Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00150)
| Name |
GTPase KRas (KRAS)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
K-Ras 2; Ki-Ras; c-K-ras; c-Ki-ras; KRAS2; RASK2
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
KRAS
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr12:25205246-25250936[-]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MTEYKLVVVGAGGVGKSALTIQLIQNHFVDEYDPTIEDSYRKQVVIDGETCLLDILDTAG
QEEYSAMRDQYMRTGEGFLCVFAINNTKSFEDIHHYREQIKRVKDSEDVPMVLVGNKCDL PSRTVDTKQAQDLARSYGIPFIETSAKTRQRVEDAFYTLVREIRQYRLKKISKEEKTPGC VKIKKCIIM Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Ras proteins bind GDP/GTP and possess intrinsic GTPase activity. Plays an important role in the regulation of cell proliferation. Plays a role in promoting oncogenic events by inducing transcriptional silencing of tumor suppressor genes (TSGs) in colorectal cancer (CRC) cells in a ZNF304-dependent manner.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
12 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.81E-06 Fold-change: -1.95E-01 Z-score: -4.85E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell viability | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| MAPK/RAS signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04010 | ||
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 |
| NCI-H441 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1561 | |
| In Vivo Model | BALB/c nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The overexpression of miR-202 was found to inhibit the Ras/MAPk pathway by targeting the kRas gene. | |||
| Disease Class: Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | [3] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.42E-01 Fold-change: -9.41E-03 Z-score: -1.47E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| PI3K/AKT signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 |
| SPC-A1 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6955 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-217 suppresses tumour development in lung cancer by targeting kRAS and enhances cell sensitivity to cisplatin. | |||
| Disease Class: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6B.0] | [10] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6B.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | HNE1 cells | Nasopharynx | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0308 |
| CNE1 cells | Throat | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6888 | |
| NP69 cells | Nasopharynx | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_F755 | |
| SUNE-1 cells | Nasopharynx | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6946 | |
| C666 cells | Nasopharyngeal | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_M597 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | microRNA-19b Promotes Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma More Sensitive to Cisplatin by Suppressing kRAS. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Acute myelocytic leukemia | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Bone marrow | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 9.27E-01 Fold-change: -7.42E-04 Z-score: -9.16E-02 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| In Vitro Model | HL60 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0002 |
| K562 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0004 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Dual luciferase reporter assay; Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Flow cytometric analysis | |||
| Mechanism Description | microRNA 217 inhibits cell proliferation and enhances chemosensitivity to doxorubicin in acute myeloid leukemia by targeting kRAS. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [4], [5], [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Cetuximab | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12V |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.98 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.96 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
-
0
|
S
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
V
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
S
S
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
D
D
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
K
H
H
K
K
E
E
K
K
170
|
M
M
S
S
K
K
D
D
G
G
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
180
|
K
K
S
S
K
K
T
T
K
K
C
C
V
V
I
I
M
M
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | EGFR/RAS signaling pathway | Activation | hsa01521 | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | LIM1215 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2574 | |||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Liquid biopsy assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Mechanisms of resistance to EGFR blockade include the emergence of kRAS, NRAS and EGFR extracellular domain mutations as well as HER2/MET alterations (27780856). kRAS and EGFR ectodomain-acquired mutations in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) have been correlated with acquired resistance to anti-EGFR monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Metastatic colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2D85.0] | [7] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Metastatic colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2D85.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Cetuximab | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61H |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.31 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.20 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
C
G
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
S
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
H
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
L
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
S
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
D
D
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
K
H
H
K
K
E
E
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | DiFi cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6895 | |||||||||
| DiFi-R cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_A2BW | ||||||||||
| Lim1215-R cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1736 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
FISH analysis; Sanger sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell viability assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Nevertheless, our functional analysis in cell models show that kRAS mutations are causally responsible for acquired resistance to cetuximab. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Cetuximab | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61H |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.31 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.20 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
