Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00371)
| Name |
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
FGFR1
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr8:38400215-38468834[-]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MWSWKCLLFWAVLVTATLCTARPSPTLPEQAQPWGAPVEVESFLVHPGDLLQLRCRLRDD
VQSINWLRDGVQLAESNRTRITGEEVEVQDSVPADSGLYACVTSSPSGSDTTYFSVNVSD ALPSSEDDDDDDDSSSEEKETDNTKPNRMPVAPYWTSPEKMEKKLHAVPAAKTVKFKCPS SGTPNPTLRWLKNGKEFKPDHRIGGYKVRYATWSIIMDSVVPSDKGNYTCIVENEYGSIN HTYQLDVVERSPHRPILQAGLPANKTVALGSNVEFMCKVYSDPQPHIQWLKHIEVNGSKI GPDNLPYVQILKTAGVNTTDKEMEVLHLRNVSFEDAGEYTCLAGNSIGLSHHSAWLTVLE ALEERPAVMTSPLYLEIIIYCTGAFLISCMVGSVIVYKMKSGTKKSDFHSQMAVHKLAKS IPLRRQVTVSADSSASMNSGVLLVRPSRLSSSGTPMLAGVSEYELPEDPRWELPRDRLVL GKPLGEGCFGQVVLAEAIGLDKDKPNRVTKVAVKMLKSDATEKDLSDLISEMEMMKMIGK HKNIINLLGACTQDGPLYVIVEYASKGNLREYLQARRPPGLEYCYNPSHNPEEQLSSKDL VSCAYQVARGMEYLASKKCIHRDLAARNVLVTEDNVMKIADFGLARDIHHIDYYKKTTNG RLPVKWMAPEALFDRIYTHQSDVWSFGVLLWEIFTLGGSPYPGVPVEELFKLLKEGHRMD KPSNCTNELYMMMRDCWHAVPSQRPTFKQLVEDLDRIVALTSNQEYLDLSMPLDQYSPSF PDTRSSTCSSGEDSVFSHEPLPEEPCLPRHPAQLANGGLKRR Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Tyrosine-protein kinase that acts as cell-surface receptor for fibroblast growth factors and plays an essential role in the regulation of embryonic development, cell proliferation, differentiation and migration. Required for normal mesoderm patterning and correct axial organization during embryonic development, normal skeletogenesis and normal development of the gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) neuronal system. Phosphorylates PLCG1, FRS2, GAB1 and SHB. Ligand binding leads to the activation of several signaling cascades. Activation of PLCG1 leads to the production of the cellular signaling molecules diacylglycerol and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Phosphorylation of FRS2 triggers recruitment of GRB2, GAB1, PIK3R1 and SOS1, and mediates activation of RAS, MAPK1/ERK2, MAPK3/ERK1 and the MAP kinase signaling pathway, as well as of the AKT1 signaling pathway. Promotes phosphorylation of SHC1, STAT1 and PTPN11/SHP2. In the nucleus, enhances RPS6KA1 and CREB1 activity and contributes to the regulation of transcription. FGFR1 signaling is down-regulated by IL17RD/SEF, and by FGFR1 ubiquitination, internalization and degradation.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
