Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00539)
| Name |
BDNF/NT-3 growth factors receptor (NTRK2)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
GP145-TrkB; Trk-B; Neurotrophic tyrosine kinase receptor type 2; TrkB tyrosine kinase; Tropomyosin-related kinase B; TRKB
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
NTRK2
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr9:84668375-85095751[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MSSWIRWHGPAMARLWGFCWLVVGFWRAAFACPTSCKCSASRIWCSDPSPGIVAFPRLEP
NSVDPENITEIFIANQKRLEIINEDDVEAYVGLRNLTIVDSGLKFVAHKAFLKNSNLQHI NFTRNKLTSLSRKHFRHLDLSELILVGNPFTCSCDIMWIKTLQEAKSSPDTQDLYCLNES SKNIPLANLQIPNCGLPSANLAAPNLTVEEGKSITLSCSVAGDPVPNMYWDVGNLVSKHM NETSHTQGSLRITNISSDDSGKQISCVAENLVGEDQDSVNLTVHFAPTITFLESPTSDHH WCIPFTVKGNPKPALQWFYNGAILNESKYICTKIHVTNHTEYHGCLQLDNPTHMNNGDYT LIAKNEYGKDEKQISAHFMGWPGIDDGANPNYPDVIYEDYGTAANDIGDTTNRSNEIPST DVTDKTGREHLSVYAVVVIASVVGFCLLVMLFLLKLARHSKFGMKGPASVISNDDDSASP LHHISNGSNTPSSSEGGPDAVIIGMTKIPVIENPQYFGITNSQLKPDTFVQHIKRHNIVL KRELGEGAFGKVFLAECYNLCPEQDKILVAVKTLKDASDNARKDFHREAELLTNLQHEHI VKFYGVCVEGDPLIMVFEYMKHGDLNKFLRAHGPDAVLMAEGNPPTELTQSQMLHIAQQI AAGMVYLASQHFVHRDLATRNCLVGENLLVKIGDFGMSRDVYSTDYYRVGGHTMLPIRWM PPESIMYRKFTTESDVWSLGVVLWEIFTYGKQPWYQLSNNEVIECITQGRVLQRPRTCPQ EVYELMLGCWQREPHMRKNIKGIHTLLQNLAKASPVYLDILG Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Receptor tyrosine kinase involved in the development and the maturation of the central and the peripheral nervous systems through regulation of neuron survival, proliferation, migration, differentiation, and synapse formation and plasticity. Receptor for BDNF/brain-derived neurotrophic factor and NTF4/neurotrophin-4. Alternatively can