Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00127) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Telithromycin
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Ketek; Levviax; TEL; HMR 3647; HMR3647; RU 66647; RU66647; HMR-3647; Ketek (TN); RU-66647; Telithromycin [USAN:BAN:INN]; Telithromycin (JAN/USAN/INN); (1R,2R,4R,6R,7R,8R,10R,13R,14S)-7-[(2S,3R,4S,6R)-4-(dimethylamino)-3-hydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy-13-ethyl-6-methoxy-2,4,6,8,10,14-hexamethyl-17-[4-(4-pyridin-3-ylimidazol-1-yl)butyl]-12,15-dioxa-17-azabicyclo[12.3.0]heptadecane-3,9,11,16-tetrone; (1R,2R,4R,6R,7R,8R,10S,13R,14S)-7-[(2S,3R,4S,6R)-4-(dimethylamino)-3-hydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy-13-ethyl-6-methoxy-2,4,6,8,10,14-hexamethyl-17-[4-(4-pyridin-3-ylimidazol-1-yl)butyl]-12,15-dioxa-17-azabicyclo[12.3.0]heptadecane-3,9,11,16-tetrone; (1R,2R,4R,6S,7R,8R,10R,13R,14S)-7-[(2S,3R,4S,6R)-4-(dimethylamino)-3-hydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy-13-ethyl-6-methoxy-2,4,6,8,10,14-hexamethyl-17-[4-(4-pyridin-3-ylimidazol-1-yl)butyl]-12,15-dioxa-17-azabicyclo[12.3.0]heptadecane-3,9,11,16-tetrone; (1R,2S,4R,6R,7R,8R,10R,13R,14S)-7-[(2S,3R,4S,6R)-4-(dimethylamino)-3-hydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy-13-ethyl-6-methoxy-2,4,6,8,10,14-hexamethyl-17-[4-(4-pyridin-3-ylimidazol-1-yl)butyl]-12,15-dioxa-17-azabicyclo[12.3.0]heptadecane-3,9,11,16-tetrone; 11,12-Dideoxy-3-des(2,6-dideoxy-3-C,3-O-dimethyl-alpha-L-altropyranosyloxy)-6-O-methyl-3-oxo-12,11-(oxycarbonylimino)-N11-[4-[4-(3-pyridyl)imidazol-1-yl]butyl]erythromycin A
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
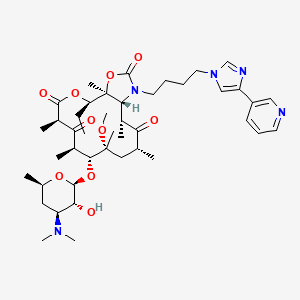
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(3 diseases)
[6]
[7]
|
||||
| Target | Bacterial 50S ribosomal RNA (Bact 50S rRNA) | NOUNIPROTAC | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C43H65N5O10
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CC[C@@H]1[C@@]2([C@@H]([C@H](C(=O)[C@@H](C[C@@]([C@@H]([C@H](C(=O)[C@H](C(=O)O1)C)C)O[C@H]3[C@@H]([C@H](C[C@H](O3)C)N(C)C)O)(C)OC)C)C)N(C(=O)O2)CCCCN4C=C(N=C4)C5=CN=CC=C5)C
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C43H65N5O10/c1-12-33-43(8)37(48(41(53)58-43)19-14-13-18-47-23-31(45-24-47)30-16-15-17-44-22-30)27(4)34(49)25(2)21-42(7,54-11)38(28(5)35(50)29(6)39(52)56-33)57-40-36(51)32(46(9)10)20-26(3)55-40/h15-17,22-29,32-33,36-38,40,51H,12-14,18-21H2,1-11H3/t25-,26-,27+,28+,29-,32+,33-,36-,37-,38-,40+,42-,43-/m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
LJVAJPDWBABPEJ-PNUFFHFMSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| VARIDT ID | |||||
| INTEDE ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: rRNA adenine N-6-methyltransferase ermE (ERME) | [1], [2], [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli AS19 | 562 | ||
| Escherichia coli AS19-RrmA- | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli DH10B | 316385 | |||
| Escherichia coli JC7623 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Methylation of specific nucleotides in rRNA is one of the means by which bacteria achieve resistance to macrolides-lincosamides-streptogramin B (MLSB) and ketolide antibiotics.ErmE dimethylation confers high resistance to all the MLSB and ketolide drugs. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Macrolide 2'-phosphotransferase II (MPHB) | [8], [9], [10] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli AG100A | 562 | ||
| Escherichia coli DB10 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli TOP10 | 83333 | |||
| Escherichia coli XL1-Blue | 562 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus RN4220 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Mph enzymes inactivate macrolides by phosphorylating the 2'-OH of the essential dimethylamino sugar, preventing it from binding the ribosome, and providing the chemical rationale for the resistance phenotype. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B resistance protein (ERMA) | [6] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Streptococcus pyogenes infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Methylation | Macrolide-binding site on the ribosome |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli AG100A | 562 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR amplification and sequence alignments assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Macrolide resistance commonly occurs due to methylation of the macrolide-binding site on the ribosome by methyltransferases encoded by the erm group of genes, Induction of erm(A) occurs by translational attenuationInduction of erm(A) occurs by translational attenuation. | |||
ICD-22: Injury/poisoning/certain external causes consequences
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Erythromycin resistance protein (ERM38) | [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Mycobacterium smegmatis infection [ICD-11: 1B2Z.3] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Mycobacterium smegmatis mc2155 | 246196 | ||
| Mycobacterium smegmatis mc2155/pMIP12 | 246196 | |||
| Mycobacterium smegmatis mc2155/pOMV20 | 246196 | |||
| Mycobacterium smegmatis mc2155/pOMV30 | 246196 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
MALDI mass spectrometry assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Erm (38) is a specific dimethyltransferase. The strain obtained drug resistance by adding two methyl groups to A2058 in Mycobacterium 23SrRNA. | |||
| Key Molecule: Erythromycin resistance protein (ERM38) | [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Mycobacterium smegmatis infection [ICD-11: 1B2Z.3] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Mycobacterium smegmatis mc2155 | 246196 | ||
| Mycobacterium smegmatis mc2155/pMIP12 | 246196 | |||
| Mycobacterium smegmatis mc2155/pOMV20 | 246196 | |||
| Mycobacterium smegmatis mc2155/pOMV30 | 246196 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
MALDI mass spectrometry assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Erm (38) is a specific dimethyltransferase. The strain obtained drug resistance by adding two methyl groups to A2058 in Mycobacterium 23SrRNA. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
