Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00130) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Ibrutinib
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
PCI-32765; Ibrutinib (BTK inhibitor)
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 6 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
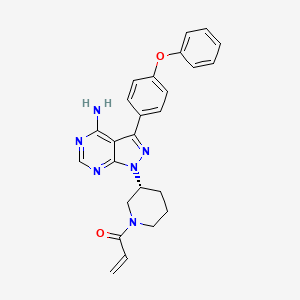
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(2 diseases)
[2]
[3]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Discovered by Cell Line Test for This Drug
(3 diseases)
[4]
[4]
[5]
|
||||
| Target | Tyrosine-protein kinase BTK (ATK) | BTK_HUMAN | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C25H24N6O2
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
C=CC(=O)N1CCC[C@H](C1)N2C3=NC=NC(=C3C(=N2)C4=CC=C(C=C4)OC5=CC=CC=C5)N
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C25H24N6O2/c1-2-21(32)30-14-6-7-18(15-30)31-25-22(24(26)27-16-28-25)23(29-31)17-10-12-20(13-11-17)33-19-8-4-3-5-9-19/h2-5,8-13,16,18H,1,6-7,14-15H2,(H2,26,27,28)/t18-/m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
XYFPWWZEPKGCCK-GOSISDBHSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| VARIDT ID | |||||
| INTEDE ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Tumor protein p53 (TP53) | [6] | |||
| Metabolic Type | Redox metabolism | |||
| Resistant Disease | Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A81.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | CD40L cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Jeko-1 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1865 | |
| Mino cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_UW35 | |
| OCI-LY10 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_8795 | |
| OCI-LY18 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1880 | |
| OCI-LY19 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1878 | |
| OCI-LY3 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_8800 | |
| SUDHL10 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1889 | |
| SUDHL4 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0539 | |
| SUDHL6 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2206 | |
| U-2932 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1896 | |
| Val cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1819 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell viability assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Treatment with AZD5991 restricted growth of DLBCL cells independent of cell of origin and overcame ibrutinib resistance in MCL cells. Mcl-1 inhibition led to mitochondrial dysfunction as manifested by mitochondrial membrane depolarization, decreased mitochondrial mass, and induction of mitophagy. This was accompanied by impairment of oxidative phosphorylation. TP53 and BAX were essential for sensitivity to Mcl-1, and oxidative phosphorylation was implicated in resistance to Mcl-1 inhibition. | |||
| Key Molecule: BCL2 associated X protein (BAX) | [6] | |||
| Metabolic Type | Redox metabolism | |||
| Resistant Disease | Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A81.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | CD40L cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Jeko-1 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1865 | |
| Mino cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_UW35 | |
| OCI-LY10 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_8795 | |
| OCI-LY18 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1880 | |
| OCI-LY19 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1878 | |
| OCI-LY3 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_8800 | |
| SUDHL10 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1889 | |
| SUDHL4 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0539 | |
| SUDHL6 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2206 | |
| U-2932 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1896 | |
| Val cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1819 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell viability assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Treatment with AZD5991 restricted growth of DLBCL cells independent of cell of origin and overcame ibrutinib resistance in MCL cells. Mcl-1 inhibition led to mitochondrial dysfunction as manifested by mitochondrial membrane depolarization, decreased mitochondrial mass, and induction of mitophagy. This was accompanied by impairment of oxidative phosphorylation. TP53 and BAX were essential for sensitivity to Mcl-1, and oxidative phosphorylation was implicated in resistance to Mcl-1 inhibition. | |||
| Key Molecule: Myeloid cell leukemia 1 (Mcl-1) | [6] | |||
| Metabolic Type | Redox metabolism | |||
| Resistant Disease | Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A81.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | CD40L cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Jeko-1 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1865 | |
| Mino cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_UW35 | |
| OCI-LY10 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_8795 | |
| OCI-LY18 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1880 | |
| OCI-LY19 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1878 | |
| OCI-LY3 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_8800 | |
| SUDHL10 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1889 | |
| SUDHL4 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0539 | |
| SUDHL6 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2206 | |
| U-2932 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1896 | |
