Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00444) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Colistin
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Colistin sulphate; Polymyxin E; Colistin sulfate, nonsterile; Polymyxin E. Sulfate; Coly-Mycin M Parenteral (TN)
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
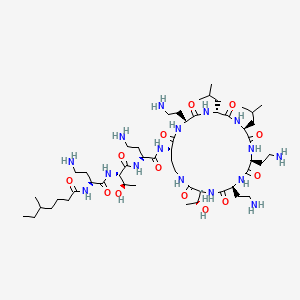
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(6 diseases)
[4]
[1]
|
||||
| Target | Bacterial Dihydropteroate synthetase (Bact folP) | DHPS_ECOLI | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C52H98N16O13
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CCC(C)CCCC(=O)N[C@@H](CCN)C(=O)N[C@@H]([C@@H](C)O)C(=O)N[C@@H](CCN)C(=O)N[C@H]1CCNC(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)[C@H](NC(=O)[C@@H](NC1=O)CCN)CC(C)C)CC(C)C)CCN)CCN)[C@@H](C)O
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C52H98N16O13/c1-9-29(6)11-10-12-40(71)59-32(13-19-53)47(76)68-42(31(8)70)52(81)64-35(16-22-56)44(73)63-37-18-24-58-51(80)41(30(7)69)67-48(77)36(17-23-57)61-43(72)33(14-20-54)62-49(78)38(25-27(2)3)66-50(79)39(26-28(4)5)65-45(74)34(15-21-55)60-46(37)75/h27-39,41-42,69-70H,9-26,53-57H2,1-8H3,(H,58,80)(H,59,71)(H,60,75)(H,61,72)(H,62,78)(H,63,73)(H,64,81)(H,65,74)(H,66,79)(H,67,77)(H,68,76)/t29 ,30-,31-,32+,33+,34+,35+,36+,37+,38+,39-,41+,42+/m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
YKQOSKADJPQZHB-QNPLFGSASA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| INTEDE ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Hydrolase (HYDE) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Salmonella enterica infection [ICD-11: 1A09.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli NEB5alpha | 562 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
In silico EMBOSS Transeq assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Mcr-1 is a phosphoethanolamine transferase that modifies cell membrane lipid A head groups with a phosphoethanolamine residue, reducing affinity to colistin. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Multifunctional fusion protein (LPXA) | [2], [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acinetobacter meningitis [ICD-11: 1D01.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Frameshift mutation | c.90del |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 19606 | 575584 | ||
| Acinetobacter baumannii FADDI008 | 470 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | A critical first step in the action of polymyxins is the electrostatic interaction between the positively charged peptide and the negatively charged lipid A, the endotoxic component of lipopolysaccharide (LPS).A. baumannii type strain ATCC 19606, colistin-resistant variants contain mutations within genes essential for lipid A biosynthesis (either lpxA, lpxC, or lpxD) and that these strains have lost the ability to produce lipid A and therefore LPS. | |||
| Key Molecule: Multifunctional fusion protein (LPXA) | [2], [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acinetobacter meningitis [ICD-11: 1D01.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.H159D |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Acinetobacter baumannii AL1844 | 470 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | A critical first step in the action of polymyxins is the electrostatic interaction between the positively charged peptide and the negatively charged lipid A, the endotoxic component of lipopolysaccharide (LPS).A. baumannii type strain ATCC 19606, colistin-resistant variants contain mutations within genes essential for lipid A biosynthesis (either lpxA, lpxC, or lpxD) and that these strains have lost the ability to produce lipid A and therefore LPS. | |||
| Key Molecule: Multifunctional fusion protein (LPXA) | [2], [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acinetobacter meningitis [ICD-11: 1D01.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | c.700C>T |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Acinetobacter baumannii AL1845 | 470 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | A critical first step in the action of polymyxins is the electrostatic interaction between the positively charged peptide and the negatively charged lipid A, the endotoxic component of lipopolysaccharide (LPS).A. baumannii type strain ATCC 19606, colistin-resistant variants contain mutations within genes essential for lipid A biosynthesis (either lpxA, lpxC, or lpxD) and that these strains have lost the ability to produce lipid A and therefore LPS. | |||
| Key Molecule: Multifunctional fusion protein (LPXA) | [2], [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acinetobacter meningitis [ICD-11: 1D01.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G68D |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Acinetobacter baumannii AL1846 | 470 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | A critical first step in the action of polymyxins is the electrostatic interaction between the positively charged peptide and the negatively charged lipid A, the endotoxic component of lipopolysaccharide (LPS).A. baumannii type strain ATCC 19606, colistin-resistant variants contain mutations within genes essential for lipid A biosynthesis (either lpxA, lpxC, or lpxD) and that these strains have lost the ability to produce lipid A and therefore LPS. | |||
