Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00356)
| Name |
Estrogen receptor alpha (ESR1)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
ER; ER-alpha; Estradiol receptor; Nuclear receptor subfamily 3 group A member 1; ESR; NR3A1
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
ESR1
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr6:151656691-152129619[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MTMTLHTKASGMALLHQIQGNELEPLNRPQLKIPLERPLGEVYLDSSKPAVYNYPEGAAY
EFNAAAAANAQVYGQTGLPYGPGSEAAAFGSNGLGGFPPLNSVSPSPLMLLHPPPQLSPF LQPHGQQVPYYLENEPSGYTVREAGPPAFYRPNSDNRRQGGRERLASTNDKGSMAMESAK ETRYCAVCNDYASGYHYGVWSCEGCKAFFKRSIQGHNDYMCPATNQCTIDKNRRKSCQAC RLRKCYEVGMMKGGIRKDRRGGRMLKHKRQRDDGEGRGEVGSAGDMRAANLWPSPLMIKR SKKNSLALSLTADQMVSALLDAEPPILYSEYDPTRPFSEASMMGLLTNLADRELVHMINW AKRVPGFVDLTLHDQVHLLECAWLEILMIGLVWRSMEHPGKLLFAPNLLLDRNQGKCVEG MVEIFDMLLATSSRFRMMNLQGEEFVCLKSIILLNSGVYTFLSSTLKSLEEKDHIHRVLD KITDTLIHLMAKAGLTLQQQHQRLAQLLLILSHIRHMSNKGMEHLYSMKCKNVVPLYDLL LEMLDAHRLHAPTSRGGASVEETDQSHLATAGSTSSHSLQKYYITGEAEGFPATV Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Nuclear hormone receptor. The steroid hormones and their receptors are involved in the regulation of eukaryotic gene expression and affect cellular proliferation and differentiation in target tissues. Ligand-dependent nuclear transactivation involves either direct homodimer binding to a palindromic estrogen response element (ERE) sequence or association with other DNA-binding transcription factors, such as AP-1/c-Jun, c-Fos, ATF-2, Sp1 and Sp3, to mediate ERE-independent signaling. Ligand binding induces a conformational change allowing subsequent or combinatorial association with multiprotein coactivator complexes through LXXLL motifs of their respective components. Mutual transrepression occurs between the estrogen receptor (ER) and NF-kappa-B in a cell-type specific manner. Decreases NF-kappa-B DNA-binding activity and inhibits NF-kappa-B-mediated transcription from the IL6 promoter and displace RELA/p65 and associated coregulators from the promoter. Recruited to the NF-kappa-B response element of the CCL2 and IL8 promoters and can displace CREBBP. Present with NF-kappa-B components RELA/p65 and NFKB1/p50 on ERE sequences. Can also act synergistically with NF-kappa-B to activate transcription involving respective recruitment adjacent response elements; the function involves CREBBP. Can activate the transcriptional activity of TFF1. Also mediates membrane-initiated estrogen signaling involving various kinase cascades. Essential for MTA1-mediated transcriptional regulation of BRCA1 and BCAS3.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
11 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Tamoxifen | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 5.93E-18 Fold-change: 9.62E-02 Z-score: 8.85E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| SkBR3 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0033 | |
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | |
| T47D cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0553 | |
| BT474 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0179 | |
| MDA-MB-453 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0418 | |
| MDA-MB-468 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0419 | |
| Hs-578T cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0332 | |
| MCF10A cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0598 | |
| MDA-MB-157 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0618 | |
| MDA-MB-361 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0620 | |
| MDA-MB-435s cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0622 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-221 and miR-222 are frequently up-regulated in ERalpha-negative breast cancer cell lines and primary tumors. The elevated level of miR-221 and miR-222 is responsible for a subset of ERalpha-negative breast tumors that express ERalpha mRNA. Furthermore, overexpression of miR-221 and miR-222 contributes to tamoxifen resistance through negative regulation of ERalpha, whereas knockdown of miR-221 and/or miR-222 restores ERalpha expression and tamoxifen sensitivity. | |||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [20] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Tamoxifen | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell viability | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| T47D cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0553 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
ATP-content assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-27a sensitizes luminal A breast cancer cells to SERM treatments based on a positive feedback loop with ERalpha. | |||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [21] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Tamoxifen | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | AKT/mTOR signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | |
| Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| LCC2 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_DP51 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Over-expression of miR-451a can enhance MCF-7 and LCC2 cell sensitivity to TAM. Opposite effects were elicited by knocking down miR-451a. TAM treatment can up-regulate 14-3-3Zeta expression, and down-regulate ERalpha expression. 14-3-3Zeta and ERalpha were shown to interact. Over-expression of miR-451a decreased 14-3-3Zeta expression and increased ERalpha expression, suppressing cell proliferation, increasing apoptosis, and reducing activation of p-AkT and p-mTOR. | |||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [19] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Tamoxifen | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | ER-alpha 36 mediated nongenomic estrogen signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04915 | |
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| SkBR3 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0033 | |
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | |
| T47D cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0553 | |
| ZR75-1 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0588 | |
| MDA-MB-436 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0623 | |
| MDA-MB-468 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0419 | |
| 184A1 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3040 | |
| HB3396 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| MEGM cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Luciferase assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Let-7 miRNAs (b and i) enhanced tamoxifen sensitivity of tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cells by targeting ER-alpha36 expression. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [3], [7], [16] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Tamoxifen | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y537S |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.60 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.50 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
-
D
-
P
-
M
-
I
-
K
300
|
-
R
-
S
-
K
-
K
-
N
-
S
-
L
-
A
-
L
S
S
310
|
L
L
T
T
A
A
D
D
Q
Q
M
M
V
V
S
S
A
A
L
L
320
|
L
L
D
D
A
A
E
E
P
P
P
P
I
I
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
330
|
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
R
R
P
P
F
F
S
S
E
E
340
|
A
A
S
S
M
M
M
M
G
G
L
L
L
L
T
T
N
N
L
L
350
|
A
A
D
D
R
R
E
E
L
L
V
V
H
H
M
M
I
I
N
N
360
|
W
W
A
A
K
K
R
R
V
V
P
P
G
G
F
F
V
V
D
D
370
|
L
L
T
T
L
L
H
H
D
D
Q
Q
V
V
H
H
L
L
L
L
380
|
E
E
C
-
A
A
W
W
L
L
E
E
I
I
L
L
M
M
I
I
390
|
G
G
L
L
V
V
W
W
R
R
S
S
M
M
E
E
H
H
P
P
400
|
G
G
K
K
L
L
L
L
F
F
A
A
P
P
N
N
L
L
L
L
410
|
L
L
D
D
R
R
N
N
Q
Q
G
G
K
K
C
-
V
V
E
E
420
|
G
G
M
M
V
V
E
E
I
I
F
F
D
D
M
M
L
L
L
L
430
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
S
S
R
R
F
F
R
R
M
M
M
M
N
N
440
|
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
E
E
E
E
F
F
V
V
C
C
L
L
K
K
450
|
S
S
I
I
I
I
L
L
L
L
N
N
S
S
G
G
V
V
Y
Y
460
|
T
T
F
F
L
L
S
S
S
S
T
T
L
L
K
K
S
S
L
L
470
|
E
E
E
E
K
K
D
D
H
H
I
I
H
H
R
R
V
V
L
L
480
|
D
D
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
T
T
L
L
I
I
H
H
L
L
490
|
M
M
A
A
K
K
A
A
G
G
L
L
T
T
L
L
Q
Q
Q
Q
500
|
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
R
R
L
L
A
A
Q
Q
L
L
L
L
L
L
510
|
I
I
L
L
S
S
H
H
I
I
R
R
H
H
M
M
S
S
N
N
520
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
E
E
H
H
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
M
M
K
K
530
|
C
-
K
K
N
N
V
V
V
V
P
P
L
L
Y
S
D
D
L
L
540
|
L
L
L
L
E
E
M
M
L
L
D
D
A
A
H
H
R
R
L
L
550
|
H
H
A
A
P
P
T
T
S
S
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | PI3K signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04151 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-exome sequencing assay; SNP Array profiling assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Tumor biopsy assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Mutations in ESR1 were detected in 4% of cancers and clustered in the ligand-binding domain. These included p.Tyr537(Cys/Asn/Ser) mutations (three patients) that have been shown to cause constitutive activation and resistance to tamoxifen therapy in breast cancer. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [7] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Tamoxifen | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D538G |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.60 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.90 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
V
-
D
-
L
-
G
-
T
-
E
290
|
-
N
-
L
-
Y
-
F
-
Q
-
S
-
N
-
A
-
M
-
K
300
|
-
R
-
S
-
K
-
K
-
N
-
S
-
L
-
A
-
L
S
S
310
|
L
L
T
T
A
A
D
D
Q
Q
M
M
V
V
S
S
A
A
L
L
320
|
L
L
D
D
A
A
E
E
P
P
P
P
I
I
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
330
|
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
R
R
P
P
F
F
S
S
E
E
340
|
A
A
S
S
M
M
M
M
G
G
L
L
L
L
T
T
N
N
L
L
350
|
A
A
D
D
R
R
E
E
L
L
V
V
H
H
M
M
I
I
N
N
360
|
W
W
A
A
K
K
R
R
V
V
P
P
G
G
F
F
V
V
D
D
370
|
L
L
T
T
L
L
H
H
D
D
Q
Q
V
V
H
H
L
L
L
L
380
|
E
E
C
C
A
A
W
W
L
L
E
E
I
I
L
L
M
M
I
I
390
|
G
G
L
L
V
V
W
W
R
R
S
S
M
M
E
E
H
H
P
P
400
|
G
G
K
K
L
L
L
L
F
F
A
A
P
P
N
N
L
L
L
L
410
|
L
L
D
D
R
R
N
N
Q
Q
G
G
K
K
C
C
V
V
E
E
420
|
G
G
M
M
V
V
E
E
I
I
F
F
D
D
M
M
L
L
L
L
430
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
S
S
R
R
F
F
R
R
M
M
M
M
N
N
440
|
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
E
E
E
E
F
F
V
V
C
C
L
L
K
K
450
|
S
S
I
I
I
I
L
L
L
L
N
N
S
S
G
G
V
V
Y
Y
460
|
T
T
F
F
L
L
S
S
S
S
T
T
L
L
K
K
S
S
L
L
470
|
E
E
E
E
K
K
D
D
H
H
I
I
H
H
R
R
V
V
L
L
480
|
D
D
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
T
T
L
L
I
I
H
H
L
L
490
|
M
M
A
A
K
K
A
A
G
G
L
L
T
T
L
L
Q
Q
Q
Q
500
|
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
R
R
L
L
A
A
Q
Q
L
L
L
L
L
L
510
|
I
I
L
L
S
S
H
H
I
I
R
R
H
H
M
M
S
S
N
N
520
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
E
E
H
H
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
M
M
K
K
530
|
C
C
K
K
N
N
V
V
V
V
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
D
G
L
L
540
|
L
L
L
L
E
E
M
M
L
L
D
D
A
A
H
H
R
R
L
L
550
|
H
H
A
A
P
P
T
T
S
S
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | In our analysis of frequently mutated oncogenes and tumor suppressors, ESR1 mutations stood out as a common and plausible event that could contribute to resistance. We found that the mutations in both Tyr537 and Asp538 strongly promoted ER signaling in absence of ligand. This was observed biochemically as increased phosphorylation on S118, increased association with AIB1, and diminished sensitivity to HSP90 inhibitors. Functionally, the mutations in vitro promoted the expression of classical ER target genes in the absence of hormone. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [3], [5], [16] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Tamoxifen | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D538G |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.60 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.90 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
