Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00397) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Anastrozole
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Anastrazole; Anastrole; Anastrozol; Arimidex; Asiolex; Astra brand of anastrozole; AstraZeneca brand of anastrozole; Zeneca brand of anastrozole; ZD 1033; ZD1033; Zeneca ZD 1033; Arimidex (TN); Arimidex (Zeneca); Arimidex, Anastrozole; ZD-1033; Anastrozole [USAN:INN:BAN]; Anastrozole (JAN/USAN/INN); Alpha,alpha,alpha',alpha'-tetramethyl-5(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-m-benzenediacetonitrile; Alpha,alpha,alpha',alpha'-Tetramethyl-5-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-m-benzenediacetonitrile; 1,3-benzenediacetonitrile, a, a,a', a'-tetramethyl-5-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl); 2,2'-(5-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-1,3-phenylene)bis(2-methylpropionitrile); 2,2'-[5-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-1,3-phenylene]bis(2-methylpropanenitrile); 2,2'-[5-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene-1,3-diyl]bis(2-methylpropanenitrile); 2-[3-(2-cyanopropan-2-yl)-5-(1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)phenyl]-2-methylpropanenitrile
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
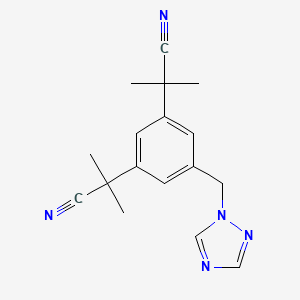
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(1 diseases)
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Discovered by Cell Line Test for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[3]
|
||||
| Target | Aromatase (CYP19A1) | CP19A_HUMAN | [2] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C17H19N5
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CC(C)(C#N)C1=CC(=CC(=C1)CN2C=NC=N2)C(C)(C)C#N
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C17H19N5/c1-16(2,9-18)14-5-13(8-22-12-20-11-21-22)6-15(7-14)17(3,4)10-19/h5-7,11-12H,8H2,1-4H3
|
||||
| InChIKey |
YBBLVLTVTVSKRW-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| VARIDT ID | |||||
| INTEDE ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Deiodinase, iodothyronine type III, opposite strand (DIO3OS) | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Metabolic Type | Glucose metabolism | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Four-week-old female athymic BALB/c nude mice, with tumor cells | Mice | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Tumor volume assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Mechanistically, DIO3OS interacts with polypyrimidine tract binding protein 1 (PTBP1) and stabilizes the mRNA of lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA) by protecting the integrity of its 3'UTR, and subsequently upregulates LDHA expression and activates glycolytic metabolism in AI-resistant breast cancer cells. Our findings highlight the role of lncRNA in regulating the key enzyme of glycolytic metabolism in response to endocrine therapies and the potential of targeting DIO3OS to reverse AI resistance in ER-positive breast cancer. | ||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Estrogen receptor alpha (ESR1) | [1], [2] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y537S |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.60 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.50 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
-
D
-
P
-
M
-
I
-
K
300
|
-
R
-
S
-
K
-
K
-
N
-
S
-
L
-
A
-
L
S
S
310
|
L
L
T
T
A
A
D
D
Q
Q
M
M
V
V
S
S
A
A
L
L
320
|
L
L
D
D
A
A
E
E
P
P
P
P
I
I
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
330
|
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
R
R
P
P
F
F
S
S
E
E
340
|
A
A
S
S
M
M
M
M
G
G
L
L
L
L
T
T
N
N
L
L
350
|
A
A
D
D
R
R
E
E
L
L
V
V
H
H
M
M
I
I
N
N
360
|
W
W
A
A
K
K
R
R
V
V
P
P
G
G
F
F
V
V
D
D
370
|
L
L
T
T
L
L
H
H
D
D
Q
Q
V
V
H
H
L
L
L
L
380
|
E
E
C
-
A
A
W
W
L
L
E
E
I
I
L
L
M
M
I
I
390
|
G
G
L
L
V
V
W
W
R
R
S
S
M
M
E
E
H
H
P
P
400
|
G
G
K
K
L
L
L
L
F
F
A
A
P
P
N
N
L
L
L
L
410
|
L
L
D
D
R
R
N
N
Q
Q
G
G
K
K
C
-
V
V
E
E
420
|
G
G
M
M
V
V
E
E
I
I
F
F
D
D
M
M
L
L
L
L
430
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
S
S
R
R
F
F
R
R
M
M
M
M
N
N
440
|
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
E
E
E
E
F
F
V
V
C
C
L
L
K
K
450
|
S
S
I
I
I
I
L
L
L
L
N
N
S
S
G
G
V
V
Y
Y
460
|
T
T
F
F
L
L
S
S
S
S
T
T
L
L
K
K
S
S
L
L
470
|
E
E
E
E
K
K
D
D
H
H
I
I
H
H
R
R
V
V
L
L
480
