Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00311)
| Name |
Cullin-4A (CUL4A)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
CUL-4A
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
CUL4A
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr13:113208193-113267108[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MADEAPRKGSFSALVGRTNGLTKPAALAAAPAKPGGAGGSKKLVIKNFRDRPRLPDNYTQ
DTWRKLHEAVRAVQSSTSIRYNLEELYQAVENLCSHKVSPMLYKQLRQACEDHVQAQILP FREDSLDSVLFLKKINTCWQDHCRQMIMIRSIFLFLDRTYVLQNSTLPSIWDMGLELFRT HIISDKMVQSKTIDGILLLIERERSGEAVDRSLLRSLLGMLSDLQVYKDSFELKFLEETN CLYAAEGQRLMQEREVPEYLNHVSKRLEEEGDRVITYLDHSTQKPLIACVEKQLLGEHLT AILQKGLDHLLDENRVPDLAQMYQLFSRVRGGQQALLQHWSEYIKTFGTAIVINPEKDKD MVQDLLDFKDKVDHVIEVCFQKNERFVNLMKESFETFINKRPNKPAELIAKHVDSKLRAG NKEATDEELERTLDKIMILFRFIHGKDVFEAFYKKDLAKRLLVGKSASVDAEKSMLSKLK HECGAAFTSKLEGMFKDMELSKDIMVHFKQHMQNQSDSGPIDLTVNILTMGYWPTYTPME VHLTPEMIKLQEVFKAFYLGKHSGRKLQWQTTLGHAVLKAEFKEGKKEFQVSLFQTLVLL MFNEGDGFSFEEIKMATGIEDSELRRTLQSLACGKARVLIKSPKGKEVEDGDKFIFNGEF KHKLFRIKINQIQMKETVEEQVSTTERVFQDRQYQIDAAIVRIMKMRKTLGHNLLVSELY NQLKFPVKPGDLKKRIESLIDRDYMERDKDNPNQYHYVA Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Core component of multiple cullin-RING-based E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complexes which mediate the ubiquitination of target proteins. As a scaffold protein may contribute to catalysis through positioning of the substrate and the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme. The