| Val cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1819 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell viability assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Treatment with AZD5991 restricted growth of DLBCL cells independent of cell of origin and overcame ibrutinib resistance in MCL cells. Mcl-1 inhibition led to mitochondrial dysfunction as manifested by mitochondrial membrane depolarization, decreased mitochondrial mass, and induction of mitophagy. This was accompanied by impairment of oxidative phosphorylation. TP53 and BAX were essential for sensitivity to Mcl-1, and oxidative phosphorylation was implicated in resistance to Mcl-1 inhibition. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Myeloid differentiation primary response protein MyD88 (MYD88) | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A81.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L265P |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | Furthermore, within ABC DLBCL, responses were significantly different depending on the specific genetic lesions. Ibrutinib-resistant tumours carry mutant MYD88 and WT CD79A/B whereas all other genotypic combinations (CD79A/BWT + MYD88WT, CD79A/Bmutant + MYD88WT and CD79A/Bmutant + MYD88mutant) were responsive to ibrutinib therapy. It is foreseeable why ibrutinib therapy is less effective in MYD88-mutated ABC-DLBCL patients because MYD88 activates NFkappa-B through a parallel pathway independent of BTK. However, it is unclear why MYD88 mutations alone are associated with ibrutinib resistance whereas the MYD88 mutations in conjunction with CD79A/B mutations appears to render ABC DLBCL ibrutinib-sensitive. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Tyrosine-protein kinase BTK (BTK) | [2] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Chronic lymphocytic leukemia [ICD-11: 2A82.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.C481S |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.40 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.33 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
-
P
-
L
-
370
|
G
-
S
-
R
-
L
-
K
-
Y
-
P
-
V
-
S
-
Q
-
380
|
Q
-
N
-
K
-
N
-
A
-
P
-
S
-
T
G
A
M
G
G
390
|
L
L
G
G
Y
Y
G
G
S
S
W
W
E
E
I
I
D
D
P
P
400
|
K
K
D
D
L
L
T
T
F
F
L
L
K
K
E
E
L
L
G
G
410
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
F
F
G
G
V
V
V
V
K
K
Y
Y
G
G
420
|
K
K
W
W
R
R
G
G
Q
Q
Y
Y
D
D
V
V
A
A
I
I
430
|
K
K
M
M
I
I
K
K
E
E
G
G
S
S
M
M
S
S
E
E
440
|
D
D
E
E
F
F
I
I
E
E
E
E
A
A
K
K
V
V
M
M
450
|
M
M
N
N
L
L
S
S
H
H
E
E
K
K
L
L
V
V
Q
Q
460
|
L
L
Y
Y
G
G
V
V
C
C
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
R
R
P
P
470
|
I
I
F
F
I
I
I
I
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
M
M
A
A
N
N
480
|
G
G
C
S
L
L
L
L
N
N
Y
Y
L
L
R
R
E
E
M
M
490
|
R
R
H
H
R
R
F
F
Q
Q
T
T
Q
Q
Q
Q
L
L
L
L
500
|
E
E
M
M
C
C
K
K
D
D
V
V
C
C
E
E
A
A
M
M
510
|
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
E
E
S
S
K
K
Q
Q
F
F
L
L
H
H
520
|
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
C
C
L
L
V
V
530
|
N
N
D
D
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
K
K
V
V
S
S
D
D
540
|
F
F
G
G
L
L
S
S
R
R
Y
Y
V
V
L
L
D
D
D
D
550
|
E
E
Y
Y
T
T
S
S
S
S
V
V
G
G
S
S
K
K
F
F
560
|
P
P
V
V
R
R
W
W
S
S
P
P
P
P
E
E
V
V
L
L
570
|
M
M
Y
Y
S
S
K
K
F
F
S
S
S
S
K
K
S
S
D
D
580
|
I
I
W
W
A
A
F
F
G
G
V
V
L
L
M
M
W
W
E
E
590
|
I
I
Y
Y
S
S
L
L
G
G
K
K
M
M
P
P
Y
Y
E
E
600
|
R
R
F
F
T
T
N
N
S
S
E
E
T
T
A
A
E
E
H
H
610
|
I
I
A
A
Q
Q
G
G
L
L
R
R
L
L
Y
Y
R
R
P
P
620
|
H
H
L
L
A
A
S
S
E
E
K
K
V
V
Y
Y
T
T
I
I
630
|
M
M
Y
Y
S
S
C
C
W
W
H
H
E
E
K
K
A
A
D
D
640
|
E
E
R
R
P
P
T
T
F
F
K
K
I
I
L
L
L
L
S
S
650
|
N
N
I
I
L
L
D
D
V
V
M
M
D
D
E
E
E
E
S
S
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | ||||||||||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |||||||||||
| NF-kB signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04218 | |||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow cytometry assay; Bone marrow biopsy assay; Lymph node biopsy assay; Physical and laboratory examinations assay; Computed tomography imaging assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | All patients except one had an early on-treatment sample available that tested negative for BTk and PLCG2 mutations, indicating expansion of subclones carrying drug-resistant mutations during treatment. Most cases of ibrutinib-resistant CLL were due to mutations in BTk and,or PLCG2 and often composed of multiple independent subclones. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Tyrosine-protein kinase BTK (BTK) | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Chronic lymphocytic leukemia [ICD-11: 2A82.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.C481S |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.40 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.33 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
-
P
-
L
-
370
|
G
-
S
-
R
-
L
-
K
-
Y
-
P
-
V
-
S
-
Q
-
380
|
Q
-
N
-
K
-
N
-
A
-
P
-
S
-
T
G
A
M
G
G
390
|
L
L
G
G
Y
Y
G
G
S
S
W
W
E
E
I
I
D
D
P
P
400
|
K
K
D
D
L
L
T
T
F
F
L
L
K
K
E
E
L
L
G
G
410
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
F
F
G
G
V
V
V
V
K
K
Y
Y
G
G
420
|
K
K
W
W
R
R
G
G
Q
Q
Y
Y
D
D
V
V
A
A
I
I
430
|
K
K
M
M
I
I
K
K
E
E
G
G
S
S
M
M
S
S
E
E
440
|
D
D
E
E
F
F
I
I
E
E
E
E
A
A
K
K
V
V
M
M
450
|
M
M
N
N
L
L
S
S
H
H
E
E
K
K
L
L
V
V
Q
Q
460
|
L
L
Y
Y
G
G
V
V
C
C
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
R
R
P
P
470
|
I
I
F
F
I
I
I
I
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
M
M
A
A
N
N
480
|
G
G
C
S
L
L
L
L
N
N
Y
Y
L
L
R
R
E
E
M
M
490
|
R
R
H
H
R
R
F
F
Q
Q
T
T
Q
Q
Q
Q
L
L
L
L
500
|
E
E
M
M
C
C
K
K
D
D
V
V
C
