Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00085) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Ceftriaxone
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Biotrakson; CTRX; Cefatriaxone; Ceftriaxon; Ceftriaxona; Ceftriaxonum; Ceftriazone; Longacef; Longaceph; Rocefin; Rocephin; Rocephine; CEFTRIAXONE SODIUM; Ceftriaxone intravenous; Ro 139904; Ceftriaxona [INN-Spanish]; Ceftriaxone (INN); Ceftriaxone (TN); Ceftriaxone [USAN:JAN]; Ceftriaxone, Disodium Salt; Ceftriaxonum [INN-Latin]; DRG-0071; Ro13-9904; Rocephin (TN); Ceftriaxone, Disodium Salt, Hemiheptahydrate; Ro-13-9904; (6R,7R)-7-(2-(2-Amino-4-thiazolyl)glyoxylamido)-8-oxo-3-(((1,2,5,6-tetrahydro-2-methyl-5,6-dioxo-as-triazin-3-yl)thio)methyl)-5-thia-1-azabicyclo(4.2.0)oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid, 7(sup 2)-(Z)-(O-methyloxime), sesquaterhydrate; (6R,7R)-7-({(2Z)-2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-2-[(methyloxy)imino]acetyl}amino)-3-{[(6-hydroxy-2-methyl-5-oxo-2,5-dihydro-1,2,4-triazin-3-yl)thio]methyl}-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid; (6R,7R)-7-[[(2Z)-2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-2-methoxyiminoacetyl]amino]-3-[(2-methyl-5,6-dioxo-1H-1,2,4-triazin-3-yl)sulfanylmethyl]-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid; (6R,7R)-7-{[(2Z)-2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-2-(methoxyimino)acetyl]amino}-3-{[(2-methyl-5,6-dioxo-1,2,5,6-tetrahydro-1,2,4-triazin-3-yl)sulfanyl]methyl}-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid; 7beta-{[(2Z)-2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-2-(methoxyimino)acetyl]amino}-3-{[(2-methyl-5,6-dioxo-1,2,5,6-tetrahydro-1,2,4-triazin-3-yl)sulfanyl]methyl}-3,4-didehydrocepham-4-carboxylic acid
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
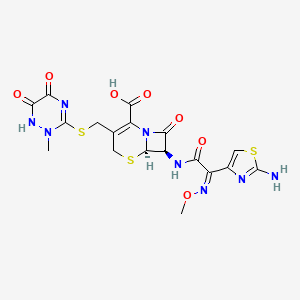
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(8 diseases)
[5]
[6]
[7]
[8]
[9]
[5]
[10]
|
||||
| Target | Bacterial Penicillin binding protein (Bact PBP) | NOUNIPROTAC | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C18H18N8O7S3
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CN1C(=NC(=O)C(=O)N1)SCC2=C(N3[C@@H]([C@@H](C3=O)NC(=O)/C(=N\\OC)/C4=CSC(=N4)N)SC2)C(=O)O
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C18H18N8O7S3/c1-25-18(22-12(28)13(29)23-25)36-4-6-3-34-15-9(14(30)26(15)10(6)16(31)32)21-11(27)8(24-33-2)7-5-35-17(19)20-7/h5,9,15H,3-4H2,1-2H3,(H2,19,20)(H,21,27)(H,23,29)(H,31,32)/b24-8-/t9-,15-/m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
VAAUVRVFOQPIGI-SPQHTLEESA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| VARIDT ID | |||||
| INTEDE ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Beta-lactamase (BLA) | [2], [3], [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D240G |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli DH10B | 316385 | ||
| Citrobacter freundii 2526/96 | 546 | |||
| Escherichia coli isolates | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | We have reported recently the DNA sequence of another Beta-lactamase, CTX- M-15, from Indian enterobacterial isolates that were resistant to both cefotaxime and ceftazidime.CTX-M-15 has a single amino acid change [Asp-240-Gly (Ambler numbering)]7 compared with CTX-M-3. | |||
| Key Molecule: Beta-lactamase (BLA) | [10] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Enterobacter cloacae infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Enterobacter cloacae strains ENLA-1 | 550 | ||
| Escherichia coli strain ECAA-1 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain ECLA-1 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain ECLA-2 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain ECLA-4 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain ECZK-1 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain ECZP-1 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain ECZU-1 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain HK225f | 562 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPAA-1 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPBE-2 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPGE-1 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPGE-2 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-1 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-10 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-2 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-3 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-4 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-5 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-6 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-7 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-8 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-9 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-1 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-10 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-11 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-12 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-13 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-4 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-6 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-7 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-8 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-9 | 573 | |||
| Salmonella enterica serotype wien strain SWLA-1 | 149384 | |||
| Salmonella enterica serotype wien strain SWLA-2 | 149384 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Hybridization experiments assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Of 60 strains with reduced susceptibility to expanded-spectrum cephalosporins which had been collected, 34 (24Klebsiella pneumoniae, 7Escherichia coli, 1Enterobacter cloacae, and 2Salmonella entericaserotypewien) hybridized with the intragenic blaSHVprobe. TheblaSHVgenes were amplified by PCR, and the presence ofblaSHV-ESBLwas established in 29 strains by restriction enzyme digests of the resulting 1,018-bp amplimers as described elsewhere. These results were confirmed by the nucleotide sequencing of all 34 amplimers. Five strains contained SHV non-ESBL enzymes. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: TolC family outer membrane protein (TOLC) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Acinetobacter baumannii AYE WT | 509173 | ||