E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase activity of the complex is dependent on the neddylation of the cullin subunit and is inhibited by the association of the deneddylated cullin subunit with TIP120A/CAND1. The functional specificity of the E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complex depends on the variable substrate recognition component. DCX(DET1-COP1) directs ubiquitination of JUN. DCX(DDB2) directs ubiquitination of XPC. DCX(DDB2) ubiquitinates histones H3-H4 and is required for efficient histone deposition during replication-coupled (H3.1) and replication-independent (H3.3) nucleosome assembly, probably by facilitating the transfer of H3 from ASF1A/ASF1B to other chaperones involved in histone deposition. DCX(DTL) plays a role in PCNA-dependent polyubiquitination of CDT1 and MDM2-dependent ubiquitination of p53/TP53 in response to radiation-induced DNA damage and during DNA replication. DCX(DTL) directs autoubiquitination of DTL. In association with DDB1 and SKP2 probably is involved in ubiquitination of CDKN1B/p27kip. Is involved in ubiquitination of HOXA9. The DDB1-CUL4A-DTL E3 ligase complex regulates the circadian clock function by mediating the ubiquitination and degradation of CRY1. A number of DCX complexes (containing either TRPC4AP or DCAF12 as substrate-recognition component) are part of the DesCEND (destruction via C-end degrons) pathway, which recognizes a C-degron located at the extreme C