|
D
D
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
T
T
L
L
I
I
H
H
L
L
490
|
M
M
A
A
K
K
A
A
G
G
L
L
T
T
L
L
Q
Q
Q
Q
500
|
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
R
R
L
L
A
A
Q
Q
L
L
L
L
L
L
510
|
I
I
L
L
S
S
H
H
I
I
R
R
H
H
M
M
S
S
N
N
520
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
E
E
H
H
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
M
M
K
K
530
|
C
-
K
K
N
N
V
V
V
V
P
P
L
L
Y
S
D
D
L
L
540
|
L
L
L
L
E
E
M
M
L
L
D
D
A
A
H
H
R
R
L
L
550
|
H
H
A
A
P
P
T
T
S
S
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Droplet digital polymerase chain reaction assay; Whole-genome sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Chest x-ray assay; Computed tomography assay; Magnetic resonance imaging assay; Positron emission tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | We have developed a ddPCR-based method for the sensitive detection and quantification of 4 representative ESR1 mutations, Y537S, Y537N, Y537C, and D538G, in 325 breast cancer specimens, in which 270 primary breast cancer and 55 MBC specimens. Whole-exome and transcriptome analysis showed that six cases harbored mutations of ESR1 affecting its ligand-binding domain (LBD), all of whom had been treated with anti-estrogens and estrogen deprivation therapies. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Estrogen receptor alpha (ESR1) | [2] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D538G |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.60 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.90 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
V
-
D
-
L
-
G
-
T
-
E
290
|
-
N
-
L
-
Y
-
F
-
Q
-
S
-
N
-
A
-
M
-
K
300
|
-
R
-
S
-
K
-
K
-
N
-
S
-
L
-
A
-
L
S
S
310
|
L
L
T
T
A
A
D
D
Q
Q
M
M
V
V
S
S
A
A
L
L
320
|
L
L
D
D
A
A
E
E
P
P
P
P
I
I
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
330
|
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
R
R
P
P
F
F
S
S
E
E
340
|
A
A
S
S
M
M
M
M
G
G
L
L
L
L
T
T
N
N
L
L
350
|
A
A
D
D
R
R
E
E
L
L
V
V
H
H
M
M
I
I
N
N
360
|
W
W
A
A
K
K
R
R
V
V
P
P
G
G
F
F
V
V
D
D
370
|
L
L
T
T
L
L
H
H
D
D
Q
Q
V
V
H
H
L
L
L
L
380
|
E
E
C
C
A
A
W
W
L
L
E
E
I
I
L
L
M
M
I
I
390
|
G
G
L
L
V
V
W
W
R
R
S
S
M
M
E
E
H
H
P
P
400
|
G
G
K
K
L
L
L
L
F
F
A
A
P
P
N
N
L
L
L
L
410
|
L
L
D
D
R
R
N
N
Q
Q
G
G
K
K
C
C
V
V
E
E
420
|
G
G
M
M
V
V
E
E
I
I
F
F
D
D
M
M
L
L
L
L
430
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
S
S
R
R
F
F
R
R
M
M
M
M
N
N
440
|
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
E
E
E
E
F
F
V
V
C
C
L
L
K
K
450
|
S
S
I
I
I
I
L
L
L
L
N
N
S
S
G
G
V
V
Y
Y
460
|
T
T
F
F
L
L
S
S
S
S
T
T
L
L
K
K
S
S
L
L
470
|
E
E
E
E
K
K
D
D
H
H
I
I
H
H
R
R
V
V
L
L
480
|
D
D
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
T
T
L
L
I
I
H
H
L
L
490
|
M
M
A
A
K
K
A
A
G
G
L
L
T
T
L
L
Q
Q
Q
Q
500
|
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
R
R
L
L
A
A
Q
Q
L
L
L
L
L
L
510
|
I
I
L
L
S
S
H
H
I
I
R
R
H
H
M
M
S
S
N
N
520
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
E
E
H
H
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
M
M
K
K
530
|
C
C
K
K
N
N
V
V
V
V
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
D
G
L
L
540
|
L
L
L
L
E
E
M
M
L
L
D
D
A
A
H
H
R
R
L
L
550
|
H
H
A
A
P
P
T
T
S
S
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Droplet digital polymerase chain reaction assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Chest x-ray assay; Computed tomography assay; Magnetic resonance imaging assay; Positron emission tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | We have developed a ddPCR-based method for the sensitive detection and quantification of 4 representative ESR1 mutations, Y537S, Y537N, Y537C, and D538G, in 325 breast cancer specimens, in which 270 primary breast cancer and 55 MBC specimens. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Estrogen receptor alpha (ESR1) | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D538G |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.60 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.90 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
V
-
D
-
L
-
G
-
T
-
E
290
|
-
N
-
L
-
Y
-
F
-
Q
-
S
-
N
-
A
-
M
-
K
300
|
-
R
-
S
-
K
-
K
-
N
-
S
-
L
-
A
-
L
S
S
310
|
L
L
T
T
A
A
D
D
Q
Q
M
M
V
V
S
S
A
A
L
L
320
|
L
L
D
D
A
A
E
E
P
P
P
P
I
I
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
330
|
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
P