C
E
E
A
A
M
M
510
|
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
E
E
S
S
K
K
Q
Q
F
F
L
L
H
H
520
|
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
C
C
L
L
V
V
530
|
N
N
D
D
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
K
K
V
V
S
S
D
D
540
|
F
F
G
G
L
L
S
S
R
R
Y
Y
V
V
L
L
D
D
D
D
550
|
E
E
Y
Y
T
T
S
S
S
S
V
V
G
G
S
S
K
K
F
F
560
|
P
P
V
V
R
R
W
W
S
S
P
P
P
P
E
E
V
V
L
L
570
|
M
M
Y
Y
S
S
K
K
F
F
S
S
S
S
K
K
S
S
D
D
580
|
I
I
W
W
A
A
F
F
G
G
V
V
L
L
M
M
W
W
E
E
590
|
I
I
Y
Y
S
S
L
L
G
G
K
K
M
M
P
P
Y
Y
E
E
600
|
R
R
F
F
T
T
N
N
S
S
E
E
T
T
A
A
E
E
H
H
610
|
I
I
A
A
Q
Q
G
G
L
L
R
R
L
L
Y
Y
R
R
P
P
620
|
H
H
L
L
A
A
S
S
E
E
K
K
V
V
Y
Y
T
T
I
I
630
|
M
M
Y
Y
S
S
C
C
W
W
H
H
E
E
K
K
A
A
D
D
640
|
E
E
R
R
P
P
T
T
F
F
K
K
I
I
L
L
L
L
S
S
650
|
N
N
I
I
L
L
D
D
V
V
M
M
D
D
E
E
E
E
S
S
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Efforts have been made to understand the functional consequences of the BTK mutation. On a structural level, the C481S mutation disrupts covalent binding, allowing for reversible, instead of strong irreversible, binding of BTK by ibrutinib. The critical biochemical role of covalent-bond formation was revealed when fluorescently tagged-ibrutinib labelled the wild-type (WT) BTK, but not the BTKC481S mutant. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Tyrosine-protein kinase BTK (BTK) | [2] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Chronic lymphocytic leukemia [ICD-11: 2A82.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.C481R |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | ||||||||||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |||||||||||
| NF-kB signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04218 | |||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow cytometry assay; Bone marrow biopsy assay; Lymph node biopsy assay; Physical and laboratory examinations assay; Computed tomography imaging assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | All patients except one had an early on-treatment sample available that tested negative for BTk and PLCG2 mutations, indicating expansion of subclones carrying drug-resistant mutations during treatment. Most cases of ibrutinib-resistant CLL were due to mutations in BTk and,or PLCG2 and often composed of multiple independent subclones. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: AKT serine/threonine kinase (AKT) | [7] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Chronic lymphocytic leukemia [ICD-11: 2A82.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Phosphorylation | Up-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | CD5+19+ cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| MEC1 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1870 | ||||||||||
| HS-5 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3720 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | NSG mice model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow cytometry assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Induction of transcription factor FoxO1 during ibrutinib therapy upregulates Rictor, an mTORC2 assembly protein, leading to phosphorylation of Akt, an essential molecule supporting CLL cell survival | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Forkhead box protein O1/Rapamycin-insensitive companion of mTOR (FOXO1/RICTOR) axis | [7] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Chronic lymphocytic leukemia [ICD-11: 2A82.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | p.Y537N |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | CD5+19+ cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| MEC1 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1870 | ||||||||||
| HS-5 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3720 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | NSG mice model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow cytometry assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Induction of transcription factor FoxO1 during ibrutinib therapy upregulates Rictor, an mTORC2 assembly protein, leading to phosphorylation of Akt, an essential molecule supporting CLL cell survival | ||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Phosphoinositide phospholipase C-gamma-2 (PLCG2) | [2] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Chronic lymphocytic leukemia [ICD-11: 2A82.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S707Y |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | ||||||||||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |||||||||||
| NF-kB signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04218 | |||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow cytometry assay; Bone marrow biopsy assay; Lymph node biopsy assay; Physical and laboratory examinations assay; Computed tomography imaging assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | All patients except one had an early on-treatment sample available that tested negative for BTk and PLCG2 mutations, indicating expansion of subclones carrying drug-resistant mutations during treatment. Most cases of ibrutinib-resistant CLL were due to mutations in BTk and,or PLCG2 and often composed of multiple independent subclones. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Phosphoinositide phospholipase C-gamma-2 (PLCG2) | [2] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Chronic lymphocytic leukemia [ICD-11: 2A82.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.P664W |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | ||||||||||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |||||||||||
