Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00418) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Iodine-131
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
IODINE-131; Iodine 131; UNII-I5X6L61HUT; I5X6L61HUT; 10043-66-0; I-131; Iodine I 131; Radioactive iodine-I131; Radioactive iodine (131I); Iodine, mol. (131I2); Iodine, isotope of mass 131; Iodine, labeled with iodine-131; I 131; 15124-39-7
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Structure |
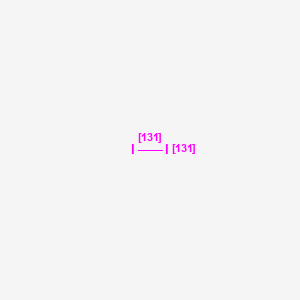
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[1]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Discovered by Cell Line Test for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[3]
|
||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
I2
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
[131I][131I]
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/I2/c1-2/i1+4,2+4
|
||||
| InChIKey |
PNDPGZBMCMUPRI-HVTJNCQCSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Solute carrier family 6 member 9 (SLC6A9) | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Papillary thyroid carcinoma [ICD-11: 2D10.1] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | |||||||||||||
| Classification of Disease | Thyroid cancer [ICD-11: 2D10] | ||||||||||||
| The Specified Disease | Thyroid carcinoma | ||||||||||||
| The Studied Tissue | Thyroid | ||||||||||||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 6.06E-17 Fold-change: -1.07E+00 Z-score: -8.75E+00 |
||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | SLC6A9/PARP1 signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04064 | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | BCPAP cells | Thyroid | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0153 | |||||||||
| TPC-1 cells | Thyroid | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6298 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | SLC6A9-5:2 overexpression was positively correlated with PARP-1 mRNA and protein levels, which restored the sensitivity of resistant thyroid cancer cells. SLC6A9 is positively correlated with PARP-1 expression, and PARP-1 inhibition makes thyroid cancer cells resistant to 131I. Upregulation of the SLC6A9-PARP-1 pathway enhanced the sensitivity to 131I treatment through energy exhaustion during excess RNA repair. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Maternally expressed 3 (MEG3) | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Thyroid carcinoma [ICD-11: 2D10.4] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | |||||||||||||
| Classification of Disease | Thyroid cancer [ICD-11: 2D10] | ||||||||||||
| The Specified Disease | Thyroid carcinoma | ||||||||||||
| The Studied Tissue | Thyroid | ||||||||||||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 9.68E-53 Fold-change: -4.29E+00 Z-score: -1.81E+01 |
||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | ||||||||||
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | |||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | TPC-1 cells | Thyroid | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6298 | |||||||||
| FTC-133 cells | Thyroid | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1219 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qPCR | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Flow cytometry assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | MEG3 expression was decreased while miR-182 expression was increased in 131I-resistant TC cells. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: hsa-mir-182 | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Thyroid carcinoma [ICD-11: 2D10.4] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | TPC-1 cells | Thyroid | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6298 | |||||||||
| FTC-133 cells | Thyroid | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1219 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR; Luciferase reporter assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Flow cytometry assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | MEG3 expression was decreased while miR-182 expression was increased in 131I-resistant TC cells. | ||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Serine/threonine-protein kinase B-raf (BRAF) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Thyroid carcinoma [ICD-11: 2D10.4] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V600E |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.55 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.20 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
420
|
M
M
D
D
R
R
G
G
S
S
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
430
|
H
H
G
G
S
S
E
E
D
D
R
R
N
N
R
R
M
M
K
K
440
|
T
T
L
L
G
G
R
R
R
R
D
D
S
S
S
S
D
D
D
D
450
|
W
W
E
E
I
I
P
P
D
D
G
G
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
V
V
460
|
G
G
Q
Q
R
R
I
I
G
G
S
S
G
G
S
S
F
F
G
G
470
|
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
K
K
G
G
K
K
W
W
H
H
G
G
D
D
480
|
V
V
A
A
V
V
K
K
M
M
L
L
N
N
V
V
T
T
A
A
490
|
P
P
T
T
P
P
Q
Q
Q
Q
L
L
Q
Q
A
A
F
F
K
K
500
|
N
N
E
E
V
V
G
G
V
V
L
L
R
R
K
K
T
T
R
R
510
|
H
H
V
V
N
N
I
I
L
L
L
L
F
F
M
M
G
G
Y
Y
520
|
S
S
T
T
K
K
P
P
Q
Q
L
L
A
A
I
I
V
V
T
T
530
|
Q
Q
W
W
C
C
E
E
G
G
S
S
S
S
L
L
Y
Y
H
H
540
|
H
H
L
L
H
H
I
I
I
I
E
E
T
T
K
K
F
F
E
E
550
|
M
M
I
I
K
K
L
L
I
I
D
D
I
I
A
A
R
R
Q
Q
560
|
T
T
A
A
Q
Q
G
G
M
M
D
D
Y
Y
L
L
H
H
A
A
570
|
K
K
S
S
I
I
I
I
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
K
K
S
S
580
|
N
N
N
N
I
I
F
F
L
L
H
H
E
E
D
D
L
L
T
T
590
|
V
V
K
K
I
I
G
G
