Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00238) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Novobiocin
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Albamix; Albamycin; Cardelmycin; Cathocin; Cathomycin; Inamycin; NOV; Novobiocina; Novobiocine; Novobiocinum; Robiocina; Sirbiocina; Spheromycin; Stilbiocina; Streptonivicin; Crystallinic acid; Novobiocin sodium salt; PA 93; U 6391; Albamycin (TN); Antibiotic PA-93; Novo-R; Novobiocin [INN:BAN]; Novobiocina [INN-Spanish]; Novobiocine [INN-French]; Novobiocinum [INN-Latin]; Streptonivicin (*Sodium salt*); [(3R,4S,5R,6R)-5-hydroxy-6-[2-hydroxy-3-[[4-hydroxy-3-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)benzoyl]amino]-8-methyl-4-oxochromen-7-yl]oxy-3-methoxy-2,2-dimethyloxan-4-yl] carbamate; N-[7-[[3-O-(Aminocarbonyl)-6-deoxy-5-C-methyl-4-O-methyl-.beta.-L-lyxo-hexopyranosyl]oxy]-4-hydroxy-8-methyl-2-oxo-2H-1-benzopyran-3-yl]-4-hydroxy-3-(3-methyl-2-butenyl); (3R,4S,5R,6R)-5-hydroxy-6-{[4-hydroxy-3-({[4-hydroxy-3-(3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl)phenyl]carbonyl}amino)-8-methyl-2-oxo-2H-chromen-7-yl]oxy}-3-methoxy-2,2-dimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-yl carbamate; (3r,4s,5r,6r)-5-hydroxy-6-[(2-hydroxy-3-{[4-hydroxy-3-(3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl)benzoyl]amino}-8-methyl-4-oxo-4h-chromen-7-yl)oxy]-3-methoxy-2,2-dimethyltetrahydro-2h-pyran-4-yl carbamate(non-preferred name); 7-(3-(O-Carbamoyl)-4-(O-methyl)-5,5-dimethyl-alpha-L-lyxopyranosyloxy)-4-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxy-3-(3-methyl-2-butenyl)benzamidol)-8-methylcumarin; 7-(Carbamoyltetrahydro-3-hydroxy-5-methoxy-6,6-dimethylpyran-2-yloxy)-4-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxy-3-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)benzamide)-8-methyl-2H-chromen-2-one
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
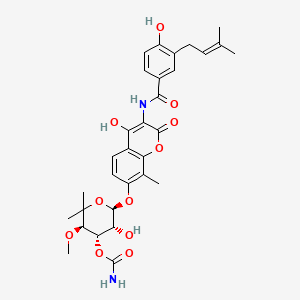
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(3 diseases)
[1]
[2]
[3]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Validated by in-vivo Model for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[4]
|
||||
| Target | DNA topoisomerase II (TOP2) |
TOP2A_HUMAN
; TOP2B_HUMAN |
[1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C31H36N2O11
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CC1=C(C=CC2=C1OC(=O)C(=C2O)NC(=O)C3=CC(=C(C=C3)O)CC=C(C)C)O[C@H]4[C@@H]([C@@H]([C@H](C(O4)(C)C)OC)OC(=O)N)O
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C31H36N2O11/c1-14(2)7-8-16-13-17(9-11-19(16)34)27(37)33-21-22(35)18-10-12-20(15(3)24(18)42-28(21)38)41-29-23(36)25(43-30(32)39)26(40-6)31(4,5)44-29/h7,9-13,23,25-26,29,34-36H,8H2,1-6H3,(H2,32,39)(H,33,37)/t23-,25+,26-,29-/m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
YJQPYGGHQPGBLI-KGSXXDOSSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: DNA gyrase subunit B (GYRB) | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R136C+p.R136H+p.R136S+p.G164V |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli HB101 | 634468 | ||
| Escherichia coli JM109 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain N4177 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain CC1 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain CC5 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain LE234 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain LE316 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Coumarins are inhibitors of the ATP hydrolysis and DNA supercoiling reactions catalysed by DNA gyrase. four mutations have been identified regaeding conferring coumarin resistance to Escherichia coli: Arg-136 to Cys, His or Ser and Gly-164 to Val.Significant differences in the susceptibility of mutant GyrB proteins to inhibition by either chlorobiocin and novobiocin or coumermycin have been found, suggesting wider contacts between coumermycin and GyrB. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Multidrug resistance protein MdtC (MDTC) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Salmonella enterica infection [ICD-11: 1A09.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium ATCC 14028s | 588858 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Quantitative real-time PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
L agar plate method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Overexpression or overproduction of mdtABC confers drug resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: Multidrug resistance protein MdtB (MDTB) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Salmonella enterica infection [ICD-11: 1A09.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium ATCC 14028s | 588858 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Quantitative real-time PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
L agar plate method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Overexpression or overproduction of mdtABC confers drug resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: Multidrug resistance protein MdtA (MDTA) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Salmonella enterica infection [ICD-11: 1A09.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium ATCC 14028s | 588858 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Quantitative real-time PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
L agar plate method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Overexpression or overproduction of mdtABC confers drug resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: Efflux pump membrane transporter (ACRD) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Salmonella enterica infection [ICD-11: 1A09.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium ATCC 14028s | 588858 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Quantitative real-time PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