| NF-kB signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04218 | |||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow cytometry assay; Bone marrow biopsy assay; Lymph node biopsy assay; Physical and laboratory examinations assay; Computed tomography imaging assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | All patients except one had an early on-treatment sample available that tested negative for BTk and PLCG2 mutations, indicating expansion of subclones carrying drug-resistant mutations during treatment. Most cases of ibrutinib-resistant CLL were due to mutations in BTk and,or PLCG2 and often composed of multiple independent subclones. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Phosphoinositide phospholipase C-gamma-2 (PLCG2) | [2] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Chronic lymphocytic leukemia [ICD-11: 2A82.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.P664S |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | ||||||||||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |||||||||||
| NF-kB signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04218 | |||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow cytometry assay; Bone marrow biopsy assay; Lymph node biopsy assay; Physical and laboratory examinations assay; Computed tomography imaging assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | All patients except one had an early on-treatment sample available that tested negative for BTk and PLCG2 mutations, indicating expansion of subclones carrying drug-resistant mutations during treatment. Most cases of ibrutinib-resistant CLL were due to mutations in BTk and,or PLCG2 and often composed of multiple independent subclones. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Phosphoinositide phospholipase C-gamma-2 (PLCG2) | [2] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Chronic lymphocytic leukemia [ICD-11: 2A82.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L845F |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | ||||||||||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |||||||||||
| NF-kB signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04218 | |||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger sequencing assay; Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow cytometry assay; Bone marrow biopsy assay; Lymph node biopsy assay; Physical and laboratory examinations assay; Computed tomography imaging assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | All patients except one had an early on-treatment sample available that tested negative for BTk and PLCG2 mutations, indicating expansion of subclones carrying drug-resistant mutations during treatment. Most cases of ibrutinib-resistant CLL were due to mutations in BTk and,or PLCG2 and often composed of multiple independent subclones. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Phosphoinositide phospholipase C-gamma-2 (PLCG2) | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Chronic lymphocytic leukemia [ICD-11: 2A82.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | p.R665W+p.L845F+p.S707Y |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | In contrast to the BTKC481S mutation, which causes eventual loss of BTK inhibition by ibrutinib, PLCG2 mutations are all potentially gain-of-function mutations. Situated downstream from BTK, PLCG2 mutations allow for continued signalling regardless of BTK activity. After stimulation with anti-IgM antibody, cells with either the PLCG2R665W or PLCG2L845F mutations were found to have sustained BCR signalling that was not inhibited by ibrutinib, as measured by calcium-flux assays and phosphorylation of ERK and AKT. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Tyrosine-protein kinase BTK (BTK) | [8] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Chronic lymphocytic leukemia [ICD-11: 2A82.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | Down-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Rho GTPases signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||||||||||
| MAPK signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04010 | |||||||||||
| WNT/beta-catenin signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | |||||||||||
| NOTCH signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04330 | |||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | HG-3 CLL cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| OSU-CLL cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_Y382 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
RNA sequencing assay; ROS assay; Ferroptosis assay; Flow cytometry assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Clinically, most ibrutinib-resistant patients (~80%) harbor a C481S mutation in the BTK protein, blocking ibrutinib from covalently binding to BTK, and/or a gain of function mutation in PLCgamma2, activating downstream BCR signaling independent of BTK inhibition. Resistance is also mediated through alternative survival pathways, such as the activation of PI3K/AKT/ERK signaling . | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Tyrosine-protein kinase BTK (BTK) | [9] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Mantle cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A85.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.C481S |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.40 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.33 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
-
P
-
L
-
370
|
G
-
S
-
R
-
L
-
K
-
Y
-
P
-
V
-
S
-
Q
-
380
|
Q
-
N
-
K
-
N
-
A
-
P
-
S
-
T
G
A
M
G
G
390
|
L
L
G
G
Y
Y
G
G
