Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00204) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Fulvestrant
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Faslodex; AstraZeneca brand of fulvestrant; Fulvestrant [USAN]; Ici 182780; ZD 182780; ZM 182780; Faslodex (TN); ZD-182780; ZD-9238; ZM-182780; Faslodex(ICI 182,780); Faslodex, ICI 182780, Fulvestrant; Fulvestrant (JAN/USAN/INN); (7R,13S,17S)-13-methyl-7-(9-(4,4,5,5,5-pentafluoropentylsulfinyl)nonyl)-7,8,9,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-decahydro-6H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,17-diol; (7R,8R,9S,13S,14S,17S)-13-methyl-7-[9-(4,4,5,5,5-pentafluoropentylsulfinyl)nonyl]-6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-decahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,17-diol; (7R,8S,9S,13S,14S,17S)-13-methyl-7-[9-(4,4,5,5,5-pentafluoropentylsulfinyl) nonyl]-6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-decahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,17-diol; (7alpha,17beta)-7-{9-[(4,4,5,5,5-pentafluoropentyl)sulfinyl]nonyl}estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17-diol; 7-(9-(4,4,5,5,5-pentafluoropentylsulfinyl)nonyl)estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17-diol; 7alpha-(9-((4,4,5,5,5,-Pentafluoropentyl)sulfinyl)nonyl)estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17beta-diol; 7alpha-(9-((4,4,5,5,5-Pentafluoropentyl)sulfinyl)nonyl)estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17beta-diol; 7alpha-[9[(4,4,5,5,5-Pentafluropentyl)sulfinyl]nonyl]-estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3, 17 beta diol; ICI
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
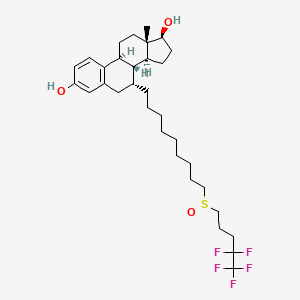
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(1 diseases)
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Discovered by Cell Line Test for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[5]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Validated by in-vivo Model for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[6]
|
||||
| Target | Estrogen receptor (ESR) | ESR1_HUMAN | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C32H47F5O3S
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
C[C@]12CC[C@H]3[C@H]([C@@H]1CC[C@@H]2O)[C@@H](CC4=C3C=CC(=C4)O)CCCCCCCCCS(=O)CCCC(C(F)(F)F)(F)F
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C32H47F5O3S/c1-30-17-15-26-25-12-11-24(38)21-23(25)20-22(29(26)27(30)13-14-28(30)39)10-7-5-3-2-4-6-8-18-41(40)19-9-16-31(33,34)32(35,36)37/h11-12,21-22,26-29,38-39H,2-10,13-20H2,1H3/t22-,26-,27+,28+,29-,30+,41 /m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
VWUXBMIQPBEWFH-WCCTWKNTSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| INTEDE ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Programmed cell death protein 4 (PDCD4) | [7] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 8.12E-04 Fold-change: 5.26E-02 Z-score: 3.37E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-21 is a miRNA that is overexpressed in most tumor types, and acts as an oncogene by targeting many suppressor genes related to proliferation, apoptosis, and invasion. miR-21 facilitates tumor growth and invasion by targeting programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4), PTEN, and Bcl-2. silencing of miR-21 sensitized ER+ breast cancer cells to TAM and FUL induced cell apoptosis. | |||
| Key Molecule: Apoptosis regulator Bcl-2 (BCL2) | [7] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-21 is a miRNA that is overexpressed in most tumor types, and acts as an oncogene by targeting many suppressor genes related to proliferation, apoptosis, and invasion. miR-21 facilitates tumor growth and invasion by targeting programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4), PTEN, and Bcl-2. silencing of miR-21 sensitized ER+ breast cancer cells to TAM and FUL induced cell apoptosis. | |||
| Key Molecule: Phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) | [7] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-21 is a miRNA that is overexpressed in most tumor types, and acts as an oncogene by targeting many suppressor genes related to proliferation, apoptosis, and invasion. miR-21 facilitates tumor growth and invasion by targeting programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4), PTEN, and Bcl-2. silencing of miR-21 sensitized ER+ breast cancer cells to TAM and FUL induced cell apoptosis. | |||
