Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00068) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Framycetin
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Neomycin; neomycin; NEOMYCIN B; Soframycin; Actiline; Mycifradin; Fradiomycin; Soframycine; Framycetinum; Framycetine; Framicetina; Neomas; Fradiomycinum; Antibiotique; Nivemycin; Actilin; Neolate; Enterfram; Myacyne; Framygen; Caswell No 595; Vonamycin powder V; Neomycin B sulfate; Neomin; Neomcin; Fradiomycin B; Neo-Rx; Neomicina [DCIT]; Framycetinum [INN-Latin]; PIMAVECORT; Neobrettin; Neo-Fradin; 119-04-0; Neomycine [INN-French]; Neomycinum [INN-Latin]; Framycetine [INN-French]; Framicetina [INN-Spanish]; USAF CB-19; Endomixin; Fraquinol; Myacine; Myciguent; NMY; Neobiotic; Neomicina; Neomycinum; Tuttomycin; VONAMYCIN; NEOMYCIN AND POLYMYXIN B SULFATES; NEOMYCIN SULFATE; Neomycin solution; Soframycin Ophthalmic; Antibiotic 10676; Antibiotic produced by Streptomyces decaris Neomycin B; Framycetin (INN); Soframycin (TN); Framycetin [INN:BAN:DCF]; Sofra-Tulle (TN); BDG-(1-4)CYY-(5-1)RIB-(3-1)IDG; BDG-(1-4)NEB-(5-1)RIB-(3-1)NED; (1R,2R,3S,4R,6S)-4,6-diamino-2-{[3-O-(2,6-diamino-2,6-dideoxy-beta-L-idopyranosyl)-beta-D-ribofuranosyl]oxy}-3-hydroxycyclohexyl 2,6-diamino-2,6-dideoxy-alpha-D-glucopyranoside; (2R,3S,4R,5R,6R)-5-amino-2-(aminomethyl)-6-[(1R,2R,3S,4R,6S)-4,6-diamino-2-[(2S,3R,4S,5R)-4-[(2R,3R,4R,5S,6S)-3-amino-6-(aminomethyl)-4,5-dihydroxyoxan-2-yl]oxy-3-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]oxy-3-hydroxycyclohexyl]oxyoxane-3,4-diol; D-Streptamine, O-2,6-diamino-2,6-dideoxy-beta-L-idopyranosyl-(1->3)-O-beta-D-ribofuranosyl-(1->5)]-O-[2,6-diamino-2,6-dideoxy-alpha-D-glucopyranosyl-(1->4)]-2-deoxy
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 3 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
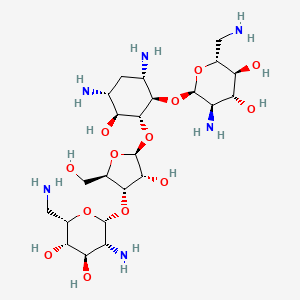
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(4 diseases)
[2]
[4]
[5]
[6]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Discovered by Cell Line Test for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[3]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Validated by in-vivo Model for This Drug
(3 diseases)
[7]
[7]
[1]
|
||||
| Target | Bacterial 16S ribosomal RNA (Bact 16S rRNA) | NOUNIPROTAC | [1] | ||
| Staphylococcus 30S ribosomal subunit (Stap-coc pbp2) | F4NA87_STAAU | [1] | |||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C23H46N6O13
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
C1[C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]1N)O[C@@H]2[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O2)CN)O)O)N)O[C@H]3[C@@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O3)CO)O[C@@H]4[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@@H](O4)CN)O)O)N)O)O)N
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C23H46N6O13/c24-2-7-13(32)15(34)10(28)21(37-7)40-18-6(27)1-5(26)12(31)20(18)42-23-17(36)19(9(4-30)39-23)41-22-11(29)16(35)14(33)8(3-25)38-22/h5-23,30-36H,1-4,24-29H2/t5-,6+,7-,8+,9-,10-,11-,12+,13-,14-,15-,16-,17-,18-,19-,20-,21-,22-,23+/m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
PGBHMTALBVVCIT-VCIWKGPPSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| INTEDE ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: AAC(6')-Ib family aminoglycoside 6'-N-acetyltransferase (AAC6IB) | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Vibrio cholerae infection [ICD-11: 1A00.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Vibrio cholerae PL107b | 666 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR and DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Commercial antimicrobial discs assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The expression of aac(6')-Ib lead to drug resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside (3'') (9) adenylyltransferase (AADA) | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Vibrio cholerae infection [ICD-11: 1A00.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Vibrio cholerae O39 strain AS634 | 666 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR and DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Commercial antimicrobial discs assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The expression of aadA1-S lead to drug resistance. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Vibrio cholerae infection [ICD-11: 1A00.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Vibrio cholerae O62 strain AS438 | 666 | ||
| Vibrio cholerae PG262(b) | 666 | |||
| Vibrio cholerae PG9 | 666 | |||
| Vibrio cholerae PL78/6 | 666 | |||
| Vibrio cholerae PL105b | 666 | |||
