Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00378) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Florfenicol
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Florfenicol; 73231-34-2; Nuflor; (-)-Florfenicol; Sch-25298; 76639-94-6; Sch 25298; Aquafen; Nuflor gold; C12H14Cl2FNO4S; UNII-9J97307Y1H; 2,2-dichloro-N-[(1R,2S)-3-fluoro-1-hydroxy-1-(4-methylsulfonylphenyl)propan-2-yl]acetamide; CHEBI:87185; MFCD00864834; D-threo-2,2-Dichloro-N-(alpha-(fluoromethyl)-beta-hydroxy-p-(methylsulfonyl)phenethyl)acetamide; 9J97307Y1H; Acetamide, 2,2-dichloro-N-((1S,2R)-1-(fluoromethyl)-2-hydroxy-2-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)ethyl)-; 2,2-dichloro-N-[(1R,2S)-3-fluoro-1-hydroxy-1-(4-methanesulfonylphenyl)propan-2-yl]acetamide; 2,2-Dichloro-N-[(1R,2S)-3-fluoro-1-hydroxy-1-(4-methylsulfonylphenyl)-2-propyl]acetamide; DSSTox_CID_25500; DSSTox_RID_80918; DSSTox_GSID_45500; 2,2-Dichloro-N-((1R,2S)-3-fluoro-1-hydroxy-1-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)propan-2-yl)acetamide; Florfenicol [USAN:INN:BAN]; 2,2-Dichloro-N-(1-(fluoromethyl)-2-hydroxy-2-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)ethyl)acetamide; NCGC00016922-01; CAS-73231-34-2; Nuflor (TN); Prestwick0_000955; Prestwick1_000955; Prestwick2_000955; Prestwick3_000955; Florfenicol (USAN/INN); SCHEMBL49425; BSPBio_000950; MLS002154071; SPBio_003099; BPBio1_001046; CHEMBL1241590; DTXSID9045500; SCHEMBL21835523; (-)-Florfenicol;SCH-25298; D-(-)-threo-2-Dichloroacetamido-3-fluoro-1-(4-methylsulfonylphenyl)-1-propanol; HMS1570P12; HMS2090I10; HMS2097P12; HMS2230K18; HMS3714P12; ZINC537733; ACT06682; HY-B1374; Aquafen; ; ; Nuflor; ; ; SCH-25298; Tox21_110683; s4201; AKOS015889457; Tox21_110683_1; AC-4340; CCG-220955; CS-4857; DB11413; KS-5028; NSC 759287; 2,2-dichloro-N-[(1S,2R)-1-(fluoromethyl)-2-hydroxy-2-(4-methylsulfonylphenyl)ethyl]acetamide; NCGC00179366-01; NCGC00179366-03; NCGC00179366-04; [R-(R*,S*)]-2,2-Dichloro-N-[1-(fluoromethyl)-2-hydroxy-2-[4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl]ethyl]acetamide; 2,2-Dichloro-N-((alphaS,betaR)-alpha-(fluoromethyl)-beta-hydroxy-p-(methylsulfonyl)phenethyl)acetamide; 2,2-Dichloro-N-[(1S,2R)-1-(fluoromethyl)-2-hydroxy-2-[4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl]ethyl]acetamide; Acetamide, 2,2-dichloro-N-(1-(fluoromethyl)-2-hydroxy-2-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)ethyl)-, (R-(R*,S*))-; Benzenesulfonic acid, 4-(2-((dichloroacetyl)amino)-3-fluoro-1-hydroxypropyl)-, methyl ester, (R-(R*,S*))-; BF166386; SMR001233384; AB0008500; (methylsulfonyl)phenyl)propan-2-yl)acetamide; AB00513976; F0811; SW197224-3; D04194; J10454; T72886; AB00513976_09; 231F342; A838774; Q408400; Florfenicol, analytical standard, for drug analysis; BRD-K11298197-001-03-9; 2,2-dichloro-N-((1R,2S)-3-fluoro-1-hydroxy-1-(4-; (1R,2S)-2-DICHLOROACETAMIDO-3-FLUORO-1-[4-(METHYLSULFONYL) PHENYL]-1-PROPANOL; (1R,2S)-2-dichloroacetamido-3-fluoro-1-[4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl]-1-propanol; 2,2-Dichlor-N-((1R,2S)-3-fluor-1-hydroxy- 1-(4-(methylsulfonyl)-phenyl)-propan-2-yl)-ethanamide; 2,2-dichloro-N-[(1R,2R)-3-fluoro-1-hydroxy-1-(4-methylsulfonylphenyl)propan-2-yl]acetamide; 2,2-dichloro-N-{(1R,2S)-3-fluoro-1-hydroxy-1-[4-(methanesulfonyl)phenyl]propan-2-yl}acetamide
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Structure |
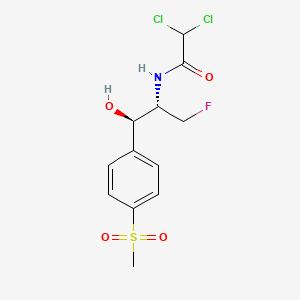
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(7 diseases)
[1]
[2]
[1]
[1]
[1]
[1]
[1]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Validated by in-vivo Model for This Drug
(3 diseases)
[3]
[4]
[5]
|
||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C12H14Cl2FNO4S
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CS(=O)(=O)C1=CC=C(C=C1)[C@H]([C@@H](CF)NC(=O)C(Cl)Cl)O
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C12H14Cl2FNO4S/c1-21(19,20)8-4-2-7(3-5-8)10(17)9(6-15)16-12(18)11(13)14/h2-5,9-11,17H,6H2,1H3,(H,16,18)/t9-,10-/m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
AYIRNRDRBQJXIF-NXEZZACHSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Carboxymethylenebutenolidase (CLCD) | [6] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli AS19 | 562 | ||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The Cfr RNA methyltransferase causes multiple resistances to peptidyl transferase inhibitors by methylation of A2503 23S rRNA.clcD codes the same enzyme. | |||
| Key Molecule: Ribosomal RNA large subunit methyltransferase (CFR ) | [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli AS19 | 562 | ||
| Escherichia coli TOP10 | 83333 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Cfr confers resistance to antibiotics binding to the peptidyl transferase center on the ribosome.The primary product of the Cfr-mediated methylation is 8-methyladenosine (m8A), a new natural RNA modification that has so far not been seen at sites other than A2503 in 23S rRNA. | |||
| Key Molecule: 23S rRNA (Adenine(2503)-C(8))-methyltransferase ClbA (CIBA) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli AS19 | 562 | ||
| Escherichia coli JW2501-1 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The cfr gene encodes the Cfr methyltransferase that methylates a single adenine in the peptidyl transferase region of bacterial ribosomes.Expression of the genes was induced in Escherichia coli, and MICs for selected antibiotics indicate that the cfr-like genes confer resistance to PhLOPSa (phenicol, lincosamide, oxazolidinone, pleuromutilin, and streptogramin A) antibiotics in the same way as the cfr gene.The Cfr-like proteins ClbA, ClbC, and ClbB confer a resistance pattern similar to that of the Cfr methyltransferase. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: ARE-ABC-F family resistance factor PoxtA (POXTA) | [8] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Staphylococcus aureus RN4220 | 1280 | ||
| Enterococcus faecalis JH2-2 | 1351 | |||