S
S
W
W
E
E
I
I
D
D
P
P
400
|
K
K
D
D
L
L
T
T
F
F
L
L
K
K
E
E
L
L
G
G
410
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
F
F
G
G
V
V
V
V
K
K
Y
Y
G
G
420
|
K
K
W
W
R
R
G
G
Q
Q
Y
Y
D
D
V
V
A
A
I
I
430
|
K
K
M
M
I
I
K
K
E
E
G
G
S
S
M
M
S
S
E
E
440
|
D
D
E
E
F
F
I
I
E
E
E
E
A
A
K
K
V
V
M
M
450
|
M
M
N
N
L
L
S
S
H
H
E
E
K
K
L
L
V
V
Q
Q
460
|
L
L
Y
Y
G
G
V
V
C
C
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
R
R
P
P
470
|
I
I
F
F
I
I
I
I
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
M
M
A
A
N
N
480
|
G
G
C
S
L
L
L
L
N
N
Y
Y
L
L
R
R
E
E
M
M
490
|
R
R
H
H
R
R
F
F
Q
Q
T
T
Q
Q
Q
Q
L
L
L
L
500
|
E
E
M
M
C
C
K
K
D
D
V
V
C
C
E
E
A
A
M
M
510
|
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
E
E
S
S
K
K
Q
Q
F
F
L
L
H
H
520
|
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
C
C
L
L
V
V
530
|
N
N
D
D
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
K
K
V
V
S
S
D
D
540
|
F
F
G
G
L
L
S
S
R
R
Y
Y
V
V
L
L
D
D
D
D
550
|
E
E
Y
Y
T
T
S
S
S
S
V
V
G
G
S
S
K
K
F
F
560
|
P
P
V
V
R
R
W
W
S
S
P
P
P
P
E
E
V
V
L
L
570
|
M
M
Y
Y
S
S
K
K
F
F
S
S
S
S
K
K
S
S
D
D
580
|
I
I
W
W
A
A
F
F
G
G
V
V
L
L
M
M
W
W
E
E
590
|
I
I
Y
Y
S
S
L
L
G
G
K
K
M
M
P
P
Y
Y
E
E
600
|
R
R
F
F
T
T
N
N
S
S
E
E
T
T
A
A
E
E
H
H
610
|
I
I
A
A
Q
Q
G
G
L
L
R
R
L
L
Y
Y
R
R
P
P
620
|
H
H
L
L
A
A
S
S
E
E
K
K
V
V
Y
Y
T
T
I
I
630
|
M
M
Y
Y
S
S
C
C
W
W
H
H
E
E
K
K
A
A
D
D
640
|
E
E
R
R
P
P
T
T
F
F
K
K
I
I
L
L
L
L
S
S
650
|
N
N
I
I
L
L
D
D
V
V
M
M
D
D
E
E
E
E
S
S
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Mantle cell lymphoma isolates | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-exome sequencing assay; Whole-transcriptome sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | This mutation enhanced BTK and AKT activation and tissue-specific proliferation of resistant MCL cells driven by CDK4 activation. It was absent, however, in patients with primary-resistance or progression following transient response to ibrutinib, suggesting alternative mechanisms of resistance. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Tyrosine-protein kinase BTK (BTK) | [9] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Mantle cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A85.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.C481S |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.40 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.33 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
-
P
-
L
-
370
|
G
-
S
-
R
-
L
-
K
-
Y
-
P
-
V
-
S
-
Q
-
380
|
Q
-
N
-
K
-
N
-
A
-
P
-
S
-
T
G
A
M
G
G
390
|
L
L
G
G
Y
Y
G
G
S
S
W
W
E
E
I
I
D
D
P
P
400
|
K
K
D
D
L
L
T
T
F
F
L
L
K
K
E
E
L
L
G
G
410
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
F
F
G
G
V
V
V
V
K
K
Y
Y
G
G
420
|
K
K
W
W
R
R
G
G
Q
Q
Y
Y
D
D
V
V
A
A
I
I
430
|
K
K
M
M
I
I
K
K
E
E
G
G
S
S
M
M
S
S
E
E
440
|
D
D
E
E
F
F
I
I
E
E
E
E
A
A
K
K
V
V
M
M
450
|
M
M
N
N
L
L
S
S
H
H
E
E
K
K
L
L
V
V
Q
Q
460
|
L
L
Y
Y
G
G
V
V
C
C
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
R
R
P
P
470
|
I
I
F
F
I
I
I
I
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
M
M
A
A
N
N
480
|
G
G
C
S
L
L
L
L
N
N
Y
Y
L
L
R
R
E
E
M
M
490
|
R
R
H
H
R
R
F
F
Q
Q
T
T
Q
Q
Q
Q
L
L
L
L
500
|
E
E
M
M
C
C
K
K
D
D
V
V
C
C
E
E
A
A
M
M
510
|
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
E
E
S
S
K
K
Q
Q
F
F
L
L
H
H
520
|
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
C
C
L
L
V
V
530
|
N
N
D
D
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
K
K
V
V
S
S
D
D
540
|
F
F
G
G
L
L
S
S
R
R
Y
Y
V
V
L
L
D
D
D
D
550
|
E
E
Y
Y
T
T
S
S
S
S
V
V
G
G
S
S
K
K
F
F
560
|
P
P
V
V
R
R
W
W
S
S
P
P
P
P
E
E
V
V
L
L
570
|
M
M
Y
Y
S
S
K
K
F
F
S
S
S
S
K
K
S
S
D
D
580
|
I
I
W
W
A
A
F
F
G
G
V
V
L
L
M
M
W
W
E
E
590
|
I
I
Y
Y
S
S
L
L
G
G
K
K
M
M
P
P
Y
Y
E
E
600
|
R
R
F
F
T
T
N
N
S
S
E
E
T
T
A
A
E
E
H
H
610
|
I
I
A
A
Q
Q
G
G
L
L
R
R
L
L
Y
Y
R
R
P
P
620
|
H
H
L
L
A
A
S
S
E
E
K
K
V
V
Y
Y
T
T
I
I
630
|
M
M
Y
Y
S
S
C
C
W
W
H
H
E
E
K
K
A
A
D
D
640
|
E
E
R
R
P
P
T
T
F
F
K
K
I
I
L
L
L
L
S
S
650
|
N
N
I
I
L
L
D
D
V
V
M
M
D
D
E
E
E
E
S
S
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Mantle cell lymphoma isolates | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-exome sequencing assay; Whole-transcriptome sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | This mutation enhanced BTK and AKT activation and tissue-specific proliferation of resistant MCL cells driven by CDK4 activation. It was absent, however, in patients with primary-resistance or progression following transient response to ibrutinib, suggesting alternative mechanisms of resistance. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Tyrosine-protein kinase BTK (BTK) | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Mantle cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A85.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.C481S |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.40 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.33 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
-
P
-
L
-
370
|
G
-
S
-
R
-
L
-
K
-
Y
-
P
-
V
-
S
-
Q
-
380
|
Q
-
N
-
K
-
N
-
A
-
P
-
S
-
T
G
A
M
G
G
390
|
L
L
G
G
Y
Y
G
G
S
S
W
W
E
E
I
I
D
D
P
P
400
|
K
K
D
D
L
L
T
T
F
F
L
L
K
K
E
E
L
L
G
G
410
|
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
F
F
G
G
V
V
V
V
K
K
Y
Y
G
G
420
|
K
K
W
W
R
R
G
G
Q
Q
Y
Y
D
D
V
V
A
A
I
I
430
|
K
K
M
M
I
I
K
K
E
E
G
G
S
S
M
M
S
S
E
E
440
|
D
D
E
E
F
F
I
I
E
E
E
E
A
A
K
K
V
V
M
M
450
|
M
M
N
N
L
L
S
S
H
H
E
E
K
K
L
L
V
V
Q
Q
460
|
L
L
Y
Y
G
G
V
V
C
C
T
T
K
K
Q
Q
R
R
P
P
470
|
I
I
F
F
I
I
I
I
T
T
E
E
Y
Y
M
M
A
A
N
N
480
|
G
G
C
S
L
L
L
L
N
N
Y
Y
L
L
R
R
E
E
M
M
490
|
R
R
H
H
R
R
F
F
Q
Q
T
T
Q
Q
Q
Q
L
L
L
L
500
|
E
E
M
M
C
C
K
K
D
D
V
V