V
-
D
-
L
-
G
-
T
-
E
290
|
-
N
-
L
-
Y
-
F
-
Q
-
S
-
N
-
A
-
M
-
K
300
|
-
R
-
S
-
K
-
K
-
N
-
S
-
L
-
A
-
L
S
S
310
|
L
L
T
T
A
A
D
D
Q
Q
M
M
V
V
S
S
A
A
L
L
320
|
L
L
D
D
A
A
E
E
P
P
P
P
I
I
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
330
|
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
R
R
P
P
F
F
S
S
E
E
340
|
A
A
S
S
M
M
M
M
G
G
L
L
L
L
T
T
N
N
L
L
350
|
A
A
D
D
R
R
E
E
L
L
V
V
H
H
M
M
I
I
N
N
360
|
W
W
A
A
K
K
R
R
V
V
P
P
G
G
F
F
V
V
D
D
370
|
L
L
T
T
L
L
H
H
D
D
Q
Q
V
V
H
H
L
L
L
L
380
|
E
E
C
C
A
A
W
W
L
L
E
E
I
I
L
L
M
M
I
I
390
|
G
G
L
L
V
V
W
W
R
R
S
S
M
M
E
E
H
H
P
P
400
|
G
G
K
K
L
L
L
L
F
F
A
A
P
P
N
N
L
L
L
L
410
|
L
L
D
D
R
R
N
N
Q
Q
G
G
K
K
C
C
V
V
E
E
420
|
G
G
M
M
V
V
E
E
I
I
F
F
D
D
M
M
L
L
L
L
430
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
S
S
R
R
F
F
R
R
M
M
M
M
N
N
440
|
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
E
E
E
E
F
F
V
V
C
C
L
L
K
K
450
|
S
S
I
I
I
I
L
L
L
L
N
N
S
S
G
G
V
V
Y
Y
460
|
T
T
F
F
L
L
S
S
S
S
T
T
L
L
K
K
S
S
L
L
470
|
E
E
E
E
K
K
D
D
H
H
I
I
H
H
R
R
V
V
L
L
480
|
D
D
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
T
T
L
L
I
I
H
H
L
L
490
|
M
M
A
A
K
K
A
A
G
G
L
L
T
T
L
L
Q
Q
Q
Q
500
|
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
R
R
L
L
A
A
Q
Q
L
L
L
L
L
L
510
|
I
I
L
L
S
S
H
H
I
I
R
R
H
H
M
M
S
S
N
N
520
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
E
E
H
H
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
M
M
K
K
530
|
C
C
K
K
N
N
V
V
V
V
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
D
G
L
L
540
|
L
L
L
L
E
E
M
M
L
L
D
D
A
A
H
H
R
R
L
L
550
|
H
H
A
A
P
P
T
T
S
S
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Circulating cell-free DNA assay; Liquid biopsy assay; Droplet digital PCR assay; Next generation assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Progression-free survival assay; Overall survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Recent studies have also highlighted the utility of ex vivo culturing of CTCs as a method of individualized drug susceptibility testing. Using this method, the authors found that CTCs have various mutations (including the p.D538G and p.Y537S ESR1 mutations), and showed that low-dose administration of the HSP90 inhibitor STA9090 alone or in combination with raloxifene and fulvestrant has growth-inhibitory effects. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [8] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Tamoxifen | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L536_D538>P |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Overall survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | All 28 patients were found to harbor ESR1 mutations affecting ligand-binding domain with the most common mutations affecting Y537 (17/28, 60.7%) and D538 (9/28, 32.1%). ESR1 mutation was found in 12.1% of a large cohort of advanced breast cancer patients. Exemestane in combination with everolimus might be a reasonable option. Prospective studies are warranted to validate these findings. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [4], [7], [9] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Tamoxifen | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y537N |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | PI3K signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04151 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-exome sequencing assay; SNP Array profiling assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Tumor biopsy assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Mutations in ESR1 were detected in 4% of cancers and clustered in the ligand-binding domain. These included p.Tyr537(Cys/Asn/Ser) mutations (three patients) that have been shown to cause constitutive activation and resistance to tamoxifen therapy in breast cancer. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [4], [7], [17] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Tamoxifen | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y537C |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | PI3K signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04151 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-exome sequencing assay; SNP Array profiling assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Tumor biopsy assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Mutations in ESR1 were detected in 4% of cancers and clustered in the ligand-binding domain. These included p.Tyr537(Cys/Asn/Ser) mutations (three patients) that have been shown to cause constitutive activation and resistance to tamoxifen therapy in breast cancer. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Tamoxifen | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L536Q |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-genome sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Whole-exome and transcriptome analysis showed that six cases harbored mutations of ESR1 affecting its ligand-binding domain (LBD), all of whom had been treated with anti-estrogens and estrogen deprivation therapies. | ||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [18] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Tamoxifen | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | ER-alpha signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04915 | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Crystal Violet Assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | microRNA-335-5p and -3p synergize to inhibit estrogen receptor alpha expression and promote tamoxifen resistance. MiRNA duplex repressed genes involved in the ERalpha signaling pathway, and enhanced resistance of MCF-7 cells to the growth inhibitory effects of tamoxifen. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [19] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Tamoxifen | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | ER-alpha 36 mediated nongenomic estrogen signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04915 | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 | |||||||||
| SkBR3 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0033 | ||||||||||
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | ||||||||||
| T47D cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0553 | ||||||||||
| ZR75-1 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0588 | ||||||||||
| MDA-MB-436 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0623 | ||||||||||
| MDA-MB-468 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0419 | ||||||||||
| 184A1 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3040 | ||||||||||
| HB3396 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| MEGM cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Luciferase assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Breast cancer patients with tumors highly expressing ER-alpha36 benefit less from tamoxifen treatment. Both mRNA and protein expression of ER-alpha36 were inhibited by let-7 mimics and enhanced by let-7 inhibitors. Our results suggested a novel regulatory mechanism of let-7 miRNAs on ER-alpha36 mediated nongenomic estrogen signal pathways and Tam resistance. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [19] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Tamoxifen | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | ER-alpha 36 mediated nongenomic estrogen signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04915 | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 | |||||||||
| SkBR3 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0033 | ||||||||||
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | ||||||||||
| T47D cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0553 | ||||||||||
| ZR75-1 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0588 | ||||||||||
| MDA-MB-436 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0623 | ||||||||||
| MDA-MB-468 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0419 | ||||||||||
| 184A1 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3040 | ||||||||||
| HB3396 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| MEGM cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Luciferase assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Breast cancer patients with tumors highly expressing ER-alpha36 benefit less from tamoxifen treatment. Both mRNA and protein expression of ER-alpha36 were inhibited by let-7 mimics and enhanced by let-7 inhibitors. Our results suggested a novel regulatory mechanism of let-7 miRNAs on ER-alpha36 mediated nongenomic estrogen signal pathways and Tam resistance. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [3], [4] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Anastrozole | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y537S |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.60 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.50 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
-
D
-
P
-
M
-
I
-
K
300
|
-
R
-
S
-
K
-
K
-
N
-
S
-
L
-
A
-
L
S
S
310
|
L
L
T
T
A
A
D
D
Q
Q
M
M
V
V
S
S
A
A
L
L
320
|
L
L
D
D
A
A
E
E
P
P
P
P
I
I
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
330
|
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
R
R
P
P
F
F
S
S
E
E
340
|
A
A
S
S
M
M
M
M
G
G
L
L
L
L
T
T
N
N
L
L
350
|
A
A
D
D
R
R
E
E
L
L
V
V
H
H
M
M
I
I
N
N
360
|
W
W
A
A
K
K
R
R
V
V
P
P
G
G
F
F
V
V
D
D
370
|
L
L
T
T
L
L
H
H
D
D
Q
Q
V
V
H
H
L
L
L
L
380
|
E
E
C
-
A
A
W
W
L
L
E
E
I
I
L
L
M
M
I
I
390
|
G
G
L
L
V
V
W
W
R
R
S
S
M
M
E
E
H
H
P
P
400
|
G
G
K
K
L
L
L
L
F
F
A
A
P
P
N
N
L
L
L
L
410
|
L
L
D
D
R
R
N
N
Q
Q
G
G
K
K
C
-
V
V
E
E
420
|
G
G
M
M
V
V
E
E
I
I
F
F
D
D
M
M
L
L
L
L
430
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
S
S
R
R
F
F
R
R
M
M
M
M
N
N
440
|
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
E
E
E
E
F
F
V
V
C
C
L
L
K
K
450
|
S
S
I
I
I
I
L
L
L
L
N
N
S
S
G
G
V
V
Y
Y
460
|
T
T
F
F
L
L
S
S
S
S
T
T
L
L
K
K
S
S
L
L
470
|
E
E
E
E
K
K
D
D
H
H
I
I
H
H
R
R
V
V
L
L
480
|
D
D
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
T
T
L
L
I
I
H
H
L
L
490
|
M
M
A
A
K
K
A
A
G
G
L
L
T
T
L
L
Q
Q
Q
Q
500
|
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
R
R
L
L
A
A
Q
Q
L
L
L
L
L
L
510
|
I
I
L
L
S
S
H
H
I
I
R
R
H
H
M
M
S
S
N
N
520
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
E
E
H
H
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
M
M
K
K
530
|
C
-
K
K
N
N
V
V
V
V
P
P
L
L
Y
S
D
D
L
L
540
|
L
L
L
L
E
E
M
M
L
L
D
D
A
A
H
H
R
R
L
L
550
|
H
H
A
A
P
P
T
T
S
S
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Droplet digital polymerase chain reaction assay; Whole-genome sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Chest x-ray assay; Computed tomography assay; Magnetic resonance imaging assay; Positron emission tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | We have developed a ddPCR-based method for the sensitive detection and quantification of 4 representative ESR1 mutations, Y537S, Y537N, Y537C, and D538G, in 325 breast cancer specimens, in which 270 primary breast cancer and 55 MBC specimens. Whole-exome and transcriptome analysis showed that six cases harbored mutations of ESR1 affecting its ligand-binding domain (LBD), all of whom had been treated with anti-estrogens and estrogen deprivation therapies. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Anastrozole | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D538G |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.60 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.90 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
V
-
D
-
L
-
G
-
T
-
E
290
|
-
N
-
L
-
Y
-
F
-
Q
-
S
-
N
-
A
-
M
-
K
300
|
-
R
-
S
-
K
-
K
-
N
-
S
-
L
-
A
-
L
S
S
310
|
L
L
T
T
A
A
D
D
Q
Q
M
M
V
V
S
S
A
A
L
L
320
|
L
L
D
D
A
A
E
E
P
P
P
P
I
I
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
330
|
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
R
R
P
P
F
F
S
S
E
E
340
|
A
A
S
S
M
M
M
M
G
G
L
L
L
L
T
T
N
N
L
L
350
|
A
A
D
D
R
R
E
E
L
L
V
V
H
H
M
M
I
I
N
N
360
|
W
W
A
A
K
K
R
R
V
V
P
P
G
G
F
F
V
V
D
D
