Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00161) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Epothilone B
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Epothilone B; Patupilone; 152044-54-7; (-)-Epothilone B; Epo B; EpoB; EPO906; EPO 906; UNII-UEC0H0URSE; EPO 906A; GNF-PF-193; CHEBI:31550; UEC0H0URSE; AK163080; Epothilone B (EPO906, Patupilone); 7,11-DIHYDROXY-8,8,10,12,16-PENTAMETHYL-3-[1-METHYL-2-(2-METHYL-THIAZOL-4-YL)VINYL]-4,17-DIOXABICYCLO[14.1.0]HEPTADECANE-5,9-DIONE; Epothilon B; Patupilone [INN]; (1S,3S,7S,10R,11S,12S,16R)-7,11-dihydroxy-8,8,10,12,16-pentamethyl-3-((E)-1-(2-methylthiazol-4-yl)prop-1-en-2-yl)-4,17-dioxabicyclo[14.1.0]heptadecane-5,9-dione
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
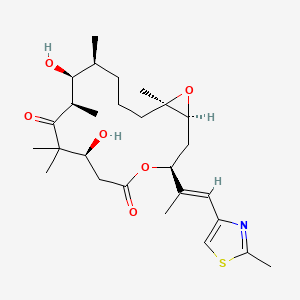
|
||||
| Target | Tubulin (TUB) | NOUNIPROTAC | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C27H41NO6S
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
C[C@H]1CCC[C@@]2([C@@H](O2)C[C@H](OC(=O)C[C@@H](C(C(=O)[C@@H]([C@H]1O)C)(C)C)O)/C(=C/C3=CSC(=N3)C)/C)C
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C27H41NO6S/c1-15-9-8-10-27(7)22(34-27)12-20(16(2)11-19-14-35-18(4)28-19)33-23(30)13-21(29)26(5,6)25(32)17(3)24(15)31/h11,14-15,17,20-22,24,29,31H,8-10,12-13H2,1-7H3/b16-11+/t15-,17+,20-,21-,22-,24-,27+/m0/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
QXRSDHAAWVKZLJ-PVYNADRNSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| INTEDE ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Zinc finger E-box-binding homeobox 2 (ZEB2) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Endometrial cancer [ICD-11: 2C76.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Endometrial cancer [ICD-11: 2C76] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Endometrial cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Uterus | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.99E-35 Fold-change: -9.00E-01 Z-score: -1.66E+01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | |
| In Vitro Model | Hec50 cells | Endometrium | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2929 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
ELISA assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Low or absent miR-200c results in aberrant expression of ZEB1 and consequent repression of E-cadherin. Reinstatement of miR-200c to such cells restores E-cadherin and dramatically reduces migration and invasion. One such gene, class IIIbeta-tubulin (TUBB3), which encodes a tubulin isotype normally found only in neuronal cells, is a direct target of miR-200c. Restoration of miR-200c increases sensitivity to microtubule-targeting agents by up to 85%. Since expression of TUBB3 is a common mechanism of resistance to microtubule-binding chemotherapeutic agents in many types of solid tumors, the ability of miR-200c to restore chemosensitivity to such agents may be explained by its ability to reduce TUBB3. | |||
| Key Molecule: Zinc finger E-box-binding homeobox 1 (ZEB1) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Endometrial cancer [ICD-11: 2C76.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Endometrial cancer [ICD-11: 2C76] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Endometrial cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Uterus | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 4.45E-43 Fold-change: -1.36E+00 Z-score: -1.98E+01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | |
| In Vitro Model | Hec50 cells | Endometrium | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2929 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
ELISA assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Low or absent miR-200c results in aberrant expression of ZEB1 and consequent repression of E-cadherin. Reinstatement of miR-200c to such cells restores E-cadherin and dramatically reduces migration and invasion. One such gene, class IIIbeta-tubulin (TUBB3), which encodes a tubulin isotype normally found only in neuronal cells, is a direct target of miR-200c. Restoration of miR-200c increases sensitivity to microtubule-targeting agents by up to 85%. Since expression of TUBB3 is a common mechanism of resistance to microtubule-binding chemotherapeutic agents in many types of solid tumors, the ability of miR-200c to restore chemosensitivity to such agents may be explained by its ability to reduce TUBB3. | |||
| Key Molecule: Protein quaking (QKI) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Endometrial cancer [ICD-11: 2C76.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Endometrial cancer [ICD-11: 2C76] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Endometrial cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Uterus | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.05E-34 Fold-change: -6.23E-01 Z-score: -1.68E+01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | |
| In Vitro Model | Hec50 cells | Endometrium | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2929 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