C
G
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
S
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
H
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
L
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
S
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
D
D
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
K
H
H
K
K
E
E
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Liquid biopsy assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Mechanisms of resistance to EGFR blockade include the emergence of kRAS, NRAS and EGFR extracellular domain mutations as well as HER2/MET alterations. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Cetuximab | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12D |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.40 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
G
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
D
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
R
V
V
D
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
Q
H
Y
K
R
E
L
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Liquid biopsy assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Mechanisms of resistance to EGFR blockade include the emergence of kRAS, NRAS and EGFR extracellular domain mutations as well as HER2/MET alterations. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Cetuximab | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Structural variation | Amplification |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Liquid biopsy assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Mechanisms of resistance to EGFR blockade include the emergence of kRAS, NRAS and EGFR extracellular domain mutations as well as HER2/MET alterations. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Metastatic colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2D85.0] | [8] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Metastatic colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2D85.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Cetuximab | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | . |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Mutations in kRAS, NRAS, and BRAF and amplification of ERBB2 and MET drive primary (de novo) resistance to anti-EGFR treatment. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [9] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Cetuximab | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | Mutations in codons 12, 13 and 61 |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | RAS/RAF/Mek/ERK signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04010 | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Colorectal cancer cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
High throughout experiment assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Circulating tumor DNA analysis | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The identification of kRAS mutations as a cause for intrinsic resistance of colorectal cancers also contributed to the identification of a mechanism for the acquired resistance. Establishment and analysis of cetuximabresistant colorectal cancer cell lines revealed that the resistant variants harbored kRAS point mutations or amplification, and the findings were confirmed in clinical specimens. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [11] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Dabrafenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61H |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.31 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.20 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
C
G
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
S
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
H
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
L
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
S
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
D
D
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
K
H
H
K
K
E
E
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | MAPK signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04010 | ||||||||||
| PI3K/AKT/PTEN signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | |||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Melanoma cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-exome sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Progression-free and overall survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | K-RAS mutations (G12C, G12R, Q61H) have been detected in resistant melanoma cell lines and in up to 7% of BRAF inhibitor-treated patients, although kRAS mutations are far less common in primary melanomas than NRAS mutations. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [11] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Dabrafenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12R |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.40 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.50 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
G
G
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
R
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
D
D
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
K
H
H
K
K
E
E
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | MAPK signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04010 | ||||||||||
| PI3K/AKT/PTEN signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | |||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Melanoma cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-exome sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Progression-free and overall survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | K-RAS mutations (G12C, G12R, Q61H) have been detected in resistant melanoma cell lines and in up to 7% of BRAF inhibitor-treated patients, although kRAS mutations are far less common in primary melanomas than NRAS mutations. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [11] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Dabrafenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12C |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.40 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.60 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
G
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
C
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
R
V
V
D
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
Q
H
Y
K
R
E
L
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | MAPK signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04010 | ||||||||||
