Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00003)
| Name |
ATP-binding cassette sub-family B5 (ABCB5)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
ABCB5 P-gp; P-glycoprotein ABCB5
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
ABCB5
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr7:20615667-20777038[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MENSERAEEMQENYQRNGTAEEQPKLRKEAVGSIEIFRFADGLDITLMILGILASLVNGA
CLPLMPLVLGEMSDNLISGCLVQTNTTNYQNCTQSQEKLNEDMTLLTLYYVGIGVAALIF GYIQISLWIITAARQTKRIRKQFFHSVLAQDIGWFDSCDIGELNTRMTDDIDKISDGIGD KIALLFQNMSTFSIGLAVGLVKGWKLTLVTLSTSPLIMASAAACSRMVISLTSKELSAYS KAGAVAEEVLSSIRTVIAFRAQEKELQRYTQNLKDAKDFGIKRTIASKVSLGAVYFFMNG TYGLAFWYGTSLILNGEPGYTIGTVLAVFFSVIHSSYCIGAAVPHFETFAIARGAAFHIF QVIDKKPSIDNFSTAGYKPESIEGTVEFKNVSFNYPSRPSIKILKGLNLRIKSGETVALV GLNGSGKSTVVQLLQRLYDPDDGFIMVDENDIRALNVRHYRDHIGVVSQEPVLFGTTISN NIKYGRDDVTDEEMERAAREANAYDFIMEFPNKFNTLVGEKGAQMSGGQKQRIAIARALV RNPKILILDEATSALDSESKSAVQAALEKASKGRTTIVVAHRLSTIRSADLIVTLKDGML AEKGAHAELMAKRGLYYSLVMSQDIKKADEQMESMTYSTERKTNSLPLHSVKSIKSDFID KAEESTQSKEISLPEVSLLKILKLNKPEWPFVVLGTLASVLNGTVHPVFSIIFAKIITMF GNNDKTTLKHDAEIYSMIFVILGVICFVSYFMQGLFYGRAGEILTMRLRHLAFKAMLYQD IAWFDEKENSTGGLTTILAIDIAQIQGATGSRIGVLTQNATNMGLSVIISFIYGWEMTFL ILSIAPVLAVTGMIETAAMTGFANKDKQELKHAGKIATEALENIRTIVSLTREKAFEQMY EEMLQTQHRNTSKKAQIIGSCYAFSHAFIYFAYAAGFRFGAYLIQAGRMTPEGMFIVFTA IAYGAMAIGETLVLAPEYSKAKSGAAHLFALLEKKPNIDSRSQEGKKPDTCEGNLEFREV SFFYPCRPDVFILRGLSLSIERGKTVAFVGSSGCGKSTSVQLLQRLYDPVQGQVLFDGVD AKELNVQWLRSQIAIVPQEPVLFNCSIAENIAYGDNSRVVPLDEIKEAANAANIHSFIEG LPEKYNTQVGLKGAQLSGGQKQRLAIARALLQKPKILLLDEATSALDNDSEKVVQHALDK ARTGRTCLVVTHRLSAIQNADLIVVLHNGKIKEQGTHQELLRNRDIYFKLVNAQSVQ Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Function |
Energy-dependent efflux transporter responsible for decreased drug accumulation in multidrug-resistant cells. Specifically present in limbal stem cells, where it plays a key role in corneal development and repair.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
15 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Fluorouracil | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Gastric cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Gastric tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 9.75E-01 Fold-change: -5.59E-04 Z-score: -3.48E-02 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| In Vitro Model | SGC7901 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0520 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-218 may inhibit efflux of ADM and oxaliplatin by down-regulating P-gp expression. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [24] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Fluorouracil | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| Cell viability | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | HCT116 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0291 |
| HCT-8 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2478 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The overexpression of PVT1 increased the mRNA and protein expression levels of multidrug resistance associated protein 1, P glycoprotein, serine/threonine protein kinase mTOR and apoptosis regulator Bcl2. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12.6] | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12.6] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Liver cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Liver tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 4.68E-02 Fold-change: -3.05E-02 Z-score: -2.04E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | HepG2 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0027 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Efflux of rhodamine123 assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Resveratrol can restore the sensitivity of Caco-2 and CEM/ADR5000 cell lines to doxorubicin, through enhancing significantly doxorubicin cytotoxicity. ABC-transporter inhibitors, classified according to their action on ABC-transporters proteins into: 1. Function inhibitors, 2. Expression inhibitors, and 3. Functional and expression inhibitors, which have an ideal characters of ABC-transporters inhibitors. Our results indicate that resveratrol falls into the class 3 inhibitors. | |||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [4] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Ovarian cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Ovarian tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 9.66E-02 Fold-change: -6.09E-02 Z-score: -1.88E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | SkOV3 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0532 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
RT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Synergistic interaction between the MDR mechanisms include ABCT proteins (P-gp, BCRP, and MDR1) and metabolic enzymes of phase I of metabolism mainly CYP3A4, phase II of metabolism mainly GST was observed. In this study, FUC alone and in combination with DOX inhibited the enzyme activities of CYP3A4 and GST and down regulated their genes. We interpret this effect as a consequence of a down-regulation of pregnane X receptor (PXR) gene. FUC overcame MDR by significantly suppressing PXR mediated pathways that regulated the expression of CYP3A and ABCB1 genes in HepG-2 cells. | |||