ELISA assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Low or absent miR-200c results in aberrant expression of ZEB1 and consequent repression of E-cadherin. Reinstatement of miR-200c to such cells restores E-cadherin and dramatically reduces migration and invasion. One such gene, class IIIbeta-tubulin (TUBB3), which encodes a tubulin isotype normally found only in neuronal cells, is a direct target of miR-200c. Restoration of miR-200c increases sensitivity to microtubule-targeting agents by up to 85%. Since expression of TUBB3 is a common mechanism of resistance to microtubule-binding chemotherapeutic agents in many types of solid tumors, the ability of miR-200c to restore chemosensitivity to such agents may be explained by its ability to reduce TUBB3. | |||
| Key Molecule: hsa-mir-200c | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Endometrial cancer [ICD-11: 2C76.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | |
| In Vitro Model | Hec50 cells | Endometrium | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2929 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
RT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
ELISA assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Low or absent miR-200c results in aberrant expression of ZEB1 and consequent repression of E-cadherin. Reinstatement of miR-200c to such cells restores E-cadherin and dramatically reduces migration and invasion. One such gene, class IIIbeta-tubulin (TUBB3), which encodes a tubulin isotype normally found only in neuronal cells, is a direct target of miR-200c. Restoration of miR-200c increases sensitivity to microtubule-targeting agents by up to 85%. Since expression of TUBB3 is a common mechanism of resistance to microtubule-binding chemotherapeutic agents in many types of solid tumors, the ability of miR-200c to restore chemosensitivity to such agents may be explained by its ability to reduce TUBB3. | |||
| Key Molecule: BDNF/NT-3 growth factors receptor (NTRK2) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Endometrial cancer [ICD-11: 2C76.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | |
| In Vitro Model | Hec50 cells | Endometrium | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2929 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
ELISA assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Low or absent miR-200c results in aberrant expression of ZEB1 and consequent repression of E-cadherin. Reinstatement of miR-200c to such cells restores E-cadherin and dramatically reduces migration and invasion. One such gene, class IIIbeta-tubulin (TUBB3), which encodes a tubulin isotype normally found only in neuronal cells, is a direct target of miR-200c. Restoration of miR-200c increases sensitivity to microtubule-targeting agents by up to 85%. Since expression of TUBB3 is a common mechanism of resistance to microtubule-binding chemotherapeutic agents in many types of solid tumors, the ability of miR-200c to restore chemosensitivity to such agents may be explained by its ability to reduce TUBB3. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Fibronectin (FN1) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Endometrial cancer [ICD-11: 2C76.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Endometrial cancer [ICD-11: 2C76] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Endometrial cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Uterus | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 8.90E-04 Fold-change: -3.04E-01 Z-score: -3.40E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | |
| In Vitro Model | Hec50 cells | Endometrium | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2929 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
ELISA assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Low or absent miR-200c results in aberrant expression of ZEB1 and consequent repression of E-cadherin. Reinstatement of miR-200c to such cells restores E-cadherin and dramatically reduces migration and invasion. One such gene, class IIIbeta-tubulin (TUBB3), which encodes a tubulin isotype normally found only in neuronal cells, is a direct target of miR-200c. Restoration of miR-200c increases sensitivity to microtubule-targeting agents by up to 85%. Since expression of TUBB3 is a common mechanism of resistance to microtubule-binding chemotherapeutic agents in many types of solid tumors, the ability of miR-200c to restore chemosensitivity to such agents may be explained by its ability to reduce TUBB3. | |||
| Key Molecule: Tubulin beta-3 chain (TUBB3) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Endometrial cancer [ICD-11: 2C76.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | |
| In Vitro Model | Hec50 cells | Endometrium | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2929 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
ELISA assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Low or absent miR-200c results in aberrant expression of ZEB1 and consequent repression of E-cadherin. Reinstatement of miR-200c to such cells restores E-cadherin and dramatically reduces migration and invasion. One such gene, class IIIbeta-tubulin (TUBB3), which encodes a tubulin isotype normally found only in neuronal cells, is a direct target of miR-200c. Restoration of miR-200c increases sensitivity to microtubule-targeting agents by up to 85%. Since expression of TUBB3 is a common mechanism of resistance to microtubule-binding chemotherapeutic agents in many types of solid tumors, the ability of miR-200c to restore chemosensitivity to such agents may be explained by its ability to reduce TUBB3. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