| PI3K/AKT/PTEN signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | |||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Melanoma cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-exome sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Progression-free and overall survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | K-RAS mutations (G12C, G12R, Q61H) have been detected in resistant melanoma cell lines and in up to 7% of BRAF inhibitor-treated patients, although kRAS mutations are far less common in primary melanomas than NRAS mutations. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | [12] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Docetaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| EGFR/RAS/MAPK signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa01521 | ||
| In Vitro Model | DU-145 cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0105 |
| PC3 cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0035 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-143 plays an important role in prostate cancer proliferation, migration and chemosensitivity by suppressing kRAS and subsequent inactivation of MAPk pathway. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [13] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Fluorouracil | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | HCT116 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0291 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT asssay; Innocyte invasion assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | microRNA-224 was differentially expressed in dysplastic colorectal disease and in isogeneic kRAS WT and mutant HCT116 cells. Antagomir-mediated miR-224 silencing in HCT116 kRAS WT cells phenocopied kRAS mutation, increased kRAS activity and ERk and AkT phosphorylation. 5-FU chemosensitivity was significantly increased in miR-224 knockdown cells, and in NIH3T3 cells expressing kRAS and BRAF mutant proteins. Bioinformatics analysis of predicted miR-224 target genes predicted altered cell proliferation, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) phenotypes that were experimentally confirmed in miR-224 knockdown cells. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [14] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | LY2835219 | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.A146V (c.437C>T) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.70 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.18 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
G
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
G
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
V
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
R
G
V
V
E
D
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
Q
K
Y
H
R
K
L
E
K
K
170
|
K
M
I
S
S
K
K
D
E
G
E
K
K
K
T
K
P
K
G
K
180
|
C
K
V
S
K
K
I
T
K
K
K
S
C
-
I
-
I
-
M
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Rapid formalin-fixed assay; Paraffin-embedded sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell counting assay | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Acute lymphocytic leukemia [ICD-11: 2B33.0] | [15] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Acute lymphocytic leukemia [ICD-11: 2B33.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Methotrexate | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61H |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.31 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.20 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
C
G
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
S
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
H
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
L
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
S
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
D
D
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
K
H
H
K
K
E
E
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Mouse model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-exome sequencing assay; Whole-genome sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow cytometric analysis assay; MTT assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Notably, drug response a.lyses in isogenic kras wild-type and kras G12D cells showed increased resistance to methotrexate (P < 0.001) upon oncogenic kras activation. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Acute lymphocytic leukemia [ICD-11: 2B33.0] | [15] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Acute lymphocytic leukemia [ICD-11: 2B33.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Methotrexate | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12D |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.40 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
G
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
D
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
R
V
V
D
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
Q
H
Y
K
R
E
L
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Mouse model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-exome sequencing assay; Whole-genome sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow cytometric analysis assay; MTT assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Notably, drug response a.lyses in isogenic kras wild-type and kras G12D cells showed increased resistance to methotrexate (P < 0.001) upon oncogenic kras activation. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [16] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Palbociclib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12V (c.35G>T) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.98 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.96 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
-
0
|
S
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
V
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
S
S
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
D
D
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
K
H
H
K
K
E
E
K
K
170
|
M
M
S
S
K
K
D
D
G
G
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
180
|
K
K
S
S
K
K
T
T
K
K
C
C
V
V
I
I
M
M
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Human NSCLC cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.G12V (c.35G>T) in gene KRAS cause the sensitivity of Palbociclib by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Panitumumab | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12V |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.98 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.96 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
-
0
|
S
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
V
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
S
S
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
D
D
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
K
H
H
K
K
E
E
K
K
170
|
M
M
S
S
K
K
D
D
G
G