| Vibrio cholerae PL141 | 666 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR and DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Commercial antimicrobial discs assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The expression of dfrA1 lead to drug resistance. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: 16S rRNA (adenine(1408)-N(1))-methyltransferase (KAMB) | [8], [9] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) | 469008 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The 16S ribosomal RNA methyltransferase enzymes that modify nucleosides in the drug binding site to provide self-resistance in aminoglycoside-producing micro-organisms have been proposed to comprise two distinct groups of S-adenosyl-l-methionine (SAM)-dependent RNA enzymes, namely the kgm and kam families. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside 3'-phosphotransferase (A3AP) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Stenotrophomonas maltophilia infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli | 668369 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR amplification assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Aph(3')-IIc significantly increases MICs of kanamycin, neomycin, butirosin, and paromomycin when expressed in Escherichia coli. Disruption of aph(3')-IIc results in decreased MICs of these drugs. | |||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside N(3)-acetyltransferase VIII (A3AC8) | [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Micromonospora chalcea infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Micromonospora chalcea strain 69-683 | 1874 | ||
| Streptomyces fradiae strain ATCC 10745 | 1319510 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Southern-blot hybridization assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In the case of S. fradiae ATCC10745, a Nm producer, an O-phosphotransferase (APH) encoded by the aphA-5 gene and an N-acetyltransferase (AAC) have been identified. The aphA-5 gene is thought to be part of a biosynthetic cluster; the sac gene is not closely linked to aph; however, high-level Nm resistance in Streptomyces requires expression of both uph and sac. Nm production has been found also in the genus Mcromonospora, especially in M. chalcea 69-683, which possesses both APH and AAC activities. Little is known of Mcromonospora molecular biology, and with a view to comparing the two Nm producers and their resistance mechanisms, we have cloned, expressed and characterised the two resistance determinants from M. chalcea and from S. frudiue. | |||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside N(3)-acetyltransferase IX (A3AC9) | [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Micromonospora chalcea infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Micromonospora chalcea strain 69-683 | 1874 | ||
| Streptomyces fradiae strain ATCC 10745 | 1319510 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Southern-blot hybridization assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In the case of S. fradiae ATCC10745, a Nm producer, an O-phosphotransferase (APH) encoded by the aphA-5 gene and an N-acetyltransferase (AAC) have been identified. The aphA-5 gene is thought to be part of a biosynthetic cluster; the sac gene is not closely linked to aph; however, high-level Nm resistance in Streptomyces requires expression of both uph and sac. Nm production has been found also in the genus Mcromonospora, especially in M. chalcea 69-683, which possesses both APH and AAC activities. Little is known of Mcromonospora molecular biology, and with a view to comparing the two Nm producers and their resistance mechanisms, we have cloned, expressed and characterised the two resistance determinants from M. chalcea and from S. frudiue. | |||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside N-acetyltransferase AAC(6')-IAP | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Lactobacillus casei infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | S. maltophilia JUNP350 | N.A. | ||
| Mechanism Description | Compared with vector control,?E. coli?expressing AAC(6')-Iap showed decreased susceptibilities to arbekacin, amikacin, dibekacin, isepamicin, neomycin, netilmicin, sisomicin, and tobramycin. Thin-layer chromatography (TLC) analysis revealed that all the aminoglycosides tested, except for apramycin and paromomycin, were acetylated by AAC(6')-Iap. These results indicated that?aac(6')-Iap?is a functional acetyltransferase that modifies the 6'-NH2?position of aminoglycosides and is involved in aminoglycoside resistance. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Acetylpolyamine amidohydrolase (APAH) | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Escherichia coli infection [ICD-11: 1A03.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Acquired |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli | 668369 | ||
| Achromobacter xylosoxydans subsp. denitrificans AX-22 | 85698 | |||