3 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10.3] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Erlotinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Pancreatic cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Pancreas | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.09E-02 Fold-change: -1.00E-01 Z-score: -2.85E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| FGF/FGFR signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa01521 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MIA PaCa-2 cells | Pancreas | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0428 |
| SW1990 cells | Pancreas | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1723 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-497 suppressed cells proliferation, decreased the percentage of S phase cells, re-sensitized cells to gemcitabine and erlotinib, and attenuated migration and invasion capacities. Furthermore, fibroblast growth factor 2 and fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 were confirmed as miR-497 targets. Overexpression of miR-497 inhibited tumor growth in vivo. Additionally, miR-497 expression was significantly downregulated in pancreatic cancer tissues compared with tumor-adjacent samples. Low expression of miR-497 was an independent adverse prognostic factor of pancreatic cancer. miR-497 plays a role in modulating the malignant phenotype and chemosensitivity of pancreatic cancer cells by directly inhibition of FGF2 and FGFR1 expression. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10.3] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Gemcitabine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| FGF/FGFR signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa01521 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MIA PaCa-2 cells | Pancreas | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0428 |
| SW1990 cells | Pancreas | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1723 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-497 suppressed cells proliferation, decreased the percentage of S phase cells, re-sensitized cells to gemcitabine and erlotinib, and attenuated migration and invasion capacities. Furthermore, fibroblast growth factor 2 and fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 were confirmed as miR-497 targets. Overexpression of miR-497 inhibited tumor growth in vivo. Additionally, miR-497 expression was significantly downregulated in pancreatic cancer tissues compared with tumor-adjacent samples. Low expression of miR-497 was an independent adverse prognostic factor of pancreatic cancer. miR-497 plays a role in modulating the malignant phenotype and chemosensitivity of pancreatic cancer cells by directly inhibition of FGF2 and FGFR1 expression. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.1] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Infigratinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Structural variation | Amplification |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | MET signalling pathway | Activation | hsa04020 | |
| ERK/MAPK signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04210 | ||
| In Vitro Model | DMS114 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1174 |
| Mechanism Description | Upregulation of the MET signalling pathway leading to re-activation of the ERK/MAPK pathway was observed in conjunction with the development of resistance to infigratinib in FGFR1-amplified DMS114 lung cancer cells. | |||
| Disease Class: Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.1] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Infigratinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Structural variation | Amplification |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | MET signalling pathway | Activation | hsa04020 | |
| ERK/MAPK signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04210 | ||
| In Vitro Model | DMS114 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1174 |
| Mechanism Description | Upregulation of the MET signalling pathway leading to re-activation of the ERK/MAPK pathway was observed in conjunction with the development of resistance to infigratinib in FGFR1-amplified DMS114 lung cancer cells. | |||