| Key Molecule: Multifunctional fusion protein (LPXA) | [2], [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acinetobacter meningitis [ICD-11: 1D01.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Frameshift mutation | c.391_421del |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 19606 | 575584 | ||
| Acinetobacter baumannii FADDI008 | 470 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | A critical first step in the action of polymyxins is the electrostatic interaction between the positively charged peptide and the negatively charged lipid A, the endotoxic component of lipopolysaccharide (LPS).A. baumannii type strain ATCC 19606, colistin-resistant variants contain mutations within genes essential for lipid A biosynthesis (either lpxA, lpxC, or lpxD) and that these strains have lost the ability to produce lipid A and therefore LPS. | |||
| Key Molecule: Multifunctional fusion protein (LPXA) | [2], [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acinetobacter meningitis [ICD-11: 1D01.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q72K |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Acinetobacter baumannii AL1848 | 470 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | A critical first step in the action of polymyxins is the electrostatic interaction between the positively charged peptide and the negatively charged lipid A, the endotoxic component of lipopolysaccharide (LPS).A. baumannii type strain ATCC 19606, colistin-resistant variants contain mutations within genes essential for lipid A biosynthesis (either lpxA, lpxC, or lpxD) and that these strains have lost the ability to produce lipid A and therefore LPS. | |||
| Key Molecule: Multifunctional fusion protein (LPXA) | [2], [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acinetobacter meningitis [ICD-11: 1D01.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Frameshift mutation | c.76_78del |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 19606 | 575584 | ||
| Acinetobacter baumannii FADDI008 | 470 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | A critical first step in the action of polymyxins is the electrostatic interaction between the positively charged peptide and the negatively charged lipid A, the endotoxic component of lipopolysaccharide (LPS).A. baumannii type strain ATCC 19606, colistin-resistant variants contain mutations within genes essential for lipid A biosynthesis (either lpxA, lpxC, or lpxD) and that these strains have lost the ability to produce lipid A and therefore LPS. | |||
| Key Molecule: Multifunctional fusion protein (LPXA) | [2], [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acinetobacter meningitis [ICD-11: 1D01.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Frameshift mutation | c.364_809del |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 19606 | 575584 | ||
| Acinetobacter baumannii FADDI008 | 470 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | A critical first step in the action of polymyxins is the electrostatic interaction between the positively charged peptide and the negatively charged lipid A, the endotoxic component of lipopolysaccharide (LPS).A. baumannii type strain ATCC 19606, colistin-resistant variants contain mutations within genes essential for lipid A biosynthesis (either lpxA, lpxC, or lpxD) and that these strains have lost the ability to produce lipid A and therefore LPS. | |||
ICD-12: Respiratory system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Transcriptional regulatory protein (PHOP) | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Klebsiella pneumoniae infection [ICD-11: CA40.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D191Y |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Klebsiella pneumoniae kp75 | 573 | ||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC 53153 | 573 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The mutated protein PhoP activates the transcription of the pmrHFIJkLM operon, the product of which leads to synthesis of L-amino-arabinose and ultimately to colistin resistance in k. pneumoniae.These modifications create a more positively charged lipopolysaccharide and thus reduce the affinity of LPS to positively charged polymyxins. | |||
| Key Molecule: Transcriptional regulatory protein (PHOP) | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Klebsiella pneumoniae infection [ICD-11: CA40.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D191Y |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Klebsiella pneumoniae kp75 | 573 | ||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC 53153 | 573 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The mutated protein PhoP activates the transcription of the pmrHFIJkLM operon, the product of which leads to synthesis of L-amino-arabinose and ultimately to colistin resistance in k. pneumoniae.These modifications create a more positively charged lipopolysaccharide and thus reduce the affinity of LPS to positively charged polymyxins. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Multifunctional fusion protein (LPXA) | [2], [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acinetobacter baumannii infection [ICD-11: CA40.4] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Frameshift mutation | c.90del |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 19606 | 575584 | ||
