Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00275) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Thalidomide
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Algosediv; Asmadion; Asmaval; Bonbrain; Bonbrrin; Calmore; Calmorex; Contergan; Corronarobetin; Distaval; Distaxal; Distoval; Ectiluran; Enterosediv; Gastrinide; Glupan; Glutanon; Grippex; Hippuzon; Imidene; Isomin; Kedavon; Kevadon; Neaufatin; Neosedyn; Neosydyn; Nerosedyn; Neufatin; Neurodyn; Neurosedin; Neurosedym; Neurosedyn; Nevrodyn; Nibrol; Noctosediv; Noxodyn; Pangul; Pantosediv; Polygripan; Profarmil; Psycholiquid; Psychotablets; Quetimid; Quietoplex; Sandormin; Sedalis; Sedimide; Sedin; Sedisperil; Sedoval; Shinnibrol; Sleepan; Slipro; Softenil; Softenon; Synovir; Talargan; Talidomida; Talidomide; Talimol; Talismol; Talizer; Telagan; Telargan; Telargean; Tensival; Thaled; Thalidomidum; Thalin; Thalinette; Thalomid; Thalomide; Theophilcholine; Valgis; Valgraine; Yodomin; Celgene Brand of Thalidomide; Talidomide [DCIT]; Thalidomide Celgene; Thalidomide Pharmion; Asidon 3; ENMD 0995; IN1061; Thalidomine USP26; Alpha-Phthalimidoglutarimide; E-217; Imida-lab; Imidan (peyta); N-Phthalimidoglutamic acid imide; N-Phthaloylglutamimide; N-Phthalylglutamic acid imide; Poly-Giron; Predni-Sediv; Pro-Bam M; Pro-ban M; Sedalis sedi-lab; Shin-naito S; THALIDOMIDE (AIDS INITIATIVE); Talidomida [INN-Spanish]; Thaled (TN); Thalidomide (soluble form); Thalidomidum [INN-Latin]; Thalomid (TM); Thalomid (TN); Thalomid, Thalidomide; Alpha-N-Phthalylglutaramide; Thalidomide [USAN:INN:BAN]; Alpha-(N-Phthalimido)glutarimide; N-Phthalyl-glutaminsaeure-imid; N-Phthalyl-glutaminsaeure-imid [German]; Thalidomide (+ and-); Thalidomide (JAN/USP/INN); N-(2,6-Dioxo-3-piperidyl)phthalimide; (+)-Thalidomide; (+-)-Thalidomide; (+/-)-THALIDOMIDE; (inverted question mark)-Thalidomide; 2,6-Dioxo-3-phthalimidopiperidine; 3-Phthalimidoglutarimide
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
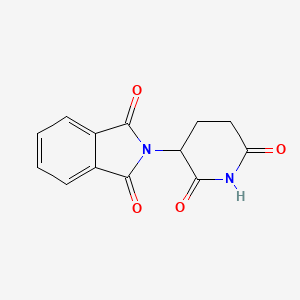
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(1 diseases)
|
||||
| Target | Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) | TNFA_HUMAN | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C13H10N2O4
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
C1CC(=O)NC(=O)C1N2C(=O)C3=CC=CC=C3C2=O
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C13H10N2O4/c16-10-6-5-9(11(17)14-10)15-12(18)7-3-1-2-4-8(7)13(15)19/h1-4,9H,5-6H2,(H,14,16,17)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
UEJJHQNACJXSKW-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| VARIDT ID | |||||
| INTEDE ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 13B (TNFSF13B) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Multiple myeloma [ICD-11: 2A83.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Multiple myeloma [ICD-11: 2A83] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Multiple myeloma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Blood | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.30E-09 Fold-change: -7.72E-01 Z-score: -7.50E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| JNk/SAPk signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | U266 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0566 |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
WST assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-202 was functioned as a modulator of BAFF expression. miR-202 over-expression sensitized MM cells to bortezomib (Bort) but less to Thalidomide (Thal) and dexamethasone (Dex). miR-202 mimics in combination with Bort inhibited MM cell survival more effectively as compared with Bort treatment alone. Our study also provided experimental evidence that JNk/SAPk signaling pathway was involved in the regulatory effect of miR-202 on drug resistance of MM cells. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: hsa-mir-202 | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Multiple myeloma [ICD-11: 2A83.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| JNk/SAPk signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | U266 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0566 |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
RT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
WST assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-202 was functioned as a modulator of BAFF expression. miR-202 over-expression sensitized MM cells to bortezomib (Bort) but less to Thalidomide (Thal) and dexamethasone (Dex). miR-202 mimics in combination with Bort inhibited MM cell survival more effectively as compared with Bort treatment alone. Our study also provided experimental evidence that JNk/SAPk signaling pathway was involved in the regulatory effect of miR-202 on drug resistance of MM cells. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Zinc finger protein Aiolos (IKZF3) | [4], [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Multiple myeloma [ICD-11: 2A83.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q147H |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | |
| PI3K/RAS signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | Bone marrow | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Gene expression profiling assay; High-resolution copy number arrays assay; Whole-exome sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Longitudinal copy number aberration (CNA) analysis | |||
| Mechanism Description | Resistance to immunomodulatory drugs (IMiD) and proteasome inhibitors was recently associated with mutations in IMiD response genes IRF4, CRBN, DDB1, CUL4A, CUL4B, IkZF1, IkZF2, and IkZF3 or in the proteasome inhibitor response genes PSMB5 and PSMG2, respectively. Mechanistically, bi-allelic loss of tumor-suppressor genes is a crucial mechanism, allowing units of selection to evade treatment-induced apoptosis with the acquisition of subsequent proliferative advantage leading to their outgrowth. | |||
| Key Molecule: Zinc finger protein Helios (IKZF2) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Multiple myeloma [ICD-11: 2A83.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | |
| PI3K/RAS signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | Bone marrow | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Gene expression profiling assay; High-resolution copy number arrays assay; Whole-exome sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Longitudinal copy number aberration (CNA) analysis | |||
| Mechanism Description | Resistance to immunomodulatory drugs (IMiD) and proteasome inhibitors was recently associated with mutations in IMiD response genes IRF4, CRBN, DDB1, CUL4A, CUL4B, IkZF1, IkZF2, and IkZF3 or in the proteasome inhibitor response genes PSMB5 and PSMG2, respectively. Mechanistically, bi-allelic loss of tumor-suppressor genes is a crucial mechanism, allowing units of selection to evade treatment-induced apoptosis with the acquisition of subsequent proliferative advantage leading to their outgrowth. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA-binding protein Ikaros (IKZF1) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Multiple myeloma [ICD-11: 2A83.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | |
| PI3K/RAS signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | Bone marrow | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Gene expression profiling assay; High-resolution copy number arrays assay; Whole-exome sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Longitudinal copy number aberration (CNA) analysis | |||
| Mechanism Description | Resistance to immunomodulatory drugs (IMiD) and proteasome inhibitors was recently associated with mutations in IMiD response genes IRF4, CRBN, DDB1, CUL4A, CUL4B, IkZF1, IkZF2, and IkZF3 or in the proteasome inhibitor response genes PSMB5 and PSMG2, respectively. Mechanistically, bi-allelic loss of tumor-suppressor genes is a crucial mechanism, allowing units of selection to evade treatment-induced apoptosis with the acquisition of subsequent proliferative advantage leading to their outgrowth. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA damage-binding protein 1 (DDB1) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Multiple myeloma [ICD-11: 2A83.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | |
| PI3K/RAS signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | Bone marrow | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Gene expression profiling assay; High-resolution copy number arrays assay; Whole-exome sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Longitudinal copy number aberration (CNA) analysis | |||
| Mechanism Description | Resistance to immunomodulatory drugs (IMiD) and proteasome inhibitors was recently associated with mutations in IMiD response genes IRF4, CRBN, DDB1, CUL4A, CUL4B, IkZF1, IkZF2, and IkZF3 or in the proteasome inhibitor response genes PSMB5 and PSMG2, respectively. Mechanistically, bi-allelic loss of tumor-suppressor genes is a crucial mechanism, allowing units of selection to evade treatment-induced apoptosis with the acquisition of subsequent proliferative advantage leading to their outgrowth. | |||
| Key Molecule: Cullin-4B (CUL4B) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Multiple myeloma [ICD-11: 2A83.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | |
| PI3K/RAS signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | Bone marrow | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Gene expression profiling assay; High-resolution copy number arrays assay; Whole-exome sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Longitudinal copy number aberration (CNA) analysis | |||
| Mechanism Description | Resistance to immunomodulatory drugs (IMiD) and proteasome inhibitors was recently associated with mutations in IMiD response genes IRF4, CRBN, DDB1, CUL4A, CUL4B, IkZF1, IkZF2, and IkZF3 or in the proteasome inhibitor response genes PSMB5 and PSMG2, respectively. Mechanistically, bi-allelic loss of tumor-suppressor genes is a crucial mechanism, allowing units of selection to evade treatment-induced apoptosis with the acquisition of subsequent proliferative advantage leading to their outgrowth. | |||
| Key Molecule: Cullin-4A (CUL4A) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Multiple myeloma [ICD-11: 2A83.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | |
| PI3K/RAS signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | Bone marrow | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Gene expression profiling assay; High-resolution copy number arrays assay; Whole-exome sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Longitudinal copy number aberration (CNA) analysis | |||
| Mechanism Description | Resistance to immunomodulatory drugs (IMiD) and proteasome inhibitors was recently associated with mutations in IMiD response genes IRF4, CRBN, DDB1, CUL4A, CUL4B, IkZF1, IkZF2, and IkZF3 or in the proteasome inhibitor response genes PSMB5 and PSMG2, respectively. Mechanistically, bi-allelic loss of tumor-suppressor genes is a crucial mechanism, allowing units of selection to evade treatment-induced apoptosis with the acquisition of subsequent proliferative advantage leading to their outgrowth. | |||
| Key Molecule: Protein cereblon (CRBN) | [2], [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Multiple myeloma [ICD-11: 2A83.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Truncating mutation | p.R283K |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | |
| PI3K/RAS signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | Bone marrow | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Gene expression profiling assay; High-resolution copy number arrays assay; Whole-exome sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Longitudinal copy number aberration (CNA) analysis | |||
| Mechanism Description | Resistance to immunomodulatory drugs (IMiD) and proteasome inhibitors was recently associated with mutations in IMiD response genes IRF4, CRBN, DDB1, CUL4A, CUL4B, IkZF1, IkZF2, and IkZF3 or in the proteasome inhibitor response genes PSMB5 and PSMG2, respectively. Mechanistically, bi-allelic loss of tumor-suppressor genes is a crucial mechanism, allowing units of selection to evade treatment-induced apoptosis with the acquisition of subsequent proliferative advantage leading to their outgrowth. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
