Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00133)
| Name |
Poly[ADP-ribose] synthase 1 (PARP1)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
PARP-1; ADP-ribosyltransferase diphtheria toxin-like 1; ARTD1; DNA ADP-ribosyltransferase PARP1; NAD(+) ADP-ribosyltransferase 1; ADPRT 1; Poly[ADP-ribose] synthase 1; Protein poly-ADP-ribosyltransferase PARP1; ADPRT; PPOL
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
PARP1
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr1:226360210-226408154[-]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MAESSDKLYRVEYAKSGRASCKKCSESIPKDSLRMAIMVQSPMFDGKVPHWYHFSCFWKV
GHSIRHPDVEVDGFSELRWDDQQKVKKTAEAGGVTGKGQDGIGSKAEKTLGDFAAEYAKS NRSTCKGCMEKIEKGQVRLSKKMVDPEKPQLGMIDRWYHPGCFVKNREELGFRPEYSASQ LKGFSLLATEDKEALKKQLPGVKSEGKRKGDEVDGVDEVAKKKSKKEKDKDSKLEKALKA QNDLIWNIKDELKKVCSTNDLKELLIFNKQQVPSGESAILDRVADGMVFGALLPCEECSG QLVFKSDAYYCTGDVTAWTKCMVKTQTPNRKEWVTPKEFREISYLKKLKVKKQDRIFPPE TSASVAATPPPSTASAPAAVNSSASADKPLSNMKILTLGKLSRNKDEVKAMIEKLGGKLT GTANKASLCISTKKEVEKMNKKMEEVKEANIRVVSEDFLQDVSASTKSLQELFLAHILSP WGAEVKAEPVEVVAPRGKSGAALSKKSKGQVKEEGINKSEKRMKLTLKGGAAVDPDSGLE HSAHVLEKGGKVFSATLGLVDIVKGTNSYYKLQLLEDDKENRYWIFRSWGRVGTVIGSNK LEQMPSKEDAIEHFMKLYEEKTGNAWHSKNFTKYPKKFYPLEIDYGQDEEAVKKLTVNPG TKSKLPKPVQDLIKMIFDVESMKKAMVEYEIDLQKMPLGKLSKRQIQAAYSILSEVQQAV SQGSSDSQILDLSNRFYTLIPHDFGMKKPPLLNNADSVQAKVEMLDNLLDIEVAYSLLRG GSDDSSKDPIDVNYEKLKTDIKVVDRDSEEAEIIRKYVKNTHATTHNAYDLEVIDIFKIE REGECQRYKPFKQLHNRRLLWHGSRTTNFAGILSQGLRIAPPEAPVTGYMFGKGIYFADM VSKSANYCHTSQGDPIGLILLGEVALGNMYELKHASHISKLPKGKHSVKGLGKTTPDPSA NISLDGVDVPLGTGISSGVNDTSLLYNEYIVYDIAQVNLKYLLKLKFNFKTSLW Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Poly-ADP-ribosyltransferase that mediates poly-ADP-ribosylation of proteins and plays a key role in DNA repair. Mediates glutamate, aspartate, serine or tyrosine ADP-ribosylation of proteins: the ADP-D-ribosyl group of NAD(+) is transferred to the acceptor carboxyl group of target residues and further ADP-ribosyl groups are transferred to the 2'-position of the terminal adenosine moiety, building up a polymer with an average chain length of 20-30 units. Serine ADP-ribosylation of proteins constitutes the primary form of ADP-ribosylation of proteins in response to DNA damage. Mainly mediates glutamate and aspartate ADP-ribosylation of target proteins in absence of HPF1. Following interaction with HPF1, catalyzes serine ADP-ribosylation of target proteins; HPF1 conferring serine specificity by completing the PARP1 active site. Also catalyzes tyrosine ADP-ribosylation of target proteins following interaction with HPF1. PARP1 initiates the repair of DNA breaks: recognizes and binds DNA breaks within chromatin and recruits HPF1, licensing serine ADP-ribosylation of target proteins, such as histones, thereby promoting decompaction of chromatin and the recruitment of repair factors leading to the reparation of DNA strand breaks. In addition to base excision repair (BER) pathway, also involved in double-strand breaks (DSBs) repair: together with TIMELESS, accumulates at DNA damage sites and promotes homologous recombination repair by mediating poly-ADP-ribosylation. Mediates the poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation of a number of proteins, including itself, APLF and CHFR. In addition to proteins, also able to ADP-ribosylate DNA: catalyzes ADP-ribosylation of DNA strand break termini containing terminal phosphates and a 2'-OH group in single- and double-stranded DNA, respectively. Required for PARP9 and DTX3L recruitment to DNA damage sites. PARP1-dependent PARP9-DTX3L-mediated ubiquitination promotes the rapid and specific recruitment of 53BP1/TP53BP1, UIMC1/RAP80, and BRCA1 to DNA damage sites. Acts as a regulator of transcription: positively regulates the transcription of MTUS1 and negatively regulates the transcription of MTUS2/TIP150. Plays a role in the positive regulation of IFNG transcription in T-helper 1 cells as part of an IFNG promoter-binding complex with TXK and EEF1A1. Involved in the synthesis of ATP in the nucleus, together with NMNAT1, PARG and NUDT5. Nuclear ATP generation is required for extensive chromatin remodeling events that are energy-consuming.