| Acinetobacter baumannii FADDI008 | 470 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | A critical first step in the action of polymyxins is the electrostatic interaction between the positively charged peptide and the negatively charged lipid A, the endotoxic component of lipopolysaccharide (LPS).A. baumannii type strain ATCC 19606, colistin-resistant variants contain mutations within genes essential for lipid A biosynthesis (either lpxA, lpxC, or lpxD) and that these strains have lost the ability to produce lipid A and therefore LPS. | |||
| Key Molecule: Multifunctional fusion protein (LPXA) | [2], [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acinetobacter baumannii infection [ICD-11: CA40.4] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.H159D |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Acinetobacter baumannii AL1844 | 470 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | A critical first step in the action of polymyxins is the electrostatic interaction between the positively charged peptide and the negatively charged lipid A, the endotoxic component of lipopolysaccharide (LPS).A. baumannii type strain ATCC 19606, colistin-resistant variants contain mutations within genes essential for lipid A biosynthesis (either lpxA, lpxC, or lpxD) and that these strains have lost the ability to produce lipid A and therefore LPS. | |||
| Key Molecule: Multifunctional fusion protein (LPXA) | [2], [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acinetobacter baumannii infection [ICD-11: CA40.4] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | c.700C>T |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Acinetobacter baumannii AL1845 | 470 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | A critical first step in the action of polymyxins is the electrostatic interaction between the positively charged peptide and the negatively charged lipid A, the endotoxic component of lipopolysaccharide (LPS).A. baumannii type strain ATCC 19606, colistin-resistant variants contain mutations within genes essential for lipid A biosynthesis (either lpxA, lpxC, or lpxD) and that these strains have lost the ability to produce lipid A and therefore LPS. | |||
| Key Molecule: Multifunctional fusion protein (LPXA) | [2], [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acinetobacter baumannii infection [ICD-11: CA40.4] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G68D |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Acinetobacter baumannii AL1846 | 470 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | A critical first step in the action of polymyxins is the electrostatic interaction between the positively charged peptide and the negatively charged lipid A, the endotoxic component of lipopolysaccharide (LPS).A. baumannii type strain ATCC 19606, colistin-resistant variants contain mutations within genes essential for lipid A biosynthesis (either lpxA, lpxC, or lpxD) and that these strains have lost the ability to produce lipid A and therefore LPS. | |||
| Key Molecule: Multifunctional fusion protein (LPXA) | [2], [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acinetobacter baumannii infection [ICD-11: CA40.4] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Frameshift mutation | c.391_421del |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 19606 | 575584 | ||
| Acinetobacter baumannii FADDI008 | 470 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | A critical first step in the action of polymyxins is the electrostatic interaction between the positively charged peptide and the negatively charged lipid A, the endotoxic component of lipopolysaccharide (LPS).A. baumannii type strain ATCC 19606, colistin-resistant variants contain mutations within genes essential for lipid A biosynthesis (either lpxA, lpxC, or lpxD) and that these strains have lost the ability to produce lipid A and therefore LPS. | |||
| Key Molecule: Multifunctional fusion protein (LPXA) | [2], [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acinetobacter baumannii infection [ICD-11: CA40.4] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q72K |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Acinetobacter baumannii AL1848 | 470 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | A critical first step in the action of polymyxins is the electrostatic interaction between the positively charged peptide and the negatively charged lipid A, the endotoxic component of lipopolysaccharide (LPS).A. baumannii type strain ATCC 19606, colistin-resistant variants contain mutations within genes essential for lipid A biosynthesis (either lpxA, lpxC, or lpxD) and that these strains have lost the ability to produce lipid A and therefore LPS. | |||
| Key Molecule: Multifunctional fusion protein (LPXA) | [2], [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acinetobacter baumannii infection [ICD-11: CA40.4] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Frameshift mutation | c.76_78del |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 19606 | 575584 | ||