| Key Molecule: Mitochondrial uncoupling protein 2 (UCP2) | [15] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04151 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | TAM and FUL treatment induced apoptosis as well as autophagy in the ER+ breast cancer cells. Autophagy is a major cause of resistance to TAM and FUL. miR-214 increased the sensitivity of breast cancers to TAM and FUL through inhibition of autophagy by targeting UCP2. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: H19, imprinted maternally expressed transcript (H19) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | ER positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| LCC2 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_DP51 | |
| LCC9 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_DP52 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qPCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
WST-8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | H19 plays a central role in maintaining endocrine therapy resistance by modulating ERalpha expression in these cells. Moreover, decreasing H19 levels using pharmacological inhibitors, that inhibit pathways regulating H19 expression in the ETR cells, helps overcome Tamoxifen and Fulvestrant-resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: hsa-mir-21 | [7] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
RT-qPCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-21 is a miRNA that is overexpressed in most tumor types, and acts as an oncogene by targeting many suppressor genes related to proliferation, apoptosis, and invasion. miR-21 facilitates tumor growth and invasion by targeting programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4), PTEN, and Bcl-2. silencing of miR-21 sensitized ER+ breast cancer cells to TAM and FUL induced cell apoptosis. | |||
| Key Molecule: hsa-mir-214 | [15] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04151 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
RT-qPCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | TAM and FUL treatment induced apoptosis as well as autophagy in the ER+ breast cancer cells. Autophagy is a major cause of resistance to TAM and FUL. miR-214 increased the sensitivity of breast cancers to TAM and FUL through inhibition of autophagy by targeting UCP2. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Estrogen receptor alpha (ESR1) | [2], [3], [4] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y537S |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.60 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.50 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
-
D
-
P
-
M
-
I
-
K
300
|
-
R
-
S
-
K
-
K
-
N
-
S
-
L
-
A
-
L
S
S
310
|
L
L
T
T
A
A
D
D
Q
Q
M
M
V
V
S
S
A
A
L
L
320
|
L
L
D
D
A
A
E
E
P
P
P
P
I
I
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
330
|
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
R
R
P
P
F
F
S
S
E
E
340
|
A
A
S
S
M
M
M
M
G
G
L
L
L
L
T
T
N
N
L
L
350
|
A
A
D
D
R
R
E
E
L
L
V
V
H
H
M
M
I
I
N
N
360
|
W
W
A
A
K
K
R
R
V
V
P
P
G
G
F
F
V
V
D
D
370
|
L
L
T
T
L
L
H
H
D
D
Q
Q
V
V
H
H
L
L
L
L
380
|
E
E
C
-
A
A
W
W
L
L
E
E
I
I
L
L
M
M
I
I
390
|
G
G
L
L
V
V
W
W
R
R
S
S
M
M
E
E
H
H
P
P
400
|
G
G
K
K
L
L
L
L
F
F
A
A
P
P
N
N
L
L
L
L
410
|
L
L
D
D
R
R
N
N
Q
Q
G
G
K
K
C
-
V
V
E
E
420
|
G
G
M
M
V
V
E
E
I
I
F
F
D
D
M
M
L
L
L
L
430
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
S
S
R
R
F
F
R
R
M
M
M
M
N
N
440
|
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
E
E
E
E
F
F
V
V
C
C
L
L
K
K
450
|
S
S
I
I
I
I
L
L
L
L
N
N
S
S
G
G
V
V
Y
Y
460
|
T
T
F
F
L
L
S
S
S
S
T
T
L
L
K
K
S
S
L
L
470
|
E
E
E
E
K
K
D
D
H
H
I
I
H
H
R
R
V
V
L
L
480
|
D
D
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
T
T
L
L
I
I
H
H
L
L
490
|
M
M
A
A
K
K
A
A
G
G
L
L
T
T
L
L
Q
Q
Q
Q
500
|
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
R
R
L
L
A
A
Q
Q
L
L
L
L
L
L
510
|
I
I
L
L
S
S
H
H
I
I
R
R
H
H
M
M
S
S
N
N
520
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
E
E
H
H
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
M
M
K
K
530
|
C
-
K
K
N
N
V
V
V
V
P
P
L
L
Y
S
D
D
L
L
540
|
L
L
L
L
E
E
M
M
L
L
D
D
A
A
H
H
R
R
L
L
550
|
H
H
A
A
P
P
T
T
S
S
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 | |||||||||
| WHIM16 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-gexome sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The ESR1-Y537S hormone-binding-domain mutation is clearly a potent cause of aromatase-inhibitor resistance. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Estrogen receptor alpha (ESR1) | [8], [9] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y537S |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.60 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.50 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
-
D
-
P
-
M
-
I
-
K
300
|
-
R
-
S
-
K
-
K
-
N
-
S
-
L
-
A
-
L
S
S
310
|
L
L
T
T
A
A
D
D
Q
Q
M
M
V
V
S
S
A
A
L
L
320
|
L
L
D
