Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00278) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Itraconazole
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Canadiol; Hyphanox; ITCZ; ITZ; Intraconazole; Itraconazol; Itraconazolum; Itrizole; Oriconazole; Orungal; Prokanazol; Sempera; Spherazole; Sporal; Sporanos; Sporanox; Sporonox; Triasporn; Itraconazol [Spanish]; Itraconazole oral solution; Itraconazolum [Latin]; R 51211; Cis-Itraconazole; Itraconazole & Bovine Lactoferrin; Itraconazole & Nyotran; Itrizole (TN); R-51211; Sporanox (TN); Itraconazole & Nyotran(Liposomal Nystatin); Itraconazole (JAN/USAN); Oriconazole, R51211, Sporanox; Itraconazole [USAN:BAN:INN:JAN]; (+-)-1-sec-Butyl-4-(p-(4-(p-(((2R*,4S*)-2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl)methoxy)phenyl)-1-piperazinyl)phenyl)-delta(sup 2)-1,2,4-triazolin-5-one; (1)-cis-4-(4-(4-(4-((2-(2,4-Dichlorophenyl)-2-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl)methoxy)phenyl)piperazin-1-yl)phenyl)-2,4-dihydro-2-sec-butyl-3H-1,2,4-triazol-3-one; 2-(butan-2-yl)-4-{4-[4-(4-{[(2R,4S)-2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl]methoxy}phenyl)piperazin-1-yl]phenyl}-2,4-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazol-3-one; 2-butan-2-yl-4-[4-[4-[4-[[(2R,4S)-2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl]methoxy]phenyl]piperazin-1-yl]phenyl]-1,2,4-triazol-3-one; 2-butan-2-yl-4-[4-[4-[4-[[(2S,4R)-2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl]methoxy]phenyl]piperazin-1-yl]phenyl]-1,2,4-triazol-3-one; 2-butan-2-yl-4-[4-[4-[4-[[2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl]methoxy]phenyl]piperazin-1-yl]phenyl]-1,2,4-triazol-3-one; 3H-1,2,4-Triazol-3-one, 4-[4-[4-[4-[[2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl]methoxy]phenyl]-1-pipera-zinyl]phenyl]-2,4-dihydro-2-(1-methylpropyl); 4-(4-{4-[4-({[(2R,4S)-2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl]methyl}oxy)phenyl]piperazin-1-yl}phenyl)-2-(1-methylpropyl)-2,4-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazol-3-one
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
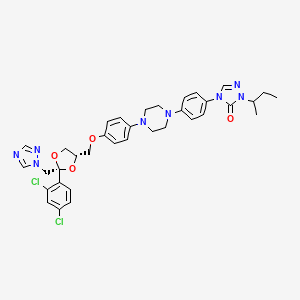
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(3 diseases)
[2]
[3]
[5]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Discovered by Cell Line Test for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[4]
|
||||
| Target | Candida Cytochrome P450 51 (Candi ERG11) | CP51_CANAL | [1] | ||
| Hedgehog signaling pathway (HS pathway) | NOUNIPROTAC | [1] | |||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C35H38Cl2N8O4
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CCC(C)N1C(=O)N(C=N1)C2=CC=C(C=C2)N3CCN(CC3)C4=CC=C(C=C4)OC[C@H]5CO[C@](O5)(CN6C=NC=N6)C7=C(C=C(C=C7)Cl)Cl
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C35H38Cl2N8O4/c1-3-25(2)45-34(46)44(24-40-45)29-7-5-27(6-8-29)41-14-16-42(17-15-41)28-9-11-30(12-10-28)47-19-31-20-48-35(49-31,21-43-23-38-22-39-43)32-13-4-26(36)18-33(32)37/h4-13,18,22-25,31H,3,14-17,19-21H2,1-2H3/t25 ,31-,35-/m0/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
VHVPQPYKVGDNFY-ZPGVKDDISA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: ABC transporter (ABCT) | [6] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Cryptococcal meningitis [ICD-11: 1D01.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Cryptococcus neoformans stiain BPY22.17 | 5207 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Southern hybridization analysis; Northern hybridization analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Rhodamine 6G accumulation assay; M27-A assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Again, disruption of CnAFR1 gene resulted in an increased susceptibility to ketoconazole and itraconazole, suggesting that these antifungal azoles are substrates for CnAfr1p. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Sterol 14-alpha demethylase cyp51A (CYP51A) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Invasive aspergillosis [ICD-11: 1F20.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G54E |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Aspergillus fumigatus strain RIT | 746128 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
NCCLS M38-P microdilution methodology assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Itraconazole resistance has been tightly linked to cyp51A mutations in the codon for Gly54, resulting in five different amino substitutions (G54k, G54V, G54R, G54E, and G54W). | |||
| Key Molecule: Sterol 14-alpha demethylase cyp51A (CYP51A) | [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Aspergillus fumigatus infection [ICD-11: 1F20.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.F46Y+p.M172V+p.N248T+p.D255E |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Aspergillus fumigatus strain | 746128 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
EUCAST broth dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Interestingly, the F46Y/M172V/N248T/D255E/E427k mutation, which has been reported to be associated with azole resistance (37), was detected in one clinical isolate from Shanghai and in one environmental isolate from Xinjiang, respectively. | |||