| Acinetobacter baumannii AYE detaabuO | 509173 | |||
| Acinetobacter baumannii AYE detaabuO Omega abuO | 509173 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Disk diffusion test assay; E-strip test assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | AbuO, an OMP, confers broad-spectrum antimicrobial resistance via active efflux in A. baumannii. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Beta-lactamase (BLA) | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Escherichia coli infection [ICD-11: 1A03.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Acquired |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli JM109 | 562 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR and molecular characterization assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Disk diffusion method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | CTX-M-55 is a novel ceftazidime-resistant CTX-M extended-spectrum Beta-lactamase, which reduced susceptibility. | |||
| Key Molecule: Beta-lactamase (BLA) | [10] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Escherichia coli infection [ICD-11: 1A03.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Enterobacter cloacae strains ENLA-1 | 550 | ||
| Escherichia coli strain ECAA-1 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain ECLA-1 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain ECLA-2 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain ECLA-4 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain ECZK-1 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain ECZP-1 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain ECZU-1 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain HK225f | 562 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPAA-1 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPBE-2 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPGE-1 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPGE-2 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-1 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-10 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-2 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-3 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-4 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-5 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-6 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-7 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-8 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-9 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-1 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-10 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-11 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-12 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-13 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-4 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-6 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-7 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-8 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-9 | 573 | |||
| Salmonella enterica serotype wien strain SWLA-1 | 149384 | |||
| Salmonella enterica serotype wien strain SWLA-2 | 149384 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Hybridization experiments assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Of 60 strains with reduced susceptibility to expanded-spectrum cephalosporins which had been collected, 34 (24Klebsiella pneumoniae, 7Escherichia coli, 1Enterobacter cloacae, and 2Salmonella entericaserotypewien) hybridized with the intragenic blaSHVprobe. TheblaSHVgenes were amplified by PCR, and the presence ofblaSHV-ESBLwas established in 29 strains by restriction enzyme digests of the resulting 1,018-bp amplimers as described elsewhere. These results were confirmed by the nucleotide sequencing of all 34 amplimers. Five strains contained SHV non-ESBL enzymes. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Beta-lactamase (BLA) | [10] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Salmonella enterica infection [ICD-11: 1A09.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Enterobacter cloacae strains ENLA-1 | 550 | ||
| Escherichia coli strain ECAA-1 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain ECLA-1 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain ECLA-2 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain ECLA-4 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain ECZK-1 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain ECZP-1 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain ECZU-1 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain HK225f | 562 | |||
| Salmonella enterica serotype wien strain SWLA-1 | 149384 | |||