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
T
T
600
|
V
E
K
K
S
S
R
R
W
W
S
S
G
G
S
S
H
H
Q
Q
610
|
F
F
E
E
Q
Q
L
L
S
S
G
G
S
S
I
I
L
L
W
W
620
|
M
M
A
A
P
P
E
E
V
V
I
I
R
R
M
M
Q
Q
D
D
630
|
K
K
N
N
P
P
Y
Y
S
S
F
F
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
640
|
Y
Y
A
A
F
F
G
G
I
I
V
V
L
L
Y
Y
E
E
L
L
650
|
M
M
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
L
L
P
P
Y
Y
S
S
N
N
I
I
660
|
N
N
N
N
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
I
I
I
I
F
F
M
M
V
V
670
|
G
G
R
R
G
G
Y
Y
L
L
S
S
P
P
D
D
L
L
S
S
680
|
K
K
V
V
R
R
S
S
N
N
C
C
P
P
K
K
A
A
M
M
690
|
K
K
R
R
L
L
M
M
A
A
E
E
C
C
L
L
K
K
K
K
700
|
K
K
R
R
D
D
E
E
R
R
P
P
L
L
F
F
P
P
Q
Q
710
|
I
I
L
L
A
A
S
S
I
I
E
E
L
L
L
L
A
A
R
R
720
|
S
S
L
L
P
P
K
K
I
I
H
H
R
R
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | ||||||||||
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | |||||||||||
| Epigenetic signaling pathway | Activation | hsa05207 | |||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Low throughput experiment assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Primary resistance appears to develop early in tumorigenesis via genetic or epigenetic events that activate pro-proliferation pathways or inhibit pathways that stimulate cell death. Loss or gain of a cell surface receptor or transporter or other alterations in the drug target pathway can also lead to resistance against pharmacological agents, as described below for PTC with the BRAFV600E mutation. BRA FV600E PTC exhibits primary resistance to RAI treatment, higher rates of tumor recurrence and metastases, and lower survival rates. Remarkably, the BRAFV600E mutation not only promotes thyroid tumor cell proliferation, adhesion, migration and invasion, but also up-regulates epigenetic pathways that silence expression of the sodium/iodide symporter. This blocks iodide uptake, which may be one cause of primary resistance to RAI. BRAF V600E PTC exhibits primary resistance to RAI treatment, higher rates of tumor recurrence and metastases, and lower survival rates. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Poly[ADP-ribose] synthase 1 (PARP1) | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Papillary thyroid carcinoma [ICD-11: 2D10.1] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | SLC6A9/PARP1 signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04064 | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | BCPAP cells | Thyroid | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0153 | |||||||||
| TPC-1 cells | Thyroid | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6298 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; qRT-PCR | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | SLC6A9-5:2 overexpression was positively correlated with PARP-1 mRNA and protein levels, which restored the sensitivity of resistant thyroid cancer cells. SLC6A9 is positively correlated with PARP-1 expression, and PARP-1 inhibition makes thyroid cancer cells resistant to 131I. Upregulation of the SLC6A9-PARP-1 pathway enhanced the sensitivity to 131I treatment through energy exhaustion during excess RNA repair. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Quinic acid (Quinate) | [2] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Thyroid gland cancer [ICD-11: 2D10.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Phenylalanine and Tyrosine metabolic signaling pathway | Activation | hsa01100 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
LC-MS/MS analysis; Infrared assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Methodology assay; LC-MC-based metabolomics assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | This study was comprised of 20 RAIR and 14 non-radioiodine refractory (non-RAIR) thyroid cancer patients. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry was used to identify differences in the serum metabolites of RAIR and non-RAIR patients. In addition, chemical assays were performed to determine the effects of the differential metabolites on iodine uptake. Metabolic pathway enrichment analysis of the differential metabolites revealed significant differences in the phenylalanine and tyrosine metabolic pathways. Notably, quinate and shikimic acid, metabolites of the tyrosine pathway, were significantly increased in the RAIR group. In contrast, the phenylalanine pathway metabolites, hippuric acid and 2-phenylacetamide, were markedly decreased in the RAIR group. Thyroid peroxidase plays an important role in catalyzing the iodination of tyrosine residues, while the ionic state of iodine promotes the iodination reaction. Quinate, shikimic acid, hippuric acid, and 2-phenylacetamide were found to be involved in the iodination of tyrosine, which is a key step in thyroid hormone synthesis. Specifically, quinate and shikimic acid were found to inhibit iodination, while hippuric acid and 2-phenylacetamide promoted iodination. Abnormalities in phenylalanine and tyrosine metabolic pathways are closely associated with iodine resistance. Tyrosine is required for thyroid hormone synthesis and could be a potential cause of iodine resistance. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Shikimic acid | [2] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Thyroid gland cancer [ICD-11: 2D10.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Phenylalanine and Tyrosine metabolic signaling pathway | Activation | hsa01100 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