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
6 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Paclitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.62E-122 Fold-change: 1.35E-01 Z-score: 3.17E+01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Mitochondrial signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04217 | |
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 |
| A549/Taxol cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_W218 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Flow cytometry assay; Transwell Invasion assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | ANRIL, also known as CDkN2B antisense RNA1, was origi.lly identified in the familial melanoma patients, it is located within the CDkN2B-CDkN2A gene cluster at chromosome 9p21. ANRIL decreases Bcl-2 expression and increases PARP expression. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77.0] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| In Vitro Model | Hela cells | Cervix uteri | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0030 |
| Siha cells | Cervix uteri | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0032 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | There was a protective role of miR-7-5p in cervical cancer cells treated with cisplatin and that miR-7-5p expression.miR-7-5p reduced energy consumption via inhibiting PARP-1 expression, and miR-7-5p increased energy generation by suppressing the expression of Bcl-2. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Epithelial ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2B5D.0] | [3] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Epithelial ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2B5D.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell cycle arrest | Activation | hsa04110 | ||
| MAPK signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | HEY cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0297 |
| SkOV3 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0532 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | GAS5 might regulate PARP1 expression by recruiting the transcription factor E2F4 to its promoter, and then affect the MAPk pathway activity and enhance sensitivity to DDP of OC both in vitro and in vivo. | |||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [4] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | SkOV3 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0532 |
| SkOV3/CDDP cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_D622 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow cytometry assay; CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR216b increases cisplatin sensitivity in ovarian cancer cells by targeting PARP1. | |||
| Disease Class: Lung small cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.2] | [5] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung small cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.2] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | NF-kappaB signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04064 | |
