Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00717) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Cilostazol
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Cilostazol; 73963-72-1; Pletal; Cilostazole; Pletaal; OPC-13013; Cilostazolum; Cilostazolum [INN-Latin]; OPC 13013; OPC 21; OPC-21; 6-[4-(1-cyclohexyltetrazol-5-yl)butoxy]-3,4-dihydro-1H-quinolin-2-one; C20H27N5O2; 6-(4-(1-Cyclohexyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)butoxy)-3,4-dihydro-2(1H)-quinolinone; 6-(4-(1-cyclohexyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)butoxy)-3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one; UNII-N7Z035406B; CHEBI:31401; 3,4-Dihydro-6-(4-(1-cyclohexyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)butoxy)-2(1H)-quinolinone; 6-(4-(1-Cyclohexyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)butoxy)-3,4-dihydrocarbostyril; 6-[4-(1-cyclohexyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)butoxy]-3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one; 6-[4-(1-cyclohexyl-1H-1,2,3,4-tetrazol-5-yl)butoxy]-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinolin-2-one; MLS000028470; 6-[4-(1-Cyclohexyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)butoxy]-3,4-dihydro-2(1H)-quinolinone; MFCD00866780; N7Z035406B; NSC-758936; NCGC00015207-07; SMR000058428; DSSTox_CID_25132; DSSTox_RID_80693; DSSTox_GSID_45132; CAS-73963-72-1; Pletal (TN); SR-01000003107; BRN 3632107; Cilostazol,(S); Cilostazol-[d11]; Cilostazol [USAN:USP:INN:BAN:JAN]; Tocris-1692; Opera_ID_488; Spectrum2_001118; Spectrum3_001170; Spectrum4_000772; Spectrum5_001762; Lopac-C-0737; CHEMBL799; C 0737; Lopac0_000218; REGID_for_CID_2754; SCHEMBL16128; BSPBio_002759; KBioGR_001184; MLS000758281; MLS000759507; MLS001076067; MLS002153891; SPECTRUM1505230; SPBio_001256; Cilostazol (JP17/USP/INN); GTPL7148; DTXSID9045132; HSDB 8312; KBio3_002259; BCPP000279; HMS1922N15; HMS2093M14; HMS2096F16; HMS2234C06; HMS3260L17; HMS3268O09; HMS3412B18; HMS3654J13; HMS3676B18; HMS3713F16; Pharmakon1600-01505230; ACT02663; BCP03724; ZINC1552174; Tox21_110098; Tox21_500218; BDBM50225508; CCG-39646; NSC758936; s1294; AKOS015855512; Cilostazol, >=98% (HPLC), powder; OPC 13013; OPC 21; Pletaal; Tox21_110098_1; AC-4334; AM90304; BCP9000530; CS-1759; DB01166; KS-5154; LP00218; MCULE-8893820969; NSC 758936; SDCCGSBI-0050206.P003; 2(1H)-Quinolinone, 3,4-dihydro-6-(4-(1-cyclohexyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)butoxy)-; 2(1H)-Quionlinone, 6-(4-(1-cyclohexyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)butoxy)-3,4-dihydro-; 6-[4-(1-Cyclohexyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)-butoxy]-3,4-dihydro-2(1H)-quinolinone; NCGC00015207-01; NCGC00015207-02; NCGC00015207-03; NCGC00015207-04; NCGC00015207-05; NCGC00015207-06; NCGC00015207-08; NCGC00015207-09; NCGC00015207-10; NCGC00015207-11; NCGC00015207-12; NCGC00015207-25; NCGC00022153-02; NCGC00022153-04; NCGC00022153-05; NCGC00022153-06; NCGC00022153-07; NCGC00260903-01; HY-17464; BCP0726000145; RETAL;PLETAL;OPC 21;PLETAAL;Cilostal; SBI-0050206.P002; EU-0100218; FT-0602474; FT-0645036; FT-0665038; SW199053-2; D01896; F20538; J90029; AB00382988-14; AB00382988_15; AB00382988_16; 963C721; A837982; Q258591; Q-200854; SR-01000003107-2; SR-01000003107-4; SR-01000003107-7; BRD-K67017579-001-04-2; BRD-K67017579-001-05-9; BRD-K67017579-001-07-5; BRD-K67017579-001-13-3; BRD-K67017579-001-17-4; SR-01000003107-10; Cilastatin sodium, Antibiotic for Culture Media Use Only; Cilostazol, United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Reference Standard; 6-[4-(1-cyclohexyl-1,2,3,4-tetrazol-5-yl)butoxy]-3,4-dihydrocarbostyril; 6-[4-(l-cyclohexyl-1,2,3,4-tetrazol-5-yl)butoxyl]-3,4-dihydrocarbostyril; Cilostazol, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material; 2(1H)-Quinolinone, 6-[4-(1-cyclohexyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)butoxy]-3,4-dihydro-; 6-(4-(1-CYCLOHEXYL-1H-TETRAZOL-5-YL)BUTOXY)QUINOLINE-2,3(1H,4H)-DIONE; 6-[4-(1-Cyclohexyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)-butoxy]-3,4-dihydro-1H-quinolin-2-one; 89332-50-3
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
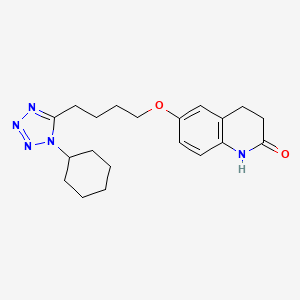
|
||||
| Target | Phosphodiesterase 3 (PDE3) | NOUNIPROTAC | [1] | ||
| Phosphodiesterase 3A (PDE3A) | PDE3A_HUMAN | [1] | |||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C20H27N5O2
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
C1CCC(CC1)N2C(=NN=N2)CCCCOC3=CC4=C(C=C3)NC(=O)CC4
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C20H27N5O2/c26-20-12-9-15-14-17(10-11-18(15)21-20)27-13-5-4-8-19-22-23-24-25(19)16-6-2-1-3-7-16/h10-11,14,16H,1-9,12-13H2,(H,21,26)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
RRGUKTPIGVIEKM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| VARIDT ID | |||||
| INTEDE ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-08: Nervous system diseases
