Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00139) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Cefepime
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Axepim; CFPM; Cefepima; Cefepimum; Cepimax; Cepimex; Maxcef; Maxipime; Cefepima [Spanish]; Cefepimum [Latin]; BMY 28142; Axepim (TN); BMY-28142; Cefepime [USAN:INN]; Cepimax (TN); Cepimex (TN); Maxcef (TN); Maxipime (TN); Cefepime (USAN/INN); (6R,7R)-7-[[(2Z)-2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-2-methoxyiminoacetyl]amino]-3-[(1-methylpyrrolidin-1-ium-1-yl)methyl]-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylate; (6R,7R)-7-{[(2Z)-2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-2-(methoxyimino)acetyl]amino}-3-[(1-methylpyrrolidinium-1-yl)methyl]-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylate; 1-(((6R,7R)-7-(2-(2-Amino-4-thiazolyl)glyoxylamido)-2-carboxy-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo(4.2.0)oct-2-en-3-yl)methyl)-1-methylpyrrolidinium hydroxide, inner salt, 7(sup 2)-(Z)-(O-methyloxime); 7beta-[(2Z)-2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-2-(methoxyimino)acetamido]-3-[(1-methylpyrrolidinium-1-yl)methyl]-3,4-didehydrocepham-4-carboxylate
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
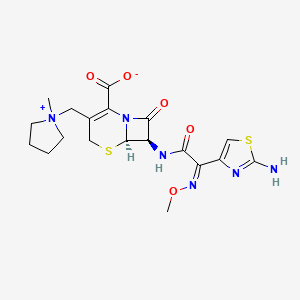
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(6 diseases)
[3]
[3]
[4]
[5]
[6]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Validated by in-vivo Model for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[7]
|
||||
| Target | Bacterial Penicillin binding protein 2 (Bact mrdA) | MRDA_ECOLI | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C19H24N6O5S2
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
C[N+]1(CCCC1)CC2=C(N3[C@@H]([C@@H](C3=O)NC(=O)/C(=N\\OC)/C4=CSC(=N4)N)SC2)C(=O)[O-]
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C19H24N6O5S2/c1-25(5-3-4-6-25)7-10-8-31-17-13(16(27)24(17)14(10)18(28)29)22-15(26)12(23-30-2)11-9-32-19(20)21-11/h9,13,17H,3-8H2,1-2H3,(H3-,20,21,22,26,28,29)/b23-12-/t13-,17-/m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
HVFLCNVBZFFHBT-ZKDACBOMSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| VARIDT ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Beta-lactamase (BLA) | [8] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli DH10B | 316385 | ||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa PU21 | 287 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain k-12 C600 | 83333 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa 104116 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa SOF-1 | 287 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Southern technique assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution technique assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolate SOF-1 was resistant to cefepime and susceptible to ceftazidime. This resistance phenotype was explained by the expression of OXA-31, which shared 98% amino acid identity with a class D beta-lactamase, OXA-1. The oxa-31 gene was located on a ca. 300-kb nonconjugative plasmid and on a class 1 integron. No additional efflux mechanism for cefepime was detected in P. aeruginosa SOF-1. Resistance to cefepime and susceptibility to ceftazidime in P. aeruginosa were conferred by OXA-1 as well. | |||
| Key Molecule: Metallo-beta-lactamase (VIM1) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Achromobacter xylosoxydans infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli | 668369 | ||
| Achromobacter xylosoxydans subsp. denitrificans AX-22 | 85698 | |||
| Escherichia coli MkD-135 | 562 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa 10145/3 | 287 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA extraction and Sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Macrodilution broth method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | A. xylosoxydans AX22 exhibited broad-spectrum resistance to Beta-lactams and aminoglycosides. The Beta-lactam resistance pattern (including piperacillin, ceftazidime, and carbapenem resistance) was unusual for this species, and the high-level carbapenem resistance suggested the production of an acquired carbapenemase. In fact, carbapenemase activity was detected in a crude extract of AX22 (specific activity, 184 +/- 12 U/mg of protein), and this activity was reduced (>80%) after incubation of the crude extract with 2 mM EDTA, suggesting the presence of a metallo-Beta-lactamase determinant. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Pyruvate decarboxylase 5 (PDC5) | [6], [9] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R79Q+p.T105A |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli TOP10 | 83333 | ||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 | 208964 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa 12B | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa kG2505 | 287 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay; Etest method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Reduced susceptibility to imipenem, ceftazidime, and cefepime was observed only with recombinant P. aeruginosa strains expressing an AmpC Beta-lactamase that had an alanine residue at position 105.Recently, several ESACs have been described from Escherichia coli contributing to reduced susceptibility to imipenem. | |||