| Escherichia coli MkD-135 | 562 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa 10145/3 | 287 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA extraction and Sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Macrodilution broth method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The aphA15 gene is the first example of an aph-like gene carried on a mobile gene cassette, and its product exhibits close similarity to the APH(3')-IIa aminoglycoside phosphotransferase encoded by Tn5 (36% amino acid identity) and to an APH(3')-IIb enzyme from Pseudomonas aeruginosa (38% amino acid identity). Expression of the cloned aphA15 gene in Escherichia coli reduced the susceptibility to kanamycin and neomycin as well as (slightly) to amikacin, netilmicin, and streptomycin. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Transmembrane protein 94 (TMEM94) | [10] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Methylation | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | S. aureus isolates | 41687 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR; Docking assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Antimicrobial susceptibility testing; Phenotypic assay; MIC assay; Checkerboard microdilution assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | This study aimed to identify the prevalence of erythromycin and erythromycin-induced resistance and assess for potential inhibitors. A total of 99 isolates were purified from various clinical sources. Phenotypic detection of macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B (MLSB)-resistance phenotypes was performed by D-test. MLSB-resistance genes were identified using PCR. Different compounds were tested for their effects on erythromycin and inducible clindamycin resistance by broth microdilution and checkerboard microdilution methods. The obtained data were evaluated using docking analysis. Ninety-one isolates were S. aureus. The prevalence of constitutive MLSB, inducible MLSB, and macrolide-streptogramin (MS) phenotypes was 39.6%, 14.3%, and 2.2%, respectively. Genes including ermC, ermA, ermB, msrA, msrB, lnuA, and mphC were found in 82.6%, 5.8%, 7.7%, 3.8%, 3.8%, 13.5%, and 3.8% of isolates, respectively. Erythromycin resistance was significantly reduced by doxorubicin, neomycin, and omeprazole. Quinine, ketoprofen, and fosfomycin combated and reversed erythromycin/clindamycin-induced resistance. This study highlighted the significance of managing antibiotic resistance and overcoming clindamycin treatment failure. Doxorubicin, neomycin, omeprazole, quinine, ketoprofen, and fosfomycin could be potential inhibitors of erythromycin and inducible clindamycin resistance. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Acetylpolyamine amidohydrolase (APAH) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pasteurella multocida infection [ICD-11: 1B99.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 | 1322345 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213 | 1280 | |||
| Pasteurella multocida 36950 | 1075089 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The analysis of one representative P. multocida isolate identified an 82 kb integrative and conjugative element (ICE) integrated into the chromosomal DNA. This ICE, designated ICEPmu1, harboured 11 resistance genes, which confer resistance to streptomycin/spectinomycin (aadA25), streptomycin (strA and strB), gentamicin (aadB), kanamycin/neomycin (aphA1), tetracycline [tetR-tet(H)], chloramphenicol/florfenicol (floR), sulphonamides (sul2), tilmicosin/clindamycin [erm(42)] or tilmicosin/tulathromycin [msr(E)-mph(E)]. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside N(3)-acetyltransferase VIII (A3AC8) | [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Streptomyces fradiae infection [ICD-11: 1C43.5] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Micromonospora chalcea strain 69-683 | 1874 | ||
| Streptomyces fradiae strain ATCC 10745 | 1319510 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Southern-blot hybridization assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In the case of S. fradiae ATCC10745, a Nm producer, an O-phosphotransferase (APH) encoded by the aphA-5 gene and an N-acetyltransferase (AAC) have been identified. The aphA-5 gene is thought to be part of a biosynthetic cluster; the sac gene is not closely linked to aph; however, high-level Nm resistance in Streptomyces requires expression of both uph and sac. | |||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside N(3)-acetyltransferase IX (A3AC9) | [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Streptomyces fradiae infection [ICD-11: 1C43.5] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Micromonospora chalcea strain 69-683 | 1874 | ||
| Streptomyces fradiae strain ATCC 10745 | 1319510 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Southern-blot hybridization assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In the case of S. fradiae ATCC10745, a Nm producer, an O-phosphotransferase (APH) encoded by the aphA-5 gene and an N-acetyltransferase (AAC) have been identified. The aphA-5 gene is thought to be part of a biosynthetic cluster; the sac gene is not closely linked to aph; however, high-level Nm resistance in Streptomyces requires expression of both uph and sac. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