| Key Molecule: Sterol 14-alpha demethylase cyp51A (CYP51A) | [8] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Aspergillosis [ICD-11: 1F20.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.I266N |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Aspergillus fumigatus strain | 746128 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Amino acid changes in CYP51a may contribute to Aspergillus fumigatus emerging itraconazole resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: Sterol 14-alpha demethylase cyp51A (CYP51A) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Aspergillus fumigatus infection [ICD-11: 1F20.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G54E |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Aspergillus fumigatus strain | 746128 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | A Point Mutation in the 14alpha-Sterol Demethylase Gene cyp51A Contributes to Itraconazole Resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus. | |||
| Key Molecule: Sterol 14-alpha demethylase cyp51A (CYP51A) | [9] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Aspergillus fumigatus infection [ICD-11: 1F20.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G54E+p.I266N |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Aspergillus fumigatus strain | 746128 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Amino acid changes in CYP51a may contribute to Aspergillus fumigatus emerging itraconazole resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: Sterol 14-alpha demethylase cyp51A (CYP51A) | [10] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Aspergillus fumigatus infection [ICD-11: 1F20.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.M220L |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Aspergillus fumigatus strain | 746128 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR amplification and sequence analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
NCCLS method M-27A with broth macrodilution techniques assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Five clinical isolates of Aspergillus fumigatus that exhibited similar patterns of reduced susceptibility to itraconazole and other triazole drugs were analyzed. Sequence analysis of genes (cyp51A and cyp51B) encoding the 14alpha-sterol demethylases revealed that all five strains harbored mutations in cyp51A resulting in the replacement of methionine at residue 220 by valine, lysine, or threonine. When the mutated cyp51A genes were introduced into an A. fumigatus wild-type strain, the transformants exhibited reduced susceptibility to all triazole agents, confirming that the mutations were responsible for the resistance phenotype. | |||
| Key Molecule: Sterol 14-alpha demethylase cyp51A (CYP51A) | [10] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Aspergillus fumigatus infection [ICD-11: 1F20.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.M220V |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Aspergillus fumigatus strain | 746128 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR amplification and sequence analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
NCCLS method M-27A with broth macrodilution techniques assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Five clinical isolates of Aspergillus fumigatus that exhibited similar patterns of reduced susceptibility to itraconazole and other triazole drugs were analyzed. Sequence analysis of genes (cyp51A and cyp51B) encoding the 14alpha-sterol demethylases revealed that all five strains harbored mutations in cyp51A resulting in the replacement of methionine at residue 220 by valine, lysine, or threonine. When the mutated cyp51A genes were introduced into an A. fumigatus wild-type strain, the transformants exhibited reduced susceptibility to all triazole agents, confirming that the mutations were responsible for the resistance phenotype. | |||
| Key Molecule: Sterol 14-alpha demethylase cyp51A (CYP51A) | [10] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Aspergillus fumigatus infection [ICD-11: 1F20.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.M220T |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Aspergillus fumigatus strain | 746128 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR amplification and sequence analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
NCCLS method M-27A with broth macrodilution techniques assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Five clinical isolates of Aspergillus fumigatus that exhibited similar patterns of reduced susceptibility to itraconazole and other triazole drugs were analyzed. Sequence analysis of genes (cyp51A and cyp51B) encoding the 14alpha-sterol demethylases revealed that all five strains harbored mutations in cyp51A resulting in the replacement of methionine at residue 220 by valine, lysine, or threonine. When the mutated cyp51A genes were introduced into an A. fumigatus wild-type strain, the transformants exhibited reduced susceptibility to all triazole agents, confirming that the mutations were responsible for the resistance phenotype. | |||