| Key Molecule: Pyruvate decarboxylase 3 (PDC3) | [6], [9] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T97A |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli TOP10 | 83333 | ||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 | 208964 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa 12B | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa kG2505 | 287 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay; Etest method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Reduced susceptibility to imipenem, ceftazidime, and cefepime was observed only with recombinant P. aeruginosa strains expressing an AmpC Beta-lactamase that had an alanine residue at position 105.Recently, several ESACs have been described from Escherichia coli contributing to reduced susceptibility to imipenem. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Metallo-beta-lactamase (VIM1) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Escherichia coli infection [ICD-11: 1A03.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Acquired |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli | 668369 | ||
| Achromobacter xylosoxydans subsp. denitrificans AX-22 | 85698 | |||
| Escherichia coli MkD-135 | 562 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa 10145/3 | 287 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA extraction and Sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Macrodilution broth method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Electroporation of Escherichia coli DH5alpha with the purified plasmid preparation yielded ampicillin-resistant transformants which contained a plasmid apparently identical to pAX22 (data not shown). DH5alpha(pAX22) produced carbapenemase activity (specific activity of crude extract, 202 +/- 14 U/mg of protein) and, compared to DH5alpha, exhibited a decreased susceptibility to several Beta-lactams. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Outer membrane porin F (OMPF) | [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Escherichia coli infection [ICD-11: 1A03.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G119D |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Enterobacter cloacae strain 201-RevM3 | 550 | ||
| Escherichia coli strain Ak101 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain BZB1107 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain DH5alpha mutS | 668369 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
SDS-PAGE assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Twofold dilutions assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Substitutions G119D and G119E, inserting a protruding acidic side chain into the pore, decreased cephalosporin and colicin susceptibilities. Cefepime diffusion was drastically altered by these mutations. Conversely, substitutions R132A and R132D, changing a residue located in the positively charged cluster, increased the rate of cephalosporin uptake without modifying colicin sensitivity. Modelling approaches suggest that G119E generates a transverse hydrogen bond dividing the pore, while the two R132 substitutions stretch the channel size. | |||
| Key Molecule: Outer membrane porin F (OMPF) | [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Escherichia coli infection [ICD-11: 1A03.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G119E |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Enterobacter cloacae strain 201-RevM3 | 550 | ||
| Escherichia coli strain Ak101 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain BZB1107 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain DH5alpha mutS | 668369 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
SDS-PAGE assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Twofold dilutions assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Substitutions G119D and G119E, inserting a protruding acidic side chain into the pore, decreased cephalosporin and colicin susceptibilities. Cefepime diffusion was drastically altered by these mutations. Conversely, substitutions R132A and R132D, changing a residue located in the positively charged cluster, increased the rate of cephalosporin uptake without modifying colicin sensitivity. Modelling approaches suggest that G119E generates a transverse hydrogen bond dividing the pore, while the two R132 substitutions stretch the channel size. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Beta-lactamase (BLA) | [6] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G27D+p.A97V+p.V205L |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 | 208964 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR amplification and sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Amino acid changes G27D, A97V, and V205L in PDC-2 led to increased cefepime MICs. | |||
