Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG01184) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Thiacetazone
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Thiacetazone; Thioacetazone; AMITHIOZONE; Ambathizon; Benzothiozane; Conteben; Benzothiozon; Thiocarbazil; Benthiozone; Thioparamizone; Parazone; Thioacetazon; Thibone; Tibon; Tubin; Siocarbazone; Tebethione; Thiacetone; Thiacetozone; Thioazetazone; Thioparamizon; Thiotebesin; Thiotebezin; Thiotebicina; Tiacetazon; Tioacetazon; Tioatsetazon; Tubercazon; Aktivan; Amitiozon; Berkazon; Domakol; Livazone; Mivizon; Myvizone; Neotibil; Neustab; Novakol; Panrone; Seroden; Tebalon; Tebecure; Tebemar; Tebethion; Tebezon; Thiomicid; Thionicid; Thizone; Tibicur; Tibizan; Tiobicina; Tiocarone; Tiosecolo; Tubigal; Antib; Diasan; Ilbion; Thibon; Tibone; Berculon A; Tebesone I; 104-06-3; Nuclon argentinian; Thiosemicarbarzone; TB I (Bayer); 4-Acetylaminobenzaldehyde thiosemicarbazone; TB I; Thiosemicarbazone; Domagk's T.B.1 conteben; Thioacetazonum; Tibione; 4'-Formylacetanilide thiosemicarbazone; Sdt 1041; Magk's T.B.1 conteben; Tb I/698; p-Acetaminobenzylidenethiosemicarbazone; Tibion; CBC 903150; p-Formylacetanilide-3-thiosemicarbazone; SQ 2321; p-Acetamidobenzaldehyde thiosemicarbazone; p-Acetoaminobenzaldehyde thiosemicarbazone; UNII-MMG78X7SSR; A 4081; 4207 RP; RP 4207; Acetamide, N-[4-[[(aminothioxomethyl)hydrazono]methyl]phenyl]-; p-Acetylaminobenzadehyde thiosemicarbazone; MMG78X7SSR; Acetamide, N-(4-(((aminothioxomethyl)hydrazono)methyl)phenyl)-; NSC3550; Acetanilide, 4'-formyl-, 4'-(thiosemicarbazone); NSC-3550; p-Acetamidobenzaldehyde thiosemicarbazon; NCGC00159389-02; NCGC00159389-03; NCGC00159389-04; p-Acetylaminobenzaldehyde thiosemicarbazone; DSSTox_CID_2593; DSSTox_RID_76650; DSSTox_GSID_22593; N-(4-((2-Carbamothioylhydrazono)methyl)phenyl)acetamide; Mirizone neustab; Tioacetazona; Thioacetazone [INN:BAN]; Thioacetazonum [INN-Latin]; Tioacetazona [INN-Spanish]; CAS-104-06-3; Tb I-698; Thiosemicarbazone (pharmaceutical); NSC 3550; EINECS 203-170-6; BRN 2810335; N-[4-[(E)-(carbamothioylhydrazono)methyl]phenyl]acetamide; N-{4-[(E)-(Carbamothioylhydrazono)methyl]phenyl}acetamide; Citazone; Acetamide, N-(4-(((aminothiomethyl)hydrazono)methylene)phenyl)-; Acetamide, N-[4-[[(aminothiomethyl)hydrazono]methylene]phenyl]-; AI3-18591; 4207RP; Citazone (TN); Acetanilide, 4'-formyl-, thiosemicarbazone; Thioacetazone (INN); SCHEMBL42515; Acetanilide, thiosemicarbazone; WLN: SUYZMNU1R DMV1; 4-14-00-00075 (Beilstein Handbook Reference); N-(4-([2-(Aminocarbothioyl)hydrazono]methyl)phenyl)acetamide; N-[4-[(E)-(carbamothioylhydrazinylidene)methyl]phenyl]acetamide; Acetamide, N1-(4-([2-(aminocarbothioyl)hydrazono]methyl)phenyl); CHEMBL375492; TB-1; Acetamide, N-[4-[[2-(aminothioxomethyl)hydrazinylidene]methyl]phenyl]-; DTXSID80859179; EX-A101; CHEBI:134958; HY-B1526; Tox21_111625; Tox21_111626; Acetanilide, 4'-(thiosemicarbazone); BDBM50247903; MFCD00022157; N-{4-[(E)-(2-carbamothioylhydrazinylidene)methyl]phenyl}acetamide; RP4207; SQ2321; STL503688; ZINC32709513; AKOS000304458; Tox21_111625_1; DB12829; SQ-2321; 4-Acetamidobenzaldehyde thiosemicarbazone; AS-71466; CS-0013329; D08584; A800888; SR-01000872620; SR-01000872620-2; N-{4-[(E)-[(carbamothioylamino)imino]methyl]phenyl}acetamide; N-(4-{(E)-[(aminocarbonothioyl)hydrazono]methyl}phenyl)acetamide; 910379-02-1; N-[4-[(2-Carbamothioylhydrazono)methyl]phenyl]acetamide;N-[4-[(E)-(carbamothioylhydrazono)methyl]phenyl]acetamide