also bind NTF3/neurotrophin-3 which is less efficient in activating the receptor but regulates neuron survival through NTRK2. Upon ligand-binding, undergoes homodimerization, autophosphorylation and activation. Recruits, phosphorylates and/or activates several downstream effectors including SHC1, FRS2, SH2B1, SH2B2 and PLCG1 that regulate distinct overlapping signaling cascades. Through SHC1, FRS2, SH2B1, SH2B2 activates the GRB2-Ras-MAPK cascade that regulates for instance neuronal differentiation including neurite outgrowth. Through the same effectors controls the Ras-PI3 kinase-AKT1 signaling cascade that mainly regulates growth and survival. Through PLCG1 and the downstream protein kinase C-regulated pathways controls synaptic plasticity. Thereby, plays a role in learning and memory by regulating both short term synaptic function and long-term potentiation. PLCG1 also leads to NF-Kappa-B activation and the transcription of genes involved in cell survival. Hence, it is able to suppress anoikis, the apoptosis resulting from loss of cell-matrix interactions. May also play a role in neutrophin-dependent calcium signaling in glial cells and mediate communication between neurons and glia.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
6 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Blood | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.15E-03 Fold-change: 9.81E-02 Z-score: 3.30E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 |
| BT474 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0179 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Celltiter glo assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | TrkB is signaling via PLCGamma, the MAP kinases or PI3k and Akt. Phosphorylation of Akt plays a pivotal role in cell survival and anti-apoptotic signaling by phosphorylating and thereby inhibiting pro-apoptotic factors like Bad or Caspase 9. Bmi1 may mediate resistance via other pathways than p53, for instance via the PI3k/Akt pathway. TrkB and Bmi1 Protein Expression is Hampered by Overexpression of miR-200c in MDA-MB 436 Cells, and cause thr resistance to Doxorubicin. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Neuroblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.11] | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Neuroblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.11] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Etoposide | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Neuroblastoma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Nervous tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 9.60E-12 Fold-change: -2.22E+00 Z-score: -1.89E+01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| PI3K/AKT signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | ||
| In Vitro Model | Kelly cells | Adrenal | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2092 |
| Sk-N-AS cells | Adrenal | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1700 | |
| SH-SY5Y cells | Abdomen | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0019 | |
| In Vivo Model | Orthotopic xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-204 direct targeting of the 3' UTR of BCL2 and NTRk2 (TrkB). BCL2 has a critical role in ensuring the survival of early developing cell types, NTRk2 is also a well-established pro-survival oncogene in neuroblastoma, signalling the activation of the PI3k/AkT pathway, a significant mechanism of drug resistance in neuroblastoma. Ectopic miR-204 expression significantly increased sensitivity to cisplatin and etoposide in vitro. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Neuroblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.11] | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Neuroblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.11] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Brain cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Nervous tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 4.03E-85 Fold-change: -2.40E-01 Z-score: -2.15E+01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| PI3K/AKT signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | ||
| In Vitro Model | Kelly cells | Adrenal | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2092 |
| Sk-N-AS cells | Adrenal | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1700 | |
| SH-SY5Y cells | Abdomen | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0019 | |
| In Vivo Model | Orthotopic xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-204 direct targeting of the 3' UTR of BCL2 and NTRk2 (TrkB). BCL2 has a critical role in ensuring the survival of early developing cell types, NTRk2 is also a well-established pro-survival oncogene in neuroblastoma, signalling the activation of the PI3k/AkT pathway, a significant mechanism of drug resistance in neuroblastoma. Ectopic miR-204 expression significantly increased sensitivity to cisplatin and etoposide in vitro. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Endometrial cancer [ICD-11: 2C76.1] | [3] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Endometrial cancer [ICD-11: 2C76.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Epothilone B | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | |
| In Vitro Model | Hec50 cells | Endometrium | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2929 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
ELISA assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Low or absent miR-200c results in aberrant expression of ZEB1 and consequent repression of E-cadherin. Reinstatement of miR-200c to such cells restores E-cadherin and dramatically reduces migration and invasion. One such gene, class IIIbeta-tubulin (TUBB3), which encodes a tubulin isotype normally found only in neuronal cells, is a direct target of miR-200c. Restoration of miR-200c increases sensitivity to microtubule-targeting agents by up to 85%. Since expression of TUBB3 is a common mechanism of resistance to microtubule-binding chemotherapeutic agents in many types of solid tumors, the ability of miR-200c to restore chemosensitivity to such agents may be explained by its ability to reduce TUBB3. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Endometrial cancer [ICD-11: 2C76.1] | [3] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Endometrial cancer [ICD-11: 2C76.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Paclitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | |
| In Vitro Model | Hec50 cells | Endometrium | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2929 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