| Disease Class: Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | [5] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Prostate cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Prostate | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.06E-05 Fold-change: -1.09E-01 Z-score: -4.94E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | DU-145 cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0105 |
| DU-145Nox1 cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0105 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunohistochemistry assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Annexin V staining assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In DU-145Nox1 tumor spheroids, expression of HIF-1alpha as well as P-gp was significantly decreased as compared to DU-145 spheroids, which resulted in an increased retention of the anticancer agent doxorubicin. Pretreatment with the free radical scavengers vitamin E and vitamin C increased the expression of P-gp as well as HIF-1alpha in Nox-1-overexpressing cells, whereas no effect of free radical scavengers was observed on mdr-1 mRNA expression. | |||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [4] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 9.17E-65 Fold-change: -3.13E-01 Z-score: -2.24E+01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
RT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Synergistic interaction between the MDR mechanisms include ABCT proteins (P-gp, BCRP, and MDR1) and metabolic enzymes of phase I of metabolism mainly CYP3A4, phase II of metabolism mainly GST was observed. In this study, FUC alone and in combination with DOX inhibited the enzyme activities of CYP3A4 and GST and down regulated their genes. We interpret this effect as a consequence of a down-regulation of pregnane X receptor (PXR) gene. FUC overcame MDR by significantly suppressing PXR mediated pathways that regulated the expression of CYP3A and ABCB1 genes in HepG-2 cells. | |||
| Disease Class: Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| In Vitro Model | SGC7901 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0520 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-218 may inhibit efflux of ADM and oxaliplatin by down-regulating P-gp expression. | |||
| Disease Class: Colon cancer [ICD-11: 2B90.1] | [22] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Colon cancer [ICD-11: 2B90.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| In Vitro Model | HT29 Cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_A8EZ |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | When miR 522 was overexpressed in the HT29/DOX cells, the protein expression levels of ABCB5 were downregulated. Furthermore, knockdown of ABCB5 significantly increased the growth inhibition rate of the HT29/DOX cells, compared with the control group. These results suggested that miR 522 may affect the sensitivity of colon cancer cell lines to DOX treatment by targeting ABCB5. | |||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [23] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7/DX1 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| Sf9 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0549 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
ATPase assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow cytometric assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Gal-2 was found to inhibit the efflux of the fluorescent P-gp substrate rhodamine 123 in cancer cells that over express P-gp with an IC50 value of approximately 0.8 M. In addition, Gal-2 was found to inhibit the efflux of therapeutic substrates of P-gp, such as doxorubicin, daunomycin and verapamil with IC50 values ranging from 0.5 uM - 2 uM. | |||
| Disease Class: Colorectal carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B91.3] | [13] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Colorectal carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B91.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | CaCo2 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0025 |
| HCT-8 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2478 | |
| NIH-G185 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_L991 | |
| NIH 3T3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0594 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | G185 cells were 27-135 fold more resistant to the cytotoxic drugs doxorubicin, vinblastine, colchicine and paclitaxel than the parental NIH 3T3 cells. Co-administration of TPGS enhanced the cytotoxicity of doxorubicin, vinblastine, paclitaxel, and colchicine in the G185 cells to levels comparable to the parental. | |||
| Disease Class: Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12.6] | [4] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12.6] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | HepG2 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0027 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