370
|
L
L
T
T
L
L
H
H
D
D
Q
Q
V
V
H
H
L
L
L
L
380
|
E
E
C
C
A
A
W
W
L
L
E
E
I
I
L
L
M
M
I
I
390
|
G
G
L
L
V
V
W
W
R
R
S
S
M
M
E
E
H
H
P
P
400
|
G
G
K
K
L
L
L
L
F
F
A
A
P
P
N
N
L
L
L
L
410
|
L
L
D
D
R
R
N
N
Q
Q
G
G
K
K
C
C
V
V
E
E
420
|
G
G
M
M
V
V
E
E
I
I
F
F
D
D
M
M
L
L
L
L
430
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
S
S
R
R
F
F
R
R
M
M
M
M
N
N
440
|
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
E
E
E
E
F
F
V
V
C
C
L
L
K
K
450
|
S
S
I
I
I
I
L
L
L
L
N
N
S
S
G
G
V
V
Y
Y
460
|
T
T
F
F
L
L
S
S
S
S
T
T
L
L
K
K
S
S
L
L
470
|
E
E
E
E
K
K
D
D
H
H
I
I
H
H
R
R
V
V
L
L
480
|
D
D
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
T
T
L
L
I
I
H
H
L
L
490
|
M
M
A
A
K
K
A
A
G
G
L
L
T
T
L
L
Q
Q
Q
Q
500
|
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
R
R
L
L
A
A
Q
Q
L
L
L
L
L
L
510
|
I
I
L
L
S
S
H
H
I
I
R
R
H
H
M
M
S
S
N
N
520
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
E
E
H
H
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
M
M
K
K
530
|
C
C
K
K
N
N
V
V
V
V
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
D
G
L
L
540
|
L
L
L
L
E
E
M
M
L
L
D
D
A
A
H
H
R
R
L
L
550
|
H
H
A
A
P
P
T
T
S
S
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Droplet digital polymerase chain reaction assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Chest x-ray assay; Computed tomography assay; Magnetic resonance imaging assay; Positron emission tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | We have developed a ddPCR-based method for the sensitive detection and quantification of 4 representative ESR1 mutations, Y537S, Y537N, Y537C, and D538G, in 325 breast cancer specimens, in which 270 primary breast cancer and 55 MBC specimens. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Anastrozole | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D538G |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.60 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.90 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
V
-
D
-
L
-
G
-
T
-
E
290
|
-
N
-
L
-
Y
-
F
-
Q
-
S
-
N
-
A
-
M
-
K
300
|
-
R
-
S
-
K
-
K
-
N
-
S
-
L
-
A
-
L
S
S
310
|
L
L
T
T
A
A
D
D
Q
Q
M
M
V
V
S
S
A
A
L
L
320
|
L
L
D
D
A
A
E
E
P
P
P
P
I
I
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
330
|
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
R
R
P
P
F
F
S
S
E
E
340
|
A
A
S
S
M
M
M
M
G
G
L
L
L
L
T
T
N
N
L
L
350
|
A
A
D
D
R
R
E
E
L
L
V
V
H
H
M
M
I
I
N
N
360
|
W
W
A
A
K
K
R
R
V
V
P
P
G
G
F
F
V
V
D
D
370
|
L
L
T
T
L
L
H
H
D
D
Q
Q
V
V
H
H
L
L
L
L
380
|
E
E
C
C
A
A
W
W
L
L
E
E
I
I
L
L
M
M
I
I
390
|
G
G
L
L
V
V
W
W
R
R
S
S
M
M
E
E
H
H
P
P
400
|
G
G
K
K
L
L
L
L
F
F
A
A
P
P
N
N
L
L
L
L
410
|
L
L
D
D
R
R
N
N
Q
Q
G
G
K
K
C
C
V
V
E
E
420
|
G
G
M
M
V
V
E
E
I
I
F
F
D
D
M
M
L
L
L
L
430
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
S
S
R
R
F
F
R
R
M
M
M
M
N
N
440
|
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
E
E
E
E
F
F
V
V
C
C
L
L
K
K
450
|
S
S
I
I
I
I
L
L
L
L
N
N
S
S
G
G
V
V
Y
Y
460
|
T
T
F
F
L
L
S
S
S
S
T
T
L
L
K
K
S
S
L
L
470
|
E
E
E
E
K
K
D
D
H
H
I
I
H
H
R
R
V
V
L
L
480
|
D
D
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
T
T
L
L
I
I
H
H
L
L
490
|
M
M
A
A
K
K
A
A
G
G
L
L
T
T
L
L
Q
Q
Q
Q
500
|
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
R
R
L
L
A
A
Q
Q
L
L
L
L
L
L
510
|
I
I
L
L
S
S
H
H
I
I
R
R
H
H
M
M
S
S
N
N
520
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
E
E
H
H
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
M
M
K
K
530
|
C
C
K
K
N
N
V
V
V
V
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
D
G
L
L
540
|
L
L
L
L
E
E
M
M
L
L
D
D
A
A
H
H
R
R
L
L
550
|
H
H
A
A
P
P
T
T
S
S
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Deep sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | We report here on a novel mutation of ERalpha, in which an A to G substitution at position 1,613 resulted in substitution of aspartic acid at position 538 to glycine (D538G). The mutation was identified in liver metastases obtained from patients who developed endocrine resistance, but not in samples of primary tumors obtained prior to commencing endocrine treatment. Structural modeling indicates that D538G substitution creates a conformational change that disrupts the interaction between the receptor and either estrogen or tamoxifen, but mimics the conformation of the activated receptor. Studies in cell lines confirmed ligand-independent, constitutive activity of the mutated receptor. Taken together, these data indicate the mutation D538G as a novel mechanism conferring acquired endocrine resistance. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Anastrozole | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y537N |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Droplet digital polymerase chain reaction assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Chest x-ray assay; Computed tomography assay; Magnetic resonance imaging assay; Positron emission tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | We have developed a ddPCR-based method for the sensitive detection and quantification of 4 representative ESR1 mutations, Y537S, Y537N, Y537C, and D538G, in 325 breast cancer specimens, in which 270 primary breast cancer and 55 MBC specimens. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Anastrozole | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y537C |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Droplet digital polymerase chain reaction assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Chest x-ray assay; Computed tomography assay; Magnetic resonance imaging assay; Positron emission tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | We have developed a ddPCR-based method for the sensitive detection and quantification of 4 representative ESR1 mutations, Y537S, Y537N, Y537C, and D538G, in 325 breast cancer specimens, in which 270 primary breast cancer and 55 MBC specimens. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [3], [4] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Exemestane | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y537S |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.60 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.50 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
-
D
-
P
-
M
-
I
-
K
300
|
-
R
-
S
-
K
-
K
-
N
-
S
-
L
-
A
-
L
S
S
310
|
L
L
T
T
A
A
D
D
Q
Q
M
M
V
V
S
S
A
A
L
L
320
|
L
L
D
D
A
A
E
E
P
P
P
P
I
I
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
330
|
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
R
R
P
P
F
F
S
S
E
E
340
|
A
A
S
S
M
M
M
M
G
G
L
L
L
L
T
T
N
N
L
L
350
|
A
A
D
D
R
R
E
E
L
L
V
V
H
H
M
M
I
I
N
N
360
|
W
W
A
A
K
K
R
R
V
V
P
P
G
G
F
F
V
V
D
D
370
|
L
L
T
T
L
L
H
H
D
D
Q
Q
V
V
H
H
L
L
L
L
380
|
E
E
C
-
A
A
W
W
L
L
E
E
I
I
L
L
M
M
I
I
390
|
G
G
L
L
V
V
W
W
R
R
S
S
M
M
E
E
H
H
P
P
400
|
G
G
K
K
L
L
L
L
F
F
A
A
P
P
N
N
L
L
L
L
410
|
L
L
D
D
R
R
N
N
Q
Q
G
G
K
K
C
-
V
V
E
E
420
|
G
G
M
M
V
V
E
E
I
I
F
F
D
D
M
M
L
L
L
L
430
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
S
S
R
R
F
F
R
R
M
M
M
M
N
N
440
|
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
E
E
E
E
F
F
V
V
C
C
L
L
K
K
450
|
S
S
I
I
I
I
L
L
L
L
N
N
S
S
G
G
V
V
Y
Y
460
|
T
T
F
F
L
L
S
S
S
S
T
T
L
L
K
K
S
S
L
L
470
|
E
E
E
E
K
K
D
D
H
H
I
I
H
H
R
R
V
V
L
L
480
|
D
D
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
T
T
L
L
I
I
H
H
L
L
490
|
M
M
A
A
K
K
A
A
G
G
L
L
T
T
L
L
Q
Q
Q
Q
500
|
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
R
R
L
L
A
A
Q
Q
L
L
L
L
L
L
510
|
I
I
L
L
S
S
H
H
I
I
R
R
H
H
M
M
S
S
N
N
520
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
E
E
H
H
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
M
M
K
K
530
|
C
-
K
K
N
N
V
V
V
V
P
P
L
L
Y
S
D
D
L
L
540
|
L
L
L
L
E
E
M
M
L
L
D
D
A
A
H
H
R
R
L
L
550
|
H
H
A
A
P
P
T
T
S
S
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Droplet digital polymerase chain reaction assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Chest x-ray assay; Computed tomography assay; Magnetic resonance imaging assay; Positron emission tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | We have developed a ddPCR-based method for the sensitive detection and quantification of 4 representative ESR1 mutations, Y537S, Y537N, Y537C, and D538G, in 325 breast cancer specimens, in which 270 primary breast cancer and 55 MBC specimens. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [4], [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Exemestane | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D538G |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.60 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.90 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
V
-
D
-
L
-
G
-
T
-
E
290
|
-
N
-
L
-
Y
-
F
-
Q
-
S
-
N
-
A
-
M
-
K
300
|
-
R
-
S
-
K
-
K
-
N
-
S
-
L
-
A
-
L
S
S
310
|
L
L
T
T
A
A
D
D
Q
Q
M
M
V
V
S
S
A
A
L
L
320
|
L
L
D
D
A
A
E
E
P
P
P
P
I
I
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
330
|
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
R
R
P
P
F
F
S
S
E
E
340
|
A
A
S
S
M
M
M
M
G
G
L
L
L
L
T
T
N
N
L
L
350
|
A
A
D
D
R
R
E
E
L
L
V
V
H
H
M
M
I
I
N
N
360
|
W
W
A
A
K
K
R
R
V
V
P
P
G
G
F
F
V
V
D
D
370
|
L
L
T
T
L
L
H
H
D
D
Q
Q
V
V
H
H
L
L
L
L
380
|
E
E
C
C
A
A
W
W
L
L
E
E
I
I
L
L
M
M
I
I
390
|
G
G
L
L
V
V
W
W
R
R
S
S
M
M
E
E
H
H
P
P
400
|
G
G
K
K
L
L
L
L
F
F
A
A
P
P
N
N
L
L
L
L
410
|
L
L
D
D
R
R
N
N
Q
Q
G
G
K
K
C
C
V
V
E
E
420
|
G
G
M
M
V
V
E
E
I
I
F
F
D
D
M
M
L
L
L
L
430
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
S
S
R
R
F
F
R
R
M
M
M
M
N
N
440
|
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
E
E
E
E
F
F
V
V
C
C
L
L
K
K
450
|
S
S
I
I
I
I
L
L
L
L
N
N
S
S
G
G
V
V
Y
Y
460
|
T
T
F
F
L
L
S
S
S
S
T
T
L
L
K
K
S
S
L
L
470
|
E
E
E
E
K
K
D
D
H
H
I
I
H
H
R
R
V
V
L
L
480
|
D
D
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
T
T
L
L
I
I
H
H
L
L
490
|
M
M
A
A
K
K
A
A
G
G
L
L
T
T
L
L
Q
Q
Q
Q
500
|
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
R
R
L
L
A
A
Q
Q
L
L
L
L
L
L
510
|
I
I
L
L
S
S
H
H
I
I
R
R
H
H
M
M
S
S
N
N
520
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
E
E
H
H
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
M
M
K
K
530
|
C
C
K
K
N
N
V
V
V
V
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
D
G
L
L
540
|
L
L
L
L
E
E
M
M
L
L
D
D
A
A
H
H
R
R
L
L
550
|
H
H
A
A
P
P
T
T
S
S
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Droplet digital polymerase chain reaction assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Chest x-ray assay; Computed tomography assay; Magnetic resonance imaging assay; Positron emission tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | We have developed a ddPCR-based method for the sensitive detection and quantification of 4 representative ESR1 mutations, Y537S, Y537N, Y537C, and D538G, in 325 breast cancer specimens, in which 270 primary breast cancer and 55 MBC specimens. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Exemestane | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y537N |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Droplet digital polymerase chain reaction assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Chest x-ray assay; Computed tomography assay; Magnetic resonance imaging assay; Positron emission tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | We have developed a ddPCR-based method for the sensitive detection and quantification of 4 representative ESR1 mutations, Y537S, Y537N, Y537C, and D538G, in 325 breast cancer specimens, in which 270 primary breast cancer and 55 MBC specimens. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Exemestane | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y537C |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Droplet digital polymerase chain reaction assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Chest x-ray assay; Computed tomography assay; Magnetic resonance imaging assay; Positron emission tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | We have developed a ddPCR-based method for the sensitive detection and quantification of 4 representative ESR1 mutations, Y537S, Y537N, Y537C, and D538G, in 325 breast cancer specimens, in which 270 primary breast cancer and 55 MBC specimens. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [5], [6], [7] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Fulvestrant | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y537S |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.60 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.50 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