| Acinetobacter baumannii FADDI008 | 470 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | A critical first step in the action of polymyxins is the electrostatic interaction between the positively charged peptide and the negatively charged lipid A, the endotoxic component of lipopolysaccharide (LPS).A. baumannii type strain ATCC 19606, colistin-resistant variants contain mutations within genes essential for lipid A biosynthesis (either lpxA, lpxC, or lpxD) and that these strains have lost the ability to produce lipid A and therefore LPS. | |||
| Key Molecule: Multifunctional fusion protein (LPXA) | [2], [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acinetobacter baumannii infection [ICD-11: CA40.4] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Frameshift mutation | c.364_809del |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 19606 | 575584 | ||
| Acinetobacter baumannii FADDI008 | 470 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | A critical first step in the action of polymyxins is the electrostatic interaction between the positively charged peptide and the negatively charged lipid A, the endotoxic component of lipopolysaccharide (LPS).A. baumannii type strain ATCC 19606, colistin-resistant variants contain mutations within genes essential for lipid A biosynthesis (either lpxA, lpxC, or lpxD) and that these strains have lost the ability to produce lipid A and therefore LPS. | |||
ICD-16: Genitourinary system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Transcriptional regulatory protein (PHOP) | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Klebsiella pneumoniae [ICD-11: CA40.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D191Y |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Klebsiella pneumoniae kp75 | 573 | ||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC 53153 | 573 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The mutated protein PhoP activates the transcription of the pmrHFIJkLM operon, the product of which leads to synthesis of L-amino-arabinose and ultimately to colistin resistance in k. pneumoniae.These modifications create a more positively charged lipopolysaccharide and thus reduce the affinity of LPS to positively charged polymyxins. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Multifunctional fusion protein (LPXA) | [2], [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acinetobacter baumannii infection [ICD-11: CA40.4] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Frameshift mutation | c.90del |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 19606 | 575584 | ||
| Acinetobacter baumannii FADDI008 | 470 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | A critical first step in the action of polymyxins is the electrostatic interaction between the positively charged peptide and the negatively charged lipid A, the endotoxic component of lipopolysaccharide (LPS).A. baumannii type strain ATCC 19606, colistin-resistant variants contain mutations within genes essential for lipid A biosynthesis (either lpxA, lpxC, or lpxD) and that these strains have lost the ability to produce lipid A and therefore LPS. | |||
| Key Molecule: Multifunctional fusion protein (LPXA) | [2], [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acinetobacter baumannii infection [ICD-11: CA40.4] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.H159D |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Acinetobacter baumannii AL1844 | 470 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | A critical first step in the action of polymyxins is the electrostatic interaction between the positively charged peptide and the negatively charged lipid A, the endotoxic component of lipopolysaccharide (LPS).A. baumannii type strain ATCC 19606, colistin-resistant variants contain mutations within genes essential for lipid A biosynthesis (either lpxA, lpxC, or lpxD) and that these strains have lost the ability to produce lipid A and therefore LPS. | |||
| Key Molecule: Multifunctional fusion protein (LPXA) | [2], [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acinetobacter baumannii infection [ICD-11: CA40.4] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | c.700C>T |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Acinetobacter baumannii AL1845 | 470 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | A critical first step in the action of polymyxins is the electrostatic interaction between the positively charged peptide and the negatively charged lipid A, the endotoxic component of lipopolysaccharide (LPS).A. baumannii type strain ATCC 19606, colistin-resistant variants contain mutations within genes essential for lipid A biosynthesis (either lpxA, lpxC, or lpxD) and that these strains have lost the ability to produce lipid A and therefore LPS. | |||
| Key Molecule: Multifunctional fusion protein (LPXA) | [2], [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acinetobacter baumannii infection [ICD-11: CA40.4] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G68D |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Acinetobacter baumannii AL1846 | 470 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | A critical first step in the action of polymyxins is the electrostatic interaction between the positively charged peptide and the negatively charged lipid A, the endotoxic component of lipopolysaccharide (LPS).A. baumannii type strain ATCC 19606, colistin-resistant variants contain mutations within genes essential for lipid A biosynthesis (either lpxA, lpxC, or lpxD) and that these strains have lost the ability to produce lipid A and therefore LPS. | |||
