Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00514)
| Name |
ATP-binding cassette sub-family C4 (ABCC4)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
MRP/cMOAT-related ABC transporter; Multi-specific organic anion transporter B; MOAT-B; Multidrug resistance-associated protein 4; MOATB; MRP4
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
ABCC4
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr13:95019835-95301475[-]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MLPVYQEVKPNPLQDANLCSRVFFWWLNPLFKIGHKRRLEEDDMYSVLPEDRSQHLGEEL
QGFWDKEVLRAENDAQKPSLTRAIIKCYWKSYLVLGIFTLIEESAKVIQPIFLGKIINYF ENYDPMDSVALNTAYAYATVLTFCTLILAILHHLYFYHVQCAGMRLRVAMCHMIYRKALR LSNMAMGKTTTGQIVNLLSNDVNKFDQVTVFLHFLWAGPLQAIAVTALLWMEIGISCLAG MAVLIILLPLQSCFGKLFSSLRSKTATFTDARIRTMNEVITGIRIIKMYAWEKSFSNLIT NLRKKEISKILRSSCLRGMNLASFFSASKIIVFVTFTTYVLLGSVITASRVFVAVTLYGA VRLTVTLFFPSAIERVSEAIVSIRRIQTFLLLDEISQRNRQLPSDGKKMVHVQDFTAFWD KASETPTLQGLSFTVRPGELLAVVGPVGAGKSSLLSAVLGELAPSHGLVSVHGRIAYVSQ QPWVFSGTLRSNILFGKKYEKERYEKVIKACALKKDLQLLEDGDLTVIGDRGTTLSGGQK ARVNLARAVYQDADIYLLDDPLSAVDAEVSRHLFELCICQILHEKITILVTHQLQYLKAA SQILILKDGKMVQKGTYTEFLKSGIDFGSLLKKDNEESEQPPVPGTPTLRNRTFSESSVW SQQSSRPSLKDGALESQDTENVPVTLSEENRSEGKVGFQAYKNYFRAGAHWIVFIFLILL NTAAQVAYVLQDWWLSYWANKQSMLNVTVNGGGNVTEKLDLNWYLGIYSGLTVATVLFGI ARSLLVFYVLVNSSQTLHNKMFESILKAPVLFFDRNPIGRILNRFSKDIGHLDDLLPLTF LDFIQTLLQVVGVVSVAVAVIPWIAIPLVPLGIIFIFLRRYFLETSRDVKRLESTTRSPV FSHLSSSLQGLWTIRAYKAEERCQELFDAHQDLHSEAWFLFLTTSRWFAVRLDAICAMFV IIVAFGSLILAKTLDAGQVGLALSYALTLMGMFQWCVRQSAEVENMMISVERVIEYTDLE KEAPWEYQKRPPPAWPHEGVIIFDNVNFMYSPGGPLVLKHLTALIKSQEKVGIVGRTGAG KSSLISALFRLSEPEGKIWIDKILTTEIGLHDLRKKMSIIPQEPVLFTGTMRKNLDPFNE HTDEELWNALQEVQLKETIEDLPGKMDTELAESGSNFSVGQRQLVCLARAILRKNQILII DEATANVDPRTDELIQKKIREKFAHCTVLTIAHRLNTIIDSDKIMVLDSGRLKEYDEPYV LLQNKESLFYKMVQQLGKAEAAALTETAKQVYFKRNYPHIGHTDHMVTNTSNGQPSTLTI FETAL Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
ATP-dependent transporter of the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) family that actively extrudes physiological compounds and xenobiotics from cells. Transports a range of endogenous molecules that have a key role in cellular communication and signaling, including cyclic nucleotides such as cyclic AMP (cAMP) and cyclic GMP (cGMP), bile acids, steroid conjugates, urate, and prostaglandins. Mediates the ATP-dependent efflux of glutathione conjugates such as leukotriene C4 (LTC4) and leukotriene B4 (LTB4) too. The presence of GSH is necessary for the ATP-dependent transport of LTB4, whereas GSH is not required for the transport of LTC4. Mediates the cotransport of bile acids with reduced glutathione (GSH). Transports a wide range of drugs and their metabolites, including anticancer, antiviral and antibiotics molecules. Confers resistance to anticancer agents such as methotrexate.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