-
D
-
P
-
M
-
I
-
K
300
|
-
R
-
S
-
K
-
K
-
N
-
S
-
L
-
A
-
L
S
S
310
|
L
L
T
T
A
A
D
D
Q
Q
M
M
V
V
S
S
A
A
L
L
320
|
L
L
D
D
A
A
E
E
P
P
P
P
I
I
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
330
|
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
R
R
P
P
F
F
S
S
E
E
340
|
A
A
S
S
M
M
M
M
G
G
L
L
L
L
T
T
N
N
L
L
350
|
A
A
D
D
R
R
E
E
L
L
V
V
H
H
M
M
I
I
N
N
360
|
W
W
A
A
K
K
R
R
V
V
P
P
G
G
F
F
V
V
D
D
370
|
L
L
T
T
L
L
H
H
D
D
Q
Q
V
V
H
H
L
L
L
L
380
|
E
E
C
-
A
A
W
W
L
L
E
E
I
I
L
L
M
M
I
I
390
|
G
G
L
L
V
V
W
W
R
R
S
S
M
M
E
E
H
H
P
P
400
|
G
G
K
K
L
L
L
L
F
F
A
A
P
P
N
N
L
L
L
L
410
|
L
L
D
D
R
R
N
N
Q
Q
G
G
K
K
C
-
V
V
E
E
420
|
G
G
M
M
V
V
E
E
I
I
F
F
D
D
M
M
L
L
L
L
430
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
S
S
R
R
F
F
R
R
M
M
M
M
N
N
440
|
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
E
E
E
E
F
F
V
V
C
C
L
L
K
K
450
|
S
S
I
I
I
I
L
L
L
L
N
N
S
S
G
G
V
V
Y
Y
460
|
T
T
F
F
L
L
S
S
S
S
T
T
L
L
K
K
S
S
L
L
470
|
E
E
E
E
K
K
D
D
H
H
I
I
H
H
R
R
V
V
L
L
480
|
D
D
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
T
T
L
L
I
I
H
H
L
L
490
|
M
M
A
A
K
K
A
A
G
G
L
L
T
T
L
L
Q
Q
Q
Q
500
|
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
R
R
L
L
A
A
Q
Q
L
L
L
L
L
L
510
|
I
I
L
L
S
S
H
H
I
I
R
R
H
H
M
M
S
S
N
N
520
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
E
E
H
H
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
M
M
K
K
530
|
C
-
K
K
N
N
V
V
V
V
P
P
L
L
Y
S
D
D
L
L
540
|
L
L
L
L
E
E
M
M
L
L
D
D
A
A
H
H
R
R
L
L
550
|
H
H
A
A
P
P
T
T
S
S
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 | |||||||||
| WHIM16 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-gexome sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The ESR1-Y537S hormone-binding-domain mutation is clearly a potent cause of aromatase-inhibitor resistance. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [3], [8] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Fulvestrant | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y537S |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.60 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.50 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
-
D
-
P
-
M
-
I
-
K
300
|
-
R
-
S
-
K
-
K
-
N
-
S
-
L
-
A
-
L
S
S
310
|
L
L
T
T
A
A
D
D
Q
Q
M
M
V
V
S
S
A
A
L
L
320
|
L
L
D
D
A
A
E
E
P
P
P
P
I
I
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
330
|
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
R
R
P
P
F
F
S
S
E
E
340
|
A
A
S
S
M
M
M
M
G
G
L
L
L
L
T
T
N
N
L
L
350
|
A
A
D
D
R
R
E
E
L
L
V
V
H
H
M
M
I
I
N
N
360
|
W
W
A
A
K
K
R
R
V
V
P
P
G
G
F
F
V
V
D
D
370
|
L
L
T
T
L
L
H
H
D
D
Q
Q
V
V
H
H
L
L
L
L
380
|
E
E
C
-
A
A
W
W
L
L
E
E
I
I
L
L
M
M
I
I
390
|
G
G
L
L
V
V
W
W
R
R
S
S
M
M
E
E
H
H
P
P
400
|
G
G
K
K
L
L
L
L
F
F
A
A
P
P
N
N
L
L
L
L
410
|
L
L
D
D
R
R
N
N
Q
Q
G
G
K
K
C
-
V
V
E
E
420
|
G
G
M
M
V
V
E
E
I
I
F
F
D
D
M
M
L
L
L
L
430
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
S
S
R
R
F
F
R
R
M
M
M
M
N
N
440
|
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
E
E
E
E
F
F
V
V
C
C
L
L
K
K
450
|
S
S
I
I
I
I
L
L
L
L
N
N
S
S
G
G
V
V
Y
Y
460
|
T
T
F
F
L
L
S
S
S
S
T
T
L
L
K
K
S
S
L
L
470
|
E
E
E
E
K
K
D
D
H
H
I
I
H
H
R
R
V
V
L
L
480
|
D
D
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
T
T
L
L
I
I
H
H
L
L
490
|
M
M
A
A
K
K
A
A
G
G
L
L
T
T
L
L
Q
Q
Q
Q
500
|
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
R
R
L
L
A
A
Q
Q
L
L
L
L
L
L
510
|
I
I
L
L
S
S
H
H
I
I
R
R
H
H
M
M
S
S
N
N
520
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
E
E
H
H
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
M
M
K
K
530
|
C
-
K
K
N
N
V
V
V
V
P
P
L
L
Y
S
D
D
L
L
540
|
L
L
L
L
E
E
M
M
L
L
D
D
A
A
H
H
R
R
L
L
550
|
H
H
A
A
P
P
T
T
S
S
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Overall survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | All 28 patients were found to harbor ESR1 mutations affecting ligand-binding domain with the most common mutations affecting Y537 (17/28, 60.7%) and D538 (9/28, 32.1%). ESR1 mutation was found in 12.1% of a large cohort of advanced breast cancer patients. Exemestane in combination with everolimus might be a reasonable option. Prospective studies are warranted to validate these findings. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [7] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Fulvestrant | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D538G |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.60 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.90 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
V
-
D
-
L
-
G
-
T
-
E
290
|
-
N
-
L
-
Y
-
F
-
Q
-
S
-
N
-
A
-
M
-
K
300
|
-
R
-
S
-
K
-
K
-
N
-
S
-
L
-
A
-
L
S
S
310
|
L
L
T
T
A
A
D
D
Q
Q
M
M
V
V
S
S
A
A
L
L
320
|
L
L
D
D
A
A
E
E
P
P
P
P
I
I
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
330
|
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
R
R
P
P
F
F
S
S
E
E
340
|
A
A
S
S
M
M
M
M
G
G
L
L
L
L
T
T
N
N
L
L
350
|
A
A
D
D
R
R
E
E
L
L
V
V
H
H
M
M
I
I
N
N
360
|
W
W
A
A
K
K
R
R
V
V
P
P
G
G
F
F
V
V
D
D
370
|
L
L
T
T
L
L
H
H
D
D
Q
Q
V
V
H
H
L
L
L
L
380
|
E
E
C
C
A
A
W
W
L
L
E
E
I
I
L
L
M
M
I
I
390
|
G
G
L
L
V
V
W
W
R
R
S
S
M
M
E
E
H
H
P
P
400
|
G
G
K
K
L
L
L
L
F
F
A
A
P
P
N
N
L
L
L
L
410
|
L
L
D
D
R
R
N
N
Q
Q
G
G
K
K
C
C
V
V
E
E
420
|
G
G
M
M
V
V
E
E
I
I
F
F
D
D
M
M
L
L
L
L
430
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
S
S
R
R
F
F
R
R
M
M
M
M
N
N
440
|
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
E
E
E
E
F
F
V
V
C
C
L
L
K
K
450
|
S
S
I
I
I
I
L
L
L
L
N
N
S
S
G
G
V
V
Y
Y
460
|
T
T
F
F
L
L
S
S
S
S
T
T
L
L
K
K
S
S
L
L
470
|
E
E
E
E
K
K
D
D
H
H
I
I
H
H
R
R
V
V
L
L
480
|
D
D
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
T
T
L
L
I
I
H
H
L
L
490
|
M
M
A
A
K
K
A
A
G
G
L
L
T
T
L
L
Q
Q
Q
Q
500
|
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
R
R
L
L
A
A
Q
Q
L
L
L
L
L
L
510
|
I
I
L
L
S
S
H
H
I
I
R
R
H
H
M
M
S
S
N
N
520
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
E
E
H
H
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
M
M
K
K
530
|
C
C
K
K
N
N
V
V
V
V
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
D
G
L
L
540
|
L
L
L
L
E
E
M
M
L
L
D
D
A
A
H
H
R
R
L
L
550
|
H
H
A
A
P
P
T
T
S
S
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | In our analysis of frequently mutated oncogenes and tumor suppressors, ESR1 mutations stood out as a common and plausible event that could contribute to resistance. We found that the mutations in both Tyr537 and Asp538 strongly promoted ER signaling in absence of ligand. This was observed biochemically as increased phosphorylation on S118, increased association with AIB1, and diminished sensitivity to HSP90 inhibitors. Functionally, the mutations in vitro promoted the expression of classical ER target genes in the absence of hormone. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [3], [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Fulvestrant | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D538G |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.60 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.90 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
V
-
D
-
L
-
G
-
T
-
E
290
|
-
N
-
L
-
Y
-
F
-
Q
-
S
-
N
-
A
-
M
-
K
300
|
-
R
-
S
-
K
-
K
-
N
-
S
-
L
-
A
-
L
S
S
310
|
L
L
T
T
A
A
D
D
Q
Q
M
M
V
V
S
S
A
A
L
L
320
|
L
L
D
D
A
A
E
E
P
P
P
P
I
I
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
330
|
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
R
R
P
P
F
F
S
S
E
E
340
|
A
A
S
S
M
M
M
M
G
G
L
L
L
L
T
T
N
N
L
L
350
|
A
A
D
D
R
R
E
E
L
L
V
V
H
H
M
M
I
I
N
N
360
|
W
W
A
A
K
K
R
R
V
V
P
P
G
G
F
F
V
V
D
D
370
|
L
L
T
T
L
L
H
H
D
D
Q
Q
V
V
H
H
L
L
L
L
380
|
E
E
C
C
A
A
W
W
L
L
E
E
I
I
L
L
M
M
I
I
390
|
G
G
L
L
V
V
W
W
R
R
S
S
M
M
E
E
H
H
P
P
400
|
G
G
K
K
L
L
L
L
F
F
A
A
P
P
N
N
L
L
L
L
410
|
L
L
D
D
R
R
N
N
Q
Q
G
G
K
K
C
C
V
V
E
E
420
|
G
G
M
M
V
V
E
E
I
I
F
F
D
D
M
M
L
L
L
L
430
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
S
S
R
R
F
F
R
R
M
M
M
M
N
N
440
|
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
E
E
E
E
F
F
V
V
C
C
L
L
K
K
450
|
S
S
I
I
I
I
L
L
L
L
N
N
S
S
G
G
V
V
Y
Y
460
|
T
T
F
F
L
L
S
S
S
S
T
T
L
L
K
K
S
S
L
L
470
|
E
E
E
E
K
K
D
D
H
H
I
I
H
H
R
R
V
V
L
L
480
|
D
D
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
T
T
L
L
I
I
H
H
L
L
490
|
M
M
A
A
K
K
A
A
G
G
L
L
T
T
L
L
Q
Q
Q
Q
500
|
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
R
R
L
L
A
A
Q
Q
L
L
L
L
L
L
510
|
I
I
L
L
S
S
H
H
I
I
R
R
H
H
M
M
S
S
N
N
520
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
E
E
H
H
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
M
M
K
K
530
|
C
C
K
K
N
N
V
V
V
V
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
D
G
L
L
540
|
L
L
L
L
E
E
M
M
L
L
D
D
A
A
H
H
R
R
L
L
550
|
H
H
A
A
P
P
T
T
S
S
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Deep sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | We report here on a novel mutation of ERalpha, in which an A to G substitution at position 1,613 resulted in substitution of aspartic acid at position 538 to glycine (D538G). The mutation was identified in liver metastases obtained from patients who developed endocrine resistance, but not in samples of primary tumors obtained prior to commencing endocrine treatment. Structural modeling indicates that D538G substitution creates a conformational change that disrupts the interaction between the receptor and either estrogen or tamoxifen, but mimics the conformation of the activated receptor. Studies in cell lines confirmed ligand-independent, constitutive activity of the mutated receptor. Taken together, these data indicate the mutation D538G as a novel mechanism conferring acquired endocrine resistance. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [9], [8] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Fulvestrant | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y537N |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Overall survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | All 28 patients were found to harbor ESR1 mutations affecting ligand-binding domain with the most common mutations affecting Y537 (17/28, 60.7%) and D538 (9/28, 32.1%). ESR1 mutation was found in 12.1% of a large cohort of advanced breast cancer patients. Exemestane in combination with everolimus might be a reasonable option. Prospective studies are warranted to validate these findings. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [4], [8] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Fulvestrant | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y537C |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Overall survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | All 28 patients were found to harbor ESR1 mutations affecting ligand-binding domain with the most common mutations affecting Y537 (17/28, 60.7%) and D538 (9/28, 32.1%). ESR1 mutation was found in 12.1% of a large cohort of advanced breast cancer patients. Exemestane in combination with everolimus might be a reasonable option. Prospective studies are warranted to validate these findings. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [8] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Fulvestrant | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L536_D538>P |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Overall survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | All 28 patients were found to harbor ESR1 mutations affecting ligand-binding domain with the most common mutations affecting Y537 (17/28, 60.7%) and D538 (9/28, 32.1%). ESR1 mutation was found in 12.1% of a large cohort of advanced breast cancer patients. Exemestane in combination with everolimus might be a reasonable option. Prospective studies are warranted to validate these findings. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [7], [10] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Fulvestrant | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y537N |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | In our analysis of frequently mutated oncogenes and tumor suppressors, ESR1 mutations stood out as a common and plausible event that could contribute to resistance. We found that the mutations in both Tyr537 and Asp538 strongly promoted ER signaling in absence of ligand. This was observed biochemically as increased phosphorylation on S118, increased association with AIB1, and diminished sensitivity to HSP90 inhibitors. Functionally, the mutations in vitro promoted the expression of classical ER target genes in the absence of hormone. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [7] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Fulvestrant | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y537C |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | In our analysis of frequently mutated oncogenes and tumor suppressors, ESR1 mutations stood out as a common and plausible event that could contribute to resistance. We found that the mutations in both Tyr537 and Asp538 strongly promoted ER signaling in absence of ligand. This was observed biochemically as increased phosphorylation on S118, increased association with AIB1, and diminished sensitivity to HSP90 inhibitors. Functionally, the mutations in vitro promoted the expression of classical ER target genes in the absence of hormone. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Fulvestrant | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L536Q |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-genome sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Whole-exome and transcriptome analysis showed that six cases harbored mutations of ESR1 affecting its ligand-binding domain (LBD), all of whom had been treated with anti-estrogens and estrogen deprivation therapies. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | [2] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Fulvestrant | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutantion | p.R183W |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | MCF7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 | |||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell proliferation assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Imlunestrant degraded ERalpha and decreased ERalpha-mediated gene expression both in vitro and in vivo. Cell proliferation and tumor growth in ESR1 wild-type (WT) and mutant models were significantly inhibited by imlunestrant. Combining imlunestrant with abemaciclib (CDK4/6 inhibitor), alpelisib (PI3K inhibitor), or everolimus (mTOR inhibitor) further enhanced tumor growth inhibition, regardless of ESR1 mutational status. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | [2] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Fulvestrant | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutantion | p.Y537N |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | MCF7 intracranial tumors mouse model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Overall survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Imlunestrant degraded ERalpha and decreased ERalpha-mediated gene expression both in vitro and in vivo. Cell proliferation and tumor growth in ESR1 wild-type (WT) and mutant models were significantly inhibited by imlunestrant. Combining imlunestrant with abemaciclib (CDK4/6 inhibitor), alpelisib (PI3K inhibitor), or everolimus (mTOR inhibitor) further enhanced tumor growth inhibition, regardless of ESR1 mutational status. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | [2] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Fulvestrant | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutantion | p.R58X |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | ESR1-WT breast cancer xenograft model; ESR1-WT mutant breast cancer xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Tumor volume assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Imlunestrant degraded ERalpha and decreased ERalpha-mediated gene expression both in vitro and in vivo. Cell proliferation and tumor growth in ESR1 wild-type (WT) and mutant models were significantly inhibited by imlunestrant. Combining imlunestrant with abemaciclib (CDK4/6 inhibitor), alpelisib (PI3K inhibitor), or everolimus (mTOR inhibitor) further enhanced tumor growth inhibition, regardless of ESR1 mutational status. | ||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Triple-negative breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.9] | [11] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Triple-negative breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.9] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Fulvestrant | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | EGFR/HER2 signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | MCF7 (Ful-R) cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | In this study, we investigated the molecular mechanism underlying the loss of ER, FOXO3a, and induction of HER2 in fulvestrant-resistant breast cancer. Short-term fulvestrant treatment degraded ER proteins via the ubiquitin-proteasome degradation pathway in MCF7 cells. MCF7 cells turn into highly proliferative cells (fulvestrant-resistant cells: Ful-R) after long-term fulvestrant treatment. These cells exhibit markedly suppressed estrogen and progesterone receptor levels. The phosphorylation of EGFR, HER2, and ERK was induced in Ful-R, and these phosphorylation inhibitors suppressed cell proliferation in Ful-R. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [3], [4] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Letrozole | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y537S |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.60 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.50 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
-
D
-
P
-
M
-
I
-
K
300
|
-
R
-
S
-
K
-
K
-
N
-
S
-
L
-
A
-
L
S
S
310
|
L
L
T
T
A
A
D
D
Q
Q
M
M
V
V
S
S
A
A
L
L
320
|
L
L
D
D
A
A
E
E
P
P
P
P
I
I
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
330
|
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
R
R
P
P
F
F
S
S
E
E
340
|
A
A
S
S
M
M
M
M
G
G
L
L
L
L
T
T
N
N
L
L
350
|
A
A
D
D
R
R
E
E
L
L
V
V
H
H
M
M
I
I
N
N
360
|
W
W
A
A
K
K
R
R
V
V
P
P
G
G
F
F
V
V
D
D
370
|
L
L
T
T
L
L
H
H
D
D
Q
Q
V
V
H
H
L
L
L
L
380
|
E
E
C
-
A
A
W
W
L
L
E
E
I
I
L
L
M
M
I
I
390
|
G
G
L
L
V
V
W
W
R
R
S
S
M
M
E
E
H
H
P
P
400
|
G
G
K
K
L
L
L
L
F
F
A
A
P
P
N
N
L
L
L
L
410
|
L
L
D
D
R
R
N
N
Q
Q
G
G
K
K
C
-
V
V
E
E
420
|
G
G
M
M
V
V
E
E
I
I
F
F
D
D
M
M
L
L
L
L
430
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
S
S
R
R
F
F
R
R
M
M
M
M
N
N
440
|
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
E
E
E
E
F
F
V
V
C
C
L
L
K
K
450
|
S
S
I
I
I
I
L
L
L
L
N
N
S
S
G
G
V
V
Y
Y
460
|
T
T
F
F
L
L
S
S
S
S
T
T
L
L
K
K
S
S
L
L
470
|
E
E
E
E
K
K
D
D
H
H
I
I
H
H
R
R
V
V
L
L
480
|
D
D
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
T
T
L
L
I
I
H
H
L
L
490
|
M
M
A
A
K
K
A
A
G
G
L
L
T
T
L
L
Q
Q
Q
Q
500
|
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
R
R
L
L
A
A
Q
Q
L
L
L
L
L
L
510
|
I
I
L
L
S
S
H
H
I
I
R
R
H
H
M
M
S
S
N
N
520
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
E
E
H
H
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
M
M
K
K
530
|
C
-
K
K
N
N
V
V
V
V
P
P
L
L
Y
S
D
D
L
L
540
|
L
L
L
L
E
E
M
M
L
L
D
D
A
A
H
H
R
R
L
L
550
|
H
H
A
A
P
P
T
T
S
S
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Droplet digital polymerase chain reaction assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Chest x-ray assay; Computed tomography assay; Magnetic resonance imaging assay; Positron emission tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | We have developed a ddPCR-based method for the sensitive detection and quantification of 4 representative ESR1 mutations, Y537S, Y537N, Y537C, and D538G, in 325 breast cancer specimens, in which 270 primary breast cancer and 55 MBC specimens. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [12] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Letrozole | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D538G |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.60 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.90 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
V
-
D
-
L
-
G
-
T
-
E
290
|
-
N
-
L
-
Y
-
F
-
Q
-
S
-
N
-
A
-
M
-
K
300
|
-
R
-
S
-
K
-
K
-
N
-
S
-
L
-
A
-
L
S
S
310
|
L
L
T
T
A
A
D
D
Q
Q
M
M
V
V
S
S
A
A
L
L
320
|
L
L
D
D
A
A
E
E
P
P
P
P
I
I
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
330
|
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
R
R
P
P
F
F
S
S
E
E
340
|
A
A
S
S
M
M
M
M
G
G
L
L
L
L
T
T
N
N
L
L
350
|
A
A
D
D
R
R
E
E
L
L
V
V
H
H
M
M
I
I
N
N
360
|
W
W
A
A
K
K
R
R
V
V
P
P
G
G
F
F
V
V
D
D
370
|
L
L
T
T
L
L
H
H
D
D
Q
Q
V
V
H
H
L
L
L
L
380
|
E
E
C
C
A
A
W
W
L
L
E
E
I
I
L
L
M
M
I
I
390
|
G
G
L
L
V
V
W
W
R
R
S
S
M
M
E
E
H
H
P
P
400
|
G
G
K
K
L
L
L
L
F
F
A
A
P
P
N
N
L
L
L
L
410
|
L
L
D
D
R
R
N
N
Q
Q
G
G
K
K
C
C
V
V
E
E
420
|
G
G
M
M
V
V
E
E
I
I
F
F
D
D
M
M
L
L
L
L
430
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
S
S
R
R
F
F
R
R
M
M
M
M
N
N
440
|
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
E
E
E
E
F
F
V
V
C
C
L
L
K
K
450
|
S
S
I
I
I
I
L
L
L
L
N
N
S
S
G
G
V
V
Y
Y
460
|
T
T
F
F
L
L
S
S
S
S
T
T
L
L
K
K
S
S
L
L
470
|
E
E
E
E
K
K
D
D
H
H
I
I
H
H
R
R
V
V
L
L
480
|
D
D
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
T
T
L
L
I
I
H
H
L
L
490
|
M
M
A
A
K
K
A
A
G
G
L
L
T
T
L
L
Q
Q
Q
Q
500
|
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
R
R
L
L
A
A
Q
Q
L
L
L
L
L
L
510
|
I
I
L
L
S
S
H
H
I
I
R
R
H
H
M
M
S
S
N
N
520
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
E
E
H
H
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
M
M
K
K
530
|
C
C
K
K
N
N
V
V
V
V
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
D
G
L
L
540
|
L
L
L
L
E
E
M
M
L
L
D
D
A
A
H
H
R
R
L
L
550
|
H
H
A
A
P
P
T
T
S
S
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; dPCR assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Acquired mutations in the estrogen-receptor gene ESR1 can be a marker of resistance to aromatase inhibitors in metastatic breast cancer. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Letrozole | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D538G |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.60 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.90 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
V
-
D
-
L
-
G
-
T
-
E
290
|
-
N
-
L
-
Y
-
F
-
Q
-
S
-
N
-
A
-
M
-
K
300
|
-
R
-
S
-
K
-
K
-
N
-
S
-
L
-
A
-
L
S
S
310
|
L
L
T
T
A
A
D
D
Q
Q
M
M
V
V
S
S
A
A
L
L
320
|
L
L
D
D
A
A
E
E
P
P
P
P
I
I
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
330
|
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
R
R
P
P
F
F
S
S
E
E
340
|
A
A
S
S
M
M
M
M
G
G
L
L
L
L
T
T
N
N
L
L
350
|
A
A
D
D
R
R
E
E
L
L
V
V
H
H
M
M
I
I
N
N
360
|
W
W
A
A
K
K
R
R
V
V
P
P
G
G
F
F
V
V
D
D
370
|
L
L
T
T
L
L
H
H
D
D
Q
Q
V
V
H
H
L
L
L
L
380
|
E
E
C
C
A
A
W
W
L
L
E
E
I
I
L
L
M
M
I
I
390
|
G
G
L
L
V
V
W
W
R
R
S
S
M
M
E
E
H
H
P
P
400
|
G
G
K
K
L
L
L
L
F
F
A
A
P
P
N
N
L
L
L
L
410
|
L
L
D
D
R
R
N
N
Q
Q
G
G
K
K
C
C
V
V
E
E
420
|
G
G
M
M
V
V
E
E
I
I
F
F
D
D
M
M
L
L
L
L
430
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
S
S
R
R
F
F
R
R
M
M
M
M
N
N
440
|
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
E
E
E
E
F
F
V
V
C
C
L
L
K
K
450
|
S
S
I
I
I
I
L
L
L
L
N
N
S
S
G
G
V
V
Y
Y
460
|
T
T
F
F
L
L
S
S
S
S
T
T
L
L
K
K
S
S
L
L
470
|
E
E
E
E
K
K
D
D
H
H
I
I
H
H
R
R
V
V
L
L
480
|
D
D
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
T
T
L
L
I
I
H
H
L
L
490
|
M
M
A
A
K
K
A
A
G
G
L
L
T
T
L
L
Q
Q
Q
Q
500
|
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
R
R
L
L
A
A
Q
Q
L
L
L
L
L
L
510
|
I
I
L
L
S
S
H
H
I
I
R
R
H
H
M
M
S
S
N
N
520
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
E
E
H
H
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
M
M
K
K
530
|
C
C
K
K
N
N
V
V
V
V
