Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00169) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Quinupristin
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Quinupristina; Quinupristine; Quinupristinum; SYB; RP 57669; Quinupristin [USAN:INN]; Quinupristina [INN-Spanish]; Quinupristine [INN-French]; Quinupristinum [INN-Latin]; RP-57669; Synercid (TN); Quinupristin (JAN/USAN/INN); 4-[4-(DIMETHYLAMINO)-N-METHYL-L-PHENYLALANINE]-5-[(2S,5R)-5-[[[(3S)-1-AZABICYCLO-[2.2.2]OCT-3-YL]THIO]METHYL]-4-OXO-2-PIPERIDINECARBOXYLIC ACID]VIRGINIAMYCIN; 5delta-(3-quinuclidinyl)thiomethylpristinamycin IA
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
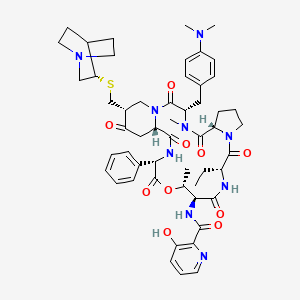
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(3 diseases)
[2]
[3]
[1]
|
||||
| Target | Bacterial Integral membrane LmrP (Bact lmrP) | Q9CDQ3_LACLA | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C53H67N9O10S
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CC[C@@H]1C(=O)N2CCC[C@H]2C(=O)N([C@H](C(=O)N3C[C@H](C(=O)C[C@H]3C(=O)N[C@H](C(=O)O[C@@H]([C@@H](C(=O)N1)NC(=O)C4=C(C=CC=N4)O)C)C5=CC=CC=C5)CS[C@@H]6CN7CCC6CC7)CC8=CC=C(C=C8)N(C)C)C
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C53H67N9O10S/c1-6-37-50(68)61-23-11-14-38(61)51(69)59(5)40(26-32-16-18-36(19-17-32)58(3)4)52(70)62-28-35(30-73-43-29-60-24-20-33(43)21-25-60)42(64)27-39(62)47(65)57-45(34-12-8-7-9-13-34)53(71)72-31(2)44(48(66)55-37)56-49(67)46-41(63)15-10-22-54-46/h7-10,12-13,15-19,22,31,33,35,37-40,43-45,63H,6,11,14,20-21,23-30H2,1-5H3,(H,55,66)(H,56,67)(H,57,65)/t31-,35+,37-,38+,39+,40+,43-,44+,45+/m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
WTHRRGMBUAHGNI-LCYNINFDSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: 23S ribosomal RNA methyltransferase Erm (ERM39) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Mycobacterium fortuitum infection [ICD-11: 1B2Z.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | Putative initiation codon GTG>CTG |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Mycobacterium peregrinum ATCC14467 | 43304 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Mueller-Hinton (MH) broth assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The erm genes are a diverse collection of methylases that add one or two methyl groups to the adenine at position 2058 (Escherichia coli numbering) of the 23S rRNA; this modification impairs the binding of macrolides to ribosomes, and thus reduces the inhibitory activity of these agents. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: MsrC (MSRC) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Enterococcus faecium meningitis [ICD-11: 1D01.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli | 668369 | ||
| Enterococcus faecium TX2465 | 1352 | |||
| Escherichia coli TX1330 | 668369 | |||
| Escherichia coli TX2046 | 668369 | |||
| Escherichia coli TX2597 | 668369 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Southern blotting assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Twofold dilutions assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The complete sequence (1,479 nucleotides) of msrC, part of which was recently reported by others using a different strain, was determined. This gene was found in 233 of 233 isolates of Enterococcus faecium but in none of 265 other enterococci. Disruption of msrC was associated with a two- to eightfold decrease in MICs of erythromycin azithromycin, tylosin, and quinupristin, suggesting that it may explain in part the apparent greater intrinsic resistance to macrolides of isolates of E. faecium relative to many streptococci. This endogenous, species-specific gene of E. faecium is 53% identical to msr(A), suggesting that it may be a remote progenitor of the acquired macrolide resistance gene found in some isolates of staphylococci. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: MsrC (MSRC) | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Enterococcus faecium meningitis [ICD-11: 1D01.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Truncated mutantion | Disruption (nt 1251 to 1879) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli | 668369 | ||
| Enterococcus faecium TX2465 | 1352 | |||
| Escherichia coli TX1330 | 668369 | |||
| Escherichia coli TX2046 | 668369 | |||
| Escherichia coli TX2597 | 668369 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Southern blotting assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Twofold dilutions assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Disruption of msrC was associated with a two- to eightfold decrease in MICs of erythromycin azithromycin, tylosin, and quinupristin, suggesting that it may explain in part the apparent greater intrinsic resistance to macrolides of isolates of E. faecium relative to many streptococci. | |||
ICD-22: Injury/poisoning/certain external causes consequences
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Erythromycin resistance protein (ERM38) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Mycobacterium smegmatis infection [ICD-11: 1B2Z.3] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Mycobacterium smegmatis mc2155 | 246196 | ||
| Mycobacterium smegmatis mc2155/pMIP12 | 246196 | |||
| Mycobacterium smegmatis mc2155/pOMV20 | 246196 | |||
| Mycobacterium smegmatis mc2155/pOMV30 | 246196 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
MALDI mass spectrometry assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Erm (38) is a specific dimethyltransferase. The strain obtained drug resistance by adding two methyl groups to A2058 in Mycobacterium 23SrRNA. | |||
| Key Molecule: Erythromycin resistance protein (ERM38) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Mycobacterium smegmatis infection [ICD-11: 1B2Z.3] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Mycobacterium smegmatis mc2155 | 246196 | ||
| Mycobacterium smegmatis mc2155/pMIP12 | 246196 | |||
| Mycobacterium smegmatis mc2155/pOMV20 | 246196 | |||
| Mycobacterium smegmatis mc2155/pOMV30 | 246196 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
MALDI mass spectrometry assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Erm (38) is a specific dimethyltransferase. The strain obtained drug resistance by adding two methyl groups to A2058 in Mycobacterium 23SrRNA. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