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
180
|
K
K
S
S
K
K
T
T
K
K
C
C
V
V
I
I
M
M
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Liquid biopsy assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Mechanisms of resistance to EGFR blockade include the emergence of kRAS, NRAS and EGFR extracellular domain mutations as well as HER2/MET alterations. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [17], [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Panitumumab | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12V |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.98 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.96 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
-
0
|
S
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
V
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
S
S
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
D
D
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
K
H
H
K
K
E
E
K
K
170
|
M
M
S
S
K
K
D
D
G
G
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
180
|
K
K
S
S
K
K
T
T
K
K
C
C
V
V
I
I
M
M
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Ligation assay; BEAMing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Progression-free survival analysis; Overall survival analysis | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Our study indicates that the resistance mutations in kRAS and other genes were highly likely to be present in a clo.l subpopulation within the tumors prior to the initiation of panitumumab therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Panitumumab | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61H |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.31 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.20 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
C
G
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
S
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
H
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
L
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
S
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
D
D
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
K
H
H
K
K
E
E
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Liquid biopsy assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Mechanisms of resistance to EGFR blockade include the emergence of kRAS, NRAS and EGFR extracellular domain mutations as well as HER2/MET alterations. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [17] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Panitumumab | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12R |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.40 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.50 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
G
G
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
R
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
D
D
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
K
H
H
K
K
E
E
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Ligation assay; BEAMing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Progression-free survival analysis; Overall survival analysis | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Our study indicates that the resistance mutations in kRAS and other genes were highly likely to be present in a clo.l subpopulation within the tumors prior to the initiation of panitumumab therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [17] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Panitumumab | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12A |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.40 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.45 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
G
S
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
A
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
D
D
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
K
H
H
K
K
E
E
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Ligation assay; BEAMing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Progression-free survival analysis; Overall survival analysis | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Our study indicates that the resistance mutations in kRAS and other genes were highly likely to be present in a clo.l subpopulation within the tumors prior to the initiation of panitumumab therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [17] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Panitumumab | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12C |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.40 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.60 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
G
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
C
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
R
V
V
D
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
Q
H
Y
K
R
E
L
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Ligation assay; BEAMing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Progression-free survival analysis; Overall survival analysis | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Our study indicates that the resistance mutations in kRAS and other genes were highly likely to be present in a clo.l subpopulation within the tumors prior to the initiation of panitumumab therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [17] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Panitumumab | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12S |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.24 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.71 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
S
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
D
D
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
K
H
H
K
K
E
E
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Ligation assay; BEAMing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Progression-free survival analysis; Overall survival analysis | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Our study indicates that the resistance mutations in kRAS and other genes were highly likely to be present in a clo.l subpopulation within the tumors prior to the initiation of panitumumab therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Panitumumab | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12D |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.40 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
G
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
D
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
R
V
V
D
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
Q
H
Y
K
R
E
L