Clinical Trial Drug(s)
2 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | AZD-4547 | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V561M (c.1681G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.63 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.96 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
G
V
A
A
G
G
460
|
V
V
S
S
E
E
Y
Y
E
E
L
L
P
P
E
E
D
D
P
P
470
|
R
R
W
W
E
E
L
L
P
P
R
R
D
D
R
R
L
L
V
V
480
|
L
L
G
G
K
K
P
P
L
L
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
F
F
490
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
L
L
A
A
E
E
A
A
I
I
G
G
500
|
L
L
D
D
K
K
D
D
K
K
P
P
N
N
R
R
V
V
T
T
510
|
K
K
V
V
A
A
V
V
K
K
M
M
L
L
K
K
S
S
D
D
520
|
A
A
T
T
E
E
K
K
D
D
L
L
S
S
D
D
L
L
I
I
530
|
S
S
E
E
M
M
E
E
M
M
M
M
K
K
M
M
I
I
G
G
540
|
K
K
H
H
K
K
N
N
I
I
I
I
N
N
L
L
L
L
G
G
550
|
A
A
C
C
T
T
Q
Q
D
D
G
G
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
V
V
560
|
I
I
V
M
E
E
Y
Y
A
A
S
S
K
K
G
G
N
N
L
L
570
|
R
R
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
Q
Q
A
A
R
R
R
R
P
P
P
P
580
|
G
G
L
L
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
S
S
H
H
590
|
N
N
P
P
E
E
E
E
Q
Q
L
L
S
S
S
S
K
K
D
D
600
|
L
L
V
V
S
S
C
C
A
A
Y
Y
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
R
R
610
|
G
G
M
M
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
A
A
S
S
K
K
K
K
C
C
620
|
I
I
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
V
V
630
|
L
L
V
V
T
T
E
E
D
D
N
N
V
V
M
M
K
K
I
I
640
|
A
A
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
R
R
D
D
I
I
H
H
650
|
H
H
I
I
D
D
Y
Y
Y
Y
K
K
K
K
T
T
T
T
N
N
660
|
G
G
R
R
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
M
M
A
A
P
P
670
|
E
E
A
A
L
L
F
F
D
D
R
R
I
I
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
680
|
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
F
F
G
G
V
V
L
L
690
|
L
L
W
W
E
E
I
I
F
F
T
T
L
L
G
G
G
G
S
S
700
|
P
P
Y
Y
P
P
G
G
V
V
P
P
V
V
E
E
E
E
L
L
710
|
F
F
K
K
L
L
L
L
K
K
E
E
G
G
H
H
R
R
M
M
720
|
D
D
K
K
P
P
S
S
N
N
C
C
T
T
N
N
E
E
L
L
730
|
Y
Y
M
M
M
M
M
M
R
R
D
D
C
C
W
W
H
H
A
A
740
|
V
V
P
P
S
S
Q
Q
R
