Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00370) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Sisomicin
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Sisomicin; Rickamicin; Sisomycin; 32385-11-8; Sissomicin; Antibiotic 6640; Antibiotic 66-40; Sch 13475; Dehydrogentamicin Cla; Sch-13475; UNII-X55XSL74YQ; X55XSL74YQ; CHEBI:9169; Sisomin; D-Streptamine, O-3-deoxy-4-C-methyl-3-(methylamino)-beta-L-arabinopyranosyl-(1-6)-O-(2,6-diamino-2,3,4,6-tetradeoxy-alpha-D-glycero-hex-4-enopyranosyl-(1-4))-2-deoxy-; Sisomicinum; Sisomicina; Sisomicine; (2R,3R,4R,5R)-2-[(1S,2S,3R,4S,6R)-4,6-diamino-3-[[(2S,3R)-3-amino-6-(aminomethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy]-2-hydroxycyclohexyl]oxy-5-methyl-4-(methylamino)oxane-3,5-diol; Sch 13475 sulfate; Sisomicine [INN-French]; Sisomicinum [INN-Latin]; Salvamina; Sisomicina [INN-Spanish]; Siseptin sulfate; (1S,2S,3R,4S,6R)-4,6-diamino-3-[(2S,3R)-3-amino-6-(aminomethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-pyran-2-yloxy]-2-hydroxycyclohexyl 3-deoxy-4-C-methyl-3-(methylamino)-beta-L-arabinopyranoside; (1s,2s,3r,4s,6r)-4,6-Diamino-3-{[(2s,3r)-3-Amino-6-(Aminomethyl)-3,4-Dihydro-2h-Pyran-2-Yl]oxy}-2-Hydroxycyclohexyl 3-Deoxy-4-C-Methyl-3-(Methylamino)-Beta-L-Arabinopyranoside; (2R,3R,4R,5R)-2-(((1S,2S,3R,4S,6R)-4,6-diamino-3-(((2S,3R)-3-amino-6-(aminomethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)oxy)-2-hydroxycyclohexyl)oxy)-5-methyl-4-(methylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3,5-diol; O-2,6-Diamino-2,3,4,6-tetradeoxy-alpha-D-glycero-hex-4-enopyranosyl-(1-4)-O-(3-deoxy-4-C-methyl-3-(methylamino)-beta-L-arabinopyranosyl-(1-6))-2-deoxy-D-streptamine; C19H37N5O7; EINECS 251-018-2; BRN 1357913; Sisomicin [USAN:INN:BAN]; Sch13475; sisomicin-sulfate; SiS; SISO; Sisomicin (USAN/INN); SCHEMBL49395; O-2,6-Diamino-2,3,4,6-tetradeoxy-alpha-D-glycero-hex-4-enopyranosyl-(1-4)-O-(3-deoxy-4-C-methyl-3-(methylamino)-beta-L-arabinopyranosyl-(1-6)-2-deoxy-D-streptamine; O-3-Deoxy-4-C-methyl-3-(methylamino)-beta-L-arabinopyranosyl-(1-4)-O-(2,6-diamino-2,3,4,6-tetradeoxy-alpha-D-glycero-hex-4-enopyranosyl-(1-6))-2-deoxy-L-streptamine; CHEMBL221886; GTPL10858; ZINC56870809; AKOS015895179; DB12604; (2S-cis)-4-O-(3-Amino-6-(aminomethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)-2-deoxy-6-O-(3-deoxy-4-C-methyl-3-(methylamino)-beta-L-arabinopyranosyl)-D-streptamine; 85S118; C00494; D02544; Q3962119; (2R,3R,4R,5R)-2-[(1S,2S,3R,4S,6R)-4,6-diamino-3-[[(2S,3R)-3-amino-6-(aminomethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy]-2-hydroxy-cyclohexoxy]-5-methyl-4-(methylamino)tetrahydropyran-3,5-diol; (2R,3R,4R,5R)-2-[(1S,2S,3R,4S,6R)-4,6-diamino-3-[[3-amino-6-(aminomethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy]-2-hydroxycyclohexyl]oxy-5-methyl-4-(methylamino)oxane-3,5-diol
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Structure |
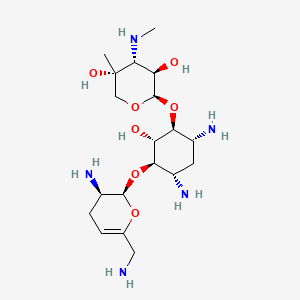
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(7 diseases)
[1]
[2]
[1]
[1]
[1]
[1]
[1]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Discovered by Cell Line Test for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[3]
|
||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C19H37N5O7
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
C[C@@]1(CO[C@@H]([C@@H]([C@H]1NC)O)O[C@H]2[C@@H](C[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]2O)O[C@@H]3[C@@H](CC=C(O3)CN)N)N)N)O
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C19H37N5O7/c1-19(27)7-28-18(13(26)16(19)24-2)31-15-11(23)5-10(22)14(12(15)25)30-17-9(21)4-3-8(6-20)29-17/h3,9-18,24-27H,4-7,20-23H2,1-2H3/t9-,10+,11-,12+,13-,14-,15+,16-,17-,18-,19+/m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
URWAJWIAIPFPJE-YFMIWBNJSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| INTEDE ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: 16S rRNA (guanine(1405)-N(7))-methyltransferase (RMTA) | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Methylation | p.M7G1405 |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) | 469008 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Protein-RNA footprinting assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Isothermal titration calorimetry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Sgm methylates G1405 in 16S rRNA to m7G, thereby rendering the ribosome resistant to 4, 6-disubstituted deoxystreptamine aminoglycosides. | |||