| Key Molecule: Sterol 14-alpha demethylase cyp51A (CYP51A) | [11] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Aspergillus fumigatus infection [ICD-11: 1F20.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.F219S |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Aspergillus fumigatus strain | 746128 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Multivariate analysis of overall survival or disease-free survival assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Each single mutationad a measurable effect on the affinity of the target enzyme for specific azole derivatives. | |||
| Key Molecule: Sterol 14-alpha demethylase cyp51A (CYP51A) | [11] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Aspergillus fumigatus infection [ICD-11: 1F20.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G138S |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Aspergillus fumigatus strain | 746128 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Multivariate analysis of overall survival or disease-free survival assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Each single mutationad a measurable effect on the affinity of the target enzyme for specific azole derivatives. | |||
| Key Molecule: Sterol 14-alpha demethylase cyp51A (CYP51A) | [11] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Aspergillus fumigatus infection [ICD-11: 1F20.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G138C |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Aspergillus fumigatus strain | 746128 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Multivariate analysis of overall survival or disease-free survival assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Each single mutationad a measurable effect on the affinity of the target enzyme for specific azole derivatives. | |||
| Key Molecule: Sterol 14-alpha demethylase cyp51A (CYP51A) | [12] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Aspergillus fumigatus infection [ICD-11: 1F20.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Tandem repeat | TR53 (GAATCACGCGGTCCGATGTGTGCTGAGCCGAATGAAAGTTGTCTAATGTCTAGAATCACGCGGTCCGATGTGTGCTGAGCCGAATGAAAGTTGTCTAATGTCTA) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Aspergillus fumigatus strain | 746128 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
RT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The azole-resistant A. fumigatus strains were detected tandem repeats (TRs) in the promoter region. | |||
| Key Molecule: Sterol 14-alpha demethylase cyp51A (CYP51A) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Invasive aspergillosis [ICD-11: 1F20.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G54V |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Aspergillus fumigatus strain RIT | 746128 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
NCCLS M38-P microdilution methodology assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Itraconazole resistance has been tightly linked to cyp51A mutations in the codon for Gly54, resulting in five different amino substitutions (G54k, G54V, G54R, G54E, and G54W). | |||
| Key Molecule: Sterol 14-alpha demethylase cyp51A (CYP51A) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Invasive aspergillosis [ICD-11: 1F20.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G54K |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Aspergillus fumigatus strain RIT | 746128 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
NCCLS M38-P microdilution methodology assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The G54k amino acid change conferred cross-resistance to both itraconazole and posaconazole (26). The replacement of the wild-type chromosomal cyp51A allele by mutant allele bearing the G161A nucleotide change in codon 54 led to the acquisition of resistance to itraconazole de novo. | |||
| Key Molecule: Sterol 14-alpha demethylase cyp51A (CYP51A) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Invasive aspergillosis [ICD-11: 1F20.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G161A |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Aspergillus fumigatus strain RIT | 746128 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
NCCLS M38-P microdilution methodology assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The G54k amino acid change conferred cross-resistance to both itraconazole and posaconazole (26). The replacement of the wild-type chromosomal cyp51A allele by mutant allele bearing the G161A nucleotide change in codon 54 led to the acquisition of resistance to itraconazole de novo. | |||
| Key Molecule: Sterol 14-alpha demethylase cyp51A (CYP51A) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Invasive aspergillosis [ICD-11: 1F20.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G54R |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Aspergillus fumigatus strain RIT | 746128 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
NCCLS M38-P microdilution methodology assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The G54k amino acid change conferred cross-resistance to both itraconazole and posaconazole (26). The replacement of the wild-type chromosomal cyp51A allele by mutant allele bearing the G161A nucleotide change in codon 54 led to the acquisition of resistance to itraconazole de novo. | |||
| Key Molecule: Sterol 14-alpha demethylase cyp51A (CYP51A) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Invasive aspergillosis [ICD-11: 1F20.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G54W |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Aspergillus fumigatus strain RIT | 746128 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