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
D
G
L
L
540
|
L
L
L
L
E
E
M
M
L
L
D
D
A
A
H
H
R
R
L
L
550
|
H
H
A
A
P
P
T
T
S
S
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-genome sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Whole-exome and transcriptome analysis showed that six cases harbored mutations of ESR1 affecting its ligand-binding domain (LBD), all of whom had been treated with anti-estrogens and estrogen deprivation therapies. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [12] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Letrozole | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y537N |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; dPCR assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Acquired mutations in the estrogen-receptor gene ESR1 can be a marker of resistance to aromatase inhibitors in metastatic breast cancer. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Letrozole | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y537N |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Droplet digital polymerase chain reaction assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Chest x-ray assay; Computed tomography assay; Magnetic resonance imaging assay; Positron emission tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | We have developed a ddPCR-based method for the sensitive detection and quantification of 4 representative ESR1 mutations, Y537S, Y537N, Y537C, and D538G, in 325 breast cancer specimens, in which 270 primary breast cancer and 55 MBC specimens. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Letrozole | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y537C |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Droplet digital polymerase chain reaction assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Chest x-ray assay; Computed tomography assay; Magnetic resonance imaging assay; Positron emission tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | We have developed a ddPCR-based method for the sensitive detection and quantification of 4 representative ESR1 mutations, Y537S, Y537N, Y537C, and D538G, in 325 breast cancer specimens, in which 270 primary breast cancer and 55 MBC specimens. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Letrozole | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L536Q |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-genome sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Whole-exome and transcriptome analysis showed that six cases harbored mutations of ESR1 affecting its ligand-binding domain (LBD), all of whom had been treated with anti-estrogens and estrogen deprivation therapies. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | LY2835219 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutantion | p.Y537N |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vivo Model | ESR1-WT breast cancer xenograft model; ESR1-WT mutant breast cancer xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Tumor volume assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Imlunestrant degraded ERalpha and decreased ERalpha-mediated gene expression both in vitro and in vivo. Cell proliferation and tumor growth in ESR1 wild-type (WT) and mutant models were significantly inhibited by imlunestrant. Combining imlunestrant with abemaciclib (CDK4/6 inhibitor), alpelisib (PI3K inhibitor), or everolimus (mTOR inhibitor) further enhanced tumor growth inhibition, regardless of ESR1 mutational status. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | MPA | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y537S |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.60 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.50 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
-
D
-
P
-
M
-
I
-
K
300
|
-
R
-
S
-
K
-
K
-
N
-
S
-
L
-
A
-
L
S
S
310
|
L
L
T
T
A
A
D
D
Q
Q
M
M
V
V
S
S
A
A
L
L
320
|
L
L
D
D
A
A
E
E
P
P
P
P
I
I
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
330
|
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
R
R
P
P
F
F
S
S
E
E
340
|
A
A
S
S
M
M
M
M
G
G
L
L
L
L
T
T
N
N
L
L
350
|
A
A
D
D
R
R
E
E
L
L
V
V
H
H
M
M
I
I
N
N
360
|
W
W
A
A
K
K
R
R
V
V
P
P
G
G
F
F
V
V
D
D
370
|
L
L
T
T
L
L
H
H
D
D
Q
Q
V
V
H
H
L
L
L
L
380
|
E
E
C
-
A
A
W
W
L
L
E
E
I
I
L
L
M
M
I
I
390
|
G
G
L
L
V
V
W
W
R
R
S
S
M
M
E
E
H
H
P
P
400
|
G
G
K
K
L
L
L
L
F
F
A
A
P
P
N
N
L
L
L
L
410
|
L
L
D
D
R
R
N
N
Q
Q
G
G
K
K
C
-
V
V
E
E
420
|
G
G
M
M
V
V
E
E
I
I
F
F
D
D
M
M
L
L
L
L
430
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
S
S
R
R
F
F
R
R
M
M
M
M
N
N
440
|
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
E
E
E
E
F
F
V
V
C
C
L
L
K
K
450
|
S
S
I
I
I
I
L
L
L
L
N
N
S
S
G
G
V
V
Y
Y
460
|
T
T
F
F
L
L
S
S
S
S
T
T
L
L
K
K
S
S
L
L
470
|
E
E
E
E
K
K
D
D
H
H
I
I
H
H
R
R
V
V
L
L
480
|
D
D
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
T
T
L
L
I
I
H
H
L
L
490
|
M
M
A
A
K
K
A
A
G
G
L
L
T
T
L
L
Q
Q
Q
Q
500
|
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
R
R
L
L
A
A
Q
Q
L
L
L
L
L
L
510
|
I
I
L
L
S
S
H
H
I
I
R
R
H
H
M
M
S
S
N
N
520
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
E
E
H
H
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
M
M
K
K
530
|
C
-
K
K
N
N
V
V
V
V
P
P
L
L
Y
S
D
D
L
L
540
|
L
L
L
L
E
E
M
M
L
L
D
D
A
A
H
H
R
R
L
L
550
|
H
H
A
A
P
P
T
T
S
S
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Droplet digital polymerase chain reaction assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Chest x-ray assay; Computed tomography assay; Magnetic resonance imaging assay; Positron emission tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | We have developed a ddPCR-based method for the sensitive detection and quantification of 4 representative ESR1 mutations, Y537S, Y537N, Y537C, and D538G, in 325 breast cancer specimens, in which 270 primary breast cancer and 55 MBC specimens. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | MPA | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D538G |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.60 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.90 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
V
-
D
-
L
-
G
-
T
-
E
290
|
-
N
-
L
-
Y
-
F
-
Q
-
S
-
N
-
A
-
M
-
K
300
|
-
R
-
S
-
K
-
K
-
N
-
S
-
L
-
A
-
L
S
S
310
|
L
L
T
T
A
A
D
D
Q
Q
M
M
V
V
S
S
A
A
L
L
320
|
L
L
D
D
A
A
E
E
P
P
P
P
I
I
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
330
|
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
R
R
P
P
F
F
S
S
E
E
340
|
A
A
S
S
M
M
M
M
G
G
L
L
L
L
T
T
N
N
L
L
350
|
A
A
D
D
R
R
E
E
L
L
V
V
H
H
M
M
I
I
N
N
360
|
W
W
A
A
K
K
R
R
V
V
P
P
G
G
F
F
V
V
D
D
370
|
L
L
T
T
L
L
H
H
D
D
Q
Q
V
V
H
H
L
L
L
L
380
|
E
E
C
C
A
A
W
W
L
L
E
E
I
I
L
L
M
M
I
I
390
|
G
G
L
L
V
V
W
W
R
R
S
S
M
M
E
E
H
H
P
P
400
|
G
G
K
K
L
L
L
L
F
F
A
A
P
P
N
N
L
L
L
L
410
|
L
L
D
D
R
R
N
N
Q
Q
G
G
K
K
C
C
V
V
E
E
420
|
G
G
M
M
V
V
E
E
I
I
F
F
D
D
M
M
L
L
L
L
430
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
S
S
R
R
F
F
R
R
M
M
M
M
N
N
440
|
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
E
E
E
E
F
F
V
V
C
C
L
L
K
K
450
|
S
S
I
I
I
I
L
L
L
L
N
N
S
S
G
G
V
V
Y
Y
460
|
T
T
F
F
L
L
S
S
S
S
T
T
L
L
K
K
S
S
L
L
470
|
E
E
E
E
K
K
D
D
H
H
I
I
H
H
R
R
V
V
L
L
480
|
D
D
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
T
T
L
L
I
I
H
H
L
L
490
|
M
M
A
A
K
K
A
A
G
G
L
L
T
T
L
L
Q
Q
Q
Q
500
|
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
R
R
L
L
A
A
Q
Q
L
L
L
L
L
L
510
|
I
I
L
L
S
S
H
H
I
I
R
R
H
H
M
M
S
S
N
N
520
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
E
E
H
H
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
M
M
K
K
530
|
C
C
K
K
N
N
V
V
V
V
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
D
G
L
L
540
|
L
L
L
L
E
E
M
M
L
L
D
D
A
A
H
H
R
R
L
L
550
|
H
H
A
A
P
P
T
T
S
S
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Droplet digital polymerase chain reaction assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Chest x-ray assay; Computed tomography assay; Magnetic resonance imaging assay; Positron emission tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | We have developed a ddPCR-based method for the sensitive detection and quantification of 4 representative ESR1 mutations, Y537S, Y537N, Y537C, and D538G, in 325 breast cancer specimens, in which 270 primary breast cancer and 55 MBC specimens. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | MPA | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y537N |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Droplet digital polymerase chain reaction assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Chest x-ray assay; Computed tomography assay; Magnetic resonance imaging assay; Positron emission tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | We have developed a ddPCR-based method for the sensitive detection and quantification of 4 representative ESR1 mutations, Y537S, Y537N, Y537C, and D538G, in 325 breast cancer specimens, in which 270 primary breast cancer and 55 MBC specimens. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: ER positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.6] | [13] | |||
| Resistant Disease | ER positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.6] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Paclitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| ZR75-1 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0588 | |
| MCF-7R cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_Y493 | |
| ZR-75-1R cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0588 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qPCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Annexin V apoptosis assay; Fow cytometry analysis | |||
| Mechanism Description | LncRNA H19 was identified as a powerful factor associated with paclitaxel (PTX) resistance in ERalpha-positive breast cancer cells, but not in ERalpha-negative breast cancer cells. LncRNA H19 was one of the downstream target molecules of ERalpha. Altered ERalpha expression may therefore change H19 levels to modulate the apoptosis response to chemotherapy in breast cancer cells. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [14] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Palbociclib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y537S |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.60 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.50 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
-
D
-
P
-
M
-
I
-
K
300
|
-
R
-
S
-
K
-
K
-
N
-
S
-
L
-
A
-
L
S
S
310
|
L
L
T
T
A
A
D
D
Q
Q
M
M
V
V
S
S
A
A
L
L
320
|
L
L
D
D
A
A
E
E
P
P
P
P
I
I
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
330
|
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
R
R
P
P
F
F
S
S
E
E
340
|
A
A
S
S
M
M
M
M
G
G
L
L
L
L
T
T
N
N
L
L
350
|
A
A
D
D
R
R
E
E
L
L
V
V
H
H
M
M
I
I
N
N
360
|
W
W
A
A
K
K
R
R
V
V
P
P
G
G
F
F
V
V
D
D
370
|
L
L
T
T
L
L
H
H
D
D
Q
Q
V
V
H
H
L
L
L
L
380
|
E
E
C
-
A
A
W
W
L
L
E
E
I
I
L
L
M
M
I
I
390
|
G
G
L
L
V
V
W
W
R
R
S
S
M
M
E
E
H
H
P
P
400
|
G
G
K
K
L
L
L
L
F
F
A
A
P
P
N
N
L
L
L
L
410
|
L
L
D
D
R
R
N
N
Q
Q
G
G
K
K
C
-
V
V
E
E
420
|
G
G
M
M
V
V
E
E
I
I
F
F
D
D
M
M
L
L
L
L
430
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
S
S
R
R
F
F
R
R
M
M
M
M
N
N
440
|
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
E
E
E
E
F
F
V
V
C
C
L
L
K
K
450
|
S
S
I
I
I
I
L
L
L
L
N
N
S
S
G
G
V
V
Y
Y
460
|
T
T
F
F
L
L
S
S
S
S
T
T
L
L
K
K
S
S
L
L
470
|
E
E
E
E
K
K
D
D
H
H
I
I
H
H
R
R
V
V
L
L
480
|
D
D
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
T
T
L
L
I
I
H
H
L
L
490
|
M
M
A
A
K
K
A
A
G
G
L
L
T
T
L
L
Q
Q
Q
Q
500
|
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
R
R
L
L
A
A
Q
Q
L
L
L
L
L
L
510
|
I
I
L
L
S
S
H
H
I
I
R
R
H
H
M
M
S
S
N
N
520
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
E
E
H
H
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
M
M
K
K
530
|
C
-
K
K
N
N
V
V
V
V
P
P
L
L
Y
S
D
D
L
L
540
|
L
L
L
L
E
E
M
M
L
L
D
D
A
A
H
H
R
R
L
L
550
|
H
H
A
A
P
P
T
T
S
S