RT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Synergistic interaction between the MDR mechanisms include ABCT proteins (P-gp, BCRP, and MDR1) and metabolic enzymes of phase I of metabolism mainly CYP3A4, phase II of metabolism mainly GST was observed. In this study, FUC alone and in combination with DOX inhibited the enzyme activities of CYP3A4 and GST and down regulated their genes. We interpret this effect as a consequence of a down-regulation of pregnane X receptor (PXR) gene. FUC overcame MDR by significantly suppressing PXR mediated pathways that regulated the expression of CYP3A and ABCB1 genes in HepG-2 cells. | |||
| Disease Class: Acute lymphocytic leukemia [ICD-11: 2B33.0] | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Acute lymphocytic leukemia [ICD-11: 2B33.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | CCRF-CEM cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0207 |
| CEM/ADR5000 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_D544 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Efflux of rhodamine123 assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Resveratrol can restore the sensitivity of Caco-2 and CEM/ADR5000 cell lines to doxorubicin, through enhancing significantly doxorubicin cytotoxicity. ABC-transporter inhibitors, classified according to their action on ABC-transporters proteins into: 1. Function inhibitors, 2. Expression inhibitors, and 3. Functional and expression inhibitors, which have an ideal characters of ABC-transporters inhibitors. Our results indicate that resveratrol falls into the class 3 inhibitors. | |||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | CaCo2 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0025 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Efflux of rhodamine123 assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Resveratrol can restore the sensitivity of Caco-2 and CEM/ADR5000 cell lines to doxorubicin, through enhancing significantly doxorubicin cytotoxicity. ABC-transporter inhibitors, classified according to their action on ABC-transporters proteins into: 1. Function inhibitors, 2. Expression inhibitors, and 3. Functional and expression inhibitors, which have an ideal characters of ABC-transporters inhibitors. Our results indicate that resveratrol falls into the class 3 inhibitors. | |||
| Disease Class: Cervical carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C77.1] | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Cervical carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C77.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Hela cells | Cervix uteri | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0030 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Efflux of rhodamine123 assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Resveratrol can restore the sensitivity of Caco-2 and CEM/ADR5000 cell lines to doxorubicin, through enhancing significantly doxorubicin cytotoxicity. ABC-transporter inhibitors, classified according to their action on ABC-transporters proteins into: 1. Function inhibitors, 2. Expression inhibitors, and 3. Functional and expression inhibitors, which have an ideal characters of ABC-transporters inhibitors. Our results indicate that resveratrol falls into the class 3 inhibitors. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [21] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell viability | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Overexpression of miR-298 down-regulated P-gp expression, increasing nuclear accumulation of doxorubicin and cytotoxicity in doxorubicin-resistant breast cancer cells. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E.3] | [3] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Paclitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Oral squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Oral cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Oral tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.68E-03 Fold-change: -3.93E-02 Z-score: -3.14E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | KB-3-1 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2088 |
| KB-8-5 cells | Mouth | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5994 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The continuous administration of low dose 5FU with Taxol significantly inhibited the tumor growth. The treatment overcomes drug resistance in tumors by down-regulating multi-drug resistance transporter protein. | |||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [29] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Paclitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7/PR cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Sulforhodamine B assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Down-regulation of LncRNA RP11-770J1.3 and TMEM25 enhanced the sensitivity of MCF-7/PR cells to paclitaxel, and inhibited the expression of MRP, BCRP and MDR1/P-gp. | |||
| Disease Class: Colorectal carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B91.3] | [13] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Colorectal carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B91.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Paclitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | CaCo2 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0025 |
| HCT-8 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2478 | |
| NIH-G185 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_L991 | |