NCCLS M38-P microdilution methodology assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Itraconazole resistance has been tightly linked to cyp51A mutations in the codon for Gly54, resulting in five different amino substitutions (G54k, G54V, G54R, G54E, and G54W). | |||
| Key Molecule: Sterol 14-alpha demethylase cyp51A (CYP51A) | [13] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Invasive aspergillosis [ICD-11: 1F20.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.P216L |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Aspergillus fumigatus strain | 746128 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
EUCAST method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Four novel mutations were found (H147Y, P216L, Y431C, and G434C). The isolate bearing the P216L mutation was resistant to itraconazole and posaconazole, whereas the isolates with Y431C and G434C showed pan-azole resistance phenotypes. | |||
| Key Molecule: Sterol 14-alpha demethylase cyp51A (CYP51A) | [13] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Invasive aspergillosis [ICD-11: 1F20.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.H147Y |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Aspergillus fumigatus strain | 746128 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
EUCAST method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Four novel mutations were found (H147Y, P216L, Y431C, and G434C). The isolate bearing the P216L mutation was resistant to itraconazole and posaconazole, whereas the isolates with Y431C and G434C showed pan-azole resistance phenotypes. | |||
| Key Molecule: Sterol 14-alpha demethylase cyp51A (CYP51A) | [13] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Invasive aspergillosis [ICD-11: 1F20.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G434C |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Aspergillus fumigatus strain | 746128 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
EUCAST method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Four novel mutations were found (H147Y, P216L, Y431C, and G434C). The isolate bearing the P216L mutation was resistant to itraconazole and posaconazole, whereas the isolates with Y431C and G434C showed pan-azole resistance phenotypes. | |||
| Key Molecule: Sterol 14-alpha demethylase cyp51A (CYP51A) | [13] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Invasive aspergillosis [ICD-11: 1F20.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y431C |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Aspergillus fumigatus strain | 746128 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
EUCAST method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Four novel mutations were found (H147Y, P216L, Y431C, and G434C). The isolate bearing the P216L mutation was resistant to itraconazole and posaconazole, whereas the isolates with Y431C and G434C showed pan-azole resistance phenotypes. | |||
| Key Molecule: Sterol 14-alpha demethylase cyp51A (CYP51A) | [14] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Invasive aspergillosis [ICD-11: 1F20.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y121F+p.T289A+p.G448S+p.M172I |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Aspergillus fumigatus strain TR463 | 746128 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR analysis | |||
| Mechanism Description | In addition, to compare the susceptibility of TR463 with those of TR34 and TR46, the high resistance of TR463/Y121F/M172I/T289A/G448S was confirmed by MIC testing, displaying a pan-triazole-resistant phenotype to posaconazole, itraconazole, and voriconazole, indicating no in vitro activity of itraconazole and voriconazole (MIC, >16 mg/liter). | |||
| Key Molecule: Sterol 14-alpha demethylase cyp51A (CYP51A) | [15] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Chronic noninvasive aspergillosis [ICD-11: 1F20.4] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.M217I |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Aspergillus terreus strain | 33178 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In vivo emergence of Aspergillus terreus with reduced azole susceptibility which is related to Cyp51a M217I alteration. | |||
| Key Molecule: Sterol 14-alpha demethylase cyp51A (CYP51A) | [16] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Invasive aspergillosis [ICD-11: 1F20.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G138C |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Aspergillus fumigatus strain | 746128 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
EUCAST broth dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Three different cyp51A mutations were found (G138C, Y431C, and G434C), of which the first two were demonstrated by heterologous expression in a hypersusceptible Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain to be at least partly responsible for elevated MICs. | |||
| Key Molecule: Sterol 14-alpha demethylase cyp51A (CYP51A) | [16] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Invasive aspergillosis [ICD-11: 1F20.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y431C |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Aspergillus fumigatus strain | 746128 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