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: ATP-binding cassette sub-family C4 (ABCC4) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Carotid artery disease [ICD-11: 8B10.Y] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Function | Inhibition |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | JAK2 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04917 | |
| STAT3 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04550 | ||
| Mechanism Description | Cilostazol has been implicated in a number of other basic pathways including the inhibition of adenosine reuptake, the inhibition of multidrug resistance protein 4, among others. Mouse models of myocardial ischemia reperfusion have associated cilostazol with attenuation of multiple inflammatory markers through activation of PPAR gamma, JAK2, and STAT3 pathways | |||
| Key Molecule: ATP-binding cassette sub-family C4 (ABCC4) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Carotid artery disease [ICD-11: 8B10.Y] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Function | Inhibition |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | JAK2 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04917 | |
| STAT3 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04550 | ||
| Mechanism Description | Cilostazol has been implicated in a number of other basic pathways including the inhibition of adenosine reuptake, the inhibition of multidrug resistance protein 4, among others. Mouse models of myocardial ischemia reperfusion have associated cilostazol with attenuation of multiple inflammatory markers through activation of PPAR gamma, JAK2, and STAT3 pathways | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Phosphodiesterase III (PDE) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Carotid artery disease [ICD-11: 8B10.Y] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Function | Inhibition |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | JAK2 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04917 | |
| STAT3 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04550 | ||
| Mechanism Description | Cilostazol has been implicated in a number of other basic pathways including the inhibition of adenosine reuptake, the inhibition of multidrug resistance protein 4, among others. Mouse models of myocardial ischemia reperfusion have associated cilostazol with attenuation of multiple inflammatory markers through activation of PPAR gamma, JAK2, and STAT3 pathways | |||
| Key Molecule: Phosphodiesterase III (PDE) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Carotid artery disease [ICD-11: 8B10.Y] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Function | Inhibition |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | JAK2 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04917 | |
| STAT3 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04550 | ||
| Mechanism Description | Cilostazol has been implicated in a number of other basic pathways including the inhibition of adenosine reuptake, the inhibition of multidrug resistance protein 4, among others. Mouse models of myocardial ischemia reperfusion have associated cilostazol with attenuation of multiple inflammatory markers through activation of PPAR gamma, JAK2, and STAT3 pathways | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: ATP-binding cassette sub-family C4 (ABCC4) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Cerebral artery disease [ICD-11: 8B26.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Function | Inhibition |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | JAK2 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04917 | |
| STAT3 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04550 | ||
| Mechanism Description | Cilostazol has been implicated in a number of other basic pathways including the inhibition of adenosine reuptake, the inhibition of multidrug resistance protein 4, among others. Mouse models of myocardial ischemia reperfusion have associated cilostazol with attenuation of multiple inflammatory markers through activation of PPAR gamma, JAK2, and STAT3 pathways | |||
| Key Molecule: ATP-binding cassette sub-family C4 (ABCC4) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Cerebral artery disease [ICD-11: 8B26.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Function | Inhibition |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | JAK2 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04917 | |
| STAT3 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04550 | ||
| Mechanism Description | Cilostazol has been implicated in a number of other basic pathways including the inhibition of adenosine reuptake, the inhibition of multidrug resistance protein 4, among others. Mouse models of myocardial ischemia reperfusion have associated cilostazol with attenuation of multiple inflammatory markers through activation of PPAR gamma, JAK2, and STAT3 pathways | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Phosphodiesterase III (PDE) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Cerebral artery disease [ICD-11: 8B26.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Function | Inhibition |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | JAK2 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04917 | |