4 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Coronary artery disease [ICD-11: BA8Z.0] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Coronary artery disease [ICD-11: BA8Z.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cilostazol | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Function | Inhibition |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | JAK2 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04917 | |
| STAT3 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04550 | ||
| Mechanism Description | Cilostazol has been implicated in a number of other basic pathways including the inhibition of adenosine reuptake, the inhibition of multidrug resistance protein 4, among others. Mouse models of myocardial ischemia reperfusion have associated cilostazol with attenuation of multiple inflammatory markers through activation of PPAR gamma, JAK2, and STAT3 pathways | |||
| Disease Class: Coronary artery disease [ICD-11: BA8Z.0] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Coronary artery disease [ICD-11: BA8Z.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cilostazol | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Function | Inhibition |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | JAK2 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04917 | |
| STAT3 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04550 | ||
| Mechanism Description | Cilostazol has been implicated in a number of other basic pathways including the inhibition of adenosine reuptake, the inhibition of multidrug resistance protein 4, among others. Mouse models of myocardial ischemia reperfusion have associated cilostazol with attenuation of multiple inflammatory markers through activation of PPAR gamma, JAK2, and STAT3 pathways | |||
| Disease Class: Cerebral artery disease [ICD-11: 8B26.2] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Cerebral artery disease [ICD-11: 8B26.2] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cilostazol | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Function | Inhibition |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | JAK2 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04917 | |
| STAT3 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04550 | ||
| Mechanism Description | Cilostazol has been implicated in a number of other basic pathways including the inhibition of adenosine reuptake, the inhibition of multidrug resistance protein 4, among others. Mouse models of myocardial ischemia reperfusion have associated cilostazol with attenuation of multiple inflammatory markers through activation of PPAR gamma, JAK2, and STAT3 pathways | |||
