Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00521)
| Name |
Myeloid differentiation primary response protein MyD88 (MYD88)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
MYD88
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr3:38138478-38143022[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MAAGGPGAGSAAPVSSTSSLPLAALNMRVRRRLSLFLNVRTQVAADWTALAEEMDFEYLE
IRQLETQADPTGRLLDAWQGRPGASVGRLLELLTKLGRDDVLLELGPSIEEDCQKYILKQ QQEEAEKPLQVAAVDSSVPRTAELAGITTLDDPLGHMPERFDAFICYCPSDIQFVQEMIR QLEQTNYRLKLCVSDRDVLPGTCVWSIASELIEKRCRRMVVVVSDDYLQSKECDFQTKFA LSLSPGAHQKRLIPIKYKAMKKEFPSILRFITVCDYTNPCTKSWFWTRLAKALSLP Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Adapter protein involved in the Toll-like receptor and IL-1 receptor signaling pathway in the innate immune response. Acts via IRAK1, IRAK2, IRF7 and TRAF6, leading to NF-kappa-B activation, cytokine secretion and the inflammatory response. Increases IL-8 transcription. Involved in IL-18-mediated signaling pathway. Activates IRF1 resulting in its rapid migration into the nucleus to mediate an efficient induction of IFN-beta, NOS2/INOS, and IL12A genes. Upon TLR8 activation by GU-rich single-stranded RNA (GU-rich RNA) derived from viruses such as SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV and HIV-1, induces IL1B release through NLRP3 inflammasome activation. MyD88-mediated signaling in intestinal epithelial cells is crucial for maintenance of gut homeostasis and controls the expression of the antimicrobial lectin REG3G in the small intestine.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
3 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Trastuzumab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 7.03E-96 Fold-change: 9.23E-02 Z-score: 2.61E+01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| NF-kappaB signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04064 | ||
| In Vitro Model | SkBR3 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0033 |
| BT474 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0179 | |
| In Vivo Model | BALB/c nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; TUNEL assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | AGAP2-AS1 could promote breast cancer growth and trastuzumab resistance by activating the NF-kB signaling pathway and upregulating MyD88 expression. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Paclitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Ovarian cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Ovarian tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 9.74E-04 Fold-change: 1.06E-01 Z-score: 4.97E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| TLR/MyD88 signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | A2780 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0134 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Transwell assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In the present study, flow cytometric assays were used to detect the apoptosis of A2780 cells after down-regulation of miRNA-149. We found that down-regulation of miRNA-149 decreased the apoptosis induced by paclitaxel when compared to the control group. Furthermore, we showed that down-regulation of miRNA-149 in A2780 cells (+) the expression of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 and inhibited the expression of the pro-apoptotic protein bax, which may have led to paclitaxel resistance. | |||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Paclitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell viability | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| SkBR3 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0033 | |
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SRB assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-155-3p acts as a tumor suppressor and reverses paclitaxel resistance via negative regulation of MYD88 in human breast cancer. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A81.0] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A81.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Ibrutinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L265P |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | Furthermore, within ABC DLBCL, responses were significantly different depending on the specific genetic lesions. Ibrutinib-resistant tumours carry mutant MYD88 and WT CD79A/B whereas all other genotypic combinations (CD79A/BWT + MYD88WT, CD79A/Bmutant + MYD88WT and CD79A/Bmutant + MYD88mutant) were responsive to ibrutinib therapy. It is foreseeable why ibrutinib therapy is less effective in MYD88-mutated ABC-DLBCL patients because MYD88 activates NFkappa-B through a parallel pathway independent of BTK. However, it is unclear why MYD88 mutations alone are associated with ibrutinib resistance whereas the MYD88 mutations in conjunction with CD79A/B mutations appears to render ABC DLBCL ibrutinib-sensitive. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia [ICD-11: 2A85.4] | [3] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia [ICD-11: 2A85.4] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Ibrutinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | p.L265P |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | The mutant, as opposed to MYD88WT, preferentially binds to p-BTK and subsequently activates NFKB. Ibrutinib treatment reduces such binding, therefore blocking downstream NFKB activation. Thus, the oncogenic activity of MYD88L265P is mediated through BTK in WM and renders cells sensitive to ibrutinib's inhibition. The fact that MYD88 mutations function differently in different cells highlight the notion that impact of a particular genetic mutation has to be determined and understood within the particular cellular context. | |||
Preclinical Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Mantle cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A85.0] | [5] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Mantle cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A85.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | IMG-2005-5 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L265P (c.794T>C) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Blood | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.L265P (c.794T>C) in gene MYD88 cause the sensitivity of IMG-2005-5 by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | |||
Investigative Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Mantle cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A85.0] | [5] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Mantle cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A85.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | IRAK-1 or IRAK-4 inhibitors | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L265P (c.794T>C) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Blood | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.L265P (c.794T>C) in gene MYD88 cause the sensitivity of IRAK-1 or IRAK-4 inhibitors by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 7.03E-96; Fold-change: 6.31E-01; Z-score: 1.88E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 1.15E-06; Fold-change: 3.87E-01; Z-score: 7.66E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
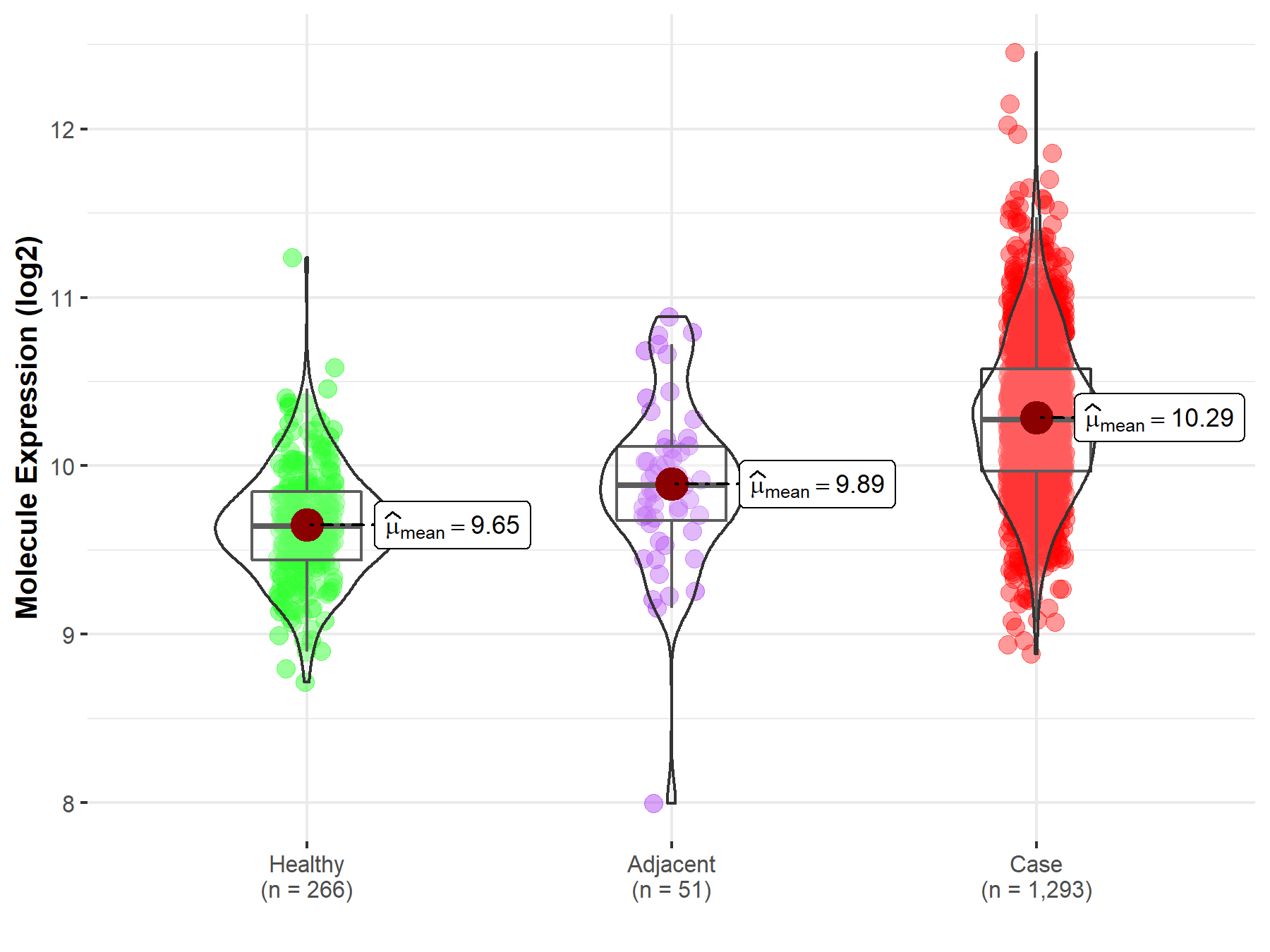
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Ovary | |
| The Specified Disease | Ovarian cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 9.74E-04; Fold-change: 6.98E-01; Z-score: 1.69E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 3.20E-01; Fold-change: 9.55E-02; Z-score: 2.41E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
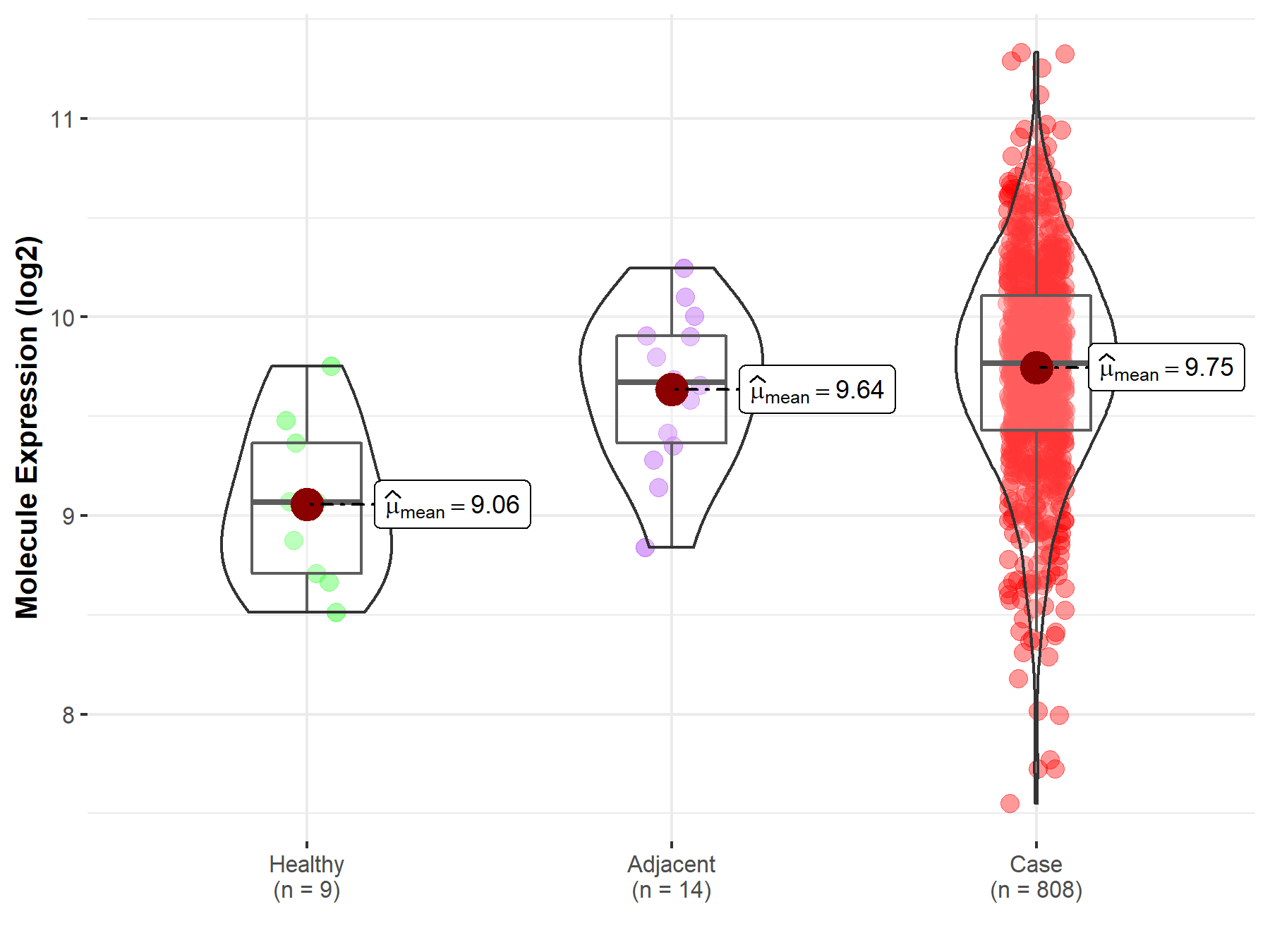
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

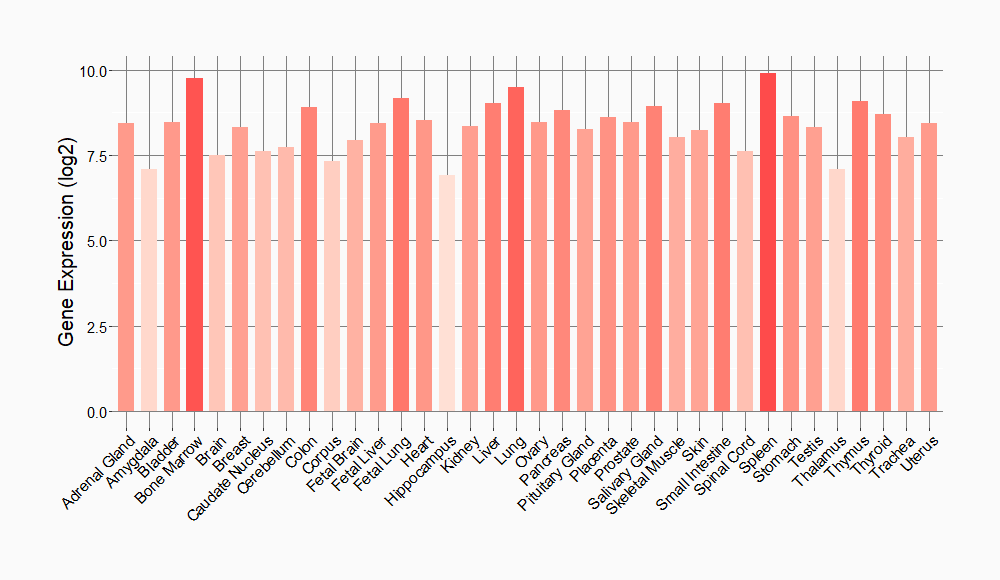
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