EUCAST broth dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Three different cyp51A mutations were found (G138C, Y431C, and G434C), of which the first two were demonstrated by heterologous expression in a hypersusceptible Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain to be at least partly responsible for elevated MICs. | |||
| Key Molecule: Sterol 14-alpha demethylase cyp51A (CYP51A) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Invasive aspergillosis [ICD-11: 1F20.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G54W |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Aspergillus fumigatus strain | 746128 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
RT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
NCCLS M38-P microdilution methodology assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | A. fumigatus is closely linked to amino acid substitutions in Cyp51A that replace Gly54 | |||
| Key Molecule: Sterol 14-alpha demethylase cyp51A (CYP51A) | [17] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Invasive aspergillosis [ICD-11: 1F20.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L98H |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Aspergillus fumigatus strain | 746128 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | We have determined that a base change causing an amino acid substitution in Cyp51A (L98H) in combination with the duplication in tandem of a 34-bp sequence in the cyp51A promoter, which is responsible for the increased level of cyp51A gene expression, accounted for the resistant phenotype. | |||
| Key Molecule: Sterol 14-alpha demethylase cyp51A (CYP51A) | [18] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pulmonary aspergillosis [ICD-11: 1F20.7] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.M217I |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | Itraconazole acts by inhibiting the fungal cytochrome P-450 dependent enzyme lanosterol 14-alpha-demethylase.The development of itraconazole resistance in A. terreus which may be associated with M217I Cyp51A mutation. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Mitochondrial protoheme IX farnesyltransferase (COX10) | [19] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Aspergillus fumigatus infection [ICD-11: 1F20.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R243Q |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Aspergillus fumigatus strain | 746128 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
NGS sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
HPLC analysis | |||
| Mechanism Description | Through next-generation sequencing (NGS), we successfully identified a new mutation (R243Q substitution) conferring azole resistance in the putative A. fumigatus farnesyltransferase Cox10 (AfCox10) (AFUB_065450). High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analysis verified that the decreased absorption of itraconazole in related Afcox10 mutants is the primary reason for itraconazole resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: CCAAT-binding factor complex subunit (HAPE) | [20] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Invasive aspergillosis [ICD-11: 1F20.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.P88L |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Aspergillus fumigatus strain | 746128 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Growth kinetic assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Discovery of a HapE mutation that causes azole resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus through whole genome sequencing and sexual crossing. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Lanosterol 14-alpha demethylase (ERG11) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Candida albicans infection [ICD-11: 1F23.Y] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y132F+p.Y205E+p.Y257H+p.D116E+p.K143Q |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Candida albicans strain | 5476 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
M27-A2 broth dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | We observed that substitutions A114S, Y132H, Y132F, k143R, Y257H, and a new k143Q substitution contributed to significant increases ( fourfold) in fluconazole and voriconazole resistance; changes in itraconazole resistance were not significant (twofold). | |||
| Key Molecule: Lanosterol 14-alpha demethylase (ERG11) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Candida albicans infection [ICD-11: 1F23.Y] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y132F+p.Y205E+p.V437I+p.D116E+p.K143Q |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Candida albicans strain | 5476 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
M27-A2 broth dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | We observed that substitutions A114S, Y132H, Y132F, k143R, Y257H, and a new k143Q substitution contributed to significant increases ( fourfold) in fluconazole and voriconazole resistance; changes in itraconazole resistance were not significant (twofold). | |||