| Key Molecule: Beta-lactamase (BLA) | [6] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.K108E |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Pseudomonas aeruginosa kG2505 | 287 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR amplification and sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Amino acid changes K108E in PDC-4 led to increased cefepime MICs. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: OXA-23 carbapenemase (BLA OXA-23) | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Cutaneous bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1B21.4] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Acinetobacter baumannii isolates | 470 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay; Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The isolate was resistant to antibiotics other than ampicillin-sulbactam and colistin, suggesting drug resistance due to carbapenemase production by OXA-23.carbapenem resistance in the isolated carbapenem-resistant A. baumannii strain was at least partially conferred by bla OXA-23-like carbapenemase. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Outer membrane porin (OMP38) | [1], [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Melioidosis [ICD-11: 1C42.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli | 668369 | ||
| Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) | 469008 | |||
| Burkholderia pseudomallei isolates | 28450 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Bps is highly resistant to many antimicrobial agents and this resistance may result from the low drug permeability of outer membrane proteins, known as porins.An Escherichia coli strain defective in most porins, but expressing BpsOmp38, exhibited considerably lower antimicrobial susceptibility than the control strain. In addition, mutation of Tyr119, the most prominent pore-lining residue in BpsOmp38, markedly altered membrane permeability, substitution with Ala (mutant BpsOmp38Y119A) enhanced uptake of the antimicrobial agents, while substitution with Phe (mutant BpsOmp38Y119F) inhibited uptake. | |||
ICD-12: Respiratory system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Bcr/CflA family efflux transporter (BCML) | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Klebsiella pneumoniae infection [ICD-11: CA40.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli DH10B | 316385 | ||
| Escherichia coli strain NCTC 50192 | 562 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strain ORI-1 | 573 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR and hybridization experiments assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution technique assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Klebsiella pneumoniae ORI-1 strain harbored a ca. 140-kb nontransferable plasmid, pTk1, that conferred an extended-spectrum cephalosporin resistance profile antagonized by the addition of clavulanic acid, tazobactam, or imipenem. The gene for GES-1 (Guiana extended-spectrum beta-lactamase) was cloned, and its protein was expressed in Escherichia coli DH10B, where this pI-5. 8 beta-lactamase of a ca. 31-kDa molecular mass conferred resistance to oxyimino cephalosporins (mostly to ceftazidime). GES-1 is weakly related to the other plasmid-located Ambler class A extended-spectrum beta-lactamases (ESBLs). | |||
| Key Molecule: Bcr/CflA family efflux transporter (BCML) | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Klebsiella pneumoniae infection [ICD-11: CA40.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Acquired |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli DH10B | 316385 | ||
| Escherichia coli strain NCTC 50192 | 562 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strain ORI-1 | 573 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR and hybridization experiments assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution technique assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Beta-Lactam MICs for k. pneumoniae ORI-1 and Escherichia coli DH10B harboring either the natural plasmid pTk1 or the recombinant plasmid pC1 were somewhat similar and might indicate the presence of an ESBL. In all cases, the ceftazidime MICs were higher than those of cefotaxime and aztreonam. Beta-Lactam MICs were always lowered by the addition of clavulanic acid or tazobactam, less so by sulbactam, and uncommonly by imipenem. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Bcr/CflA family efflux transporter (BCML) | [5] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Klebsiella pneumoniae infection [ICD-11: CA40.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Antagonism |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli DH10B | 316385 | ||
| Escherichia coli strain NCTC 50192 | 562 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strain ORI-1 | 573 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR and hybridization experiments assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution technique assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Inhibition studies, as measured by IC50 values with benzylpenicillin as the substrate, showed that GES-1 was inhibited by clavulanic acid (5 uM) and tazobactam (2.5 uM) and strongly inhibited by imipenem (0.1 uM). Beta-Lactam MICs were always lowered by the addition of clavulanic acid or tazobactam, less so by sulbactam, and uncommonly by imipenem. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