D
A
A
E
E
P
P
P
P
I
I
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
330
|
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
R
R
P
P
F
F
S
S
E
E
340
|
A
A
S
S
M
M
M
M
G
G
L
L
L
L
T
T
N
N
L
L
350
|
A
A
D
D
R
R
E
E
L
L
V
V
H
H
M
M
I
I
N
N
360
|
W
W
A
A
K
K
R
R
V
V
P
P
G
G
F
F
V
V
D
D
370
|
L
L
T
T
L
L
H
H
D
D
Q
Q
V
V
H
H
L
L
L
L
380
|
E
E
C
-
A
A
W
W
L
L
E
E
I
I
L
L
M
M
I
I
390
|
G
G
L
L
V
V
W
W
R
R
S
S
M
M
E
E
H
H
P
P
400
|
G
G
K
K
L
L
L
L
F
F
A
A
P
P
N
N
L
L
L
L
410
|
L
L
D
D
R
R
N
N
Q
Q
G
G
K
K
C
-
V
V
E
E
420
|
G
G
M
M
V
V
E
E
I
I
F
F
D
D
M
M
L
L
L
L
430
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
S
S
R
R
F
F
R
R
M
M
M
M
N
N
440
|
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
E
E
E
E
F
F
V
V
C
C
L
L
K
K
450
|
S
S
I
I
I
I
L
L
L
L
N
N
S
S
G
G
V
V
Y
Y
460
|
T
T
F
F
L
L
S
S
S
S
T
T
L
L
K
K
S
S
L
L
470
|
E
E
E
E
K
K
D
D
H
H
I
I
H
H
R
R
V
V
L
L
480
|
D
D
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
T
T
L
L
I
I
H
H
L
L
490
|
M
M
A
A
K
K
A
A
G
G
L
L
T
T
L
L
Q
Q
Q
Q
500
|
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
R
R
L
L
A
A
Q
Q
L
L
L
L
L
L
510
|
I
I
L
L
S
S
H
H
I
I
R
R
H
H
M
M
S
S
N
N
520
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
E
E
H
H
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
M
M
K
K
530
|
C
-
K
K
N
N
V
V
V
V
P
P
L
L
Y
S
D
D
L
L
540
|
L
L
L
L
E
E
M
M
L
L
D
D
A
A
H
H
R
R
L
L
550
|
H
H
A
A
P
P
T
T
S
S
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Overall survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | All 28 patients were found to harbor ESR1 mutations affecting ligand-binding domain with the most common mutations affecting Y537 (17/28, 60.7%) and D538 (9/28, 32.1%). ESR1 mutation was found in 12.1% of a large cohort of advanced breast cancer patients. Exemestane in combination with everolimus might be a reasonable option. Prospective studies are warranted to validate these findings. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Estrogen receptor alpha (ESR1) | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D538G |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.60 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.90 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
V
-
D
-
L
-
G
-
T
-
E
290
|
-
N
-
L
-
Y
-
F
-
Q
-
S
-
N
-
A
-
M
-
K
300
|
-
R
-
S
-
K
-
K
-
N
-
S
-
L
-
A
-
L
S
S
310
|
L
L
T
T
A
A
D
D
Q
Q
M
M
V
V
S
S
A
A
L
L
320
|
L
L
D
D
A
A
E
E
P
P
P
P
I
I
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
330
|
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
R
R
P
P
F
F
S
S
E
E
340
|
A
A
S
S
M
M
M
M
G
G
L
L
L
L
T
T
N
N
L
L
350
|
A
A
D
D
R
R
E
E
L
L
V
V
H
H
M
M
I
I
N
N
360
|
W
W
A
A
K
K
R
R
V
V
P
P
G
G
F
F
V
V
D
D
370
|
L
L
T
T
L
L
H
H
D
D
Q
Q
V
V
H
H
L
L
L
L
380
|
E
E
C
C
A
A
W
W
L
L
E
E
I
I
L
L
M
M
I
I
390
|
G
G
L
L
V
V
W
W
R
R
S
S
M
M
E
E
H
H
P
P
400
|
G
G
K
K
L
L
L
L
F
F
A
A
P
P
N
N
L
L
L
L
410
|
L
L
D
D
R
R
N
N
Q
Q
G
G
K
K
C
C
V
V
E
E
420
|
G
G
M
M
V
V
E
E
I
I
F
F
D
D
M
M
L
L
L
L
430
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
S
S
R
R
F
F
R
R
M
M
M
M
N
N
440
|
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
E
E
E
E
F
F
V
V
C
C
L
L
K
K
450
|
S
S
I
I
I
I
L
L
L
L
N
N
S
S
G
G
V
V
Y
Y
460
|
T
T
F
F
L
L
S
S
S
S
T
T
L
L
K
K
S
S
L
L
470
|
E
E
E
E
K
K
D
D
H
H
I
I
H
H
R
R
V
V
L
L
480
|
D
D
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
T
T
L
L
I
I
H
H
L
L
490
|
M
M
A
A
K
K
A
A
G
G
L
L
T
T
L
L
Q
Q
Q
Q
500
|
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
R
R
L
L
A
A
Q
Q
L
L
L
L
L
L
510
|
I
I
L
L
S
S
H
H
I
I
R
R
H
H
M
M
S
S
N
N
520
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
E
E
H
H
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
M
M
K
K
530
|
C
C
K
K
N
N
V
V
V
V
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
D
G
L
L
540
|
L
L
L
L
E
E
M
M
L
L
D
D
A
A
H
H
R
R
L
L
550
|
H
H
A
A
P
P
T
T
S
S
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | In our analysis of frequently mutated oncogenes and tumor suppressors, ESR1 mutations stood out as a common and plausible event that could contribute to resistance. We found that the mutations in both Tyr537 and Asp538 strongly promoted ER signaling in absence of ligand. This was observed biochemically as increased phosphorylation on S118, increased association with AIB1, and diminished sensitivity to HSP90 inhibitors. Functionally, the mutations in vitro promoted the expression of classical ER target genes in the absence of hormone. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Estrogen receptor alpha (ESR1) | [8], [4] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D538G |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.60 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.90 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