C
C
E
E
A
A
M
M
510
|
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
E
E
S
S
K
K
Q
Q
F
F
L
L
H
H
520
|
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
C
C
L
L
V
V
530
|
N
N
D
D
Q
Q
G
G
V
V
V
V
K
K
V
V
S
S
D
D
540
|
F
F
G
G
L
L
S
S
R
R
Y
Y
V
V
L
L
D
D
D
D
550
|
E
E
Y
Y
T
T
S
S
S
S
V
V
G
G
S
S
K
K
F
F
560
|
P
P
V
V
R
R
W
W
S
S
P
P
P
P
E
E
V
V
L
L
570
|
M
M
Y
Y
S
S
K
K
F
F
S
S
S
S
K
K
S
S
D
D
580
|
I
I
W
W
A
A
F
F
G
G
V
V
L
L
M
M
W
W
E
E
590
|
I
I
Y
Y
S
S
L
L
G
G
K
K
M
M
P
P
Y
Y
E
E
600
|
R
R
F
F
T
T
N
N
S
S
E
E
T
T
A
A
E
E
H
H
610
|
I
I
A
A
Q
Q
G
G
L
L
R
R
L
L
Y
Y
R
R
P
P
620
|
H
H
L
L
A
A
S
S
E
E
K
K
V
V
Y
Y
T
T
I
I
630
|
M
M
Y
Y
S
S
C
C
W
W
H
H
E
E
K
K
A
A
D
D
640
|
E
E
R
R
P
P
T
T
F
F
K
K
I
I
L
L
L
L
S
S
650
|
N
N
I
I
L
L
D
D
V
V
M
M
D
D
E
E
E
E
S
S
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | PIK3/AKT signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04211 | ||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Efforts have been made to understand the functional consequences of the BTK mutation. On a structural level, the C481S mutation disrupts covalent binding, allowing for reversible, instead of strong irreversible, binding of BTK by ibrutinib. The critical biochemical role of covalent-bond formation was revealed when fluorescently tagged-ibrutinib labelled the wild-type (WT) BTK, but not the BTKC481S mutant. | ||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: ROR1 antisense RNA 1 (ROR1-AS1) | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Mantle cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A85.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | HEK293T cells | Kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0063 | |||||||||
| Granta cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| JVM2 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1319 | ||||||||||
| Mino cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_UW35 | ||||||||||
| Z138 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B077 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
3H-thymidine incorporation assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Overexpression of ROR1-AS1 LncRNA promoted growth of MCL cells while decreased sensitivity to the treatment with drugs ibrutinib and dexamethasone. | ||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Early growth response protein 1 (EGR1) | [10] | ||||||||||||
| Metabolic Type | Glucose metabolism | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Mantle cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A85.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Mice, with fresh tissue from patient | Mice | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
RNA seq | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell viability assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The overexpression of EGR1 in ibrutinib-resistant cells is likely to result from the transcription factor TCF4-mediated EGR1 transcription and EGR1 self-regulation. Genetic and pharmacological inhibition of EGR1 restores the sensitivity of the resistant cells to ibrutinib, suggesting a role EGR1 plays in ibrutinib resistance. The underlying mechanism is that EGR1 mediates metabolic reprogramming to mitochondrial OXPHOS by transcriptional activation of PDP1, which increases ATP production. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3A (DNMT3A) | [11] | ||||||||||||
| Metabolic Type | Mitochondrial metabolism | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Mantle cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A85.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Mino cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_UW35 | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR; Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
IC50 assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | We provide evidence that DNMT3A contributes to ibrutinib resistance in MCL by increasing mitochondrial biogenesis and OXPHOS. Recent clinical studies demonstrated the potential of BTKis as a first-line treatment option for MCL. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3A (DNMT3A) | [11] | ||||||||||||
| Metabolic Type | Mitochondrial metabolism | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Mantle cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A85.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Rec-1 cells | Lymph | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1884 | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR; Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
IC50 assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | We provide evidence that DNMT4A contributes to ibrutinib resistance in MCL by increasing mitochondrial biogenesis and OXPHOS. Recent clinical studies demonstrated the potential of BTKis as a first-line treatment option for MCL. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3A (DNMT3A) | [11] | ||||||||||||
| Metabolic Type | Mitochondrial metabolism | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Mantle cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A85.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Jeko-1 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1865 | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR; Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
IC50 assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | We provide evidence that DNMT5A contributes to ibrutinib resistance in MCL by increasing mitochondrial biogenesis and OXPHOS. Recent clinical studies demonstrated the potential of BTKis as a first-line treatment option for MCL. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3A (DNMT3A) | [11] | ||||||||||||