| NIH 3T3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0594 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | G185 cells were 27-135 fold more resistant to the cytotoxic drugs doxorubicin, vinblastine, colchicine and paclitaxel than the parental NIH 3T3 cells. Co-administration of TPGS enhanced the cytotoxicity of doxorubicin, vinblastine, paclitaxel, and colchicine in the G185 cells to levels comparable to the parental. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Malignant pleural mesothelioma [ICD-11: 2C26.0] | [26] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Malignant pleural mesothelioma [ICD-11: 2C26.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Paclitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 |
| H69 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_8121 | |
| H69AR cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3513 | |
| MSTO-211H cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1430 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | micro-RNA149 confers taxane resistance to malignant mesothelioma cells via upregulation of P-glycoprotein expression. | |||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [27] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Paclitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | SkOV3 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0532 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-181a level in chemoresistant (CR) cancer tissues were significantly higher than in chemosensitive (CS) cancer tissues and in normal tissue. SkOV3/PTX cells had significantly higher expression of miR-181a and N-cadherin than SkOV3 cells. SkOV3 cells had decreased E-cadherin expression and increased N-cadherin expression after enforced miR-181a expression, while SkOV3/PTX cells had increased E-cadherin expression and decreased N-cadherin expression after miR-181a knockdown. SkOV3 cells had increased P-gp expression after enforced miR-181a expression. Following MTT assay and flow cytometry analysis both confirmed that miR-181a overexpression decreased the PTX sensitivity of SkOV3 cells and while miR-181a inhibition increased the sensitivity of SkOV3/PTX cells. miR-181a is an important oncomiR significantly increased in chemoresistant ovarian cancer. Its upregulation is associated with increased level of EMT and decreased cell apoptosis induced by PTX treatment. | |||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [28] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Paclitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| SkBR3 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0033 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-21 inhibitors induced sensitivity of MCF-7/PR and SkBR-3/PR cells to paclitaxel. And miR-21 mimic can increase the expression of MDR1, Bcl-2/Bax and change cell morphology from parental cells to resistant cells. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Merkel cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C34.0] | [6] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Merkel cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C34.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Carboplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | MKL-2 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_D027 |
| WaGa cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_E998 | |
| MKL-1 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2600 | |
| MS-1 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_IQ55 | |
| In Vivo Model | NSG mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR; Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | These findings in patient specimens were consistent with the possibility that ABCB5+ MCC cells are preferentially resistant to treatment with the first-line chemotherapeutic agents, carboplatin and etoposide. | |||
| Disease Class: Merkel cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C34.0] | [6] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Merkel cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C34.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Carboplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | MKL-2 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_D027 |
| WaGa cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_E998 | |
| MKL-1 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2600 | |
| MS-1 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_IQ55 | |
| In Vivo Model | NSG mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR; Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | These findings in patient specimens were consistent with the possibility that ABCB5+ MCC cells are preferentially resistant to treatment with the first-line chemotherapeutic agents, carboplatin and etoposide. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.3] | [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | TE-1 cells | Esophagus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1759 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | TUG1 promoted DDP resistance in TE-1 and TE-1/DDP cells by promoting cell proliferation, suppressing cell apoptosis, and elevating protein expression of the classical multi-drug resistance-related P-gp. | |||