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Liquid biopsy assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Mechanisms of resistance to EGFR blockade include the emergence of kRAS, NRAS and EGFR extracellular domain mutations as well as HER2/MET alterations. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [17] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Panitumumab | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12D |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.40 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
G
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
D
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
R
V
V
D
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
Q
H
Y
K
R
E
L
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Ligation assay; BEAMing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Progression-free survival analysis; Overall survival analysis | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Our study indicates that the resistance mutations in kRAS and other genes were highly likely to be present in a clo.l subpopulation within the tumors prior to the initiation of panitumumab therapy. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [18] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Panitumumab | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | . |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | EGFR/RAS signaling pathway | Activation | hsa01521 | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | LIM1215 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2574 | |||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Liquid biopsies assay; Functional analyses of cell populations assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Acquired resistance to EGFR blockade is driven by the emergence of kRAS/NRAS mutations or the development of EGFR extracellular domain (ECD) variants, which impair antibody binding. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Panitumumab | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Structural variation | Amplification |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Liquid biopsy assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Mechanisms of resistance to EGFR blockade include the emergence of kRAS, NRAS and EGFR extracellular domain mutations as well as HER2/MET alterations. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [19] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Regorafenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12V (c.35G>T) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.98 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.96 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
-
0
|
S
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
V
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
S
S
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
D
D
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
K
H
H
K
K
E
E
K
K
170
|
M
M
S
S
K
K
D
D
G
G
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
180
|
K
K
S
S
K
K
T
T
K
K
C
C
V
V
I
I
M
M
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | KRAS cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |||||||||
| G12C cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
KRAS testing/KRAS quantification assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [19] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Regorafenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12R (c.34G>C) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.40 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.50 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
G
G
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
R
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
D
D
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
K
H
H
K
K
E
E
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | KRAS cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |||||||||
| G12C cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
KRAS testing/KRAS quantification assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [19] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Regorafenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12A (c.35G>C) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.40 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.45 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
G
S
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
A
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
D
D
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
K
H
H
K
K
E
E
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | KRAS cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |||||||||
| G12C cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
KRAS testing/KRAS quantification assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [19] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Regorafenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12C (c.34G>T) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.40 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.60 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
G
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
C
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
R
V
V
D
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
Q
H
Y
K
R
E
L
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | KRAS cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |||||||||
| G12C cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
KRAS testing/KRAS quantification assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [19] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Regorafenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12S (c.34G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.24 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.71 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
S
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
D
D
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
K
H
H
K
K
E
E
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | KRAS cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |||||||||
| G12C cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
KRAS testing/KRAS quantification assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [19] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Regorafenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12D (c.35G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.40 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
G
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
D
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
R
V
V
D
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
Q
H
Y
K
R
E
L
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | KRAS cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |||||||||
| G12C cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