| Disease Class: Cerebral artery disease [ICD-11: 8B26.2] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Cerebral artery disease [ICD-11: 8B26.2] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cilostazol | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Function | Inhibition |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | JAK2 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04917 | |
| STAT3 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04550 | ||
| Mechanism Description | Cilostazol has been implicated in a number of other basic pathways including the inhibition of adenosine reuptake, the inhibition of multidrug resistance protein 4, among others. Mouse models of myocardial ischemia reperfusion have associated cilostazol with attenuation of multiple inflammatory markers through activation of PPAR gamma, JAK2, and STAT3 pathways | |||
| Disease Class: Carotid artery disease [ICD-11: 8B10.Y] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Carotid artery disease [ICD-11: 8B10.Y] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cilostazol | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Function | Inhibition |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | JAK2 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04917 | |
| STAT3 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04550 | ||
| Mechanism Description | Cilostazol has been implicated in a number of other basic pathways including the inhibition of adenosine reuptake, the inhibition of multidrug resistance protein 4, among others. Mouse models of myocardial ischemia reperfusion have associated cilostazol with attenuation of multiple inflammatory markers through activation of PPAR gamma, JAK2, and STAT3 pathways | |||
| Disease Class: Carotid artery disease [ICD-11: 8B10.Y] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Carotid artery disease [ICD-11: 8B10.Y] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cilostazol | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Function | Inhibition |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | JAK2 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04917 | |
| STAT3 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04550 | ||
| Mechanism Description | Cilostazol has been implicated in a number of other basic pathways including the inhibition of adenosine reuptake, the inhibition of multidrug resistance protein 4, among others. Mouse models of myocardial ischemia reperfusion have associated cilostazol with attenuation of multiple inflammatory markers through activation of PPAR gamma, JAK2, and STAT3 pathways | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell metastasis | Inhibition | hsa05205 | |