| Key Molecule: Lanosterol 14-alpha demethylase (ERG11) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Candida albicans infection [ICD-11: 1F23.Y] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.A114S+p.Y205E+p.Y257H+p.V437I |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Candida albicans strain | 5476 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
M27-A2 broth dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | We observed that substitutions A114S, Y132H, Y132F, k143R, Y257H, and a new k143Q substitution contributed to significant increases ( fourfold) in fluconazole and voriconazole resistance; changes in itraconazole resistance were not significant (twofold). | |||
| Key Molecule: Lanosterol 14-alpha demethylase (ERG11) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Candida albicans infection [ICD-11: 1F23.Y] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y205E+p.V437I+p.Y132H+p.G472R |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Candida albicans strain | 5476 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
M27-A2 broth dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | We observed that substitutions A114S, Y132H, Y132F, k143R, Y257H, and a new k143Q substitution contributed to significant increases ( fourfold) in fluconazole and voriconazole resistance; changes in itraconazole resistance were not significant (twofold). | |||
| Key Molecule: Lanosterol 14-alpha demethylase (ERG11) | [21] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Recurrent oropharyngeal candidiasis [ICD-11: 1F23.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y132H |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Candida albicans strain YkkB-13 | 5476 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Gene Sequencing asay; RFLP assay; Immunoblotting assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Disk diffusion assays; Microbroth dilution MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Site-directed mutagenesis of a wild-type CYP51A1 gene was performed to estimate the effect of each of these mutations on resistance to azole derivatives. Each single mutation, with the exception of G129A, had a measurable effect on the affinity of the target enzyme for specific azole derivatives. | |||
| Key Molecule: Lanosterol 14-alpha demethylase (ERG11) | [21] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Recurrent oropharyngeal candidiasis [ICD-11: 1F23.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G464S |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Candida albicans strain YkkB-13 | 5476 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Gene Sequencing asay; RFLP assay; Immunoblotting assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Disk diffusion assays; Microbroth dilution MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Site-directed mutagenesis of a wild-type CYP51A1 gene was performed to estimate the effect of each of these mutations on resistance to azole derivatives. Each single mutation, with the exception of G129A, had a measurable effect on the affinity of the target enzyme for specific azole derivatives. | |||
| Key Molecule: Lanosterol 14-alpha demethylase (ERG11) | [21] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Recurrent oropharyngeal candidiasis [ICD-11: 1F23.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R467K |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Candida albicans strain YkkB-13 | 5476 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Gene Sequencing asay; RFLP assay; Immunoblotting assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Disk diffusion assays; Microbroth dilution MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Site-directed mutagenesis of a wild-type CYP51A1 gene was performed to estimate the effect of each of these mutations on resistance to azole derivatives. Each single mutation, with the exception of G129A, had a measurable effect on the affinity of the target enzyme for specific azole derivatives. | |||
| Key Molecule: Lanosterol 14-alpha demethylase (ERG11) | [21] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Recurrent oropharyngeal candidiasis [ICD-11: 1F23.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S405F+p.Y132H |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Candida albicans strain YkkB-13 | 5476 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Gene Sequencing asay; RFLP assay; Immunoblotting assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Disk diffusion assays; Microbroth dilution MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Site-directed mutagenesis of a wild-type CYP51A1 gene was performed to estimate the effect of each of these mutations on resistance to azole derivatives. Each single mutation, with the exception of G129A, had a measurable effect on the affinity of the target enzyme for specific azole derivatives. | |||
| Key Molecule: Lanosterol 14-alpha demethylase (ERG11) | [21] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Recurrent oropharyngeal candidiasis [ICD-11: 1F23.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G464S+p.Y132H |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Candida albicans strain YkkB-13 | 5476 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Gene Sequencing asay; RFLP assay; Immunoblotting assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Disk diffusion assays; Microbroth dilution MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Site-directed mutagenesis of a wild-type CYP51A1 gene was performed to estimate the effect of each of these mutations on resistance to azole derivatives. Each single mutation, with the exception of G129A, had a measurable effect on the affinity of the target enzyme for specific azole derivatives. | |||