| Metabolic Type | Mitochondrial metabolism | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Mantle cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A85.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Z138 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B077 | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR; Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
IC50 assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | We provide evidence that DNMT6A contributes to ibrutinib resistance in MCL by increasing mitochondrial biogenesis and OXPHOS. Recent clinical studies demonstrated the potential of BTKis as a first-line treatment option for MCL. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3A (DNMT3A) | [11] | ||||||||||||
| Metabolic Type | Mitochondrial metabolism | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Mantle cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A85.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Mouse, with tumor cells | Mice | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR; Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Tumor volume assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | We provide evidence that DNMT7A contributes to ibrutinib resistance in MCL by increasing mitochondrial biogenesis and OXPHOS. Recent clinical studies demonstrated the potential of BTKis as a first-line treatment option for MCL. | ||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Caspase recruitment domain-containing protein 11 (CARD11) | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Mantle cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A85.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y361C |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | BCR/NF-kB signaling pathway | Activation | hsa05200 | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | JVM2 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1319 | |||||||||
| Mino cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_UW35 | ||||||||||
| Z138 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B077 | ||||||||||
| Jeko-1 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1865 | ||||||||||
| Granta-519 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1818 | ||||||||||
| Rec-1 cells | Lymph | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1884 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-exome sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Drug inhibition assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Based on in vitro cell line-based experiments, overexpression of CARD11 mutants were demonstrated to confer resistance to the BCR inhibitor ibrutinib and NF-kB-inhibitor lenalidomide. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Caspase recruitment domain-containing protein 11 (CARD11) | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Mantle cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A85.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G123S |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | BCR/NF-kB signaling pathway | Activation | hsa05200 | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | JVM2 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1319 | |||||||||
| Mino cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_UW35 | ||||||||||
| Z138 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B077 | ||||||||||
| Jeko-1 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1865 | ||||||||||
| Granta-519 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1818 | ||||||||||
| Rec-1 cells | Lymph | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1884 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-exome sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Drug inhibition assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Based on in vitro cell line-based experiments, overexpression of CARD11 mutants were demonstrated to confer resistance to the BCR inhibitor ibrutinib and NF-kB-inhibitor lenalidomide. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Caspase recruitment domain-containing protein 11 (CARD11) | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Mantle cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A85.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D357E |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | BCR/NF-kB signaling pathway | Activation | hsa05200 | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | JVM2 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1319 | |||||||||
| Mino cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_UW35 | ||||||||||
| Z138 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B077 | ||||||||||
| Jeko-1 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1865 | ||||||||||
| Granta-519 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1818 | ||||||||||
| Rec-1 cells | Lymph | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1884 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-exome sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Drug inhibition assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Based on in vitro cell line-based experiments, overexpression of CARD11 mutants were demonstrated to confer resistance to the BCR inhibitor ibrutinib and NF-kB-inhibitor lenalidomide. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Caspase recruitment domain-containing protein 11 (CARD11) | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Mantle cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A85.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D230N |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | BCR/NF-kB signaling pathway | Activation | hsa05200 | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | JVM2 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1319 | |||||||||