terminus of target proteins, leading to their ubiquitination and degradation. The DCX(AMBRA1) complex is a master regulator of the transition from G1 to S cell phase by mediating ubiquitination of phosphorylated cyclin-D (CCND1, CCND2 and CCND3). The DCX(AMBRA1) complex also acts as a regulator of Cul5-RING (CRL5) E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complexes by mediating ubiquitination and degradation of Elongin-C (ELOC) component of CRL5 complexes. With CUL4B, contributes to ribosome biogenesis.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
3 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.15E-67 Fold-change: 1.07E-01 Z-score: 2.00E+01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTiter AQueous One Solution Cell Proliferation Assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | H19 LncRNA plays a leading role in breast cancer chemoresistance, mediated mainly through a H19-CUL4A-ABCB1/MDR1 pathway. H19 overexpression was contributed to cancer cell resistance to anthracyclines and paclitaxel. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Multiple myeloma [ICD-11: 2A83.0] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Multiple myeloma [ICD-11: 2A83.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Lenalidomide | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | |
| PI3K/RAS signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | Bone marrow | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Gene expression profiling assay; High-resolution copy number arrays assay; Whole-exome sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Longitudinal copy number aberration (CNA) analysis | |||
| Mechanism Description | Resistance to immunomodulatory drugs (IMiD) and proteasome inhibitors was recently associated with mutations in IMiD response genes IRF4, CRBN, DDB1, CUL4A, CUL4B, IkZF1, IkZF2, and IkZF3 or in the proteasome inhibitor response genes PSMB5 and PSMG2, respectively. Mechanistically, bi-allelic loss of tumor-suppressor genes is a crucial mechanism, allowing units of selection to evade treatment-induced apoptosis with the acquisition of subsequent proliferative advantage leading to their outgrowth. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Multiple myeloma [ICD-11: 2A83.0] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Multiple myeloma [ICD-11: 2A83.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Thalidomide | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | |
| PI3K/RAS signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | Bone marrow | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Gene expression profiling assay; High-resolution copy number arrays assay; Whole-exome sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Longitudinal copy number aberration (CNA) analysis | |||