| Key Molecule: Lanosterol 14-alpha demethylase (ERG11) | [21] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Recurrent oropharyngeal candidiasis [ICD-11: 1F23.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G464S+p.R467K |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Candida albicans strain YkkB-13 | 5476 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Gene Sequencing asay; RFLP assay; Immunoblotting assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Disk diffusion assays; Microbroth dilution MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Site-directed mutagenesis of a wild-type CYP51A1 gene was performed to estimate the effect of each of these mutations on resistance to azole derivatives. Each single mutation, with the exception of G129A, had a measurable effect on the affinity of the target enzyme for specific azole derivatives. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Pleiotropic ABC efflux transporter of multiple drugs CDR1 (CDR1) | [22] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Recurrent oropharyngeal candidiasis [ICD-11: 1F23.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Deletion mutation | Deleteion |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Candida albicans strain DSY448 | 5476 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR; Southern blotting analysis; Northern blottling analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Growth differences between the different C. albicans strains assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The delta cdr1 C. albicans mutant DSY448 was hypersusceptible to the azole derivatives fluconazole, itraconazole, and ketoconazole, thus showing that the ABC transporter Cdr1 can use these compounds as substrates. And this could be attributed to a less efficient fluconazole efflux activity because of the absence of the ABC transporter Cdr1 in the delta cdr1 mutant. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Tethering factor for nuclear proteasome STS1 (STS1) | [23] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Recurrent oropharyngeal candidiasis [ICD-11: 1F23.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Deletion mutation | Deleteion |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain | 4932 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qPCR; TEF3 probe assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Microbroth dilution MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The S. cerevisiae sts1 deletion mutant was hypersusceptible to all three azole derivatives used in the study, which is a strong indication that Sts1, a close homolog of Cdr1, is implicated in their transport. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Lanosterol 14-alpha demethylase (ERG11) | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Mycotic vaginitis [ICD-11: 1F2Y.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.P49R+p.E266D+p.T486P+p.V488I |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Candida albicans strain | 5476 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Northern blot analysis; DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Resistance mechanisms that have been identified include overexpression of the MDR1 gene encoding a drug efflux pump, increased expression of the CDR1 and CDR2 genes, overexpression of the ERG11 gene coding for the FLU target enzyme, and alterations in the structure of Erg11p. | |||
| Key Molecule: Lanosterol 14-alpha demethylase (ERG11) | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Mycotic vaginitis [ICD-11: 1F2Y.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y33C |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Candida albicans strain | 5476 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Northern blot analysis; DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Resistance mechanisms that have been identified include overexpression of the MDR1 gene encoding a drug efflux pump, increased expression of the CDR1 and CDR2 genes, overexpression of the ERG11 gene coding for the FLU target enzyme, and alterations in the structure of Erg11p. | |||
| Key Molecule: Lanosterol 14-alpha demethylase (ERG11) | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Mycotic vaginitis [ICD-11: 1F2Y.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y39C |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Candida albicans strain | 5476 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Northern blot analysis; DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Resistance mechanisms that have been identified include overexpression of the MDR1 gene encoding a drug efflux pump, increased expression of the CDR1 and CDR2 genes, overexpression of the ERG11 gene coding for the FLU target enzyme, and alterations in the structure of Erg11p. | |||