R
P
P
T
T
F
F
K
K
Q
Q
750
|
L
L
V
V
E
E
D
D
L
L
D
D
R
R
I
I
V
V
A
A
760
|
L
L
T
T
S
S
N
N
Q
Q
E
E
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | STAT3 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04550 | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | L6 cells | Skeletal muscle | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | CVCL_0385 | |||||||||
| H1581 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1479 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
SDS-PAGE assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Transwell migration assay; Matrigel invasion assay; Proliferation assay; MTT assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The V561M mutation biases cells towards a more mesenchymal phenotype, including increased levels of proliferation, migration, invasion and anchorage-independent growth, which was confirmed using CyTOF, a novel single cell analysis tool. Using shRNA knockdown, loss of STAT3 restored sensitivity of cancer cells expressing V561M FGFR1 to AZD4547. Thus, the data demonstrate that combination therapies including FGFR and STAT3 may overcome V561M FGFR1 driven drug resistance in the clinic. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | PRN1371 | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V561M (c.1681G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.63 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.96 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
G
V
A
A
G
G
460
|
V
V
S
S
E
E
Y
Y
E
E
L
L
P
P
E
E
D
D
P
P
470
|
R
R
W
W
E
E
L
L
P
P
R
R
D
D
R
R
L
L
V
V
480
|
L
L
G
G
K
K
P
P
L
L
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
F
F
490
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
L
L
A
A
E
E
A
A
I
I
G
G
500
|
L
L
D
D
K
K
D
D
K
K
P
P
N
N
R
R
V
V
T
T
510
|
K
K
V
V
A
A
V
V
K
K
M
M
L
L
K
K
S
S
D
D
520
|
A
A
T
T
E
E
K
K
D
D
L
L
S
S
D
D
L
L
I
I
530
|
S
S
E
E
M
M
E
E
M
M
M
M
K
K
M
M
I
I
G
G
540
|
K
K
H
H
K
K
N
N
I
I
I
I
N
N
L
L
L
L
G
G
550
|
A
A
C
C
T
T
Q
Q
D
D
G
G
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
V
V
560
|
I
I
V
M
E
E
Y
Y
A
A
S
S
K
K
G
G
N
N
L
L
570
|
R
R
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
Q