| Key Molecule: 16S rRNA (guanine(1405)-N(7))-methyltransferase (RMTA) | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Intergeneric lateral gene transfer |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Pseudomonas aeruginosa AR-2 | 287 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR screening assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The 16S rRNA methylase gene has undergone intergeneric horizontal gene transfer from some aminoglycoside producing microorganisms to Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which is called rmtA. rmtA protect bacterial 16S rRNA from intrinsic aminoglycosides by methylation. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside N(6')-acetyltransferase type 1 (A6AC1) | [6] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 | 208964 | ||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa Nk0001 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa Nk0002 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa Nk0003 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa Nk0004 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa Nk0005 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa Nk0006 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa Nk0007 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa Nk0008 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa Nk0009 | 287 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Micro-dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Recombinant AAC(6')-Iag protein showed aminoglycoside 6'-N-acetyltransferase activity using thin-layer chromatography (TLC) and MS spectrometric analysis. Escherichia coli carrying aac(6')-Iag showed resistance to amikacin, arbekacin, dibekacin, isepamicin, kanamycin, sisomicin, and tobramycin; but not to gentamicin.AAC(6')-Iag is a functional acetyltransferase that modifies alternate amino groups on the AGs. | |||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside acetyltransferase (AAC) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli DH5alpha | 668369 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR mapping and sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Macrodilution broth method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Aac(3)-Ic gene could contribute to aminoglycoside resistance with a pattern typical of AAC(3)-I enzymes. | |||
| Key Molecule: Gentamicin 3'-acetyltransferase (AACC1) | [7], [8] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli strain BN | 562 | ||
| Escherichia coli strain J62 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain k12 W3110 | 83333 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay; disk diffusion test assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The most common mechanisms of resistance to aminoglycoside-aminocyclitol (AG) antibiotics in bacteria are exerted by enzymatic modification which results in failure of their binding to ribosomal targets and in prevention of uptake by the cell. | |||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside N-acetyltransferase AAC(6')-IAP | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Lactobacillus casei infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | S. maltophilia JUNP350 | N.A. | ||
| Mechanism Description | Compared with vector control,?E. coli?expressing AAC(6')-Iap showed decreased susceptibilities to arbekacin, amikacin, dibekacin, isepamicin, neomycin, netilmicin, sisomicin, and tobramycin. Thin-layer chromatography (TLC) analysis revealed that all the aminoglycosides tested, except for apramycin and paromomycin, were acetylated by AAC(6')-Iap. These results indicated that?aac(6')-Iap?is a functional acetyltransferase that modifies the 6'-NH2?position of aminoglycosides and is involved in aminoglycoside resistance. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Bifunctional AAC/APH (AAC/APH) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gram-negative pathogens infection [ICD-11: 1B74-1G40] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) | 469008 | ||
| Escherichia coli JM83 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