| Disease Class: Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | [8] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| Cell viability | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | SGC7901 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0520 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The IC50 of CDDP in the SGC7901/CDDP-miR-30a mimics group was decreased to 8.56 M (P<0.001 vs. SGC7901/CDDP group), indicating increased chemosensitivity following miR-30a transfectionand the expression of P-gp protein was notably elevated in SGC7901/CDDP cells compared with SGC7901 cells. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Endometrial cancer [ICD-11: 2C76.1] | [9] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Endometrial cancer [ICD-11: 2C76.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell autophagy | Activation | hsa04140 | |
| In Vitro Model | Ishikawa cells | Endometrium | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2529 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Dual-color autophagy reporter assay; CCK8 assay; Flow cytometric analysis | |||
| Mechanism Description | HOTAIR can regulate the cisplatin-resistance ability of human endometrial cancer cells through the regulation of autophagy by increasing Beclin-1, MDR, and P-gp expression. | |||
| Disease Class: Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | [10] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| In Vitro Model | BGC823 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3360 |
| MkN-45 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0434 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR129 reversed cisplatin-resistance through inhibiting the P-gp expression in GC cells. miR129 activated the intrinsic apoptotic pathway via upregulating caspase-9 and caspase-3. | |||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [11] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | A2780 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0134 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The expression of miR-23a in drug-resistance ovarian cancer A2780 cell lines obviously increased; The expression of Runx3 gene could be inhibited by the combination of miR-23a and Runx3 3'UTR domain, which restricted the effect of Runx3 gene on the silence of MDR1 expression; The expression of P-gp in drug-resistance tumor cell was obviously up-regulated, therefore the resistance mechanism was achieved by the classic resistance mechanism; If the expression of miR-23a was inhibited, the regulatory effect decreased, and the expression level of Runx3 increased, and the silent effect of MDR1 expression by Runx3 improved. The expression of P-gp decreased, so the classic resistance mechanism was also inhibited to various degrees, and then the sensitivity of cisplatin to drug-resistance increased. | |||
| Disease Class: Head and neck cancer [ICD-11: 2D42.0] | [12] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Head and neck cancer [ICD-11: 2D42.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | AKT/mTOR signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04150 | |
| Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | ||
| Cell survival | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| IL-1beta/IL-8/CXCR1 signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04060 | ||
| In Vitro Model | GNM cells | Oral | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_WL58 |
| SAS cells | Oral | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1675 | |
| In Vivo Model | BALB/c nude mice xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Oral cancer cells with sh-LINC00963 exhibited lower resistance to cisplatin or 5-FU compared to sh-Luc control. Moreover, the percentage and protein expression level of ABCB5 (ATP-binding cassette, subfamily B (MDR/TAP), member 5) was significantly reduced in both SAS and GNM cells with sh-LINC00963 knockdown. As an ATP-binding cassette transporter, ABCB5 has been known to act as a drug efflux transporter and confer multidrug resistance in diverse malign. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B91.3] | [13] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Colorectal carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B91.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Colchicine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | CaCo2 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0025 |
| HCT-8 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2478 | |
| NIH-G185 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_L991 | |
| NIH 3T3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0594 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | G185 cells were 27-135 fold more resistant to the cytotoxic drugs doxorubicin, vinblastine, colchicine and paclitaxel than the parental NIH 3T3 cells. Co-administration of TPGS enhanced the cytotoxicity of doxorubicin, vinblastine, paclitaxel, and colchicine in the G185 cells to levels comparable to the parental. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [14] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Daunorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7/DX1 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| Sf9 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0549 | |
| HCMEC/D3 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_U985 | |
