Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00386) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Tiamulin
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Tiamulin; 55297-95-5; Thiamutilin; Tiamulina; Tiamuline; Tiamulinum; Tiamulin pamoate; UNII-E38WZ4U54R; Denagard (TN); E38WZ4U54R; CHEBI:44137; Denagard; Tiavet P; (3aS,4R,5S,6S,8R,9R,9aR,10R)-6-ethenyl-5-hydroxy-4,6,9,10-tetramethyl-1-oxodecahydro-3a,9-propanocyclopenta[8]annulen-8-yl {[2-(diethylamino)ethyl]sulfanyl}acetate; Tiamulina [Italian]; AC1LCVRY; Tiamuline [INN-French]; Tiamulinum [INN-Latin]; Tiamulina [INN-Spanish]; HSDB 7026; Tiamulin [USAN:USP:INN:BAN]; EINECS 259-580-0; BRN 2229396; Tiamulin (USP/INN); SQ 14055; CHEMBL1234521; DTXSID2046701; SCHEMBL18232392; 14-Deoxy-14-((2-diethylaminoethyl-thio)-acetoxy)mutiline; (hydroxy-tetramethyl-oxo-vinyl-[ ]yl) 2-(2-diethylaminoethylsulfanyl)acetate; HY-B2060; ZINC4217557; BBL036673; STL559052; DB11468; ((2-(Diethylamino)ethyl)thio)-, 6-ethenyldecahydro-5-hydroxy-4,6,9,10-tetramethyl-1-oxo-3a,9-propano-3aH-cyclopentacycloocten-8-yl ester (3aS-(3aalpha,4beta,5alpha,6alpha,8beta,9alpha,9abeta,10S*))-; ((2-(Diethylamino)ethyl)thio)acetic acid 8-ester with (3aS,4R,5S,6S,8R,9R,9aR,10R)-octahydro-5,8-dihydroxy-4,6,9,10)-tetramethyl-6-vinyl-3a,9-propano-3aH-cyclopentacycloocten-1(4H)-one; ((2-(Diethylamino)ethyl)thio)acetic acid 8-ester with (3aS,4R,5S,6S,8R,9R,9aR,10R)-octahydro-5,8-dihydroxy-4,6,9,10-tetramethyl-6-vinyl-3a,9-propano-3aH-cyclopentacycloocten-1(4H)-one; Acetic acid, [[2-(diethylamino)ethyl]thio]-,(3aS,4R,5S,6S,8R,9R,9aR,10R)-6-ethenyldecahydro-5-hydroxy-4,6,9,10-tetramethyl-1-oxo-3a,9-propano-3aH-cyclopentacycloocten-8-ylester; SO 14055; CS-0014153; D06127; Q7800111; (3aS,4R,5S,6S,8R,9R,9aR,10R)-5-hydroxy-4,6,9,10-tetramethyl-1-oxo-6-vinyldecahydro-3a,9-propanocyclopenta[8]annulen-8-yl {[2-(diethylamino)ethyl]sulfanyl}acetate; (3aS,4R,5S,6S,8R,9R,9aR,10R)-6-Ethenyl-5-hydroxy- 4,6,9,10-tetramethyl-1-oxodecahydro-3a,9-propano-3aH-cyclopentacycloocten-8-yl [[2-(diethylamino)ethyl]sulfanyl]acetate; 3-[2-[3-[[4-[[[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)-4-hydroxy-3-phosphonooxy-tetrahydrofuran-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxy-phosphoryl]oxy-hydroxy-phosphoryl]oxy-2-hydroxy-3,3-dimethyl-butanoyl]amino]propanoylamino]ethylsulfanylcarbonyl]-4-hydroxy-4-(2-naphthyl)butanoic acid; Acetic acid, ((2-(diethylamino)ethyl)thio)-, (3aS,4R,5S,6S,8R,9R,9aR,10R)-6-ethenyldecahydro-5-hydroxy-4,6,9,10-tetramethyl-1-oxo-3a,9-propano-3aH-cyclopentacycloocten-8-yl ester; Acetic acid, ((2-(diethylamino)ethyl)thio)-, 6-ethenyldecahydro-5-hydroxy-4,6,9,10-tetramethyl-1-oxo-3a,9-propano-3aH-cyclopentacycloocten-8-yl ester (3aS-(3aalpha,4beta,5alpha,6alpha,8beta,9alpha,9abeta,10S*))-
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Structure |
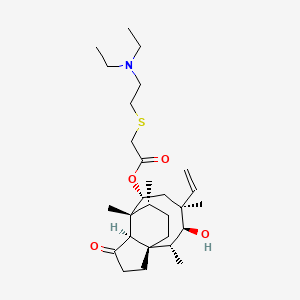
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(9 diseases)
[1]
[1]
[1]
[1]
[1]
[1]
[1]
[1]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Validated by in-vivo Model for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[4]
|
||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C28H47NO4S
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CCN(CC)CCSCC(=O)O[C@@H]1C[C@@]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@@]23CC[C@H]([C@@]1([C@@H]2C(=O)CC3)C)C)C)O)(C)C=C
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C28H47NO4S/c1-8-26(6)17-22(33-23(31)18-34-16-15-29(9-2)10-3)27(7)19(4)11-13-28(20(5)25(26)32)14-12-21(30)24(27)28/h8,19-20,22,24-25,32H,1,9-18H2,2-7H3/t19-,20+,22-,24+,25+,26-,27+,28+/m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
UURAUHCOJAIIRQ-QGLSALSOSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Carboxymethylenebutenolidase (CLCD) | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli AS19 | 562 | ||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The Cfr RNA methyltransferase causes multiple resistances to peptidyl transferase inhibitors by methylation of A2503 23S rRNA.clcD codes the same enzyme. | |||