Q
A
A
R
R
R
R
P
P
P
P
580
|
G
G
L
L
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
S
S
H
H
590
|
N
N
P
P
E
E
E
E
Q
Q
L
L
S
S
S
S
K
K
D
D
600
|
L
L
V
V
S
S
C
C
A
A
Y
Y
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
R
R
610
|
G
G
M
M
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
A
A
S
S
K
K
K
K
C
C
620
|
I
I
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
V
V
630
|
L
L
V
V
T
T
E
E
D
D
N
N
V
V
M
M
K
K
I
I
640
|
A
A
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
R
R
D
D
I
I
H
H
650
|
H
H
I
I
D
D
Y
Y
Y
Y
K
K
K
K
T
T
T
T
N
N
660
|
G
G
R
R
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
M
M
A
A
P
P
670
|
E
E
A
A
L
L
F
F
D
D
R
R
I
I
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
680
|
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
F
F
G
G
V
V
L
L
690
|
L
L
W
W
E
E
I
I
F
F
T
T
L
L
G
G
G
G
S
S
700
|
P
P
Y
Y
P
P
G
G
V
V
P
P
V
V
E
E
E
E
L
L
710
|
F
F
K
K
L
L
L
L
K
K
E
E
G
G
H
H
R
R
M
M
720
|
D
D
K
K
P
P
S
S
N
N
C
C
T
T
N
N
E
E
L
L
730
|
Y
Y
M
M
M
M
M
M
R
R
D
D
C
C
W
W
H
H
A
A
740
|
V
V
P
P
S
S
Q
Q
R
R
P
P
T
T
F
F
K
K
Q
Q
750
|
L
L
V
V
E
E
D
D
L
L
D
D
R
R
I
I
V
V
A
A
760
|
L
L
T
T
S
S
N
N
Q
Q
E
E
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | FGF/FGFR signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa01521 | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | HCT116 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0291 | |||||||||
| Hep3B cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0326 | ||||||||||
| RT4 cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0036 | ||||||||||
| NCI-H716 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1581 | ||||||||||
| RT112 cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1670 | ||||||||||
| AN3CA cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0028 | ||||||||||
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | ||||||||||
| SNU878 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5102 | ||||||||||
| SNU16 cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0076 | ||||||||||
| OPM2 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1625 | ||||||||||
| LI7 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3840 | ||||||||||