ELISA assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Low or absent miR-200c results in aberrant expression of ZEB1 and consequent repression of E-cadherin. Reinstatement of miR-200c to such cells restores E-cadherin and dramatically reduces migration and invasion. One such gene, class IIIbeta-tubulin (TUBB3), which encodes a tubulin isotype normally found only in neuronal cells, is a direct target of miR-200c. Restoration of miR-200c increases sensitivity to microtubule-targeting agents by up to 85%. Since expression of TUBB3 is a common mechanism of resistance to microtubule-binding chemotherapeutic agents in many types of solid tumors, the ability of miR-200c to restore chemosensitivity to such agents may be explained by its ability to reduce TUBB3. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Endometrial cancer [ICD-11: 2C76.1] | [3] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Endometrial cancer [ICD-11: 2C76.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Vincristine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | |
| In Vitro Model | Hec50 cells | Endometrium | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2929 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
ELISA assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Low or absent miR-200c results in aberrant expression of ZEB1 and consequent repression of E-cadherin. Reinstatement of miR-200c to such cells restores E-cadherin and dramatically reduces migration and invasion. One such gene, class IIIbeta-tubulin (TUBB3), which encodes a tubulin isotype normally found only in neuronal cells, is a direct target of miR-200c. Restoration of miR-200c increases sensitivity to microtubule-targeting agents by up to 85%. Since expression of TUBB3 is a common mechanism of resistance to microtubule-binding chemotherapeutic agents in many types of solid tumors, the ability of miR-200c to restore chemosensitivity to such agents may be explained by its ability to reduce TUBB3. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