KRAS testing/KRAS quantification assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [11] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Vemurafenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61H |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.31 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.20 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
C
G
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
S
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
H
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
L
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
S
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
D
D
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
K
H
H
K
K
E
E
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | MAPK signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04010 | ||||||||||
| PI3K/AKT/PTEN signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | |||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Melanoma cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-exome sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Progression-free and overall survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | K-RAS mutations (G12C, G12R, Q61H) have been detected in resistant melanoma cell lines and in up to 7% of BRAF inhibitor-treated patients, although kRAS mutations are far less common in primary melanomas than NRAS mutations. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [11] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Vemurafenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12R |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.40 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.50 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
G
G
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
R
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
D
D
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
K
H
H
K
K
E
E
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | MAPK signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04010 | ||||||||||
| PI3K/AKT/PTEN signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | |||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Melanoma cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-exome sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Progression-free and overall survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | K-RAS mutations (G12C, G12R, Q61H) have been detected in resistant melanoma cell lines and in up to 7% of BRAF inhibitor-treated patients, although kRAS mutations are far less common in primary melanomas than NRAS mutations. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [11] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Vemurafenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12C |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.40 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.60 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
G
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
C
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
R
V
V
D
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
Q
H
Y
K
R
E
L
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | MAPK signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04010 | ||||||||||
| PI3K/AKT/PTEN signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | |||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Melanoma cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-exome sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Progression-free and overall survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | K-RAS mutations (G12C, G12R, Q61H) have been detected in resistant melanoma cell lines and in up to 7% of BRAF inhibitor-treated patients, although kRAS mutations are far less common in primary melanomas than NRAS mutations. | ||||||||||||
Clinical Trial Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C10.0] | [20] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C10.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | MK-2206 | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12D (c.35G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.40 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
G
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
D
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
R
V
V
D
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
Q
H
Y
K
R
E
L
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.G12D (c.35G>A) in gene KRAS cause the sensitivity of MK-2206 by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | ||||||||||||
Discontinued Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [21], [22] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Rociletinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.A146T |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.70 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.18 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
G
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
G
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
T
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
R
G
V
V
E
D
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
Q
K
Y
H
R
K
L
E
K
K
170
|
K
M
I
S
S
K
K
D
E
G
E
K
K
K
T
K
P
K
G
K
180
|
C
K
V
S
K
K
I
T
K
K
K
S
C
-
I
-
I
-
M
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Circulating tumour DNA analysis; Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Progression-free survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Similarly,resistance to the third-generation inhibitor rociletinib may not only be mediated by EGFR (L798I, C797S) mutations, but also by alterations of MET, PIk3CA, ERRB2, and kRAS, and by the negative selection of T790M-mutant subclones. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [21], [22] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Rociletinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q61H |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.31 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.20 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
C
G
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
S
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
H
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
L
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
S
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
D
D
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
K
H
H
K
K
E
E