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow Cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | QT2C2Me2 (8) inhibited P-gp transport of R123, calcein-AM, doxorubicin, BODIPY-FL-verapamil, and [3H]-daunorubicin similarly to QT2C2 (1), with IC50 values in the low micromolar range. These IC50 values were 13- to 75-fold lower than those for the QT monomer. These results indicated that both dimers are effective P-gp inhibitor. | |||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [15] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Daunorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | CR1R12 cells | N.A. | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| NIH-G185 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_L991 | |
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
propidium iodide staining assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In a NIH-G185 cell line presenting an overexpressed amount of the human transporter P-gp, cholesterol caused dramatic inhibition of daunorubicin transport with an IC(50) of about 8 microM yet had no effect on the parent cell line nor rhodamine 123 transport. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Heart failure [ICD-11: BD10.0] | [16] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Heart failure [ICD-11: BD10.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Digoxin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | CaCo2 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0025 |
| LS-180 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0397 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Rhodamine 123 fluorometric assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Chronic use of Saint John's wort (SJW) has been shown to lower the bioavailability for a variety of co-administered drugs including indinavir, cyclosporin, and digoxin. Decreases in intestinal absorption through induction of the multidrug resistance transporter, P-glycoprotein (P-gp), may explain decreased bioavaila. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Heart failure [ICD-11: BD10.0] | [17] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Heart failure [ICD-11: BD10.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Digoxin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | CaCo2 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0025 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Bi-directional transport assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In addition to expression in tumor cells, the ATP-dependent P-gp efflux transporter is localized in a variety of normal tissues including the apical membranes of the epithelial cells lining the luminal surface of the enterocytes in the small intestine/gastrointestinal tract, the biliary canalicular membranes of hepatocytes, the apical luminal membranes of the proximal tubular epithelial cells in the kidney, and the plasma membranes of brain capillary endothelial cells forming the blood-brain barrier (BBB). P-gp in these tissues functions as a drug efflux pump greatly affecting substrate absorption, distribution, and excretion. Loxapine (as the succinate salt) was evaluated as a P-gp substrate, and inhibitor of P-gp mediated transport of digoxin in vitro in Caco-2 cells. Loxapine was not a substrate for P-gp but did exhibit weak-to-moderate inhibition (IC50 = 9.1 uM). | |||
| Disease Class: Heart failure [ICD-11: BD10.0] | [18], [19], [20] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Heart failure [ICD-11: BD10.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Digoxin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | CaCo2 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0025 |
| MDCk-MDR1(Canis lupus familiaris (Dog)) | Kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_S586 | |
| IPS cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qPCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Ussing chamber system assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Digoxin and fexofenadine (each 5 uM) were selected as P-gp substrates, and sulfasalazine and rosuvastatin (each 5 uM) were selected as BCRP substrates to evaluate the efflux transport mediated by P-gp and BCRP. PSC833 (15 uM) and ko143 (15 uM) were used as typical inhibitors of P-gp and BCRP, respectively. Serosal-to-mucosal transport of all the tested P-gp and BCRP substrate drugs was significantly decreased or tended to decrease in the presence of P-gp/BCRP inhibitor cocktail. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Merkel cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C34.0] | [6] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Merkel cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C34.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Etoposide | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | MKL-2 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_D027 |
| WaGa cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_E998 | |
| MKL-1 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2600 | |
| MS-1 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_IQ55 | |
| In Vivo Model | NSG mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR; Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | These findings in patient specimens were consistent with the possibility that ABCB5+ MCC cells are preferentially resistant to treatment with the first-line chemotherapeutic agents, carboplatin and etoposide. | |||