| Key Molecule: Lanosterol 14-alpha demethylase (ERG11) | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Mycotic vaginitis [ICD-11: 1F2Y.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.K119L |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Candida albicans strain | 5476 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Northern blot analysis; DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Resistance mechanisms that have been identified include overexpression of the MDR1 gene encoding a drug efflux pump, increased expression of the CDR1 and CDR2 genes, overexpression of the ERG11 gene coding for the FLU target enzyme, and alterations in the structure of Erg11p. | |||
| Key Molecule: Lanosterol 14-alpha demethylase (ERG11) | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Mycotic vaginitis [ICD-11: 1F2Y.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T494A |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Candida albicans strain | 5476 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Northern blot analysis; DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Resistance mechanisms that have been identified include overexpression of the MDR1 gene encoding a drug efflux pump, increased expression of the CDR1 and CDR2 genes, overexpression of the ERG11 gene coding for the FLU target enzyme, and alterations in the structure of Erg11p. | |||
| Key Molecule: Lanosterol 14-alpha demethylase (ERG11) | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Mycotic vaginitis [ICD-11: 1F2Y.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L491V |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Candida albicans strain | 5476 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Northern blot analysis; DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Resistance mechanisms that have been identified include overexpression of the MDR1 gene encoding a drug efflux pump, increased expression of the CDR1 and CDR2 genes, overexpression of the ERG11 gene coding for the FLU target enzyme, and alterations in the structure of Erg11p. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Multidrug resistance protein 1 (ABCB1) | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Mycotic vaginitis [ICD-11: 1F2Y.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Candida albicans strain | 5476 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Northern blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Resistance mechanisms that have been identified include overexpression of the MDR1 gene encoding a drug efflux pump, increased expression of the CDR1 and CDR2 genes, overexpression of the ERG11 gene coding for the FLU target enzyme, and alterations in the structure of Erg11p. | |||
ICD-12: Respiratory system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Lanosterol 14-alpha demethylase (CYP51A1) | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Cystic fibrosis [ICD-11: CA25.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | S. minutisporum | 41687 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Fluorescent reporter assay; GC-MS | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Antifungal susceptibility assay; Membrane fluidity assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | SCFM increases Scedosporium/Lomentospora azole tolerance.Azole resistance is partially due to the efflux pump activity.SCFM leads to decrease in sterol membrane content and increase in membrane fluidity.Scedosporium/Lomentospora species undergo cellular adaptations in SCFM that favours their growth in face of the challenges imposed by azole antifungals. | |||
| Key Molecule: Ergosterol | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Cystic fibrosis [ICD-11: CA25.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | S. minutisporum | 41687 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Fluorescent reporter assay; GC-MS | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Antifungal susceptibility assay; Membrane fluidity assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | SCFM increases Scedosporium/Lomentospora azole tolerance.Azole resistance is partially due to the efflux pump activity.SCFM leads to decrease in sterol membrane content and increase in membrane fluidity.Scedosporium/Lomentospora species undergo cellular adaptations in SCFM that favours their growth in face of the challenges imposed by azole antifungals. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Calcium-transporting ATPase type 2C member 1 | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Cystic fibrosis [ICD-11: CA25.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | S. minutisporum | 41687 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Fluorescent reporter assay; GC-MS | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Antifungal susceptibility assay; Membrane fluidity assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | SCFM increases Scedosporium/Lomentospora azole tolerance.Azole resistance is partially due to the efflux pump activity.SCFM leads to decrease in sterol membrane content and increase in membrane fluidity.Scedosporium/Lomentospora species undergo cellular adaptations in SCFM that favours their growth in face of the challenges imposed by azole antifungals. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