SDS-PAGE assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Aminoglycoside 2"-phosphotransferases are the major aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes in clinical isolates of enterococci and staphylococci.APH(2")-If. This enzyme confers resistance to the 4,6-disubstituted aminoglycosides kanamycin, tobramycin, dibekacin, gentamicin, and sisomicin, but not to arbekacin, amikacin, isepamicin, or netilmicin. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Bifunctional AAC/APH (AAC/APH) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Sepsis [ICD-11: 1G40.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) | 469008 | ||
| Escherichia coli JM83 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
SDS-PAGE assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Aminoglycoside 2"-phosphotransferases are the major aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes in clinical isolates of enterococci and staphylococci.APH(2")-If. This enzyme confers resistance to the 4,6-disubstituted aminoglycosides kanamycin, tobramycin, dibekacin, gentamicin, and sisomicin, but not to arbekacin, amikacin, isepamicin, or netilmicin. | |||
ICD-11: Circulatory system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Bifunctional AAC/APH (AAC/APH) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Infective endocarditis [ICD-11: BB40.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) | 469008 | ||
| Escherichia coli JM83 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
SDS-PAGE assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Aminoglycoside 2"-phosphotransferases are the major aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes in clinical isolates of enterococci and staphylococci.APH(2")-If. This enzyme confers resistance to the 4,6-disubstituted aminoglycosides kanamycin, tobramycin, dibekacin, gentamicin, and sisomicin, but not to arbekacin, amikacin, isepamicin, or netilmicin. | |||
ICD-12: Respiratory system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Bifunctional AAC/APH (AAC/APH) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Respiratory trac infection [ICD-11: CA45.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) | 469008 | ||
| Escherichia coli JM83 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
SDS-PAGE assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Aminoglycoside 2"-phosphotransferases are the major aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes in clinical isolates of enterococci and staphylococci.APH(2")-If. This enzyme confers resistance to the 4,6-disubstituted aminoglycosides kanamycin, tobramycin, dibekacin, gentamicin, and sisomicin, but not to arbekacin, amikacin, isepamicin, or netilmicin. | |||
ICD-13: Digestive system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Bifunctional AAC/APH (AAC/APH) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gram-negative pathogens infection [ICD-11: 1B74-1G40] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) | 469008 | ||
| Escherichia coli JM83 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
SDS-PAGE assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Aminoglycoside 2"-phosphotransferases are the major aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes in clinical isolates of enterococci and staphylococci.APH(2")-If. This enzyme confers resistance to the 4,6-disubstituted aminoglycosides kanamycin, tobramycin, dibekacin, gentamicin, and sisomicin, but not to arbekacin, amikacin, isepamicin, or netilmicin. | |||
ICD-16: Genitourinary system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Bifunctional AAC/APH (AAC/APH) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gram-negative pathogens infection [ICD-11: 1B74-1G40] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) | 469008 | ||
| Escherichia coli JM83 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
SDS-PAGE assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Aminoglycoside 2"-phosphotransferases are the major aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes in clinical isolates of enterococci and staphylococci.APH(2")-If. This enzyme confers resistance to the 4,6-disubstituted aminoglycosides kanamycin, tobramycin, dibekacin, gentamicin, and sisomicin, but not to arbekacin, amikacin, isepamicin, or netilmicin. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