V
-
D
-
L
-
G
-
T
-
E
290
|
-
N
-
L
-
Y
-
F
-
Q
-
S
-
N
-
A
-
M
-
K
300
|
-
R
-
S
-
K
-
K
-
N
-
S
-
L
-
A
-
L
S
S
310
|
L
L
T
T
A
A
D
D
Q
Q
M
M
V
V
S
S
A
A
L
L
320
|
L
L
D
D
A
A
E
E
P
P
P
P
I
I
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
330
|
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
R
R
P
P
F
F
S
S
E
E
340
|
A
A
S
S
M
M
M
M
G
G
L
L
L
L
T
T
N
N
L
L
350
|
A
A
D
D
R
R
E
E
L
L
V
V
H
H
M
M
I
I
N
N
360
|
W
W
A
A
K
K
R
R
V
V
P
P
G
G
F
F
V
V
D
D
370
|
L
L
T
T
L
L
H
H
D
D
Q
Q
V
V
H
H
L
L
L
L
380
|
E
E
C
C
A
A
W
W
L
L
E
E
I
I
L
L
M
M
I
I
390
|
G
G
L
L
V
V
W
W
R
R
S
S
M
M
E
E
H
H
P
P
400
|
G
G
K
K
L
L
L
L
F
F
A
A
P
P
N
N
L
L
L
L
410
|
L
L
D
D
R
R
N
N
Q
Q
G
G
K
K
C
C
V
V
E
E
420
|
G
G
M
M
V
V
E
E
I
I
F
F
D
D
M
M
L
L
L
L
430
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
S
S
R
R
F
F
R
R
M
M
M
M
N
N
440
|
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
E
E
E
E
F
F
V
V
C
C
L
L
K
K
450
|
S
S
I
I
I
I
L
L
L
L
N
N
S
S
G
G
V
V
Y
Y
460
|
T
T
F
F
L
L
S
S
S
S
T
T
L
L
K
K
S
S
L
L
470
|
E
E
E
E
K
K
D
D
H
H
I
I
H
H
R
R
V
V
L
L
480
|
D
D
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
T
T
L
L
I
I
H
H
L
L
490
|
M
M
A
A
K
K
A
A
G
G
L
L
T
T
L
L
Q
Q
Q
Q
500
|
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
R
R
L
L
A
A
Q
Q
L
L
L
L
L
L
510
|
I
I
L
L
S
S
H
H
I
I
R
R
H
H
M
M
S
S
N
N
520
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
E
E
H
H
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
M
M
K
K
530
|
C
C
K
K
N
N
V
V
V
V
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
D
G
L
L
540
|
L
L
L
L
E
E
M
M
L
L
D
D
A
A
H
H
R
R
L
L
550
|
H
H
A
A
P
P
T
T
S
S
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Deep sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | We report here on a novel mutation of ERalpha, in which an A to G substitution at position 1,613 resulted in substitution of aspartic acid at position 538 to glycine (D538G). The mutation was identified in liver metastases obtained from patients who developed endocrine resistance, but not in samples of primary tumors obtained prior to commencing endocrine treatment. Structural modeling indicates that D538G substitution creates a conformational change that disrupts the interaction between the receptor and either estrogen or tamoxifen, but mimics the conformation of the activated receptor. Studies in cell lines confirmed ligand-independent, constitutive activity of the mutated receptor. Taken together, these data indicate the mutation D538G as a novel mechanism conferring acquired endocrine resistance. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Estrogen receptor alpha (ESR1) | [10], [9] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y537N |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Overall survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | All 28 patients were found to harbor ESR1 mutations affecting ligand-binding domain with the most common mutations affecting Y537 (17/28, 60.7%) and D538 (9/28, 32.1%). ESR1 mutation was found in 12.1% of a large cohort of advanced breast cancer patients. Exemestane in combination with everolimus might be a reasonable option. Prospective studies are warranted to validate these findings. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Estrogen receptor alpha (ESR1) | [11], [9] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y537C |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Overall survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | All 28 patients were found to harbor ESR1 mutations affecting ligand-binding domain with the most common mutations affecting Y537 (17/28, 60.7%) and D538 (9/28, 32.1%). ESR1 mutation was found in 12.1% of a large cohort of advanced breast cancer patients. Exemestane in combination with everolimus might be a reasonable option. Prospective studies are warranted to validate these findings. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Estrogen receptor alpha (ESR1) | [9] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L536_D538>P |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Overall survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | All 28 patients were found to harbor ESR1 mutations affecting ligand-binding domain with the most common mutations affecting Y537 (17/28, 60.7%) and D538 (9/28, 32.1%). ESR1 mutation was found in 12.1% of a large cohort of advanced breast cancer patients. Exemestane in combination with everolimus might be a reasonable option. Prospective studies are warranted to validate these findings. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Estrogen receptor alpha (ESR1) | [3], [12] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y537N |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | In our analysis of frequently mutated oncogenes and tumor suppressors, ESR1 mutations stood out as a common and plausible event that could contribute to resistance. We found that the mutations in both Tyr537 and Asp538 strongly promoted ER signaling in absence of ligand. This was observed biochemically as increased phosphorylation on S118, increased association with AIB1, and diminished sensitivity to HSP90 inhibitors. Functionally, the mutations in vitro promoted the expression of classical ER target genes in the absence of hormone. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Estrogen receptor alpha (ESR1) | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y537C |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | In our analysis of frequently mutated oncogenes and tumor suppressors, ESR1 mutations stood out as a common and plausible event that could contribute to resistance. We found that the mutations in both Tyr537 and Asp538 strongly promoted ER signaling in absence of ligand. This was observed biochemically as increased phosphorylation on S118, increased association with AIB1, and diminished sensitivity to HSP90 inhibitors. Functionally, the mutations in vitro promoted the expression of classical ER target genes in the absence of hormone. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Estrogen receptor alpha (ESR1) | [8] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L536Q |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-genome sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Whole-exome and transcriptome analysis showed that six cases harbored mutations of ESR1 affecting its ligand-binding domain (LBD), all of whom had been treated with anti-estrogens and estrogen deprivation therapies. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Estrogen receptor alpha (ESR1) | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutantion | p.R183W |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | MCF7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 | |||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell proliferation assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Imlunestrant degraded ERalpha and decreased ERalpha-mediated gene expression both in vitro and in vivo. Cell proliferation and tumor growth in ESR1 wild-type (WT) and mutant models were significantly inhibited by imlunestrant. Combining imlunestrant with abemaciclib (CDK4/6 inhibitor), alpelisib (PI3K inhibitor), or everolimus (mTOR inhibitor) further enhanced tumor growth inhibition, regardless of ESR1 mutational status. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 3 (IGFBP3) | [13] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 FulR cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting assay; qPCR | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell viability assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Elevated expression of IGFBP-3 is associated with fulvestrant resistance in MCF-7 cells. MCF-7FulR cells expressed significantly higher levels of IGFBP-3 transcript and protein compared to parental cells. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Estrogen receptor alpha (ESR1) | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutantion | p.Y537N |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | MCF7 intracranial tumors mouse model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Overall survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Imlunestrant degraded ERalpha and decreased ERalpha-mediated gene expression both in vitro and in vivo. Cell proliferation and tumor growth in ESR1 wild-type (WT) and mutant models were significantly inhibited by imlunestrant. Combining imlunestrant with abemaciclib (CDK4/6 inhibitor), alpelisib (PI3K inhibitor), or everolimus (mTOR inhibitor) further enhanced tumor growth inhibition, regardless of ESR1 mutational status. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Estrogen receptor (ESR1) | [14] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | MCF7 LTLT cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| In Vivo Model | NSG mice model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