| Disease Class: Merkel cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C34.0] | [6] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Merkel cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C34.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Etoposide | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | MKL-2 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_D027 |
| WaGa cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_E998 | |
| MKL-1 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2600 | |
| MS-1 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_IQ55 | |
| In Vivo Model | NSG mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR; Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | These findings in patient specimens were consistent with the possibility that ABCB5+ MCC cells are preferentially resistant to treatment with the first-line chemotherapeutic agents, carboplatin and etoposide. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Seasonal allergic rhinitis [ICD-11: CA08.0] | [20] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Seasonal allergic rhinitis [ICD-11: CA08.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Fexofenadine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qPCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Ussing chamber system assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Digoxin and fexofenadine (each 5 uM) were selected as P-gp substrates, and sulfasalazine and rosuvastatin (each 5 uM) were selected as BCRP substrates to evaluate the efflux transport mediated by P-gp and BCRP. PSC833 (15 uM) and ko143 (15 uM) were used as typical inhibitors of P-gp and BCRP, respectively. Serosal-to-mucosal transport of all the tested P-gp and BCRP substrate drugs was significantly decreased or tended to decrease in the presence of P-gp/BCRP inhibitor cocktail. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | [16] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Indinavir | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | CaCo2 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0025 |
| LS-180 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0397 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Rhodamine 123 fluorometric assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Chronic use of Saint John's wort (SJW) has been shown to lower the bioavailability for a variety of co-administered drugs including indinavir, cyclosporin, and digoxin. Decreases in intestinal absorption through induction of the multidrug resistance transporter, P-glycoprotein (P-gp), may explain decreased bioavaila. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Diarrhea [ICD-11: DA90.0] | [25] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Diarrhea [ICD-11: DA90.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Loperamide | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Activity | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | CaCo2 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0025 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
In vitro Caco-2 cell permeability experiments assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Respiration assessments assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | P-glycoprotein is an ATP-dependent efflux pump that transports a wide variety of agents out of cells at the blood-brain barrier, thereby restricting CNS penetration of many drugs, including LOP. TPV is a substrate for and an inducer of P-gp activity. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Oxaliplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| In Vitro Model | SGC7901 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0520 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-218 may inhibit efflux of ADM and oxaliplatin by down-regulating P-gp expression. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Arrhythmia [ICD-11: BC9Y.0] | [14] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Arrhythmia [ICD-11: BC9Y.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Verapamil | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7/DX1 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| Sf9 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0549 | |
| HCMEC/D3 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_U985 | |
| In Vivo Model | Male Sprague-Dawley Rats Brain Capillary Isolation | Mus musculus | ||
| Mechanism Description | In P-gp overexpressing cells and in human brain capillary endothelial hCMEC/D3 cells, the dimer with the shortest tether length (QT2C2) was the most potent inhibitor showing >80-fold better inhibition of P-gp-mediated transport than monomeric QT. QT2C2Me2 increased the accumulation of the P-gp substrate verapamil in rat brain in situ three times more than QT. | |||
| Disease Class: Cerebrovascular disease [ICD-11: 8B22.0] | [14] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Cerebrovascular disease [ICD-11: 8B22.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Verapamil | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7/DX1 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| Sf9 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0549 | |