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
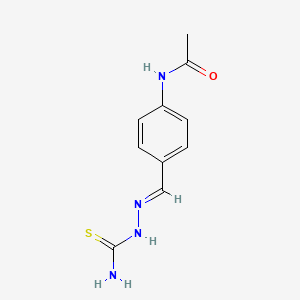
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Validated by in-vivo Model for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[1]
|
||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C10H12N4OS
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CC(=O)NC1=CC=C(C=C1)/C=N/NC(=S)N
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C10H12N4OS/c1-7(15)13-9-4-2-8(3-5-9)6-12-14-10(11)16/h2-6H,1H3,(H,13,15)(H3,11,14,16)/b12-6+
|
||||
| InChIKey |
SRVJKTDHMYAMHA-WUXMJOGZSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| INTEDE ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: FAD-containing monooxygenase EthA (ETHA) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Mycobacterium abscessus infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Mycobacterium abscessus strain CIP104536T | 36809 | ||
| Mycobacterium bolletii strain CIP108541T | 319705 | |||
| Mycobacterium massiliense strain CIP108297T | 319705 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-genome sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Microdilution method | |||
| Mechanism Description | TAC, like ethionamide, requires activation by the flavin-containing monooxygenase EthA. EthR, whose gene is adjacent to ethA in M. tuberculosis and in M. smegmatis, represses the transcription of ethA, subsequently preventing the conversion of the prodrugs to active molecules. EthR belongs to the TetR/CamR family of transcriptional regulators that negatively regulates the expression of EthA. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Siderophore exporter (MMPL5) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Mycobacterium abscessus infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Mycobacterium abscessus strain CIP104536T | 36809 | ||
| Mycobacterium bolletii strain CIP108541T | 319705 | |||
| Mycobacterium massiliense strain CIP108297T | 319705 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-genome sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Microdilution method | |||
| Mechanism Description | Importantly, mutations in the transcriptional TetR repressor MAB_4384, with concomitant upregulation of the divergently oriented adjacent genes encoding an MmpS5/MmpL5 efflux pump system, accounted for high cross-resistance levels among all three compounds. | |||
| Key Molecule: Siderophore export accessory protein MmpS5 (mmpS5) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Mycobacterium abscessus infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Mycobacterium abscessus strain CIP104536T | 36809 | ||
| Mycobacterium bolletii strain CIP108541T | 319705 | |||
| Mycobacterium massiliense strain CIP108297T | 319705 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-genome sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Microdilution method | |||
| Mechanism Description | Importantly, mutations in the transcriptional TetR repressor MAB_4384, with concomitant upregulation of the divergently oriented adjacent genes encoding an MmpS5/MmpL5 efflux pump system, accounted for high cross-resistance levels among all three compounds. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