| Key Molecule: Multifunctional fusion protein (LPXA) | [2], [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acinetobacter baumannii infection [ICD-11: CA40.4] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Frameshift mutation | c.391_421del |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 19606 | 575584 | ||
| Acinetobacter baumannii FADDI008 | 470 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | A critical first step in the action of polymyxins is the electrostatic interaction between the positively charged peptide and the negatively charged lipid A, the endotoxic component of lipopolysaccharide (LPS).A. baumannii type strain ATCC 19606, colistin-resistant variants contain mutations within genes essential for lipid A biosynthesis (either lpxA, lpxC, or lpxD) and that these strains have lost the ability to produce lipid A and therefore LPS. | |||
| Key Molecule: Multifunctional fusion protein (LPXA) | [2], [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acinetobacter baumannii infection [ICD-11: CA40.4] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q72K |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Acinetobacter baumannii AL1848 | 470 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | A critical first step in the action of polymyxins is the electrostatic interaction between the positively charged peptide and the negatively charged lipid A, the endotoxic component of lipopolysaccharide (LPS).A. baumannii type strain ATCC 19606, colistin-resistant variants contain mutations within genes essential for lipid A biosynthesis (either lpxA, lpxC, or lpxD) and that these strains have lost the ability to produce lipid A and therefore LPS. | |||
| Key Molecule: Multifunctional fusion protein (LPXA) | [2], [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acinetobacter baumannii infection [ICD-11: CA40.4] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Frameshift mutation | c.76_78del |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 19606 | 575584 | ||
| Acinetobacter baumannii FADDI008 | 470 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | A critical first step in the action of polymyxins is the electrostatic interaction between the positively charged peptide and the negatively charged lipid A, the endotoxic component of lipopolysaccharide (LPS).A. baumannii type strain ATCC 19606, colistin-resistant variants contain mutations within genes essential for lipid A biosynthesis (either lpxA, lpxC, or lpxD) and that these strains have lost the ability to produce lipid A and therefore LPS. | |||
| Key Molecule: Multifunctional fusion protein (LPXA) | [2], [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acinetobacter baumannii infection [ICD-11: CA40.4] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Frameshift mutation | c.364_809del |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 19606 | 575584 | ||
| Acinetobacter baumannii FADDI008 | 470 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | A critical first step in the action of polymyxins is the electrostatic interaction between the positively charged peptide and the negatively charged lipid A, the endotoxic component of lipopolysaccharide (LPS).A. baumannii type strain ATCC 19606, colistin-resistant variants contain mutations within genes essential for lipid A biosynthesis (either lpxA, lpxC, or lpxD) and that these strains have lost the ability to produce lipid A and therefore LPS. | |||
ICD-21: Symptoms/clinical signs/unclassified clinical findings
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Multifunctional fusion protein (LPXA) | [2], [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acinetobacter baumannii infection [ICD-11: CA40.4] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Frameshift mutation | c.90del |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 19606 | 575584 | ||
| Acinetobacter baumannii FADDI008 | 470 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | A critical first step in the action of polymyxins is the electrostatic interaction between the positively charged peptide and the negatively charged lipid A, the endotoxic component of lipopolysaccharide (LPS).A. baumannii type strain ATCC 19606, colistin-resistant variants contain mutations within genes essential for lipid A biosynthesis (either lpxA, lpxC, or lpxD) and that these strains have lost the ability to produce lipid A and therefore LPS. | |||
| Key Molecule: Multifunctional fusion protein (LPXA) | [2], [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acinetobacter baumannii infection [ICD-11: CA40.4] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.H159D |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Acinetobacter baumannii AL1844 | 470 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | A critical first step in the action of polymyxins is the electrostatic interaction between the positively charged peptide and the negatively charged lipid A, the endotoxic component of lipopolysaccharide (LPS).A. baumannii type strain ATCC 19606, colistin-resistant variants contain mutations within genes essential for lipid A biosynthesis (either lpxA, lpxC, or lpxD) and that these strains have lost the ability to produce lipid A and therefore LPS. | |||