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Breast cancer tissue | N.A. | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Digital PCR assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | We show that clonal evolution occurs frequently during treatment, reflecting substantial sub-clonal complexity in breast cancer that has progressed after prior endocrine therapy. RB1 mutations emerged only in the palbociclib plus fulvestrant arm and in a minority of patients (6/127, 4.7%, p=0.041). New driver mutations emerged in PIK3CA (p=0.00069) and ESR1 after treatment in both arms, in particular ESR1 Y537S (p=0.0037). Evolution of driver gene mutations was uncommon in patients progressing early on palbociclib plus fulvestrant but common in patients progressing later on treatment. These findings inform future treatment strategies to address resistance to palbociclib plus fulvestrant. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | [15] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Ribociclib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutations | D1194A |
||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
GeneSeq assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Bayesian mixed-effects model assay; McNemar testing | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Toremifene | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y537C |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Droplet digital polymerase chain reaction assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Chest x-ray assay; Computed tomography assay; Magnetic resonance imaging assay; Positron emission tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | We have developed a ddPCR-based method for the sensitive detection and quantification of 4 representative ESR1 mutations, Y537S, Y537N, Y537C, and D538G, in 325 breast cancer specimens, in which 270 primary breast cancer and 55 MBC specimens. | |||
Preclinical Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | [7] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Hormone therapy | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y537S (c.1610A>C) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.60 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.50 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
-
D
-
P
-
M
-
I
-
K
300
|
-
R
-
S
-
K
-
K
-
N
-
S
-
L
-
A
-
L
S
S
310
|
L
L
T
T
A
A
D
D
Q
Q
M
M
V
V
S
S
A
A
L
L
320
|
L
L
D
D
A
A
E
E
P
P
P
P
I
I
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
330
|
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
R
R
P
P
F
F
S
S
E
E
340
|
A
A
S
S
M
M
M
M
G
G
L
L
L
L
T
T
N
N
L
L
350
|
A
A
D
D
R
R
E
E
L
L
V
V
H
H
M
M
I
I
N
N
360
|
W
W
A
A
K
K
R
R
V
V
P
P
G
G
F
F
V
V
D
D
370
|
L
L
T
T
L
L
H
H
D
D
Q
Q
V
V
H
H
L
L
L
L
380
|
E
E
C
-
A
A
W
W
L
L
E
E
I
I
L
L
M
M
I
I
390
|
G
G
L
L
V
V
W
W
R
R
S
S
M
M
E
E
H
H
P
P
400
|
G
G
K
K
L
L
L
L
F
F
A
A
P
P
N
N
L
L
L
L
410
|
L
L
D
D
R
R
N
N
Q
Q
G
G
K
K
C
-
V
V
E
E
420
|
G
G
M
M
V
V
E
E
I
I
F
F
D
D
M
M
L
L
L
L
430
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
S
S
R
R
F
F
R
R
M
M
M
M
N
N
440
|
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
E
E
E
E
F
F
V
V
C
C
L
L
K
K
450
|
S
S
I
I
I
I
L
L
L
L
N
N
S
S
G
G
V
V
Y
Y
460
|
T
T
F
F
L
L
S
S
S
S
T
T
L
L
K
K
S
S
L
L
470
|
E
E
E
E
K
K
D
D
H
H
I
I
H
H
R
R
V
V
L
L
480
|
D
D
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
T
T
L
L
I
I
H
H
L
L
490
|
M
M
A
A
K
K
A
A
G
G
L
L
T
T
L
L
Q
Q
Q
Q
500
|
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
R
R
L
L
A
A
Q
Q
L
L
L
L
L
L
510
|
I
I
L
L
S
S
H
H
I
I
R
R
H
H
M
M
S
S
N
N
520
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
E
E
H
H
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
M
M
K
K
530
|
C
-
K
K
N
N
V
V
V
V
P
P
L
L
Y
S
D
D
L
L
540
|
L
L
L
L
E
E
M
M
L
L
D
D
A
A
H
H
R
R
L
L
550
|
H
H
A
A
P
P
T
T
S
S
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | MDA-MB-231cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | |||||||||
| ZR75-1 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0588 | ||||||||||
| MDA-MB-361 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0620 | ||||||||||
| MDA-MB-231cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | ||||||||||
| SkBR3 MCF7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| MCF Tet-On cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_V332 | ||||||||||
| Ishikawa cells | Endometrium | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2529 | ||||||||||
| MCF Tet-On cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_V332 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Nu/Nu athymic BALB/c female mouse model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IMPACT assay; Western blot analysis; Luciferase assays; Microarrays assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MSKCC assay | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | [7] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Hormone therapy | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D538G (c.1613A>G) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.60 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.90 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
V
-
D
-
L
-
G
-
T
-
E
290
|
-
N
-
L
-
Y
-
F
-
Q
-
S
-
N
-
A
-
M
-
K
300
|
-
R
-
S
-
K
-
K
-
N
-
S
-
L
-
A
-
L
S
S
310
|
L
L
T
T
A
A
D
D
Q
Q
M
M
V
V
S
S
A
A
L
L
320
|
L
L
D
D
A
A
E
E
P
P
P
P
I
I
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
330
|
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
R
R
P
P
F
F
S
S
E
E
340
|
A
A
S
S
M
M
M
M
G
G
L
L
L
L
T
T
N
N
L
L
350
|
A
A
D
D
R
R
E
E
L
L
V
V
H
H
M
M
I
I
N
N
360
|
W
W
A
A
K
K
R
R
V
V
P
P
G
G
F
F
V
V
D
D
370
|
L
L
T
T
L
L
H
H
D
D
Q
Q
V
V
H
H
L
L
L
L
380
|
E
E
C
C
A
A
W
W
L
L
E
E
I
I
L
L
M
M
I
I
390
|
G
G
L
L
V
V
W
W
R
R
S
S
M
M
E
E
H
H
P
P
400
|
G
G
K
K
L
L
L
L
F
F
A
A
P
P
N
N
L
L
L
L
410
|
L
L
D
D
R
R
N
N
Q
Q
G
G
K
K
C
C
V
V
E
E
420
|
G
G
M
M
V
V
E
E
I
I
F
F
D
D
M
M
L
L
L
L
430
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
S
S
R
R
F
F
R
R
M
M
M
M
N
N
440
|
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
E
E
E
E
F
F
V
V
C
C
L
L
K
K
450
|
S
S
I
I
I
I
L
L
L
L
N
N
S
S
G
G
V
V
Y
Y
460
|
T
T
F
F
L
L
S
S
S
S
T
T
L
L
K
K
S
S
L
L
470
|
E
E
E
E
K
K
D
D
H
H
I
I
H
H
R
R
V
V
L
L
480
|
D
D
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
T
T
L
L
I
I
H
H
L
L
490
|
M
M
A
A
K
K
A
A
G
G
L
L
T
T
L
L
Q
Q
Q
Q
500
|
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
R
R
L
L
A
A
Q
Q
L
L
L
L
L
L
510
|
I
I
L
L
S
S
H
H
I
I
R
R
H
H
M
M
S
S
N
N
520
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
E
E
H
H
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
M
M
K
K
530
|
C
C
K
K
N
N
V
V
V
V
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
D
G
L
L
540
|
L
L
L
L
E
E
M
M
L
L
D
D
A
A
H
H
R
R
L
L
550
|
H
H
A
A
P
P
T
T
S
S
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | MDA-MB-231cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | |||||||||
| ZR75-1 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0588 | ||||||||||
| MDA-MB-361 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0620 | ||||||||||
| MDA-MB-231cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | ||||||||||
| SkBR3 MCF7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| MCF Tet-On cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_V332 | ||||||||||
| Ishikawa cells | Endometrium | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2529 | ||||||||||
| MCF Tet-On cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_V332 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Nu/Nu athymic BALB/c female mouse model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IMPACT assay; Western blot analysis; Luciferase assays; Microarrays assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MSKCC assay | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | [7] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Hormone therapy | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L536Q (c.1607_1608delTCinsAA) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | MDA-MB-231cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | |||||||||
| ZR75-1 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0588 | ||||||||||
| MDA-MB-361 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0620 | ||||||||||
| MDA-MB-231cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | ||||||||||
| SkBR3 MCF7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| MCF Tet-On cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_V332 | ||||||||||
| Ishikawa cells | Endometrium | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2529 | ||||||||||
| MCF Tet-On cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_V332 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Nu/Nu athymic BALB/c female mouse model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IMPACT assay; Western blot analysis; Luciferase assays; Microarrays assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MSKCC assay | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | [7] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Hormone therapy | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y537N (c.1609T>A) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | MDA-MB-231cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | |||||||||
| ZR75-1 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0588 | ||||||||||
| MDA-MB-361 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0620 | ||||||||||
| MDA-MB-231cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | ||||||||||
| SkBR3 MCF7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| MCF Tet-On cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_V332 | ||||||||||
| Ishikawa cells | Endometrium | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2529 | ||||||||||
| MCF Tet-On cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_V332 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Nu/Nu athymic BALB/c female mouse model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IMPACT assay; Western blot analysis; Luciferase assays; Microarrays assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MSKCC assay | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | [7] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Hormone therapy | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y537C (c.1610A>G) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | MDA-MB-231cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | |||||||||
| ZR75-1 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0588 | ||||||||||
| MDA-MB-361 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0620 | ||||||||||
| MDA-MB-231cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | ||||||||||
| SkBR3 MCF7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| MCF Tet-On cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_V332 | ||||||||||
| Ishikawa cells | Endometrium | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2529 | ||||||||||
| MCF Tet-On cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_V332 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Nu/Nu athymic BALB/c female mouse model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IMPACT assay; Western blot analysis; Luciferase assays; Microarrays assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MSKCC assay | ||||||||||||
Investigative Drug(s)
4 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Anastrazola/Goserelin | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D538G |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.60 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.90 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
V
-
D
-
L
-
G
-
T
-
E
290
|
-
N
-
L
-
Y
-
F
-
Q
-
S
-
N
-
A
-
M
-
K
300
|
-
R
-
S
-
K
-
K
-
N
-
S
-
L
-
A
-
L
S
S
310
|
L
L
T
T
A
A
D
D
Q
Q
M
M
V
V
S
S
A
A
L
L
320
|
L
L
D
D
A
A
E
E
P
P
P
P
I
I
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
330
|
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
R
R
P
P
F
F
S
S
E
E
340
|
A
A
S
S
M
M
M
M
G
G
L
L
L
L
T
T
N
N
L
L
350
|
A
A
D
D
R
R
E
E
L
L
V
V
H
H
M
M
I
I
N
N
360
|
W
W
A
A
K
K
R
R
V
V
P
P
G
G
F
F
V
V
D
D
370
|
L
L
T
T
L
L
H
H
D
D
Q
Q
V
V
H
H
L
L
L
L
380
|
E
E
C
C
A
A
W
W
L
L
E
E
I
I
L
L
M
M
I
I
390
|
G
G
L
L
V
V
W
W
R
R
S
S
M
M
E
E
H
H
P
P
400
|
G
G
K
K
L
L
