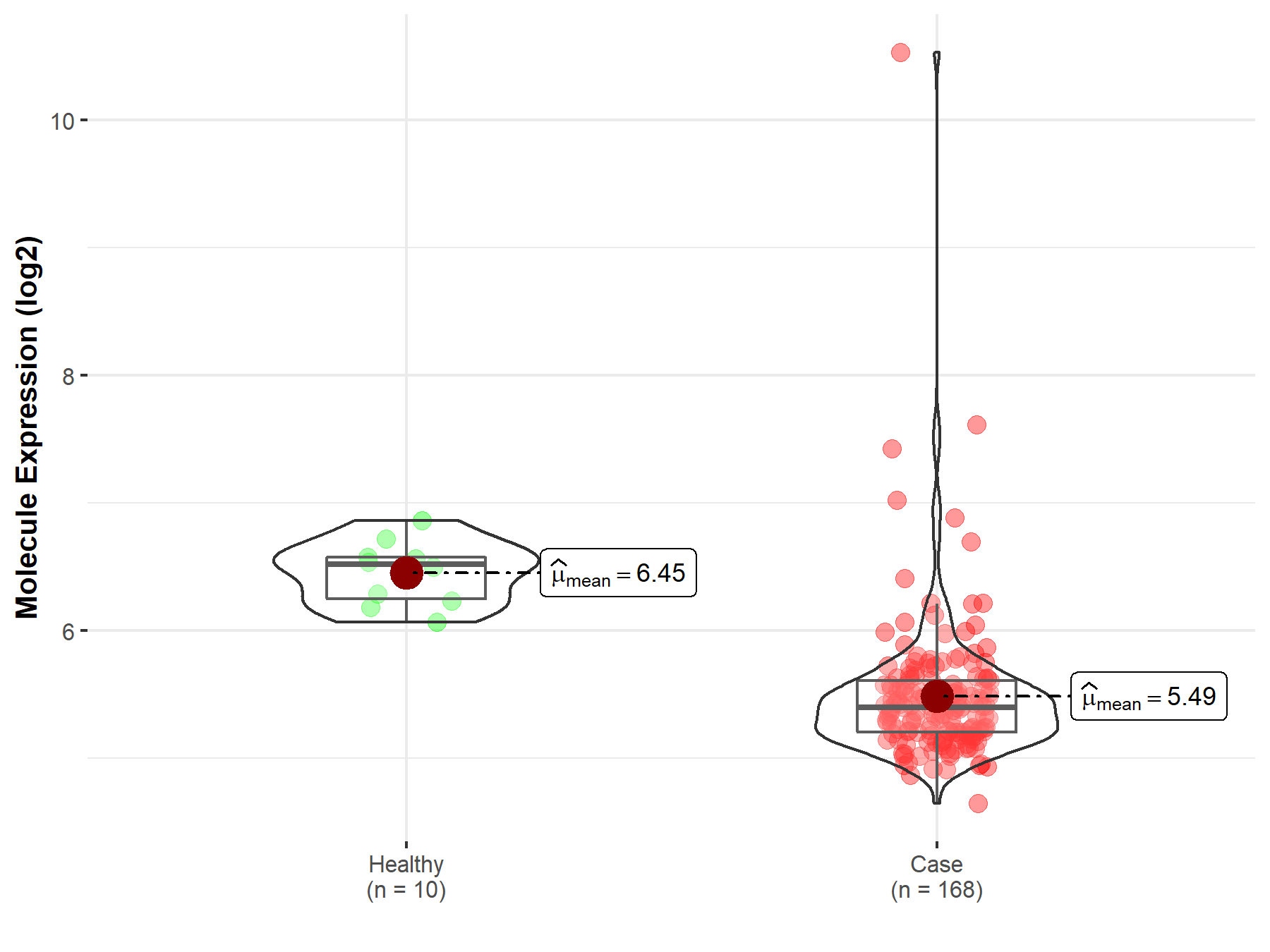
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung | |
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.65E-01; Fold-change: -4.23E-02; Z-score: -8.52E-02 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 1.58E-03; Fold-change: -2.14E-01; Z-score: -3.48E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
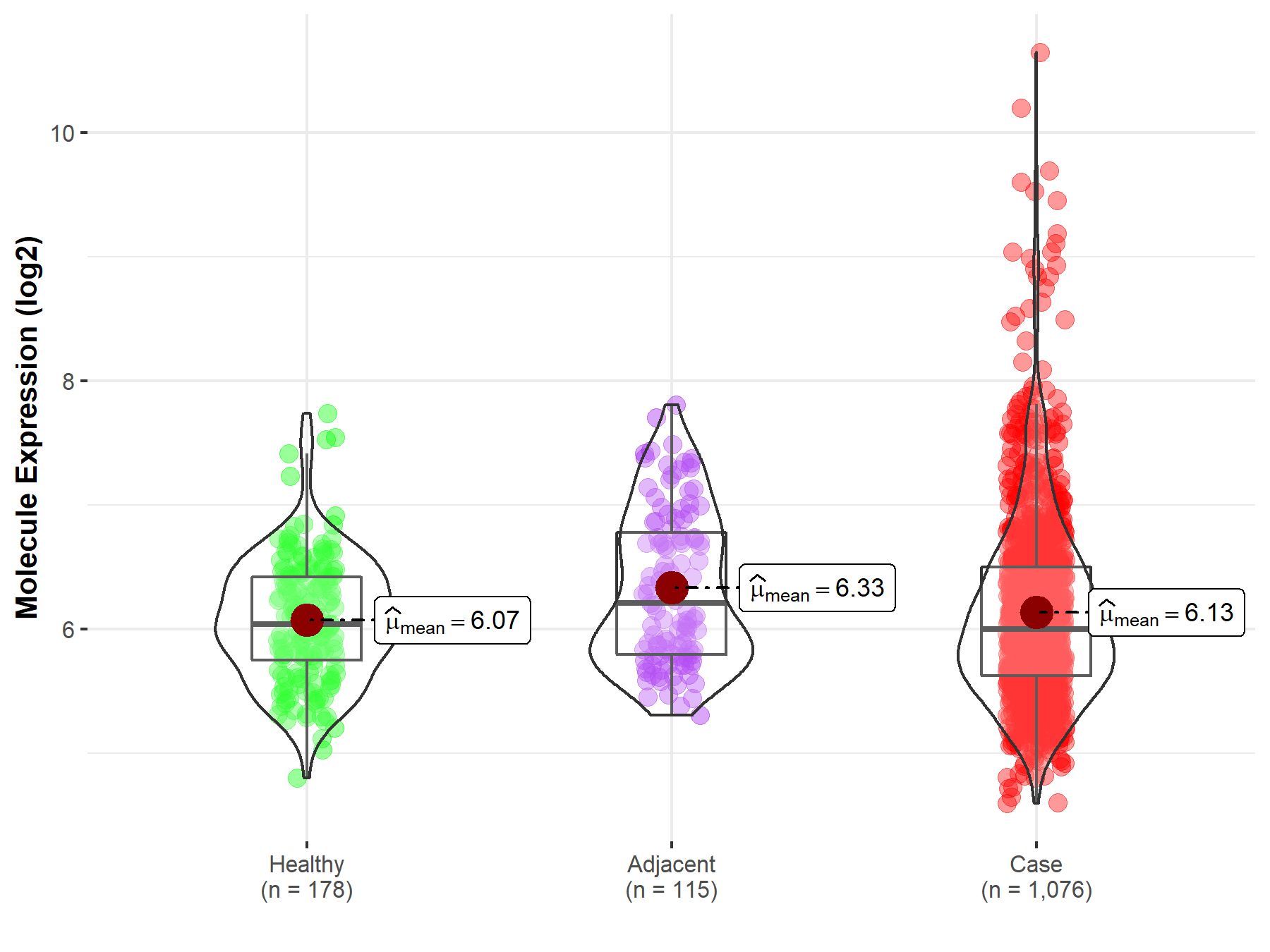
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Skin | |
| The Specified Disease | Melanoma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.60E-01; Fold-change: -3.39E-01; Z-score: -2.30E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
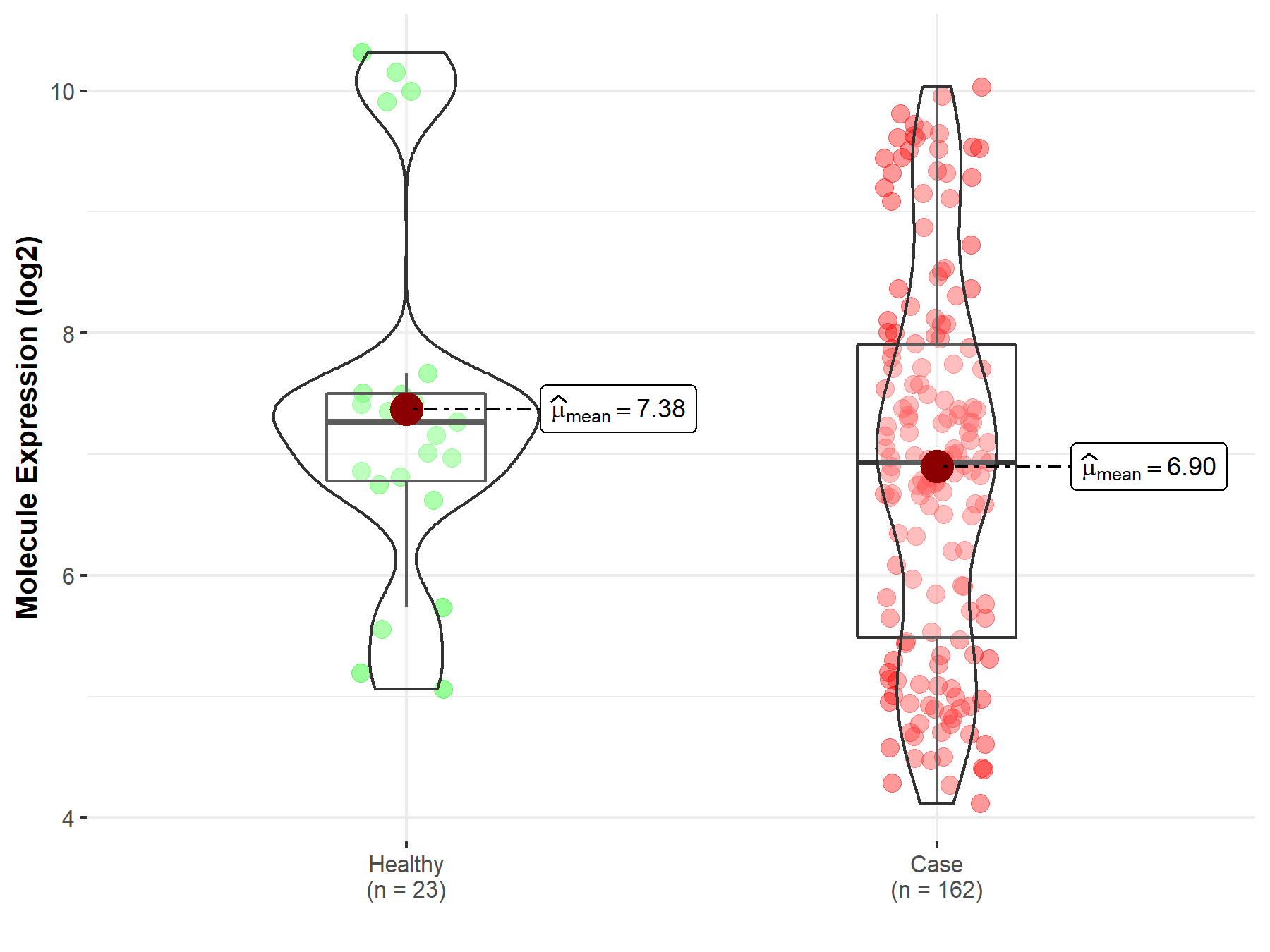
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.04E-65; Fold-change: -8.87E-01; Z-score: -1.53E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 2.77E-16; Fold-change: -9.49E-01; Z-score: -1.79E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
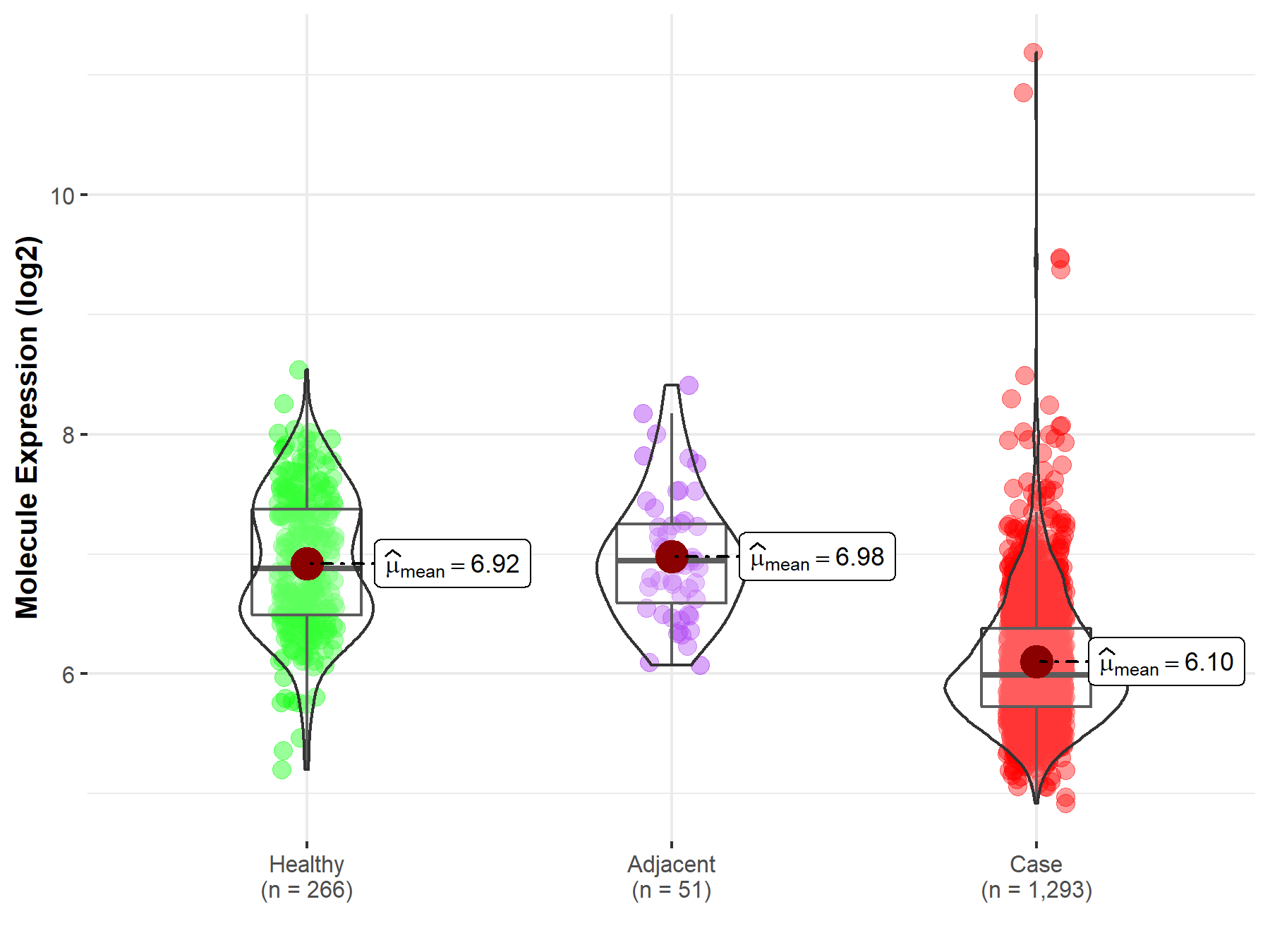
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Prostate | |
| The Specified Disease | Prostate cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 