| Escherichia coli Mach1 T1R | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth dilution test assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The poxtA gene encodes a protein that is 32% identical to OptrA and exhibits structural features typical of the F lineage of the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) protein superfamily that cause antibiotic resistance by ribosomal protection. | |||
| Key Molecule: Protein pexA (PEXA) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli | 668369 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Nucleotide sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In its natural host, pexA could provide protection against chloramphenicol and florfenicol excreted by Streptomyces spp. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Colibactin polyketide synthase ClbC (CLBC) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli AS19 | 562 | ||
| Escherichia coli JW2501-1 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The cfr gene encodes the Cfr methyltransferase that methylates a single adenine in the peptidyl transferase region of bacterial ribosomes.Expression of the genes was induced in Escherichia coli, and MICs for selected antibiotics indicate that the cfr-like genes confer resistance to PhLOPSa (phenicol, lincosamide, oxazolidinone, pleuromutilin, and streptogramin A) antibiotics in the same way as the cfr gene.The Cfr-like proteins ClbA, ClbC, and ClbB confer a resistance pattern similar to that of the Cfr methyltransferase. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Lincomycin resistance efflux pump (LMRS) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Superficial skin infection by Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B21.3] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli kAM32 | 562 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus OM505 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | LmrS is a multidrug efflux pump of the major facilitator superfamily from staphylococcus aureus. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Ribosomal RNA large subunit methyltransferase N (CFRC) | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gram-negative bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1B74-1G40] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli HB101 | 634468 | ||
| Clostridioides difficile T10 | 1215084 | |||
| Clostridium bolteae 90B3 | 997895 | |||
| Escherichia coli TG1 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Disk diffusion methods assay; agar dilution methods assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The cfr gene encodes a 23S rRNA methyltransferase, which causes C-8 modification in A2503 located in the peptidyl transferase region of bacterial ribosome.This mechanism confers PhLOPSA (phenicols, lincosamides, oxazolidinones, pleuromutilins, and streptogramin A) resistance. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Bcr/CflA family efflux transporter (BCML) | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pasteurella multocida infection [ICD-11: 1B99.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 | 1322345 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213 | 1280 | |||
| Pasteurella multocida 36950 | 1075089 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The analysis of one representative P. multocida isolate identified an 82 kb integrative and conjugative element (ICE) integrated into the chromosomal DNA. This ICE, designated ICEPmu1, harboured 11 resistance genes, which confer resistance to streptomycin/spectinomycin (aadA25), streptomycin (strA and strB), gentamicin (aadB), kanamycin/neomycin (aphA1), tetracycline [tetR-tet(H)], chloramphenicol/florfenicol (floR), sulphonamides (sul2), tilmicosin/clindamycin [erm(42)] or tilmicosin/tulathromycin [msr(E)-mph(E)]. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Lincomycin resistance efflux pump (LMRS) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli kAM32 | 562 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus OM505 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | LmrS is a multidrug efflux pump of the major facilitator superfamily from staphylococcus aureus. | |||
ICD-11: Circulatory system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Lincomycin resistance efflux pump (LMRS) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli kAM32 | 562 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus OM505 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | LmrS is a multidrug efflux pump of the major facilitator superfamily from staphylococcus aureus. | |||
ICD-12: Respiratory system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Lincomycin resistance efflux pump (LMRS) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli kAM32 | 562 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus OM505 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | LmrS is a multidrug efflux pump of the major facilitator superfamily from staphylococcus aureus. | |||
ICD-21: Symptoms/clinical signs/unclassified clinical findings
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Lincomycin resistance efflux pump (LMRS) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli kAM32 | 562 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus OM505 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | LmrS is a multidrug efflux pump of the major facilitator superfamily from staphylococcus aureus. | |||
ICD-22: Injury/poisoning/certain external causes consequences
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Lincomycin resistance efflux pump (LMRS) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli kAM32 | 562 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus OM505 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | LmrS is a multidrug efflux pump of the major facilitator superfamily from staphylococcus aureus. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
