Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00043) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Zithromax
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Azithromycin; Zithromax; 83905-01-5; Azithromycinum; Azithromycine; Sumamed; Zitromax; Zmax; Hemomycin; Azitrocin; Azasite; Azenil; Aritromicina; Zitrotek; Zithrax; Mixoterin; Setron; Aziwok; Zitrim; Aztrin; Zifin; Tobil; Zmas; Zeto; Azithromycinum [Latin]; Azithromycine [French]; Zithromax IV; AZITHROMYCIN DIHYDRATE; Misultina; Azitromax; Z-Pak; Tromix; Aritromicina [Spanish]; Azitromicina; CP-62993; UNII-J2KLZ20U1M; DRG-0104; CCRIS 1961; HSDB 7205; Azithromycin (anhydrous); C38H72N2O12; BRN 5387583; J2KLZ20U1M; Azythromycin; CHEBI:2955
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
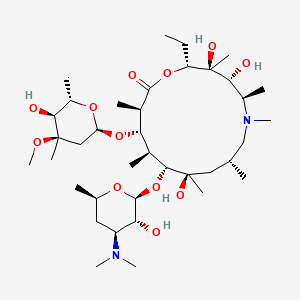
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(9 diseases)
[2]
[3]
[4]
[6]
[7]
[8]
[9]
[10]
[1]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Discovered by Cell Line Test for This Drug
(2 diseases)
[5]
[11]
|
||||
| Target | Bacterial 50S ribosomal RNA (Bact 50S rRNA) | NOUNIPROTAC | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C38H72N2O12
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CC[C@@H]1[C@@]([C@@H]([C@H](N(C[C@@H](C[C@@]([C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](C(=O)O1)C)O[C@H]2C[C@@]([C@H]([C@@H](O2)C)O)(C)OC)C)O[C@H]3[C@@H]([C@H](C[C@H](O3)C)N(C)C)O)(C)O)C)C)C)O)(C)O
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C38H72N2O12/c1-15-27-38(10,46)31(42)24(6)40(13)19-20(2)17-36(8,45)33(52-35-29(41)26(39(11)12)16-21(3)48-35)22(4)30(23(5)34(44)50-27)51-28-18-37(9,47-14)32(43)25(7)49-28/h20-33,35,41-43,45-46H,15-19H2,1-14H3/t20-,21-,22+,23-,24-,25+,26+,27-,28+,29-,30+,31-,32+,33-,35+,36-,37-,38-/m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
MQTOSJVFKKJCRP-BICOPXKESA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| VARIDT ID | |||||
| INTEDE ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: erm(X)cj (Unclear) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Corynebacterium jeikeium infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Frameshift mutation | Codon 216 frame shift |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032 | 196627 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213 | 1280 | |||
| Corynebacterium diphtheriae isolate | 1717 | |||
| Corynebacterium glutamicum kO8 | 1718 | |||
| Corynebacterium jeikeium isolates | 38289 | |||
| Escherichia coli ATCC 25923 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain XL1-Blue MRF9 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Southern blotting assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Disk diffusion methods assay; agar dilution methods assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Abundant amplificationproducts of slightly less than 400 bp were generated from DNAisolated from the 17 MLSb-resistant strains, whereas no am-plification products were generated with the DNA isolatedfrom the three susceptible strains. The DNA sequences of the amplification products showed 95% identity to the erm(X) gene isolated from a C. xerosis strain,erm(X)cx or ermCX. Thus, MLSb resistance in C. jeikeiumis associated with the presence of an allele, erm(X)cj, of the class Xermgenes. The first 215 amino acids of the predicted polypeptides for strains CJ12 and CJ21 are 93.5 and 98.6% identical to Erm(X)cx, the Erm protein from C. xerosi. The major difference between the two Erm(X)cj polypeptides and the Erm(X)cx polypeptide is a frame shift within codon 216. This results in the Erm(X)cj polypeptides being 31 amino acids longer than Erm(X)cx. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: 23s rRNA | [11] | |||
| Resistant Disease | syphilis [ICD-11: 1A60.Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | A1518/1519 |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | SS14 cells | N.A. | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Susceptibility and recovery assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The experiments carried out to evaluate?T pallidum?resistance to macrolides showed that azithromycin was effective against?T pallidum?strains that did not have either of the 23S rRNA gene mutations (A2058G or A2059G) conferring resistance to macrolides, remained ineffective for two strains (SS14 and UW330B) carrying either one of the aforementioned mutations. | |||
| Key Molecule: 23s rRNA | [12] | |||
| Resistant Disease | syphilis [ICD-11: 1A60.Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | A1518/1519 |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | UW330B cells | N.A. | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Susceptibility and recovery assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The experiments carried out to evaluate?T pallidum?resistance to macrolides showed that azithromycin was effective against?T pallidum?strains that did not have either of the 23S rRNA gene mutations (A2058G or A2059G) conferring resistance to macrolides, remained ineffective for two strains (SS14 and UW330B) carrying either one of the aforementioned mutations. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B resistance protein (ERMA) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Streptococcus pyogenes infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | Macrolide-binding site on the ribosome |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli AG100A | 562 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR amplification and sequence alignments assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | E. coli transformed with mutant erm(A) harbouring G98A, A137C or C140T mutations (phenotypes 1 and 2) did not express high-level azithromycin or clindamycin resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: Macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B resistance protein (ERMA) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Streptococcus pyogenes infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G98A |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli AG100A | 562 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR amplification and sequence alignments assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | E. coli transformed with mutant erm(A) harbouring G98A, A137C or C140T mutations (phenotypes 1 and 2) did not express high-level azithromycin or clindamycin resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: Macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B resistance protein (ERMA) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Streptococcus pyogenes infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.A137C |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli AG100A | 562 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR amplification and sequence alignments assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | E. coli transformed with mutant erm(A) harbouring G98A, A137C or C140T mutations (phenotypes 1 and 2) did not express high-level azithromycin or clindamycin resistance. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: 23S ribosomal RNA methyltransferase Erm34 (ERM34) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacillus clausii infection [ICD-11: 1C4Y.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Methylation | Ribosomal methylation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Bacillus clausii ATCC 21536 | 79880 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Cloning experiments and gene seqencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | This pattern of resistance generally due to the presence of an erm gene encoding a ribosomal methylase. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: 23s rRNA | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acinetobacter meningitis [ICD-11: 1D01.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | A2059G |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | M. pneumoniae M129 | 2093 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
GeneSeq assay; PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Antimicrobial susceptibility assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Since the secondary treatment choice for pediatric patients is very limited, we decided to look for potential new treatment strategies in macrolide drugs and investigate possible new mechanisms of resistance. We performed an in vitro selection of mutants resistant to five macrolides (erythromycin, roxithromycin, azithromycin, josamycin, and midecamycin) by inducing the parent M. pneumoniae strain M129 with increasing concentrations of the drugs. The evolving cultures in every passage were tested for their antimicrobial susceptibilities to eight drugs and mutations known to be associated with macrolide resistance by PCR and sequencing. The final selected mutants were also analyzed by whole-genome sequencing. Results showed that roxithromycin is the drug that most easily induces resistance (at 0.25 mg/L, with two passages, 23 days), while with midecamycin it is most difficult (at 5.12 mg/L, with seven passages, 87 days). Point mutations C2617A/T, A2063G, or A2064C in domain V of 23S rRNA were detected in mutants resistant to the 14- and 15-membered macrolides, while A2067G/C was selected for the 16-membered macrolides. Single amino acid changes (G72R, G72V) in ribosomal protein L4 emerged during the induction by midecamycin. Genome sequencing identified sequence variations in dnaK, rpoC, glpK, MPN449, and in one of the hsdS (MPN365) genes in the mutants. Mutants induced by the 14- or 15-membered macrolides were resistant to all macrolides, while those induced by the 16-membered macrolides (midecamycin and josamycin) remained susceptible to the 14- and 15-membered macrolides. In summary, these data demonstrated that midecamycin is less potent in inducing resistance than other macrolides, and the induced resistance is restrained to the 16-membered macrolides, suggesting a potential benefit of using midecamycin as a first treatment choice if the strain is susceptible. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: MsrC (MSRC) | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Enterococcus faecium meningitis [ICD-11: 1D01.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli | 668369 | ||
| Enterococcus faecium TX2465 | 1352 | |||
| Escherichia coli TX1330 | 668369 | |||
| Escherichia coli TX2046 | 668369 | |||
| Escherichia coli TX2597 | 668369 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Southern blotting assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Twofold dilutions assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The complete sequence (1,479 nucleotides) of msrC, part of which was recently reported by others using a different strain, was determined. This gene was found in 233 of 233 isolates of Enterococcus faecium but in none of 265 other enterococci. Disruption of msrC was associated with a two- to eightfold decrease in MICs of erythromycin azithromycin, tylosin, and quinupristin, suggesting that it may explain in part the apparent greater intrinsic resistance to macrolides of isolates of E. faecium relative to many streptococci. This endogenous, species-specific gene of E. faecium is 53% identical to msr(A), suggesting that it may be a remote progenitor of the acquired macrolide resistance gene found in some isolates of staphylococci. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: MsrC (MSRC) | [4] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Enterococcus faecium meningitis [ICD-11: 1D01.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Truncated mutantion | Disruption (nt 1251 to 1879) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli | 668369 | ||
| Enterococcus faecium TX2465 | 1352 | |||
| Escherichia coli TX1330 | 668369 | |||
| Escherichia coli TX2046 | 668369 | |||
| Escherichia coli TX2597 | 668369 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Southern blotting assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Twofold dilutions assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Disruption of msrC was associated with a two- to eightfold decrease in MICs of erythromycin azithromycin, tylosin, and quinupristin, suggesting that it may explain in part the apparent greater intrinsic resistance to macrolides of isolates of E. faecium relative to many streptococci. | |||
ICD-13: Digestive system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: 23S rRNA (cytidine-2'-O)-methyltransferase TlyA (TLYA) | [6] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Traveler's diarrhea [ICD-11: DA90.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.A2075G |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Campylobacter jejuni isolates | 197 | ||
| Campylobacter jejuni ATCC 33560 | 197 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Gene sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
E-test assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Point mutation occurred on the 23S rRNA gene at the A2075G transitions, and the number of mutated gene copies was proportional to azithromycin resistance. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