7.43E-04; Fold-change: -5.92E-01; Z-score: -8.22E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
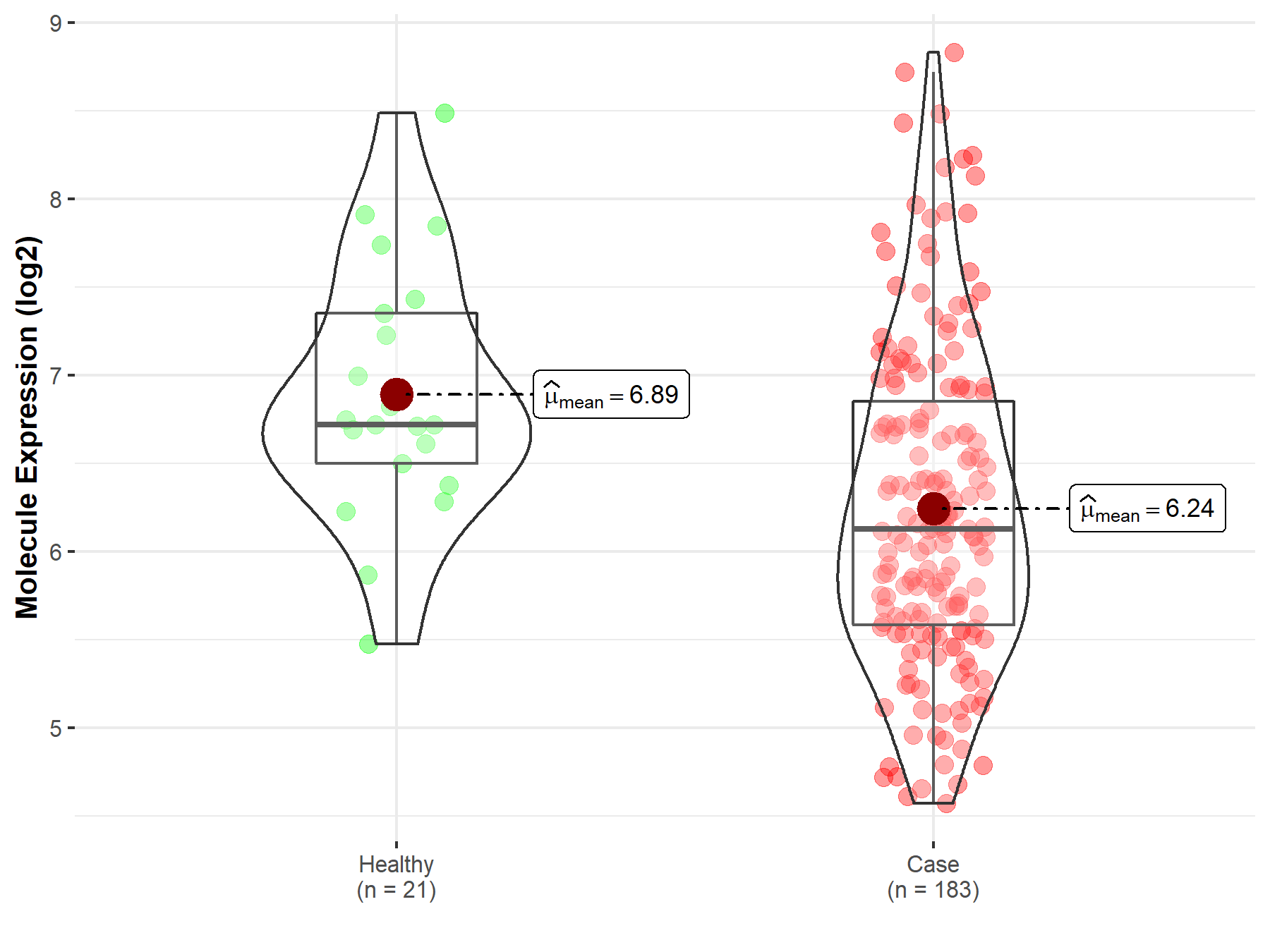
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

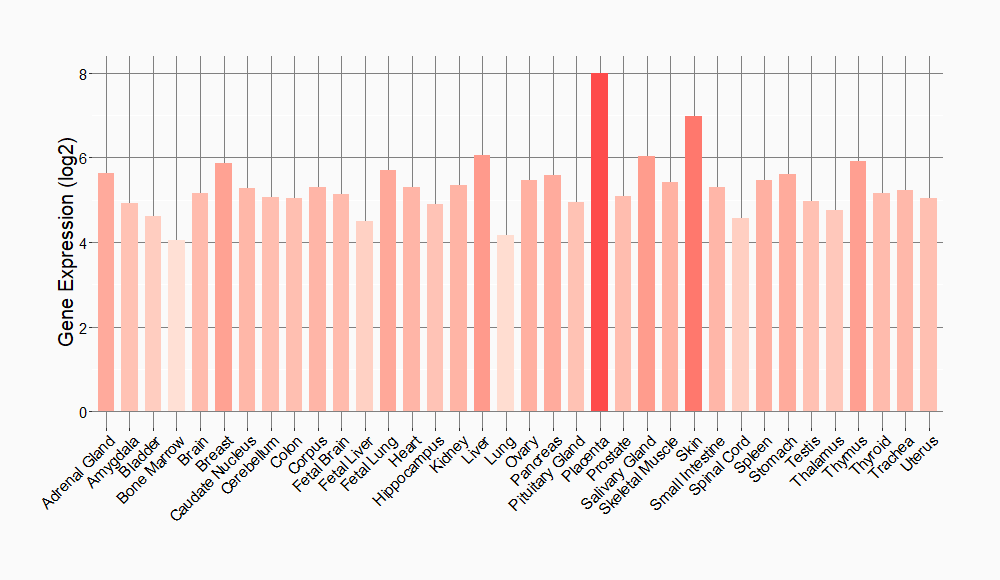
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