| JHH7 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2805 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Promega assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | PRN1371 exhibits potent and durable pathway inhibition, and robust antiproliferative activity. PRN1371 demonstrates prolonged FGFR inhibition in vivo. | ||||||||||||
Preclinical Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | FIIN-1 | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V561M (c.1681G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.63 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.96 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
G
V
A
A
G
G
460
|
V
V
S
S
E
E
Y
Y
E
E
L
L
P
P
E
E
D
D
P
P
470
|
R
R
W
W
E
E
L
L
P
P
R
R
D
D
R
R
L
L
V
V
480
|
L
L
G
G
K
K
P
P
L
L
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
F
F
490
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
L
L
A
A
E
E
A
A
I
I
G
G
500
|
L
L
D
D
K
K
D
D
K
K
P
P
N
N
R
R
V
V
T
T
510
|
K
K
V
V
A
A
V
V
K
K
M
M
L
L
K
K
S
S
D
D
520
|
A
A
T
T
E
E
K
K
D
D
L
L
S
S
D
D
L
L
I
I
530
|
S
S
E
E
M
M
E
E
M
M
M
M
K
K
M
M
I
I
G
G
540
|
K
K
H
H
K
K
N
N
I
I
I
I
N
N
L
L
L
L
G
G
550
|
A
A
C
C
T
T
Q
Q
D
D
G
G
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
V
V
560
|
I
I
V
M
E
E
Y
Y
A
A
S
S
K
K
G
G
N
N
L
L
570
|
R
R
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
Q
Q
A
A
R
R
R
R
P
P
P
P
580
|
G
G
L
L
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
S
S
H
H
590
|
N
N
P
P
E
E
E
E
Q
Q
L
L
S
S
S
S
K
K
D
D
600
|
L
L
V
V
S
S
C
C
A
A
Y
Y
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
R
R
610
|
G
G
M
M
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
A
A
S
S
K
K
K
K
C
C
620
|
I
I
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
V
V
630
|
L
L
V
V
T
T
E
E
D
D
N
N
V
V
M
M
K
K
I
I
640
|
A
A
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
R
R
D
D
I
I
H
H
650
|
H
H
I
I
D
D
Y
Y
Y
Y
K
K
K
K
T
T
T
T
N
N
660
|
G
G
R
R
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
M
M
A
A
P
P
670
|
E
E
A
A
L
L
F
F
D
D
R
R
I
I
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
680
|
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
F
F
G
G
V
V
L
L
690
|
L