| Salmonella enterica serotype wien strain SWLA-2 | 149384 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPAA-1 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPBE-2 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPGE-1 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPGE-2 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPLA-1 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPLA-10 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPLA-2 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPLA-3 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPLA-4 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPLA-5 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPLA-6 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPLA-7 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPLA-8 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPLA-9 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPZU-1 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPZU-10 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPZU-11 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPZU-12 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPZU-13 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPZU-4 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPZU-6 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPZU-7 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPZU-8 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains kPZU-9 | 573 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Hybridization experiments assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Of 60 strains with reduced susceptibility to expanded-spectrum cephalosporins which had been collected, 34 (24Klebsiella pneumoniae, 7Escherichia coli, 1Enterobacter cloacae, and 2Salmonella entericaserotypewien) hybridized with the intragenic blaSHVprobe. TheblaSHVgenes were amplified by PCR, and the presence ofblaSHV-ESBLwas established in 29 strains by restriction enzyme digests of the resulting 1,018-bp amplimers as described elsewhere. These results were confirmed by the nucleotide sequencing of all 34 amplimers. Five strains contained SHV non-ESBL enzymes. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Probable peptidoglycan D,D-transpeptidase PenA (PENA) | [11], [12], [13] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gonococcal infection [ICD-11: 1A70.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.A311V |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Neisseria gonorrhoeae FA19 | 528352 | ||
| Neisseria gonorrhoeae FA6140 | 528353 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay; broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The penA gene,which encodes penicillin-binding protein 2 (PBP2), from H041 (penA41) is a mosaic penA allele similar to mosaic alleles conferring intermediate-level cephalosporin resistance.Tthree novel mutations, A311V, V316P, and T483S, that, when incorporated into the mosaic penA35 allele, are responsible for essentially all of the additional resistance conferred by penA41. Two of these mutations, A311V and T316P, are located near the active-site nucleophile Ser310, in a region previously shown to harbor mutations that increase resistance, whereas the remaining mutation, T483S, is in a different location in the structure of PBP2, where it may interact with the Beta-lactam carboxylate. | |||
| Key Molecule: Probable peptidoglycan D,D-transpeptidase PenA (PENA) | [11], [12], [13] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gonococcal infection [ICD-11: 1A70.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T316P |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Neisseria gonorrhoeae FA19 | 528352 | ||
| Neisseria gonorrhoeae FA6140 | 528353 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay; broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The penA gene,which encodes penicillin-binding protein 2 (PBP2), from H041 (penA41) is a mosaic penA allele similar to mosaic alleles conferring intermediate-level cephalosporin resistance.Tthree novel mutations, A311V, V316P, and T483S, that, when incorporated into the mosaic penA35 allele, are responsible for essentially all of the additional resistance conferred by penA41. Two of these mutations, A311V and T316P, are located near the active-site nucleophile Ser310, in a region previously shown to harbor mutations that increase resistance, whereas the remaining mutation, T483S, is in a different location in the structure of PBP2, where it may interact with the Beta-lactam carboxylate. | |||
| Key Molecule: Probable peptidoglycan D,D-transpeptidase PenA (PENA) | [11], [12], [13] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gonococcal infection [ICD-11: 1A70.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.A311V+p.T316P |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Neisseria gonorrhoeae FA19 | 528352 | ||
| Neisseria gonorrhoeae FA6140 | 528353 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay; broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The penA gene,which encodes penicillin-binding protein 2 (PBP2), from H041 (penA41) is a mosaic penA allele similar to mosaic alleles conferring intermediate-level cephalosporin resistance.Tthree novel mutations, A311V, V316P, and T483S, that, when incorporated into the mosaic penA35 allele, are responsible for essentially all of the additional resistance conferred by penA41. Two of these mutations, A311V and T316P, are located near the active-site nucleophile Ser310, in a region previously shown to harbor mutations that increase resistance, whereas the remaining mutation, T483S, is in a different location in the structure of PBP2, where it may interact with the Beta-lactam carboxylate. | |||
| Key Molecule: Probable peptidoglycan D,D-transpeptidase PenA (PENA) | [11], [12], [13] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gonococcal infection [ICD-11: 1A70.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T483S |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Neisseria gonorrhoeae FA19 | 528352 | ||
| Neisseria gonorrhoeae FA6140 | 528353 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay; broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The penA gene,which encodes penicillin-binding protein 2 (PBP2), from H041 (penA41) is a mosaic penA allele similar to mosaic alleles conferring intermediate-level cephalosporin resistance.Tthree novel mutations, A311V, V316P, and T483S, that, when incorporated into the mosaic penA35 allele, are responsible for essentially all of the additional resistance conferred by penA41. Two of these mutations, A311V and T316P, are located near the active-site nucleophile Ser310, in a region previously shown to harbor mutations that increase resistance, whereas the remaining mutation, T483S, is in a different location in the structure of PBP2, where it may interact with the Beta-lactam carboxylate. | |||