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Circulating tumour DNA analysis; Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Progression-free survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Similarly,resistance to the third-generation inhibitor rociletinib may not only be mediated by EGFR (L798I, C797S) mutations, but also by alterations of MET, PIk3CA, ERRB2, and kRAS, and by the negative selection of T790M-mutant subclones. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [21], [22] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Rociletinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12A |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.40 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.45 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
G
S
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
A
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
D
D
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
K
H
H
K
K
E
E
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Circulating tumour DNA analysis; Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Progression-free survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Similarly,resistance to the third-generation inhibitor rociletinib may not only be mediated by EGFR (L798I, C797S) mutations, but also by alterations of MET, PIk3CA, ERRB2, and kRAS, and by the negative selection of T790M-mutant subclones. | ||||||||||||
Preclinical Drug(s)
2 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [23] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Dactolisib/Selumetinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.A146T (c.436G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.70 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.18 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
G
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
G
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
T
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
R
G
V
V
E
D
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
Q
K
Y
H
R
K
L
E
K
K
170
|
K
M
I
S
S
K
K
D
E
G
E
K
K
K
T
K
P
K
G
K
180
|
C
K
V
S
K
K
I
T
K
K
K
S
C
-
I
-
I
-
M
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Liver | N.A. | |||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Female nonobese diabetic/severe combined immunodeficient (NOD/SCID) mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunohistochemistry assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.A146T (c.436G>A) in gene KRAS cause the sensitivity of Dactolisib + Selumetinib by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [24] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Dactolisib/Selumetinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12D (c.35G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.40 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
G
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
D
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
R
V
V
D
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
Q
H
Y
K
R
E
L
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.G12D (c.35G>A) in gene KRAS cause the sensitivity of Dactolisib + Selumetinib by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [23] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Dactolisib/Selumetinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G13D (c.38G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.01 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.40 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
-
G
-
G
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
G
G
D
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
R
V
V
D
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
Q
H
Y
K
R
E
L
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Liver | N.A. | |||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Female nonobese diabetic/severe combined immunodeficient (NOD/SCID) mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunohistochemistry assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.G13D (c.38G>A) in gene KRAS cause the sensitivity of Dactolisib + Selumetinib by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [23] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Selumetinib/Dactolisib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12V (c.35G>T) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.98 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.96 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
-
0
|
S
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
V
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
S
S
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
D
D
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
K
H
H
K
K
E
E
K
K
170
|
M
M
S
S
K
K
D
D
G
G
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
180
|
K
K
S
S
K
K
T
T
K
K
C
C
V
V
I
I
M
M
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Liver | N.A. | |||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Female nonobese diabetic/severe combined immunodeficient (NOD/SCID) mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunohistochemistry assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.G12V (c.35G>T) in gene KRAS cause the sensitivity of Selumetinib + Dactolisib by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [23] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Selumetinib/Dactolisib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.A146V (c.437C>T) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.70 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.18 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
G
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
G
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
V
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
R
G
V
V
E
D
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
Q
K
Y
H
R
K
L
E
K
K
170
|
K
M
I
S
S
K
K
D
E
G
E
K
K
K
T
K
P
K
G
K
180
|
C
K
V
S
K
K
I
T
K
K
K
S
C
-
I
-
I
-
M
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Liver | N.A. | |||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Female nonobese diabetic/severe combined immunodeficient (NOD/SCID) mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunohistochemistry assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.A146V (c.437C>T) in gene KRAS cause the sensitivity of Selumetinib + Dactolisib by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [23] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Selumetinib/Dactolisib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12C (c.34G>T) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.40 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.60 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
G
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
C
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
R
V
V
D
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
Q
H
Y
K
R
E
L