L
W
W
E
E
I
I
F
F
T
T
L
L
G
G
G
G
S
S
700
|
P
P
Y
Y
P
P
G
G
V
V
P
P
V
V
E
E
E
E
L
L
710
|
F
F
K
K
L
L
L
L
K
K
E
E
G
G
H
H
R
R
M
M
720
|
D
D
K
K
P
P
S
S
N
N
C
C
T
T
N
N
E
E
L
L
730
|
Y
Y
M
M
M
M
M
M
R
R
D
D
C
C
W
W
H
H
A
A
740
|
V
V
P
P
S
S
Q
Q
R
R
P
P
T
T
F
F
K
K
Q
Q
750
|
L
L
V
V
E
E
D
D
L
L
D
D
R
R
I
I
V
V
A
A
760
|
L
L
T
T
S
S
N
N
Q
Q
E
E
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | |||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTiter-Glo Luminescent Cell Viability Assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.V561M (c.1681G>A) in gene FGFR1 cause the sensitivity of FIIN-1 by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Pancreas | |
| The Specified Disease | Pancreatic cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.09E-02; Fold-change: -5.79E-01; Z-score: -8.25E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 1.51E-10; Fold-change: -7.65E-01; Z-score: -9.93E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
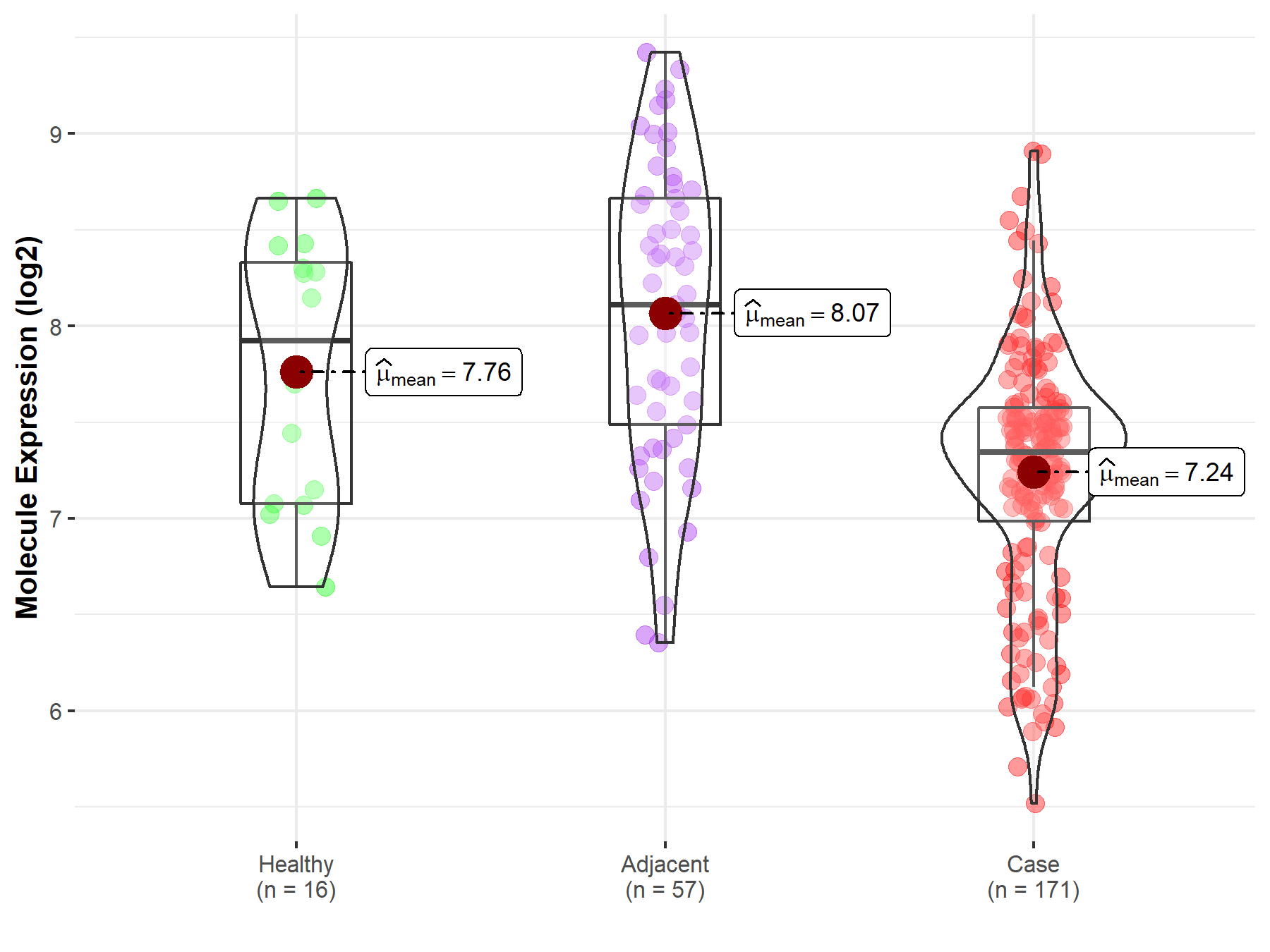
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Liver | |
| The Specified Disease | Liver cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.18E-03; Fold-change: -1.21E-01; Z-score: -5.86E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 3.61E-03; Fold-change: -8.13E-02; Z-score: -2.77E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Other Disease Section | p-value: 5.22E-01; Fold-change: -7.72E-02; Z-score: -4.71E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
Molecule expression in tissue other than the diseased tissue of patients
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
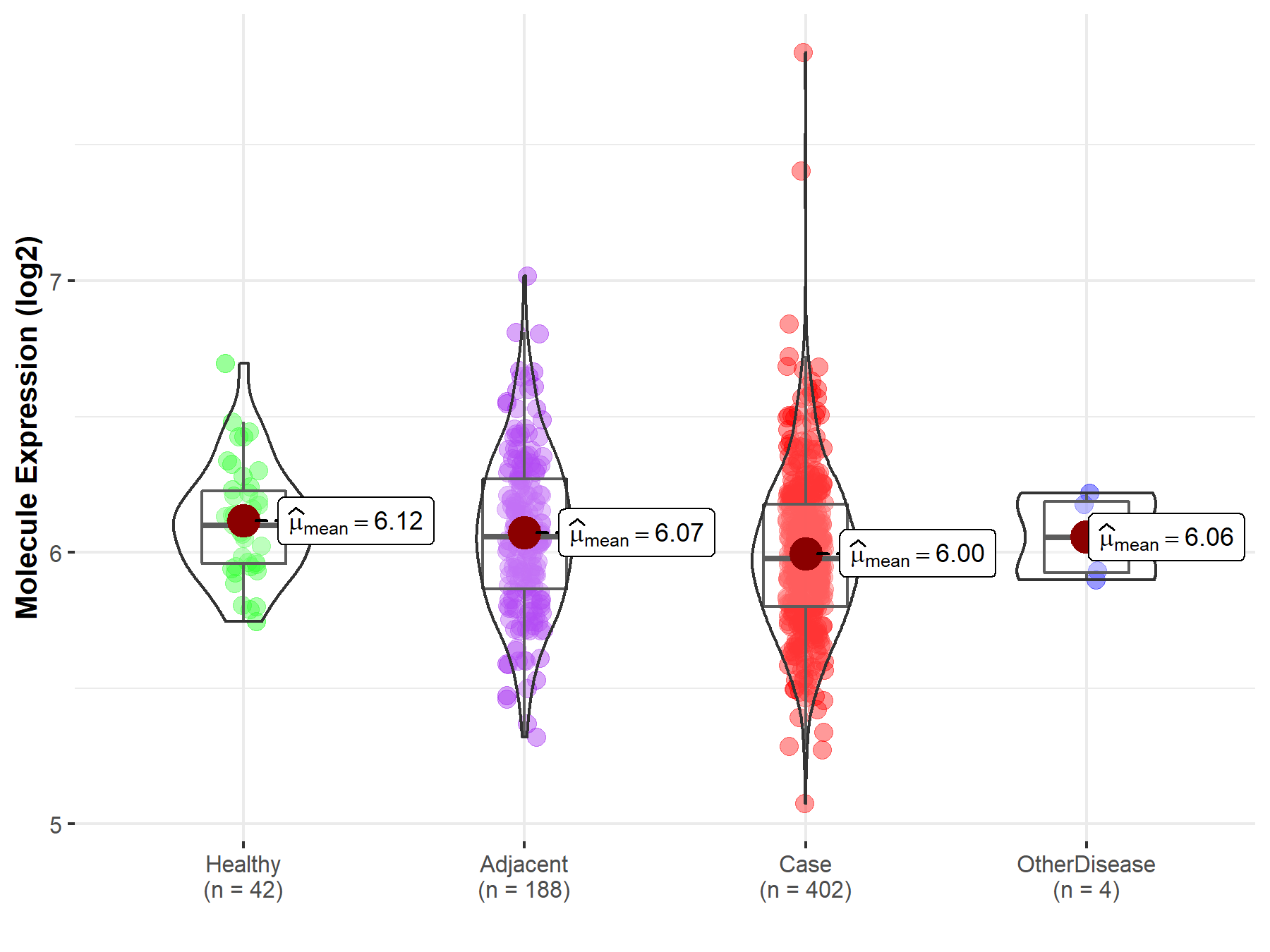
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung | |
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.41E-12; Fold-change: -2.79E-01; Z-score: -8.43E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 9.04E-11; Fold-change: -3.59E-01; Z-score: -8.30E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
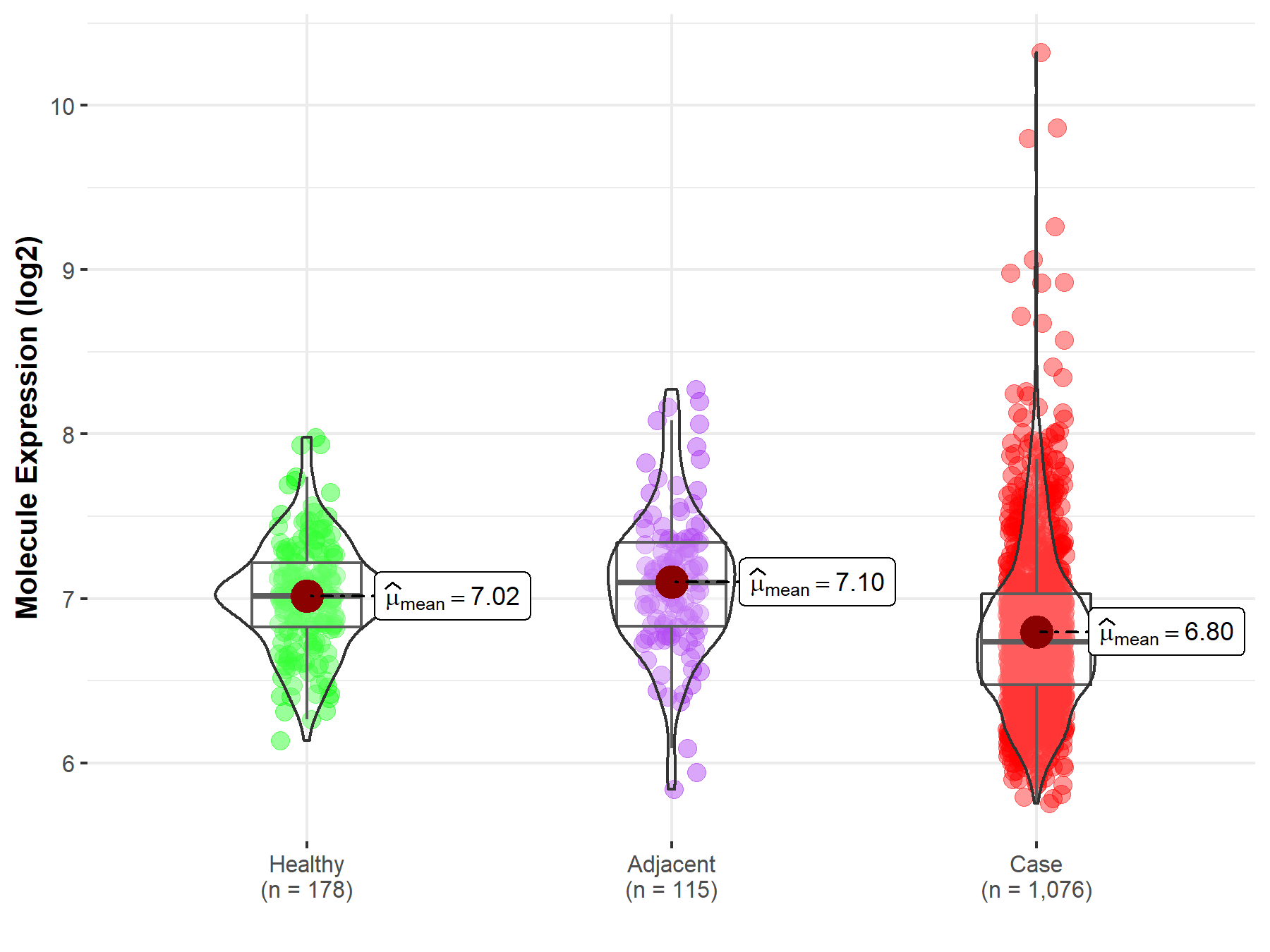
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

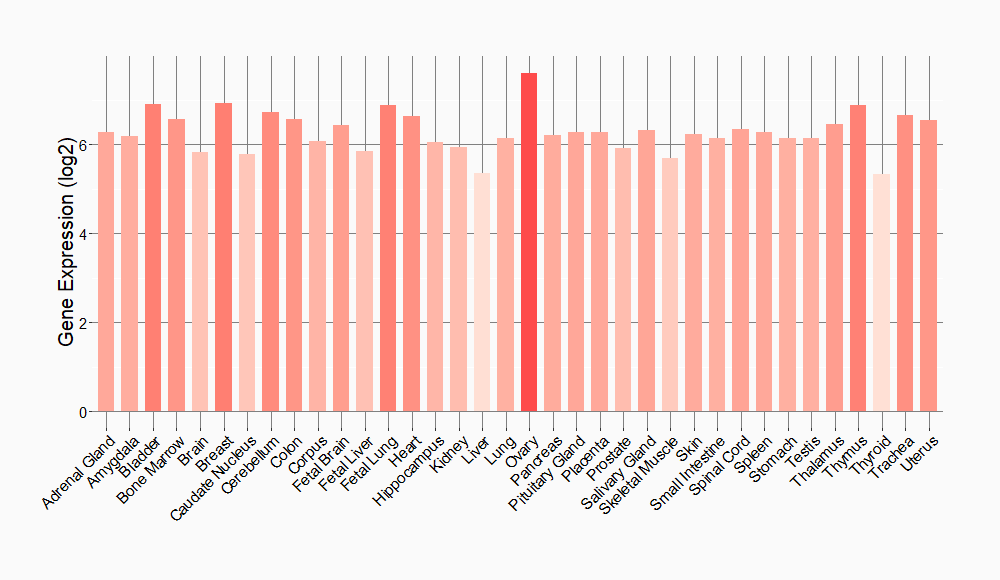
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