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| HEK293T cells | Kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0063 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Flow cytometry assay; Transwell assay; Scratch assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The combination of downregulation of ABCC4 with overexpression of miR-124-3p significantly increased sensitivity to ADR in MCF-7-ADR cells. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Kawasaki disease [ICD-11: 4A44.5] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Kawasaki disease [ICD-11: 4A44.5] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Intravenous immunoglobulin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | SNP | rs1751034 |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Blood sample | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR | |||
| Mechanism Description | Patients with 3-6 risk genotypes had significantly higher risk of IVIG resistance in KD than those with 0-2 risk genotypes, especially in children aged less than or equal to months and males. This is the first study in which MRP4 gene SNPs were found to be associated with IVIG resistance in KD. | |||
| Disease Class: Kawasaki disease [ICD-11: 4A44.5] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Kawasaki disease [ICD-11: 4A44.5] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Intravenous immunoglobulin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | The homozygous of MRP4 gene rs1751034 C allele is significantly associated with IVIG resistance in KD, especially in patients younger than 5 years old and boys. | |||
| Disease Class: Kawasaki disease [ICD-11: 4A44.5] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Kawasaki disease [ICD-11: 4A44.5] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Intravenous immunoglobulin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | The homozygous of MRP4 gene rs1751034 C allele is significantly associated with IVIG resistance in KD, especially in patients younger than 5 years old and boys. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Pediculosis [ICD-11: 1G00.0] | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pediculosis [ICD-11: 1G00.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Ivermectin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Pediculus humanus | 121225 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Disk diffusion assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Phylogenetic relatedness of P450 and ABC transporter genes over-transcribed following ivermectin exposure.Knockdown of CYP9AG2 P450 and ABCC4 transporter gene expression by RNA interference and subsequent increase in the sensitivity of lice to ivermectin. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Chronic myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A20.0] | [5] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Chronic myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A20.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Ivermectin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | K562/FLM cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_E7CM |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | It was found that ivermectin effectively suppressed the expression of autophagy and transport proteins in K562/FLM cells, reduced the activity of the aforementioned phosphoproteins, and promoted apoptotic cell death. The significant effects of ivermectin might offer a novel therapeutic strategy to overcome flumatinib resistance and optimize the treatment outcomes of CML. | |||
Clinical Trial Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Chronic myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A20.0] | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Chronic myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A20.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Flumatinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | K562/FLM cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_E7CM |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Through cellular experimentation, we explored the resistance mechanisms, which indicated that K562/FLM cells evade flumatinib cytotoxicity by enhancing autophagy, increasing the expression of membrane transport proteins, particularly P-glycoprotein, ABCC1 and ABCC4, as well as enhancing phosphorylation of p-EGFR, p-ERK and p-STAT3 proteins. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 6.84E-05; Fold-change: 8.79E-02; Z-score: 1.77E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 2.71E-03; Fold-change: -4.95E-03; Z-score: -1.73E-02 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
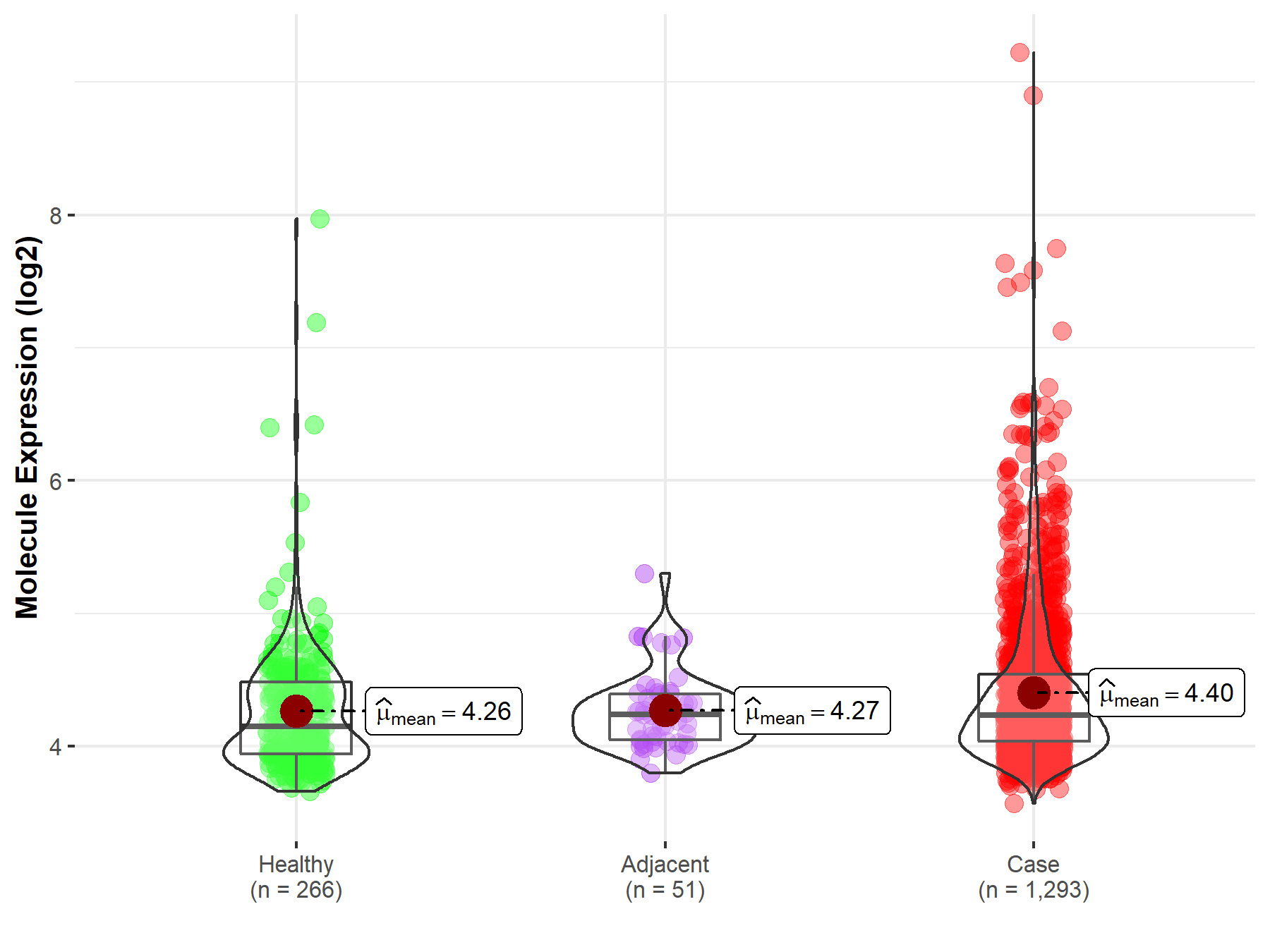
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
ICD Disease Classification 11

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Peripheral blood | |
| The Specified Disease | Coronary artery disease | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 5.62E-01; Fold-change: -1.57E-01; Z-score: -8.51E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
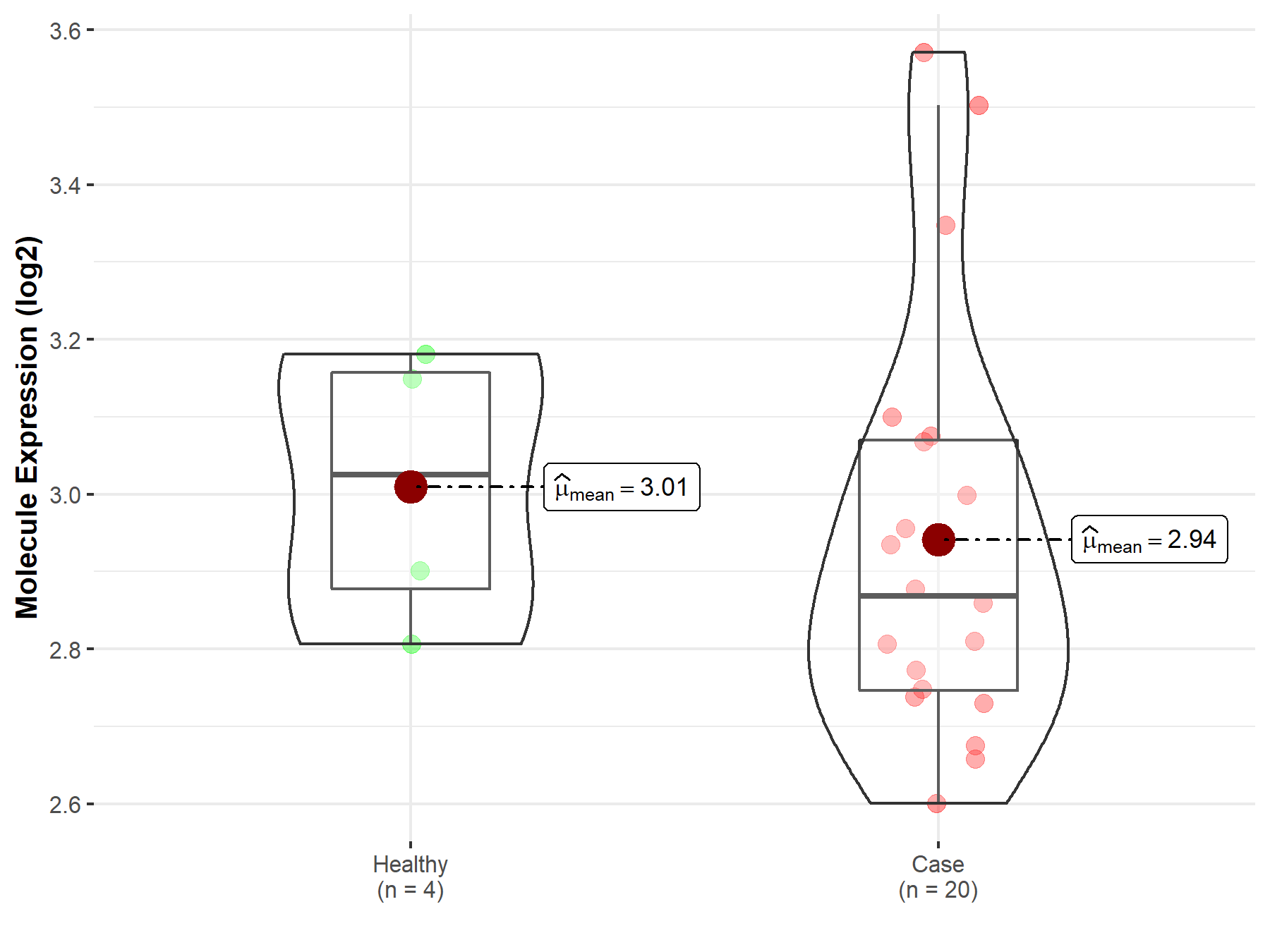
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

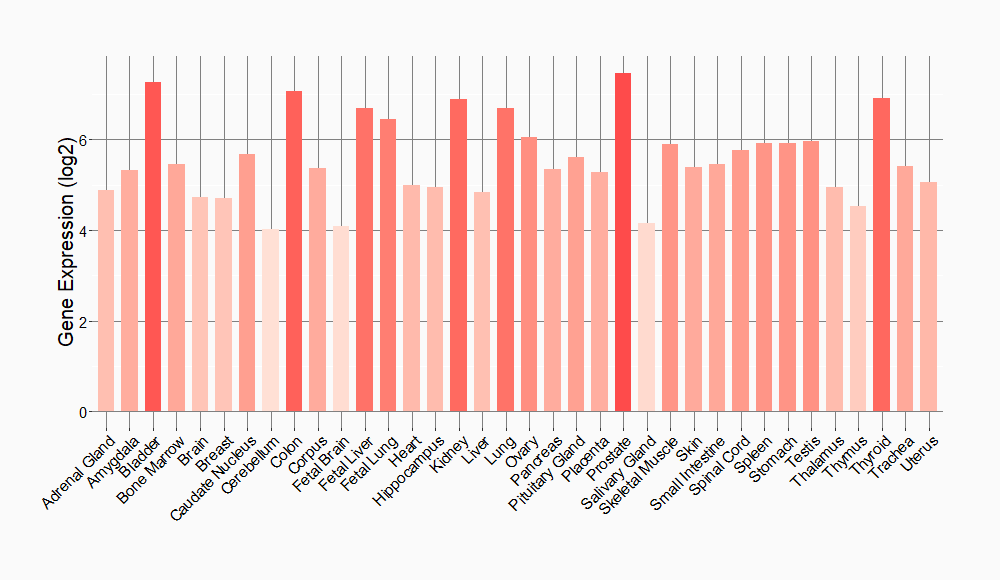
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