| In Vitro Model | H69 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_8121 |
| H69AR cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3513 | |
| H446 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1562 | |
| H446/DDP cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_RT21 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR; Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Annexin V-PE Apoptosis assay; Flow cytometry assay; Wound healing assay; Colony formation assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR335 might affect the chemosensitivity and radiosensitivity of SCLC by targeting PARP-1, which further affected NF-kB P65 protein levels, hence NF-kB pathway was involved in the regulation network. | |||
| Disease Class: Esophageal adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.2] | [6] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Esophageal adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.2] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | |
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | OE33 cellss | Esophagus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0471 |
| HEEpiC cells | Esophagus | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| JHesoAD1 cells | Esophagus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_8098 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Luciferase reporter assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The DNA damage repair protein poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP1) is a bona fide target of miR-223, miR-223 up-regulation is also associated with reduced PARP1 transcripts, and an increased sensitivity to cis-diamminedichloroplatinum (II) (Cisplatin), Doxorubicin and Mitomycin C. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lung small cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.2] | [5] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung small cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.2] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | NF-kappaB signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04064 | |
| In Vitro Model | H69 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_8121 |
| H69AR cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3513 | |
| H446 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1562 | |
| H446/DDP cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_RT21 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR; Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Annexin V-PE Apoptosis assay; Flow cytometry assay; Wound healing assay; Colony formation assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Overexpression of miR335 sensitized human SCLC cells to chemotherapy and radiotherapy, promoted cell apoptosis and inhibited cell migration ability of human SCLC in vitro, and inhibited tumor growth in vivo. Overexpression of miR335 decreased the expression of PARP-1 mRNA and protein, and NF-kB protein levels were correspondingly downregulated, thus regulating the chemo-radiosensitivity of SCLC. | |||
| Disease Class: Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51.0] | [7] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| PI3K/AKT signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 |
| T47D cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0553 | |
| ZR75-1 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0588 | |