| Key Molecule: Probable peptidoglycan D,D-transpeptidase PenA (PENA) | [11], [12], [13] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gonococcal infection [ICD-11: 1A70.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T483S+p.A311V+p.T316P |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Neisseria gonorrhoeae FA19 | 528352 | ||
| Neisseria gonorrhoeae FA6140 | 528353 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay; broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The penA gene,which encodes penicillin-binding protein 2 (PBP2), from H041 (penA41) is a mosaic penA allele similar to mosaic alleles conferring intermediate-level cephalosporin resistance.Tthree novel mutations, A311V, V316P, and T483S, that, when incorporated into the mosaic penA35 allele, are responsible for essentially all of the additional resistance conferred by penA41. Two of these mutations, A311V and T316P, are located near the active-site nucleophile Ser310, in a region previously shown to harbor mutations that increase resistance, whereas the remaining mutation, T483S, is in a different location in the structure of PBP2, where it may interact with the Beta-lactam carboxylate. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Type IV pilus biogenesis and competence protein PilQ (PILQ) | [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gonococcal infection [ICD-11: 1A70.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G666K |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Neisseria gonorrhoeae PR100 | 485 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR amplification and DNA sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Antibiotic resistance mediated by penC is the result of a Glu-666 to Lys missense mutation in the pilQ gene that interferes with the formation of the SDS-resistant high-molecular-mass PilQ secretin complex, disrupts piliation, and decreases transformation frequency by 50-fold. | |||
ICD-12: Respiratory system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Beta-lactamase (BLA) | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Klebsiella pneumoniae [ICD-11: CA40.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Acquired |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates | 573 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR and molecular characterization assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Disk diffusion method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | CTX-M-55 is a novel ceftazidime-resistant CTX-M extended-spectrum Beta-lactamase, which reduced susceptibility. | |||
| Key Molecule: Beta-lactamase (BLA) | [10] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Klebsiella pneumoniae infection [ICD-11: CA40.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Enterobacter cloacae strains ENLA-1 | 550 | ||
| Escherichia coli strain ECAA-1 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain ECLA-1 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain ECLA-2 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain ECLA-4 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain ECZK-1 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain ECZP-1 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain ECZU-1 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain HK225f | 562 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPAA-1 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPBE-2 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPGE-1 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPGE-2 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-1 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-10 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-2 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-3 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-4 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-5 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-6 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-7 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-8 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPLA-9 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-1 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-10 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-11 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-12 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-13 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-4 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-6 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-7 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-8 | 573 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains KPZU-9 | 573 | |||
| Salmonella enterica serotype wien strain SWLA-1 | 149384 | |||
| Salmonella enterica serotype wien strain SWLA-2 | 149384 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Hybridization experiments assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Of 60 strains with reduced susceptibility to expanded-spectrum cephalosporins which had been collected, 34 (24Klebsiella pneumoniae, 7Escherichia coli, 1Enterobacter cloacae, and 2Salmonella entericaserotypewien) hybridized with the intragenic blaSHVprobe. TheblaSHVgenes were amplified by PCR, and the presence ofblaSHV-ESBLwas established in 29 strains by restriction enzyme digests of the resulting 1,018-bp amplimers as described elsewhere. These results were confirmed by the nucleotide sequencing of all 34 amplimers. Five strains contained SHV non-ESBL enzymes. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