L agar plate method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Overexpression or overproduction of acrD confers drug resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: Multidrug export protein EmrA (EMRA) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Salmonella enterica infection [ICD-11: 1A09.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium ATCC 14028s | 588858 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Quantitative real-time PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
L agar plate method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Overexpression or overproduction of emrAB confers drug resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: Multidrug export protein EmrB (EMRB) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Salmonella enterica infection [ICD-11: 1A09.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium ATCC 14028s | 588858 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Quantitative real-time PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
L agar plate method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Overexpression or overproduction of emrAB confers drug resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: Efflux pump membrane transporter MdsA (MDSA) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Salmonella enterica infection [ICD-11: 1A09.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium ATCC 14028s | 588858 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Quantitative real-time PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
L agar plate method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Overexpression or overproduction of MdsABC confers drug resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: Efflux pump membrane transporter MdsB (MDSB) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Salmonella enterica infection [ICD-11: 1A09.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium ATCC 14028s | 588858 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Quantitative real-time PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
L agar plate method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Overexpression or overproduction of MdsABC confers drug resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: Efflux pump membrane transporter MdsC (MDSC) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Salmonella enterica infection [ICD-11: 1A09.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium ATCC 14028s | 588858 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Quantitative real-time PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
L agar plate method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Overexpression or overproduction of MdsABC confers drug resistance. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: DNA topoisomerase 4 subunit B (PARE) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G78S |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Staphylococcus aureus RN4220 | 1280 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR amplification and DNA sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Twofold agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | At first, successive point mutations specifically occurred in gyrB; next, a point mutation occurred in parE; finally, a point mutation occurred in gyrB again. The accumulation of mutations in both the gyrB and the parE genes is associated with high-level resistance to novobiocin. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA topoisomerase 4 subunit B (PARE) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R136G |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Staphylococcus aureus RN4220 | 1280 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR amplification and DNA sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Twofold agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | At first, successive point mutations specifically occurred in gyrB; next, a point mutation occurred in parE; finally, a point mutation occurred in gyrB again. The accumulation of mutations in both the gyrB and the parE genes is associated with high-level resistance to novobiocin. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA topoisomerase 4 subunit B (PARE) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.A89G |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Staphylococcus aureus RN4220 | 1280 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR amplification and DNA sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Twofold agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | At first, successive point mutations specifically occurred in gyrB; next, a point mutation occurred in parE; finally, a point mutation occurred in gyrB again. The accumulation of mutations in both the gyrB and the parE genes is associated with high-level resistance to novobiocin. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA topoisomerase 4 subunit B (PARE) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S128L |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Staphylococcus aureus RN4220 | 1280 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR amplification and DNA sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Twofold agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | At first, successive point mutations specifically occurred in gyrB; next, a point mutation occurred in parE; finally, a point mutation occurred in gyrB again. The accumulation of mutations in both the gyrB and the parE genes is associated with high-level resistance to novobiocin. | |||
ICD-12: Respiratory system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Multidrug efflux SMR transporter (ABES) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acinetobacter baumannii infection [ICD-11: CA40.4] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli kAM32 | 562 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Fluorometric efflux assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth dilution assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The abeS gene product conferred resistance to various antimicrobial compounds through an efflux mechanism. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