| HCC1937 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0290 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-124 may be involved in DNA repair by directly targeting ATMIN and PARP1, suggesting that multiple DNA repair pathways are affected by miR-124 and therefore manipulation of miR-124 level/activity may improve the efficacy of chemotherapies that induce DNA damage. repression of ATMIN (+) the HR repair defect induced by miR-124, and restoration of ATMIN reversed the effect of miR-124 overexpression in breast cancer cells. Therefore, it is intriguing to further speculate which of the multiple roles of ATMIN is specifically affected in breast carcinogenesis. On the other hand, PARP1-mediated processes play a role in oncogenesis, cancer progression, and therapeutic resistance. | |||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [7] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| PI3K/AKT signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 |
| T47D cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0553 | |
| ZR75-1 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0588 | |
| HCC1937 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0290 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-124 may be involved in DNA repair by directly targeting ATMIN and PARP1, suggesting that multiple DNA repair pathways are affected by miR-124 and therefore manipulation of miR-124 level/activity may improve the efficacy of chemotherapies that induce DNA damage. repression of ATMIN (+) the HR repair defect induced by miR-124, and restoration of ATMIN reversed the effect of miR-124 overexpression in breast cancer cells. Therefore, it is intriguing to further speculate which of the multiple roles of ATMIN is specifically affected in breast carcinogenesis. On the other hand, PARP1-mediated processes play a role in oncogenesis, cancer progression, and therapeutic resistance. | |||
| Disease Class: Esophageal adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.2] | [6] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Esophageal adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.2] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | |
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | OE33 cellss | Esophagus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0471 |
| HEEpiC cells | Esophagus | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| JHesoAD1 cells | Esophagus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_8098 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Luciferase reporter assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The DNA damage repair protein poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP1) is a bona fide target of miR-223, miR-223 up-regulation is also associated with reduced PARP1 transcripts, and an increased sensitivity to cis-diamminedichloroplatinum (II) (Cisplatin), Doxorubicin and Mitomycin C. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lung small cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.2] | [5] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung small cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.2] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Etoposide | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | NF-kappaB signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04064 | |
| In Vitro Model | H69 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_8121 |
| H69AR cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3513 | |
| H446 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1562 | |