| Key Molecule: Multifunctional fusion protein (LPXA) | [2], [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acinetobacter baumannii infection [ICD-11: CA40.4] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | c.700C>T |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Acinetobacter baumannii AL1845 | 470 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | A critical first step in the action of polymyxins is the electrostatic interaction between the positively charged peptide and the negatively charged lipid A, the endotoxic component of lipopolysaccharide (LPS).A. baumannii type strain ATCC 19606, colistin-resistant variants contain mutations within genes essential for lipid A biosynthesis (either lpxA, lpxC, or lpxD) and that these strains have lost the ability to produce lipid A and therefore LPS. | |||
| Key Molecule: Multifunctional fusion protein (LPXA) | [2], [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acinetobacter baumannii infection [ICD-11: CA40.4] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G68D |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Acinetobacter baumannii AL1846 | 470 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | A critical first step in the action of polymyxins is the electrostatic interaction between the positively charged peptide and the negatively charged lipid A, the endotoxic component of lipopolysaccharide (LPS).A. baumannii type strain ATCC 19606, colistin-resistant variants contain mutations within genes essential for lipid A biosynthesis (either lpxA, lpxC, or lpxD) and that these strains have lost the ability to produce lipid A and therefore LPS. | |||
| Key Molecule: Multifunctional fusion protein (LPXA) | [2], [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acinetobacter baumannii infection [ICD-11: CA40.4] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Frameshift mutation | c.391_421del |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 19606 | 575584 | ||
| Acinetobacter baumannii FADDI008 | 470 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | A critical first step in the action of polymyxins is the electrostatic interaction between the positively charged peptide and the negatively charged lipid A, the endotoxic component of lipopolysaccharide (LPS).A. baumannii type strain ATCC 19606, colistin-resistant variants contain mutations within genes essential for lipid A biosynthesis (either lpxA, lpxC, or lpxD) and that these strains have lost the ability to produce lipid A and therefore LPS. | |||
| Key Molecule: Multifunctional fusion protein (LPXA) | [2], [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acinetobacter baumannii infection [ICD-11: CA40.4] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q72K |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Acinetobacter baumannii AL1848 | 470 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | A critical first step in the action of polymyxins is the electrostatic interaction between the positively charged peptide and the negatively charged lipid A, the endotoxic component of lipopolysaccharide (LPS).A. baumannii type strain ATCC 19606, colistin-resistant variants contain mutations within genes essential for lipid A biosynthesis (either lpxA, lpxC, or lpxD) and that these strains have lost the ability to produce lipid A and therefore LPS. | |||
| Key Molecule: Multifunctional fusion protein (LPXA) | [2], [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acinetobacter baumannii infection [ICD-11: CA40.4] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Frameshift mutation | c.76_78del |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 19606 | 575584 | ||
| Acinetobacter baumannii FADDI008 | 470 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | A critical first step in the action of polymyxins is the electrostatic interaction between the positively charged peptide and the negatively charged lipid A, the endotoxic component of lipopolysaccharide (LPS).A. baumannii type strain ATCC 19606, colistin-resistant variants contain mutations within genes essential for lipid A biosynthesis (either lpxA, lpxC, or lpxD) and that these strains have lost the ability to produce lipid A and therefore LPS. | |||
| Key Molecule: Multifunctional fusion protein (LPXA) | [2], [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acinetobacter baumannii infection [ICD-11: CA40.4] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Frameshift mutation | c.364_809del |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 19606 | 575584 | ||
| Acinetobacter baumannii FADDI008 | 470 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | A critical first step in the action of polymyxins is the electrostatic interaction between the positively charged peptide and the negatively charged lipid A, the endotoxic component of lipopolysaccharide (LPS).A. baumannii type strain ATCC 19606, colistin-resistant variants contain mutations within genes essential for lipid A biosynthesis (either lpxA, lpxC, or lpxD) and that these strains have lost the ability to produce lipid A and therefore LPS. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