| Mino cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_UW35 | ||||||||||
| Z138 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B077 | ||||||||||
| Jeko-1 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1865 | ||||||||||
| Granta-519 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1818 | ||||||||||
| Rec-1 cells | Lymph | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1884 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-exome sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Drug inhibition assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Based on in vitro cell line-based experiments, overexpression of CARD11 mutants were demonstrated to confer resistance to the BCR inhibitor ibrutinib and NF-kB-inhibitor lenalidomide. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Caspase recruitment domain-containing protein 11 (CARD11) | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Mantle cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A85.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | BCR/NF-kB signaling pathway | Activation | hsa05200 | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | JVM2 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1319 | |||||||||
| Mino cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_UW35 | ||||||||||
| Z138 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B077 | ||||||||||
| Jeko-1 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1865 | ||||||||||
| Granta-519 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1818 | ||||||||||
| Rec-1 cells | Lymph | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1884 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Drug inhibition assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Based on in vitro cell line-based experiments, overexpression of CARD11 mutants were demonstrated to confer resistance to the BCR-inhibitor ibrutinib and NF-kB-inhibitor lenalidomide. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: CXC chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4) | [12] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia [ICD-11: 2A85.4] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | . |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | CXCR4 mutation led to ibrutinib in the waldenstrom macroglobulinemia. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: CXC chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4) | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia [ICD-11: 2A85.4] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | p.S338X |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | ||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | CXCR4 is a transmembrance chemokine receptor that is internalized upon binding to its ligand CXCL12 and subsequently signals through G-proteins to activate the AKT and ERK pathways. The CXCR4 pathway plays an important role in lymphocyte migration and homing. CXCR4WHIM-like are prevalent somatic mutations, present in 30% of patients with WM. It was recently demonstrated that CXCR4S338X, the most common WHIM-like mutation, reduces CXCR4 receptor internalization and allows for sustained enzymatic activity of AKT and ERK and subsequent increased cell survival. When cells are exposed to ibrutinb, CXCR4S338X-carrying WM cells, compared to CXCR4WT cells, exhibit reduced apoptosis. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Myeloid differentiation primary response protein MyD88 (MYD88) | [4] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia [ICD-11: 2A85.4] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | p.L265P |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | The mutant, as opposed to MYD88WT, preferentially binds to p-BTK and subsequently activates NFKB. Ibrutinib treatment reduces such binding, therefore blocking downstream NFKB activation. Thus, the oncogenic activity of MYD88L265P is mediated through BTK in WM and renders cells sensitive to ibrutinib's inhibition. The fact that MYD88 mutations function differently in different cells highlight the notion that impact of a particular genetic mutation has to be determined and understood within the particular cellular context. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: hsa-mir-214 | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | DU-145 cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0105 |
| LNCaP cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0395 | |
| PC3 cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0035 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
RT-qPCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | microRNA-214 targets PTk6 to inhibit tumorigenic potential and increase drug sensitivity of prostate cancer cells. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Protein-tyrosine kinase 6 (PTK6) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | DU-145 cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0105 |
| LNCaP cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0395 | |
| PC3 cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0035 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | microRNA-214 targets PTk6 to inhibit tumorigenic potential and increase drug sensitivity of prostate cancer cells. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