| H446/DDP cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_RT21 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR; Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Annexin V-PE Apoptosis assay; Flow cytometry assay; Wound healing assay; Colony formation assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Overexpression of miR335 sensitized human SCLC cells to chemotherapy and radiotherapy, promoted cell apoptosis and inhibited cell migration ability of human SCLC in vitro, and inhibited tumor growth in vivo. Overexpression of miR335 decreased the expression of PARP-1 mRNA and protein, and NF-kB protein levels were correspondingly downregulated, thus regulating the chemo-radiosensitivity of SCLC. | |||
| Disease Class: Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51.0] | [7] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Etoposide | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| PI3K/AKT signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 |
| T47D cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0553 | |
| ZR75-1 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0588 | |
| HCC1937 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0290 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-124 may be involved in DNA repair by directly targeting ATMIN and PARP1, suggesting that multiple DNA repair pathways are affected by miR-124 and therefore manipulation of miR-124 level/activity may improve the efficacy of chemotherapies that induce DNA damage. repression of ATMIN (+) the HR repair defect induced by miR-124, and restoration of ATMIN reversed the effect of miR-124 overexpression in breast cancer cells. Therefore, it is intriguing to further speculate which of the multiple roles of ATMIN is specifically affected in breast carcinogenesis. On the other hand, PARP1-mediated processes play a role in oncogenesis, cancer progression, and therapeutic resistance. | |||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [7] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Etoposide | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| PI3K/AKT signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 |
| T47D cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0553 | |
| ZR75-1 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0588 | |
| HCC1937 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0290 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-124 may be involved in DNA repair by directly targeting ATMIN and PARP1, suggesting that multiple DNA repair pathways are affected by miR-124 and therefore manipulation of miR-124 level/activity may improve the efficacy of chemotherapies that induce DNA damage. repression of ATMIN (+) the HR repair defect induced by miR-124, and restoration of ATMIN reversed the effect of miR-124 overexpression in breast cancer cells. Therefore, it is intriguing to further speculate which of the multiple roles of ATMIN is specifically affected in breast carcinogenesis. On the other hand, PARP1-mediated processes play a role in oncogenesis, cancer progression, and therapeutic resistance. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12.6] | [8] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12.6] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Fluorouracil | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Phosphorylation | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| Cell colony | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell viability | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | Huh-7 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0336 |
| BEL-7402 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5492 | |
| HepG2 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0027 | |
| HCCLM3 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6832 | |
| Hep3B cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0326 | |