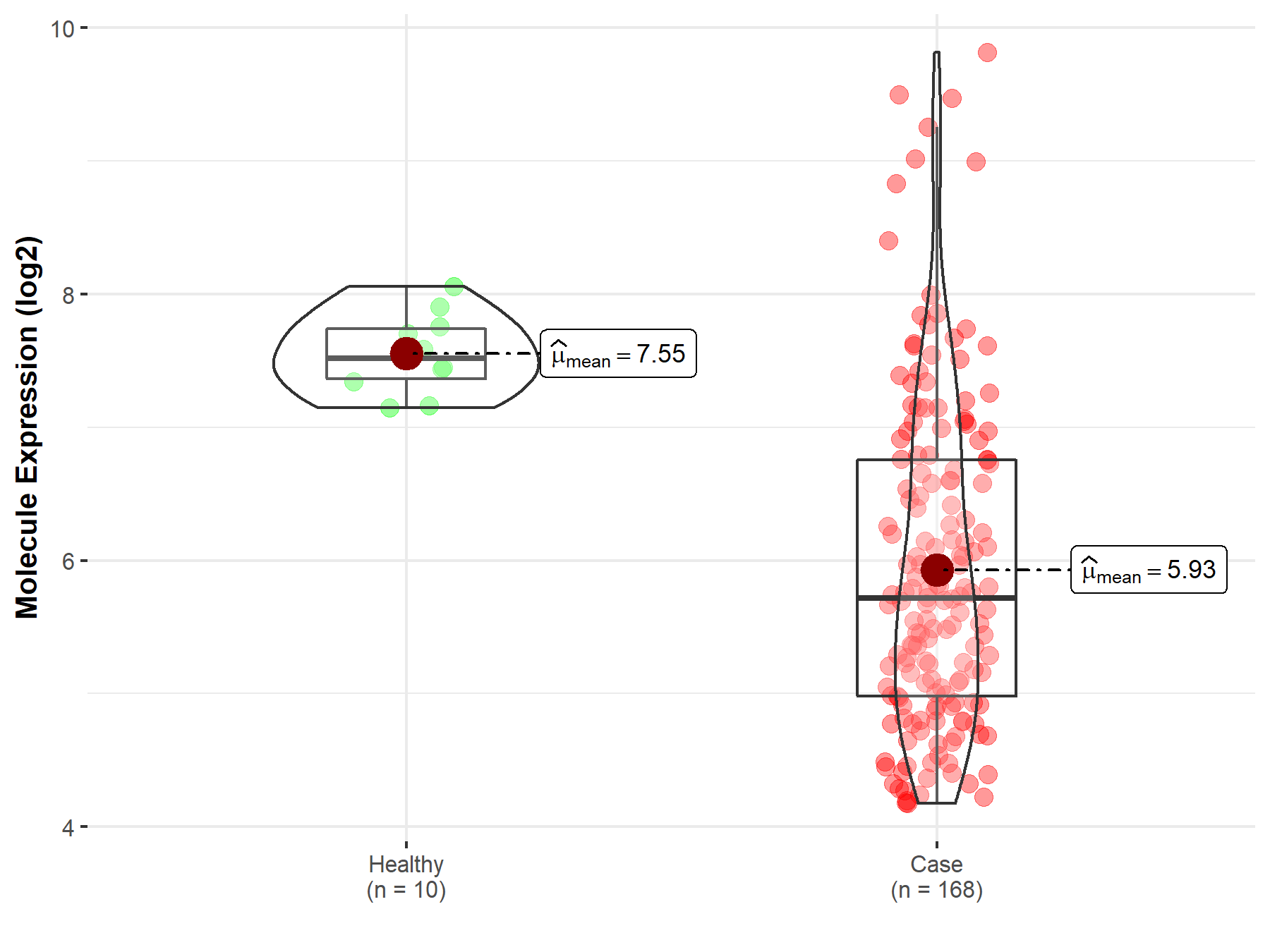
| The Studied Tissue | Nervous tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Brain cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 4.03E-85; Fold-change: -1.71E+00; Z-score: -1.77E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
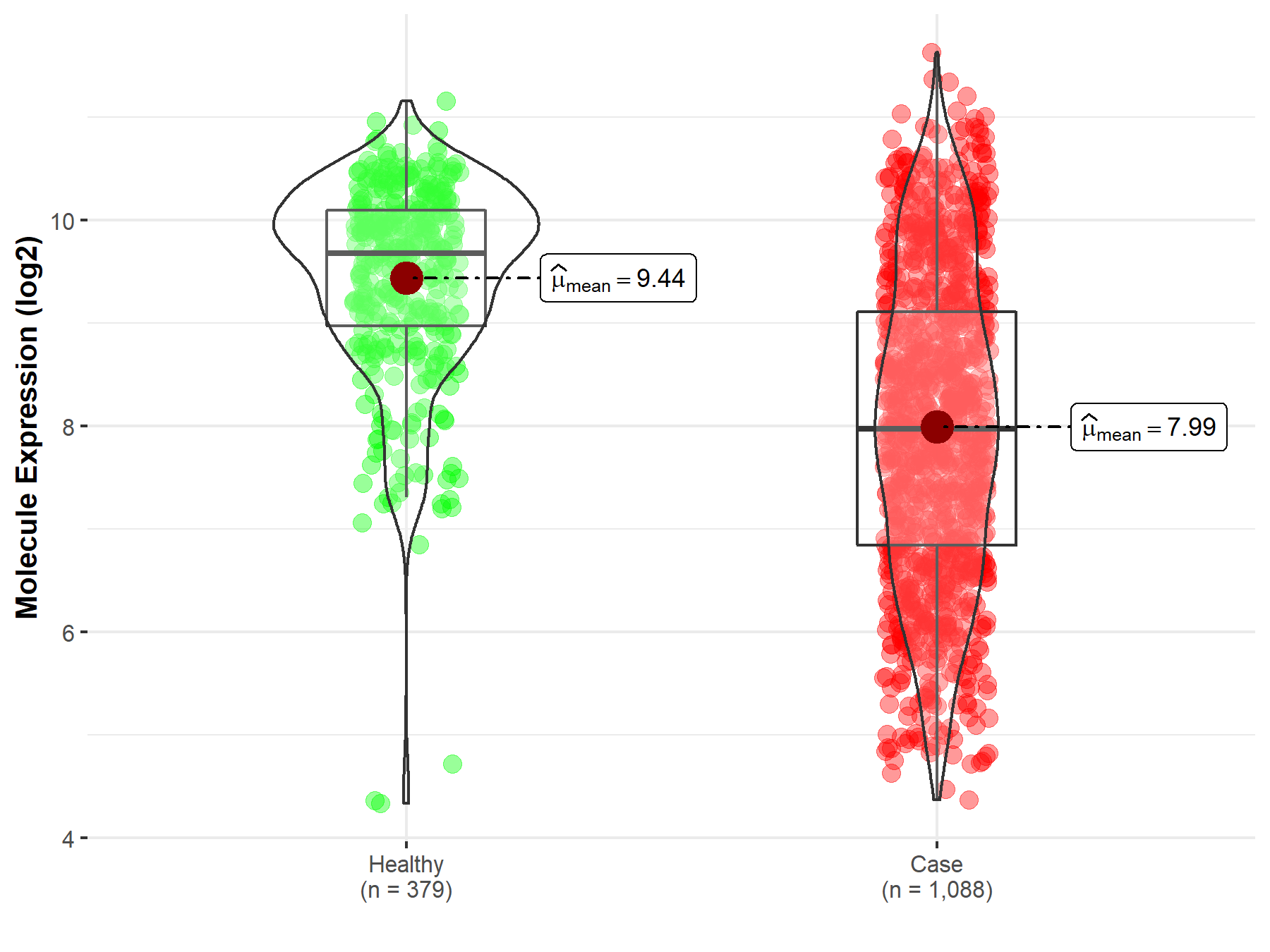
| The Studied Tissue | Brainstem tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Glioma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.55E-01; Fold-change: 1.13E+00; Z-score: 2.24E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | White matter | |
| The Specified Disease | Glioma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.51E-01; Fold-change: 4.68E-01; Z-score: 4.52E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
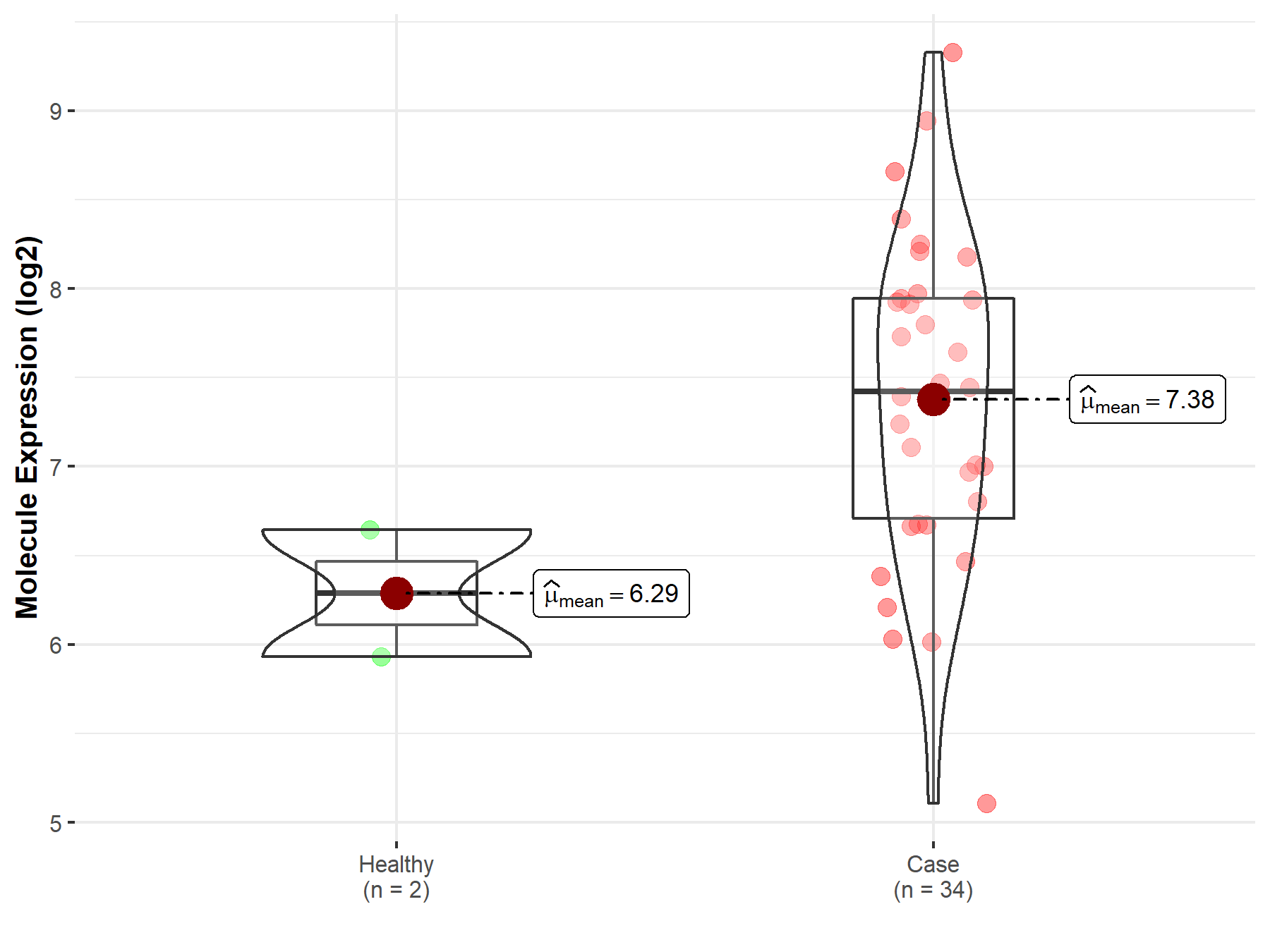
| The Studied Tissue | Brainstem tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Neuroectodermal tumor | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.11E-13; Fold-change: -1.80E+00; Z-score: -5.94E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
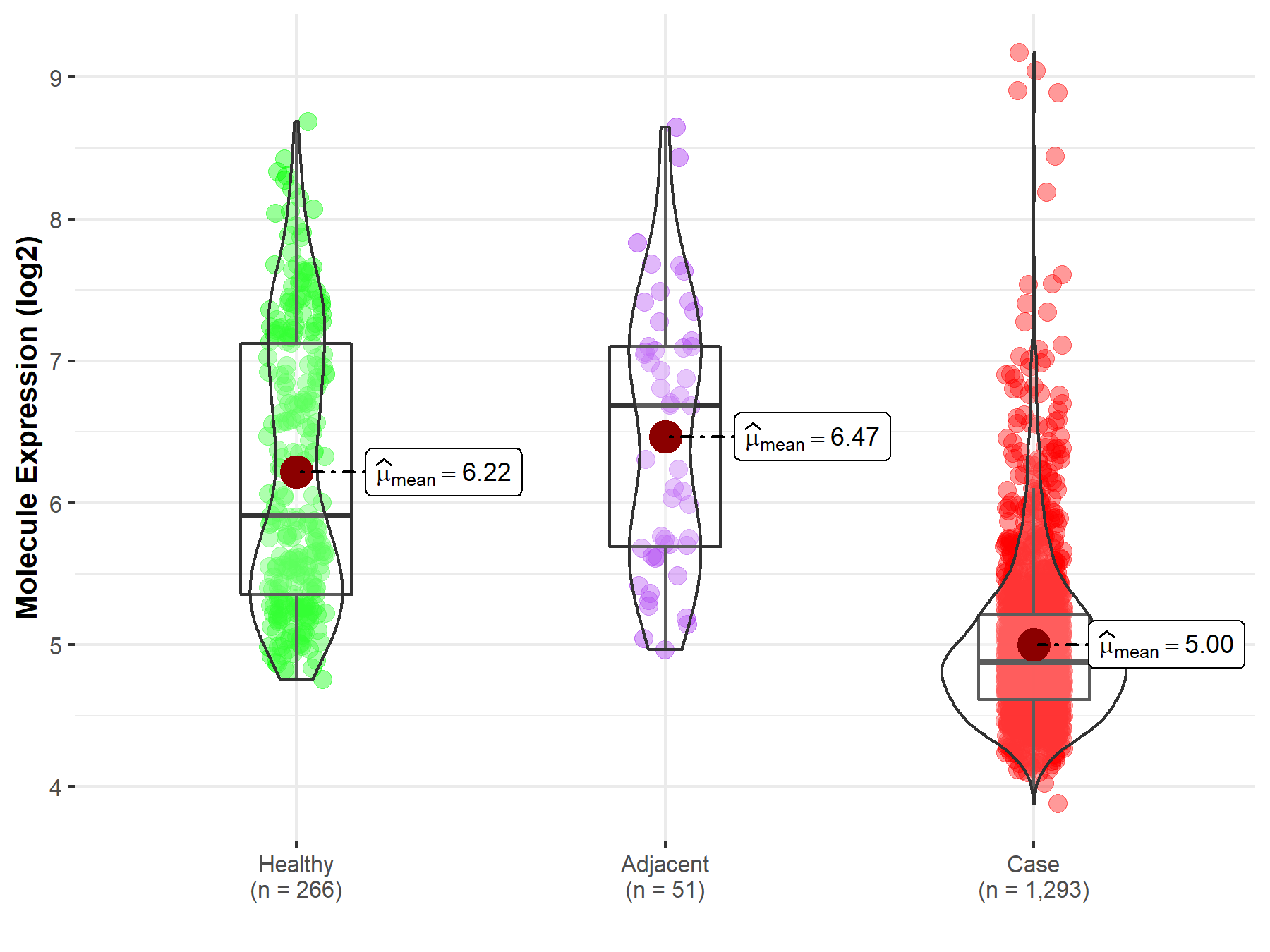
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.43E-56; Fold-change: -1.03E+00; Z-score: -1.06E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 2.31E-15; Fold-change: -1.81E+00; Z-score: -1.94E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

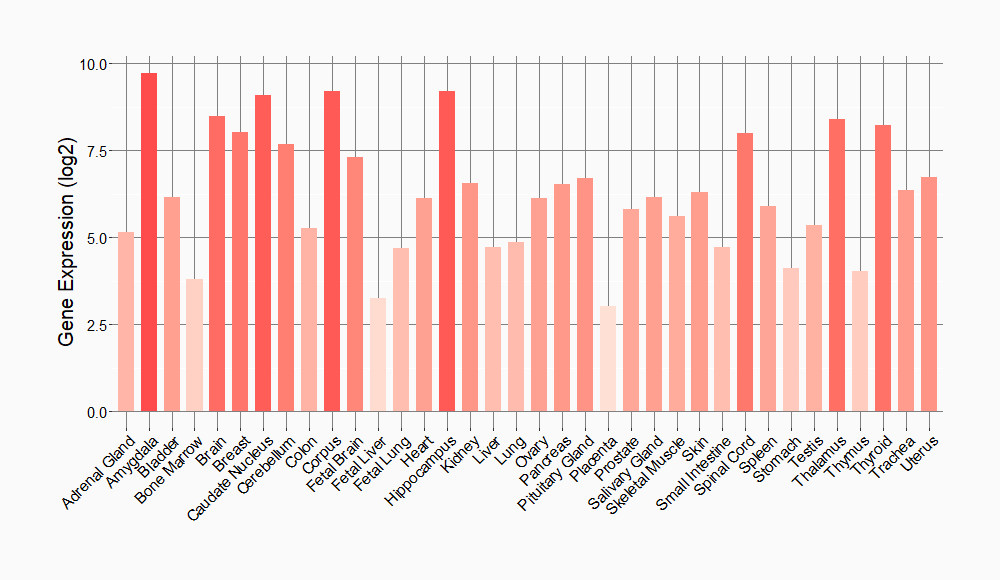
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