| Key Molecule: Ribosomal RNA large subunit methyltransferase (CFR ) | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli AS19 | 562 | ||
| Escherichia coli TOP10 | 83333 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Cfr confers resistance to antibiotics binding to the peptidyl transferase center on the ribosome.The primary product of the Cfr-mediated methylation is 8-methyladenosine (m8A), a new natural RNA modification that has so far not been seen at sites other than A2503 in 23S rRNA. | |||
| Key Molecule: 23S rRNA (Adenine(2503)-C(8))-methyltransferase ClbA (CIBA) | [6] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli AS19 | 562 | ||
| Escherichia coli JW2501-1 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The cfr gene encodes the Cfr methyltransferase that methylates a single adenine in the peptidyl transferase region of bacterial ribosomes.Expression of the genes was induced in Escherichia coli, and MICs for selected antibiotics indicate that the cfr-like genes confer resistance to PhLOPSa (phenicol, lincosamide, oxazolidinone, pleuromutilin, and streptogramin A) antibiotics in the same way as the cfr gene.The Cfr-like proteins ClbA, ClbC, and ClbB confer a resistance pattern similar to that of the Cfr methyltransferase. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: ABC transporter ATP-binding protein (ABCP) | [2], [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T450I |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli TOP10 | 83333 | ||
| Enterococcus faecium HM1070 | 1352 | |||
| Enterococcus faecium UCN80 | 1352 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | ABC systems constitute one of the largest families of proteins, with most of them being involved in import and export, often called ABC transporters.Several of these class 2 ABC systems have been involved in MLS resistance, such as Msr-, Vga-, or Lsa-like proteins.The observed profile of cross-resistance to lincosamides, streptogramins A, and pleuromutilins conferred by Eat(A)v was similar to those conferred by other Lsa-like proteins. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Colibactin polyketide synthase ClbC (CLBC) | [6] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli AS19 | 562 | ||
| Escherichia coli JW2501-1 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The cfr gene encodes the Cfr methyltransferase that methylates a single adenine in the peptidyl transferase region of bacterial ribosomes.Expression of the genes was induced in Escherichia coli, and MICs for selected antibiotics indicate that the cfr-like genes confer resistance to PhLOPSa (phenicol, lincosamide, oxazolidinone, pleuromutilin, and streptogramin A) antibiotics in the same way as the cfr gene.The Cfr-like proteins ClbA, ClbC, and ClbB confer a resistance pattern similar to that of the Cfr methyltransferase. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: ABC protein lsaC (lsaC-Unclear) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Streptococcus agalactiae infection [ICD-11: 1B21.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli TOP10 | 83333 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213 | 1280 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae UCN70 | 1311 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae isolates | 1311 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae BM132 | 1319 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Expression of this novel gene, named lsa(C), in S. agalactiae BM132 after cloning led to an increase in MICs of lincomycin (0.06 to 4 ug/ml), clindamycin (0.03 to 2 ug/ml), dalfopristin (2 to >32 ug/ml), and tiamulin (0.12 to 32 ug/ml), whereas no change in MICs of erythromycin (0.06 ug/ml), azithromycin (0.03 ug/ml), spiramycin (0.25 ug/ml), telithromycin (0.03 ug/ml), and quinupristin (8 ug/ml) was observed. The phenotype was renamed the LS(A)P phenotype on the basis of cross-resistance to lincosamides, streptogramins A, and pleuromutilins. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: ABC protein lsaC (lsaC-Unclear) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Streptococcus agalactiae infection [ICD-11: 1B21.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli TOP10 | 83333 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213 | 1280 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae UCN70 | 1311 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae isolates | 1311 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae BM132 | 1319 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Expression of this novel gene, named lsa(C), in S. agalactiae BM132 after cloning led to an increase in MICs of lincomycin (0.06 to 4 ug/ml), clindamycin (0.03 to 2 ug/ml), dalfopristin (2 to >32 ug/ml), and tiamulin (0.12 to 32 ug/ml), whereas no change in MICs of erythromycin (0.06 ug/ml), azithromycin (0.03 ug/ml), spiramycin (0.25 ug/ml), telithromycin (0.03 ug/ml), and quinupristin (8 ug/ml) was observed. The phenotype was renamed the LS(A)P phenotype on the basis of cross-resistance to lincosamides, streptogramins A, and pleuromutilins. | |||
ICD-11: Circulatory system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: ABC protein lsaC (lsaC-Unclear) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Streptococcus agalactiae infection [ICD-11: 1B21.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli TOP10 | 83333 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213 | 1280 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae UCN70 | 1311 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae isolates | 1311 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae BM132 | 1319 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Expression of this novel gene, named lsa(C), in S. agalactiae BM132 after cloning led to an increase in MICs of lincomycin (0.06 to 4 ug/ml), clindamycin (0.03 to 2 ug/ml), dalfopristin (2 to >32 ug/ml), and tiamulin (0.12 to 32 ug/ml), whereas no change in MICs of erythromycin (0.06 ug/ml), azithromycin (0.03 ug/ml), spiramycin (0.25 ug/ml), telithromycin (0.03 ug/ml), and quinupristin (8 ug/ml) was observed. The phenotype was renamed the LS(A)P phenotype on the basis of cross-resistance to lincosamides, streptogramins A, and pleuromutilins. | |||
ICD-12: Respiratory system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: ABC protein lsaC (lsaC-Unclear) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Streptococcus agalactiae infection [ICD-11: 1B21.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli TOP10 | 83333 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213 | 1280 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae UCN70 | 1311 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae isolates | 1311 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae BM132 | 1319 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Expression of this novel gene, named lsa(C), in S. agalactiae BM132 after cloning led to an increase in MICs of lincomycin (0.06 to 4 ug/ml), clindamycin (0.03 to 2 ug/ml), dalfopristin (2 to >32 ug/ml), and tiamulin (0.12 to 32 ug/ml), whereas no change in MICs of erythromycin (0.06 ug/ml), azithromycin (0.03 ug/ml), spiramycin (0.25 ug/ml), telithromycin (0.03 ug/ml), and quinupristin (8 ug/ml) was observed. The phenotype was renamed the LS(A)P phenotype on the basis of cross-resistance to lincosamides, streptogramins A, and pleuromutilins. | |||
ICD-15: Musculoskeletal/connective-tissue diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: ABC protein lsaC (lsaC-Unclear) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Streptococcus agalactiae infection [ICD-11: 1B21.