| SMMC7721 cells | Uterus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0534 | |
| MHCC97-L cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_4973 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 analysis; EdU analysis; Transwell assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | MALAT1 deficiency related increase in sensitivity of liver cancer cells was associated with regulation of NF-kB. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Esophageal adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.2] | [6] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Esophageal adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.2] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Mitomycin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | |
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | OE33 cellss | Esophagus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0471 |
| HEEpiC cells | Esophagus | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| JHesoAD1 cells | Esophagus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_8098 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Luciferase reporter assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The DNA damage repair protein poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP1) is a bona fide target of miR-223, miR-223 up-regulation is also associated with reduced PARP1 transcripts, and an increased sensitivity to cis-diamminedichloroplatinum (II) (Cisplatin), Doxorubicin and Mitomycin C. | |||
Clinical Trial Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51.0] | [7] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Camptothecin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| PI3K/AKT signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 |
| T47D cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0553 | |
| ZR75-1 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0588 | |
| HCC1937 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0290 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-124 may be involved in DNA repair by directly targeting ATMIN and PARP1, suggesting that multiple DNA repair pathways are affected by miR-124 and therefore manipulation of miR-124 level/activity may improve the efficacy of chemotherapies that induce DNA damage. repression of ATMIN (+) the HR repair defect induced by miR-124, and restoration of ATMIN reversed the effect of miR-124 overexpression in breast cancer cells. Therefore, it is intriguing to further speculate which of the multiple roles of ATMIN is specifically affected in breast carcinogenesis. On the other hand, PARP1-mediated processes play a role in oncogenesis, cancer progression, and therapeutic resistance. | |||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [7] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Camptothecin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| PI3K/AKT signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 |
| T47D cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0553 | |
| ZR75-1 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0588 | |
| HCC1937 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0290 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-124 may be involved in DNA repair by directly targeting ATMIN and PARP1, suggesting that multiple DNA repair pathways are affected by miR-124 and therefore manipulation of miR-124 level/activity may improve the efficacy of chemotherapies that induce DNA damage. repression of ATMIN (+) the HR repair defect induced by miR-124, and restoration of ATMIN reversed the effect of miR-124 overexpression in breast cancer cells. Therefore, it is intriguing to further speculate which of the multiple roles of ATMIN is specifically affected in breast carcinogenesis. On the other hand, PARP1-mediated processes play a role in oncogenesis, cancer progression, and therapeutic resistance. | |||