GeneSeq assay; Western blot assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Tumor growth assay; Histological assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | In a model of AI-resistant breast cancer without ESR1 mutations, LAS alone or combined with PAL inhibited the growth of primary tumors more effectively than FUL. In addition, the LAS/PAL combination significantly reduced bone metastases. These results suggest that LAS alone or in combination with a CDK4/6i may be a promising therapy for patients with AI-resistant breast cancer, independent of ESR1 mutations. These results also suggest that LAS might be effective in tumors that express low levels of ERalpha. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Estrogen receptor alpha (ESR1) | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutantion | p.R58X |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | ESR1-WT breast cancer xenograft model; ESR1-WT mutant breast cancer xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Tumor volume assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Imlunestrant degraded ERalpha and decreased ERalpha-mediated gene expression both in vitro and in vivo. Cell proliferation and tumor growth in ESR1 wild-type (WT) and mutant models were significantly inhibited by imlunestrant. Combining imlunestrant with abemaciclib (CDK4/6 inhibitor), alpelisib (PI3K inhibitor), or everolimus (mTOR inhibitor) further enhanced tumor growth inhibition, regardless of ESR1 mutational status. | ||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Estrogen receptor alpha (ESR1) | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Triple-negative breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.9] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | EGFR/HER2 signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | MCF7 (Ful-R) cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | In this study, we investigated the molecular mechanism underlying the loss of ER, FOXO3a, and induction of HER2 in fulvestrant-resistant breast cancer. Short-term fulvestrant treatment degraded ER proteins via the ubiquitin-proteasome degradation pathway in MCF7 cells. MCF7 cells turn into highly proliferative cells (fulvestrant-resistant cells: Ful-R) after long-term fulvestrant treatment. These cells exhibit markedly suppressed estrogen and progesterone receptor levels. The phosphorylation of EGFR, HER2, and ERK was induced in Ful-R, and these phosphorylation inhibitors suppressed cell proliferation in Ful-R. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Triple-negative breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.9] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Phosphorylation | Down-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | EGFR/HER2 signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | MCF7 (Ful-R) cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | In this study, we investigated the molecular mechanism underlying the loss of ER, FOXO3a, and induction of HER2 in fulvestrant-resistant breast cancer. Short-term fulvestrant treatment degraded ER proteins via the ubiquitin-proteasome degradation pathway in MCF7 cells. MCF7 cells turn into highly proliferative cells (fulvestrant-resistant cells: Ful-R) after long-term fulvestrant treatment. These cells exhibit markedly suppressed estrogen and progesterone receptor levels. The phosphorylation of EGFR, HER2, and ERK was induced in Ful-R, and these phosphorylation inhibitors suppressed cell proliferation in Ful-R. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Progesterone receptor (PGR) | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Triple-negative breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.9] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | EGFR/HER2 signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | MCF7 (Ful-R) cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | In this study, we investigated the molecular mechanism underlying the loss of ER, FOXO3a, and induction of HER2 in fulvestrant-resistant breast cancer. Short-term fulvestrant treatment degraded ER proteins via the ubiquitin-proteasome degradation pathway in MCF7 cells. MCF7 cells turn into highly proliferative cells (fulvestrant-resistant cells: Ful-R) after long-term fulvestrant treatment. These cells exhibit markedly suppressed estrogen and progesterone receptor levels. The phosphorylation of EGFR, HER2, and ERK was induced in Ful-R, and these phosphorylation inhibitors suppressed cell proliferation in Ful-R. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Oncogenic epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Triple-negative breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.9] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | EGFR/HER2 signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | MCF7 (Ful-R) cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | In this study, we investigated the molecular mechanism underlying the loss of ER, FOXO3a, and induction of HER2 in fulvestrant-resistant breast cancer. Short-term fulvestrant treatment degraded ER proteins via the ubiquitin-proteasome degradation pathway in MCF7 cells. MCF7 cells turn into highly proliferative cells (fulvestrant-resistant cells: Ful-R) after long-term fulvestrant treatment. These cells exhibit markedly suppressed estrogen and progesterone receptor levels. The phosphorylation of EGFR, HER2, and ERK was induced in Ful-R, and these phosphorylation inhibitors suppressed cell proliferation in Ful-R. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Oncogenic epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Triple-negative breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.9] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Phosphorylation | Up-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | EGFR/HER2 signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | MCF7 (Ful-R) cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | In this study, we investigated the molecular mechanism underlying the loss of ER, FOXO3a, and induction of HER2 in fulvestrant-resistant breast cancer. Short-term fulvestrant treatment degraded ER proteins via the ubiquitin-proteasome degradation pathway in MCF7 cells. MCF7 cells turn into highly proliferative cells (fulvestrant-resistant cells: Ful-R) after long-term fulvestrant treatment. These cells exhibit markedly suppressed estrogen and progesterone receptor levels. The phosphorylation of EGFR, HER2, and ERK was induced in Ful-R, and these phosphorylation inhibitors suppressed cell proliferation in Ful-R. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Estrogen receptor (ESR1) | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Triple-negative breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.9] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | EGFR/HER2 signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | MCF7 (Ful-R) cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | In this study, we investigated the molecular mechanism underlying the loss of ER, FOXO3a, and induction of HER2 in fulvestrant-resistant breast cancer. Short-term fulvestrant treatment degraded ER proteins via the ubiquitin-proteasome degradation pathway in MCF7 cells. MCF7 cells turn into highly proliferative cells (fulvestrant-resistant cells: Ful-R) after long-term fulvestrant treatment. These cells exhibit markedly suppressed estrogen and progesterone receptor levels. The phosphorylation of EGFR, HER2, and ERK was induced in Ful-R, and these phosphorylation inhibitors suppressed cell proliferation in Ful-R. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 (ERBB2) | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Triple-negative breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.9] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | EGFR/HER2 signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | MCF7 (Ful-R) cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | In this study, we investigated the molecular mechanism underlying the loss of ER, FOXO3a, and induction of HER2 in fulvestrant-resistant breast cancer. Short-term fulvestrant treatment degraded ER proteins via the ubiquitin-proteasome degradation pathway in MCF7 cells. MCF7 cells turn into highly proliferative cells (fulvestrant-resistant cells: Ful-R) after long-term fulvestrant treatment. These cells exhibit markedly suppressed estrogen and progesterone receptor levels. The phosphorylation of EGFR, HER2, and ERK was induced in Ful-R, and these phosphorylation inhibitors suppressed cell proliferation in Ful-R. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 (ERBB2) | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Triple-negative breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.9] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Phosphorylation | Down-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | EGFR/HER2 signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | MCF7 (Ful-R) cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | In this study, we investigated the molecular mechanism underlying the loss of ER, FOXO3a, and induction of HER2 in fulvestrant-resistant breast cancer. Short-term fulvestrant treatment degraded ER proteins via the ubiquitin-proteasome degradation pathway in MCF7 cells. MCF7 cells turn into highly proliferative cells (fulvestrant-resistant cells: Ful-R) after long-term fulvestrant treatment. These cells exhibit markedly suppressed estrogen and progesterone receptor levels. The phosphorylation of EGFR, HER2, and ERK was induced in Ful-R, and these phosphorylation inhibitors suppressed cell proliferation in Ful-R. | ||||||||||||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