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli TOP10 | 83333 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213 | 1280 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae UCN70 | 1311 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae isolates | 1311 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae BM132 | 1319 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Expression of this novel gene, named lsa(C), in S. agalactiae BM132 after cloning led to an increase in MICs of lincomycin (0.06 to 4 ug/ml), clindamycin (0.03 to 2 ug/ml), dalfopristin (2 to >32 ug/ml), and tiamulin (0.12 to 32 ug/ml), whereas no change in MICs of erythromycin (0.06 ug/ml), azithromycin (0.03 ug/ml), spiramycin (0.25 ug/ml), telithromycin (0.03 ug/ml), and quinupristin (8 ug/ml) was observed. The phenotype was renamed the LS(A)P phenotype on the basis of cross-resistance to lincosamides, streptogramins A, and pleuromutilins. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: ABC protein lsaC (lsaC-Unclear) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Streptococcus agalactiae inection [ICD-11: FB84.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli TOP10 | 83333 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213 | 1280 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae UCN70 | 1311 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae isolates | 1311 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae BM132 | 1319 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Expression of this novel gene, named lsa(C), in S. agalactiae BM132 after cloning led to an increase in MICs of lincomycin (0.06 to 4 ug/ml), clindamycin (0.03 to 2 ug/ml), dalfopristin (2 to >32 ug/ml), and tiamulin (0.12 to 32 ug/ml), whereas no change in MICs of erythromycin (0.06 ug/ml), azithromycin (0.03 ug/ml), spiramycin (0.25 ug/ml), telithromycin (0.03 ug/ml), and quinupristin (8 ug/ml) was observed. The phenotype was renamed the LS(A)P phenotype on the basis of cross-resistance to lincosamides, streptogramins A, and pleuromutilins. | |||
ICD-16: Genitourinary system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: ABC protein lsaC (lsaC-Unclear) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Klebsiella pneumoniae [ICD-11: CA40.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli TOP10 | 83333 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213 | 1280 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae UCN70 | 1311 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae isolates | 1311 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae BM132 | 1319 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Expression of this novel gene, named lsa(C), in S. agalactiae BM132 after cloning led to an increase in MICs of lincomycin (0.06 to 4 ug/ml), clindamycin (0.03 to 2 ug/ml), dalfopristin (2 to >32 ug/ml), and tiamulin (0.12 to 32 ug/ml), whereas no change in MICs of erythromycin (0.06 ug/ml), azithromycin (0.03 ug/ml), spiramycin (0.25 ug/ml), telithromycin (0.03 ug/ml), and quinupristin (8 ug/ml) was observed. The phenotype was renamed the LS(A)P phenotype on the basis of cross-resistance to lincosamides, streptogramins A, and pleuromutilins. | |||
ICD-21: Symptoms/clinical signs/unclassified clinical findings
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: ABC protein lsaC (lsaC-Unclear) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Streptococcus agalactiae infection [ICD-11: 1B21.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli TOP10 | 83333 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213 | 1280 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae UCN70 | 1311 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae isolates | 1311 | |||
| Streptococcus agalactiae BM132 | 1319 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Expression of this novel gene, named lsa(C), in S. agalactiae BM132 after cloning led to an increase in MICs of lincomycin (0.06 to 4 ug/ml), clindamycin (0.03 to 2 ug/ml), dalfopristin (2 to >32 ug/ml), and tiamulin (0.12 to 32 ug/ml), whereas no change in MICs of erythromycin (0.06 ug/ml), azithromycin (0.03 ug/ml), spiramycin (0.25 ug/ml), telithromycin (0.03 ug/ml), and quinupristin (8 ug/ml) was observed. The phenotype was renamed the LS(A)P phenotype on the basis of cross-resistance to lincosamides, streptogramins A, and pleuromutilins. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