Investigative Drug(s)
3 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Papillary thyroid carcinoma [ICD-11: 2D10.1] | [9] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Papillary thyroid carcinoma [ICD-11: 2D10.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Iodine-131 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | SLC6A9/PARP1 signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04064 | |
| In Vitro Model | BCPAP cells | Thyroid | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0153 |
| TPC-1 cells | Thyroid | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6298 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; qRT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | SLC6A9-5:2 overexpression was positively correlated with PARP-1 mRNA and protein levels, which restored the sensitivity of resistant thyroid cancer cells. SLC6A9 is positively correlated with PARP-1 expression, and PARP-1 inhibition makes thyroid cancer cells resistant to 131I. Upregulation of the SLC6A9-PARP-1 pathway enhanced the sensitivity to 131I treatment through energy exhaustion during excess RNA repair. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51.0] | [7] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Iridium | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| PI3K/AKT signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 |
| T47D cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0553 | |
| ZR75-1 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0588 | |
| HCC1937 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0290 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-124 may be involved in DNA repair by directly targeting ATMIN and PARP1, suggesting that multiple DNA repair pathways are affected by miR-124 and therefore manipulation of miR-124 level/activity may improve the efficacy of chemotherapies that induce DNA damage. repression of ATMIN (+) the HR repair defect induced by miR-124, and restoration of ATMIN reversed the effect of miR-124 overexpression in breast cancer cells. Therefore, it is intriguing to further speculate which of the multiple roles of ATMIN is specifically affected in breast carcinogenesis. On the other hand, PARP1-mediated processes play a role in oncogenesis, cancer progression, and therapeutic resistance. | |||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [7] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Iridium | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| PI3K/AKT signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 |
| T47D cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0553 | |
| ZR75-1 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0588 | |
| HCC1937 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0290 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-124 may be involved in DNA repair by directly targeting ATMIN and PARP1, suggesting that multiple DNA repair pathways are affected by miR-124 and therefore manipulation of miR-124 level/activity may improve the efficacy of chemotherapies that induce DNA damage. repression of ATMIN (+) the HR repair defect induced by miR-124, and restoration of ATMIN reversed the effect of miR-124 overexpression in breast cancer cells. Therefore, it is intriguing to further speculate which of the multiple roles of ATMIN is specifically affected in breast carcinogenesis. On the other hand, PARP1-mediated processes play a role in oncogenesis, cancer progression, and therapeutic resistance. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [10] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | N-methyl-n-nitro-n-nitrosoguanidine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | HCC1806 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1258 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Dual luciferase reporter assay; Western blot analysis; RT-qPCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Annexin V assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Down-regulation of PARP1 by miR891b sensitizes human breast cancer cells to alkylating chemotherapeutic drugs. miR891b increased the sensitivity of the HCC1806 cells to the cytotoxic effects of MNNG through suppressing cell proliferation and increasing the percentage of apoptotic cells. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Esophagus | |
| The Specified Disease | Esophageal cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 1.43E-03; Fold-change: 5.95E-01; Z-score: 2.76E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
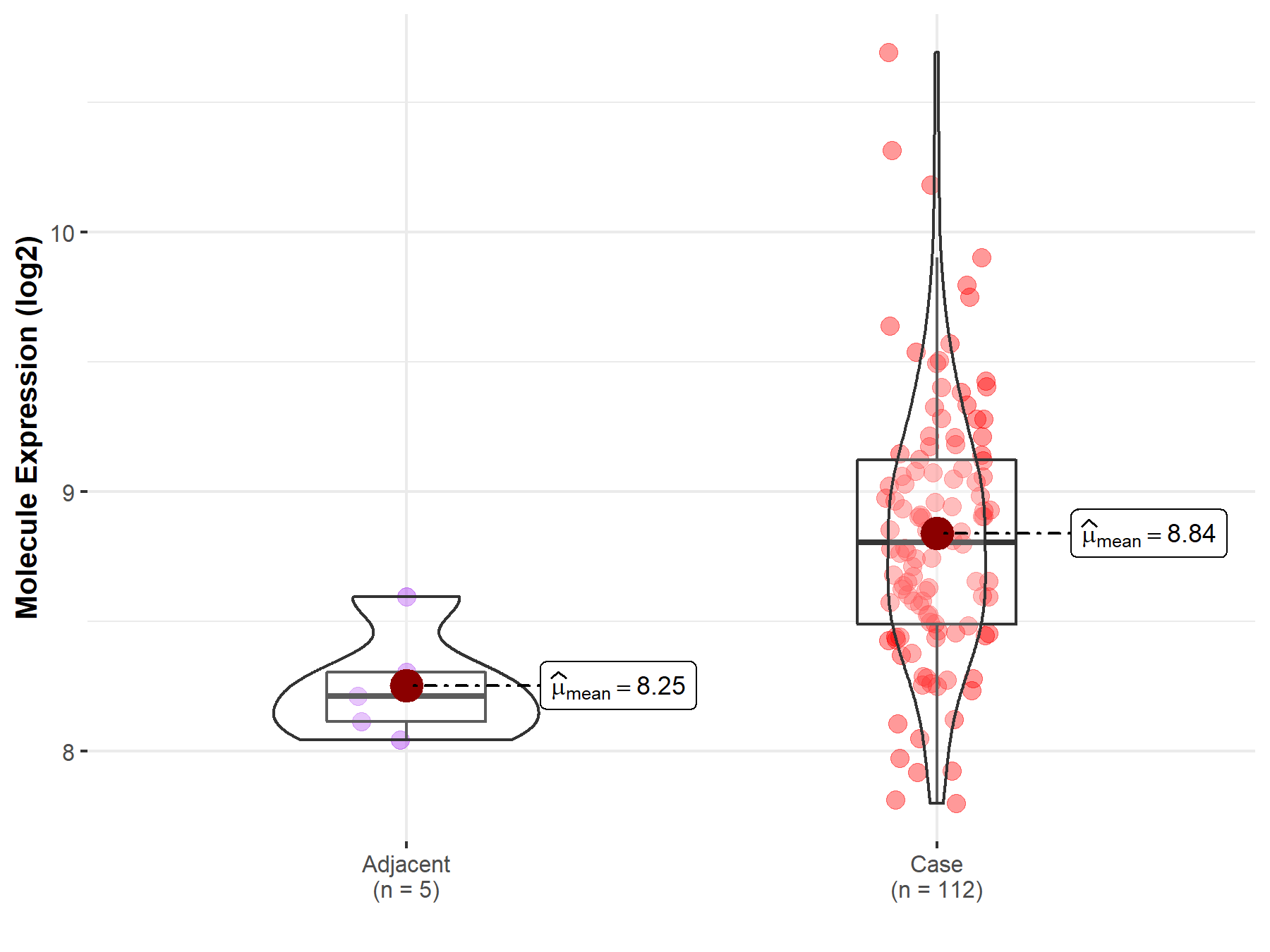
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Liver | |
| The Specified Disease | Liver cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 6.48E-13; Fold-change: 6.45E-01; Z-score: 1.61E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 1.59E-57; Fold-change: 7.53E-01; Z-score: 1.91E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Other Disease Section | p-value: 4.69E-02; Fold-change: 8.69E-01; Z-score: 1.79E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
Molecule expression in tissue other than the diseased tissue of patients
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
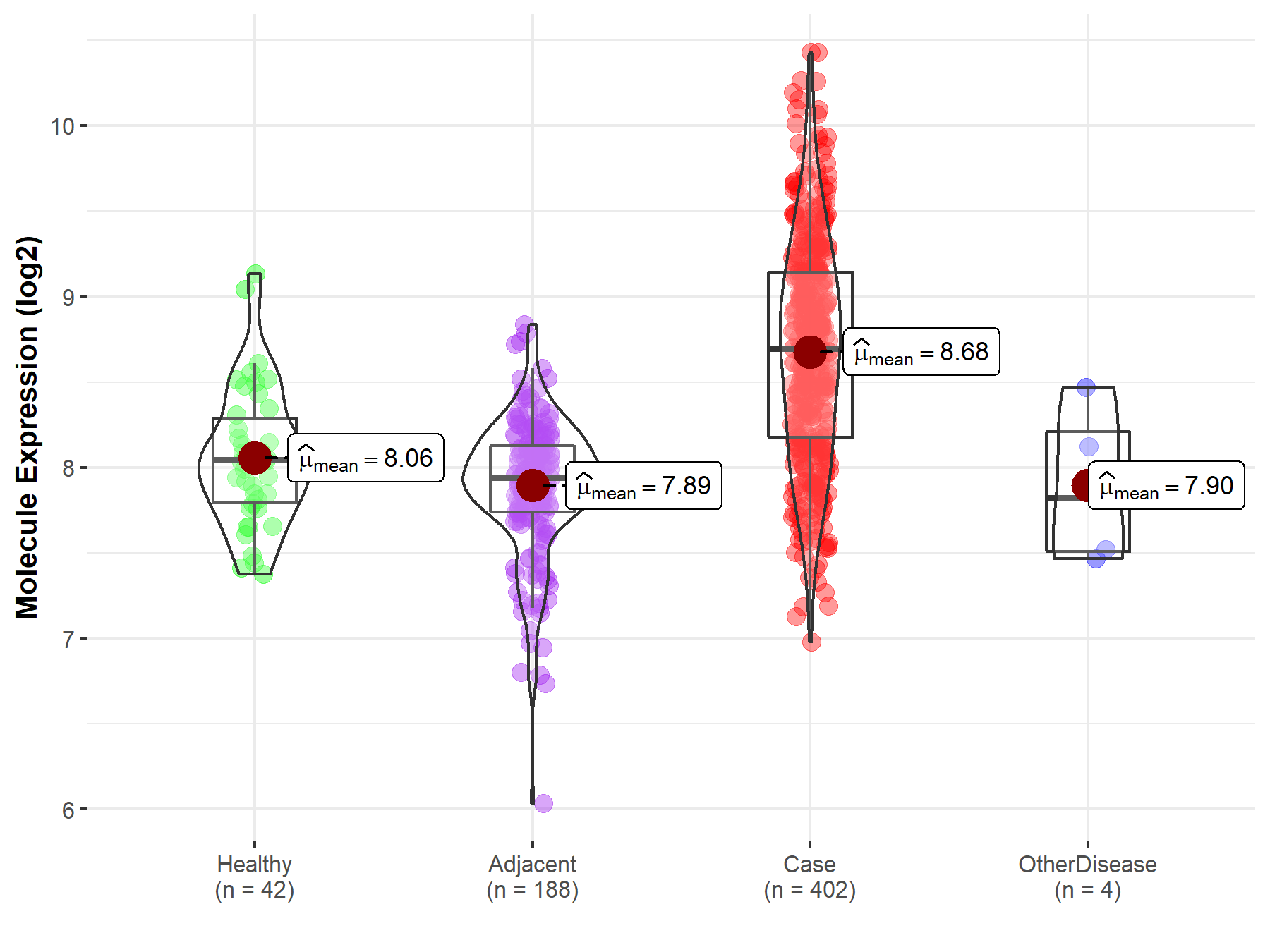
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung | |
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.62E-122; Fold-change: 7.73E-01; Z-score: 3.00E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 3.19E-73; Fold-change: 7.68E-01; Z-score: 2.92E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
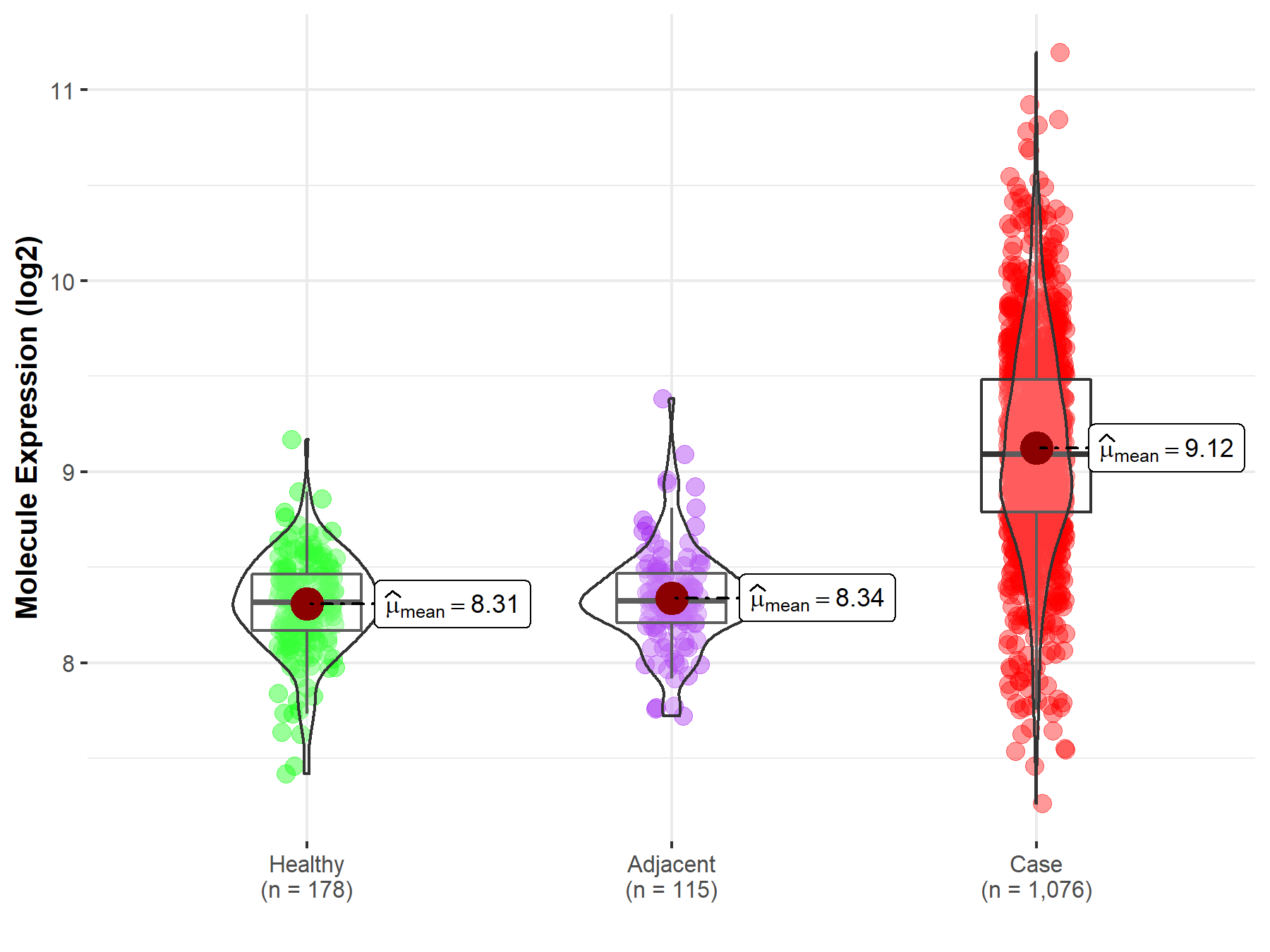
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.53E-134; Fold-change: 8.79E-01; Z-score: 2.45E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 2.00E-17; Fold-change: 8.23E-01; Z-score: 1.94E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
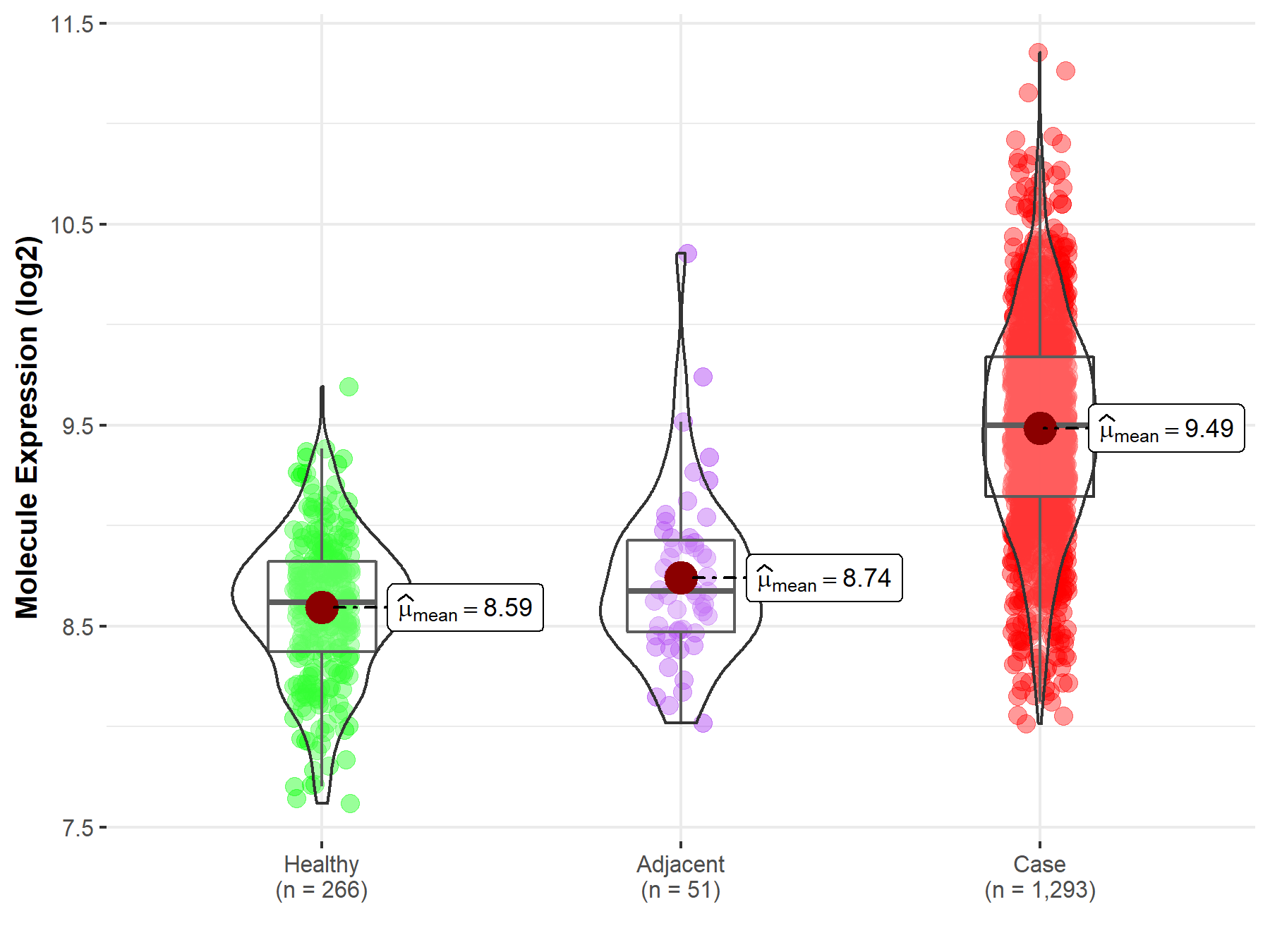
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Ovary | |
| The Specified Disease | Ovarian cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 5.01E-05; Fold-change: 1.02E+00; Z-score: 2.68E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 1.99E-02; Fold-change: 5.82E-01; Z-score: 9.55E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
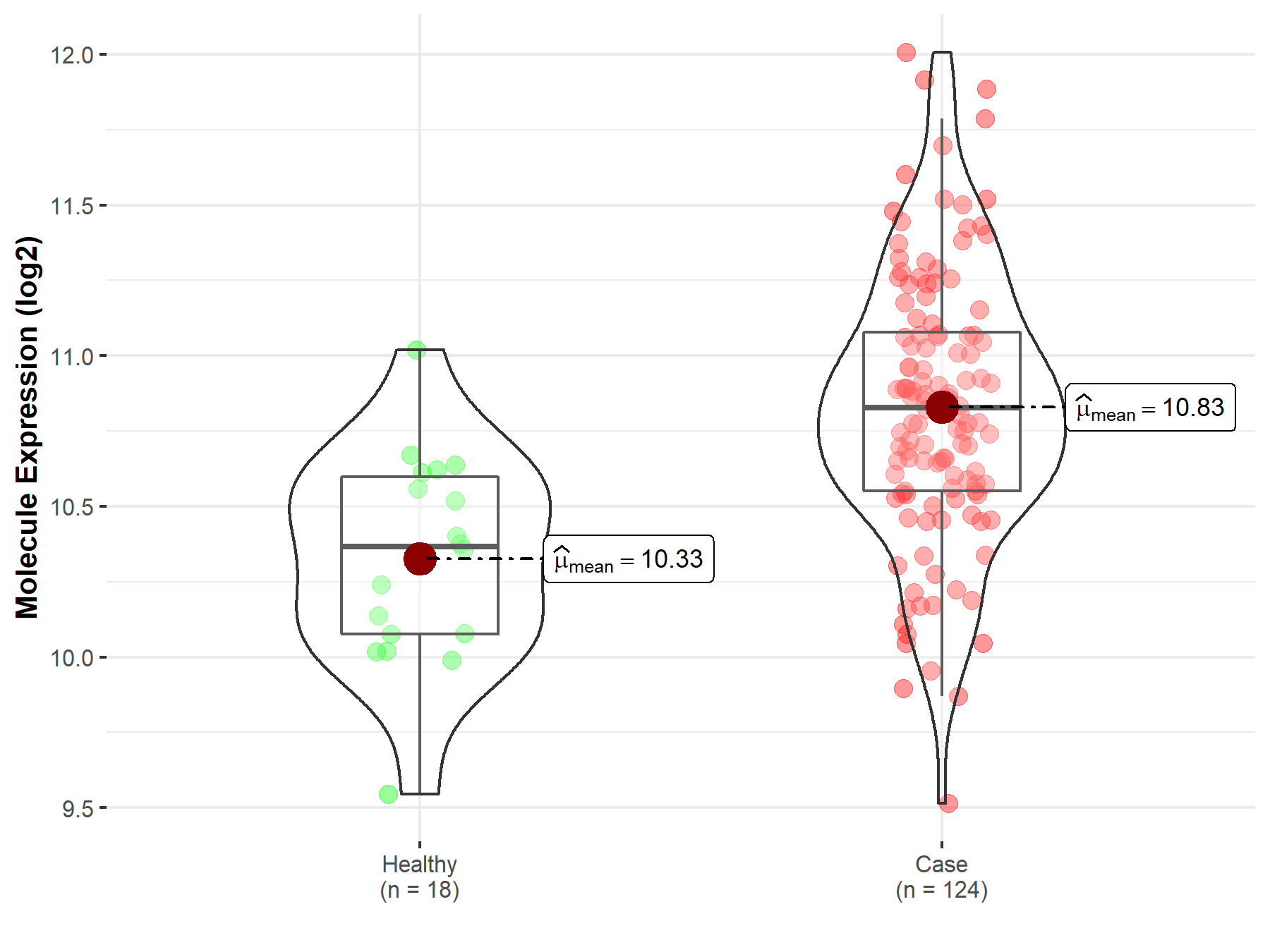
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Cervix uteri | |
| The Specified Disease | Cervical cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 8.54E-06; Fold-change: 4.61E-01; Z-score: 1.33E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Thyroid | |
| The Specified Disease | Thyroid cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.88E-01; Fold-change: 6.39E-02; Z-score: 1.33E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 2.03E-07; Fold-change: 2.76E-01; Z-score: 8.47E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
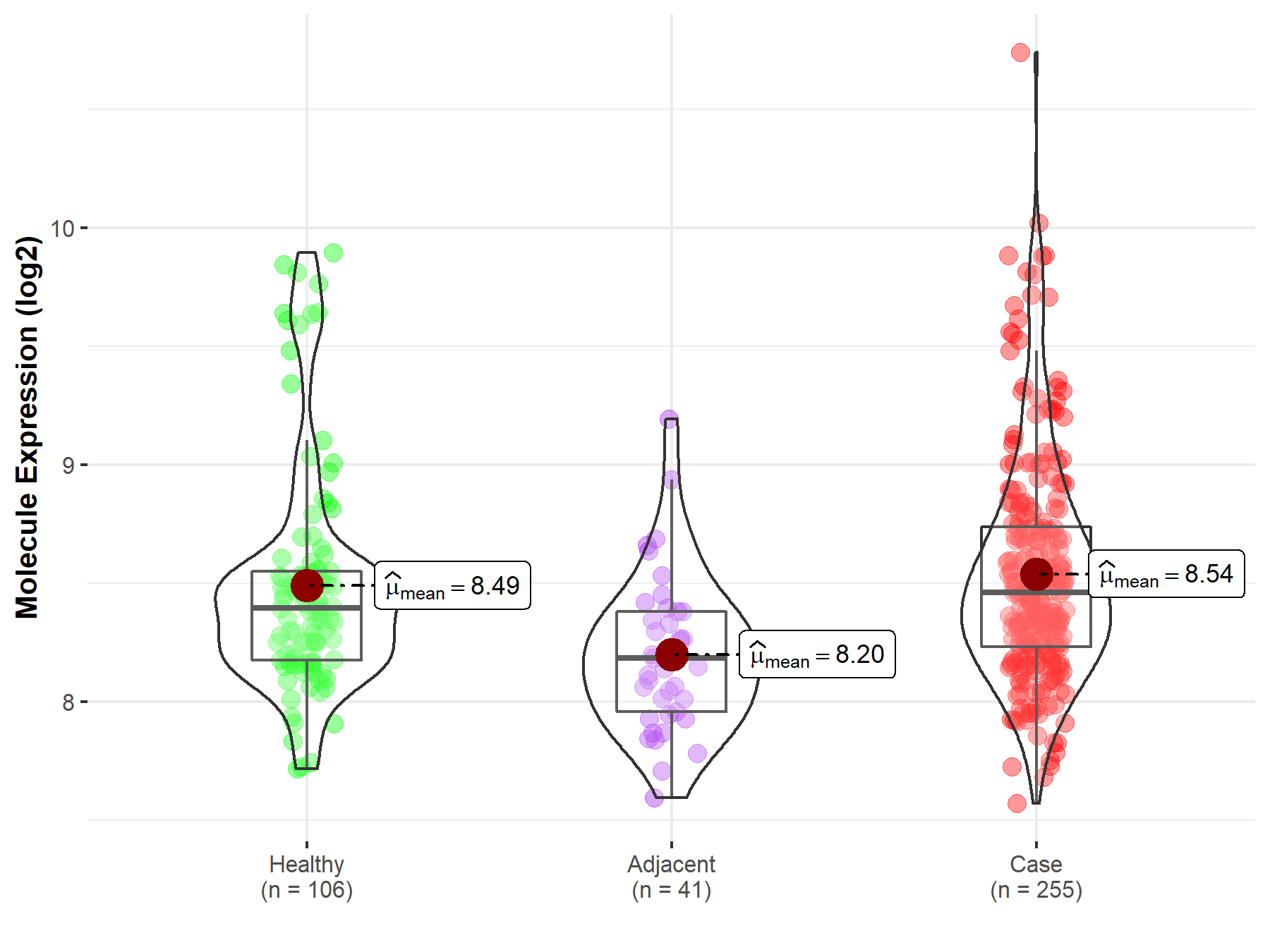
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

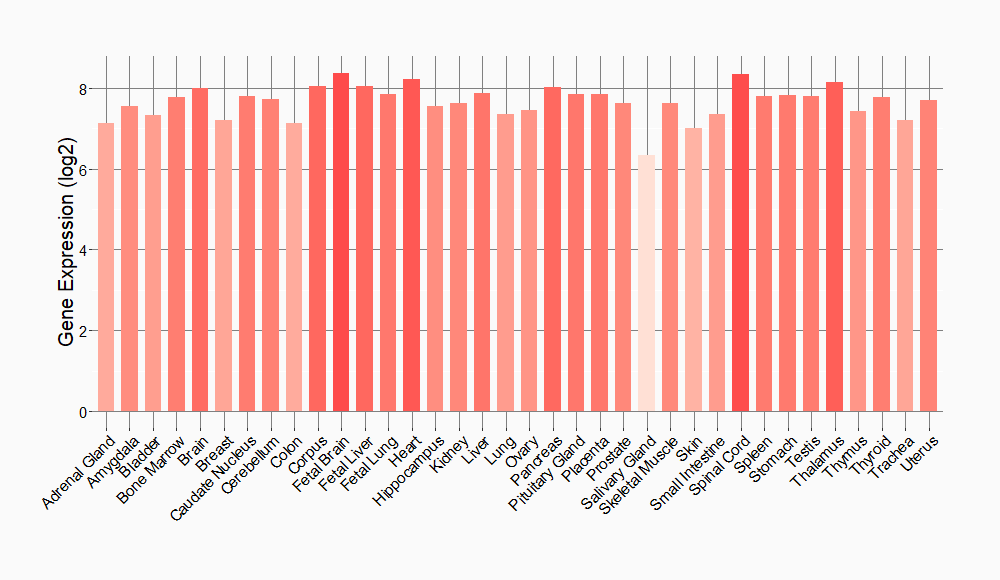
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