| Mechanism Description | Resistance to immunomodulatory drugs (IMiD) and proteasome inhibitors was recently associated with mutations in IMiD response genes IRF4, CRBN, DDB1, CUL4A, CUL4B, IkZF1, IkZF2, and IkZF3 or in the proteasome inhibitor response genes PSMB5 and PSMG2, respectively. Mechanistically, bi-allelic loss of tumor-suppressor genes is a crucial mechanism, allowing units of selection to evade treatment-induced apoptosis with the acquisition of subsequent proliferative advantage leading to their outgrowth. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Bone marrow | |
| The Specified Disease | Multiple myeloma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.87E-01; Fold-change: 7.20E-02; Z-score: 2.96E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
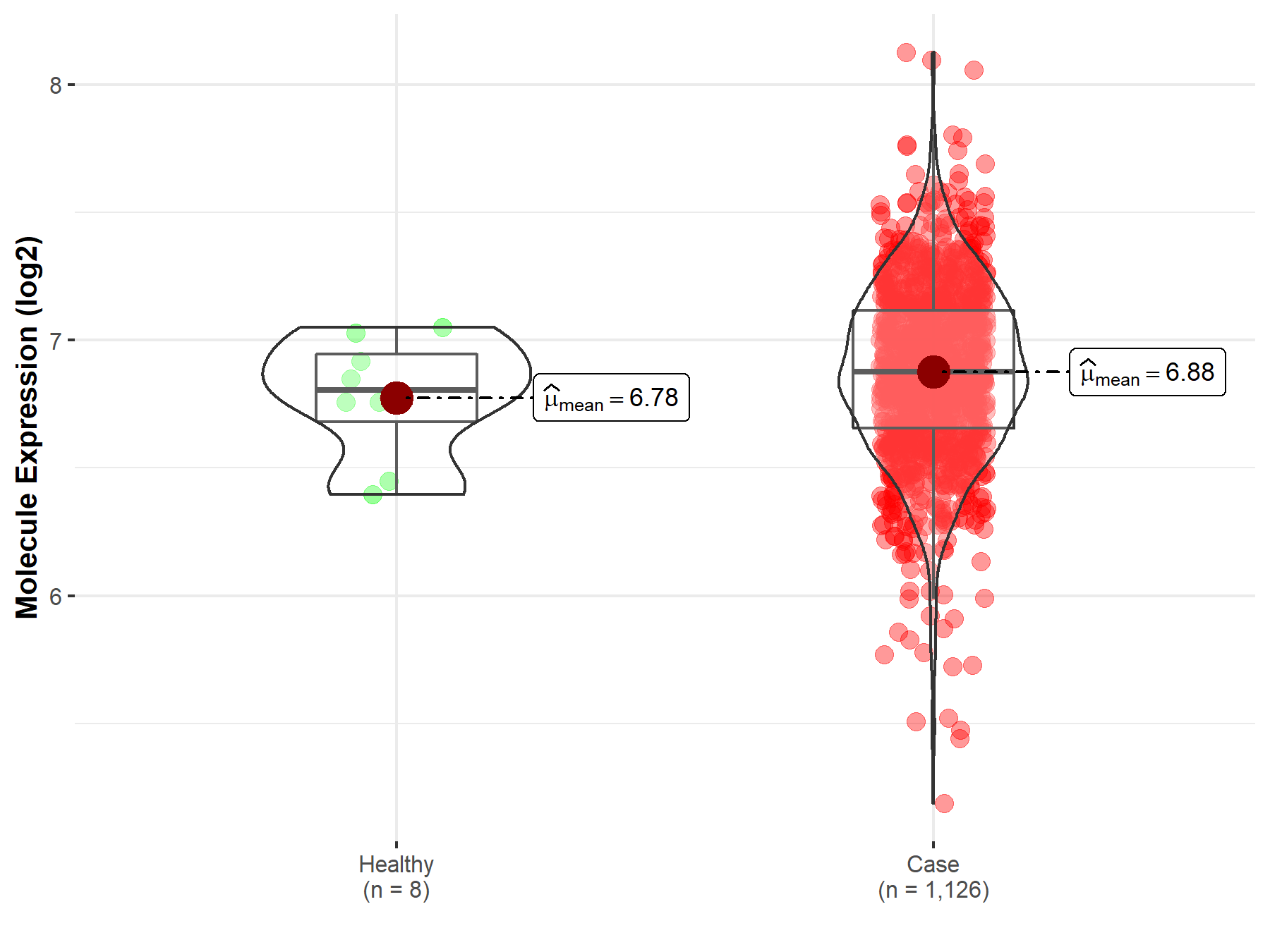
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | Peripheral blood | |
| The Specified Disease | Multiple myeloma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 9.94E-01; Fold-change: 2.28E-02; Z-score: 8.75E-02 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
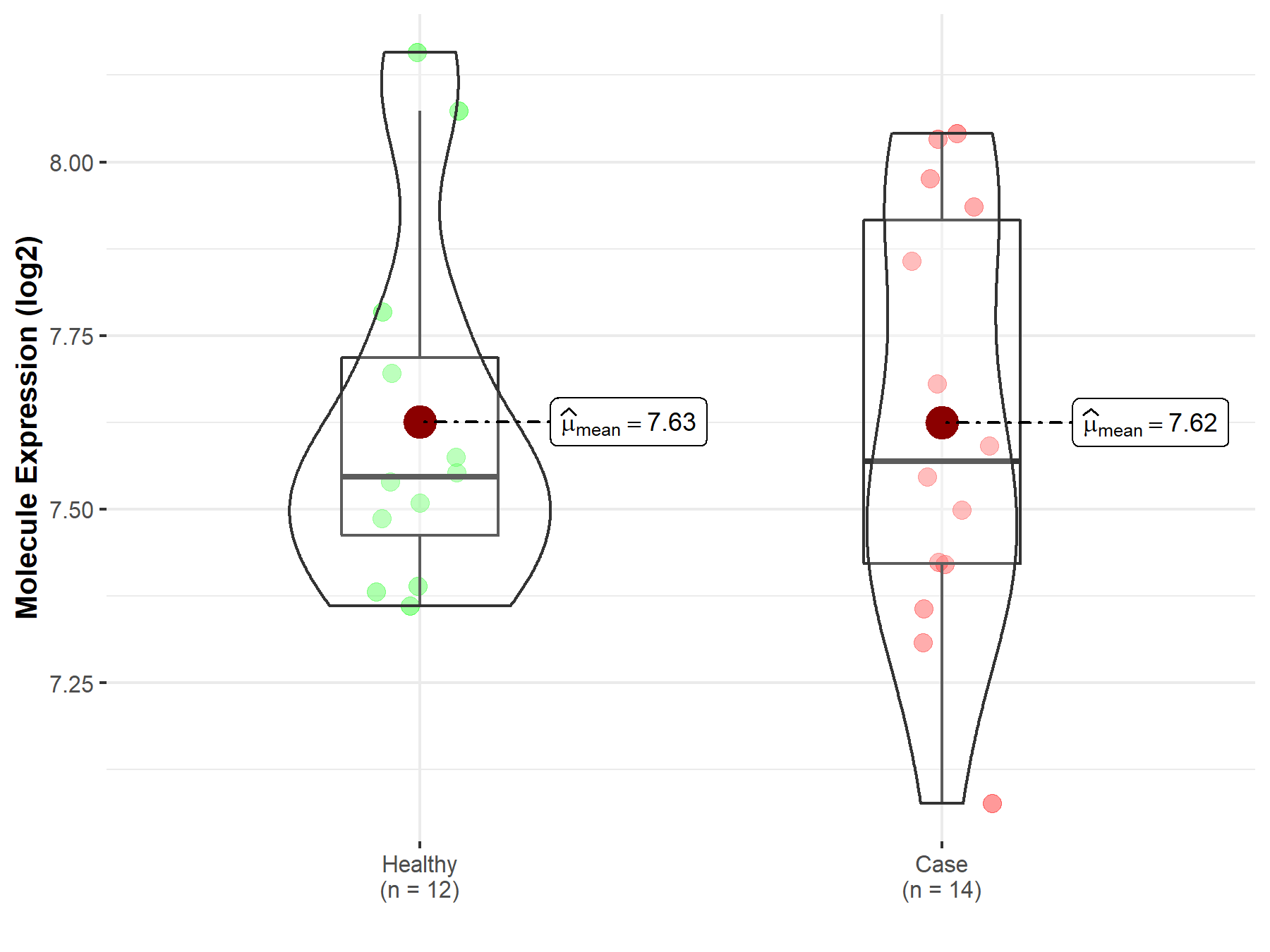
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.15E-67; Fold-change: 5.31E-01; Z-score: 1.40E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 1.19E-07; Fold-change: 3.61E-01; Z-score: 8.61E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
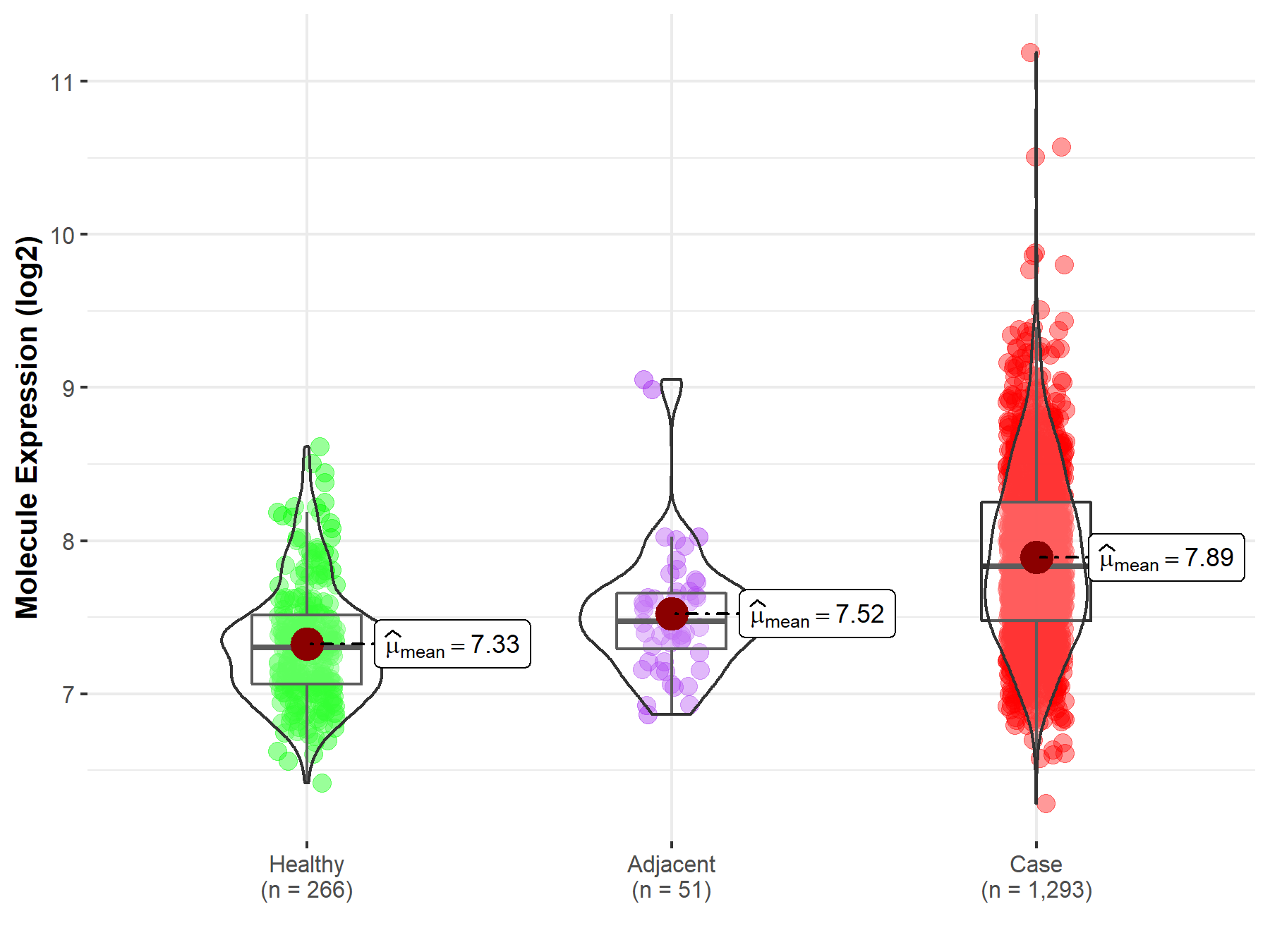
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

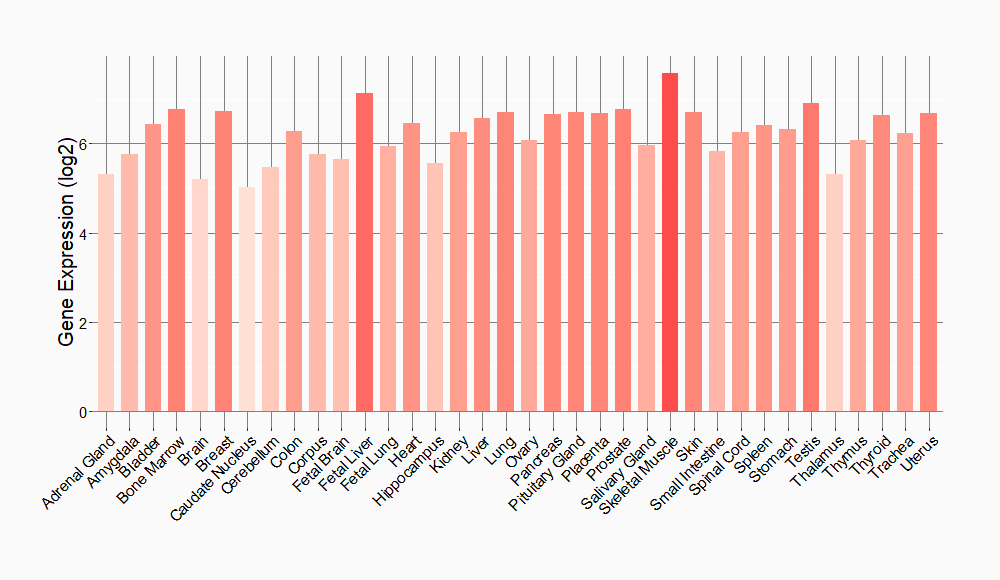
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