P
T
T
R
R
P
P
F
F
S
S
E
E
340
|
A
A
S
S
M
M
M
M
G
G
L
L
L
L
T
T
N
N
L
L
350
|
A
A
D
D
R
R
E
E
L
L
V
V
H
H
M
M
I
I
N
N
360
|
W
W
A
A
K
K
R
R
V
V
P
P
G
G
F
F
V
V
D
D
370
|
L
L
T
T
L
L
H
H
D
D
Q
Q
V
V
H
H
L
L
L
L
380
|
E
E
C
C
A
A
W
W
L
L
E
E
I
I
L
L
M
M
I
I
390
|
G
G
L
L
V
V
W
W
R
R
S
S
M
M
E
E
H
H
P
P
400
|
G
G
K
K
L
L
L
L
F
F
A
A
P
P
N
N
L
L
L
L
410
|
L
L
D
D
R
R
N
N
Q
Q
G
G
K
K
C
C
V
V
E
E
420
|
G
G
M
M
V
V
E
E
I
I
F
F
D
D
M
M
L
L
L
L
430
|
A
A
T
T
S
S
S
S
R
R
F
F
R
R
M
M
M
M
N
N
440
|
L
L
Q
Q
G
G
E
E
E
E
F
F
V
V
C
C
L
L
K
K
450
|
S
S
I
I
I
I
L
L
L
L
N
N
S
S
G
G
V
V
Y
Y
460
|
T
T
F
F
L
L
S
S
S
S
T
T
L
L
K
K
S
S
L
L
470
|
E
E
E
E
K
K
D
D
H
H
I
I
H
H
R
R
V
V
L
L
480
|
D
D
K
K
I
I
T
T
D
D
T
T
L
L
I
I
H
H
L
L
490
|
M
M
A
A
K
K
A
A
G
G
L
L
T
T
L
L
Q
Q
Q
Q
500
|
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
R
R
L
L
A
A
Q
Q
L
L
L
L
L
L
510
|
I
I
L
L
S
S
H
H
I
I
R
R
H
H
M
M
S
S
N
N
520
|
K
K
G
G
M
M
E
E
H
H
L
L
Y
Y
S
S
M
M
K
K
530
|
C
C
K
K
N
N
V
V
V
V
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
D
G
L
L
540
|
L
L
L
L
E
E
M
M
L
L
D
D
A
A
H
H
R
R
L
L
550
|
H
H
A
A
P
P
T
T
S
S
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Deep sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | We report here on a novel mutation of ERalpha, in which an A to G substitution at position 1,613 resulted in substitution of aspartic acid at position 538 to glycine (D538G). The mutation was identified in liver metastases obtained from patients who developed endocrine resistance, but not in samples of primary tumors obtained prior to commencing endocrine treatment. Structural modeling indicates that D538G substitution creates a conformational change that disrupts the interaction between the receptor and either estrogen or tamoxifen, but mimics the conformation of the activated receptor. Studies in cell lines confirmed ligand-independent, constitutive activity of the mutated receptor. Taken together, these data indicate the mutation D538G as a novel mechanism conferring acquired endocrine resistance. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Estrogen receptor alpha (ESR1) | [2] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y537N |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Droplet digital polymerase chain reaction assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Chest x-ray assay; Computed tomography assay; Magnetic resonance imaging assay; Positron emission tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | We have developed a ddPCR-based method for the sensitive detection and quantification of 4 representative ESR1 mutations, Y537S, Y537N, Y537C, and D538G, in 325 breast cancer specimens, in which 270 primary breast cancer and 55 MBC specimens. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Estrogen receptor alpha (ESR1) | [2] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y537C |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Droplet digital polymerase chain reaction assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Chest x-ray assay; Computed tomography assay; Magnetic resonance imaging assay; Positron emission tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | We have developed a ddPCR-based method for the sensitive detection and quantification of 4 representative ESR1 mutations, Y537S, Y537N, Y537C, and D538G, in 325 breast cancer specimens, in which 270 primary breast cancer and 55 MBC specimens. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: BQ323636.1 | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | AR signalling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 BQ cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| ZR-75 BQ cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Mechanistic study indicates that BQ overexpression enhances androgen receptor (AR) activity and in the presence of anastrozole, causes hyper-activation of AR signalling, which unexpectedly enhanced cell proliferation, through increased expression of?CDK2,?CDK4, and?CCNE1. BQ overexpression reverses the effect of anastrozole in ER+ve breast cancer in an AR-dependent manner, whilst co-treatment with the AR antagonist bicalutamide recovered its therapeutic effect both?in vitro?and?in vivo. Thus, for BQ-overexpressing breast cancer, targeting AR can combat anastrozole resistance. | ||||||||||||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