LC-MS/MS analysis; Infrared assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Methodology assay; LC-MC-based metabolomics assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | This study was comprised of 20 RAIR and 14 non-radioiodine refractory (non-RAIR) thyroid cancer patients. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry was used to identify differences in the serum metabolites of RAIR and non-RAIR patients. In addition, chemical assays were performed to determine the effects of the differential metabolites on iodine uptake. Metabolic pathway enrichment analysis of the differential metabolites revealed significant differences in the phenylalanine and tyrosine metabolic pathways. Notably, quinate and shikimic acid, metabolites of the tyrosine pathway, were significantly increased in the RAIR group. In contrast, the phenylalanine pathway metabolites, hippuric acid and 2-phenylacetamide, were markedly decreased in the RAIR group. Thyroid peroxidase plays an important role in catalyzing the iodination of tyrosine residues, while the ionic state of iodine promotes the iodination reaction. Quinate, shikimic acid, hippuric acid, and 2-phenylacetamide were found to be involved in the iodination of tyrosine, which is a key step in thyroid hormone synthesis. Specifically, quinate and shikimic acid were found to inhibit iodination, while hippuric acid and 2-phenylacetamide promoted iodination. Abnormalities in phenylalanine and tyrosine metabolic pathways are closely associated with iodine resistance. Tyrosine is required for thyroid hormone synthesis and could be a potential cause of iodine resistance. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Hippuric acid | [2] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Thyroid gland cancer [ICD-11: 2D10.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Phenylalanine and Tyrosine metabolic signaling pathway | Activation | hsa01100 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
LC-MS/MS analysis; Infrared assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Methodology assay; LC-MC-based metabolomics assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | This study was comprised of 20 RAIR and 14 non-radioiodine refractory (non-RAIR) thyroid cancer patients. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry was used to identify differences in the serum metabolites of RAIR and non-RAIR patients. In addition, chemical assays were performed to determine the effects of the differential metabolites on iodine uptake. Metabolic pathway enrichment analysis of the differential metabolites revealed significant differences in the phenylalanine and tyrosine metabolic pathways. Notably, quinate and shikimic acid, metabolites of the tyrosine pathway, were significantly increased in the RAIR group. In contrast, the phenylalanine pathway metabolites, hippuric acid and 2-phenylacetamide, were markedly decreased in the RAIR group. Thyroid peroxidase plays an important role in catalyzing the iodination of tyrosine residues, while the ionic state of iodine promotes the iodination reaction. Quinate, shikimic acid, hippuric acid, and 2-phenylacetamide were found to be involved in the iodination of tyrosine, which is a key step in thyroid hormone synthesis. Specifically, quinate and shikimic acid were found to inhibit iodination, while hippuric acid and 2-phenylacetamide promoted iodination. Abnormalities in phenylalanine and tyrosine metabolic pathways are closely associated with iodine resistance. Tyrosine is required for thyroid hormone synthesis and could be a potential cause of iodine resistance. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: 2-Phenylacetamide | [2] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Thyroid gland cancer [ICD-11: 2D10.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Phenylalanine and Tyrosine metabolic signaling pathway | Activation | hsa01100 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
LC-MS/MS analysis; Infrared assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Methodology assay; LC-MC-based metabolomics assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | This study was comprised of 20 RAIR and 14 non-radioiodine refractory (non-RAIR) thyroid cancer patients. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry was used to identify differences in the serum metabolites of RAIR and non-RAIR patients. In addition, chemical assays were performed to determine the effects of the differential metabolites on iodine uptake. Metabolic pathway enrichment analysis of the differential metabolites revealed significant differences in the phenylalanine and tyrosine metabolic pathways. Notably, quinate and shikimic acid, metabolites of the tyrosine pathway, were significantly increased in the RAIR group. In contrast, the phenylalanine pathway metabolites, hippuric acid and 2-phenylacetamide, were markedly decreased in the RAIR group. Thyroid peroxidase plays an important role in catalyzing the iodination of tyrosine residues, while the ionic state of iodine promotes the iodination reaction. Quinate, shikimic acid, hippuric acid, and 2-phenylacetamide were found to be involved in the iodination of tyrosine, which is a key step in thyroid hormone synthesis. Specifically, quinate and shikimic acid were found to inhibit iodination, while hippuric acid and 2-phenylacetamide promoted iodination. Abnormalities in phenylalanine and tyrosine metabolic pathways are closely associated with iodine resistance. Tyrosine is required for thyroid hormone synthesis and could be a potential cause of iodine resistance. | ||||||||||||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