| HCMEC/D3 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_U985 | |
| In Vivo Model | Male Sprague-Dawley Rats Brain Capillary Isolation | Mus musculus | ||
| Mechanism Description | In P-gp overexpressing cells and in human brain capillary endothelial hCMEC/D3 cells, the dimer with the shortest tether length (QT2C2) was the most potent inhibitor showing >80-fold better inhibition of P-gp-mediated transport than monomeric QT. QT2C2Me2 increased the accumulation of the P-gp substrate verapamil in rat brain in situ three times more than QT. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B91.3] | [13] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Colorectal carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B91.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Vinblastine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | CaCo2 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0025 |
| HCT-8 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2478 | |
| NIH-G185 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_L991 | |
| NIH 3T3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0594 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | G185 cells were 27-135 fold more resistant to the cytotoxic drugs doxorubicin, vinblastine, colchicine and paclitaxel than the parental NIH 3T3 cells. Co-administration of TPGS enhanced the cytotoxicity of doxorubicin, vinblastine, paclitaxel, and colchicine in the G185 cells to levels comparable to the parental. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 01

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | White matter | |
| The Specified Disease | HIV infection | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.16E-02; Fold-change: -3.89E-02; Z-score: -1.76E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
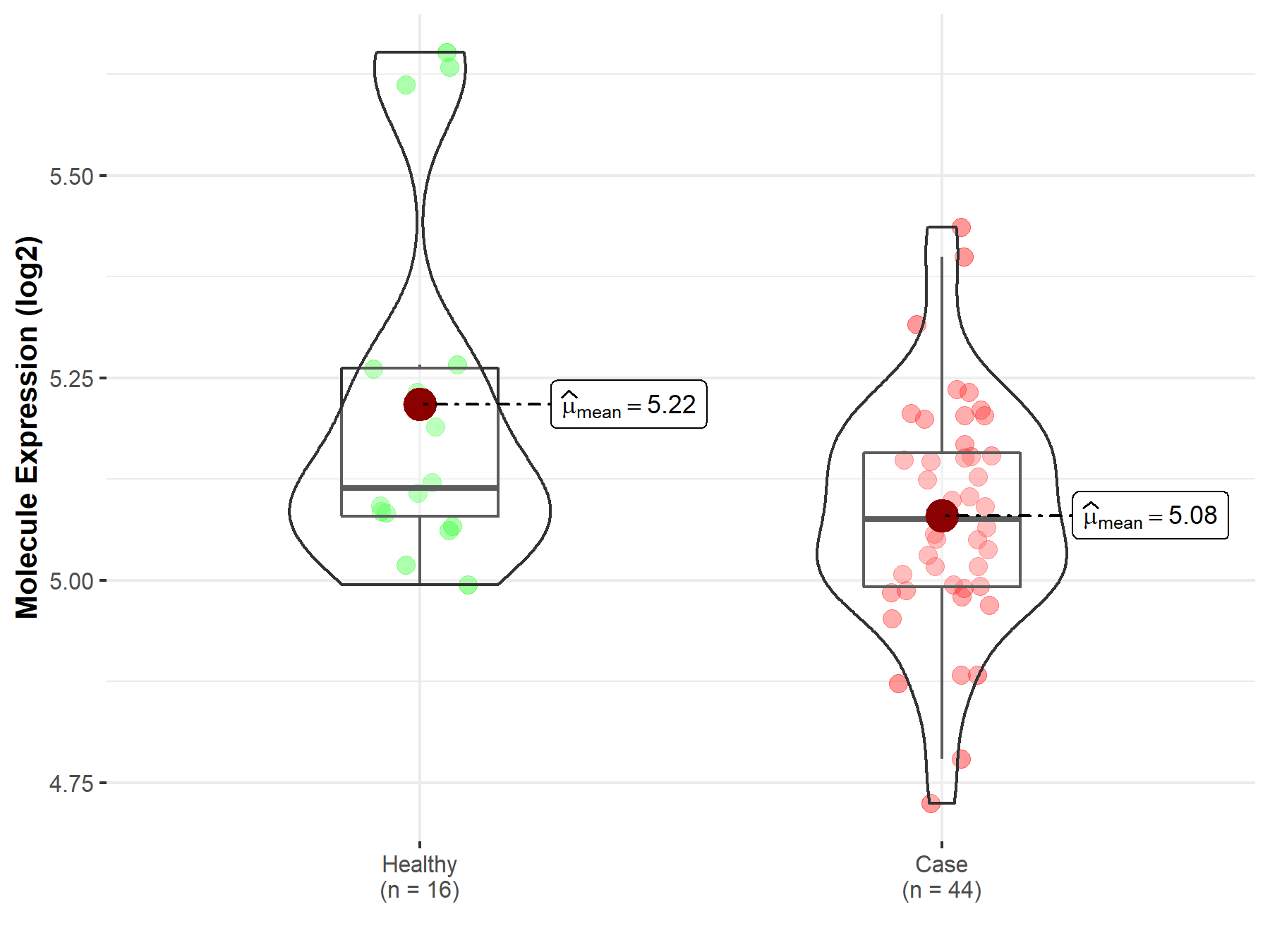
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Oral tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.68E-03; Fold-change: -2.21E-01; Z-score: -1.43E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 4.05E-01; Fold-change: -7.09E-02; Z-score: -3.35E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
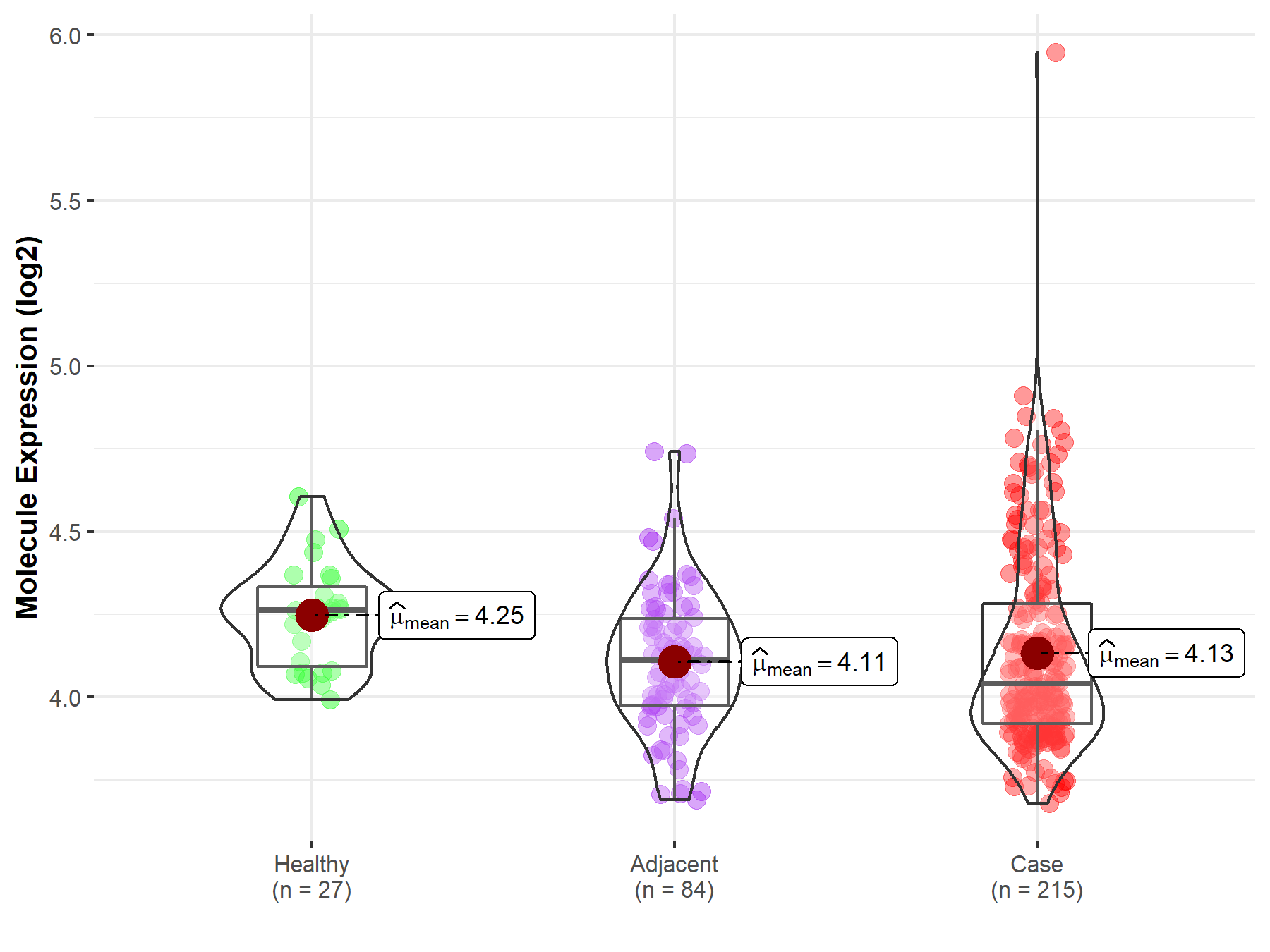
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Esophagus | |
| The Specified Disease | Esophageal cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 6.59E-01; Fold-change: 2.77E-02; Z-score: 3.28E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
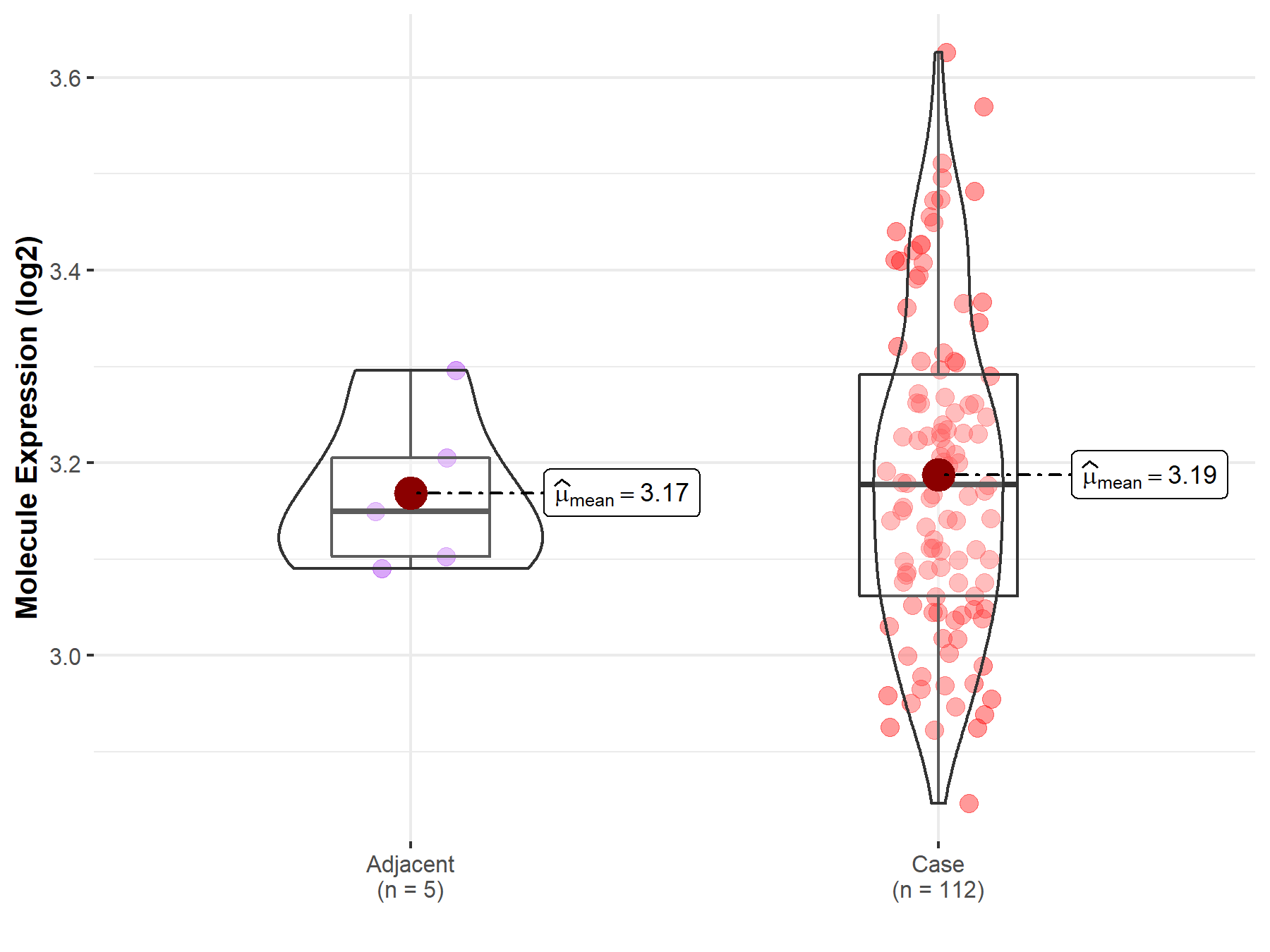
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Gastric tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Gastric cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 9.75E-01; Fold-change: -5.81E-02; Z-score: -1.00E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 2.15E-02; Fold-change: 1.42E-01; Z-score: 6.76E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Colon | |
| The Specified Disease | Colon cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.65E-02; Fold-change: 4.86E-02; Z-score: 2.73E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 7.97E-02; Fold-change: -1.85E-02; Z-score: -8.03E-02 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
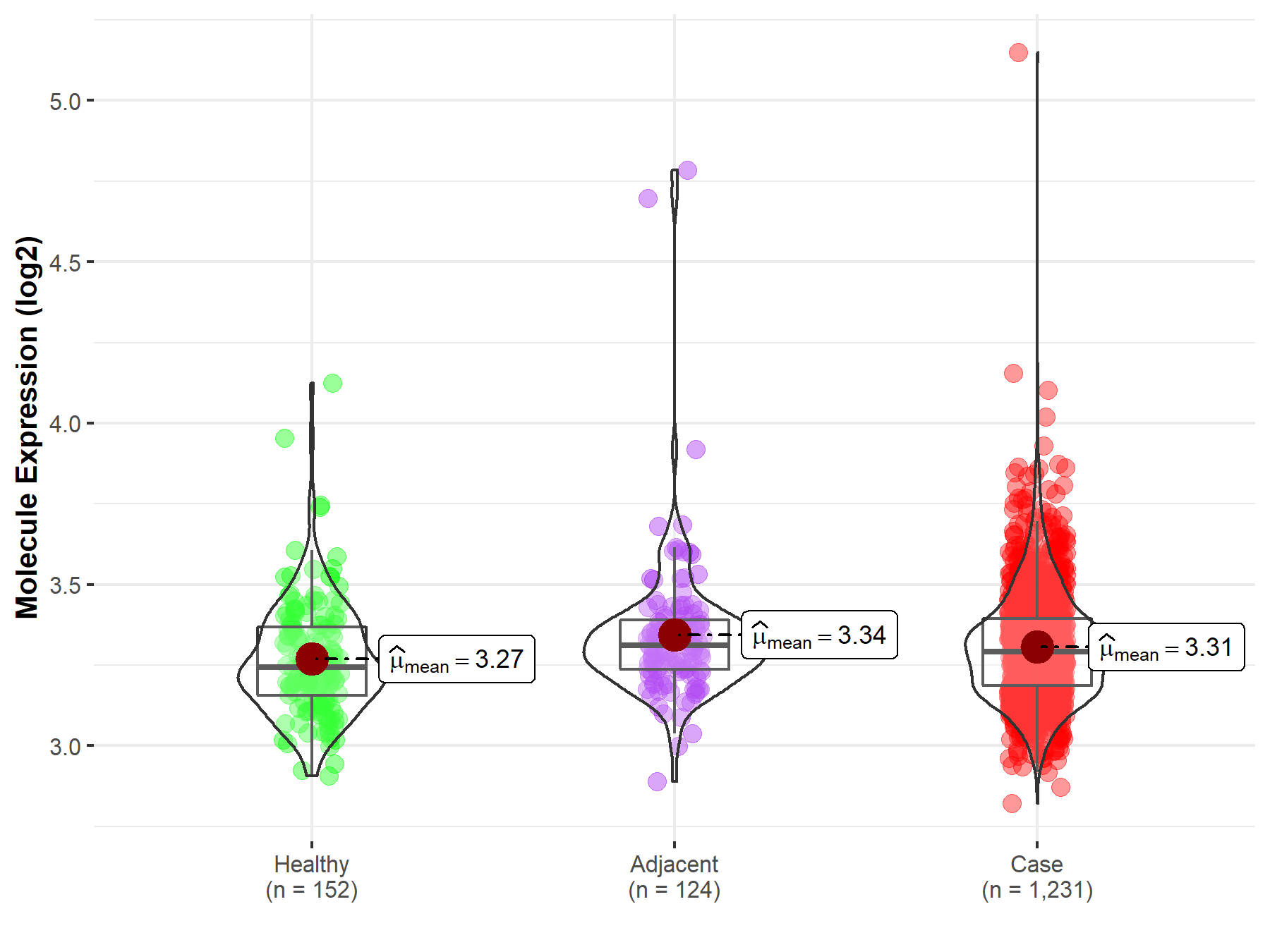
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Liver | |
| The Specified Disease | Liver cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 4.68E-02; Fold-change: -3.20E-02; Z-score: -1.58E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 6.13E-01; Fold-change: -5.25E-03; Z-score: -3.20E-02 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Other Disease Section | p-value: 8.57E-01; Fold-change: 1.94E-02; Z-score: 1.23E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
Molecule expression in tissue other than the diseased tissue of patients
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
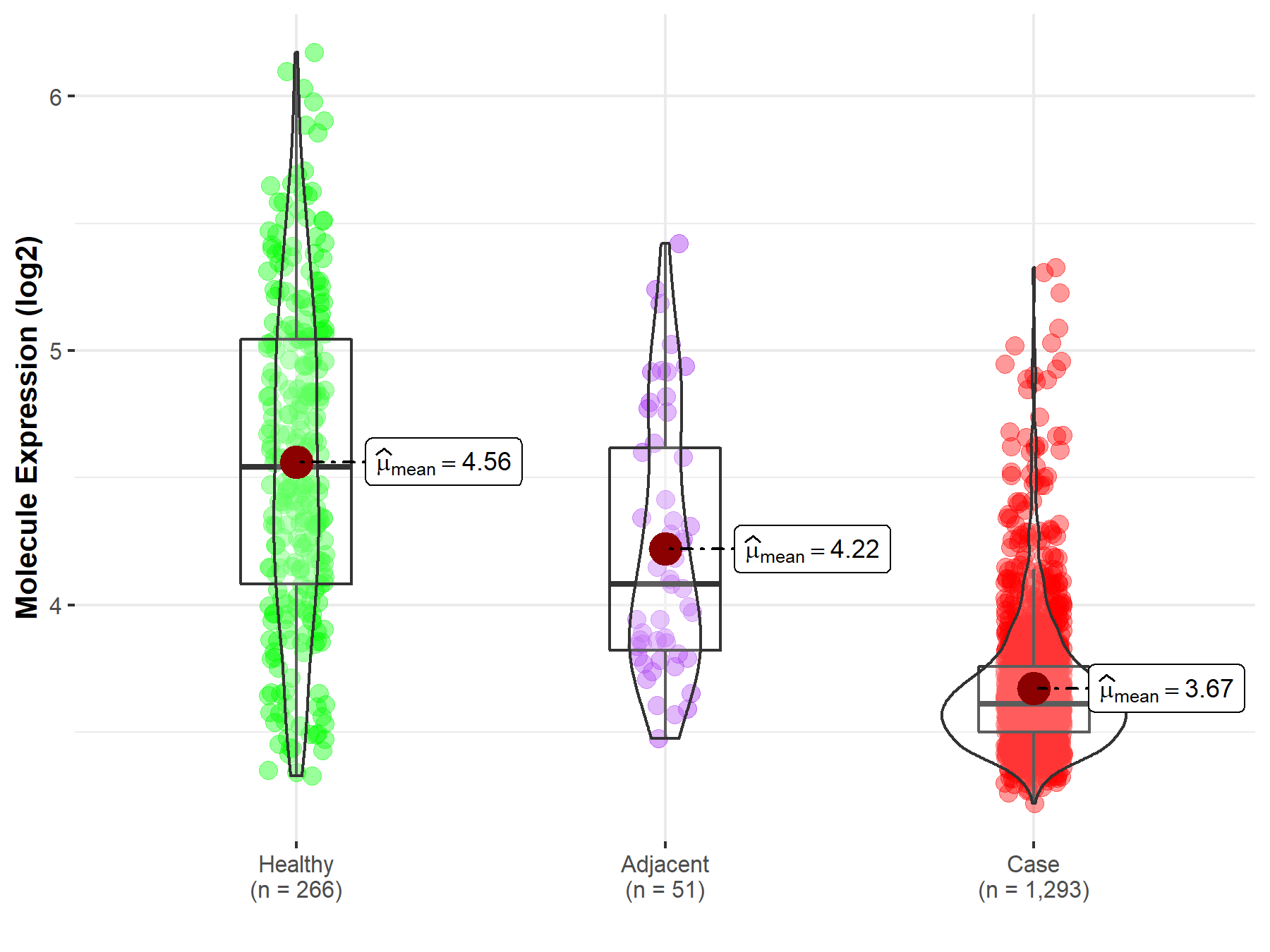
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 9.17E-65; Fold-change: -9.31E-01; Z-score: -1.46E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 4.41E-10; Fold-change: -4.72E-01; Z-score: -9.33E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Ovary | |
| The Specified Disease | Ovarian cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 9.66E-02; Fold-change: -1.03E-01; Z-score: -4.35E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 6.42E-01; Fold-change: -3.62E-02; Z-score: -1.91E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
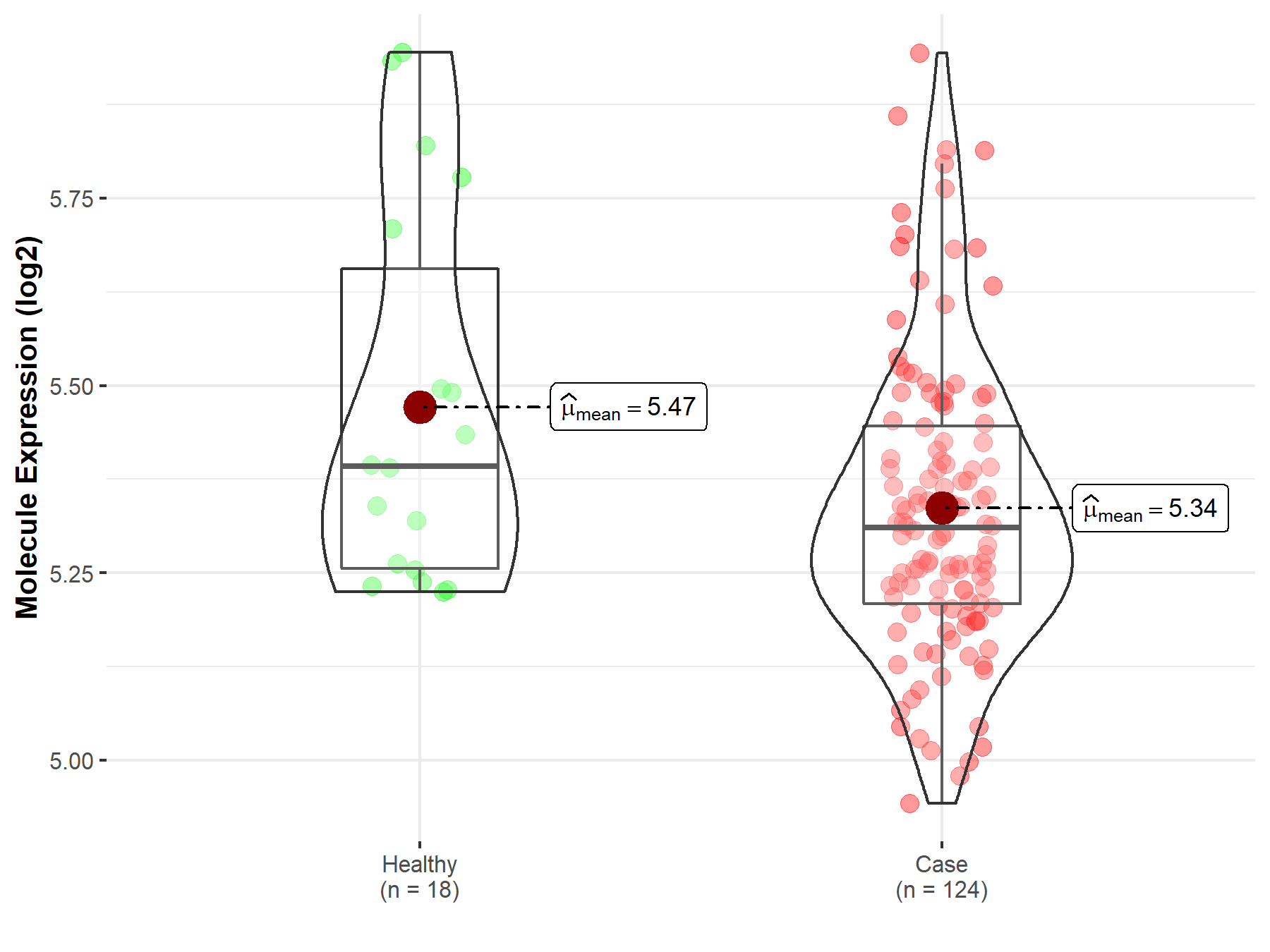
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Cervix uteri | |
| The Specified Disease | Cervical cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 4.19E-02; Fold-change: -8.22E-02; Z-score: -3.25E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
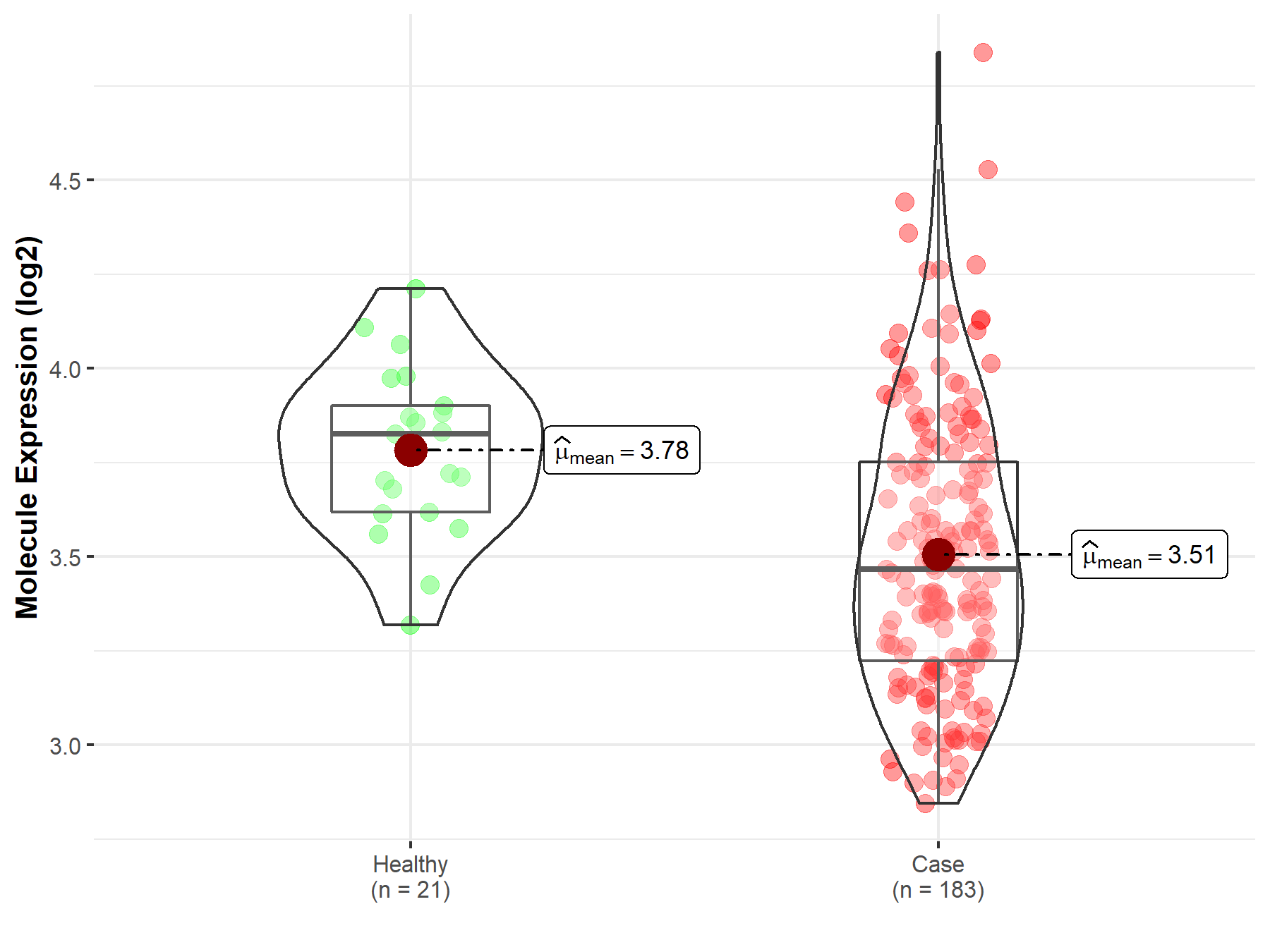
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Prostate | |
| The Specified Disease | Prostate cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.06E-05; Fold-change: -3.59E-01; Z-score: -1.60E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Head and neck tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Head and neck cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 4.39E-01; Fold-change: 6.00E-03; Z-score: 4.62E-02 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