| STAT3 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04550 | ||
| Mechanism Description | Cilostazol has been implicated in a number of other basic pathways including the inhibition of adenosine reuptake, the inhibition of multidrug resistance protein 4, among others. Mouse models of myocardial ischemia reperfusion have associated cilostazol with attenuation of multiple inflammatory markers through activation of PPAR gamma, JAK2, and STAT3 pathways | |||
| Key Molecule: Phosphodiesterase III (PDE) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Cerebral artery disease [ICD-11: 8B26.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Function | Inhibition |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | JAK2 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04917 | |
| STAT3 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04550 | ||
| Mechanism Description | Cilostazol has been implicated in a number of other basic pathways including the inhibition of adenosine reuptake, the inhibition of multidrug resistance protein 4, among others. Mouse models of myocardial ischemia reperfusion have associated cilostazol with attenuation of multiple inflammatory markers through activation of PPAR gamma, JAK2, and STAT3 pathways | |||
ICD-11: Circulatory system diseases
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: ATP-binding cassette sub-family C4 (ABCC4) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Coronary artery disease [ICD-11: BA8Z.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Function | Inhibition |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | JAK2 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04917 | |
| STAT3 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04550 | ||
| Mechanism Description | Cilostazol has been implicated in a number of other basic pathways including the inhibition of adenosine reuptake, the inhibition of multidrug resistance protein 4, among others. Mouse models of myocardial ischemia reperfusion have associated cilostazol with attenuation of multiple inflammatory markers through activation of PPAR gamma, JAK2, and STAT3 pathways | |||
| Key Molecule: ATP-binding cassette sub-family C4 (ABCC4) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Coronary artery disease [ICD-11: BA8Z.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Function | Inhibition |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | JAK2 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04917 | |
| STAT3 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04550 | ||
| Mechanism Description | Cilostazol has been implicated in a number of other basic pathways including the inhibition of adenosine reuptake, the inhibition of multidrug resistance protein 4, among others. Mouse models of myocardial ischemia reperfusion have associated cilostazol with attenuation of multiple inflammatory markers through activation of PPAR gamma, JAK2, and STAT3 pathways | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Phosphodiesterase III (PDE) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Coronary artery disease [ICD-11: BA8Z.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Function | Inhibition |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | JAK2 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04917 | |
| STAT3 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04550 | ||
| Mechanism Description | Cilostazol has been implicated in a number of other basic pathways including the inhibition of adenosine reuptake, the inhibition of multidrug resistance protein 4, among others. Mouse models of myocardial ischemia reperfusion have associated cilostazol with attenuation of multiple inflammatory markers through activation of PPAR gamma, JAK2, and STAT3 pathways | |||
| Key Molecule: Phosphodiesterase III (PDE) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Coronary artery disease [ICD-11: BA8Z.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Function | Inhibition |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | JAK2 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04917 | |
| STAT3 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04550 | ||
| Mechanism Description | Cilostazol has been implicated in a number of other basic pathways including the inhibition of adenosine reuptake, the inhibition of multidrug resistance protein 4, among others. Mouse models of myocardial ischemia reperfusion have associated cilostazol with attenuation of multiple inflammatory markers through activation of PPAR gamma, JAK2, and STAT3 pathways | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