L
L
F
F
A
A
P
P
N
N
L
L
L
L
410
|
L
L
D
D
R
R
N
N
Q
Q
G
G
K
K
C
C
V
V
E
E
420
|
G
G
M
M
V
V
E
E
I
I
F
F
D
D
M
M
L
L
L
L
430
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
S
S
R
R
F
F
R
R
M
M
M
M
N
N
440
|
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
E
E
E
E
F
F
V
V
C
C
L
L
K
K
450
|
S
S
I
I
I
I
L
L
L
L
N
N
S
S
G
G
V
V
Y
Y
460
|
T
T
F
F
L
L
S
S
S
S
T
T
L
L
K
K
S
S
L
L
470
|
E
E
E
E
K
K
D
D
H
H
I
I
H
H
R
R
V
V
L
L
480
|
D
D
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
T
T
L
L
I
I
H
H
L
L
490
|
M
M
A
A
K
K
A
A
G
G
L
L
T
T
L
L
Q
Q
Q
Q
500
|
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
R
R
L
L
A
A
Q
Q
L
L
L
L
L
L
510
|
I
I
L
L
S
S
H
H
I
I
R
R
H
H
M
M
S
S
N
N
520
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
E
E
H
H
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
M
M
K
K
530
|
C
C
K
K
N
N
V
V
V
V
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
D
G
L
L
540
|
L
L
L
L
E
E
M
M
L
L
D
D
A
A
H
H
R
R
L
L
550
|
H
H
A
A
P
P
T
T
S
S
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Deep sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | We report here on a novel mutation of ERalpha, in which an A to G substitution at position 1,613 resulted in substitution of aspartic acid at position 538 to glycine (D538G). The mutation was identified in liver metastases obtained from patients who developed endocrine resistance, but not in samples of primary tumors obtained prior to commencing endocrine treatment. Structural modeling indicates that D538G substitution creates a conformational change that disrupts the interaction between the receptor and either estrogen or tamoxifen, but mimics the conformation of the activated receptor. Studies in cell lines confirmed ligand-independent, constitutive activity of the mutated receptor. Taken together, these data indicate the mutation D538G as a novel mechanism conferring acquired endocrine resistance. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Anti-estrogens | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.P535H (c.1604C>A) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | MDA-MB-231cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 |
| ZR75-1 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0588 | |
| MDA-MB-361 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0620 | |
| MDA-MB-231cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | |
| SkBR3 MCF7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| MCF Tet-On cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_V332 | |
| Ishikawa cells | Endometrium | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2529 | |
| MCF Tet-On cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_V332 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nu/Nu athymic BALB/c female mouse model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
IMPACT assay; Western blot analysis; Luciferase assays; Microarrays assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MSKCC assay | |||
| Disease Class: Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Anti-estrogens | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E380Q (c.1138G>C) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Disease Class: Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Anti-estrogens | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L536X (c.1606_1608) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [8] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Exemestane/Everolimus | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y537S |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.60 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.50 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
-
D
-
P
-
M
-
I
-
K
300
|
-
R
-
S
-
K
-
K
-
N
-
S
-
L
-
A
-
L
S
S
310
|
L
L
T
T
A
A
D
D
Q
Q
M
M
V
V
S
S
A
A
L
L
320
|
L
L
D
D
A
A
E
E
P
P
P
P
I
I
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
330
|
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
R
R
P
P
F
F
S
S
E
E
340
|
A
A
S
S
M
M
M
M
G
G
L
L
L
L
T
T
N
N
L
L
350
|
A
A
D
D
R
R
E
E
L
L
V
V
H
H
M
M
I
I
N
N
360
|
W
W
A
A
K
K
R
R
V
V
P
P
G
G
F
F
V
V
D
D
370
|
L
L
T
T
L
L
H
H
D
D
Q
Q
V
V
H
H
L
L
L
L
380
|
E
E
C
-
A
A
W
W
L
L
E
E
I
I
L
L
M
M
I
I
390
|
G
G
L
L
V
V
W
W
R
R
S
S
M
M
E
E
H
H
P
P
400
|
G
G
K
K
L
L
L
L
F
F
A
A
P
P
N
N
L
L
L
L
410
|
L
L
D
D
R
R
N
N
Q
Q
G
G
K
K
C
-
V
V
E
E
420
|
G
G
M
M
V
V
E
E
I
I
F
F
D
D
M
M
L
L
L
L
430
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
S
S
R
R
F
F
R
R
M
M
M
M
N
N
440
|
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
E
E
E
E
F
F
V
V
C
C
L
L
K
K
450
|
S
S
I
I
I
I
L
L
L
L
N
N
S
S
G
G
V
V
Y
Y
460
|
T
T
F
F
L
L
S
S
S
S
T
T
L
L
K
K
S
S
L
L
470
|
E
E
E
E
K
K
D
D
H
H
I
I
H
H
R
R
V
V
L
L
480
|
D
D
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
T
T
L
L
I
I
H
H
L
L
490
|
M
M
A
A
K
K
A
A
G
G
L
L
T
T
L
L
Q
Q
Q
Q
500
|
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
R
R
L
L
A
A
Q
Q
L
L
L
L
L
L
510
|
I
I
L
L
S
S
H
H
I
I
R
R
H
H
M
M
S
S
N
N
520
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
E
E
H
H
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
M
M
K
K
530
|
C
-
K
K
N
N
V
V
V
V
P
P
L
L
Y
S
D
D
L
L
540
|
L
L
L
L
E
E
M
M
L
L
D
D
A
A
H
H
R
R
L
L
550
|
H
H
A
A
P
P
T
T
S
S
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Overall survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | All 28 patients were found to harbor ESR1 mutations affecting ligand-binding domain with the most common mutations affecting Y537 (17/28, 60.7%) and D538 (9/28, 32.1%). ESR1 mutation was found in 12.1% of a large cohort of advanced breast cancer patients. Exemestane in combination with everolimus might be a reasonable option. Prospective studies are warranted to validate these findings. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [8] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Exemestane/Everolimus | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D538G |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.60 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.90 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
V
-
D
-
L
-
G
-
T
-
E
290
|
-
N
-
L
-
Y
-
F
-
Q
-
S
-
N
-
A
-
M
-
K
300
|
-
R
-
S
-
K
-
K
-
N
-
S
-
L
-
A
-
L
S
S
310
|
L
L
T
T
A
A
D
D
Q
Q
M
M
V
V
S
S
A
A
L
L
320
|
L
L
D
D
A
A
E
E
P
P
P
P
I
I
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
330
|
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
R
R
P
P
F
F
S
S
E
E
340
|
A
A
S
S
M
M
M
M
G
G
L
L
L
L
T
T
N
N
L
L
350
|
A
A
D
D
R
R
E
E
L
L
V
V
H
H
M
M
I
I
N
N
360
|
W
W
A
A
K
K
R
R
V
V
P
P
G
G
F
F
V
V
D
D
370
|
L
L
T
T
L
L
H
H
D
D
Q
Q
V
V
H
H
L
L
L
L
380
|
E
E
C
C
A
A
W
W
L
L
E
E
I
I
L
L
M
M
I
I
390
|
G
G
L
L
V
V
W
W
R
R
S
S
M
M
E
E
H
H
P
P
400
|
G
G
K
K
L
L
L
L
F
F
A
A
P
P
N
N
L
L
L
L
410
|
L
L
D
D
R
R
N
N
Q
Q
G
G
K
K
C
C
V
V
E
E
420
|
G
G
M
M
V
V
E
E
I
I
F
F
D
D
M
M
L
L
L
L
430
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
S
S
R
R
F
F
R
R
M
M
M
M
N
N
440
|
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
E
E
E
E
F
F
V
V
C
C
L
L
K
K
450
|
S
S
I
I
I
I
L
L
L
L
N
N
S
S
G
G
V
V
Y
Y
460
|
T
T
F
F
L
L
S
S
S
S
T
T
L
L
K
K
S
S
L
L
470
|
E
E
E
E
K
K
D
D
H
H
I
I
H
H
R
R
V
V
L
L
480
|
D
D
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
T
T
L
L
I
I
H
H
L
L
490
|
M
M
A
A
K
K
A
A
G
G
L
L
T
T
L
L
Q
Q
Q
Q
500
|
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
R
R
L
L
A
A
Q
Q
L
L
L
L
L
L
510
|
I
I
L
L
S
S
H
H
I
I
R
R
H
H
M
M
S
S
N
N
520
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
E
E
H
H
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
M
M
K
K
530
|
C
C
K
K
N
N
V
V
V
V
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
D
G
L
L
540
|
L
L
L
L
E
E
M
M
L
L
D
D
A
A
H
H
R
R
L
L
550
|
H
H
A
A
P
P
T
T
S
S
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Overall survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | All 28 patients were found to harbor ESR1 mutations affecting ligand-binding domain with the most common mutations affecting Y537 (17/28, 60.7%) and D538 (9/28, 32.1%). ESR1 mutation was found in 12.1% of a large cohort of advanced breast cancer patients. Exemestane in combination with everolimus might be a reasonable option. Prospective studies are warranted to validate these findings. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [8] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Exemestane/Everolimus | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L536_D538>P |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Overall survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | All 28 patients were found to harbor ESR1 mutations affecting ligand-binding domain with the most common mutations affecting Y537 (17/28, 60.7%) and D538 (9/28, 32.1%). ESR1 mutation was found in 12.1% of a large cohort of advanced breast cancer patients. Exemestane in combination with everolimus might be a reasonable option. Prospective studies are warranted to validate these findings. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Tamoxifen/Goserelin | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D538G |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.60 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.90 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
V
-
D
-
L
-
G
-
T
-
E
290
|
-
N
-
L
-
Y
-
F
-
Q
-
S
-
N
-
A
-
M
-
K
300
|
-
R
-
S
-
K
-
K
-
N
-
S
-
L
-
A
-
L
S
S
310
|
L
L
T
T
A
A
D
D
Q
Q
M
M
V
V
S
S
A
A
L
L
320
|
L
L
D
D
A
A
E
E
P
P
P
P
I
I
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
330
|
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
R
R
P
P
F
F
S
S
E
E
340
|
A
A
S
S
M
M
M
M
G
G
L
L
L
L
T
T
N
N
L
L
350
|
A
A
D
D
R
R
E
E
L
L
V
V
H
H
M
M
I
I
N
N
360
|
W
W
A
A
K
K
R
R
V
V
P
P
G
G
F
F
V
V
D
D
370
|
L
L
T
T
L
L
H
H
D
D
Q
Q
V
V
H
H
L
L
L
L
380
|
E
E
C
C
A
A
W
W
L
L
E
E
I
I
L
L
M
M
I
I
390
|
G
G
L
L
V
V
W
W
R
R
S
S
M
M
E
E
H
H
P
P
400
|
G
G
K
K
L
L
L
L
F
F
A
A
P
P
N
N
L
L
L
L
410
|
L
L
D
D
R
R
N
N
Q
Q
G
G
K
K
C
C
V
V
E
E
420
|
G
G
M
M
V
V
E
E
I
I
F
F
D
D
M
M
L
L
L
L
430
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
S
S
R
R
F
F
R
R
M
M
M
M
N
N
440
|
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
E
E
E
E
F
F
V
V
C
C
L
L
K
K
450
|
S
S
I
I
I
I
L
L
L
L
N
N
S
S
G
G
V
V
Y
Y
460
|
T
T
F
F
L
L
S
S
S
S
T
T
L
L
K
K
S
S
L
L
470
|
E
E
E
E
K
K
D
D
H
H
I
I
H
H
R
R
V
V
L
L
480
|
D
D
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
T
T
L
L
I
I
H
H
L
L
490
|
M
M
A
A
K
K
A
A
G
G
L
L
T
T
L
L
Q
Q
Q
Q
500
|
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
R
R
L
L
A
A
Q
Q
L
L
L
L
L
L
510
|
I
I
L
L
S
S
H
H
I
I
R
R
H
H
M
M
S
S
N
N
520
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
E
E
H
H
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
M
M
K
K
530
|
C
C
K
K
N
N
V
V
V
V
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
D
G
L
L
540
|
L
L
L
L
E
E
M
M
L
L
D
D
A
A
H
H
R
R
L
L
550
|
H
H
A
A
P
P
T
T
S
S
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Deep sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | We report here on a novel mutation of ERalpha, in which an A to G substitution at position 1,613 resulted in substitution of aspartic acid at position 538 to glycine (D538G). The mutation was identified in liver metastases obtained from patients who developed endocrine resistance, but not in samples of primary tumors obtained prior to commencing endocrine treatment. Structural modeling indicates that D538G substitution creates a conformational change that disrupts the interaction between the receptor and either estrogen or tamoxifen, but mimics the conformation of the activated receptor. Studies in cell lines confirmed ligand-independent, constitutive activity of the mutated receptor. Taken together, these data indicate the mutation D538G as a novel mechanism conferring acquired endocrine resistance. | ||||||||||||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 5.93E-18; Fold-change: 1.85E-01; Z-score: 3.67E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 7.59E-09; Fold-change: 3.83E-01; Z-score: 7.27E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
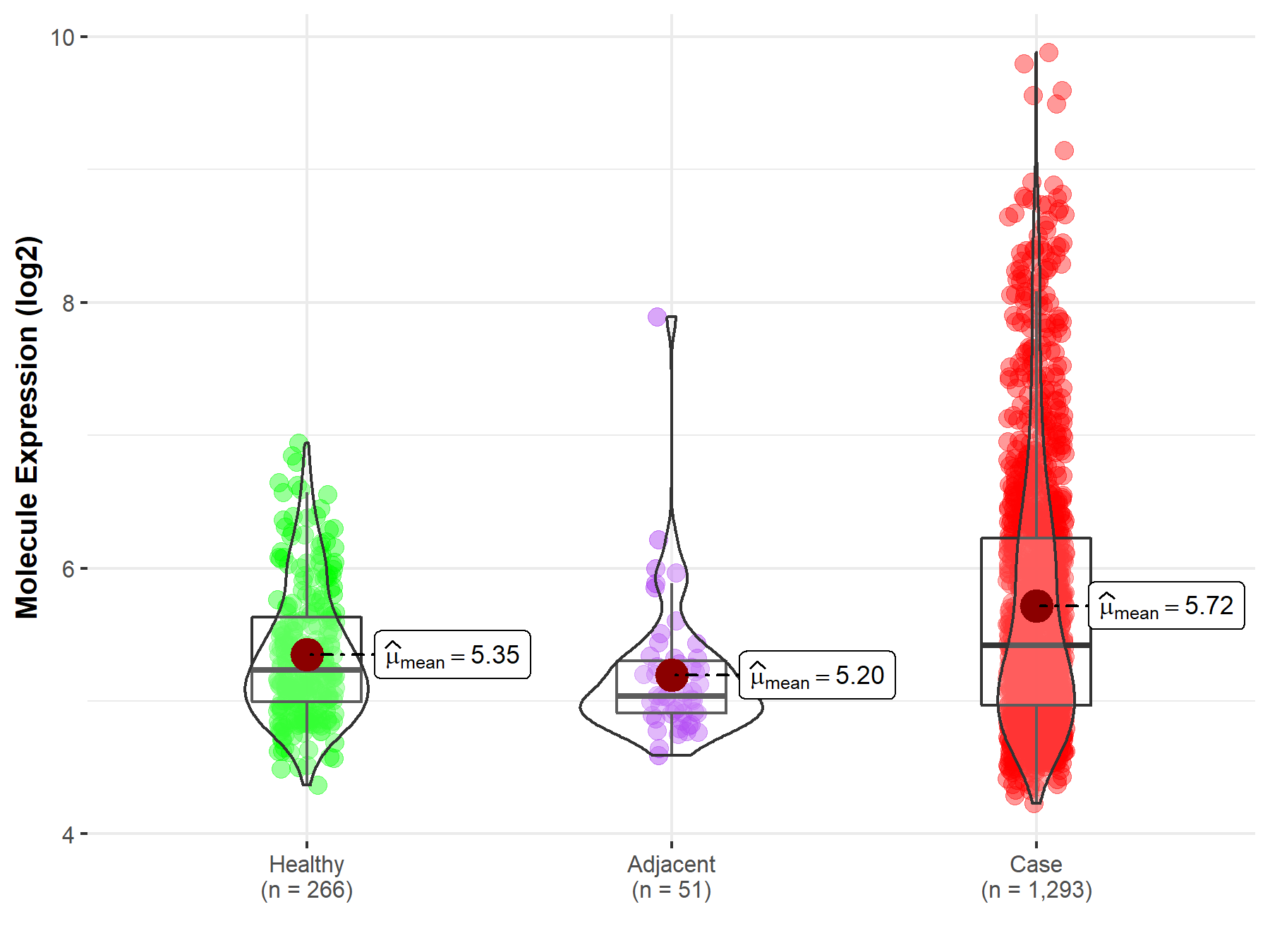
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
