Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00106) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Linezolid
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Linezlid; ZLD; Zyvox; Zyvoxa; Zyvoxam; Zyvoxid; PNU 100766; U 100766; Linezolid & VRC3375; Linezolid [USAN:INN]; PNU-100766; U-100766; Zyvox (TN); Zyvoxam (TN); Zyvoxid (TN); NDA 21-130 Zyvox (linezolid tablets); NDA 21-131 Zyvox for injection (linezolid injection); NDA 21-132 Zyvox oral suspension (linzolid oral suspension); Linezolid (JAN/USAN/INN); PNU-100766, U-100766, Zyvoxid, Zyvoxam, Linezolid; N-((3-(3-fluoro-4-morpholinylphenyl)-2-oxo-5-oxazolidinyl)methyl)acetamide; N-(((S)-3-(3-Fluoro-4-morpholinophenyl)-2-oxo-5-oxazolidinyl)methyl)acetamide; N-[[(5S)-3-(3-fluoro-4-morpholin-4-ylphenyl)-2-oxo-1,3-oxazolidin-5-yl]methyl]acetamide; N-({5S)-3-[3-Fluoro-4-(4-morpholinyl)phenyl]-2-oxo-1,3-oxazolidin-5-yl}methyl)acetamide, N-[[(S)-3-(3-Fluoro-4-morpholinophenyl)-2-oxo-5-oxazolidinyl]methyl]acetamide; (S)-N-[[3-(3-fluoro-4-morpholinylphenyl)-2-oxo-5-oxazolidinyl]methyl]acetamide; 111GE017
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
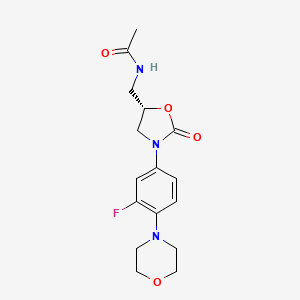
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(7 diseases)
[2]
[3]
[2]
[2]
[2]
[2]
[2]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Validated by in-vivo Model for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[4]
|
||||
| Target | Bacterial 23S ribosomal RNA (Bact 23S rRNA) | NOUNIPROTAC | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C16H20FN3O4
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CC(=O)NC[C@H]1CN(C(=O)O1)C2=CC(=C(C=C2)N3CCOCC3)F
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C16H20FN3O4/c1-11(21)18-9-13-10-20(16(22)24-13)12-2-3-15(14(17)8-12)19-4-6-23-7-5-19/h2-3,8,13H,4-7,9-10H2,1H3,(H,18,21)/t13-/m0/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
TYZROVQLWOKYKF-ZDUSSCGKSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| VARIDT ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Carboxymethylenebutenolidase (CLCD) | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli AS19 | 562 | ||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The Cfr RNA methyltransferase causes multiple resistances to peptidyl transferase inhibitors by methylation of A2503 23S rRNA.clcD codes the same enzyme. | |||
| Key Molecule: Ribosomal RNA large subunit methyltransferase (CFR ) | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli AS19 | 562 | ||
| Escherichia coli TOP10 | 83333 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Cfr confers resistance to antibiotics binding to the peptidyl transferase center on the ribosome.The primary product of the Cfr-mediated methylation is 8-methyladenosine (m8A), a new natural RNA modification that has so far not been seen at sites other than A2503 in 23S rRNA. | |||
| Key Molecule: 23S rRNA (Adenine(2503)-C(8))-methyltransferase ClbA (CIBA) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli AS19 | 562 | ||
| Escherichia coli JW2501-1 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The cfr gene encodes the Cfr methyltransferase that methylates a single adenine in the peptidyl transferase region of bacterial ribosomes.Expression of the genes was induced in Escherichia coli, and MICs for selected antibiotics indicate that the cfr-like genes confer resistance to PhLOPSa (phenicol, lincosamide, oxazolidinone, pleuromutilin, and streptogramin A) antibiotics in the same way as the cfr gene.The Cfr-like proteins ClbA, ClbC, and ClbB confer a resistance pattern similar to that of the Cfr methyltransferase. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: ARE-ABC-F family resistance factor PoxtA (POXTA) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Staphylococcus aureus RN4220 | 1280 | ||
| Enterococcus faecalis JH2-2 | 1351 | |||
| Escherichia coli Mach1 T1R | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth dilution test assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The poxtA gene encodes a protein that is 32% identical to OptrA and exhibits structural features typical of the F lineage of the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) protein superfamily that cause antibiotic resistance by ribosomal protection. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Colibactin polyketide synthase ClbC (CLBC) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli AS19 | 562 | ||
| Escherichia coli JW2501-1 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The cfr gene encodes the Cfr methyltransferase that methylates a single adenine in the peptidyl transferase region of bacterial ribosomes.Expression of the genes was induced in Escherichia coli, and MICs for selected antibiotics indicate that the cfr-like genes confer resistance to PhLOPSa (phenicol, lincosamide, oxazolidinone, pleuromutilin, and streptogramin A) antibiotics in the same way as the cfr gene.The Cfr-like proteins ClbA, ClbC, and ClbB confer a resistance pattern similar to that of the Cfr methyltransferase. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Lincomycin resistance efflux pump (LMRS) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Superficial skin infection by Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B21.3] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli kAM32 | 562 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus OM505 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | LmrS is a multidrug efflux pump of the major facilitator superfamily from staphylococcus aureus. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Lincomycin resistance efflux pump (LMRS) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli kAM32 | 562 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus OM505 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | LmrS is a multidrug efflux pump of the major facilitator superfamily from staphylococcus aureus. | |||
ICD-11: Circulatory system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Lincomycin resistance efflux pump (LMRS) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli kAM32 | 562 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus OM505 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | LmrS is a multidrug efflux pump of the major facilitator superfamily from staphylococcus aureus. | |||
ICD-12: Respiratory system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Lincomycin resistance efflux pump (LMRS) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli kAM32 | 562 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus OM505 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | LmrS is a multidrug efflux pump of the major facilitator superfamily from staphylococcus aureus. | |||
ICD-21: Symptoms/clinical signs/unclassified clinical findings
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Lincomycin resistance efflux pump (LMRS) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli kAM32 | 562 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus OM505 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | LmrS is a multidrug efflux pump of the major facilitator superfamily from staphylococcus aureus. | |||
ICD-22: Injury/poisoning/certain external causes consequences
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Lincomycin resistance efflux pump (LMRS) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli kAM32 | 562 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus OM505 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | LmrS is a multidrug efflux pump of the major facilitator superfamily from staphylococcus aureus. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