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Liver | N.A. | |||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Female nonobese diabetic/severe combined immunodeficient (NOD/SCID) mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunohistochemistry assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.G12C (c.34G>T) in gene KRAS cause the sensitivity of Selumetinib + Dactolisib by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [23] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Selumetinib/Dactolisib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12D (c.35G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.40 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
G
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
D
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
R
V
V
D
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
Q
H
Y
K
R
E
L
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Liver | N.A. | |||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Female nonobese diabetic/severe combined immunodeficient (NOD/SCID) mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunohistochemistry assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.G12D (c.35G>A) in gene KRAS cause the sensitivity of Selumetinib + Dactolisib by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | ||||||||||||
Investigative Drug(s)
5 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [25] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Docetaxel/Selumetinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12V (c.35G>T) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.98 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.96 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
-
0
|
S
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
V
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
S
S
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
D
D
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
K
H
H
K
K
E
E
K
K
170
|
M
M
S
S
K
K
D
D
G
G
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
K
180
|
K
K
S
S
K
K
T
T
K
K
C
C
V
V
I
I
M
M
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Lung | N.A. | |||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [25] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Docetaxel/Selumetinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12C (c.34G>T) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.40 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.60 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
G
-
M
M
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
K
K
L
L
V
V
V
V
V
V
10
|
G
G
A
A
G
C
G
G
V
V
G
G
K
K
S
S
A
A
L
L
20
|
T
T
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
I
I
Q
Q
N
N
H
H
F
F
V
V
30
|
D
D
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
I
I
E
E
D
D
S
S
40
|
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
I
I
D
D
G
G
E
E
50
|
T
T
C
C
L
L
L
L
D
D
I
I
L
L
D
D
T
T
A
A
60
|
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
A
A
M
M
R
R
D
D
70
|
Q
Q
Y
Y
M
M
R
R
T
T
G
G
E
E
G
G
F
F
L
L
80
|
C
C
V
V
F
F
A
A
I
I
N
N
N
N
T
T
K
K
S
S
90
|
F
F
E
E
D
D
I
I
H
H
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
Q
Q
100
|
I
I
K
K
R
R
V
V
K
K
D
D
S
S
E
E
D
D
V
V
110
|
P
P
M
M
V
V
L
L
V
V
G
G
N
N
K
K
C
C
D
D
120
|
L
L
P
P
S
S
R
R
T
T
V
V
D
D
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
130
|
A
A
Q
Q
D
D
L
L
A
A
R
R
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
I
I
140
|
P
P
F
F
I
I
E
E
T
T
S
S
A
A
K
K
T
T
R
R
150
|
Q
Q
G
R
V
V
D
E
D
D
A
A
F
F
Y
Y
T
T
L
L
160
|
V
V
R
R
E
E
I
I
R
R
K
Q
H
Y
K
R
E
L
K
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Lung | N.A. | |||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [26] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | EGFR inhibitors | |||
| Molecule Alteration | IF-deletion | p.M1_E37 (c.1-11_111) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | EGFR signaling pathway | Activation | hsa01521 | |
| In Vitro Model | Colorectal | N.A. | ||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C10.0] | [27] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C10.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Gemcitabine/Trametinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Other | p.G12_G13 (c.34_39) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Pancreas | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Plasma analysis | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [28] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Irinotecan/Selumetinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | IF-deletion | p.M1_E37 (c.1-11_111) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Colon | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Tumor evaluation assay | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Acute lymphocytic leukemia [ICD-11: 2B33.0] | [29] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Acute lymphocytic leukemia [ICD-11: 2B33.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | MEK inhibitors | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G12 (c.34_36) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Bone marrow | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTiter 96 Aqueous One assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.G12 (c.34_36) in gene KRAS cause the sensitivity of MEK inhibitors by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Bone marrow | |
| The Specified Disease | Acute myeloid leukemia | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 9.27E-01; Fold-change: -9.51E-02; Z-score: -2.66E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
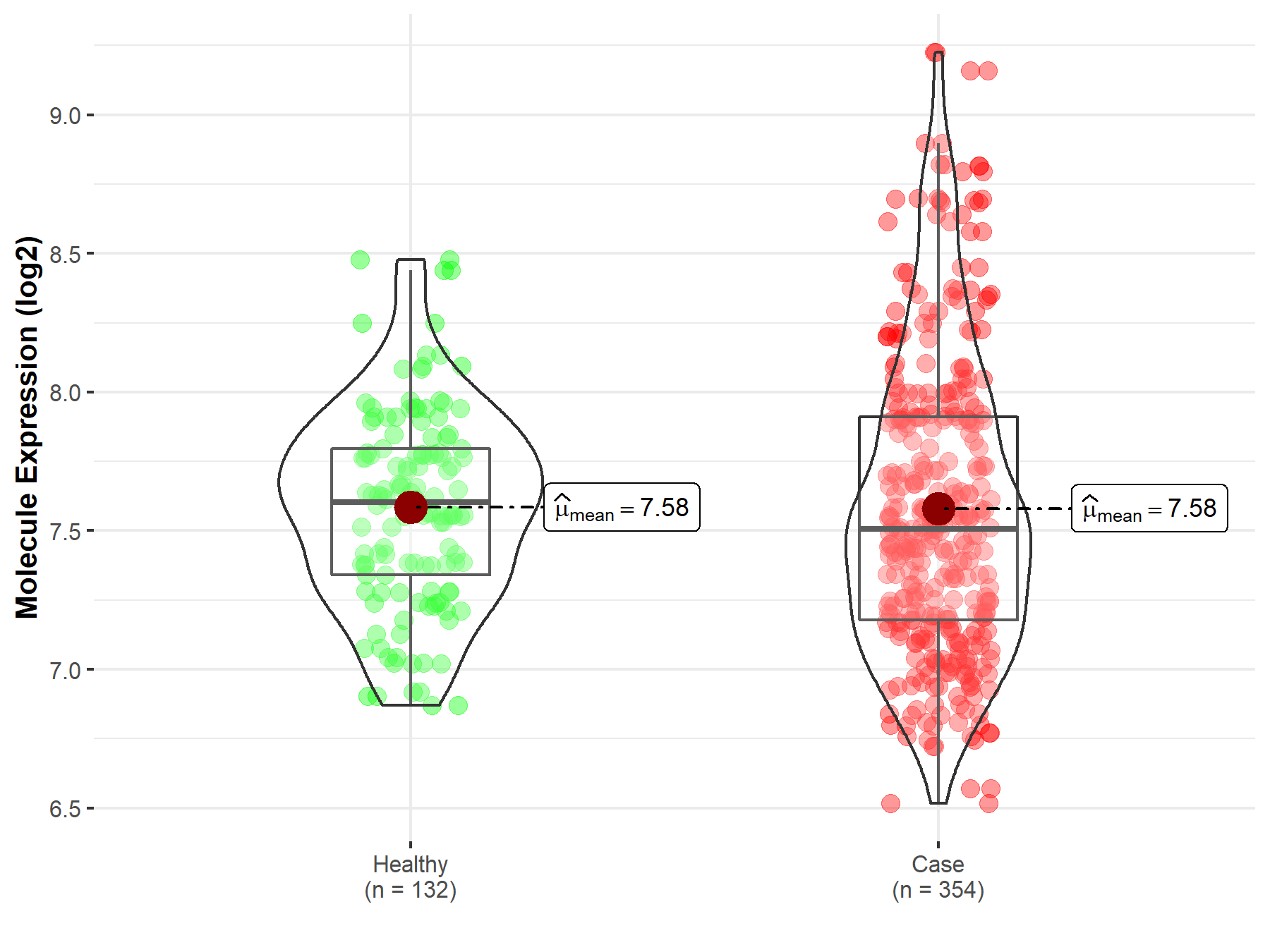
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Pancreas | |
| The Specified Disease | Pancreatic cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 6.08E-02; Fold-change: -4.12E-01; Z-score: -4.58E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 2.76E-04; Fold-change: -3.60E-01; Z-score: -7.28E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
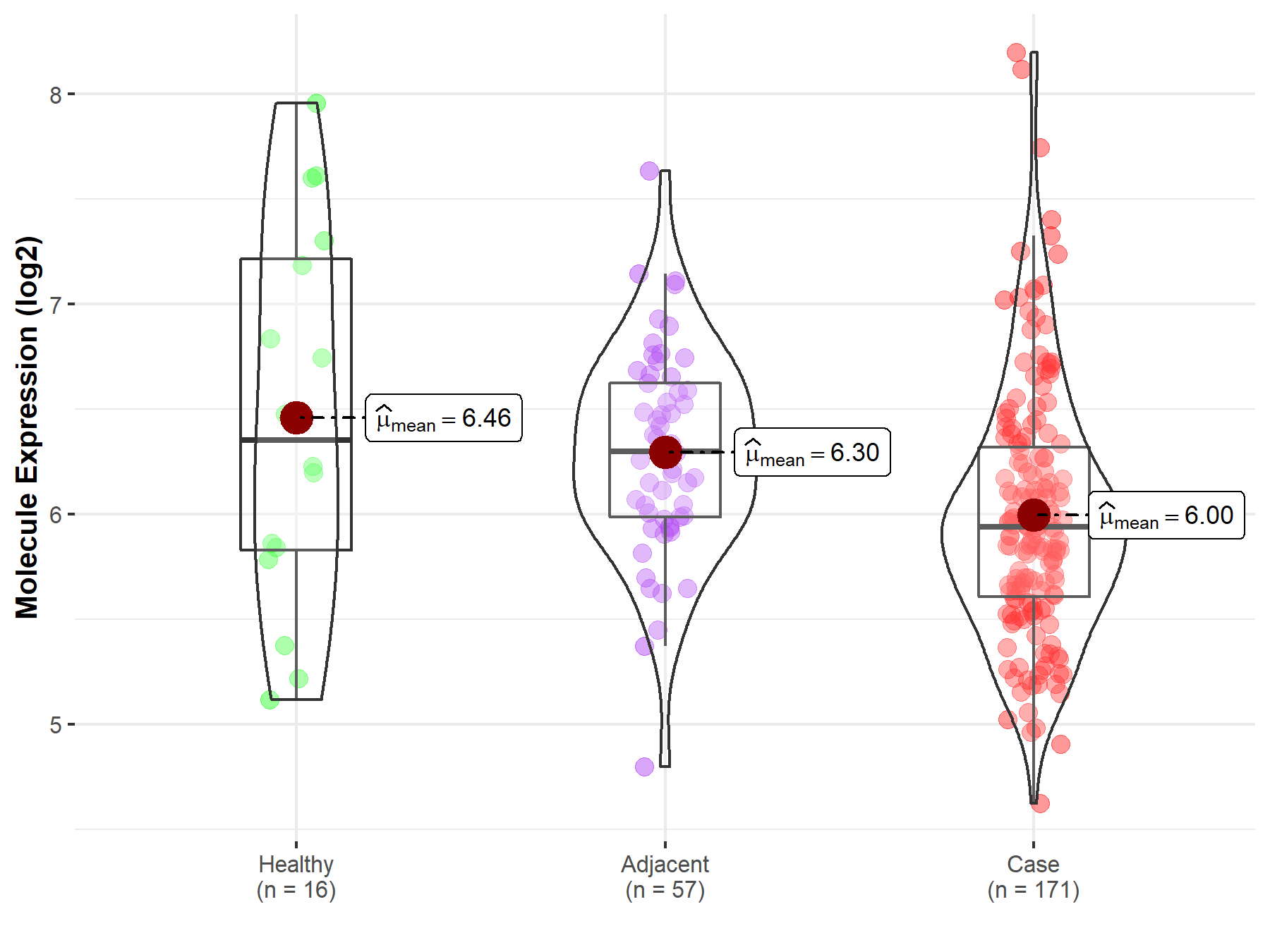
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung | |
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.42E-01; Fold-change: 1.64E-04; Z-score: 5.14E-04 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 6.62E-02; Fold-change: 3.26E-02; Z-score: 9.01E-02 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
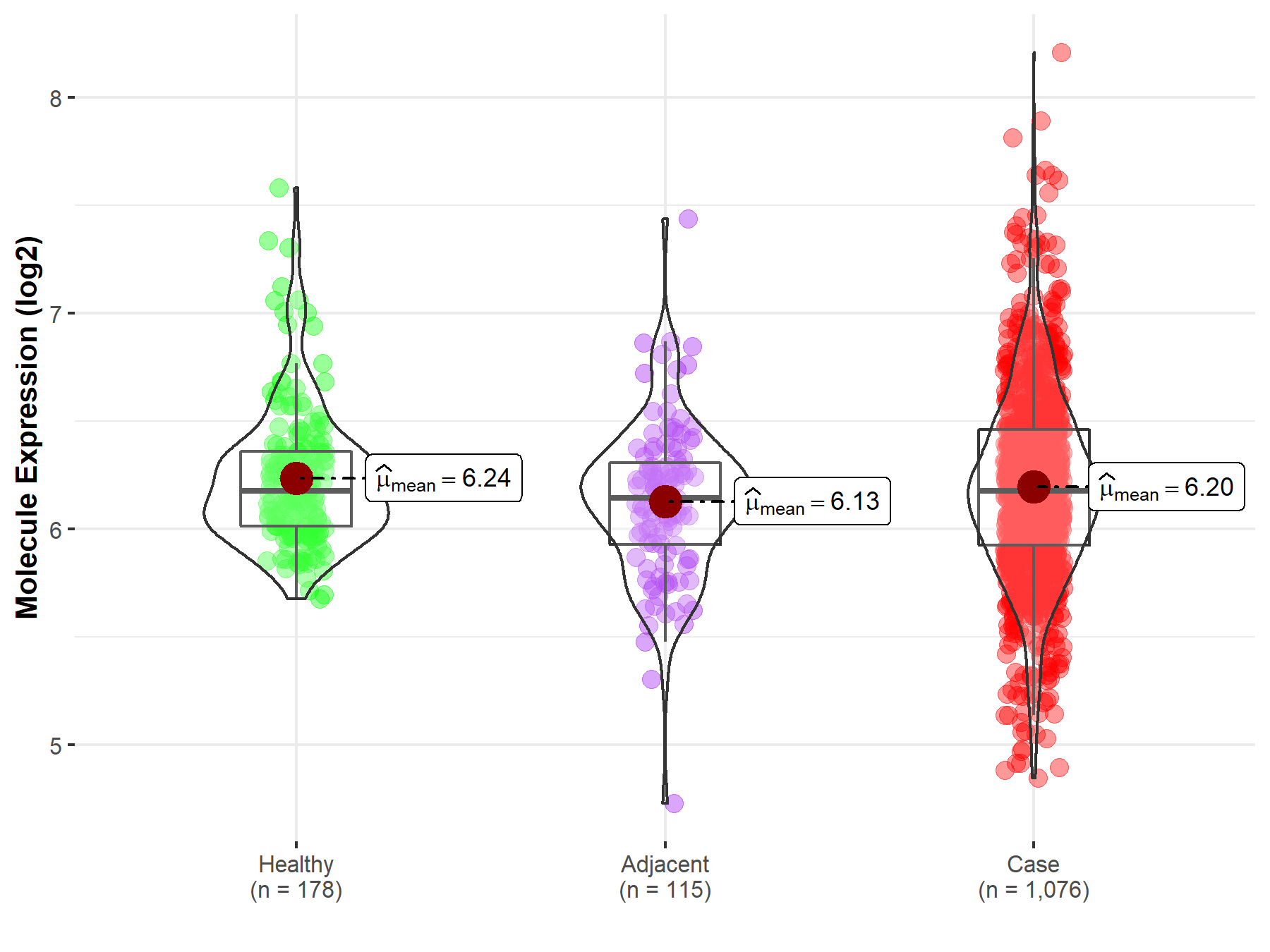
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Skin | |
| The Specified Disease | Melanoma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.52E-01; Fold-change: 2.56E-02; Z-score: 2.99E-02 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Prostate | |
| The Specified Disease | Prostate cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.81E-02; Fold-change: 5.02E-01; Z-score: 4.86E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
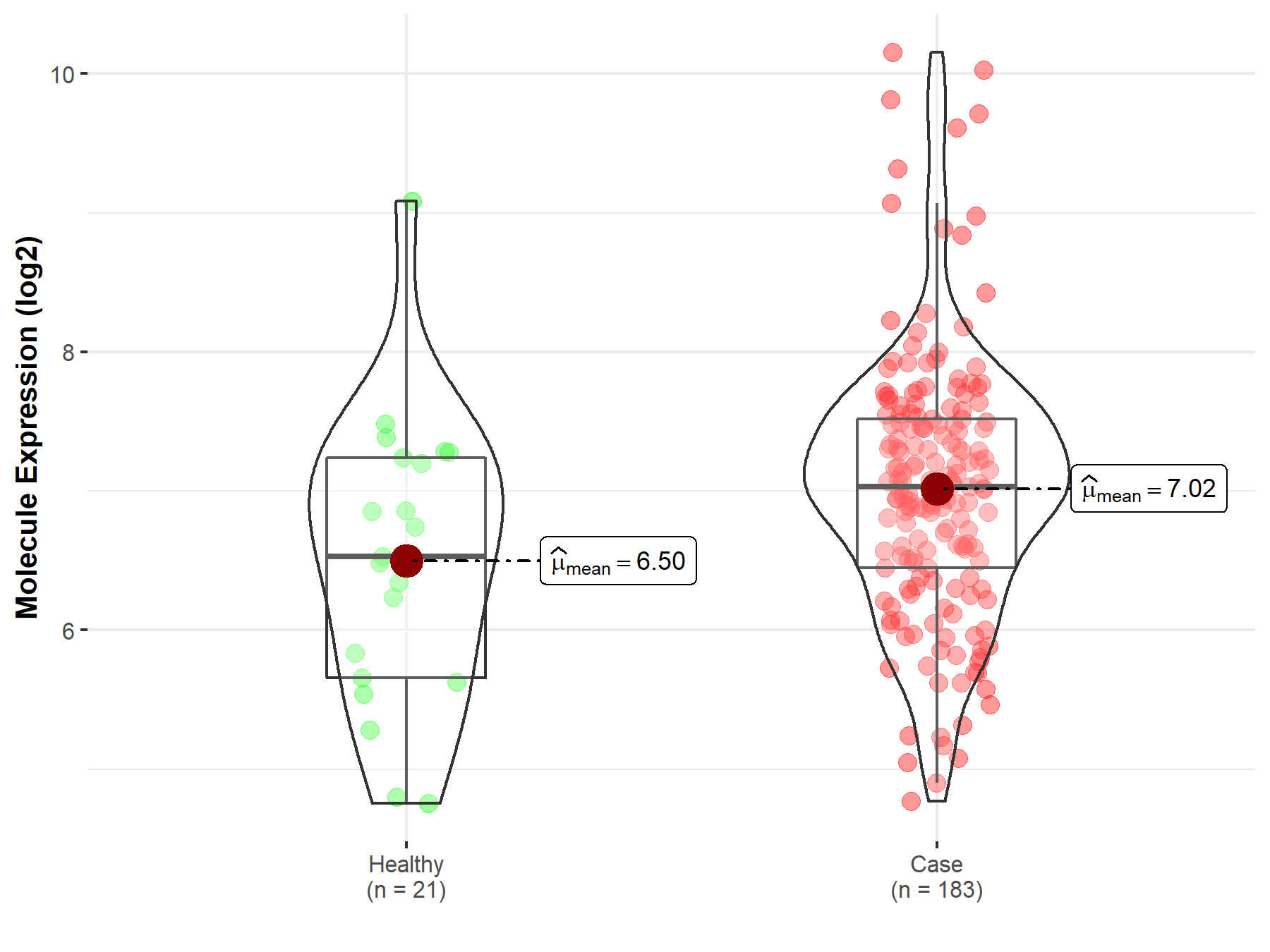
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
